

Common Problem-Solving Models & How to Use Them
Problem – solving models are step-by-step processes that provide a framework for addressing challenges. Problems arise in every facet of life. From work. to home. to friends and family, problems and conflicts can make life difficult and interfere with our physical and mental well-being. Understanding how to approach problems when they arise and implementing problem-solving techniques can make the journey through a problem less onerous on ourselves and those around us.
By building a structured problem-solving process, you can begin to build muscle memory by repeatedly practicing the same approach, and eventually, you may even begin to find yourself solving complex problems . Building a problem-solving model for each of the situations where you may encounter a problem can give you a path forward, even when the most difficult of problems arise.
This article will explore the concept of problem-solving models and dive into examples of such models and how to use them. It will also outline the benefits of implementing a problem-solving model in each area of life and why these problem-solving methods can have a large impact on your overall well-being. The goal of this article is to help you identify effective problem-solving strategies and develop critical thinking to generate solutions for any problem that comes your way.
Problem-Solving Model Defined
The first step in creating a problem-solving plan is to understand what we mean when we say problem-solving models. A problem-solving model is a step-by-step process that helps a team identify and effectively solve problems that they may encounter. This problem-solving approach gives the team the muscle memory and guide to address a conflict and resolve disputes quickly and effectively.
There are common problem-solving models that many teams have implemented, but there is also the freedom to shape a method to fit the needs of a specific situation. These models often rely on various problem-solving techniques to identify the root cause of the issue and find the best solution. This article will explore some common problem-solving models as well as general problem-solving techniques to help a team engage with and solve problems effectively.
Benefits of Implementing Problem-Solving Models
Before we discuss the exact models for problem-solving, it can be helpful to discuss why problem-solving models are beneficial in the first place. There are a variety of benefits to having a plan in place when a problem arises, but a few important benefits are listed below.
Guide Posts
When a team encounters a problem and has a guide for how to approach and solve the problem, it can be a relief to know that they have a process to fall back on when the issue cannot be resolved quickly from the beginning. A problem-solving strategy will serve as a guide for the parties to know which steps to take next and how to identify the appropriate solution.
It can also clarify when the issue needs to stay within the team, and when the issue needs to be escalated to someone in a position with more authority. It can also help the entire team solve complex problems without creating an issue out of the way the team solves the problem. It gives the team a blueprint to work from and encourages them to find a good solution.
Creative Solutions That Last
When the team or family has a way to fall back on to solve a problem, it takes some of the pressure off of coming up with the process and allows the parties to focus on identifying the relevant information and coming up with various potential solutions to the issue. By using a problem-solving method, the parties can come up with different solutions and find common ground with the best solution. This can be stifled if the team is too focused on figuring out how to solve the problem.
Additionally, the solutions that the parties come up with through problem-solving tools will often address the root cause of the issue and stop the team from having to revisit the same problem over and over again. This can lead to overall productivity and well-being and help the team continue to output quality work. By encouraging collaboration and creativity, a problem-solving technique will often keep solving problems between the parties moving forward and possibly even address them before they show up.
Common Models to Use in the Problem-Solving Process
Several models can be applied to a complex problem and create possible solutions. These range from common and straightforward to creative and in-depth to identify the most effective ways to solve a problem. This section will discuss and break down the problem-solving models that are most frequently used.
Standard Problem-Solving Process
When you search for a problem-solving technique, chances are you will find the standard model for saving problems. This model identifies and uses several important steps that will often be used in other models as well, so it can be helpful to begin the model-building process with an understanding of this model as a base. Other models often draw from this process and adapt one or more of the steps to help create additional options. Each of these steps works to accomplish a specific goal in furtherance of a solution.
Define the Problem
The first step in addressing a problem is to create a clear definition of the issue at hand. This will often require the team to communicate openly and honestly to place parameters around the issue. As the team defines the problem, it will be clear what needs to be solved and what pieces of the conflict are ancillary to the major issue. It helps to find the root causes of the issue and begin a process to address that rather than the symptoms of the problem. The team can also create a problem statement, which outlines the parameters of the problem and what needs to be fixed.
In addition to open and honest communication, other techniques can help to identify the root cause and define the problem. This includes a thorough review of the processes and steps that are currently used in the task and whether any of those steps are directly or indirectly causing the problem.
This includes reviewing how tasks are done, how communication is shared, and the current partners and team members that work together to identify if any of those are part of the issue. It is also the time to identify if some of the easy fixes or new tools would solve the problem and what the impact would be.
It is also important to gain a wide understanding of the problem from all of the people involved. Many people will have opinions on what is going on, but it is also important to understand the facts over the opinions that are affecting the problem. This can also help you identify if the problem is arising from a boundary or standard that is not being met or honored. By gathering data and understanding the source of the problem, the process of solving it can begin.
Generate Solutions
The next step in the basic process is to generate possible solutions to the problem. At this step, it is less important to evaluate how each of the options will play out and how they may change the process and more important to identify solutions that could address the issue. This includes solutions that support the goals of the team and the task, and the team can also identify short and long-term solutions.
The team should work to brainstorm as many viable solutions as possible to give them the best options to consider moving forward. They cannot pick the first solution that is proposed and consider it a successful problem-solving process.
Evaluate and Select
After a few good options have been identified, the next step is to evaluate the options and pick the most viable option that also supports the goals of the team or organization. This includes looking at each of the possible solutions and determining how they would either encourage or hinder the goals and standards of the team. These should evaluated without bias toward the solution proposed or the person putting forward the solution. Additionally, the team should consider both actual outcomes that have happened in the past and predicted instances that may occur if the solution is chosen.
Each solution should be evaluated by considering if the solution would solve the current problem without causing additional issues, the willingness of the team to buy in and implement the solution, and the actual ability of the team to implement the solution.
Participation and honesty from all team members will make the process go more smoothly and ensure that the best option for everyone involved is selected. Once the team picks the option they would like to use for the specific problem, they should clearly define what the solution is and how it should be implemented. There should also be a strategy for how to evaluate the effectiveness of the solution.
Implement the Solution and Follow Up
Once a solution is chosen, a team will often assume that the work of solving problems is complete. However, the final step in the basic model is an important step to determine if the matter is resolved or if additional options are needed. After the solution has been implemented by the team, the members of the team must provide feedback and identify any potential obstacles that may have been missed in the decision-making process.
This encourages long-term solutions for the problem and helps the team to continue to move forward with their work. It also gives the team a sense of ownership and an example of how to evaluate an idea in the future.
If the solution is not working the way that it should, the team will often need to adapt the option, or they may get to the point where they scrap the option and attempt another. Solving a problem is not always a linear process, and encouraging reform and change within the process will help the team find the answer to the issues that they face.
GROW Method
Another method that is similar to the standard method is the G.R.O.W. method. This method has very similar steps to the standard method, but the catchiness of the acronym helps a team approach the problem from the same angle each time and work through the method quickly.
The first step in the method is to identify a goal, which is what the “g” stands for in “grow.” To establish a goal, the team will need to look at the issues that they are facing and identify what they would like to accomplish and solve through the problem-solving process. The team will likely participate in conversations that identify the issues that they are facing and what they need to resolve.
The next step is to establish the current reality that the group is facing. This helps them to determine where they currently are and what needs to be done to move them forward. This can help the group establish a baseline for where they started and what they would like to change.
The next step is to find any obstacles that may be blocking the group from achieving their goal. This is where the main crux of the issues that the group is facing will come out. This is also helpful in giving the group a chance to find ways around these obstacles and toward a solution.
Way Forward
After identifying the obstacles and potential ways to avoid them, the group will then need to pick the best way to move forward and approach their goal together. Here, they will need to create steps to move forward with that goal.
Divide and Conquer
Another common problem-solving method is the divide-and-conquer method. Here, instead of the entire team working through each step of the process as a large group, they split up the issue into smaller problems that can be solved and have individual members or small groups work through the smaller problems. Once each group is satisfied with the solution to the problem, they present it to the larger group to consider along with the other options.
This process can be helpful if there is a large team attempting to solve a large and complex problem. It is also beneficial because it can be used in teams with smaller, specialized teams within it because it allows each smaller group to focus on what they know best.
However, it does encourage the parties to shy away from collaboration on the overall issue, and the different solutions that each proposes may not be possible when combined and implemented.
For this reason, it is best to use this solution when approaching complex problems with large teams and the ability to combine several problem-solving methods into one.
Six Thinking Hats
The Six Thinking Hats theory is a concept designed for a team with a lot of differing conflict styles and problem-solving techniques. This method was developed to help sort through the various techniques that people may use and help a team find a solution that works for everyone involved. It helps to organize thinking and lead the conversation to the best possible solution.
Within this system, there are six different “hats” that identify with the various aspects of the decision-making process: the overall process, idea generation, intuition and emotions, values, information gathering, and caution or critical thinking. The group agrees to participate in the process by agreeing on which of the hats the group is wearing at a given moment. This helps set parameters and expectations around what the group is attempting to achieve at any moment.
This system is particularly good in a group with different conflict styles or where people have a hard time collecting and organizing their thoughts. It can be incredibly beneficial for complex problems with many moving parts. It can also help groups identify how each of the smaller sections relates to the big picture and help create new ideas to answer the overall problem.
However, it can derail if the group focuses too heavily or for too long on one of the “hats.” The group should ensure that they have a facilitator to guide them through the process and ensure that each idea and section is considered adequately.
Trial and Error
The trial and error process takes over the evaluation and selection process and instead chooses to try out each of the alternatives to determine what the best option would be. It allows the team to gather data on each of the options and how they apply practically. It also provides the ability for the team to have an example of each possible answer to help a decision-maker determine what the best option is.
Problem-solving methods that focus on trial and error can be helpful when a team has a simple problem or a lot of time to test potential solutions, gather data, and determine an answer to the issue.
It can also be helpful when the team has a sense of the best guess for a solution but wants to test it out to determine if the data supports that option, or if they have several viable options and would like to identify the best one. However, it can be incredibly time-consuming to test each of the options and evaluate how they went. Time can often be saved by evaluating each option and selecting the best to test.
Other Problem-Solving Skills
In addition to the methods outlined above, other problem-solving skills can be used regardless of the model that is used. These techniques can round out the problem-solving process and help address either specific steps in the overall method or alter the step in some way to help it fit a specific situation.
Ask Good Questions
One of the best ways to work through any of the problem-solving models is to ask good questions. This will help the group find the issue at the heart of the problem and address that issue rather than the symptoms. The best questions will also help the group find viable solutions and pick the solution that the group can use to move forward. The more creative the questions , the more likely that they will produce innovative solutions.
Take a Step Back
Occasionally, paying attention to a problem too much can give the group tunnel vision and harm the overall processes that the group is using. Other times, the focus can lead to escalations in conflict. When this happens, it can be helpful to set aside the problem and give the group time to calm down. Once they have a chance to reconsider the options and how they apply, they can approach the issue with a new sense of purpose and determination. This can lead to additional creative solutions that may help the group find a new way forward.
Final Thoughts
Problem-solving can be a daunting part of life. However, with a good problem-solving method and the right techniques, problems can be addressed well and quickly. Applying some of these options outlined in this article can give you a head start in solving your next problem and any others that arise.
To learn more about problem-solving models, problem-solving activities, and more, contact ADR Times !
Must-read Articles:

- Recent Posts

- Personal Injury Settlement Amounts Examples - August 12, 2024
- Writing an Effective Problem Statement - August 5, 2024
- 14 Home Insurance Claim Adjuster Secret Tactics - July 29, 2024
40 problem-solving techniques and processes
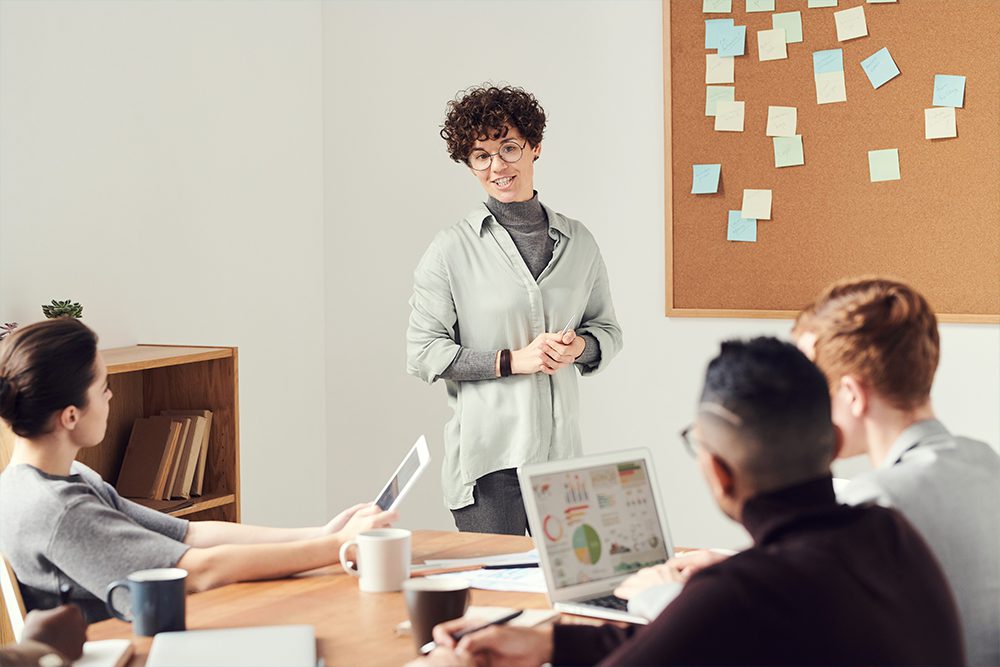

All teams and organizations encounter challenges. Approaching those challenges without a structured problem solving process can end up making things worse.
Proven problem solving techniques such as those outlined below can guide your group through a process of identifying problems and challenges , ideating on possible solutions , and then evaluating and implementing the most suitable .
In this post, you'll find problem-solving tools you can use to develop effective solutions. You'll also find some tips for facilitating the problem solving process and solving complex problems.
Design your next session with SessionLab
Join the 150,000+ facilitators using SessionLab.
Recommended Articles
A step-by-step guide to planning a workshop, 54 great online tools for workshops and meetings, how to create an unforgettable training session in 8 simple steps.
- 18 Free Facilitation Resources We Think You’ll Love
What is problem solving?
Problem solving is a process of finding and implementing a solution to a challenge or obstacle. In most contexts, this means going through a problem solving process that begins with identifying the issue, exploring its root causes, ideating and refining possible solutions before implementing and measuring the impact of that solution.
For simple or small problems, it can be tempting to skip straight to implementing what you believe is the right solution. The danger with this approach is that without exploring the true causes of the issue, it might just occur again or your chosen solution may cause other issues.
Particularly in the world of work, good problem solving means using data to back up each step of the process, bringing in new perspectives and effectively measuring the impact of your solution.
Effective problem solving can help ensure that your team or organization is well positioned to overcome challenges, be resilient to change and create innovation. In my experience, problem solving is a combination of skillset, mindset and process, and it’s especially vital for leaders to cultivate this skill.
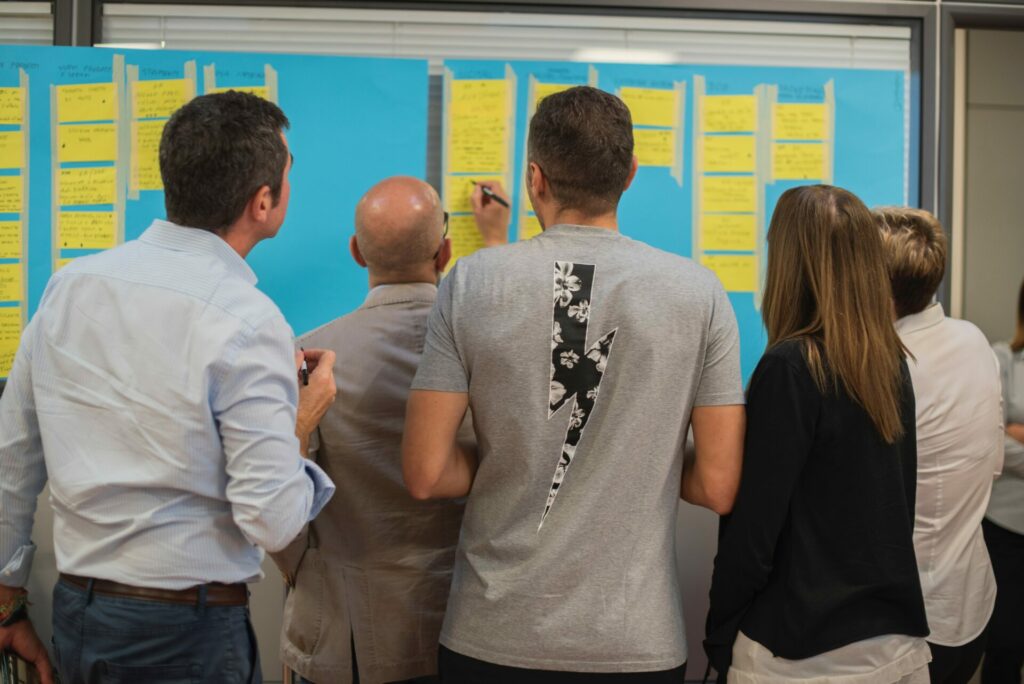

What is the seven step problem solving process?
A problem solving process is a step-by-step framework from going from discovering a problem all the way through to implementing a solution.
With practice, this framework can become intuitive, and innovative companies tend to have a consistent and ongoing ability to discover and tackle challenges when they come up.
You might see everything from a four step problem solving process through to seven steps. While all these processes cover roughly the same ground, I’ve found a seven step problem solving process is helpful for making all key steps legible.
We’ll outline that process here and then follow with techniques you can use to explore and work on that step of the problem solving process with a group.
The seven-step problem solving process is:
1. Problem identification
The first stage of any problem solving process is to identify the problem(s) you need to solve. This often looks like using group discussions and activities to help a group surface and effectively articulate the challenges they’re facing and wish to resolve.
Be sure to align with your team on the exact definition and nature of the problem you’re solving. An effective process is one where everyone is pulling in the same direction – ensure clarity and alignment now to help avoid misunderstandings later.
2. Problem analysis and refinement
The process of problem analysis means ensuring that the problem you are seeking to solve is the right problem . Choosing the right problem to solve means you are on the right path to creating the right solution.
At this stage, you may look deeper at the problem you identified to try and discover the root cause at the level of people or process. You may also spend some time sourcing data, consulting relevant parties and creating and refining a problem statement.
Problem refinement means adjusting scope or focus of the problem you will be aiming to solve based on what comes up during your analysis. As you analyze data sources, you might discover that the root cause means you need to adjust your problem statement. Alternatively, you might find that your original problem statement is too big to be meaningful approached within your current project.
Remember that the goal of any problem refinement is to help set the stage for effective solution development and deployment. Set the right focus and get buy-in from your team here and you’ll be well positioned to move forward with confidence.
3. Solution generation
Once your group has nailed down the particulars of the problem you wish to solve, you want to encourage a free flow of ideas connecting to solving that problem. This can take the form of problem solving games that encourage creative thinking or techniquess designed to produce working prototypes of possible solutions.
The key to ensuring the success of this stage of the problem solving process is to encourage quick, creative thinking and create an open space where all ideas are considered. The best solutions can often come from unlikely places and by using problem solving techniques that celebrate invention, you might come up with solution gold.
4. Solution development
No solution is perfect right out of the gate. It’s important to discuss and develop the solutions your group has come up with over the course of following the previous problem solving steps in order to arrive at the best possible solution. Problem solving games used in this stage involve lots of critical thinking, measuring potential effort and impact, and looking at possible solutions analytically.
During this stage, you will often ask your team to iterate and improve upon your front-running solutions and develop them further. Remember that problem solving strategies always benefit from a multitude of voices and opinions, and not to let ego get involved when it comes to choosing which solutions to develop and take further.
Finding the best solution is the goal of all problem solving workshops and here is the place to ensure that your solution is well thought out, sufficiently robust and fit for purpose.
5. Decision making and planning
Nearly there! Once you’ve got a set of possible, you’ll need to make a decision on which to implement. This can be a consensus-based group decision or it might be for a leader or major stakeholder to decide. You’ll find a set of effective decision making methods below.
Once your group has reached consensus and selected a solution, there are some additional actions that also need to be decided upon. You’ll want to work on allocating ownership of the project, figure out who will do what, how the success of the solution will be measured and decide the next course of action.
Set clear accountabilities, actions, timeframes, and follow-ups for your chosen solution. Make these decisions and set clear next-steps in the problem solving workshop so that everyone is aligned and you can move forward effectively as a group.
Ensuring that you plan for the roll-out of a solution is one of the most important problem solving steps. Without adequate planning or oversight, it can prove impossible to measure success or iterate further if the problem was not solved.
6. Solution implementation
This is what we were waiting for! All problem solving processes have the end goal of implementing an effective and impactful solution that your group has confidence in.
Project management and communication skills are key here – your solution may need to adjust when out in the wild or you might discover new challenges along the way. For some solutions, you might also implement a test with a small group and monitor results before rolling it out to an entire company.
You should have a clear owner for your solution who will oversee the plans you made together and help ensure they’re put into place. This person will often coordinate the implementation team and set-up processes to measure the efficacy of your solution too.
7. Solution evaluation
So you and your team developed a great solution to a problem and have a gut feeling it’s been solved. Work done, right? Wrong. All problem solving strategies benefit from evaluation, consideration, and feedback.
You might find that the solution does not work for everyone, might create new problems, or is potentially so successful that you will want to roll it out to larger teams or as part of other initiatives.
None of that is possible without taking the time to evaluate the success of the solution you developed in your problem solving model and adjust if necessary.
Remember that the problem solving process is often iterative and it can be common to not solve complex issues on the first try. Even when this is the case, you and your team will have generated learning that will be important for future problem solving workshops or in other parts of the organization.
It’s also worth underlining how important record keeping is throughout the problem solving process. If a solution didn’t work, you need to have the data and records to see why that was the case. If you go back to the drawing board, notes from the previous workshop can help save time.
What does an effective problem solving process look like?
Every effective problem solving process begins with an agenda . In our experience, a well-structured problem solving workshop is one of the best methods for successfully guiding a group from exploring a problem to implementing a solution.
The format of a workshop ensures that you can get buy-in from your group, encourage free-thinking and solution exploration before making a decision on what to implement following the session.
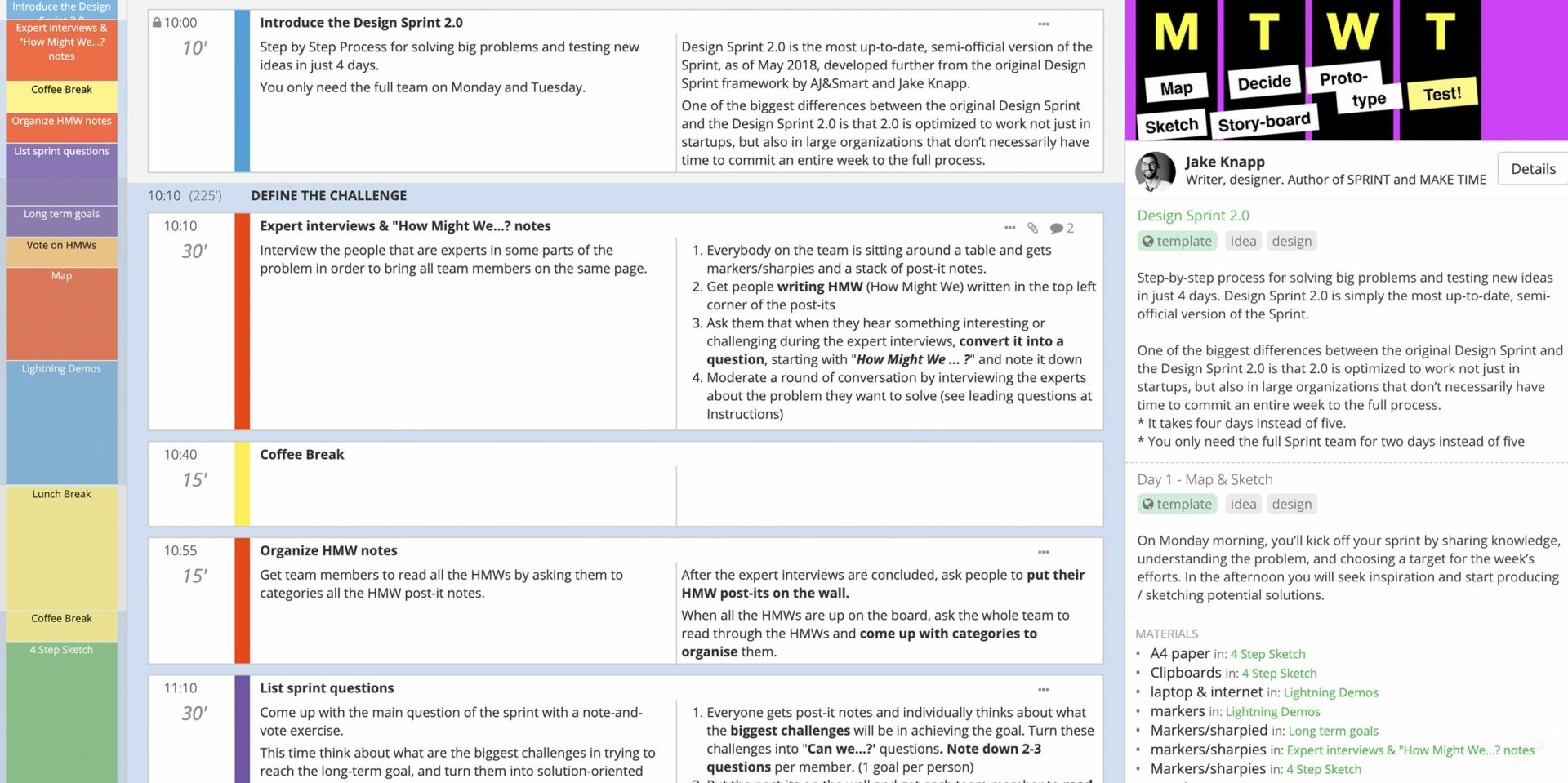
This Design Sprint 2.0 template is an effective problem solving process from top agency AJ&Smart. It’s a great format for the entire problem solving process, with four-days of workshops designed to surface issues, explore solutions and even test a solution.
Check it for an example of how you might structure and run a problem solving process and feel free to copy and adjust it your needs!
For a shorter process you can run in a single afternoon, this remote problem solving agenda will guide you effectively in just a couple of hours.
Whatever the length of your workshop, by using SessionLab, it’s easy to go from an idea to a complete agenda . Start by dragging and dropping your core problem solving activities into place . Add timings, breaks and necessary materials before sharing your agenda with your colleagues.
The resulting agenda will be your guide to an effective and productive problem solving session that will also help you stay organized on the day!
Complete problem-solving methods
In this section, we’ll look at in-depth problem-solving methods that provide a complete end-to-end process for developing effective solutions. These will help guide your team from the discovery and definition of a problem through to delivering the right solution.
If you’re looking for an all-encompassing method or problem-solving model, these processes are a great place to start. They’ll ask your team to challenge preconceived ideas and adopt a mindset for solving problems more effectively.
Six Thinking Hats
Individual approaches to solving a problem can be very different based on what team or role an individual holds. It can be easy for existing biases or perspectives to find their way into the mix, or for internal politics to direct a conversation.
Six Thinking Hats is a classic method for identifying the problems that need to be solved and enables your team to consider them from different angles, whether that is by focusing on facts and data, creative solutions, or by considering why a particular solution might not work.
Like all problem-solving frameworks, Six Thinking Hats is effective at helping teams remove roadblocks from a conversation or discussion and come to terms with all the aspects necessary to solve complex problems.
The Six Thinking Hats #creative thinking #meeting facilitation #problem solving #issue resolution #idea generation #conflict resolution The Six Thinking Hats are used by individuals and groups to separate out conflicting styles of thinking. They enable and encourage a group of people to think constructively together in exploring and implementing change, rather than using argument to fight over who is right and who is wrong.
Lightning Decision Jam
Featured courtesy of Jonathan Courtney of AJ&Smart Berlin, Lightning Decision Jam is one of those strategies that should be in every facilitation toolbox. Exploring problems and finding solutions is often creative in nature, though as with any creative process, there is the potential to lose focus and get lost.
Unstructured discussions might get you there in the end, but it’s much more effective to use a method that creates a clear process and team focus.
In Lightning Decision Jam, participants are invited to begin by writing challenges, concerns, or mistakes on post-its without discussing them before then being invited by the moderator to present them to the group.
From there, the team vote on which problems to solve and are guided through steps that will allow them to reframe those problems, create solutions and then decide what to execute on.
By deciding the problems that need to be solved as a team before moving on, this group process is great for ensuring the whole team is aligned and can take ownership over the next stages.
Lightning Decision Jam (LDJ) #action #decision making #problem solving #issue analysis #innovation #design #remote-friendly It doesn’t matter where you work and what your job role is, if you work with other people together as a team, you will always encounter the same challenges: Unclear goals and miscommunication that cause busy work and overtime Unstructured meetings that leave attendants tired, confused and without clear outcomes. Frustration builds up because internal challenges to productivity are not addressed Sudden changes in priorities lead to a loss of focus and momentum Muddled compromise takes the place of clear decision- making, leaving everybody to come up with their own interpretation. In short, a lack of structure leads to a waste of time and effort, projects that drag on for too long and frustrated, burnt out teams. AJ&Smart has worked with some of the most innovative, productive companies in the world. What sets their teams apart from others is not better tools, bigger talent or more beautiful offices. The secret sauce to becoming a more productive, more creative and happier team is simple: Replace all open discussion or brainstorming with a structured process that leads to more ideas, clearer decisions and better outcomes. When a good process provides guardrails and a clear path to follow, it becomes easier to come up with ideas, make decisions and solve problems. This is why AJ&Smart created Lightning Decision Jam (LDJ). It’s a simple and short, but powerful group exercise that can be run either in-person, in the same room, or remotely with distributed teams.
Problem Definition Process
While problems can be complex, the problem-solving methods you use to identify and solve those problems can often be simple in design.
By taking the time to truly identify and define a problem before asking the group to reframe the challenge as an opportunity, this method is a great way to enable change.
Begin by identifying a focus question and exploring the ways in which it manifests before splitting into five teams who will each consider the problem using a different method: escape, reversal, exaggeration, distortion or wishful. Teams develop a problem objective and create ideas in line with their method before then feeding them back to the group.
This method is great for enabling in-depth discussions while also creating space for finding creative solutions too!
Problem Definition #problem solving #idea generation #creativity #online #remote-friendly A problem solving technique to define a problem, challenge or opportunity and to generate ideas.
The 5 Whys
Sometimes, a group needs to go further with their strategies and analyze the root cause at the heart of organizational issues. An RCA or root cause analysis is the process of identifying what is at the heart of business problems or recurring challenges.
The 5 Whys is a simple and effective method of helping a group go find the root cause of any problem or challenge and conduct analysis that will deliver results.
By beginning with the creation of a problem statement and going through five stages to refine it, The 5 Whys provides everything you need to truly discover the cause of an issue.
The 5 Whys #hyperisland #innovation This simple and powerful method is useful for getting to the core of a problem or challenge. As the title suggests, the group defines a problems, then asks the question “why” five times, often using the resulting explanation as a starting point for creative problem solving.
World Cafe is a simple but powerful facilitation technique to help bigger groups to focus their energy and attention on solving complex problems.
World Cafe enables this approach by creating a relaxed atmosphere where participants are able to self-organize and explore topics relevant and important to them which are themed around a central problem-solving purpose. Create the right atmosphere by modeling your space after a cafe and after guiding the group through the method, let them take the lead!
Making problem-solving a part of your organization’s culture in the long term can be a difficult undertaking. More approachable formats like World Cafe can be especially effective in bringing people unfamiliar with workshops into the fold.
World Cafe #hyperisland #innovation #issue analysis World Café is a simple yet powerful method, originated by Juanita Brown, for enabling meaningful conversations driven completely by participants and the topics that are relevant and important to them. Facilitators create a cafe-style space and provide simple guidelines. Participants then self-organize and explore a set of relevant topics or questions for conversation.
Discovery & Action Dialogue (DAD)
One of the best approaches is to create a safe space for a group to share and discover practices and behaviors that can help them find their own solutions.
With DAD, you can help a group choose which problems they wish to solve and which approaches they will take to do so. It’s great at helping remove resistance to change and can help get buy-in at every level too!
This process of enabling frontline ownership is great in ensuring follow-through and is one of the methods you will want in your toolbox as a facilitator.
Discovery & Action Dialogue (DAD) #idea generation #liberating structures #action #issue analysis #remote-friendly DADs make it easy for a group or community to discover practices and behaviors that enable some individuals (without access to special resources and facing the same constraints) to find better solutions than their peers to common problems. These are called positive deviant (PD) behaviors and practices. DADs make it possible for people in the group, unit, or community to discover by themselves these PD practices. DADs also create favorable conditions for stimulating participants’ creativity in spaces where they can feel safe to invent new and more effective practices. Resistance to change evaporates as participants are unleashed to choose freely which practices they will adopt or try and which problems they will tackle. DADs make it possible to achieve frontline ownership of solutions.
Design Sprint 2.0
Want to see how a team can solve big problems and move forward with prototyping and testing solutions in a few days? The Design Sprint 2.0 template from Jake Knapp, author of Sprint, is a complete agenda for a with proven results.
Developing the right agenda can involve difficult but necessary planning. Ensuring all the correct steps are followed can also be stressful or time-consuming depending on your level of experience.
Use this complete 4-day workshop template if you are finding there is no obvious solution to your challenge and want to focus your team around a specific problem that might require a shortcut to launching a minimum viable product or waiting for the organization-wide implementation of a solution.
Open space technology
Open space technology- developed by Harrison Owen – creates a space where large groups are invited to take ownership of their problem solving and lead individual sessions. Open space technology is a great format when you have a great deal of expertise and insight in the room and want to allow for different takes and approaches on a particular theme or problem you need to be solved.
Start by bringing your participants together to align around a central theme and focus their efforts. Explain the ground rules to help guide the problem-solving process and then invite members to identify any issue connecting to the central theme that they are interested in and are prepared to take responsibility for.
Once participants have decided on their approach to the core theme, they write their issue on a piece of paper, announce it to the group, pick a session time and place, and post the paper on the wall. As the wall fills up with sessions, the group is then invited to join the sessions that interest them the most and which they can contribute to, then you’re ready to begin!
Everyone joins the problem-solving group they’ve signed up to, record the discussion and if appropriate, findings can then be shared with the rest of the group afterward.
Open Space Technology #action plan #idea generation #problem solving #issue analysis #large group #online #remote-friendly Open Space is a methodology for large groups to create their agenda discerning important topics for discussion, suitable for conferences, community gatherings and whole system facilitation
Techniques to identify and analyze problems
Using a problem-solving method to help a team identify and analyze a problem can be a quick and effective addition to any workshop or meeting.
While further actions are always necessary, you can generate momentum and alignment easily, and these activities are a great place to get started.
We’ve put together this list of techniques to help you and your team with problem identification, analysis, and discussion that sets the foundation for developing effective solutions.
Let’s take a look!
Fishbone Analysis
Organizational or team challenges are rarely simple, and it’s important to remember that one problem can be an indication of something that goes deeper and may require further consideration to be solved.
Fishbone Analysis helps groups to dig deeper and understand the origins of a problem. It’s a great example of a root cause analysis method that is simple for everyone on a team to get their head around.
Participants in this activity are asked to annotate a diagram of a fish, first adding the problem or issue to be worked on at the head of a fish before then brainstorming the root causes of the problem and adding them as bones on the fish.
Using abstractions such as a diagram of a fish can really help a team break out of their regular thinking and develop a creative approach.
Fishbone Analysis #problem solving ##root cause analysis #decision making #online facilitation A process to help identify and understand the origins of problems, issues or observations.
Problem Tree
Encouraging visual thinking can be an essential part of many strategies. By simply reframing and clarifying problems, a group can move towards developing a problem solving model that works for them.
In Problem Tree, groups are asked to first brainstorm a list of problems – these can be design problems, team problems or larger business problems – and then organize them into a hierarchy. The hierarchy could be from most important to least important or abstract to practical, though the key thing with problem solving games that involve this aspect is that your group has some way of managing and sorting all the issues that are raised.
Once you have a list of problems that need to be solved and have organized them accordingly, you’re then well-positioned for the next problem solving steps.
Problem tree #define intentions #create #design #issue analysis A problem tree is a tool to clarify the hierarchy of problems addressed by the team within a design project; it represents high level problems or related sublevel problems.
SWOT Analysis
Chances are you’ve heard of the SWOT Analysis before. This problem-solving method focuses on identifying strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats is a tried and tested method for both individuals and teams.
Start by creating a desired end state or outcome and bare this in mind – any process solving model is made more effective by knowing what you are moving towards. Create a quadrant made up of the four categories of a SWOT analysis and ask participants to generate ideas based on each of those quadrants.
Once you have those ideas assembled in their quadrants, cluster them together based on their affinity with other ideas. These clusters are then used to facilitate group conversations and move things forward.
SWOT analysis #gamestorming #problem solving #action #meeting facilitation The SWOT Analysis is a long-standing technique of looking at what we have, with respect to the desired end state, as well as what we could improve on. It gives us an opportunity to gauge approaching opportunities and dangers, and assess the seriousness of the conditions that affect our future. When we understand those conditions, we can influence what comes next.
Agreement-Certainty Matrix
Not every problem-solving approach is right for every challenge, and deciding on the right method for the challenge at hand is a key part of being an effective team.
The Agreement Certainty matrix helps teams align on the nature of the challenges facing them. By sorting problems from simple to chaotic, your team can understand what methods are suitable for each problem and what they can do to ensure effective results.
If you are already using Liberating Structures techniques as part of your problem-solving strategy, the Agreement-Certainty Matrix can be an invaluable addition to your process. We’ve found it particularly if you are having issues with recurring problems in your organization and want to go deeper in understanding the root cause.
Agreement-Certainty Matrix #issue analysis #liberating structures #problem solving You can help individuals or groups avoid the frequent mistake of trying to solve a problem with methods that are not adapted to the nature of their challenge. The combination of two questions makes it possible to easily sort challenges into four categories: simple, complicated, complex , and chaotic . A problem is simple when it can be solved reliably with practices that are easy to duplicate. It is complicated when experts are required to devise a sophisticated solution that will yield the desired results predictably. A problem is complex when there are several valid ways to proceed but outcomes are not predictable in detail. Chaotic is when the context is too turbulent to identify a path forward. A loose analogy may be used to describe these differences: simple is like following a recipe, complicated like sending a rocket to the moon, complex like raising a child, and chaotic is like the game “Pin the Tail on the Donkey.” The Liberating Structures Matching Matrix in Chapter 5 can be used as the first step to clarify the nature of a challenge and avoid the mismatches between problems and solutions that are frequently at the root of chronic, recurring problems.
Organizing and charting a team’s progress can be important in ensuring its success. SQUID (Sequential Question and Insight Diagram) is a great model that allows a team to effectively switch between giving questions and answers and develop the skills they need to stay on track throughout the process.
Begin with two different colored sticky notes – one for questions and one for answers – and with your central topic (the head of the squid) on the board. Ask the group to first come up with a series of questions connected to their best guess of how to approach the topic. Ask the group to come up with answers to those questions, fix them to the board and connect them with a line. After some discussion, go back to question mode by responding to the generated answers or other points on the board.
It’s rewarding to see a diagram grow throughout the exercise, and a completed SQUID can provide a visual resource for future effort and as an example for other teams.
SQUID #gamestorming #project planning #issue analysis #problem solving When exploring an information space, it’s important for a group to know where they are at any given time. By using SQUID, a group charts out the territory as they go and can navigate accordingly. SQUID stands for Sequential Question and Insight Diagram.
To continue with our nautical theme, Speed Boat is a short and sweet activity that can help a team quickly identify what employees, clients or service users might have a problem with and analyze what might be standing in the way of achieving a solution.
Methods that allow for a group to make observations, have insights and obtain those eureka moments quickly are invaluable when trying to solve complex problems.
In Speed Boat, the approach is to first consider what anchors and challenges might be holding an organization (or boat) back. Bonus points if you are able to identify any sharks in the water and develop ideas that can also deal with competitors!
Speed Boat #gamestorming #problem solving #action Speedboat is a short and sweet way to identify what your employees or clients don’t like about your product/service or what’s standing in the way of a desired goal.
The Journalistic Six
Some of the most effective ways of solving problems is by encouraging teams to be more inclusive and diverse in their thinking.
Based on the six key questions journalism students are taught to answer in articles and news stories, The Journalistic Six helps create teams to see the whole picture. By using who, what, when, where, why, and how to facilitate the conversation and encourage creative thinking, your team can make sure that the problem identification and problem analysis stages of the are covered exhaustively and thoughtfully. Reporter’s notebook and dictaphone optional.
The Journalistic Six – Who What When Where Why How #idea generation #issue analysis #problem solving #online #creative thinking #remote-friendly A questioning method for generating, explaining, investigating ideas.
Individual and group perspectives are incredibly important, but what happens if people are set in their minds and need a change of perspective in order to approach a problem more effectively?
Flip It is a method we love because it is both simple to understand and run, and allows groups to understand how their perspectives and biases are formed.
Participants in Flip It are first invited to consider concerns, issues, or problems from a perspective of fear and write them on a flip chart. Then, the group is asked to consider those same issues from a perspective of hope and flip their understanding.
No problem and solution is free from existing bias and by changing perspectives with Flip It, you can then develop a problem solving model quickly and effectively.
Flip It! #gamestorming #problem solving #action Often, a change in a problem or situation comes simply from a change in our perspectives. Flip It! is a quick game designed to show players that perspectives are made, not born.
LEGO Challenge
Now for an activity that is a little out of the (toy) box. LEGO Serious Play is a facilitation methodology that can be used to improve creative thinking and problem-solving skills.
The LEGO Challenge includes giving each member of the team an assignment that is hidden from the rest of the group while they create a structure without speaking.
What the LEGO challenge brings to the table is a fun working example of working with stakeholders who might not be on the same page to solve problems. Also, it’s LEGO! Who doesn’t love LEGO!
LEGO Challenge #hyperisland #team A team-building activity in which groups must work together to build a structure out of LEGO, but each individual has a secret “assignment” which makes the collaborative process more challenging. It emphasizes group communication, leadership dynamics, conflict, cooperation, patience and problem solving strategy.
What, So What, Now What?
If not carefully managed, the problem identification and problem analysis stages of the problem-solving process can actually create more problems and misunderstandings.
The What, So What, Now What? problem-solving activity is designed to help collect insights and move forward while also eliminating the possibility of disagreement when it comes to identifying, clarifying, and analyzing organizational or work problems.
Facilitation is all about bringing groups together so that might work on a shared goal and the best problem-solving strategies ensure that teams are aligned in purpose, if not initially in opinion or insight.
Throughout the three steps of this game, you give everyone on a team to reflect on a problem by asking what happened, why it is important, and what actions should then be taken.
This can be a great activity for bringing our individual perceptions about a problem or challenge and contextualizing it in a larger group setting. This is one of the most important problem-solving skills you can bring to your organization.
W³ – What, So What, Now What? #issue analysis #innovation #liberating structures You can help groups reflect on a shared experience in a way that builds understanding and spurs coordinated action while avoiding unproductive conflict. It is possible for every voice to be heard while simultaneously sifting for insights and shaping new direction. Progressing in stages makes this practical—from collecting facts about What Happened to making sense of these facts with So What and finally to what actions logically follow with Now What . The shared progression eliminates most of the misunderstandings that otherwise fuel disagreements about what to do. Voila!
Journalists
Problem analysis can be one of the most important and decisive stages of all problem-solving tools. Sometimes, a team can become bogged down in the details and are unable to move forward.
Journalists is an activity that can avoid a group from getting stuck in the problem identification or problem analysis stages of the process.
In Journalists, the group is invited to draft the front page of a fictional newspaper and figure out what stories deserve to be on the cover and what headlines those stories will have. By reframing how your problems and challenges are approached, you can help a team move productively through the process and be better prepared for the steps to follow.
Journalists #vision #big picture #issue analysis #remote-friendly This is an exercise to use when the group gets stuck in details and struggles to see the big picture. Also good for defining a vision.
Problem-solving techniques for brainstorming solutions
Now you have the context and background of the problem you are trying to solving, now comes the time to start ideating and thinking about how you’ll solve the issue.
Here, you’ll want to encourage creative, free thinking and speed. Get as many ideas out as possible and explore different perspectives so you have the raw material for the next step.
Looking at a problem from a new angle can be one of the most effective ways of creating an effective solution. TRIZ is a problem-solving tool that asks the group to consider what they must not do in order to solve a challenge.
By reversing the discussion, new topics and taboo subjects often emerge, allowing the group to think more deeply and create ideas that confront the status quo in a safe and meaningful way. If you’re working on a problem that you’ve tried to solve before, TRIZ is a great problem-solving method to help your team get unblocked.
Making Space with TRIZ #issue analysis #liberating structures #issue resolution You can clear space for innovation by helping a group let go of what it knows (but rarely admits) limits its success and by inviting creative destruction. TRIZ makes it possible to challenge sacred cows safely and encourages heretical thinking. The question “What must we stop doing to make progress on our deepest purpose?” induces seriously fun yet very courageous conversations. Since laughter often erupts, issues that are otherwise taboo get a chance to be aired and confronted. With creative destruction come opportunities for renewal as local action and innovation rush in to fill the vacuum. Whoosh!
Mindspin
Brainstorming is part of the bread and butter of the problem-solving process and all problem-solving strategies benefit from getting ideas out and challenging a team to generate solutions quickly.
With Mindspin, participants are encouraged not only to generate ideas but to do so under time constraints and by slamming down cards and passing them on. By doing multiple rounds, your team can begin with a free generation of possible solutions before moving on to developing those solutions and encouraging further ideation.
This is one of our favorite problem-solving activities and can be great for keeping the energy up throughout the workshop. Remember the importance of helping people become engaged in the process – energizing problem-solving techniques like Mindspin can help ensure your team stays engaged and happy, even when the problems they’re coming together to solve are complex.
MindSpin #teampedia #idea generation #problem solving #action A fast and loud method to enhance brainstorming within a team. Since this activity has more than round ideas that are repetitive can be ruled out leaving more creative and innovative answers to the challenge.
The Creativity Dice
One of the most useful problem solving skills you can teach your team is of approaching challenges with creativity, flexibility, and openness. Games like The Creativity Dice allow teams to overcome the potential hurdle of too much linear thinking and approach the process with a sense of fun and speed.
In The Creativity Dice, participants are organized around a topic and roll a dice to determine what they will work on for a period of 3 minutes at a time. They might roll a 3 and work on investigating factual information on the chosen topic. They might roll a 1 and work on identifying the specific goals, standards, or criteria for the session.
Encouraging rapid work and iteration while asking participants to be flexible are great skills to cultivate. Having a stage for idea incubation in this game is also important. Moments of pause can help ensure the ideas that are put forward are the most suitable.
The Creativity Dice #creativity #problem solving #thiagi #issue analysis Too much linear thinking is hazardous to creative problem solving. To be creative, you should approach the problem (or the opportunity) from different points of view. You should leave a thought hanging in mid-air and move to another. This skipping around prevents premature closure and lets your brain incubate one line of thought while you consciously pursue another.
Idea and Concept Development
Brainstorming without structure can quickly become chaotic or frustrating. In a problem-solving context, having an ideation framework to follow can help ensure your team is both creative and disciplined.
In this method, you’ll find an idea generation process that encourages your group to brainstorm effectively before developing their ideas and begin clustering them together. By using concepts such as Yes and…, more is more and postponing judgement, you can create the ideal conditions for brainstorming with ease.
Idea & Concept Development #hyperisland #innovation #idea generation Ideation and Concept Development is a process for groups to work creatively and collaboratively to generate creative ideas. It’s a general approach that can be adapted and customized to suit many different scenarios. It includes basic principles for idea generation and several steps for groups to work with. It also includes steps for idea selection and development.
Problem-solving techniques for developing and refining solutions
The success of any problem-solving process can be measured by the solutions it produces. After you’ve defined the issue, explored existing ideas, and ideated, it’s time to develop and refine your ideas in order to bring them closer to a solution that actually solves the problem.
Use these problem-solving techniques when you want to help your team think through their ideas and refine them as part of your problem solving process.
Improved Solutions
After a team has successfully identified a problem and come up with a few solutions, it can be tempting to call the work of the problem-solving process complete. That said, the first solution is not necessarily the best, and by including a further review and reflection activity into your problem-solving model, you can ensure your group reaches the best possible result.
One of a number of problem-solving games from Thiagi Group, Improved Solutions helps you go the extra mile and develop suggested solutions with close consideration and peer review. By supporting the discussion of several problems at once and by shifting team roles throughout, this problem-solving technique is a dynamic way of finding the best solution.
Improved Solutions #creativity #thiagi #problem solving #action #team You can improve any solution by objectively reviewing its strengths and weaknesses and making suitable adjustments. In this creativity framegame, you improve the solutions to several problems. To maintain objective detachment, you deal with a different problem during each of six rounds and assume different roles (problem owner, consultant, basher, booster, enhancer, and evaluator) during each round. At the conclusion of the activity, each player ends up with two solutions to her problem.
Four Step Sketch
Creative thinking and visual ideation does not need to be confined to the opening stages of your problem-solving strategies. Exercises that include sketching and prototyping on paper can be effective at the solution finding and development stage of the process, and can be great for keeping a team engaged.
By going from simple notes to a crazy 8s round that involves rapidly sketching 8 variations on their ideas before then producing a final solution sketch, the group is able to iterate quickly and visually. Problem-solving techniques like Four-Step Sketch are great if you have a group of different thinkers and want to change things up from a more textual or discussion-based approach.
Four-Step Sketch #design sprint #innovation #idea generation #remote-friendly The four-step sketch is an exercise that helps people to create well-formed concepts through a structured process that includes: Review key information Start design work on paper, Consider multiple variations , Create a detailed solution . This exercise is preceded by a set of other activities allowing the group to clarify the challenge they want to solve. See how the Four Step Sketch exercise fits into a Design Sprint
Ensuring that everyone in a group is able to contribute to a discussion is vital during any problem solving process. Not only does this ensure all bases are covered, but its then easier to get buy-in and accountability when people have been able to contribute to the process.
1-2-4-All is a tried and tested facilitation technique where participants are asked to first brainstorm on a topic on their own. Next, they discuss and share ideas in a pair before moving into a small group. Those groups are then asked to present the best idea from their discussion to the rest of the team.
This method can be used in many different contexts effectively, though I find it particularly shines in the idea development stage of the process. Giving each participant time to concretize their ideas and develop them in progressively larger groups can create a great space for both innovation and psychological safety.
1-2-4-All #idea generation #liberating structures #issue analysis With this facilitation technique you can immediately include everyone regardless of how large the group is. You can generate better ideas and more of them faster than ever before. You can tap the know-how and imagination that is distributed widely in places not known in advance. Open, generative conversation unfolds. Ideas and solutions are sifted in rapid fashion. Most importantly, participants own the ideas, so follow-up and implementation is simplified. No buy-in strategies needed! Simple and elegant!
15% Solutions
Some problems are simpler than others and with the right problem-solving activities, you can empower people to take immediate actions that can help create organizational change.
Part of the liberating structures toolkit, 15% solutions is a problem-solving technique that focuses on finding and implementing solutions quickly. A process of iterating and making small changes quickly can help generate momentum and an appetite for solving complex problems.
Problem-solving strategies can live and die on whether people are onboard. Getting some quick wins is a great way of getting people behind the process.
It can be extremely empowering for a team to realize that problem-solving techniques can be deployed quickly and easily and delineate between things they can positively impact and those things they cannot change.
15% Solutions #action #liberating structures #remote-friendly You can reveal the actions, however small, that everyone can do immediately. At a minimum, these will create momentum, and that may make a BIG difference. 15% Solutions show that there is no reason to wait around, feel powerless, or fearful. They help people pick it up a level. They get individuals and the group to focus on what is within their discretion instead of what they cannot change. With a very simple question, you can flip the conversation to what can be done and find solutions to big problems that are often distributed widely in places not known in advance. Shifting a few grains of sand may trigger a landslide and change the whole landscape.
Problem-solving techniques for making decisions and planning
After your group is happy with the possible solutions you’ve developed, now comes the time to choose which to implement. There’s more than one way to make a decision and the best option is often dependant on the needs and set-up of your group.
Sometimes, it’s the case that you’ll want to vote as a group on what is likely to be the most impactful solution. Other times, it might be down to a decision maker or major stakeholder to make the final decision. Whatever your process, here’s some techniques you can use to help you make a decision during your problem solving process.
How-Now-Wow Matrix
The problem-solving process is often creative, as complex problems usually require a change of thinking and creative response in order to find the best solutions. While it’s common for the first stages to encourage creative thinking, groups can often gravitate to familiar solutions when it comes to the end of the process.
When selecting solutions, you don’t want to lose your creative energy! The How-Now-Wow Matrix from Gamestorming is a great problem-solving activity that enables a group to stay creative and think out of the box when it comes to selecting the right solution for a given problem.
Problem-solving techniques that encourage creative thinking and the ideation and selection of new solutions can be the most effective in organisational change. Give the How-Now-Wow Matrix a go, and not just for how pleasant it is to say out loud.
How-Now-Wow Matrix #gamestorming #idea generation #remote-friendly When people want to develop new ideas, they most often think out of the box in the brainstorming or divergent phase. However, when it comes to convergence, people often end up picking ideas that are most familiar to them. This is called a ‘creative paradox’ or a ‘creadox’. The How-Now-Wow matrix is an idea selection tool that breaks the creadox by forcing people to weigh each idea on 2 parameters.
Impact and Effort Matrix
All problem-solving techniques hope to not only find solutions to a given problem or challenge but to find the best solution. When it comes to finding a solution, groups are invited to put on their decision-making hats and really think about how a proposed idea would work in practice.
The Impact and Effort Matrix is one of the problem-solving techniques that fall into this camp, empowering participants to first generate ideas and then categorize them into a 2×2 matrix based on impact and effort.
Activities that invite critical thinking while remaining simple are invaluable. Use the Impact and Effort Matrix to move from ideation and towards evaluating potential solutions before then committing to them.
Impact and Effort Matrix #gamestorming #decision making #action #remote-friendly In this decision-making exercise, possible actions are mapped based on two factors: effort required to implement and potential impact. Categorizing ideas along these lines is a useful technique in decision making, as it obliges contributors to balance and evaluate suggested actions before committing to them.
If you’ve followed each of the problem-solving steps with your group successfully, you should move towards the end of your process with heaps of possible solutions developed with a specific problem in mind. But how do you help a group go from ideation to putting a solution into action?
Dotmocracy – or Dot Voting -is a tried and tested method of helping a team in the problem-solving process make decisions and put actions in place with a degree of oversight and consensus.
One of the problem-solving techniques that should be in every facilitator’s toolbox, Dot Voting is fast and effective and can help identify the most popular and best solutions and help bring a group to a decision effectively.
Dotmocracy #action #decision making #group prioritization #hyperisland #remote-friendly Dotmocracy is a simple method for group prioritization or decision-making. It is not an activity on its own, but a method to use in processes where prioritization or decision-making is the aim. The method supports a group to quickly see which options are most popular or relevant. The options or ideas are written on post-its and stuck up on a wall for the whole group to see. Each person votes for the options they think are the strongest, and that information is used to inform a decision.
Straddling the gap between decision making and planning, MoSCoW is a simple and effective method that allows a group team to easily prioritize a set of possible options.
Use this method in a problem solving process by collecting and summarizing all your possible solutions and then categorize them into 4 sections: “Must have”, “Should have”, “Could have”, or “Would like but won‘t get”.
This method is particularly useful when its less about choosing one possible solution and more about prioritorizing which to do first and which may not fit in the scope of your project. In my experience, complex challenges often require multiple small fixes, and this method can be a great way to move from a pile of things you’d all like to do to a structured plan.
MoSCoW #define intentions #create #design #action #remote-friendly MoSCoW is a method that allows the team to prioritize the different features that they will work on. Features are then categorized into “Must have”, “Should have”, “Could have”, or “Would like but won‘t get”. To be used at the beginning of a timeslot (for example during Sprint planning) and when planning is needed.
When it comes to managing the rollout of a solution, clarity and accountability are key factors in ensuring the success of the project. The RAACI chart is a simple but effective model for setting roles and responsibilities as part of a planning session.
Start by listing each person involved in the project and put them into the following groups in order to make it clear who is responsible for what during the rollout of your solution.
- Responsibility (Which person and/or team will be taking action?)
- Authority (At what “point” must the responsible person check in before going further?)
- Accountability (Who must the responsible person check in with?)
- Consultation (Who must be consulted by the responsible person before decisions are made?)
- Information (Who must be informed of decisions, once made?)
Ensure this information is easily accessible and use it to inform who does what and who is looped into discussions and kept up to date.
RAACI #roles and responsibility #teamwork #project management Clarifying roles and responsibilities, levels of autonomy/latitude in decision making, and levels of engagement among diverse stakeholders.
Problem-solving warm-up activities
All facilitators know that warm-ups and icebreakers are useful for any workshop or group process. Problem-solving workshops are no different.
Use these problem-solving techniques to warm up a group and prepare them for the rest of the process. Activating your group by tapping into some of the top problem-solving skills can be one of the best ways to see great outcomes from your session.
Check-in / Check-out
Solid processes are planned from beginning to end, and the best facilitators know that setting the tone and establishing a safe, open environment can be integral to a successful problem-solving process. Check-in / Check-out is a great way to begin and/or bookend a problem-solving workshop. Checking in to a session emphasizes that everyone will be seen, heard, and expected to contribute.
If you are running a series of meetings, setting a consistent pattern of checking in and checking out can really help your team get into a groove. We recommend this opening-closing activity for small to medium-sized groups though it can work with large groups if they’re disciplined!
Check-in / Check-out #team #opening #closing #hyperisland #remote-friendly Either checking-in or checking-out is a simple way for a team to open or close a process, symbolically and in a collaborative way. Checking-in/out invites each member in a group to be present, seen and heard, and to express a reflection or a feeling. Checking-in emphasizes presence, focus and group commitment; checking-out emphasizes reflection and symbolic closure.
Doodling Together
Thinking creatively and not being afraid to make suggestions are important problem-solving skills for any group or team, and warming up by encouraging these behaviors is a great way to start.
Doodling Together is one of our favorite creative ice breaker games – it’s quick, effective, and fun and can make all following problem-solving steps easier by encouraging a group to collaborate visually. By passing cards and adding additional items as they go, the workshop group gets into a groove of co-creation and idea development that is crucial to finding solutions to problems.
Doodling Together #collaboration #creativity #teamwork #fun #team #visual methods #energiser #icebreaker #remote-friendly Create wild, weird and often funny postcards together & establish a group’s creative confidence.
Show and Tell
You might remember some version of Show and Tell from being a kid in school and it’s a great problem-solving activity to kick off a session.
Asking participants to prepare a little something before a workshop by bringing an object for show and tell can help them warm up before the session has even begun! Games that include a physical object can also help encourage early engagement before moving onto more big-picture thinking.
By asking your participants to tell stories about why they chose to bring a particular item to the group, you can help teams see things from new perspectives and see both differences and similarities in the way they approach a topic. Great groundwork for approaching a problem-solving process as a team!
Show and Tell #gamestorming #action #opening #meeting facilitation Show and Tell taps into the power of metaphors to reveal players’ underlying assumptions and associations around a topic The aim of the game is to get a deeper understanding of stakeholders’ perspectives on anything—a new project, an organizational restructuring, a shift in the company’s vision or team dynamic.
Constellations
Who doesn’t love stars? Constellations is a great warm-up activity for any workshop as it gets people up off their feet, energized, and ready to engage in new ways with established topics. It’s also great for showing existing beliefs, biases, and patterns that can come into play as part of your session.
Using warm-up games that help build trust and connection while also allowing for non-verbal responses can be great for easing people into the problem-solving process and encouraging engagement from everyone in the group. Constellations is great in large spaces that allow for movement and is definitely a practical exercise to allow the group to see patterns that are otherwise invisible.
Constellations #trust #connection #opening #coaching #patterns #system Individuals express their response to a statement or idea by standing closer or further from a central object. Used with teams to reveal system, hidden patterns, perspectives.
Draw a Tree
Problem-solving games that help raise group awareness through a central, unifying metaphor can be effective ways to warm-up a group in any problem-solving model.
Draw a Tree is a simple warm-up activity you can use in any group and which can provide a quick jolt of energy. Start by asking your participants to draw a tree in just 45 seconds – they can choose whether it will be abstract or realistic.
Once the timer is up, ask the group how many people included the roots of the tree and use this as a means to discuss how we can ignore important parts of any system simply because they are not visible.
All problem-solving strategies are made more effective by thinking of problems critically and by exposing things that may not normally come to light. Warm-up games like Draw a Tree are great in that they quickly demonstrate some key problem-solving skills in an accessible and effective way.
Draw a Tree #thiagi #opening #perspectives #remote-friendly With this game you can raise awarness about being more mindful, and aware of the environment we live in.
Closing activities for a problem-solving process
Each step of the problem-solving workshop benefits from an intelligent deployment of activities, games, and techniques. Bringing your session to an effective close helps ensure that solutions are followed through on and that you also celebrate what has been achieved.
Here are some problem-solving activities you can use to effectively close a workshop or meeting and ensure the great work you’ve done can continue afterward.
One Breath Feedback
Maintaining attention and focus during the closing stages of a problem-solving workshop can be tricky and so being concise when giving feedback can be important. It’s easy to incur “death by feedback” should some team members go on for too long sharing their perspectives in a quick feedback round.
One Breath Feedback is a great closing activity for workshops. You give everyone an opportunity to provide feedback on what they’ve done but only in the space of a single breath. This keeps feedback short and to the point and means that everyone is encouraged to provide the most important piece of feedback to them.
One breath feedback #closing #feedback #action This is a feedback round in just one breath that excels in maintaining attention: each participants is able to speak during just one breath … for most people that’s around 20 to 25 seconds … unless of course you’ve been a deep sea diver in which case you’ll be able to do it for longer.
Who What When Matrix
Matrices feature as part of many effective problem-solving strategies and with good reason. They are easily recognizable, simple to use, and generate results.
The Who What When Matrix is a great tool to use when closing your problem-solving session by attributing a who, what and when to the actions and solutions you have decided upon. The resulting matrix is a simple, easy-to-follow way of ensuring your team can move forward.
Great solutions can’t be enacted without action and ownership. Your problem-solving process should include a stage for allocating tasks to individuals or teams and creating a realistic timeframe for those solutions to be implemented or checked out. Use this method to keep the solution implementation process clear and simple for all involved.
Who/What/When Matrix #gamestorming #action #project planning With Who/What/When matrix, you can connect people with clear actions they have defined and have committed to.
Response cards
Group discussion can comprise the bulk of most problem-solving activities and by the end of the process, you might find that your team is talked out!
Providing a means for your team to give feedback with short written notes can ensure everyone is head and can contribute without the need to stand up and talk. Depending on the needs of the group, giving an alternative can help ensure everyone can contribute to your problem-solving model in the way that makes the most sense for them.
Response Cards is a great way to close a workshop if you are looking for a gentle warm-down and want to get some swift discussion around some of the feedback that is raised.
Response Cards #debriefing #closing #structured sharing #questions and answers #thiagi #action It can be hard to involve everyone during a closing of a session. Some might stay in the background or get unheard because of louder participants. However, with the use of Response Cards, everyone will be involved in providing feedback or clarify questions at the end of a session.
Tips for effective problem solving
Problem-solving activities are only one part of the puzzle. While a great method can help unlock your team’s ability to solve problems, without a thoughtful approach and strong facilitation the solutions may not be fit for purpose.
Let’s take a look at some problem-solving tips you can apply to any process to help it be a success!
Clearly define the problem
Jumping straight to solutions can be tempting, though without first clearly articulating a problem, the solution might not be the right one. Many of the problem-solving activities below include sections where the problem is explored and clearly defined before moving on.
This is a vital part of the problem-solving process and taking the time to fully define an issue can save time and effort later. A clear definition helps identify irrelevant information and it also ensures that your team sets off on the right track.
Don’t jump to conclusions
It’s easy for groups to exhibit cognitive bias or have preconceived ideas about both problems and potential solutions. Be sure to back up any problem statements or potential solutions with facts, research, and adequate forethought.
The best techniques ask participants to be methodical and challenge preconceived notions. Make sure you give the group enough time and space to collect relevant information and consider the problem in a new way. By approaching the process with a clear, rational mindset, you’ll often find that better solutions are more forthcoming.
Try different approaches
Problems come in all shapes and sizes and so too should the methods you use to solve them. If you find that one approach isn’t yielding results and your team isn’t finding different solutions, try mixing it up. You’ll be surprised at how using a new creative activity can unblock your team and generate great solutions.
Don’t take it personally
Depending on the nature of your team or organizational problems, it’s easy for conversations to get heated. While it’s good for participants to be engaged in the discussions, ensure that emotions don’t run too high and that blame isn’t thrown around while finding solutions.
You’re all in it together, and even if your team or area is seeing problems, that isn’t necessarily a disparagement of you personally. Using facilitation skills to manage group dynamics is one effective method of helping conversations be more constructive.
Get the right people in the room
Your problem-solving method is often only as effective as the group using it. Getting the right people on the job and managing the number of people present is important too!
If the group is too small, you may not get enough different perspectives to effectively solve a problem. If the group is too large, you can go round and round during the ideation stages.
Creating the right group makeup is also important in ensuring you have the necessary expertise and skillset to both identify and follow up on potential solutions. Carefully consider who to include at each stage to help ensure your problem-solving method is followed and positioned for success.
Create psychologically safe spaces for discussion
Identifying a problem accurately also requires that all members of a group are able to contribute their views in an open and safe manner.
It can be tough for people to stand up and contribute if the problems or challenges are emotive or personal in nature. Try and create a psychologically safe space for these kinds of discussions and where possible, create regular opportunities for challenges to be brought up organically.
Document everything
The best solutions can take refinement, iteration, and reflection to come out. Get into a habit of documenting your process in order to keep all the learnings from the session and to allow ideas to mature and develop. Many of the methods below involve the creation of documents or shared resources. Be sure to keep and share these so everyone can benefit from the work done!
Bring a facilitator
Facilitation is all about making group processes easier. With a subject as potentially emotive and important as problem-solving, having an impartial third party in the form of a facilitator can make all the difference in finding great solutions and keeping the process moving. Consider bringing a facilitator to your problem-solving session to get better results and generate meaningful solutions!
Develop your problem-solving skills
It takes time and practice to be an effective problem solver. While some roles or participants might more naturally gravitate towards problem-solving, it can take development and planning to help everyone create better solutions.
You might develop a training program, run a problem-solving workshop or simply ask your team to practice using the techniques below. Check out our post on problem-solving skills to see how you and your group can develop the right mental process and be more resilient to issues too!
Design a great agenda
Workshops are a great format for solving problems. With the right approach, you can focus a group and help them find the solutions to their own problems. But designing a process can be time-consuming and finding the right activities can be difficult.
Check out our workshop planning guide to level-up your agenda design and start running more effective workshops. Need inspiration? Check out templates designed by expert facilitators to help you kickstart your process!
Save time and effort creating an effective problem solving process
A structured problem solving process is a surefire way of solving tough problems, discovering creative solutions and driving organizational change. But how can you design for successful outcomes?
With SessionLab, it’s easy to design engaging workshops that deliver results. Drag, drop and reorder blocks to build your agenda. When you make changes or update your agenda, your session timing adjusts automatically , saving you time on manual adjustments.
Collaborating with stakeholders or clients? Share your agenda with a single click and collaborate in real-time. No more sending documents back and forth over email.
Explore how to use SessionLab to design effective problem solving workshops or watch this five minute video to see the planner in action!

Over to you
The problem-solving process can often be as complicated and multifaceted as the problems they are set-up to solve. With the right problem-solving techniques and a mix of exercises designed to guide discussion and generate purposeful ideas, we hope we’ve given you the tools to find the best solutions as simply and easily as possible.
Is there a problem-solving technique that you are missing here? Do you have a favorite activity or method you use when facilitating? Let us know in the comments below, we’d love to hear from you!
James Smart is Head of Content at SessionLab. He’s also a creative facilitator who has run workshops and designed courses for establishments like the National Centre for Writing, UK. He especially enjoys working with young people and empowering others in their creative practice.
thank you very much for these excellent techniques
Certainly wonderful article, very detailed. Shared!
Your list of techniques for problem solving can be helpfully extended by adding TRIZ to the list of techniques. TRIZ has 40 problem solving techniques derived from methods inventros and patent holders used to get new patents. About 10-12 are general approaches. many organization sponsor classes in TRIZ that are used to solve business problems or general organiztational problems. You can take a look at TRIZ and dwonload a free internet booklet to see if you feel it shound be included per your selection process.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Going from a mere idea to a workshop that delivers results for your clients can feel like a daunting task. In this piece, we will shine a light on all the work behind the scenes and help you learn how to plan a workshop from start to finish. On a good day, facilitation can feel like effortless magic, but that is mostly the result of backstage work, foresight, and a lot of careful planning. Read on to learn a step-by-step approach to breaking the process of planning a workshop into small, manageable chunks. The flow starts with the first meeting with a client to define the purposes of a workshop.…

Effective online tools are a necessity for smooth and engaging virtual workshops and meetings. But how do you choose the right ones? Do you sometimes feel that the good old pen and paper or MS Office toolkit and email leaves you struggling to stay on top of managing and delivering your workshop? Fortunately, there are plenty of great workshop tools to make your life easier when you need to facilitate a meeting and lead workshops. In this post, we’ll share our favorite online tools you can use to make your life easier and run better workshops and meetings. In fact, there are plenty of free online workshop tools and meeting…

How does learning work? A clever 9-year-old once told me: “I know I am learning something new when I am surprised.” The science of adult learning tells us that, in order to learn new skills (which, unsurprisingly, is harder for adults to do than kids) grown-ups need to first get into a specific headspace. In a business, this approach is often employed in a training session where employees learn new skills or work on professional development. But how do you ensure your training is effective? In this guide, we'll explore how to create an effective training session plan and run engaging training sessions. As team leader, project manager, or consultant,…
Design your next workshop with SessionLab
Join the 150,000 facilitators using SessionLab
Sign up for free
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
Additional menu

The 5 steps of the solving problem process
August 17, 2023 by MindManager Blog
Whether you run a business, manage a team, or work in an industry where change is the norm, it may feel like something is always going wrong. Thankfully, becoming proficient in the problem solving process can alleviate a great deal of the stress that business issues can create.
Understanding the right way to solve problems not only takes the guesswork out of how to deal with difficult, unexpected, or complex situations, it can lead to more effective long-term solutions.
In this article, we’ll walk you through the 5 steps of problem solving, and help you explore a few examples of problem solving scenarios where you can see the problem solving process in action before putting it to work.
Understanding the problem solving process
When something isn’t working, it’s important to understand what’s at the root of the problem so you can fix it and prevent it from happening again. That’s why resolving difficult or complex issues works best when you apply proven business problem solving tools and techniques – from soft skills, to software.
The problem solving process typically includes:
- Pinpointing what’s broken by gathering data and consulting with team members.
- Figuring out why it’s not working by mapping out and troubleshooting the problem.
- Deciding on the most effective way to fix it by brainstorming and then implementing a solution.
While skills like active listening, collaboration, and leadership play an important role in problem solving, tools like visual mapping software make it easier to define and share problem solving objectives, play out various solutions, and even put the best fit to work.
Before you can take your first step toward solving a problem, you need to have a clear idea of what the issue is and the outcome you want to achieve by resolving it.
For example, if your company currently manufactures 50 widgets a day, but you’ve started processing orders for 75 widgets a day, you could simply say you have a production deficit.
However, the problem solving process will prove far more valuable if you define the start and end point by clarifying that production is running short by 25 widgets a day, and you need to increase daily production by 50%.
Once you know where you’re at and where you need to end up, these five steps will take you from Point A to Point B:
- Figure out what’s causing the problem . You may need to gather knowledge and evaluate input from different documents, departments, and personnel to isolate the factors that are contributing to your problem. Knowledge visualization software like MindManager can help.
- Come up with a few viable solutions . Since hitting on exactly the right solution – right away – can be tough, brainstorming with your team and mapping out various scenarios is the best way to move forward. If your first strategy doesn’t pan out, you’ll have others on tap you can turn to.
- Choose the best option . Decision-making skills, and software that lets you lay out process relationships, priorities, and criteria, are invaluable for selecting the most promising solution. Whether it’s you or someone higher up making that choice, it should include weighing costs, time commitments, and any implementation hurdles.
- Put your chosen solution to work . Before implementing your fix of choice, you should make key personnel aware of changes that might affect their daily workflow, and set up benchmarks that will make it easy to see if your solution is working.
- Evaluate your outcome . Now comes the moment of truth: did the solution you implemented solve your problem? Do your benchmarks show you achieved the outcome you wanted? If so, congratulations! If not, you’ll need to tweak your solution to meet your problem solving goal.
In practice, you might not hit a home-run with every solution you execute. But the beauty of a repeatable process like problem solving is that you can carry out steps 4 and 5 again by drawing from the brainstorm options you documented during step 2.
Examples of problem solving scenarios
The best way to get a sense of how the problem solving process works before you try it for yourself is to work through some simple scenarios.
Here are three examples of how you can apply business problem solving techniques to common workplace challenges.
Scenario #1: Manufacturing
Building on our original manufacturing example, you determine that your company is consistently short producing 25 widgets a day and needs to increase daily production by 50%.
Since you’d like to gather data and input from both your manufacturing and sales order departments, you schedule a brainstorming session to discover the root cause of the shortage.
After examining four key production areas – machines, materials, methods, and management – you determine the cause of the problem: the material used to manufacture your widgets can only be fed into your equipment once the machinery warms up to a specific temperature for the day.
Your team comes up with three possible solutions.
- Leave your machinery running 24 hours so it’s always at temperature.
- Invest in equipment that heats up faster.
- Find an alternate material for your widgets.
After weighing the expense of the first two solutions, and conducting some online research, you decide that switching to a comparable but less expensive material that can be worked at a lower temperature is your best option.
You implement your plan, monitor your widget quality and output over the following week, and declare your solution a success when daily production increases by 100%.
Scenario #2: Service Delivery
Business training is booming and you’ve had to onboard new staff over the past month. Now you learn that several clients have expressed concern about the quality of your recent training sessions.
After speaking with both clients and staff, you discover there are actually two distinct factors contributing to your quality problem:
- The additional conference room you’ve leased to accommodate your expanding training sessions has terrible acoustics
- The AV equipment you’ve purchased to accommodate your expanding workforce is on back-order – and your new hires have been making do without
You could look for a new conference room or re-schedule upcoming training sessions until after your new equipment arrives. But your team collaboratively determines that the best way to mitigate both issues at once is by temporarily renting the high-quality sound and visual system they need.
Using benchmarks that include several weeks of feedback from session attendees, and random session spot-checks you conduct personally, you conclude the solution has worked.
Scenario #3: Marketing
You’ve invested heavily in product marketing, but still can’t meet your sales goals. Specifically, you missed your revenue target by 30% last year and would like to meet that same target this year.
After collecting and examining reams of information from your sales and accounting departments, you sit down with your marketing team to figure out what’s hindering your success in the marketplace.
Determining that your product isn’t competitively priced, you map out two viable solutions.
- Hire a third-party specialist to conduct a detailed market analysis.
- Drop the price of your product to undercut competitors.
Since you’re in a hurry for results, you decide to immediately reduce the price of your product and market it accordingly.
When revenue figures for the following quarter show sales have declined even further – and marketing surveys show potential customers are doubting the quality of your product – you revert back to your original pricing, revisit your problem solving process, and implement the market analysis solution instead.
With the valuable information you gain, you finally arrive at just the right product price for your target market and sales begin to pick up. Although you miss your revenue target again this year, you meet it by the second quarter of the following year.
Kickstart your collaborative brainstorming sessions and try MindManager for free today !
Ready to take the next step?
MindManager helps boost collaboration and productivity among remote and hybrid teams to achieve better results, faster.
Why choose MindManager?
MindManager® helps individuals, teams, and enterprises bring greater clarity and structure to plans, projects, and processes. It provides visual productivity tools and mind mapping software to help take you and your organization to where you want to be.
Explore MindManager
Learning Materials
- Business Studies
- Combined Science
- Computer Science
- Engineering
- English Literature
- Environmental Science
- Human Geography
- Macroeconomics
- Microeconomics
- Problem-solving Models and Strategies
Have you ever been confronted with a challenging problem and had no idea how to even begin working on it? For instance, let's say you have two upcoming exams on the same day, and you are unsure how to prepare for them. Or, let's say you are solving a complex math problem, but you are stuck and don't know how to proceed. In these moments, problem-solving strategies and models can help us tackle difficult problems by guiding us with well-known approaches or plans to follow.
Create learning materials about Problem-solving Models and Strategies with our free learning app!
- Instand access to millions of learning materials
- Flashcards, notes, mock-exams and more
- Everything you need to ace your exams
Millions of flashcards designed to help you ace your studies
- Cell Biology
Step 01: What do you know?
- Mrs. Grave gives 1 penny on Day 1, 2 pennies on Day 2, and 4 pennies on Day 3.
- Each day the amount of money will double.
- Paul does his tasks for 5 days.
Step 02: What do you want to know?
You curious to figure out how much money will Paul have in total after 5 days of doing his tasks. We want to solve the problem by formulating a simpler one.
Step 01: What does David know?
- The number of players starting the tournament:8
- Only winners can advance to the next round
Step 02: What does David want to know?
David wants to compare the number of players in the second round to the number that starts the tournament. To solve the problem, David can use a diagram.
Step 01: What do you know?
- Slices of tomatoes and cucumber were used.
- The total number of slices used is 60.
- The ratio of cucumbers to tomatoes is 4:6
- The ratio simplifies to 2:3
Step 02: What do you want to know?
We need to know the number of both cucumber and tomato slices. We want to solve the problem by doing a table.
Trial and error is a problem solving strategy.
The IDEAL method is one type of problem-solving model:
Anticipate outcome is one step of problem-solving for Polya's Four-Step problem-solving model?
Problem solving strategies help us to solve a problem efficiently
What are the steps to solve a problem efficiently?
We can recheck our provided solution by doing the following:
Name the two problem-solving models.
- Applied Mathematics
- Decision Maths
- Discrete Mathematics
- Logic and Functions
- Mechanics Maths
- Probability and Statistics
- ASA Theorem
- Absolute Convergence
- Absolute Value Equations and Inequalities
- Absolute Values
- Abstract algebra
- Addition and Multiplication of series
- Addition and Subtraction of Rational Expressions
- Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication and Division
- Algebra of limits
- Algebra over a field
- Algebraic Expressions
- Algebraic Fractions
- Algebraic K-theory
- Algebraic Notation
- Algebraic Representation
- Algebraic curves
- Algebraic geometry
- Algebraic number theory
- Algebraic topology
- Analyzing Graphs of Polynomials
- Angle Conversion
- Angle Measure
- Angle Of Depression
- Angle Of Elevation
- Angles in Polygons
- Angular geometry
- Approximation and Estimation
- Area and Perimeter of Quadrilaterals
- Area of Triangles
- Argand Diagram
- Arithmetic Sequences
- Associative algebra
- Average Rate of Change
- Banach algebras
- Bearing In Trigonometry
- Bijective Functions
- Bilinear forms
- Binomial Expansion
- Binomial Theorem
- Bounded Sequence
- C*-algebras
- Category theory
- Cauchy Sequence
- Cayley Hamilton Theorem
- Central Angles
- Circle Theorems
- Circles Maths
- Clifford algebras
- Cofunction Identities
- Cohomology theory
- Combinatorics
- Common Factors
- Common Multiples
- Commutative algebra
- Compact Set
- Completing the Square
- Complex Numbers
- Composite Figures
- Composite Functions
- Composition of Functions
- Compound Interest
- Compound Units
- Congruence Equations
- Conic Sections
- Connected Set
- Construction and Loci
- Continuity and Uniform convergence
- Continuity of derivative
- Continuity of real valued functions
- Continuous Function
- Convergent Sequence
- Converting Metrics
- Convexity and Concavity
- Coordinate Geometry
- Coordinates in Four Quadrants
- Cosecant Ratios
- Cosine Ratios
- Cotangent Ratios
- Coupled First-order Differential Equations
- Cubic Function Graph
- Cyclic Quadrilaterals
- Data Transformations
- De Moivre's Theorem
- Deductive Reasoning
- Definite Integrals
- Derivative of a real function
- Deriving Equations
- Determinant Of Inverse Matrix
- Determinant of Matrix
- Determinants
- Diagonalising Matrix
- Differentiability of real valued functions
- Differential Equations
- Differential algebra
- Differentiation
- Differentiation Rules
- Differentiation from First Principles
- Differentiation of Hyperbolic Functions
- Direct and Inverse proportions
- Direct variation
- Discontinuity
- Disjoint and Overlapping Events
- Disproof By Counterexample
- Distance formula
- Distance from a Point to a Line
- Divergent Sequence
- Divisibility Tests
- Division algebras
- Double Angle and Half Angle Formulas
- Drawing Conclusions from Examples
- Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors
- Elliptic curves
- Equation of Line in 3D
- Equation of a Perpendicular Bisector
- Equation of a circle
- Equations and Identities
- Equations and Inequalities
- Equicontinuous families of functions
- Estimation in Real Life
- Euclidean Algorithm
- Evaluating and Graphing Polynomials
- Even Functions
- Exponential Form of Complex Numbers
- Exponential Rules
- Exponentials and Logarithms
- Expression Math
- Expressions and Formulas
- Faces Edges and Vertices
- Factoring Polynomials
- Factoring Quadratic Equations
- Factorising expressions
- Fermat's Little Theorem
- Field theory
- Finding Maxima and Minima Using Derivatives
- Finding Rational Zeros
- Finding The Area
- First Fundamental Theorem
- First-order Differential Equations
- Forms of Quadratic Functions
- Fourier analysis
- Fractional Powers
- Fractional Ratio
- Fractions and Decimals
- Fractions and Factors
- Fractions in Expressions and Equations
- Fractions, Decimals and Percentages
- Function Basics
- Functional Analysis
- Fundamental Counting Principle
- Fundamental Theorem of Algebra
- Generating Terms of a Sequence
- Geometric Sequence
- Gradient and Intercept
- Gram-Schmidt Process
- Graphical Representation
- Graphing Rational Functions
- Graphing Trigonometric Functions
- Graphs And Differentiation
- Graphs Of Exponents And Logarithms
- Graphs of Common Functions
- Graphs of Trigonometric Functions
- Greatest Common Divisor
- Grothendieck topologies
- Group Mathematics
- Group representations
- Growth and Decay
- Growth of Functions
- Gröbner bases
- Harmonic Motion
- Hermitian algebra
- Higher Derivatives
- Highest Common Factor
- Homogeneous System of Equations
- Homological algebra
- Homotopy theory
- Hopf algebras
- Ideal theory
- Imaginary Unit And Polar Bijection
- Implicit differentiation
- Indirect variation
- Inductive Reasoning
- Inequalities Maths
- Infinite geometric series
- Injective functions
- Injective linear transformation
- Instantaneous Rate of Change
- Integrating Ex And 1x
- Integrating Polynomials
- Integrating Trigonometric Functions
- Integration
- Integration By Parts
- Integration By Substitution
- Integration Using Partial Fractions
- Integration of Hyperbolic Functions
- Interest calculations
- Invariant Points
- Inverse Hyperbolic Functions
- Inverse Matrices
- Inverse and Joint Variation
- Inverse functions
- Inverse of a Matrix and System of Linear equation
- Invertible linear transformation
- Irrational numbers
- Isosceles Triangles Trigonometry
- Iterative Methods
- Jordan algebras
- Knot theory
- L'hopitals Rule
- Lattice theory
- Law Of Cosines In Algebra
- Law Of Sines In Algebra
- Laws of Logs
- Leibnitz's Theorem
- Lie algebras
- Limits of Accuracy
- Linear Algebra
- Linear Combination
- Linear Expressions
- Linear Independence
- Linear Systems
- Linear Transformation
- Linear Transformations of Matrices
- Linear graphs
- Location of Roots
- Logarithm Base
- Lower and Upper Bounds
- Lowest Common Denominator
- Lowest Common Multiple
- Math formula
- Matrix Addition And Subtraction
- Matrix Calculations
- Matrix Determinant
- Matrix Multiplication
- Matrix inverses
- Matrix operations
- Mean value theorem
- Metric and Imperial Units
- Midpoint formula
- Misleading Graphs
- Mixed Expressions
- Modelling with First-order Differential Equations
- Modular Arithmetic
- Module theory
- Modulus Functions
- Modulus and Phase
- Monoidal categories
- Monotonic Function
- Multiples of Pi
- Multiplication and Division of Fractions
- Multiplicative Relationship
- Multiplicative ideal theory
- Multiplying And Dividing Rational Expressions
- Natural Logarithm
- Natural Numbers
- Non-associative algebra
- Normed spaces
- Number Line
- Number Systems
- Number Theory
- Numerical Methods
- Odd functions
- Open Sentences and Identities
- Operation with Complex Numbers
- Operations With Matrices
- Operations with Decimals
- Operations with Polynomials
- Operator algebras
- Order of Operations
- Orthogonal groups
- Orthogonality
- Parallel Lines
- Parametric Differentiation
- Parametric Equations
- Parametric Hyperbolas
- Parametric Integration
- Parametric Parabolas
- Partial Fractions
- Pascal's Triangle
- Percentage Increase and Decrease
- Perimeter of a Triangle
- Permutations and Combinations
- Perpendicular Lines
- Phase Shift
- Points Lines and Planes
- Pointwise convergence
- Poisson algebras
- Polynomial Graphs
- Polynomial division
- Polynomial rings
- Polynomials
- Powers Roots And Radicals
- Powers and Exponents
- Powers and Roots
- Prime Factorization
- Prime Numbers
- Product Rule
- Product of polynomials
- Product-to-sum Formulas
- Proof and Mathematical Induction
- Proof by Contradiction
- Proof by Deduction
- Proof by Exhaustion
- Proof by Induction
- Properties of Determinants
- Properties of Exponents
- Properties of Riemann Integral
- Properties of dimension
- Properties of eigenvalues and eigenvectors
- Proving an Identity
- Pythagorean Identities
- Quadratic Equations
- Quadratic Function Graphs
- Quadratic Graphs
- Quadratic forms
- Quadratic functions
- Quadrilaterals
- Quantum groups
- Quotient Rule
- Radian Measure
- Radical Functions
- Rates of Change
- Ratio Fractions
- Ratio and Root test
- Rational Exponents
- Rational Expressions
- Rational Functions
- Rational Numbers and Fractions
- Rationalizing denominators
- Ratios as Fractions
- Real Numbers
- Rearrangement
- Reciprocal Graphs
- Recurrence Relation
- Recursion and Special Sequences
- Reduced Row Echelon Form
- Reducible Differential Equations
- Remainder and Factor Theorems
- Representation Of Complex Numbers
- Representation theory
- Rewriting Formulas and Equations
- Riemann integral for step function
- Riemann surfaces
- Riemannian geometry
- Right Triangle Trigonometry
- Ring theory
- Roots Of Unity
- Roots of Complex Numbers
- Roots of Polynomials
- SAS Theorem
- SSS Theorem
- Scalar Products
- Scalar Triple Product
- Scale Drawings and Maps
- Scale Factors
- Scalene Triangles Trigonometry
- Scientific Notation
- Secant Ratios
- Second Fundamental Theorem
- Second Order Recurrence Relation
- Second-order Differential Equations
- Sector of a Circle
- Segment of a Circle
- Sequence and series of real valued functions
- Sequence of Real Numbers
- Sequences and Series
- Series Maths
- Series of non negative terms
- Series of real numbers
- Sigma notation
- Similar Triangles
- Similar and Congruent Shapes
- Similarity and diagonalisation
- Simple Interest
- Simple algebras
- Simplifying Fractions
- Simplifying Radicals
- Simultaneous Equations
- Sine Ratios
- Sine and Cosine Rules
- Sinusoidal Graphs
- Slope formulas
- Slope-intercept form
- Small Angle Approximation
- Solving Linear Equations
- Solving Linear Systems
- Solving Oblique Triangles
- Solving Quadratic Equations
- Solving Radical Inequalities
- Solving Rational Equations
- Solving Right Triangles
- Solving Simultaneous Equations Using Matrices
- Solving Systems of Inequalities
- Solving Trigonometric Equations
- Solving and Graphing Quadratic Equations
- Solving and Graphing Quadratic Inequalities
- Spanning Set
- Special Products
- Special Sequences
- Spherical Trigonometry
- Standard Form
- Standard Integrals
- Standard Unit
- Standard form equations
- Stone Weierstrass theorem
- Straight Line Graphs
- Subsequence
- Substraction and addition of fractions
- Sum and Difference of Angles Formulas
- Sum of Natural Numbers
- Sum-to-product Formulas
- Summation by Parts
- Supremum and Infimum
- Surjective functions
- Surjective linear transformation
- System of Linear Equations
- Tables and Graphs
- Tangent Ratios
- Tangent of a Circle
- Tangent rule
- Taylor theorem
- The Quadratic Formula and the Discriminant
- Topological groups
- Torsion theories
- Transformations
- Transformations geometry
- Transformations of Graphs
- Transformations of Roots
- Translations of Trigonometric Functions
- Transversals
- Triangle Rules
- Triangle trigonometry
- Trigonometric Functions
- Trigonometric Functions of General Angles
- Trigonometric Identities
- Trigonometric Identities Sum Angles
- Trigonometric Proofs
- Trigonometric Ratios
- Trigonometric Ratios Of Complementary Angles
- Trigonometry
- Trigonometry Height And Distance
- Trigonometry Word Problems
- Turning Points
- Types of Functions
- Types of Numbers
- Types of Triangles
- Uniform convergence
- Unit Circle
- Universal algebra
- Upper and Lower Bounds
- Valuation theory
- Variable expressions
- Variables in Algebra
- Vector Notation
- Vector Space
- Vector spaces
- Verifying Trigonometric Identities
- Vertex form
- Volume calculations
- Volumes of Revolution
- Von Neumann algebras
- Writing Equations
- Writing Linear Equations
- Zariski topology
- secant lines
- slope formula
- Theoretical and Mathematical Physics
In this article, we explore problem-solving strategies and models that can be applied to solve problems. Then, we practice applying these models in some example exercises.
Problem-solving strategies and model descriptions
Oftentimes in mathematics, there is more than one way to solve a problem. Using problem-solving strategies can help you approach problems in a structured and logical manner to improve your efficiency.
Problem-solving strategies are models based on previous experience that provide a recommended approach for solving problems or analyzing potential solutions.
Problem-solving strategies involve steps like understanding, planning, and organizing, for example. While problem-solving strategies cannot guarantee an easier solution to a problem, they do provide techniques and tools that act as a guide for success.
Types of problem-solving models and strategies
Many models and strategies are developed based on the nature of the problem at hand. In this article, we discuss two well-known models that are designed to address various types of problems, including:
Polya's f our-step problem-solving model
IDEAL problem-solving model
Let's look at these two models in detail.
A mathematician named George Polya developed a model called the Polya f our-step problem-solving model to approach and solve various kinds of problems. This method has the following steps:
Understand the problem
Devise a plan, carry out the plan.
John Bransford and Barry Stein also proposed a five-step model named IDEAL to resolve a problem with a sound and methodical approach. The IDEAL model is based on the following steps:
- Identify The Problem
- Define An Outcome
- Explore Possible Strategies
- Anticipate Outcomes & Act
- Look And Learn
Using either of these two models to help you identify and approach problems methodically can help make it easier to solve them.
Polya's four-step problem-solving model
Polya's f our-step problem-solving model can be used to solve day-to-day problems as well as mathematical and other academic problems. As seen briefly, the steps of this problem-solving model include: understanding the problem, creating and carrying out a plan, and looking back. Let's look at these steps in more detail to understand how they are used.
This is a critical initial step. Simply put, if you don't fully understand the problem, you won't be able to identify a solution. You can understand a problem better by reviewing all of the inputs and available information, including its conditions and circumstances. Reading and understanding the problem helps you to organize the information as well as assign the relevant variables.
The following techniques can be applied during this problem-solving step:
Read the problem out loud to process it better.
List or summarize the important information to find out what is given and what is still missing.
Sketch a detailed diagram as a visual aid, depending on the problem.
Visualize a scenario about the problem to put it into context.
Use keyword analysis to identify the necessary operations (i.e., pay attention to important words and phrases such as "how many," "times," or "total").
Now that you have taken the time to properly understand the problem, you can devise a plan on how to proceed further to solve it. During this second step, you identify what strategy to follow to arrive at a solution. When considering a strategy to use, it's important to consider exactly what it is that you want to know.
Some problem-solving strategies include:
Identify the pattern from the given information and use it.
Use the guess-and-check method.
Work backward by using potential answers.
Apply a specific formula for the problem.
Eliminate the possibilities that don't work out.
Solve a simpler version of the problem first.
Form an equation and solve it.
During this third step, you solve the problem by applying your chosen strategy. For example, if you planned to solve the problem by drawing a graph, then during this step, you draw the graph using the information gathered in the previous steps. Here, you test your problem-solving skills and find if the solution works or not.
Below are some points to keep in mind when solving the problem:
Be systematic in your approach when implementing a strategy.
Check the work and see whether the solution works in all relevant cases.
Be flexible and change the strategy if necessary.
Keep solving and don't give up.
At this fourth step, you check your solution. This can be done by solving the problem in another way or simply by confirming that your solution makes sense. This step helps you decide if any improvements are needed for your solution. You may choose to check after solving an individual problem or after solving an entire set. Checking the problem carefully also helps you to reflect on the process and improve your methods for future problem solving.
The IDEAL problem-solving model was developed by Bransford and Stein as a guide for understanding and solving problems. This method is used in both education and industry. The IDEAL problem-solving model consists of five steps: identifying the problem, describing the outcome, exploring the possible strategies, anticipating the outcome, and looking back to learn. Let us explore these steps in detail by considering them one by one.
I dentify the problem - In this first step, you identify and understand the problem. To do this, you evaluate which information is provided and available, and you identify the unknown variables and missing information.
D escribe the outcome - In this second step, you define the result you are seeking. This matters because a problem might have multiple potential results, so you need to clarify which outcomes in particular you are aiming for. Defining an outcome clarifies the path that must be taken to solving the problem.
E xplore possible strategies - Now that you have considered the desired outcome, you are ready to brainstorm and explore different strategies and techniques to solve your particular problem.
A nticipate outcomes and act - From the previous step, you already have explored different strategies and techniques. During this step, you review and evaluate them in order to choose the best one to act on. Your selection should consider the benefits and drawbacks of the strategy and whether it can ultimately lead to the desired outcome. After making your selection, you act on it and apply the technique to the given problem.
L ook and learn - The final step to solving problems with this method is to consider whether the applied technique worked and if the needed results were obtained. Also, an additional step is learning from the current problem and its methods to make problem solving more efficient in the future.
Examples of problem-solving models and strategies
Here are some solved examples of the problem-solving models and strategies discussed above.
Find the number when two times the sum of \(3\) and that number is thrice that number plus \(4\). Solve this problem with Polya's f our-step problem-solving model .
Solution: We will follow the steps of Polya's f our-step problem-solving model as mentioned above to find the number.
Step 1 : Understand the problem.
By reading and understanding the question, we denote the unknown number as \(x\).
Step 2 : Devise a plan.
We see that two times \(x\) is added to \(3\) to make it equal to thrice the \(x\) plus \(4\). So, we can determine that forming an equation to solve the mathematical problem is a reasonable plan. Therefore, we form an equation by going step by step:
First we add \(x\) with \(3\) and multiply it with \(2\).
\begin{equation}\tag{1}\Rightarrow 2(x+3)\end{equation}
Then, we form the second part of the equation for thrice the \(x\) plus \(4\).
\begin{equation}\tag{2}\Rightarrow 3x+4\end{equation}
Hence, equating both sides \((1)\) and \((2)\) we get,
\[2(x+3)=3x+4\]
Step 3 : Carry out the plan.
Now, we algebraically solve the equation above.
\begin{align}2(x+3) &=3x+4 \\2x+6 &= 3x+4 \\3x-2x &= 6-4 \\x &=2\end{align}
Step 4 : Look back.
By inputting the value of 2 in our equation, we see that two times \(2+3\) is \(10\) and three times \(2\) plus \(4\) is also 10. Hence, the left side and right side are equal. So, our solution is satisfied.
Hence, the number is \(2\).
A string is \(48 cm\) long. It is cut into two pieces such that one piece is three times that of the other piece. What is the length of each piece?
Solution : Let us work on this problem using the IDEAL problem-solving method.
Step 1 : Identify the problem.
We are given a length of a string, and we know that it is cut into two parts, whereby one part is three times longer than the other. As the length of the longer piece of string is dependent on the shorter string, we assume only one variable, say \(x\).
Step 2 : Describe the outcome.
From the problem, we understand that we need to find the length of each piece of string. And we need the results such that the total length of both the pieces should be \(48 cm\).
Step 3 : Explore possible strategies.
There are multiple ways to solve this problem. One way to solve it is by using the trial-and-error method. Also, as one length is dependent on another, the other way is to form an equation to solve for the unknown variable algebraically.
Step 4 : Anticipate outcomes and act.
From the above step, we have two methods by which we can solve the given problem. Let's find out which method is more efficient and solve the problem by applying it.
For the trial-and-error method, we need to assume value(s) one at a time for the variable and then solve for it individually until we get the total of 48.
That is, suppose we consider \(x=1\).
Then, by the condition, the second piece is three times the first piece.
\[\Rightarrow 3x=3(1)=3\]
Then the length of both pieces should be:
\[\Rightarrow 1+3=4\neq 48\]
Hence, our assumption is wrong. So, we need to consider another value. For this method, we continue this process until we find the total of \(48\). We can see that proceeding this way is time-consuming. So, let us apply the other method instead.
In this method, we form an equation and solve it to obtain the unknown variable's value. We know that one piece is three times the other piece. Therefore, let the length of one piece be \(x\). Then the length of the other piece is \(3x\).
Now, as the string is \(48 cm\) long, it should be considered as a sum of both of its pieces.
\begin{align}&\Rightarrow x+3x=48 \\&\Rightarrow 4x=48 \\&\Rightarrow x=\frac{48}{4} \\&\Rightarrow x=12 \\\end{align}
So, the length of one piece is \(12cm\). The length of the other piece is \(3x=3(12)=36cm\).
Step 5: Look and learn
Let's take a look to see if our answers are correct. The unknown variable value we obtained is \(12\). Using it to find the other piece we get a value of \(36\). Now, adding both of them, we get:
\[\Rightarrow 12+36=48\].
Here, we got the correct total length. Hence, our calculations and applied method are right.
Problem-solving strategies and models - Key takeaways
- Problem-solving strategies are models developed based on previous experience that provide a recommended approach for analyzing potential solutions for problems.
- Two common models include Polya's Four-Step Problem-Solving Model and the IDEAL problem-solving model.
- Polya's Four-Step Problem-Solving Model has the following steps: 1) Understand the problem, 2) Devise a plan, 3) Carry out the plan, and 4) Looking back.
- The IDEAL model is based on the following steps: 1) Identify The Problem, 2) Define An Outcome, 3) Explore Possible Strategies, 4) Anticipate Outcomes and Act, 5) Look And Learn.
Flashcards in Problem-solving Models and Strategies 15
24 cucumber slices and 36 tomato slices is one solution

Learn with 15 Problem-solving Models and Strategies flashcards in the free StudySmarter app
We have 14,000 flashcards about Dynamic Landscapes.
Already have an account? Log in
Frequently Asked Questions about Problem-solving Models and Strategies
What are problem-solving models?
Problem-solving models are models developed based on previous experience that provide a recommended approach for solving problems or analyzing potential solutions.
What are types of problem-solving?
The most basic types of problem-solving are Polya's four-step problem-solving model and the IDEAL problem-solving model.
What are the strategies to problem-solve efficiently?
The strategies to solve a problem efficiently are to understand it, determine the correct method, solve it and verify and learn from it.
What are the lists of problem-solving models in algebra?
In algebra, any problem can be solved using Polya's four-step problem-solving model and IDEAL problem-solving model.
What are the 5 problem-solving strategies?
The 5 problem-solving strategies are 1. Identify The Problem, 2. Define An Outcome, 3. Explore Possible Strategies, 4. Anticipate Outcomes & Act, 5. Look And Learn.
Test your knowledge with multiple choice flashcards
Step 01: What do you know? Mrs. Grave gives 1 penny on Day 1, 2 pennies on Day 2, and 4 pennies on Day 3.Each day the amount of money will double. Paul does his tasks for 5 days.Step 02: What do you want to know?You curious to figure out how much money will Paul have in total after 5 days of doing his tasks. We want to solve the problem by formulating a simpler one.
Step 01: What does David know? The number of players starting the tournament:8 Only winners can advance to the next roundStep 02: What does David want to know?David wants to compare the number of players in the second round to the number that starts the tournament. To solve the problem, David can use a diagram.
Step 01: What do you know?Slices of tomatoes and cucumber were used.The total number of slices used is 60.The ratio of cucumbers to tomatoes is 4:6The ratio simplifies to 2:3Step 02: What do you want to know? We need to know the number of both cucumber and tomato slices. We want to solve the problem by doing a table.

Join the StudySmarter App and learn efficiently with millions of flashcards and more!
Keep learning, you are doing great.
Discover learning materials with the free StudySmarter app

About StudySmarter
StudySmarter is a globally recognized educational technology company, offering a holistic learning platform designed for students of all ages and educational levels. Our platform provides learning support for a wide range of subjects, including STEM, Social Sciences, and Languages and also helps students to successfully master various tests and exams worldwide, such as GCSE, A Level, SAT, ACT, Abitur, and more. We offer an extensive library of learning materials, including interactive flashcards, comprehensive textbook solutions, and detailed explanations. The cutting-edge technology and tools we provide help students create their own learning materials. StudySmarter’s content is not only expert-verified but also regularly updated to ensure accuracy and relevance.

StudySmarter Editorial Team
Team Math Teachers
- 11 minutes reading time
- Checked by StudySmarter Editorial Team
Study anywhere. Anytime.Across all devices.
Create a free account to save this explanation..
Save explanations to your personalised space and access them anytime, anywhere!
By signing up, you agree to the Terms and Conditions and the Privacy Policy of StudySmarter.
Sign up to highlight and take notes. It’s 100% free.
Join over 22 million students in learning with our StudySmarter App
The first learning app that truly has everything you need to ace your exams in one place
- Flashcards & Quizzes
- AI Study Assistant
- Study Planner
- Smart Note-Taking

Get unlimited access with a free StudySmarter account.
- Instant access to millions of learning materials.
- Flashcards, notes, mock-exams, AI tools and more.
- Everything you need to ace your exams.

What is Problem Solving? (Steps, Techniques, Examples)
By Status.net Editorial Team on May 7, 2023 — 5 minutes to read
What Is Problem Solving?
Definition and importance.
Problem solving is the process of finding solutions to obstacles or challenges you encounter in your life or work. It is a crucial skill that allows you to tackle complex situations, adapt to changes, and overcome difficulties with ease. Mastering this ability will contribute to both your personal and professional growth, leading to more successful outcomes and better decision-making.
Problem-Solving Steps
The problem-solving process typically includes the following steps:
- Identify the issue : Recognize the problem that needs to be solved.
- Analyze the situation : Examine the issue in depth, gather all relevant information, and consider any limitations or constraints that may be present.
- Generate potential solutions : Brainstorm a list of possible solutions to the issue, without immediately judging or evaluating them.
- Evaluate options : Weigh the pros and cons of each potential solution, considering factors such as feasibility, effectiveness, and potential risks.
- Select the best solution : Choose the option that best addresses the problem and aligns with your objectives.
- Implement the solution : Put the selected solution into action and monitor the results to ensure it resolves the issue.
- Review and learn : Reflect on the problem-solving process, identify any improvements or adjustments that can be made, and apply these learnings to future situations.
Defining the Problem
To start tackling a problem, first, identify and understand it. Analyzing the issue thoroughly helps to clarify its scope and nature. Ask questions to gather information and consider the problem from various angles. Some strategies to define the problem include:
- Brainstorming with others
- Asking the 5 Ws and 1 H (Who, What, When, Where, Why, and How)
- Analyzing cause and effect
- Creating a problem statement
Generating Solutions
Once the problem is clearly understood, brainstorm possible solutions. Think creatively and keep an open mind, as well as considering lessons from past experiences. Consider:
- Creating a list of potential ideas to solve the problem
- Grouping and categorizing similar solutions
- Prioritizing potential solutions based on feasibility, cost, and resources required
- Involving others to share diverse opinions and inputs
Evaluating and Selecting Solutions
Evaluate each potential solution, weighing its pros and cons. To facilitate decision-making, use techniques such as:
- SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats)
- Decision-making matrices
- Pros and cons lists
- Risk assessments
After evaluating, choose the most suitable solution based on effectiveness, cost, and time constraints.

Implementing and Monitoring the Solution
Implement the chosen solution and monitor its progress. Key actions include:
- Communicating the solution to relevant parties
- Setting timelines and milestones
- Assigning tasks and responsibilities
- Monitoring the solution and making adjustments as necessary
- Evaluating the effectiveness of the solution after implementation
Utilize feedback from stakeholders and consider potential improvements. Remember that problem-solving is an ongoing process that can always be refined and enhanced.
Problem-Solving Techniques
During each step, you may find it helpful to utilize various problem-solving techniques, such as:
- Brainstorming : A free-flowing, open-minded session where ideas are generated and listed without judgment, to encourage creativity and innovative thinking.
- Root cause analysis : A method that explores the underlying causes of a problem to find the most effective solution rather than addressing superficial symptoms.
- SWOT analysis : A tool used to evaluate the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats related to a problem or decision, providing a comprehensive view of the situation.
- Mind mapping : A visual technique that uses diagrams to organize and connect ideas, helping to identify patterns, relationships, and possible solutions.
Brainstorming
When facing a problem, start by conducting a brainstorming session. Gather your team and encourage an open discussion where everyone contributes ideas, no matter how outlandish they may seem. This helps you:
- Generate a diverse range of solutions
- Encourage all team members to participate
- Foster creative thinking
When brainstorming, remember to:
- Reserve judgment until the session is over
- Encourage wild ideas
- Combine and improve upon ideas
Root Cause Analysis
For effective problem-solving, identifying the root cause of the issue at hand is crucial. Try these methods:
- 5 Whys : Ask “why” five times to get to the underlying cause.
- Fishbone Diagram : Create a diagram representing the problem and break it down into categories of potential causes.
- Pareto Analysis : Determine the few most significant causes underlying the majority of problems.
SWOT Analysis
SWOT analysis helps you examine the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats related to your problem. To perform a SWOT analysis:
- List your problem’s strengths, such as relevant resources or strong partnerships.
- Identify its weaknesses, such as knowledge gaps or limited resources.
- Explore opportunities, like trends or new technologies, that could help solve the problem.
- Recognize potential threats, like competition or regulatory barriers.
SWOT analysis aids in understanding the internal and external factors affecting the problem, which can help guide your solution.
Mind Mapping
A mind map is a visual representation of your problem and potential solutions. It enables you to organize information in a structured and intuitive manner. To create a mind map:
- Write the problem in the center of a blank page.
- Draw branches from the central problem to related sub-problems or contributing factors.
- Add more branches to represent potential solutions or further ideas.
Mind mapping allows you to visually see connections between ideas and promotes creativity in problem-solving.
Examples of Problem Solving in Various Contexts
In the business world, you might encounter problems related to finances, operations, or communication. Applying problem-solving skills in these situations could look like:
- Identifying areas of improvement in your company’s financial performance and implementing cost-saving measures
- Resolving internal conflicts among team members by listening and understanding different perspectives, then proposing and negotiating solutions
- Streamlining a process for better productivity by removing redundancies, automating tasks, or re-allocating resources
In educational contexts, problem-solving can be seen in various aspects, such as:
- Addressing a gap in students’ understanding by employing diverse teaching methods to cater to different learning styles
- Developing a strategy for successful time management to balance academic responsibilities and extracurricular activities
- Seeking resources and support to provide equal opportunities for learners with special needs or disabilities
Everyday life is full of challenges that require problem-solving skills. Some examples include:
- Overcoming a personal obstacle, such as improving your fitness level, by establishing achievable goals, measuring progress, and adjusting your approach accordingly
- Navigating a new environment or city by researching your surroundings, asking for directions, or using technology like GPS to guide you
- Dealing with a sudden change, like a change in your work schedule, by assessing the situation, identifying potential impacts, and adapting your plans to accommodate the change.
- How to Resolve Employee Conflict at Work [Steps, Tips, Examples]
- How to Write Inspiring Core Values? 5 Steps with Examples
- 30 Employee Feedback Examples (Positive & Negative)
How to master the seven-step problem-solving process
In this episode of the McKinsey Podcast , Simon London speaks with Charles Conn, CEO of venture-capital firm Oxford Sciences Innovation, and McKinsey senior partner Hugo Sarrazin about the complexities of different problem-solving strategies.
Podcast transcript
Simon London: Hello, and welcome to this episode of the McKinsey Podcast , with me, Simon London. What’s the number-one skill you need to succeed professionally? Salesmanship, perhaps? Or a facility with statistics? Or maybe the ability to communicate crisply and clearly? Many would argue that at the very top of the list comes problem solving: that is, the ability to think through and come up with an optimal course of action to address any complex challenge—in business, in public policy, or indeed in life.
Looked at this way, it’s no surprise that McKinsey takes problem solving very seriously, testing for it during the recruiting process and then honing it, in McKinsey consultants, through immersion in a structured seven-step method. To discuss the art of problem solving, I sat down in California with McKinsey senior partner Hugo Sarrazin and also with Charles Conn. Charles is a former McKinsey partner, entrepreneur, executive, and coauthor of the book Bulletproof Problem Solving: The One Skill That Changes Everything [John Wiley & Sons, 2018].
Charles and Hugo, welcome to the podcast. Thank you for being here.
Hugo Sarrazin: Our pleasure.
Charles Conn: It’s terrific to be here.
Simon London: Problem solving is a really interesting piece of terminology. It could mean so many different things. I have a son who’s a teenage climber. They talk about solving problems. Climbing is problem solving. Charles, when you talk about problem solving, what are you talking about?
Charles Conn: For me, problem solving is the answer to the question “What should I do?” It’s interesting when there’s uncertainty and complexity, and when it’s meaningful because there are consequences. Your son’s climbing is a perfect example. There are consequences, and it’s complicated, and there’s uncertainty—can he make that grab? I think we can apply that same frame almost at any level. You can think about questions like “What town would I like to live in?” or “Should I put solar panels on my roof?”
You might think that’s a funny thing to apply problem solving to, but in my mind it’s not fundamentally different from business problem solving, which answers the question “What should my strategy be?” Or problem solving at the policy level: “How do we combat climate change?” “Should I support the local school bond?” I think these are all part and parcel of the same type of question, “What should I do?”
I’m a big fan of structured problem solving. By following steps, we can more clearly understand what problem it is we’re solving, what are the components of the problem that we’re solving, which components are the most important ones for us to pay attention to, which analytic techniques we should apply to those, and how we can synthesize what we’ve learned back into a compelling story. That’s all it is, at its heart.
I think sometimes when people think about seven steps, they assume that there’s a rigidity to this. That’s not it at all. It’s actually to give you the scope for creativity, which often doesn’t exist when your problem solving is muddled.
Simon London: You were just talking about the seven-step process. That’s what’s written down in the book, but it’s a very McKinsey process as well. Without getting too deep into the weeds, let’s go through the steps, one by one. You were just talking about problem definition as being a particularly important thing to get right first. That’s the first step. Hugo, tell us about that.
Hugo Sarrazin: It is surprising how often people jump past this step and make a bunch of assumptions. The most powerful thing is to step back and ask the basic questions—“What are we trying to solve? What are the constraints that exist? What are the dependencies?” Let’s make those explicit and really push the thinking and defining. At McKinsey, we spend an enormous amount of time in writing that little statement, and the statement, if you’re a logic purist, is great. You debate. “Is it an ‘or’? Is it an ‘and’? What’s the action verb?” Because all these specific words help you get to the heart of what matters.
Want to subscribe to The McKinsey Podcast ?
Simon London: So this is a concise problem statement.
Hugo Sarrazin: Yeah. It’s not like “Can we grow in Japan?” That’s interesting, but it is “What, specifically, are we trying to uncover in the growth of a product in Japan? Or a segment in Japan? Or a channel in Japan?” When you spend an enormous amount of time, in the first meeting of the different stakeholders, debating this and having different people put forward what they think the problem definition is, you realize that people have completely different views of why they’re here. That, to me, is the most important step.
Charles Conn: I would agree with that. For me, the problem context is critical. When we understand “What are the forces acting upon your decision maker? How quickly is the answer needed? With what precision is the answer needed? Are there areas that are off limits or areas where we would particularly like to find our solution? Is the decision maker open to exploring other areas?” then you not only become more efficient, and move toward what we call the critical path in problem solving, but you also make it so much more likely that you’re not going to waste your time or your decision maker’s time.
How often do especially bright young people run off with half of the idea about what the problem is and start collecting data and start building models—only to discover that they’ve really gone off half-cocked.
Hugo Sarrazin: Yeah.
Charles Conn: And in the wrong direction.
Simon London: OK. So step one—and there is a real art and a structure to it—is define the problem. Step two, Charles?
Charles Conn: My favorite step is step two, which is to use logic trees to disaggregate the problem. Every problem we’re solving has some complexity and some uncertainty in it. The only way that we can really get our team working on the problem is to take the problem apart into logical pieces.
What we find, of course, is that the way to disaggregate the problem often gives you an insight into the answer to the problem quite quickly. I love to do two or three different cuts at it, each one giving a bit of a different insight into what might be going wrong. By doing sensible disaggregations, using logic trees, we can figure out which parts of the problem we should be looking at, and we can assign those different parts to team members.
Simon London: What’s a good example of a logic tree on a sort of ratable problem?
Charles Conn: Maybe the easiest one is the classic profit tree. Almost in every business that I would take a look at, I would start with a profit or return-on-assets tree. In its simplest form, you have the components of revenue, which are price and quantity, and the components of cost, which are cost and quantity. Each of those can be broken out. Cost can be broken into variable cost and fixed cost. The components of price can be broken into what your pricing scheme is. That simple tree often provides insight into what’s going on in a business or what the difference is between that business and the competitors.
If we add the leg, which is “What’s the asset base or investment element?”—so profit divided by assets—then we can ask the question “Is the business using its investments sensibly?” whether that’s in stores or in manufacturing or in transportation assets. I hope we can see just how simple this is, even though we’re describing it in words.
When I went to work with Gordon Moore at the Moore Foundation, the problem that he asked us to look at was “How can we save Pacific salmon?” Now, that sounds like an impossible question, but it was amenable to precisely the same type of disaggregation and allowed us to organize what became a 15-year effort to improve the likelihood of good outcomes for Pacific salmon.
Simon London: Now, is there a danger that your logic tree can be impossibly large? This, I think, brings us onto the third step in the process, which is that you have to prioritize.
Charles Conn: Absolutely. The third step, which we also emphasize, along with good problem definition, is rigorous prioritization—we ask the questions “How important is this lever or this branch of the tree in the overall outcome that we seek to achieve? How much can I move that lever?” Obviously, we try and focus our efforts on ones that have a big impact on the problem and the ones that we have the ability to change. With salmon, ocean conditions turned out to be a big lever, but not one that we could adjust. We focused our attention on fish habitats and fish-harvesting practices, which were big levers that we could affect.
People spend a lot of time arguing about branches that are either not important or that none of us can change. We see it in the public square. When we deal with questions at the policy level—“Should you support the death penalty?” “How do we affect climate change?” “How can we uncover the causes and address homelessness?”—it’s even more important that we’re focusing on levers that are big and movable.
Would you like to learn more about our Strategy & Corporate Finance Practice ?
Simon London: Let’s move swiftly on to step four. You’ve defined your problem, you disaggregate it, you prioritize where you want to analyze—what you want to really look at hard. Then you got to the work plan. Now, what does that mean in practice?
Hugo Sarrazin: Depending on what you’ve prioritized, there are many things you could do. It could be breaking the work among the team members so that people have a clear piece of the work to do. It could be defining the specific analyses that need to get done and executed, and being clear on time lines. There’s always a level-one answer, there’s a level-two answer, there’s a level-three answer. Without being too flippant, I can solve any problem during a good dinner with wine. It won’t have a whole lot of backing.
Simon London: Not going to have a lot of depth to it.
Hugo Sarrazin: No, but it may be useful as a starting point. If the stakes are not that high, that could be OK. If it’s really high stakes, you may need level three and have the whole model validated in three different ways. You need to find a work plan that reflects the level of precision, the time frame you have, and the stakeholders you need to bring along in the exercise.
Charles Conn: I love the way you’ve described that, because, again, some people think of problem solving as a linear thing, but of course what’s critical is that it’s iterative. As you say, you can solve the problem in one day or even one hour.
Charles Conn: We encourage our teams everywhere to do that. We call it the one-day answer or the one-hour answer. In work planning, we’re always iterating. Every time you see a 50-page work plan that stretches out to three months, you know it’s wrong. It will be outmoded very quickly by that learning process that you described. Iterative problem solving is a critical part of this. Sometimes, people think work planning sounds dull, but it isn’t. It’s how we know what’s expected of us and when we need to deliver it and how we’re progressing toward the answer. It’s also the place where we can deal with biases. Bias is a feature of every human decision-making process. If we design our team interactions intelligently, we can avoid the worst sort of biases.
Simon London: Here we’re talking about cognitive biases primarily, right? It’s not that I’m biased against you because of your accent or something. These are the cognitive biases that behavioral sciences have shown we all carry around, things like anchoring, overoptimism—these kinds of things.
Both: Yeah.
Charles Conn: Availability bias is the one that I’m always alert to. You think you’ve seen the problem before, and therefore what’s available is your previous conception of it—and we have to be most careful about that. In any human setting, we also have to be careful about biases that are based on hierarchies, sometimes called sunflower bias. I’m sure, Hugo, with your teams, you make sure that the youngest team members speak first. Not the oldest team members, because it’s easy for people to look at who’s senior and alter their own creative approaches.
Hugo Sarrazin: It’s helpful, at that moment—if someone is asserting a point of view—to ask the question “This was true in what context?” You’re trying to apply something that worked in one context to a different one. That can be deadly if the context has changed, and that’s why organizations struggle to change. You promote all these people because they did something that worked well in the past, and then there’s a disruption in the industry, and they keep doing what got them promoted even though the context has changed.
Simon London: Right. Right.
Hugo Sarrazin: So it’s the same thing in problem solving.
Charles Conn: And it’s why diversity in our teams is so important. It’s one of the best things about the world that we’re in now. We’re likely to have people from different socioeconomic, ethnic, and national backgrounds, each of whom sees problems from a slightly different perspective. It is therefore much more likely that the team will uncover a truly creative and clever approach to problem solving.
Simon London: Let’s move on to step five. You’ve done your work plan. Now you’ve actually got to do the analysis. The thing that strikes me here is that the range of tools that we have at our disposal now, of course, is just huge, particularly with advances in computation, advanced analytics. There’s so many things that you can apply here. Just talk about the analysis stage. How do you pick the right tools?
Charles Conn: For me, the most important thing is that we start with simple heuristics and explanatory statistics before we go off and use the big-gun tools. We need to understand the shape and scope of our problem before we start applying these massive and complex analytical approaches.
Simon London: Would you agree with that?
Hugo Sarrazin: I agree. I think there are so many wonderful heuristics. You need to start there before you go deep into the modeling exercise. There’s an interesting dynamic that’s happening, though. In some cases, for some types of problems, it is even better to set yourself up to maximize your learning. Your problem-solving methodology is test and learn, test and learn, test and learn, and iterate. That is a heuristic in itself, the A/B testing that is used in many parts of the world. So that’s a problem-solving methodology. It’s nothing different. It just uses technology and feedback loops in a fast way. The other one is exploratory data analysis. When you’re dealing with a large-scale problem, and there’s so much data, I can get to the heuristics that Charles was talking about through very clever visualization of data.
You test with your data. You need to set up an environment to do so, but don’t get caught up in neural-network modeling immediately. You’re testing, you’re checking—“Is the data right? Is it sound? Does it make sense?”—before you launch too far.
Simon London: You do hear these ideas—that if you have a big enough data set and enough algorithms, they’re going to find things that you just wouldn’t have spotted, find solutions that maybe you wouldn’t have thought of. Does machine learning sort of revolutionize the problem-solving process? Or are these actually just other tools in the toolbox for structured problem solving?
Charles Conn: It can be revolutionary. There are some areas in which the pattern recognition of large data sets and good algorithms can help us see things that we otherwise couldn’t see. But I do think it’s terribly important we don’t think that this particular technique is a substitute for superb problem solving, starting with good problem definition. Many people use machine learning without understanding algorithms that themselves can have biases built into them. Just as 20 years ago, when we were doing statistical analysis, we knew that we needed good model definition, we still need a good understanding of our algorithms and really good problem definition before we launch off into big data sets and unknown algorithms.
Simon London: Step six. You’ve done your analysis.
Charles Conn: I take six and seven together, and this is the place where young problem solvers often make a mistake. They’ve got their analysis, and they assume that’s the answer, and of course it isn’t the answer. The ability to synthesize the pieces that came out of the analysis and begin to weave those into a story that helps people answer the question “What should I do?” This is back to where we started. If we can’t synthesize, and we can’t tell a story, then our decision maker can’t find the answer to “What should I do?”
Simon London: But, again, these final steps are about motivating people to action, right?
Charles Conn: Yeah.
Simon London: I am slightly torn about the nomenclature of problem solving because it’s on paper, right? Until you motivate people to action, you actually haven’t solved anything.
Charles Conn: I love this question because I think decision-making theory, without a bias to action, is a waste of time. Everything in how I approach this is to help people take action that makes the world better.
Simon London: Hence, these are absolutely critical steps. If you don’t do this well, you’ve just got a bunch of analysis.
Charles Conn: We end up in exactly the same place where we started, which is people speaking across each other, past each other in the public square, rather than actually working together, shoulder to shoulder, to crack these important problems.
Simon London: In the real world, we have a lot of uncertainty—arguably, increasing uncertainty. How do good problem solvers deal with that?
Hugo Sarrazin: At every step of the process. In the problem definition, when you’re defining the context, you need to understand those sources of uncertainty and whether they’re important or not important. It becomes important in the definition of the tree.
You need to think carefully about the branches of the tree that are more certain and less certain as you define them. They don’t have equal weight just because they’ve got equal space on the page. Then, when you’re prioritizing, your prioritization approach may put more emphasis on things that have low probability but huge impact—or, vice versa, may put a lot of priority on things that are very likely and, hopefully, have a reasonable impact. You can introduce that along the way. When you come back to the synthesis, you just need to be nuanced about what you’re understanding, the likelihood.
Often, people lack humility in the way they make their recommendations: “This is the answer.” They’re very precise, and I think we would all be well-served to say, “This is a likely answer under the following sets of conditions” and then make the level of uncertainty clearer, if that is appropriate. It doesn’t mean you’re always in the gray zone; it doesn’t mean you don’t have a point of view. It just means that you can be explicit about the certainty of your answer when you make that recommendation.
Simon London: So it sounds like there is an underlying principle: “Acknowledge and embrace the uncertainty. Don’t pretend that it isn’t there. Be very clear about what the uncertainties are up front, and then build that into every step of the process.”
Hugo Sarrazin: Every step of the process.
Simon London: Yeah. We have just walked through a particular structured methodology for problem solving. But, of course, this is not the only structured methodology for problem solving. One that is also very well-known is design thinking, which comes at things very differently. So, Hugo, I know you have worked with a lot of designers. Just give us a very quick summary. Design thinking—what is it, and how does it relate?
Hugo Sarrazin: It starts with an incredible amount of empathy for the user and uses that to define the problem. It does pause and go out in the wild and spend an enormous amount of time seeing how people interact with objects, seeing the experience they’re getting, seeing the pain points or joy—and uses that to infer and define the problem.
Simon London: Problem definition, but out in the world.
Hugo Sarrazin: With an enormous amount of empathy. There’s a huge emphasis on empathy. Traditional, more classic problem solving is you define the problem based on an understanding of the situation. This one almost presupposes that we don’t know the problem until we go see it. The second thing is you need to come up with multiple scenarios or answers or ideas or concepts, and there’s a lot of divergent thinking initially. That’s slightly different, versus the prioritization, but not for long. Eventually, you need to kind of say, “OK, I’m going to converge again.” Then you go and you bring things back to the customer and get feedback and iterate. Then you rinse and repeat, rinse and repeat. There’s a lot of tactile building, along the way, of prototypes and things like that. It’s very iterative.
Simon London: So, Charles, are these complements or are these alternatives?
Charles Conn: I think they’re entirely complementary, and I think Hugo’s description is perfect. When we do problem definition well in classic problem solving, we are demonstrating the kind of empathy, at the very beginning of our problem, that design thinking asks us to approach. When we ideate—and that’s very similar to the disaggregation, prioritization, and work-planning steps—we do precisely the same thing, and often we use contrasting teams, so that we do have divergent thinking. The best teams allow divergent thinking to bump them off whatever their initial biases in problem solving are. For me, design thinking gives us a constant reminder of creativity, empathy, and the tactile nature of problem solving, but it’s absolutely complementary, not alternative.
Simon London: I think, in a world of cross-functional teams, an interesting question is do people with design-thinking backgrounds really work well together with classical problem solvers? How do you make that chemistry happen?
Hugo Sarrazin: Yeah, it is not easy when people have spent an enormous amount of time seeped in design thinking or user-centric design, whichever word you want to use. If the person who’s applying classic problem-solving methodology is very rigid and mechanical in the way they’re doing it, there could be an enormous amount of tension. If there’s not clarity in the role and not clarity in the process, I think having the two together can be, sometimes, problematic.
The second thing that happens often is that the artifacts the two methodologies try to gravitate toward can be different. Classic problem solving often gravitates toward a model; design thinking migrates toward a prototype. Rather than writing a big deck with all my supporting evidence, they’ll bring an example, a thing, and that feels different. Then you spend your time differently to achieve those two end products, so that’s another source of friction.
Now, I still think it can be an incredibly powerful thing to have the two—if there are the right people with the right mind-set, if there is a team that is explicit about the roles, if we’re clear about the kind of outcomes we are attempting to bring forward. There’s an enormous amount of collaborativeness and respect.
Simon London: But they have to respect each other’s methodology and be prepared to flex, maybe, a little bit, in how this process is going to work.
Hugo Sarrazin: Absolutely.
Simon London: The other area where, it strikes me, there could be a little bit of a different sort of friction is this whole concept of the day-one answer, which is what we were just talking about in classical problem solving. Now, you know that this is probably not going to be your final answer, but that’s how you begin to structure the problem. Whereas I would imagine your design thinkers—no, they’re going off to do their ethnographic research and get out into the field, potentially for a long time, before they come back with at least an initial hypothesis.

Want better strategies? Become a bulletproof problem solver
Hugo Sarrazin: That is a great callout, and that’s another difference. Designers typically will like to soak into the situation and avoid converging too quickly. There’s optionality and exploring different options. There’s a strong belief that keeps the solution space wide enough that you can come up with more radical ideas. If there’s a large design team or many designers on the team, and you come on Friday and say, “What’s our week-one answer?” they’re going to struggle. They’re not going to be comfortable, naturally, to give that answer. It doesn’t mean they don’t have an answer; it’s just not where they are in their thinking process.
Simon London: I think we are, sadly, out of time for today. But Charles and Hugo, thank you so much.
Charles Conn: It was a pleasure to be here, Simon.
Hugo Sarrazin: It was a pleasure. Thank you.
Simon London: And thanks, as always, to you, our listeners, for tuning into this episode of the McKinsey Podcast . If you want to learn more about problem solving, you can find the book, Bulletproof Problem Solving: The One Skill That Changes Everything , online or order it through your local bookstore. To learn more about McKinsey, you can of course find us at McKinsey.com.
Charles Conn is CEO of Oxford Sciences Innovation and an alumnus of McKinsey’s Sydney office. Hugo Sarrazin is a senior partner in the Silicon Valley office, where Simon London, a member of McKinsey Publishing, is also based.
Explore a career with us
Related articles.

Strategy to beat the odds

Five routes to more innovative problem solving
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Starting the research process
- What Is a Fishbone Diagram? | Templates & Examples
What Is a Fishbone Diagram? | Templates & Examples
Published on January 2, 2023 by Tegan George . Revised on January 29, 2024.
A fishbone diagram is a problem-solving approach that uses a fish-shaped diagram to model possible root causes of problems and troubleshoot possible solutions. It is also called an Ishikawa diagram, after its creator, Kaoru Ishikawa, as well as a herringbone diagram or cause-and-effect diagram.
Fishbone diagrams are often used in root cause analysis , to troubleshoot issues in quality management or product development. They are also used in the fields of nursing and healthcare, or as a brainstorming and mind-mapping technique many students find helpful.
Table of contents
How to make a fishbone diagram, fishbone diagram templates, fishbone diagram examples, advantages and disadvantages of fishbone diagrams, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about fishbone diagrams.
A fishbone diagram is easy to draw, or you can use a template for an online version.
- Your fishbone diagram starts out with an issue or problem. This is the “head” of the fish, summarized in a few words or a small phrase.
- Next, draw a long arrow, which serves as the fish’s backbone.
- From here, you’ll draw the first “bones” directly from the backbone, in the shape of small diagonal lines going right-to-left. These represent the most likely or overarching causes of your problem.
- Branching off from each of these first bones, create smaller bones containing contributing information and necessary detail.
- When finished, your fishbone diagram should give you a wide-view idea of what the root causes of the issue you’re facing could be, allowing you to rank them or choose which could be most plausible.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
There are no built-in fishbone diagram templates in Microsoft programs, but we’ve made a few free ones for you to use that you can download below. Alternatively, you can make one yourself using the following steps:
- In a fresh document, go to Insert > Shapes
- Draw a long arrow from left to right, and add a text box on the right-hand side. These serve as the backbone and the head of the fish.
- Next, add lines jutting diagonally from the backbone. These serve as the ribs, or the contributing factors to the main problem.
- Next, add horizontal lines jutting from each central line. These serve as the potential causes of the problem.
Lastly, add text boxes to label each function.
You can try your hand at filling one in yourself using the various blank fishbone diagram templates below, in the following formats:
Fishbone diagram template Excel
Download our free Excel template below!
Fishbone diagram template Word
Download our free Word template below!
Fishbone diagram template PowerPoint
Download our free PowerPoint template below!
Fishbone diagrams are used in a variety of settings, both academic and professional. They are particularly popular in healthcare settings, particularly nursing, or in group brainstorm study sessions. In the business world, they are an often-used tool for quality assurance or human resources professionals.
Fishbone diagram example #1: Climate change
Let’s start with an everyday example: what are the main causes of climate change?
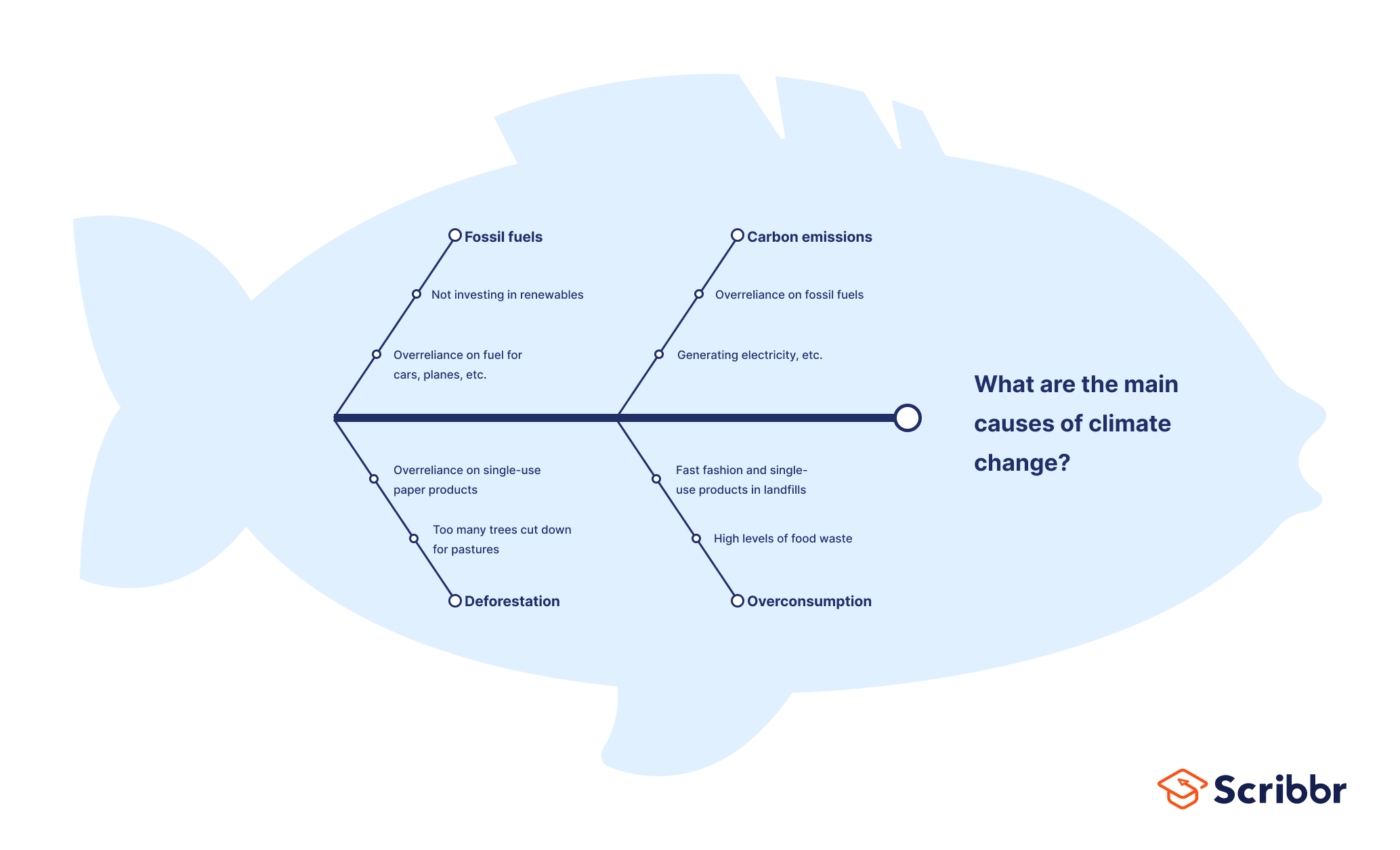
Fishbone diagram example #2: Healthcare and nursing
Fishbone diagrams are often used in nursing and healthcare to diagnose patients with unclear symptoms, or to streamline processes or fix ongoing problems. For example: why have surveys shown a decrease in patient satisfaction?
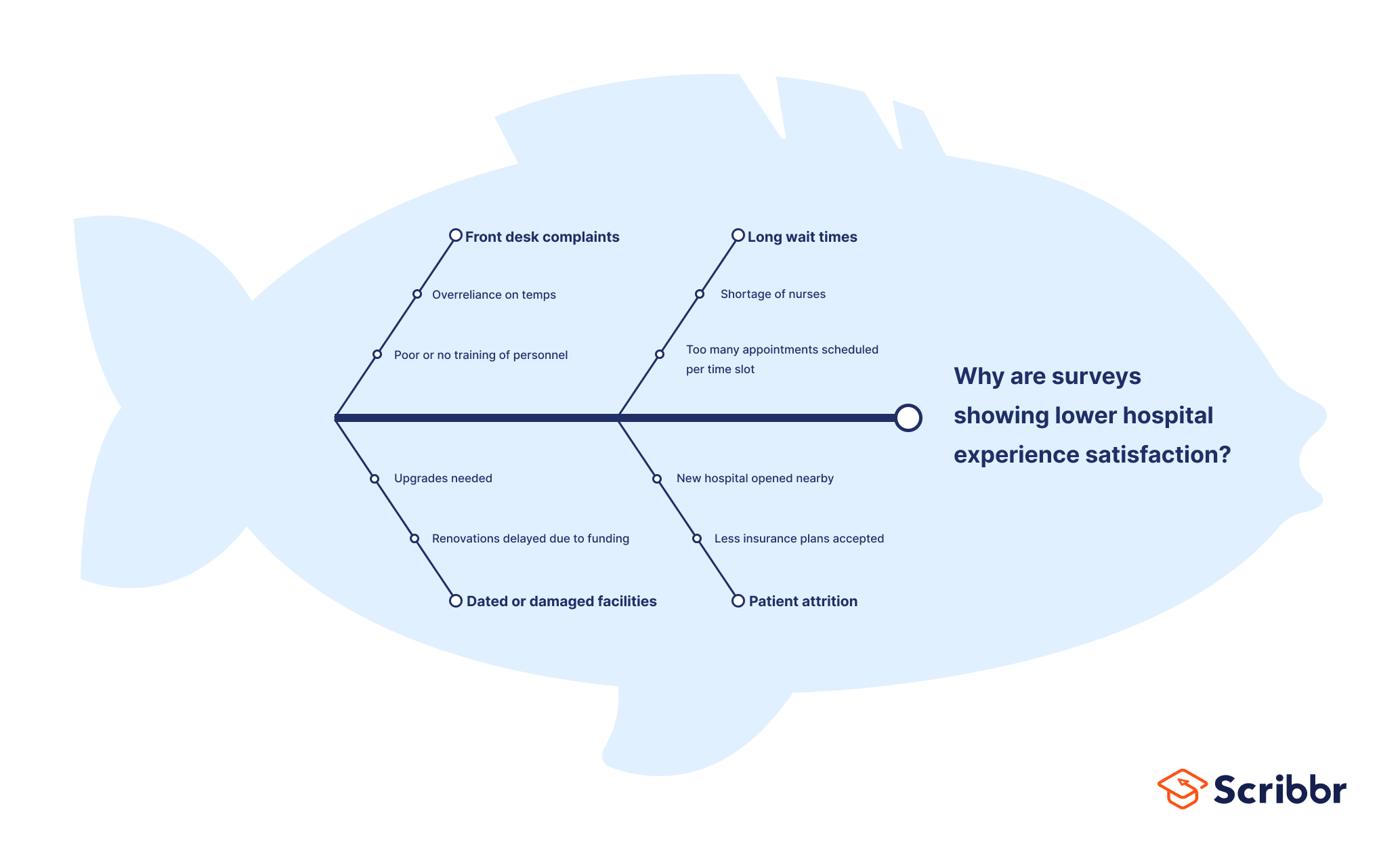
Fishbone diagram example #3: Quality assurance
QA professionals also use fishbone diagrams to troubleshoot usability issues, such as: why is the website down?
Fishbone diagram example #4: HR
Lastly, an HR example: why are employees leaving the company?
Fishbone diagrams come with advantages and disadvantages.
- Great tool for brainstorming and mind-mapping, either individually or in a group project.
- Can help identify causal relationships and clarify relationships between variables .
- Constant iteration of “why” questions really drills down to root problems and elegantly simplifies even complex issues.
Disadvantages
- Can lead to incorrect or inconsistent conclusions if the wrong assumptions are made about root causes or the wrong variables are prioritized.
- Fishbone diagrams are best suited to short phrases or simple ideas—they can get cluttered and confusing easily.
- Best used in the exploratory research phase, since they cannot provide true answers, only suggestions.
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
Methodology
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
Fishbone diagrams have a few different names that are used interchangeably, including herringbone diagram, cause-and-effect diagram, and Ishikawa diagram.
These are all ways to refer to the same thing– a problem-solving approach that uses a fish-shaped diagram to model possible root causes of problems and troubleshoot solutions.
Fishbone diagrams (also called herringbone diagrams, cause-and-effect diagrams, and Ishikawa diagrams) are most popular in fields of quality management. They are also commonly used in nursing and healthcare, or as a brainstorming technique for students.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
George, T. (2024, January 29). What Is a Fishbone Diagram? | Templates & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved August 12, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/research-process/fishbone-diagram/
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, how to define a research problem | ideas & examples, data collection | definition, methods & examples, exploratory research | definition, guide, & examples, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
Weekly dose of self-improvement
The easy 4 step problem-solving process (+ examples)
This is the 4 step problem-solving process that I taught to my students for math problems, but it works for academic and social problems as well.

Every problem may be different, but effective problem solving asks the same four questions and follows the same method.
- What’s the problem? If you don’t know exactly what the problem is, you can’t come up with possible solutions. Something is wrong. What are we going to do about this? This is the foundation and the motivation.
- What do you need to know? This is the most important part of the problem. If you don’t know exactly what the problem is, you can’t come up with possible solutions.
- What do you already know? You already know something related to the problem that will help you solve the problem. It’s not always obvious (especially in the real world), but you know (or can research) something that will help.
- What’s the relationship between the two? Here is where the heavy brainstorming happens. This is where your skills and abilities come into play. The previous steps set you up to find many potential solutions to your problem, regardless of its type.
When I used to tutor kids in math and physics , I would drill this problem-solving process into their heads. This methodology works for any problem, regardless of its complexity or difficulty. In fact, if you look at the various advances in society, you’ll see they all follow some variation of this problem-solving technique.
“The gap between understanding and misunderstanding can best be bridged by thought!” ― Ernest Agyemang Yeboah
Generally speaking, if you can’t solve the problem then your issue is step 3 or step 4; you either don’t know enough or you’re missing the connection.
Good problem solvers always believe step 3 is the issue. In this case, it’s a simple matter of learning more. Less skilled problem solvers believe step 4 is the root cause of their difficulties. In this instance, they simply believe they have limited problem-solving skills.
This is a fixed versus growth mindset and it makes a huge difference in the effort you put forth and the belief you have in yourself to make use of this step-by-step process. These two mindsets make a big difference in your learning because, at its core, learning is problem-solving.
Let’s dig deeper into the 4 steps. In this way, you can better see how to apply them to your learning journey.
Step 1: What’s the problem?
The ability to recognize a specific problem is extremely valuable.
Most people only focus on finding solutions. While a “solutions-oriented” mindset is a good thing, sometimes it pays to focus on the problem. When you focus on the problem, you often make it easier to find a viable solution to it.
When you know the exact nature of the problem, you shorten the time frame needed to find a solution. This reminds me of a story I was once told.
When does the problem-solving process start?
The process starts after you’ve identified the exact nature of the problem.
Homeowners love a well-kept lawn but hate mowing the grass.
Many companies and inventors raced to figure out a more time-efficient way to mow the lawn. Some even tried to design robots that would do the mowing. They all were chasing the solution, but only one inventor took the time to understand the root cause of the problem.
Most people figured that the problem was the labor required to maintain a lawn. The actual problem was just the opposite: maintaining a lawn was labor-intensive. The rearrangement seems trivial, but it reveals the true desire: a well-maintained lawn.
The best solution? Remove maintenance from the equation. A lawn made of artificial grass solved the problem . Hence, an application of Astroturf was discovered.
This way, the law always looked its best. Taking a few moments to apply critical thinking identified the true nature of the problem and yielded a powerful solution.
An example of choosing the right problem to work the problem-solving process on
One thing I’ve learned from tutoring high school students in math : they hate word problems.
This is because they make the student figure out the problem. Finding the solution to a math problem is already stressful. Forcing the student to also figure out what problem needs solving is another level of hell.
Word problems are not always clear about what needs to be solved. They also have the annoying habit of adding extraneous information. An ordinary math problem does not do this. For example, compare the following two problems:
What’s the height of h?
A radio station tower was built in two sections. From a point 87 feet from the base of the tower, the angle of elevation of the top of the first section is 25º, and the angle of elevation of the top of the second section is 40º. To the nearest foot, what is the height of the top section of the tower?
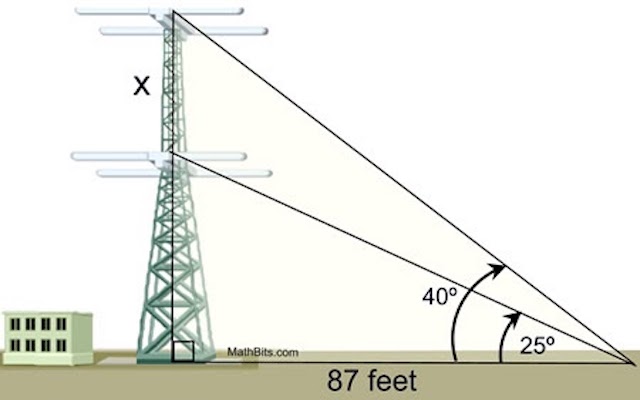
The first is a simple problem. The second is a complex problem. The end goal in both is the same.
The questions require the same knowledge (trigonometric functions), but the second is more difficult for students. Why? The second problem does not make it clear what the exact problem is. Before mathematics can even begin, you must know the problem, or else you risk solving the wrong one.
If you understand the problem, finding the solution is much easier. Understanding this, ironically, is the biggest problem for people.
Problem-solving is a universal language
Speaking of people, this method also helps settle disagreements.
When we disagree, we rarely take the time to figure out the exact issue. This happens for many reasons, but it always results in a misunderstanding. When each party is clear with their intentions, they can generate the best response.
Education systems fail when they don’t consider the problem they’re supposed to solve. Foreign language education in America is one of the best examples.
The problem is that students can’t speak the target language. It seems obvious that the solution is to have students spend most of their time speaking. Unfortunately, language classes spend a ridiculous amount of time learning grammar rules and memorizing vocabulary.
The problem is not that the students don’t know the imperfect past tense verb conjugations in Spanish. The problem is that they can’t use the language to accomplish anything. Every year, kids graduate from American high schools without the ability to speak another language, despite studying one for 4 years.
Well begun is half done
Before you begin to learn something, be sure that you understand the exact nature of the problem. This will make clear what you need to know and what you can discard. When you know the exact problem you’re tasked with solving, you save precious time and energy. Doing this increases the likelihood that you’ll succeed.
Step 2: What do you need to know?
All problems are the result of insufficient knowledge. To solve the problem, you must identify what you need to know. You must understand the cause of the problem. If you get this wrong, you won’t arrive at the correct solution.
Either you’ll solve what you thought was the problem, only to find out this wasn’t the real issue and now you’ve still got trouble or you won’t and you still have trouble. Either way, the problem persists.
If you solve a different problem than the correct one, you’ll get a solution that you can’t use. The only thing that wastes more time than an unsolved problem is solving the wrong one.
Imagine that your car won’t start. You replace the alternator, the starter, and the ignition switch. The car still doesn’t start. You’ve explored all the main solutions, so now you consider some different solutions.
Now you replace the engine, but you still can’t get it to start. Your replacements and repairs solved other problems, but not the main one: the car won’t start.
Then it turns out that all you needed was gas.
This example is a little extreme, but I hope it makes the point. For something more relatable, let’s return to the problem with language learning.
You need basic communication to navigate a foreign country you’re visiting; let’s say Mexico. When you enroll in a Spanish course, they teach you a bunch of unimportant words and phrases. You stick with it, believing it will eventually click.
When you land, you can tell everyone your name and ask for the location of the bathroom. This does not help when you need to ask for directions or tell the driver which airport terminal to drop you off at.
Finding the solution to chess problems works the same way
The book “The Amateur Mind” by IM Jeremy Silman improved my chess by teaching me how to analyze the board.
It’s only with a proper analysis of imbalances that you can make the best move. Though you may not always choose the correct line of play, the book teaches you how to recognize what you need to know . It teaches you how to identify the problem—before you create an action plan to solve it.

The problem-solving method always starts with identifying the problem or asking “What do you need to know?”. It’s only after you brainstorm this that you can move on to the next step.
Learn the method I used to earn a physics degree, learn Spanish, and win a national boxing title
- I was a terrible math student in high school who wrote off mathematics. I eventually overcame my difficulties and went on to earn a B.A. Physics with a minor in math
- I pieced together the best works on the internet to teach myself Spanish as an adult
- *I didn’t start boxing until the very old age of 22, yet I went on to win a national championship, get a high-paying amateur sponsorship, and get signed by Roc Nation Sports as a profession.
I’ve used this method to progress in mentally and physically demanding domains.
While the specifics may differ, I believe that the general methods for learning are the same in all domains.
This free e-book breaks down the most important techniques I’ve used for learning.
Step 3: What do you already know?
The only way to know if you lack knowledge is by gaining some in the first place. All advances and solutions arise from the accumulation and implementation of prior information. You must first consider what it is that you already know in the context of the problem at hand.
Isaac Newton once said, “If I have seen further, it is by standing on the shoulders of giants.” This is Newton’s way of explaining that his advancements in physics and mathematics would be impossible if it were not for previous discoveries.
Mathematics is a great place to see this idea at work. Consider the following problem:
What is the domain and range of y=(x^2)+6?
This simple algebra problem relies on you knowing a few things already. You must know:
- The definition of “domain” and “range”
- That you can never square any real number and get a negative
Once you know those things, this becomes easy to solve. This is also how we learn languages.
An example of the problem-solving process with a foreign language
Anyone interested in serious foreign language study (as opposed to a “crash course” or “survival course”) should learn the infinitive form of verbs in their target language. You can’t make progress without them because they’re the root of all conjugations. It’s only once you have a grasp of the infinitives that you can completely express yourself. Consider the problem-solving steps applied in the following example.
I know that I want to say “I don’t eat eggs” to my Mexican waiter. That’s the problem.
I don’t know how to say that, but last night I told my date “No bebo alcohol” (“I don’t drink alcohol”). I also know the infinitive for “eat” in Spanish (comer). This is what I already know.
Now I can execute the final step of problem-solving.
Step 4: What’s the relationship between the two?
I see the connection. I can use all of my problem-solving strategies and methods to solve my particular problem.
I know the infinitive for the Spanish word “drink” is “beber” . Last night, I changed it to “bebo” to express a similar idea. I should be able to do the same thing to the word for “eat”.
“No como huevos” is a pretty accurate guess.
In the math example, the same process occurs. You don’t know the answer to “What is the domain and range of y=(x^2)+6?” You only know what “domain” and “range” mean and that negatives aren’t possible when you square a real number.
A domain of all real numbers and a range of all numbers equal to and greater than six is the answer.
This is relating what you don’t know to what you already do know. The solutions appear simple, but walking through them is an excellent demonstration of the process of problem-solving.
In most cases, the solution won’t be this simple, but the process or finding it is the same. This may seem trivial, but this is a model for thinking that has served the greatest minds in history.
A recap of the 4 steps of the simple problem-solving process
- What’s the problem? There’s something wrong. There’s something amiss.
- What do you need to know? This is how to fix what’s wrong.
- What do you already know? You already know something useful that will help you find an effective solution.
- What’s the relationship between the previous two? When you use what you know to help figure out what you don’t know, there is no problem that won’t yield.
Learning is simply problem-solving. You’ll learn faster if you view it this way.
What was once complicated will become simple.
What was once convoluted will become clear.

Ed Latimore
I’m a writer, competitive chess player, Army veteran, physicist, and former professional heavyweight boxer. My work focuses on self-development, realizing your potential, and sobriety—speaking from personal experience, having overcome both poverty and addiction.
Follow me on Twitter.

Developing foreign language skills
What follows are methods I’ve discovered and used to improve in all of these areas, which have, in turn, made it even easier to use and learn the language.

Pimsleur language system review—old but still good
The Pimsleur language program offers a framework you can use to learn a language. I’ve used the program. Here are my experiences.

Pimsleur vs Duolingo: Choosing the best language learning app
Pimsleur and Duolingo are two popular language-learning apps to help you learn a new language. This guide will help you decide which app will work best for you.
The Six Step Problem Solving Model

What is The Six Step Problem Solving Model?
The Six Step Problem Solving Model is a widely recognized and effective approach to addressing and resolving complex problems in personal and professional settings. This model provides a structured and systematic process for analyzing, identifying, and resolving issues, making it an indispensable tool for individuals, teams, and organizations.
Problem-solving is the process of identifying and resolving issues or obstacles that hinder the attainment of a goal. It is a critical skill that is highly valued in both personal and professional settings.
Whether you are a business owner, an employee, or an individual, the ability to solve problems effectively is essential for success.
According to a report by the World Economic Forum, problem-solving, critical thinking, and creativity are among the top skills that will be in demand in the job market by 2025.
This highlights the importance of problem-solving as a skill in the professional world. However, problem-solving is not limited to the workplace, it is also crucial in everyday life.
For instance, when faced with a personal challenge or a difficult situation, the ability to identify and solve the problem is key to achieving a desirable outcome.
The Six Step Problem Solving Model was first introduced by Kepner and Tregoe in the 1960s, who were management consultants known for their work in the field of decision-making and problem-solving. They proposed a rational and logical approach that was based on a rigorous analysis of the problem and its underlying causes, followed by a deliberate and careful selection of solutions that would address the root cause of the problem.
Since then, the Six Step Problem Solving Model has been widely adopted and modified by many organizations and industries, and it continues to be a useful and effective tool for addressing complex issues in a structured and systematic manner.
In this article, we will explore each step of the model in detail and provide examples of how it can be applied in real-world situations.
I have listed below all Six Steps in detail:
Step 1: Identify The Problem
Identifying the problem is the first step in the Six-Step Problem Solving Model. This step is critical because it sets the foundation for the rest of the problem-solving process.
The four sub-steps of this stage include:
Selection of the problem to be analyzed
The first sub-step in this stage is to select the problem that needs to be analyzed. This could be any issue that is causing problems for your personal or professional life. It could be a product or service that is not meeting customer expectations, a process that is causing delays, or any other problem that needs to be addressed.
Clear definition of the problem and establishment of a precise problem statement
Once you have identified the problem to be analyzed, the next step is to define it clearly and establish a precise problem statement. This step involves defining the problem in clear and concise terms so that everyone involved in the problem-solving process understands the issue at hand.
For example, if the problem is related to product quality, the problem statement could be: “Our product is not meeting the quality standards expected by our customers, which is resulting in negative feedback and decreased sales.”
Setting a measurable goal for the problem-solving effort
After defining the problem, the next step is to set a measurable goal for the problem-solving effort. This goal should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound ( SMART ). The goal should be aligned with the overall objectives of the organization and should focus on addressing the root cause of the problem.
For example, if the problem is related to product quality, the goal could be: “To improve product quality by reducing defects by 50% within the next three months.”
Establishing a process for coordinating with and gaining approval of leadership
The final sub-step in this stage is to establish a process for coordinating with and gaining approval of leadership. This involves identifying the stakeholders who will be involved in the problem-solving process and obtaining their buy-in and support for the process.
For example, if the problem is related to product quality, the stakeholders could include the quality control team, production team, and senior management. It is important to involve all stakeholders in the process to ensure that everyone is aligned and committed to finding a solution to the problem.
Step 2: Analyze The Problem
Identification of the processes that impact the problem and selection of one.
To analyze the problem effectively, you need to identify the processes that impact the problem and select one. The selected process should be relevant to the problem and the one that can be analyzed to identify the root cause.
For example, if a company is experiencing a high employee turnover rate, the process that needs to be analyzed could be the hiring process, employee training process, or employee feedback process.
Listing the steps in the process as it currently exists
Once you have identified the process, you need to list all the steps in the process as it currently exists. This will help you identify where the problem is occurring and what steps need to be changed to solve the problem.
For instance, in the case of employee turnover rate, the steps in the hiring process could be job posting, resume screening, initial interview, background check, reference check, and final interview.
Mapping the process
After listing the steps, you need to map the process. This involves creating a visual representation of the process flow. Mapping the process helps in identifying the bottlenecks, redundancies, and inefficiencies in the process.
Validation of the map of the process
The next step is to validate the map of the process. This involves reviewing the map with the stakeholders involved in the process and confirming that it accurately represents the process flow.
Identification of potential causes of the problem
With the process map validated, the next step is to identify potential causes of the problem. This can be done by brainstorming with the stakeholders and identifying the areas where the process is not functioning effectively.
For instance, in the hiring process, potential causes of employee turnover rate could be a lack of a comprehensive background check, inadequate employee training, or poor job fit.
Collection and analysis of data related to the problem
After identifying potential causes, you need to collect and analyze data related to the problem. This can include employee feedback surveys, turnover data, job satisfaction data, and any other relevant data.
Verification or revision of the original problem statement
Based on the analysis, you may need to verify or revise the original problem statement. This ensures that the problem statement accurately reflects the problem being solved.
Identification of root causes of the problem
With the data analyzed, you can identify the root causes of the problem. Root causes are the underlying reasons why the problem is occurring.
For example, in the hiring process, the root cause of employee turnover could be the inadequate employee training, which leads to employees feeling unprepared for the job.
Collection of additional data if needed to verify root causes
To verify the root causes identified, you may need to collect additional data. This ensures that the solutions developed address the actual root cause of the problem, leading to long-term and sustainable solutions.
The second step of the Six Step Problem Solving Model is critical in identifying the root cause of the problem. By analyzing the process and identifying potential causes and root causes, you can develop effective solutions to solve the problem.
Step 3: Develop The Solutions
After identifying the root causes of the problem, it’s time to develop solutions. This step involves the following:
Establishment of criteria for selecting a solution
When selecting a solution, it’s important to establish criteria that will help in evaluating and selecting the best solution. The criteria should be measurable, objective, and specific to the problem. Some criteria that can be used include:
- Feasibility: Can the solution be implemented with the available resources?
- Effectiveness: Will the solution solve the problem?
- Cost: Is the cost of the solution within the budget?
- Time: Will the solution be implemented within the required time frame?
Generation of potential solutions that will address the root causes of the problem
Brainstorming is a great way to generate potential solutions. Gather a team of individuals who are knowledgeable about the problem and its root causes. Encourage them to think creatively and come up with as many potential solutions as possible. It’s important to involve stakeholders who will be affected by the solution in the brainstorming process to ensure that their concerns are considered.
Use any of the 12 techniques of brainstorming from our brainstorming toolbox .
Selection of a solution
Once potential solutions have been generated, it’s time to select the best one. Use the established criteria to evaluate each solution and determine which one is the best fit. It’s important to involve stakeholders in the selection process to ensure buy-in and support for the chosen solution.
Gaining approval and support for the chosen solution
Before implementing the solution, it’s important to gain approval and support from leadership and other stakeholders. Present the chosen solution and its benefits to the decision-makers, and address any concerns they may have. Get their approval and support before moving forward with implementation.
Planning the solution
After gaining approval, it’s time to plan the solution. This involves creating an action plan that outlines the steps needed to implement the solution, who will be responsible for each step, and when each step will be completed. It’s important to have a realistic timeline and to involve all stakeholders in the planning process. Ensure that resources are available for implementation, and that all necessary training and communication plans are in place.
Step 4: Implement A Solution
Once the solution has been selected and approved, it’s time to put the plan into action. This step involves implementing the chosen solution on a trial or pilot basis to see how it performs. Here are the key components of this step:
Implementation of the chosen solution on a trial or pilot basis
Before implementing the solution fully, it’s important to test it out on a smaller scale to see how it works. This allows you to identify any potential problems or issues and make adjustments as needed. By implementing the solution on a trial or pilot basis, you can ensure that it will work effectively when it’s rolled out more broadly.
If the Problem Solving Process is being used as a standalone, continue to Step 5
If the Six Step Problem Solving Model is being used as a standalone process, it’s time to move on to Step 5, which involves evaluating the results of the solution. This step is critical to ensure that the solution is working as intended and achieving the desired results.
Step 5: Evaluate The Results
Gathering of data on the solution.
Once the chosen solution has been implemented, it is important to gather data on its effectiveness. This data can come in various forms, such as customer feedback, sales figures, or productivity metrics. The key is to gather enough data to make an informed decision about the success or failure of the solution.
Analysis of the data on the solution
After collecting the necessary data, it is important to analyze it thoroughly to determine whether or not the solution has achieved the desired results. This analysis can involve statistical methods, surveys, or other evaluation techniques. The goal is to determine whether or not the solution has been successful and to identify any areas where improvements can be made.
Achievement of the desired results?
Based on the analysis of the data, it is necessary to determine whether or not the solution has achieved the desired results. This can involve comparing the actual results to the goals established in Step 1, or it can involve evaluating the overall impact of the solution on the organization or individual.
If YES, go to Step 6.
If the solution has achieved the desired results, it is time to move on to Step 6. This step involves standardizing the solution and capitalizing on any new opportunities that may have arisen as a result of the problem-solving process.
If NO, go back to Step 1.
If the solution has not achieved the desired results, it is necessary to go back to Step 1 and repeat the problem-solving process. This may involve refining the problem statement, identifying new potential causes, or generating new potential solutions. The key is to remain flexible and open to new ideas throughout the problem-solving process.
Step 6: Standardize The Solution (and Capitalize on New Opportunities)
Once the solution has been implemented and evaluated, it’s time to standardize the solution and capitalize on new opportunities. This step involves making sure that the solution is integrated into the organization’s standard operating procedures and that everyone involved knows how to use it effectively.
Identification of Systemic Changes and Training Needs for Full Implementation
When identifying systemic changes, it’s important to look at how the solution fits into the larger context of the organization. This includes looking at processes, policies, and procedures to see where changes need to be made to fully implement the solution.
Training is also crucial in the standardization process. Employees need to know how to use the solution properly and effectively. This can include training on new processes, tools, and technologies.
Adoption of the Solution
Once the solution has been standardized, it’s time to adopt it fully. This means integrating it into the organization’s operations and ensuring that everyone is using it consistently. This can involve making changes to job descriptions, updating policies and procedures, and making sure that everyone has the necessary tools and resources to use the solution effectively.
Planning Ongoing Monitoring of the Solution
Even after the solution has been adopted, it’s important to continue monitoring its effectiveness. This can involve setting up monitoring and reporting systems to track progress and identify areas for improvement. Regular review meetings can also help to keep the solution on track and ensure that it is meeting the organization’s goals and objectives.
Continuing to Look for Incremental Improvements to Refine the Solution
While the solution may have solved the initial problem, there is always room for improvement. This can involve looking for ways to make the solution more efficient, effective, or user-friendly. This can include gathering feedback from employees and customers, analyzing data to identify areas for improvement, and looking for ways to optimize processes and procedures.
Looking for Another Improvement Opportunity
Finally, it’s important to keep looking for new improvement opportunities. The Six Step Problem Solving Model is an iterative process, and there is always room for improvement. This can involve looking at other areas of the organization that could benefit from problem-solving and using the same process to identify and implement solutions.
In conclusion, the six-step problem-solving model is an effective approach for addressing problems and making improvements in personal and professional settings. The model involves identifying the problem, analyzing it, developing solutions, implementing the solution, evaluating the results, and standardizing the solution.
To summarize, the six steps of problem-solving include:
- Identify the problem
- Analyze the problem
- Develop the solutions
- Implement the solution
- Evaluate the results
- Standardize the solution (and capitalize on new opportunities)
Problem-solving and continuous improvement are critical skills for personal and professional growth.
By utilizing this model, individuals and organizations can become more efficient, productive, and effective in addressing challenges and achieving their goals.
- American Society for Quality. (2019). Root Cause Analysis .
- Hames, S. (2017). The 5 Whys Method
- Fass, M. (2020). The Six-Step Problem-Solving Process. Harvard Business Review .
- The Six-Step Problem-Solving Process by the University of California, San Francisco
- The Importance of Problem-Solving Skills in the Workplace by The Balance Careers.

Marty Hoffman
Related articles.

Self-Determination Theory (SDT)
Scientific management theory, lean management, french and raven’s five forms of power.


McKinsey Problem Solving: Six steps to solve any problem and tell a persuasive story
The McKinsey problem solving process is a series of mindset shifts and structured approaches to thinking about and solving challenging problems. It is a useful approach for anyone working in the knowledge and information economy and needs to communicate ideas to other people.
Over the past several years of creating StrategyU, advising an undergraduates consulting group and running workshops for clients, I have found over and over again that the principles taught on this site and in this guide are a powerful way to improve the type of work and communication you do in a business setting.
When I first set out to teach these skills to the undergraduate consulting group at my alma mater, I was still working at BCG. I was spending my day building compelling presentations, yet was at a loss for how to teach these principles to the students I would talk with at night.
Through many rounds of iteration, I was able to land on a structured process and way of framing some of these principles such that people could immediately apply them to their work.
While the “official” McKinsey problem solving process is seven steps, I have outline my own spin on things – from experience at McKinsey and Boston Consulting Group. Here are six steps that will help you solve problems like a McKinsey Consultant:
Step #1: School is over, stop worrying about “what” to make and worry about the process, or the “how”
When I reflect back on my first role at McKinsey, I realize that my biggest challenge was unlearning everything I had learned over the previous 23 years. Throughout school you are asked to do specific things. For example, you are asked to write a 5 page paper on Benjamin Franklin — double spaced, 12 font and answering two or three specific questions.
In school, to be successful you follow these rules as close as you can. However, in consulting there are no rules on the “what.” Typically the problem you are asked to solve is ambiguous and complex — exactly why they hire you. In consulting, you are taught the rules around the “how” and have to then fill in the what.
The “how” can be taught and this entire site is founded on that belief. Here are some principles to get started:
Step #2: Thinking like a consultant requires a mindset shift
There are two pre-requisites to thinking like a consultant. Without these two traits you will struggle:
- A healthy obsession looking for a “better way” to do things
- Being open minded to shifting ideas and other approaches
In business school, I was sitting in one class when I noticed that all my classmates were doing the same thing — everyone was coming up with reasons why something should should not be done.
As I’ve spent more time working, I’ve realized this is a common phenomenon. The more you learn, the easier it becomes to come up with reasons to support the current state of affairs — likely driven by the status quo bias — an emotional state that favors not changing things. Even the best consultants will experience this emotion, but they are good at identifying it and pushing forward.
Key point : Creating an effective and persuasive consulting like presentation requires a comfort with uncertainty combined with a slightly delusional belief that you can figure anything out.
Step #3: Define the problem and make sure you are not solving a symptom
Before doing the work, time should be spent on defining the actual problem. Too often, people are solutions focused when they think about fixing something. Let’s say a company is struggling with profitability. Someone might define the problem as “we do not have enough growth.” This is jumping ahead to solutions — the goal may be to drive more growth, but this is not the actual issue. It is a symptom of a deeper problem.
Consider the following information:
- Costs have remained relatively constant and are actually below industry average so revenue must be the issue
- Revenue has been increasing, but at a slowing rate
- This company sells widgets and have had no slowdown on the number of units it has sold over the last five years
- However, the price per widget is actually below where it was five years ago
- There have been new entrants in the market in the last three years that have been backed by Venture Capital money and are aggressively pricing their products below costs
In a real-life project there will definitely be much more information and a team may take a full week coming up with a problem statement . Given the information above, we may come up with the following problem statement:
Problem Statement : The company is struggling to increase profitability due to decreasing prices driven by new entrants in the market. The company does not have a clear strategy to respond to the price pressure from competitors and lacks an overall product strategy to compete in this market.
Step 4: Dive in, make hypotheses and try to figure out how to “solve” the problem
Now the fun starts!
There are generally two approaches to thinking about information in a structured way and going back and forth between the two modes is what the consulting process is founded on.
First is top-down . This is what you should start with, especially for a newer “consultant.” This involves taking the problem statement and structuring an approach. This means developing multiple hypotheses — key questions you can either prove or disprove.
Given our problem statement, you may develop the following three hypotheses:
- Company X has room to improve its pricing strategy to increase profitability
- Company X can explore new market opportunities unlocked by new entrants
- Company X can explore new business models or operating models due to advances in technology
As you can see, these three statements identify different areas you can research and either prove or disprove. In a consulting team, you may have a “workstream leader” for each statement.
Once you establish the structure you you may shift to the second type of analysis: a bottom-up approach . This involves doing deep research around your problem statement, testing your hypotheses, running different analysis and continuing to ask more questions. As you do the analysis, you will begin to see different patterns that may unlock new questions, change your thinking or even confirm your existing hypotheses. You may need to tweak your hypotheses and structure as you learn new information.
A project vacillates many times between these two approaches. Here is a hypothetical timeline of a project:

Step 5: Make a slides like a consultant
The next step is taking the structure and research and turning it into a slide. When people see slides from McKinsey and BCG, they see something that is compelling and unique, but don’t really understand all the work that goes into those slides. Both companies have a healthy obsession (maybe not to some people!) with how things look, how things are structured and how they are presented.
They also don’t understand how much work is spent on telling a compelling “story.” The biggest mistake people make in the business world is mistaking showing a lot of information versus telling a compelling story. This is an easy mistake to make — especially if you are the one that did hours of analysis. It may seem important, but when it comes down to making a slide and a presentation, you end up deleting more information rather than adding. You really need to remember the following:
Data matters, but stories change hearts and minds
Here are four quick ways to improve your presentations:
Tip #1 — Format, format, format
Both McKinsey and BCG had style templates that were obsessively followed. Some key rules I like to follow:
- Make sure all text within your slide body is the same font size (harder than you would think)
- Do not go outside of the margins into the white space on the side
- All titles throughout the presentation should be 2 lines or less and stay the same font size
- Each slide should typically only make one strong point
Tip #2 — Titles are the takeaway
The title of the slide should be the key insight or takeaway and the slide area should prove the point. The below slide is an oversimplification of this:

Even in consulting, I found that people struggled with simplifying a message to one key theme per slide. If something is going to be presented live, the simpler the better. In reality, you are often giving someone presentations that they will read in depth and more information may make sense.
To go deeper, check out these 20 presentation and powerpoint tips .
Tip #3 — Have “MECE” Ideas for max persuasion
“MECE” means mutually exclusive, collectively exhaustive — meaning all points listed cover the entire range of ideas while also being unique and differentiated from each other.
An extreme example would be this:
- Slide title: There are seven continents
- Slide content: The seven continents are North America, South America, Europe, Africa Asia, Antarctica, Australia
The list of continents provides seven distinct points that when taken together are mutually exclusive and collectively exhaustive . The MECE principle is not perfect — it is more of an ideal to push your logic in the right direction. Use it to continually improve and refine your story.
Applying this to a profitability problem at the highest level would look like this:
Goal: Increase profitability
2nd level: We can increase revenue or decrease costs
3rd level: We can increase revenue by selling more or increasing prices
Each level is MECE. It is almost impossible to argue against any of this (unless you are willing to commit accounting fraud!).
Tip #4 — Leveraging the Pyramid Principle
The pyramid principle is an approach popularized by Barbara Minto and essential to the structured problem solving approach I learned at McKinsey. Learning this approach has changed the way I look at any presentation since.
Here is a rough outline of how you can think about the pyramid principle as a way to structure a presentation:

As you build a presentation, you may have three sections for each hypothesis. As you think about the overall story, the three hypothesis (and the supporting evidence) will build on each other as a “story” to answer the defined problem. There are two ways to think about doing this — using inductive or deductive reasoning:

If we go back to our profitability example from above, you would say that increasing profitability was the core issue we developed. Lets assume that through research we found that our three hypotheses were true. Given this, you may start to build a high level presentation around the following three points:

These three ideas not only are distinct but they also build on each other. Combined, they tell a story of what the company should do and how they should react. Each of these three “points” may be a separate section in the presentation followed by several pages of detailed analysis. There may also be a shorter executive summary version of 5–10 pages that gives the high level story without as much data and analysis.
Step 6: The only way to improve is to get feedback and continue to practice
Ultimately, this process is not something you will master overnight. I’ve been consulting, either working for a firm or on my own for more than 10 years and am still looking for ways to make better presentations, become more persuasive and get feedback on individual slides.
The process never ends.
The best way to improve fast is to be working on a great team . Look for people around you that do this well and ask them for feedback. The more feedback, the more iterations and more presentations you make, the better you will become. Good luck!
If you enjoyed this post, you’ll get a kick out of all the free lessons I’ve shared that go a bit deeper. Check them out here .
Do you have a toolkit for business problem solving? I created Think Like a Strategy Consultant as an online course to make the tools of strategy consultants accessible to driven professionals, executives, and consultants. This course teaches you how to synthesize information into compelling insights, structure your information in ways that help you solve problems, and develop presentations that resonate at the C-Level. Click here to learn more or if you are interested in getting started now, enroll in the self-paced version ($497) or hands-on coaching version ($997). Both versions include lifetime access and all future updates.
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pocket (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
26 Expert-Backed Problem Solving Examples – Interview Answers
Published: February 13, 2023
Interview Questions and Answers
Actionable advice from real experts:

Biron Clark
Former Recruiter

Contributor
Dr. Kyle Elliott
Career Coach

Hayley Jukes
Editor-in-Chief

Biron Clark , Former Recruiter
Kyle Elliott , Career Coach

Hayley Jukes , Editor
As a recruiter , I know employers like to hire people who can solve problems and work well under pressure.
A job rarely goes 100% according to plan, so hiring managers are more likely to hire you if you seem like you can handle unexpected challenges while staying calm and logical.
But how do they measure this?
Hiring managers will ask you interview questions about your problem-solving skills, and they might also look for examples of problem-solving on your resume and cover letter.
In this article, I’m going to share a list of problem-solving examples and sample interview answers to questions like, “Give an example of a time you used logic to solve a problem?” and “Describe a time when you had to solve a problem without managerial input. How did you handle it, and what was the result?”
- Problem-solving involves identifying, prioritizing, analyzing, and solving problems using a variety of skills like critical thinking, creativity, decision making, and communication.
- Describe the Situation, Task, Action, and Result ( STAR method ) when discussing your problem-solving experiences.
- Tailor your interview answer with the specific skills and qualifications outlined in the job description.
- Provide numerical data or metrics to demonstrate the tangible impact of your problem-solving efforts.
What are Problem Solving Skills?
Problem-solving is the ability to identify a problem, prioritize based on gravity and urgency, analyze the root cause, gather relevant information, develop and evaluate viable solutions, decide on the most effective and logical solution, and plan and execute implementation.
Problem-solving encompasses other skills that can be showcased in an interview response and your resume. Problem-solving skills examples include:
- Critical thinking
- Analytical skills
- Decision making
- Research skills
- Technical skills
- Communication skills
- Adaptability and flexibility
Why is Problem Solving Important in the Workplace?
Problem-solving is essential in the workplace because it directly impacts productivity and efficiency. Whenever you encounter a problem, tackling it head-on prevents minor issues from escalating into bigger ones that could disrupt the entire workflow.
Beyond maintaining smooth operations, your ability to solve problems fosters innovation. It encourages you to think creatively, finding better ways to achieve goals, which keeps the business competitive and pushes the boundaries of what you can achieve.
Effective problem-solving also contributes to a healthier work environment; it reduces stress by providing clear strategies for overcoming obstacles and builds confidence within teams.
Examples of Problem-Solving in the Workplace
- Correcting a mistake at work, whether it was made by you or someone else
- Overcoming a delay at work through problem solving and communication
- Resolving an issue with a difficult or upset customer
- Overcoming issues related to a limited budget, and still delivering good work through the use of creative problem solving
- Overcoming a scheduling/staffing shortage in the department to still deliver excellent work
- Troubleshooting and resolving technical issues
- Handling and resolving a conflict with a coworker
- Solving any problems related to money, customer billing, accounting and bookkeeping, etc.
- Taking initiative when another team member overlooked or missed something important
- Taking initiative to meet with your superior to discuss a problem before it became potentially worse
- Solving a safety issue at work or reporting the issue to those who could solve it
- Using problem solving abilities to reduce/eliminate a company expense
- Finding a way to make the company more profitable through new service or product offerings, new pricing ideas, promotion and sale ideas, etc.
- Changing how a process, team, or task is organized to make it more efficient
- Using creative thinking to come up with a solution that the company hasn’t used before
- Performing research to collect data and information to find a new solution to a problem
- Boosting a company or team’s performance by improving some aspect of communication among employees
- Finding a new piece of data that can guide a company’s decisions or strategy better in a certain area
Problem-Solving Examples for Recent Grads/Entry-Level Job Seekers
- Coordinating work between team members in a class project
- Reassigning a missing team member’s work to other group members in a class project
- Adjusting your workflow on a project to accommodate a tight deadline
- Speaking to your professor to get help when you were struggling or unsure about a project
- Asking classmates, peers, or professors for help in an area of struggle
- Talking to your academic advisor to brainstorm solutions to a problem you were facing
- Researching solutions to an academic problem online, via Google or other methods
- Using problem solving and creative thinking to obtain an internship or other work opportunity during school after struggling at first
How To Answer “Tell Us About a Problem You Solved”
When you answer interview questions about problem-solving scenarios, or if you decide to demonstrate your problem-solving skills in a cover letter (which is a good idea any time the job description mentions problem-solving as a necessary skill), I recommend using the STAR method.
STAR stands for:
It’s a simple way of walking the listener or reader through the story in a way that will make sense to them.
Start by briefly describing the general situation and the task at hand. After this, describe the course of action you chose and why. Ideally, show that you evaluated all the information you could given the time you had, and made a decision based on logic and fact. Finally, describe the positive result you achieved.
Note: Our sample answers below are structured following the STAR formula. Be sure to check them out!
EXPERT ADVICE

Dr. Kyle Elliott , MPA, CHES Tech & Interview Career Coach caffeinatedkyle.com
How can I communicate complex problem-solving experiences clearly and succinctly?
Before answering any interview question, it’s important to understand why the interviewer is asking the question in the first place.
When it comes to questions about your complex problem-solving experiences, for example, the interviewer likely wants to know about your leadership acumen, collaboration abilities, and communication skills, not the problem itself.
Therefore, your answer should be focused on highlighting how you excelled in each of these areas, not diving into the weeds of the problem itself, which is a common mistake less-experienced interviewees often make.
Tailoring Your Answer Based on the Skills Mentioned in the Job Description
As a recruiter, one of the top tips I can give you when responding to the prompt “Tell us about a problem you solved,” is to tailor your answer to the specific skills and qualifications outlined in the job description.
Once you’ve pinpointed the skills and key competencies the employer is seeking, craft your response to highlight experiences where you successfully utilized or developed those particular abilities.
For instance, if the job requires strong leadership skills, focus on a problem-solving scenario where you took charge and effectively guided a team toward resolution.
By aligning your answer with the desired skills outlined in the job description, you demonstrate your suitability for the role and show the employer that you understand their needs.
Amanda Augustine expands on this by saying:
“Showcase the specific skills you used to solve the problem. Did it require critical thinking, analytical abilities, or strong collaboration? Highlight the relevant skills the employer is seeking.”
Interview Answers to “Tell Me About a Time You Solved a Problem”
Now, let’s look at some sample interview answers to, “Give me an example of a time you used logic to solve a problem,” or “Tell me about a time you solved a problem,” since you’re likely to hear different versions of this interview question in all sorts of industries.
The example interview responses are structured using the STAR method and are categorized into the top 5 key problem-solving skills recruiters look for in a candidate.
1. Analytical Thinking

Situation: In my previous role as a data analyst , our team encountered a significant drop in website traffic.
Task: I was tasked with identifying the root cause of the decrease.
Action: I conducted a thorough analysis of website metrics, including traffic sources, user demographics, and page performance. Through my analysis, I discovered a technical issue with our website’s loading speed, causing users to bounce.
Result: By optimizing server response time, compressing images, and minimizing redirects, we saw a 20% increase in traffic within two weeks.
2. Critical Thinking

Situation: During a project deadline crunch, our team encountered a major technical issue that threatened to derail our progress.
Task: My task was to assess the situation and devise a solution quickly.
Action: I immediately convened a meeting with the team to brainstorm potential solutions. Instead of panicking, I encouraged everyone to think outside the box and consider unconventional approaches. We analyzed the problem from different angles and weighed the pros and cons of each solution.
Result: By devising a workaround solution, we were able to meet the project deadline, avoiding potential delays that could have cost the company $100,000 in penalties for missing contractual obligations.
3. Decision Making

Situation: As a project manager , I was faced with a dilemma when two key team members had conflicting opinions on the project direction.
Task: My task was to make a decisive choice that would align with the project goals and maintain team cohesion.
Action: I scheduled a meeting with both team members to understand their perspectives in detail. I listened actively, asked probing questions, and encouraged open dialogue. After carefully weighing the pros and cons of each approach, I made a decision that incorporated elements from both viewpoints.
Result: The decision I made not only resolved the immediate conflict but also led to a stronger sense of collaboration within the team. By valuing input from all team members and making a well-informed decision, we were able to achieve our project objectives efficiently.
4. Communication (Teamwork)

Situation: During a cross-functional project, miscommunication between departments was causing delays and misunderstandings.
Task: My task was to improve communication channels and foster better teamwork among team members.
Action: I initiated regular cross-departmental meetings to ensure that everyone was on the same page regarding project goals and timelines. I also implemented a centralized communication platform where team members could share updates, ask questions, and collaborate more effectively.
Result: Streamlining workflows and improving communication channels led to a 30% reduction in project completion time, saving the company $25,000 in operational costs.
5. Persistence
Situation: During a challenging sales quarter, I encountered numerous rejections and setbacks while trying to close a major client deal.
Task: My task was to persistently pursue the client and overcome obstacles to secure the deal.
Action: I maintained regular communication with the client, addressing their concerns and demonstrating the value proposition of our product. Despite facing multiple rejections, I remained persistent and resilient, adjusting my approach based on feedback and market dynamics.
Result: After months of perseverance, I successfully closed the deal with the client. By closing the major client deal, I exceeded quarterly sales targets by 25%, resulting in a revenue increase of $250,000 for the company.
Tips to Improve Your Problem-Solving Skills
Throughout your career, being able to showcase and effectively communicate your problem-solving skills gives you more leverage in achieving better jobs and earning more money .
So to improve your problem-solving skills, I recommend always analyzing a problem and situation before acting.
When discussing problem-solving with employers, you never want to sound like you rush or make impulsive decisions. They want to see fact-based or data-based decisions when you solve problems.
Don’t just say you’re good at solving problems. Show it with specifics. How much did you boost efficiency? Did you save the company money? Adding numbers can really make your achievements stand out.
To get better at solving problems, analyze the outcomes of past solutions you came up with. You can recognize what works and what doesn’t.
Think about how you can improve researching and analyzing a situation, how you can get better at communicating, and deciding on the right people in the organization to talk to and “pull in” to help you if needed, etc.
Finally, practice staying calm even in stressful situations. Take a few minutes to walk outside if needed. Step away from your phone and computer to clear your head. A work problem is rarely so urgent that you cannot take five minutes to think (with the possible exception of safety problems), and you’ll get better outcomes if you solve problems by acting logically instead of rushing to react in a panic.
You can use all of the ideas above to describe your problem-solving skills when asked interview questions about the topic. If you say that you do the things above, employers will be impressed when they assess your problem-solving ability.
More Interview Resources
- 3 Answers to “How Do You Handle Stress?”
- How to Answer “How Do You Handle Conflict?” (Interview Question)
- Sample Answers to “Tell Me About a Time You Failed”

About the Author
Biron Clark is a former executive recruiter who has worked individually with hundreds of job seekers, reviewed thousands of resumes and LinkedIn profiles, and recruited for top venture-backed startups and Fortune 500 companies. He has been advising job seekers since 2012 to think differently in their job search and land high-paying, competitive positions. Follow on Twitter and LinkedIn .
Read more articles by Biron Clark
About the Contributor
Kyle Elliott , career coach and mental health advocate, transforms his side hustle into a notable practice, aiding Silicon Valley professionals in maximizing potential. Follow Kyle on LinkedIn .

About the Editor
Hayley Jukes is the Editor-in-Chief at CareerSidekick with five years of experience creating engaging articles, books, and transcripts for diverse platforms and audiences.
Continue Reading
12 Expert-Approved Responses to ‘What Makes You Unique?’ in Job Interviews
15 most common pharmacist interview questions and answers, 15 most common paralegal interview questions and answers, top 30+ funny interview questions and answers, 60 hardest interview questions and answers, 100+ best ice breaker questions to ask candidates, top 20 situational interview questions (& sample answers), 15 most common physical therapist interview questions and answers.
Social Work Graduate
Resources for social work graduates
Various social work practice approaches
Blogs added to / updated regularly
https://www.facebook.com/socialworkgraduate
https://www.instagram.com/socialworkgraduate/
- Oct 2, 2020
Practice Model: Problem Solving
Perlman’s model, planned change process model, practice approach based on planned change model
This page has three sections:
Background Material that provides the context for the topic
A suggested Practice Approach
A list of Supporting Material / References
Feedback welcome!
Background Material
Different authors look at the problem-solving model in varying ways.
Murdach (2007) suggests the principal stages of Perlman’s problem-solving model are simply:
problem definition,
problem analysis (including the generation and review of alternatives), and
the need for specific decision about a course of action (including methods of monitoring and evaluating the results of such action).
Chenowith and Lehmann (2008) describe a planned change process model:

Chenowith and Lehman also suggest the model outlined in the Practice Approach that follows. It consists of four phases:
The engagement phase involves making contact, exploring needs and setting preliminary goals.
The assessment phase involves collecting information, prioritising issues and agreeing on action.
The intervention phase involves implementing and modifying strategies to achieve goals.
The evaluation phase involves reviewing what has happened, celebrating progress and either concluding the work or negotiating a continued relationship.
- Practice Approach

Supporting Material
(available on request)
Chenoweth, L. M. D. (2014). Road to Social Work and Human Service Practice. South Melbourne: Cengage Learning Australia. Retrieved from http://ebookcentral.proquest.com/lib/une/detail.action?docID=1696405
Coady, N, & Lehmann, P. (2008). The problem-solving model: A framework for integrating science and art of practice. In N. Coady & P. Lehmann, Theoretical Perspectives for Direct Social Work Practice (pp. 67-86). New York: Springer Publishing Company. Retrieved from http://ebookcentral.proquest.com/lib/une/detail.action?docID=326279
Murdach, A. D. (2007). Helen Harris Perlman and the problem solving method. Retrieved from https://allisonmurdach.wordpress.com/2011/05/05/helen-harris-perlman-and-the-problem-solving-model/
Recent Posts
An Everyday Social Work Approach
Practice Model: Solution-Focused Approach
Practice Model: Task Centred

Critical & Creative Thinking - OER & More Resources: IDEAL problem solving
- Self evaluation
- Creating goals
- Creating personal mission statement
- Creative Thinking
- Problem Solving
- IDEAL problem solving
- CRITICAL THINKING
- Critical Thinking Tips
- Logic Terms
- Logic Traps
- Free OER Textbooks
- More Thinking: OER
- Ethics - OER Textbooks
- Evidence-Based Critical Thinking
- BELIEFS & BIAS
- Limits of Perception
- Reality & Assumptions
- Stereotypes & Race
- MAKING YOUR CASE
- Argument (OER)
- Inductive Arguments
- Information Literacy: Be Savvy about your Sources
- Persuasive Speaking (OER)
- Philosophy & Thinking
- WiPhi Philosophy Project
- Browse All Guides
VM: I had to inter-library loan this item to read the original content. This is highly cited throughout literature, so I wanted to have a good grasp on what it covered. Here are my notes and commentary:
- Full text From TNtech.edu: "Ideal Problem Solver, 2 ed." (c) 1984, 1993 more... less... Thanks to Center for Assessment & Improvement of Learning - Reports & Publications"
- Full text from ERIC: The IDEAL Workplace: Strategies for Improving Learning, Problem Solving, and Creativity
- Show your support: The Ideal Problem Solver: A Guide to Improving Thinking, Learning, and Creativity Second Edition
The reason you should learn the IDEAL method is so you don't need to avoid problems. The more know about and practice problem solving, the easier it gets. It is learnable skill. It also prompts you to look for problems and solutions instead of just doing things the same old way.
Improvement of problem solving skills.
Model for analyzing the processes that underlie effective problem solving.
IDEAL Model for improving problem solving (Verbatim copy of Fig 2.1; p.12)
I = Identifying the problem.
D = Define and represent the problem.
E = Explore possible strategies.
A = Act on the strategies.
L = Look back and evaluate the effects of your activities.
ELABORATION:
I = Identifying that there is a problem that, once described as a problem, may be solved or improved.
D = Define and represent the problem. Draw it instead of trying to imagine it.
E = Explore possible strategies & alternative approaches or viewpoints.
General strategies: Break problem down into small simple problems. Working a problem backwards. Build scale model Try simulation experiment, with smaller or simpler sets.
A = Act on the strategies. Try, then reflect or recall. Actively try learning strategy.
L = Look back and evaluate the effects of your activities. Look at results of learning strategy used: Does it work to allow full recall?
"Many students make the mistake of assuming that they have "learned" adequately if the information seems to make sense as they read it in a textbook or hear it in a lecture." (p. 23" Must use or practice, recall, or paraphrase - in order to evaluate effectiveness of learning.
Math: Do example problems before looking at solution to practice concepts. Look at solution to see where you went wrong (or not).
Don't let the test be the first time you evaluate your understanding of material
Problem identification and definition.
Proof of concept - act/look/evaluate.
To find an answer to a problem, you can dig deeper, or dig somewhere else.
Question assumptions about limits The old - think outside the box- strategy.
When memorizing, know what you need to remember Definitions? Concepts? Graphs? Dates? each teacher has different priorities...ask them what to focus on
Ways to solve problem of learning new information.
Techniques for improving memory.
Short term meomory
Long term memory
Remembering people's names
Studying for an essay test.
Using cues to retrieve information. For example, you can remember IDEAL first and that will help you reconstruct the idea of how to solve problems.
Some strategies for remembering information:
Make a story full of memorable images.
Funny obnoxious "vivid images" or "mental pictures" are more memorabl e. (Ex: random words in a list, passwords, people's names. Banana vomit haunts me.)
Rehearse over and over - over learn. (Ex: Memorizing a phone number 867-5309 )
Rehearse words in groups - chunking. (Ex: Memorizing a part in a play, poems, pledges, short stories.)
Organize words into conceptual categories - Look for unifying relationships. (Recall, order not important. Ex: Shopping list, points in an essay.)
Look for similarities and coincidences in the words themselves. (Ex: How many words have e's, or 2 syllables, or have pun-ishing homonyms)
The feet that use the manual transmission car pedals are, from left to right: C ( L eft-foot) utch , the B( R ight-foot) ake , and the A ccelerato ( R ight-foot)
Does order mimic alphabetical order? The manual transmission car pedals are, from left to right, the C lutch, the B rake, and the A ccelerator )
Use Acronyms I dentify D efine E xplore A ct L ook
Acronym- easily remembered word: FACE

Acrostic- easily remembered phrase: E very G ood B oy D eserves F udge
- Modified image source: Commons.wikimedia.org
Don't waste time studying what you already know
Image - Name Strategy:
What is unique about the person? What is unique about their name?
Find a relationship between the two.
Other Pairing Strategies:
method of loci: arranging words to be remembered in association with familiar location or path .
Peg-word method: arranging words to be remembered in association with number order or alphabet letter order .
Strategies to comprehend new information.
more difficult than
Strategies to memorize new information.
Learning with understanding - comprehending new information.
Knowledge of CORE CONCEPTS in a field SIMPLIFIES problem solving.
Ways to approach a problem of learning information that seems to be arbitrary:
Over-learn: rehearse the facts until they are mastered. 2+2=4
Find relationships between images or words that are memorable: story telling, silmilarieties, vivid images, pegging, etc.
When a concept seems unclear, learn more about it.
Memory- can be of seemingly arbitrary words or numbers: ROTE (Ex. Facts and relationships) appearance
Comprehension - is understanding significance or relationships or function
Novices often forced to memorize information until they learn enough (related concepts and context) to understand it.
The mere memorization of information rarely provides useful conceptual tools that enable one to solve new problems later on. (p. 61,69)
Taking notes will not necessarily lead to effective recall prompts. How do you know when you understand material? Self-test by trying to explain material to another person.That will expose gaps in understanding.
Recall answers or solve problems out of order to be sure you know which concepts to apply and why.
Look at mistakes made as soon as possible, and learn where you went wrong.
Uses of information require more or less precision in understanding, depending on context. (A pilot must know more about an airplane than a passenger.)
Evaluation basics: evaluate factual claims look for flaws in logic question assumptions that form the basis of the argument
Correlation does not necessarily prove cause and effect.
Importance of being able to criticize ideas and generate alternatives.
Strategies for effective criticism.
Strategies for formulating creative solutions.
Finding/understanding implicit assumptions that hamper brainstorming.
Strategies for making implicit assumptions explicit.
"The uncreative mind can spot wrong answers, but it takes a creative mnd to spot wrong questions ." Emphasis added. - Anthony Jay, (p.93)
Making implicit assumptions explicit: look for inconsistencies question assumptions make predictions analyze worst case get feedback & criticism from others
Increase generation of novel ideas: break down problem into smaller parts analyze properties on a simpler level use analogies use brainstorming give it a rest, sleep on it don't be in a hurry, let ideas incubate: talk to others, read, keep the problem in the back of your mind try to communicate your ideas as clearly as possible, preferably in writing. attempting to write or teach an idea can function as a discovery technique
Strategies for Effective Communication
What we are trying to accomplish (goal)
Evaluating communication fro effectiveness:
Identify and Define: Have you given audience basis to understand different points of view about a topic? Different problem definitions can lead to different solutions. Did you Explore pros and cons of different strategies? Did you take Action and then Look at consequences? Did you organize your content into main points that are easy to identify and remeber?
Did you use analogies and background information to put facts into context?
Did you make sure your facts were accurate and did you avoid making assumptions?Always check for logical fallacies and inconsistencies. Did you include information that is novel and useful, instead of just regurgitating what everyone already knows?
After you communicate, get feedback and evaluate your strategies. Look for effects, and learn from your mistakes. (p. 117)
Identify and Define what (problem) you want to communicate, with respect to your audience and your goals. Explore strategies for communicating your ideas.Act - based on your strategies. Look at effects.
Summaries of Useful Attitudes and Strategies: Anybody can use the IDEAL system to improve their problem solving skills.
Related Resources:
- Teaching The IDEAL Problem-Solving Method To Diverse Learners Written by: Amy Sippl
- << Previous: Problem Solving
- Next: CRITICAL THINKING >>
- Last Updated: Aug 13, 2024 8:34 AM
- URL: https://library.fvtc.edu/Thinking
About Us • Contact Us • FVTC Terms of Service • Sitemap FVTC Mission, Vision, Values & Purposes • FVTC Privacy Statement • FVTC Library Services Accessibility Statement DISCLAIMER: Any commercial mentions on our website are for instructional purposes only. Our guides are not a substitute for professional legal or medical advice. Fox Valley Technical College • Library Services • 1825 N. Bluemound Drive • Room G113 Appleton, WI 54912-2277 • United States • (920) 735-5653 © 2024 • Fox Valley Technical College • All Rights Reserved.
The https://library.fvtc.edu/ pages are hosted by SpringShare. Springshare Privacy Policy.
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
How to Solve Problems
- Laura Amico

To bring the best ideas forward, teams must build psychological safety.
Teams today aren’t just asked to execute tasks: They’re called upon to solve problems. You’d think that many brains working together would mean better solutions, but the reality is that too often problem-solving teams fall victim to inefficiency, conflict, and cautious conclusions. The two charts below will help your team think about how to collaborate better and come up with the best solutions for the thorniest challenges.
- Laura Amico is a former senior editor at Harvard Business Review.
Partner Center
- International
- Education Jobs
- Schools directory
- Resources Education Jobs Schools directory News Search

Maths Bar Model Problems
Subject: Mathematics
Age range: 7-11
Resource type: Lesson (complete)
Last updated
8 August 2024
- Share through email
- Share through twitter
- Share through linkedin
- Share through facebook
- Share through pinterest

This resource includes two similar PowerPoints (one of which enforces the RUCSAC method for problem solving). These PowerPoints contain an example for the teacher to model, as well as guided practice examples. A WAGOLL is also provided to support the steps of the teacher modelling. Independent activities are also included.
This resource focuses on teaching children to use bar models to solve problems that are difficult to visualise.
Tes paid licence How can I reuse this?
Your rating is required to reflect your happiness.
It's good to leave some feedback.
Something went wrong, please try again later.
This resource hasn't been reviewed yet
To ensure quality for our reviews, only customers who have purchased this resource can review it
Report this resource to let us know if it violates our terms and conditions. Our customer service team will review your report and will be in touch.
Not quite what you were looking for? Search by keyword to find the right resource:

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Learn about problem-solving models and the benefits of using them in the workplace, then review the six-step process for how to use these models effectively.
This article will explore the concept of problem-solving models and dive into examples of such models and how to use them. It will also outline the benefits of implementing a problem-solving model in each area of life and why these problem-solving methods can have a large impact on your overall well-being.
Create innovative solutions and solve tough challenges with these problem-solving techniques and tips for running an effective problem solving process.
In this article, we'll walk you through the 5 steps of problem solving, and help you explore a few examples of problem solving scenarios where you can see the problem solving process in action before putting it to work.
Problem-solving strategies are models based on previous experience that provide a recommended approach for solving problems or analyzing potential solutions. Problem-solving strategies involve steps like understanding, planning, and organizing, for example.
The problem-solving process typically includes the following steps: Identify the issue: Recognize the problem that needs to be solved. Analyze the situation: Examine the issue in depth, gather all relevant information, and consider any limitations or constraints that may be present. Generate potential solutions: Brainstorm a list of possible ...
Classic problem solving often gravitates toward a model; design thinking migrates toward a prototype. Rather than writing a big deck with all my supporting evidence, they'll bring an example, a thing, and that feels different.
What is the Six Step Problem-Solving Model? It is a collaborative and systematic approach to addressing problems. Instead of tackling issues haphazardly, this model encourages a sequential process ...
The 8D problem solving model establishes a permanent corrective action based on statistical analysis of the problem and focuses on the origin of the problem by determining its root causes. Although it originally comprised eight stages, or disciplines, the eight disciplines system was later augmented by an initial planning stage.
A fishbone diagram is a problem-solving approach that uses a fish-shaped diagram to model possible root causes of problems and troubleshoot solutions.
Got a problem to solve? From school to relationships, we look at examples of problem-solving strategies and how to use them.
This is the 4 step problem-solving process that I taught to my students for math problems, but it works for academic and social problems as well.
The Problem-Solving Process In order to effectively manage and run a successful organization, leadership must guide their employees and develop problem-solving techniques. Finding a suitable solution for issues can be accomplished by following the basic four-step problem-solving process and methodology outlined below.
SIX-STEP PROBLEM SOLVING MODEL Problem solving models are used to address many issues that come up on a daily basis in the workplace. These problems may be technical or issue-based. While many of you have probably already engaged in solving problems, you have probably used many different approaches in order to achieve a solution. Issues and operational problems in a committee can be solved ...
Problem-solving is the capacity to identify and describe a problem and generate solutions to fix it. Problem-solving involves other executive functioning behaviors as well, including attentional control, planning, and task initiation. Individuals might use time management, emotional control, or organization skills to solve problems as well.
What is The Six Step Problem Solving Model? The Six Step Problem Solving Model is a widely recognized and effective approach to addressing and resolving complex problems in personal and professional settings. This model provides a structured and systematic process for analyzing, identifying, and resolving issues, making it an indispensable tool for individuals, teams, and organizations.
Learn how to use the five steps in the FOCUS Model, starting with Find the problem, and then Organize a team, to refine your business processes.
The McKinsey problem solving process is a series of mindset shifts and structured approaches to thinking about and solving challenging problems. It is a useful approach for anyone working in the knowledge and information economy and needs to communicate ideas to other people.
Our career experts provide insights into problem-solving examples that you can use in job interviews, complete with sample answers and expert tips.
Murdach (2007) suggests the principal stages of Perlman's problem-solving model are simply: problem definition, problem analysis (including the generation and review of alternatives), and. the need for specific decision about a course of action (including methods of monitoring and evaluating the results of such action).
Chapter 2 Improvement of problem solving skills. Model for analyzing the processes that underlie effective problem solving. IDEAL Model for improving problem solving (Verbatim copy of Fig 2.1; p.12) I = Identifying the problem. D = Define and represent the problem. E = Explore possible strategies.
How to Solve Problems. To bring the best ideas forward, teams must build psychological safety. Teams today aren't just asked to execute tasks: They're called upon to solve problems. You'd ...
In reflection of these challenges, model-based systems aim at representing the knowledge about a class of real-world systems as a library of models with a maximum of versatility and re-use to different system instances and for different tasks, providing model-based problem solving engines that support or automate the
This resource includes two similar PowerPoints (one of which enforces the RUCSAC method for problem solving). These PowerPoints contain an example for the teacher to model, as well as guided practice examples.