How To Structure A Comparative Essay (VCE English Tips)
What is a comparative essay.
The comparative essay, in only its second year of being on the VCE English syllabus, is a cause for confusion for many students and teachers alike. Read on for one simple way to structure a comparative essay.

Comparative essay structure
How to write an introduction for a comparative essay.
This can be structured in much the same way as a text response essay. Here, the only difference is that you will need to introduce both texts. Do not forget to make use of comparative language, which is an element of the VCAA criteria, which requires that students discuss "meaningful connections , similarities or differences between the texts”. Your introduction must address your overall contention, specific to the prompt, which should be an idea or concept running through your essay.
How to write a body paragraph for a comparative essay
Aim for around two to four body paragraphs, which should be developed using breadth and a wide scope of ideas. A good way to construct these paragraphs is to base each around a premise or main idea, and you will explore both texts through the lens of this premise.
You can choose either to compare both texts throughout the paragraph, or to go into depth in one text and then transition into exploring the other. No matter which method you choose, make you mention to which extent the two texts are similar or different (it's not enough to say "they are different" or "they are similar").
Relate the end of your body paragraph back to the overall contention, bringing both texts explicitly into focus.
How to write a conclusion for a comparative essay
Like the intro, this can be very similar to a text response conclusion! Make sure to be clear and concise, and sum up your main points from your body paragraphs. Aim to end with a strong, clear point of analysis, shining new meaning on both texts.
Comparative Essay Writing Tips
- Create an Outline: Develop a well-organised outline to keep your essay focused and ensure a logical flow of arguments. This framework serves as a roadmap, guiding you from one point to the next. Always connect your arguments back to your thesis statement for coherence.
- Reference Throughout the Process: Avoid last-minute referencing by incorporating it into your writing process. Cite sources as you go to maintain accuracy and credibility. This practice helps in seamlessly integrating evidence to support your comparisons.
- Highlight Differences and Similarities: Emphasise both differences and similarities between the subjects you're comparing. Provide a clear analysis of how they relate, diverge, or intersect. This enhances the depth of your comparison and adds richness to your essay.
- Utilise Concrete Examples: Enhance the persuasiveness of your writing by using specific examples. Illustrate your points with concrete instances that support your comparisons. This not only reinforces your arguments but also adds clarity to your overall narrative.
- Incorporate Comparative Vocabulary: make sure your essay contains appropriate terminology and comparative words, such as: "On the contrary," "Although," "Furthermore," "Similar to," "Unlike," "In the same way," "Likewise," "Compared to," "In contrast," "Yet," and "On the one hand...on the other hand."
- Collaborate for Improvement: Seek input from others, whether through an English tutor or a study group. Collaborating with peers can provide valuable insights and help refine your work. Different perspectives contribute to a more comprehensive and polished essay.
- Prioritise Drafting: Aim to draft your essay as early as possible. Getting your initial thoughts on paper makes the editing process more manageable. Remember, a first draft is easier to edit than starting with a blank page
- Proofread and Edit: Finally, proofread and edit your essay. Pay attention to grammar, spelling, and overall clarity. A well-polished essay enhances the overall impact of your comparative analysis.
If you loved this article, you will LOVE all of our other articles, such as: How To Take Notes To Maximise Success , 2U Maths Tips from a Past Student (98 in 2U Maths)! and Tips on Studying for Exams – Learnmate Tutoring .
About Learnmate
Learnmate is a trusted Australian community platform that connects students who want 1:1 or small group study support, with tutors who are looking to share their knowledge and earn an income. From primary school to high school subjects — from science and maths to niche subjects like visual communication — Learnmate can help you improve academic performance or boost confidence, at your pace with the tutor that you choose.
We pride ourselves in offering a reliable and positive experience for both our students and tutors. Every tutor that joins the platform is vetted to meet a level of academic excellence, teaching qualification or relevant experience. All tutors are provided the opportunity to complete professional training.
Students and parents can easily find and screen for tutors based on their location, their subject results or skill level, and whether they provide in-person or online sessions. Learnmate is proud to provide tutors in Melbourne , Sydney , Geelong , Brisbane , Hobart , Canberra , Perth & Adelaide , and other locations.
Learnmate also has tutors for all curriculums: HSC , IB , QCE , BSSS, SACE , TASC, WACE , VCE and UMAT
Go online and let Learnmate help you get ahead. Start your search today.
"> "> share this post.
Article Author
Find online & in-person tutors near you, recent posts.

How to Choose the Right Primary School Tutor for Your Child
You’ve decided to get your child a tutor. Great! But what now? With so many tutors available across multiple platforms,...
August 2, 2024

Ultimate Guide to GAMSAT: Preparation Tips and Exam Overview
The Graduate Australian Medical School Admissions Test (GAMSAT) is an intensive exam targeted at undergraduate students who wish to apply...
August 1, 2024

Understanding Bad and Doubtful Debts in VCE Accounting
In this blog, we seek to understand how businesses deal with uncertainty around future cash flows from accounts receivable, in...


No products in the cart.
Insight: Engage
Writing a comparative essay.
This week, Insight writer and English teacher Melanie Flower outlines steps you can take to write your best comparative essay.
The comparative essay is still a relatively new element of VCE English, only becoming part of the Study Design in 2016. However, while the Area of Study is new, your essay should still have a clear and largely familiar structure, with an introduction, body and conclusion. Last year every topic in Section B of the VCE English examination included the word ‘compare’, and it is essential to note that the comparison of texts is the central requirement for this response, even if the word does not explicitly appear in the topic.
The comparative essay can be tackled in a variety of ways, and it is worth experimenting with different approaches throughout the semester to find the one that suits your strengths.
Read the topic carefully
Make sure that you understand exactly what the topic is asking you to do. The topic might invite a broad thematic comparison, which requires a thoughtful understanding of the ways a particular theme is explored in both texts. Other topics focus on an aspect of the texts’ construction, such as characterisation or setting, and require you to show an understanding of the texts’ form and genre.
You could also encounter a topic that contains one or two quotes. This type of topic necessitates a very thorough knowledge of your texts, as you need to recognise the context of each quote, identify the key ideas being addressed in each, and understand how these ideas are explored in both texts.
Give roughly equal weight to each text
Each text pairing has been carefully chosen to offer points of comparison, in terms of both similarities and differences. While you may have a preference for one text over the other, it is essential that you do not allow this to limit the scope of your discussion. One easy way to make sure that you are addressing both texts equally is to balance every point, example or quote from one text with an equivalent from the other. This can be done in the planning stages, giving you a wealth of material to use in your essay.
Choose your preferred structure
The broad structure of a comparative essay is already very familiar to you, and consists of an introduction, several body paragraphs and a conclusion. The introduction should include a clear contention that alerts the reader to your response to the topic, as well as the main ideas your essay will explore. It must contain references to both texts. Similarly, your conclusion should summarise the points you have made and leave the reader with a clear understanding of your position on the topic. These elements are common to all analytical text response essays. The difference in a comparative response is in the way the body paragraphs are structured and organised. You essentially have two basic options for the body: the block approach or the woven approach.
- The block approach: This approach involves devoting a paragraph or two to each text, examining the ways each of them address the ideas raised by the topic. The final body paragraphs pull this material together and discuss the similarities and differences between the texts’ approach to the central ideas explored in the essay. This structure appears straightforward, but it can be challenging to maintain a strong connection between the texts when discussing them in isolation. A careful use of linking words is essential to ensure that the essay is cohesive and the comparison of texts remains at the fore.
- The woven approach: Using a more sophisticated structure, the woven essay draws evidence from both texts within each body paragraph. Topic sentences focus on an aspect of the ideas raised by the topic rather than on individual texts or characters, leaving you free to explore material from both sources in the paragraph. It can be challenging to move between two texts, although with practice, this will become easier. One useful strategy is to begin your discussion of a particular idea with a sentence addressing text 1. Then start the next sentence with a linking word or phrase that leads to a statement about text 2’s perspective on the same idea. A third sentence links both texts, adding an overall position statement. This approach allows you to move smoothly between the texts while also engaging in deep analysis of their ideas.
Focus on differences as well as similarities
We tend to be very alert to similarities between texts, which are usually relatively simple to identify; however, often the most interesting discussion will devolve from a consideration of the differences. These provide an opportunity to explore contrasting situations and points of view, thus demonstrating your engagement with both the texts and the ideas they present.
Use linking words and phrases
When moving the discussion between texts, regardless of the overall essay structure you have chosen, use appropriate linking words and phrases to maintain fluency and cohesion. These links help your reader to understand the connection between the ideas you are discussing, whether they are similarities or contrasts.
Phrases that you can use to discuss similarities include:
similarly, likewise, in the same way, also, along similar lines, in the same fashion .
Phrases useful for indicating contrast include:
in contrast, on the other hand, unlike (text 1), regardless, however, conversely, on the contrary, nevertheless .
Used purposefully, these words and phrases help guide your reader through your discussion, ensuring that they understand the relationship between the texts and the ideas explored in your response.
Explore a range of elements
To add depth to your response, consider a variety of textual elements in your discussion. While the topic may prompt you to focus on character or theme, your response will have more depth if you are able to draw other aspects of the texts into your discussion. You could note the impact of the narrative voice, reflect on how structure shapes a reader’s responses, consider the influence of genre on the texts’ construction, or acknowledge differences in style or authorial purpose. All of these elements provide you with opportunities to consider the texts as constructs, leading to a more complex and sophisticated analysis.
_____________
The comparative essay is a challenging, but ultimately satisfying, opportunity to explore intertextual connections. By considering the different perspectives offered by carefully paired texts, you can enrich your understanding of both texts and draw new meanings from them. Ultimately, the best way to find an essay style that works for you is to experiment. Try a few different approaches, note the feedback you receive from your teacher, and use this to finetune your approach. Remember that examiners are not looking for a single, standard essay format. They are interested in your ideas and your genuine responses to the texts, and whichever structure best allows you to present these is the most appropriate structure for you.
Need help with your comparative essays? Insight has two Insight Sample Essays for each List 2 text comparison for English. Each high-level essay features annotations with assessor comments identifying the elements of the essay that work and areas for improvement, as well as tips on how to approach the essay topic and appropriate strategies for analysis.
Insight Sample Essays are produced by Insight Publications, an independent Australian educational publisher.
Photo credit: maradon333/shutterstock
Share this blog
*By using the Insight: Engage blog, you agree to the terms and conditions on this website .
Insight Engage Categories
- Argument and persuasive language
- Creative Text Response
- Creative Writing
- Exam preparation
- Handwriting
- Listening Comprehension
- Listening skills
- Queensland General English
- Reading and comparing texts
- Reading and creating texts
- Sample Essays & Text Articles
- Shakespeare
- Study techniques
- Text Analysis
- Text Guides & Comparisons
- Textbooks & Resources
- Theory of Knowledge
- Uncategorized
- VCE English
- VCE English as a Additional Language (EAL)
- VCE English Language
- VCE English Literature
- VCE text comparison
- Year 10 English
- Year 11 English
- Year 12 EAL
- Year 12 English
- Year 9 English
- 3/350 Charman Road Cheltenham, Victoria 3192
- [email protected]
Insight Publications is an independent Australian-owned company with over 50 years of experience publishing English resources for secondary teachers and students. We develop innovative, engaging and evolving English resources to challenge, to inspire and to enrich learning.
Information
- Credit Reporting Policy
- Insight Catalogue
- Privacy Policy
- Returns Policy
- Shipping Information
- Terms & Conditions
- +61 3 8571 4950
In the spirit of reconciliation, Insight Publications acknowledges the Traditional Custodians of Country throughout Australia and their connections to land, sea and community. We pay our respect to their Elders past and present and extend that respect to all Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander peoples today.
Get the Reddit app
Divided in ranking, united in struggle. This subreddit will cater to every question, concern and meme you have!
ENGLISH ARGUMENT ANALYSIS
hey everyone! I need some assistance with argument analysis. I can generally write pretty well when I’m only given one text but for my sac, we are required to write a comparative analysis. I’m a little confused on how I should structure my piece. My plan is to write separate paragraphs analysing both texts and then one paragraph on comparison but then I feel like my analysis will be way too long and I only have an hour to write it. Any advice??
By continuing, you agree to our User Agreement and acknowledge that you understand the Privacy Policy .
Enter the 6-digit code from your authenticator app
You’ve set up two-factor authentication for this account.
Enter a 6-digit backup code
Create your username and password.
Reddit is anonymous, so your username is what you’ll go by here. Choose wisely—because once you get a name, you can’t change it.
Reset your password
Enter your email address or username and we’ll send you a link to reset your password
Check your inbox
An email with a link to reset your password was sent to the email address associated with your account
Choose a Reddit account to continue
VCE Study Tips
English Language

Private Tutoring

Only one more step to getting your FREE text response mini-guide!
Simply fill in the form below, and the download will start straight away
English & EAL
The Ultimate Guide to VCE Text Response
May 7, 2019

Want insider tips? Sign up here!
Go ahead and tilt your mobile the right way (portrait). the kool kids don't use landscape....
Updated 19/01/2021
1. What Is Text Response? 2. What Are You Expected To Cover? (Text Response Criteria) 3. School Assessed Coursework (SAC), Exams and Allocated Marks 4. How To Prepare for Your Text Response SAC and Exam 5. How To Write a Text Response
1. What Is Text Response?
Like its name, Text Response is when you respond to a text. The most popular texts are novels and films; however, plays, poetry and short stories are also common. Your response will be in the form of an essay, in which you discuss themes, ideas and characters. Recall all the novels and films you've studied since Year 7 (there'll be quite a few!). You should be very familiar with the process of watching a film or reading a novel, participating in class discussions about themes and characters, and finally, submitting an essay based on the text.
As you graduate into higher year levels, you spend each year revising and improving on TEEL, learning to better incorporate quotes and formulating even longer essays than the year before (remember when you thought you couldn't possibly write an essay more than 500 words?).
The good news is, all of that learning is now funnelled into VCE’s Text Response, one of the three parts of the VCE English study design. Text Response, officially known as ‘Reading and Responding’ in the study design, is the first Area of study (AoS 1) - meaning that the majority of students will tackle the Text Response SAC in Term 1. Let's get into it!
2. What Are You Expected To Cover? ( Text Response Criteria)
What are teachers and examiners expecting to see in your essays? Below are the VCE criteria for Text Response essays.
Note: Some schools may express the following points differently, however, they should all boil down to the same points - what is necessary in a Text Response essay.
a) Critically analyse texts and the ways in which authors construct meaning;
Much of the ‘meaning’ in a novel/film comes instinctively to readers. Why is it that we can automatically distinguish between a protagonist from an antagonist? Why is it that we know whether or not the author supports or denounces an idea?
Here you need to start looking at how the author constructs their texts and why they have made that choice. For example, the author describes a protagonist using words with positive connotations (kind, brave, charming), whereas the antagonist is described with words using negative connotations (vain, egocentric, selfish).
For example, 'in Harry Potter , by describing the protagonist Harry as "brave", the author JK Rowling exhibits the idea of how possessing bravery when making tough choices or facing challenges is a strong and positive trait.'
b) Analyse the social, historical and/or cultural values embodied in texts;
Society, history and culture all shape and influence us in our beliefs and opinions. Authors use much of what they’ve obtained from the world around them and employ this knowledge to their writing. Understanding their values embodied in texts can help us as readers, identity and appreciate theme and character representations.
For example, 'through the guilty verdict of Tom Robinson in To Kill A Mockingbird , Harper Lee expresses the belief that the American legal system in the 1930s was not always fair or just.'
For more information on context and authorial intent in VCE English, read Tim's blog, Context and Authorial Intention in VCE English, or Olivia's on what authorial intent is and why it's important .
c) Discuss and compare possible interpretations of texts using evidence from the text;
Be open to the idea that many texts can be interpreted in many ways. Texts are rarely concrete and simple. Take The Bible , a book that is one of the most popular and famous books in history but is interpreted differently by every person. Acknowledging more than one perspective on a certain aspect of the text, or acknowledging that perhaps the writer is intentionally ambiguous, is a valuable skill that demonstrates you have developed a powerful insight into your text.
For example, 'in The Thing Around Your Neck , feminist readers condone Adichie's stories which all revolve around women either as protagonist or as narrators, giving voice to the disempowered gender in Nigerian society.'
d) Use appropriate metalanguage to construct a supported analysis of a text;
While you should absolutely know how to embed quotes in your essay like a boss , you want to have other types of evidence in your Text Response essay. You must discuss how the author uses the form that he/she is writing in to develop their discussion. This encompasses a huge breadth of things from metaphors to structure to language.
For example, 'The personification of Achilles as "wolf, a violator of every law of men and gods", illustrates his descent from human to animal….' or 'Malouf’s constant use of the present voice and the chapter divisions allow the metaphor of time to demonstrate the futility and omnipresence of war…'.
To learn more about metalanguage, read our ' What Is Metalanguage? ' post.
e) Control and effectiveness of language use, as appropriate to the task
When examiners read essays, they are expected to get through about 12-15 essays in an hour! This results in approximately 5 minutes to read, get their head around, and grade your essay - not much time at all! It is so vital that you don’t give the examiner an opportunity to take away marks because they have to reread certain parts of your essay due to poor expression and grammar.
For further advice on the above criteria points, read Emily's (English study score 46): Year 12: How To Turn Your Text Response Essays From Average to A+ .
3. School Assessed Coursework (SAC), Exams and Allocated Marks
Reading and Creating is assessed in Unit 1 (Year 11) and Unit 3 (Year 12). The number of allocated marks are:
- Unit 1 - dependant on school
- Unit 3 English – 30 marks
- Unit 3 EAL – 40 marks
Exactly when Text Response is assessed within each unit is dependent on each school; some schools at the start of the Unit, others at the end. The time allocated to your SAC is also school-based. Often, schools use one or more periods combined, depending on how long each of your periods last. Teachers can ask you to write anywhere from 800 to 1000 words for your essay (keep in mind that it’s about quality, not quantity!)
In your exam, you get a whopping total of 3 hours to write 3 essays (Text Response, Comparative and Language Analysis). The general guide is 60 minutes on Text Response, however, it is up to you exactly how much time you decide to dedicate to this section of the exam. Your Text Response essay will be graded out of 10 by two different examiners. Your two unique marks from these examiners will be combined, with 20 as the highest possible mark.

4. How To Prepare for Your Text Response SAC and Exam
Preparation is a vital component in how you perform in your SACs and exam so it’s always a good idea to find out what is your best way to approach assessments. This is just to get you thinking on the different study methods you can try before a SAC. Here are my top strategies (ones I actually used in VCE) for Text Response preparation that can be done any time of year (including holidays - see How To Recharge Your Motivation Over the School Holidays for more tips):
a) Reread your book (or rewatch the film)
After all the learning and discussion you’ve had with your teacher and peers, you should have now developed a solid foundation of knowledge. Rereading a book enables you to refresh your memory on subplots, popular passages and most importantly, helps you fill in any missing gaps in knowledge. Take this as an opportunity to get familiar with the parts of the texts you're less confident with, or to examine a particular theme that you know you're weaker in (HINT: A good place to start is to make sure you know the difference between themes, motifs and symbols !)
b) Do a close analysis
This is like an advanced version of rereading a book. A 'close analysis' - a term stolen from VCE Literature (thanks Lit!) - is basically where you select a passage (a short chapter or a few pages), and analyse it in detail.
As you move through the passage, you can pick out interesting word choices made by the author and try to interpret why they have made this choice. Doing a close analysis will immensely strengthen your metalanguage analysis skills, and also give you the opportunity to stand out from other students because you can offer unique and original analysis and evidence in your essay. I know this can be a bit confusing, so this video below shows a full close analysis of a Macbeth passage in action:
c) Read and watch Lisa's Study Guides' resources
Doing this study all by yourself can be rather daunting, so we've got your back. We specialise in supporting VCE English by creating helpful videos, study guides and ebooks. Here are some just to get your started:
YouTube Videos
We create general Text Response advice videos like this:
We also create text-specific videos:
And if you just need general study advice, we've got you covered too:
Check out our entire YouTube channel (and don't forget to subscribe for regular new videos!).
Study Guides
Our awesome team of English high-achievers have written up study guides based on popular VCE texts. Here's a compilation of all the ones we've covered so far:
After Darkness by Christine Piper
Cosi by Louis Nowra
Extinction by Hannie Rayson
Flames by Robbie Arnott
False Claims of Colonial Thieves by Charmaine Papertalk Green and John Kinsella
Go Went Gone by Jenny Erpenbeck
Like a House on Fire by Kate Kennedy
Measure for Measure by William Shakespeare
Old/New World Selected Poems by Peter Skrzynecki
On The Waterfront by Elia Kazan
Ransom by David Malouf
Rear Window by Alfred Hitchcock
Runaway by Alice Munro
Station Eleven by Emily St John Mandel
Sunset Boulevard by Billy Wilder (Analysis of Film Techniques)
Sunset Boulevard by Billy Wilder (Incorporating Cinematic Features into your VCE Essay)
The Crucible by Arthur Miller
The Complete Maus by Art Spiegelman
The Erratics by Vicki Laveau-Harvie (Setting)
The Erratics by Vicki Laveau-Harvie (Breakdown of Themes & Quotes)
The Golden Age by Joan London
The Lieutenant by Kate Grenville
The Secret River by Kate Grenville
The White Girl by Tony Birch
To Kill a Mockingbird by Harper Lee
William Wordsworth: Poems Selected by Seamus Heaney
Women of Troy by Euripides (Don Taylor's version)
Year of Wonders by Geraldine Brooks
Tip: You can download and save many of these study guides for your own study use! How good is that?

And if that isn't enough, I'd highly recommend my How To Write A Killer Text Response ebook.
Most people seem to the think the most difficult part of Text Response is the writing component - and they're not completely wrong. However, what I've found is that not even students place emphasis on the brainstorming, preparation and planning of Text Response.
Think about it - if you don't come to the table with the best ideas, then how can you expect your essay to achieve A+? Even if you write an exceptional essay, if it doesn't answer the prompt, your teacher won't be sticking a smiley face on your work. We need to avoid these common teacher criticisms, and I have no doubt you've experienced at least once the dreaded, 'you're not answering the prompt', 'you could've used a better example' or 'more in-depth analysis needed'.
Enter my golden strategy - the THINK and EXECUTE strategy . This is a strategy I developed over the past 10 years of tutoring, and I've seen my students improve their marks every time. The THINK and EXECUTE strategy breaks up your Text Response into two parts - first the THINK, then the EXECUTE. Only with the unique THINK approach, will you then be able to EXECUTE your essay to its optimum potential, leading yourself to achieve those higher marks.
To learn more about the THINK and EXECUTE strategy, download my ebook sample on the shop page or at the bottom of this blog, or check out the video below:
d) Get your hands on essay topics
Often, teachers will provide you with a list of prompts to practice before your SAC. Some teachers can be kind enough to hint you in the direction of a particular prompt that may be on the SAC. If your teacher hasn’t distributed any, don’t be afraid to ask.
We have a number of free essay topics curated by our team at LSG, check some of them out. Also go scroll back up to our list of study guides above, as most of those also have essay prompts included:
All the Light We Cannot See Essay Topics Like a House on Fire Essay Topics The Handmaid's Tale Essay Topics
e) Brainstorm and write plans
Once you've done some preliminary revision, it's time to write plans! Plans will help ensure you stick to your essay topic and have a clear outline of what your essay will cover. This clarity is crucial to success in a Text Response essay.
Doing plans is also an extremely time-efficient way to approach SACs. Rather than slaving away hours upon hours over writing essays, writing plans can will save you the burnout and will get you feeling confident faster.
I've curated essay topic breakdown videos based on specific VCE texts. In these videos, I explore keywords, ideas and how I'd plan an essay with corresponding examples/evidence.
f) Write essays
Yes, sad, but it’s a fact. Writers only get better by actually writing . Even if you just tackle a couple of essays then at least you will have started to develop a thinking process that will help you to set out arguments logically, utilise important quotes and time yourself against the clock. It will help you write faster as well – something that is a major problem for many students. With that said, let's get into how to write a Text Response next.
Take a look at some of the essays our amazing LSG team have written:
After Darkness Essay Topic Breakdown
All the Light We Cannot See Essay Topic Breakdown
Extinction A+ Essay Topic Breakdown
Station Eleven Essay Topic Breakdown
Women of Troy Essay Topic Breakdown
If you need any more tips on how to learn your text in-depth, Susan's (English study score 50) Steps for Success in Text Study guide provides a clear pathway for how to approach your text and is a must read for VCE English students!
And, if you're studying a text you hate (ugh!) be sure to check out Lavinia's guide which teaches you how to do well even when you don't like your text !
5. How To Write a Text Response
Before you start writing, make sure you're familiar with The Five Types of Text Response Prompts . Understanding the different types will help you move beyond a 'basic' one-size-fits-all structure.
Introduction
In an introduction, you're expected to have the following:
- Context (or background)
- Author's name
- Title of text
- Main arguments
Here's an example from Vindhya (English study score 46), in her post Dissecting an A+ Essay Using 'The Golden Age' by Joan London :
Perhaps nothing exemplifies the power of love and recognition more than the bond between Albert Sutton and his older sister, Lizzie, in Joan London’s ‘The Golden Age’. Many of London’s characters exhibit suffering that requires compassion and support to heal and grow, to distinguish present from past. However, London explores the perspectives of such characters from different aspects of trauma, and emphasise that love and recognition do not always work to heal and mature. Frank Gold, the novel’s resident “sneaky” boy who adjusts to newfound life in the Golden Age Convalescent Home seeks love as an adult, rather than eliciting sympathy as a supposed victim. Here love and recognition are unsuccessful in amending Frank’s troubles when given from the perspective of an outsider, a judgemental onlooker. In a similar sense, Ida Gold seeks recognition not from Australia, who she views as a ‘backwater’, but validation in herself after having been ousted from her Hungarian identity. London, however, makes sure to emphasise the impact that Sullivan has on Frank Gold’s life. Sullivan, a boy only a few years older than Frank, seems content with his future, with his fate, despite his sacrifice of rugby and conventional life. There is a lacking sense of urgency for love and recognition in Sullivan’s life, rather, it appears that Sullivan accepts his fate, regardless of his father’s sympathy or support. Thus, London explores a myriad of ways in which love and recognition may or may not heal wounds inflicted upon individuals.
Try to keep your introduction to the point. There's no need to prolong an introduction just to make a set number of sentences. It's always better to be concise and succinct, and then move into your main body paragraphs where the juicy contents of your essay resides.
Body Paragraph
Most of you will be familiar with TEEL. TEEL can stand for:
- T opic sentence
- L inking sentence
If your teacher or school teaches you something slightly different - that's okay too. At the end of the day the foundations are the same.
Early in the novel, London makes reference to Norm White, the resident groundskeeper of The Golden Age Convalescent Home. Norm White hands Frank Gold a cigarette, 'as if to say a man has the right to smoke in peace'. Here, there is a complete disregard for rule and convention, an idea that London emphasises throughout the text. This feature provides a counter-cultural experience for Frank, pushing him to realise that he is a strong human being rather than a mere victim. This is a clear contrast to the “babyishness” of the home, and is used as evidence of true humanity in an era where society judged upon the unconventional. Frank yearns for a traditional Australian life after his trauma in Hungary; 'his own memory…lodged like an attic in the front part of his brain'. Hedwiga and Julia Marai’s caring of him pushed him towards fear and reluctance to trust, yet also pressured him to seek acceptance in a world that ostracises him for his Jewish heritage and polio diagnosis. This here is why Frank desires a mature, adult connection – love that regards him as an equal human being. Frank seeks Elsa’s love and company as she too loathes being reduced to a victim, an object of pity. Frank thereafter uses humour to joke of his wounds; 'we Jews have to be on the lookout'. Elsa sees 'a look in his eyes that she recognised', thus their bond enables both characters to heal. London alludes that Frank requires love and recognition not from the perspective of a sorrowful onlooker, rather he longs to be recognised as a mature adult.
Conclusions should be short and sweet.
Although trauma is often treated with love and compassion, London details different perspectives on this idea. Whilst Frank Gold requires a specific kind of recognition, Ida and Meyer seek validation in themselves and their relationship, whilst Sullivan is at ease with his fate and does not yearn sympathy from his father.
For further detail from Sarah (English study score 45), read her advice on 5 Tips for a Mic-Drop Worthy Essay Conclusion .
That's it for the Ultimate Guide to VCE Text Response . Good luck!
*Originally posted in 2011, this blog post has been revised for the latest English study design.
Get our FREE VCE English Text Response mini-guide
Now quite sure how to nail your text response essays? Then download our free mini-guide, where we break down the art of writing the perfect text-response essay into three comprehensive steps. Click below to get your own copy today!

Struggling to answer the essay topic?
Has your teacher ever told you:
"You're not answering the prompt"
"You're going off topic"
Then you're not alone! If you struggle to understand and stay on topic, learn how to answer the prompt every time with our How To Write A Killer Text Response study guide.

1. Summary 2. Historical Context 3. Character Analysis 4. Theme Analysis 5. Sample Essay Topics 6. Essay Topic Breakdown
Year of Wonders is usually studied in the Australian curriculum Area of Study 1 - Reading and Comparing. For a detailed guide on Comparative, check out our Ultimate Guide to VCE Comparative .
However, Year of Wonders may also be studied in Area of Study 1 - Text Response. For a detailed guide on Text Response, check out our Ultimate Guide to VCE Text Response .
Year of Wonders is set in the small English village of Eyam in 1665, as the town struggles through a deadly outbreak of the bubonic plague. While the characters and events are fictional, author Geraldine Brooks based the novel on the true story of Eyam, whose inhabitants, at the urging of their vicar, courageously decided to quarantine themselves to restrict the spread of the contagion and protect other rural townships.
The experience of the plague provides Brooks fertile ground to develop characters that illustrate the extremes of human nature ; displaying the dignity or depravity, self-sacrifice or self-interest that people are capable of when faced with terror, pain and the unknown . She explores the consequences of a catastrophe on an isolated, insular and deeply religious community and we see characters exhibit tireless dedication and heroism, or succumb to depression, exploitation and sometimes murderous depravity.
The novel illustrates that adversity can bring out the best and worst of people and that faith can be challenged and eroded. The novel explores how crises affect human behaviour, beliefs and values and reveal the real character of a community under pressure. Our job while studying this text is to consider how all the different responses to an external crisis contribute to an analysis of human nature .
2. Historical Context
Year of Wonders belongs to the genre of historical fiction (meaning it is fictional but based on historical events) and aims to capture and present the historical context accurately. The context of Year of Wonders is important to understand as it informs a lot of the division and instability in Eyam during the isolation and crisis of the plague (we explain in more detail why context is so important in Context and Authorial Intent in VCE English ).
In 1658, only 7 years before the novel opens, Puritan statesmen Oliver Cromwell (who defeated King Charles I in the English Civil War and ruled as Lord Protector of the British Isles from 1653) died and Charles II, heir to the throne, returned from exile to rule England as King. Charles II replaced Cromwell’s rigid puritanism with the more relaxed Anglicanism and his reign began the dynamic period known as the Restoration. During the civil war and Cromwell’s rule, all the past certainties – the monarchy and the Church – had been repeatedly challenged and overturned. This all happened during the lifetime of the Eyam villagers presented in the novel and the recent religious upheaval in Britain was beginning to influence the conservative and puritan congregation of Eyam as the old puritan rector was replaced with Anglican vicar Michael Mompellion. The tension between the puritans and Anglicans is evident early in the novel and is exacerbated by the arrival of the plague, causing further internal fission.
The 17th century also marked the beginning of modern medicine and the Age of Enlightenment. During the Enlightenment, people began to privilege reason and sensory evidence from the material world over biblical orthodoxy as the primary sources of knowledge. The Enlightenment advanced ideals such as progress, liberty, tolerance, egalitarianism and the scientific method. These values are reflected in the liberal characters of Anna, Elinor, Mem and Anys Gowdie, and to an extent, Michael Mompellion. However, we also see the limited reaches of the Enlightenment in characters who succumb to superstition or self-flagellation when the plague arrives. This was a time when religious faith was frequently challenged and redefined .
3. Character Analysis
The novel is narrated in the first person by protagonist Anna Frith . Anna, a young widow, mother and housemaid, becomes the town’s nurse and midwife during the plague alongside her employer and friend Elinor Mompellion. Anna is a compelling protagonist and narrator because she is part of the ordinary, working-class life of the village, but also has access to the gentry in her work for the Mompellions, meaning readers can see how the plague affected all social groups.
At the beginning of the novel, Anna is in many ways very conventional. Aside from her intelligence and desire to learn, evidenced by her interest and quick proficiency in learning to read, Anna married young, is a dedicated mother, had an incomplete education and never thought to question the town’s orthodox religious beliefs. However, it is revealed early that she has progressive views on class and morality and as the novel progresses, the extraordinary circumstances of the plague evoke in her heroism and courage. Brooks notes, Anna 'shrugs off the social and religious mores that would keep a weaker woman in her place'. During the plague, Anna becomes the village’s voice of reason and an indispensable figure due to her expanding medical knowledge, tenacity, resourcefulness and tireless generosity.
Michael Mompellion
Michael Mompellion is Eyam’s Anglican preacher, having been appointed three years earlier after Charles II returned to England and replaced Puritan clergies. Generally, Mompellion is altruistic and open-minded : softening strict class divisions, combatting superstition and embracing a scientific approach to the plague. When the plague arrives, the local gentry (the Bradfords) flee and due to his charisma and position in the Church, he becomes the town’s unofficial leader. Mompellion persuades the townspeople to go into self-imposed quarantine to prevent the spread of the plague. His personal charisma, powerful rhetoric and indefatigable dedication to his work mean he can motivate and inspire his parishioners.
Mompellion’s unwavering commitment to his beliefs makes him a good leader, but we also see that his single-minded religious zeal can lead to harsh irrationality and hypocrisy. While progressive on issues such as class divisions, Mompellion is conservative – bordering on fanatic – when it comes to female sexuality . When his beloved wife Elinor dies, it is revealed that Mompellion denied her sexual intimacy for their entire marriage to punish her for the premarital affair and abortion she had as a teenager. Mompellion realises upon Elinor’s death that he extended forgiveness and understanding to all but his wife and, recognising his own hypocrisy and cruelty , he suffers a breakdown and loses much of his religious faith . Through Anna’s eyes, we see Mompellion shift from a character of moral infallibility, to a flawed and inconsistent man of a more ambiguous character .
Elinor Mompellion
Elinor is Mompellion’s wife and Anna’s employer and teacher. By the end of the novel, Anna and Elinor are confidantes and friends and their friendship arguably forms one of the strongest emotional cores of the novel, sustaining both women through enormous strain and hardship. Elinor teaches Anna to read and seems not to notice or care about their different social strata, treating everyone equally . Elinor came from a very wealthy family and initially had little practical knowledge of the hardships and necessities of life. During the plague, she confronts pain, suffering and true sacrifice. Because of her beauty, fragility and generosity, the whole town – and especially Anna – view her as a paragon of virtue and the embodiment of innocence. However, Elinor reveals that as a teenager she had a premarital relationship that resulted in an illegitimate pregnancy which she ended through abortion. Elinor considers herself to be permanently marked by sin and is plagued by the guilt of her adolescent mistakes, but her commitment to atone through service and working to help others is admirable.
Anys and Mem Gowdie
Anys and her aunt Mem are the town’s healers and midwives. Both women live on the margins of society , as their knowledge of herbal medicines and power to heal certain ailments causes fear and suspicion . Additionally, Anys further alienates the villagers by having conspicuous affairs with married village men. Anna admires Anys’ herbal knowledge and healing skill and her autonomy and unashamed sexuality , which were rare for women at the time. When the plague breaks out, Anys and Mem are murdered by a mob of hysterical townspeople , who believe they are witches responsible for the plague. This episode shows the power and acute danger of superstition and hysteria .
Josiah and Aphra Bont
Josiah 'Joss' Bont is Anna’s estranged father and Aphra is Anna’s stepmother. Brooks depicts them as unsympathetic and unforgivable , if understandable, villains as they both seek to profit off the heavy misfortune of others. Joss abused Anna greatly throughout her childhood, and while she manages to forgive him due to the suffering of his own youth, when he cruelly exploits villagers in his position as gravedigger, Anna finds his actions irredeemable. As gravedigger, Joss charged exorbitant fees from desperate people to bury their dead, regularly stole from the beleaguered families and attempted to bury a wealthy plague sufferer alive to loot his home.
Aphra is similarly amoral and greedy. Although her love for her children is shown to be strong, she capitalises on the fear and superstition of her neighbours by selling fake charms while pretending to be Anys Gowdie’s ghost. After the death of her husband and children, Aphra becomes completely deranged, dismembering and refusing to bury the rotting corpses of her children and eventually murdering Elinor. Aphra’s fate and actions show how prolonged catastrophe and suffering can totally erode an individual’s sanity .
The Bradford Family
The Bradford family are arrogant and pretentious. When the plague arrived in Eyam they also proved themselves self-serving and opportunistic , exploiting their wealth and status as part of the gentry to flee Eyam instead of enduring the quarantine with the rest of the village. They provide a foil to the Mompellions , who are of similar status and are newcomers to Eyam with fewer historical ties and thus expectations of loyalty. The two upper-class families provide directly opposite responses to the crisis, with Brooks clearly condemning the cowardice and selfishness exhibited by the Bradfords.
Social Convention and Human Nature in a Crisis
Perhaps the most significant theme or exploration of the novel is what happens to an individual’s character and community norms in a crisis . Year of Wonders depicts a small and isolated community that experiences intense adversity from the plague and, because of their self-imposed quarantine, are additionally isolated from the stabilising forces of broader society. These factors cause the people of Eyam to increasingly abandon their social conventions and descend into chaos and Brooks raises the question of whether people can live harmoniously without a strong social code. She suggests that societal cohesion is the result of social pressure rather than innate to our nature. The social norms and protocols of Eyam collapse under the pressure of the plague, allowing discerning observers like Anna to explore the validity and value of her society’s fundamental values . Eyam’s experience of the plague demonstrates that some norms, like the limited role of women and the strict class divisions , do not need to be so repressive, while other norms and social virtues, like the rule of law and justice , are proved even more essential for their absence as order and civility disintegrate.
Brooks also explores the response of individuals to extreme and enduring adversity and questions whether crises reveal someone’s true nature or instead force them to act out of character .
Anna and Elinor are examples of characters who respond to the crisis of the plague, amongst other real hardships, with a steadfast commitment to their principles. Their innate charity and work ethic are only strengthened and bolstered by the demands of the plague . However, not all residents of Eyam respond to the plague with courage and decency. Many descend into fear and hysteria, while others become malevolent and exploitative in their efforts to protect themselves. The Bonts and the Bradfords are examples of people who act with appalling selfishness, yet Brooks is careful to illustrate them as cruel and self-serving even before the plague . Thus, Brooks appears to argue that our actions under intense duress are intensifications of our true nature .
Faith, Suffering and Science
A major theme explored in the novel is the role of faith in people’s lives and throughout the novel faith, superstition and emerging science contend with each other . Before the plague, the townspeople believe whole-heartedly in God’s divine plan – that the good and bad things that happened to them were God’s rewards or punishments for their virtues or sins. However, the plague makes this worldview unsupportable as the unremitting suffering of plague victims, depicted through gory and vividly gruesome descriptions , demonstrates that their suffering is not commensurate with their sin and that no one can deserve this fate. In particular, it is the suffering of children that most intensely shakes Anna’s faith in a divine plan. Her two young sons are early victims of the plague and their youth and innocence mean it is impossible to justify their deaths as punishment for sin. The sheer tragedy of the plague causes Anna to realise that faith in God’s plan is inadequate to explain suffering and tragedy and she looks for another explanation. This leads her to use science and medicine to ameliorate pain. By focusing on discovering possible cures or pain relievers, Anna and Elinor are indirectly treating the plague as just a 'thing in nature', eschewing the prevailing religious view that the plague is the result of God’s wrath . Their emerging scientific worldview does not rely on God’s presence and intervention in the material world and Anna loses her religious faith.
However, the scientific method and worldview were only in its very nascent form and most people held a firm belief in supernatural intervention, making the townspeople prone to superstition and, in their ignorance and fear, murderous mob hysteria .
Women and Female Sexuality
Women in Eyam had lived highly circumscribed and restricted lives until the crisis of the plague disrupted the social order. The behaviour and speech of women were heavily policed and punished . In a particularly horrifying episode, Joss puts his wife in a muzzle and parades her through the village after she publicly criticises him. While Joss is undeniably an all-round bad guy, his misogyny cannot be dismissed as singular to him. Even Mompellion, an altruistic and in some ways quite progressive man, takes a very harsh stance on female sexuality. Although he preached to adulterous male villagers such as Jakob Merrill that 'as God made us lustful so he understands and forgives', he denied Elinor forgiveness for her teenage sexual relationship and was unfathomably rageful when he discovers Jane Martin having sex outside of marriage. However, Brooks criticises the taboo on female sexuality and shows that sexual desire is an awakening and liberating force for Anna, twice helping her to come out of deep depressions and reminding her that life has joy and meaning.
There are strong feminist undertones throughout the novel as each female character exhibits strengths that the male characters do not and challenges the limitations of her role, expressing desire for more personal autonomy and agency . From the beginning of the novel, Anna admires the sexual freedom of Anys Gowdie and the ability of Elinor to unreservedly pursue her intellectual interests. During the plague, Anna finds herself eschewing her old role and social position and assuming many challenging and indispensable responsibilities that would have been unthinkable for any woman – especially a young single working-class woman – before the plague.
Leadership and Judgement in Times of Crisis
The text explores both the power of religious leaders to influence public opinion and the ability of strong and courageous individuals to rise to positions of respect and authority in a crisis. Mompellion’s natural leadership and rhetorical skill keep the community calm and bring out the spirit of self-sacrifice in them. His clear dedication to his work and parishioners inspires trust in the community, and although Mompellion comes to doubt his judgement, it is undeniable that his strong leadership and assumption of huge responsibility saved countless lives. Anna also emerges as an unofficial leader; she becomes an essential figure and the voice of reason in Eyam. The community’s newfound respect for Anna is evident in the way she is listened to and adhered to and her confidence in firmly and decisively addressing and directing men and those of a higher social class.
We see examples of powerful leadership in the novel, but we also see how an overwhelming crisis can lead to a shortage of clear leadership and expose flaws in existing governing systems. Eyam relied on its gentry (Colonel Bradford) and vicar (Michael Mompellion) to adjudicate and administer justice. However, on the advent of the plague, the Bradfords fled from Eyam and Mompellion became overwhelmed by work, leaving the townspeople to frequently administer their own justice through group tribunals or vigilante action. Additionally, the extreme circumstances of the plague mean the town must deal with crimes it has never faced before and is unsure how to punish. Brooks explores what it means to achieve justice when the only means available are faulty. There are many examples of miscarriages of justice which forces readers to think about the necessity of a strong, fair and prompt judicial system and the weaknesses inherent in these institutions.
5. Sample Essay Topics
- How does Year of Wonders explore the concept of social responsibility?
- ‘In stressful times, we often doubt what we most strongly believe.’ How is this idea explored in Year of Wonders ?
- ‘Year of Wonders suggests that, in a time of crisis, it is more important than ever to hold on to traditional values.’ Discuss.
- ‘How little we know, I thought, of the people we live amongst.’ What does the text say about community and one’s understanding of reality?
- ‘Year of Wonders explores human failings in a time of crisis.’ Discuss
Now it’s your turn! Give these essay topics a go using the analysis you’ve learnt in this blog.
6. Essay Topic Breakdown
Whenever you get a new essay topic, you can use LSG’s THINK and EXECUTE strategy , a technique to help you write better VCE essays. This essay topic breakdown will focus on the THINK part of the strategy. If you’re unfamiliar with this strategy, then check it out in How To Write A Killer Text Response .
Within the THINK strategy, we have 3 steps, or ABC. These ABC components are:
Step 1: A nalyse
Step 2: B rainstorm
Step 3: C reate a Plan
Theme-Based Essay Prompt: ‘ Year of Wonders is a story of great courage in the face of extreme adversity.’ Discuss.
Not sure what we mean by ‘Theme-Based Essay Prompt’? Then, you’ll want to learn more about the 5 types of essay prompts here .
Step 1: Analyse
The starting point of any theme-based prompt is the ideas, and while this prompt characterises the novel as one essentially about courage, it is more generally exploring the theme of how people responded to the various challenges of the plague. ‘Discuss’ questions give you scope to partially agree, disagree, or extend the prompt . It is okay to ultimately agree with the prompt but to also demonstrate the complexity and nuance of the author’s intentions, and I think that is the best approach for this essay!
Step 2: Brainstorm
As we’ve already discussed, Year of Wonders depicts a community experiencing an acute crisis and Brooks presents the very worst and very best of human nature. There are characters who display enormous courage (Anna and Elinor), others who are cowardly (the Bradfords) and those who exploit others’ hardships for their own gain (Joss Bont). There is also an entire supporting cast of characters who individually display neither extreme courage nor cowardice but who muddle through a terrible situation with numb apathy . There is also the opportunity to define what courage means here – after all, the decision to isolate themselves within the boundaries of Eyam took immense courage from all the villagers, who knew full well that they would inevitably be exposed to the deadly contagion.
Step 3: Create a Plan
Paragraph 1: [Agree] The novel is grounded in and revolves around the initial courageous decision of the villagers of Eyam to quarantine themselves and risk their own lives to protect others from the spread of the bubonic plague.
- Focus on the initial act of courage and the knowing self-sacrifice that this decision required from every single person in Eyam.
- As the event that forms the basis of this work of historical fiction , a logical argument can be made that this first act of courage in adversity forms the foundation of the novel and therefore affirms the idea that Year of Wonders is about great courage.
- However, importantly, this decision was an act of community courage that anticipated future adversity but was taken before many of the villagers had actually experienced the acute hardship and suffering of the plague . This is why it is important to now discuss the courage shown by individuals in the midst of extreme adversity [link].
Paragraph 2: [Agree] The individuals who displayed courage, hope and conviction in the face of acute personal adversity demonstrate the enormous power of courage to steel us through a crisis .
- Anna and the Mompellions concentrate on helping others and their service helped keep some degree of social order and provided comfort to victims of the plague. What they were able to achieve and provide for the community (and how much worse the situation would have been without their courageous assumption of responsibility) illustrates Brooks' high respect for courage and service.
- To demonstrate additional analytical thinking, you might consider discussing the fact that these characters were not courageous solely out of charity , but that having an occupation and something to keep them busy and focused actually became a personal survival mechanism . This further highlights the absolutely pivotal role of courage in adversity and is only reinforced through the contrast with the ignoble behaviour of those characters who did not behave courageously and forthrightly [link].
Paragraph 3: [Partial disagree] However, Year of Wonders shows how adversity can provoke extremes of human behaviour and is thus also a story of human failings under immense pressure, with many characters motivated by cowardice and self-interested opportunism .
- Here, you should discuss the dishonourable behaviour of the Bonts, the Bradfords and the hysterical mob that murdered the Gowdie women . Your aim should not only be to explain that they behaved without courage, but also to focus on the negative repercussions their behaviour had for them and the community This will help you build an analytical argument that Brooks’ core message is about the power and necessity of courage in the face of adversity .
- Ultimately, while no character escapes from the pain and loss of the plague , Brooks provides illustrations of how different people responded to their shared suffering and it is clear that she believes that the best way to respond to adversity is with the courage and strength to face the challenge head on.
If you found this essay breakdown helpful, let us know if you’d be interested in a complete LSG Year of Wonders Study Guide where we would cover 5 A+ fully written sample essays with EVERY essay annotated and broken down on HOW and WHY the essays achieved A+ so you can reach your English goals!
3. Main Characters
4. Minor Characters
5. Dissecting an A+ Essay using 'The Golden Age'
6. Creative Essay Topic Brainstorm
7. Essay Topics
The Golden Age is usually studied in the Australian curriculum under Area of Study 1 - Text Response. For a detailed guide on Text Response, check out our VCE Text Response Study Guide.
Even though this hasn’t been one of the more popular choices on the VCE text list, Joan London’s The Golden Age is a personal favourite of mine for a number of reasons. This is a novel about the experiences of children recovering from polio inside a convalescent home in Perth. With a sympathetic and warm approach, London tells the tragic yet brave stories of these children, as well as the stories of their parents and carers.
The novel essentially revolves around Frank Gold, a Hungarian Jew and a war refugee, and London blends his mature voice with the innocence of a coming-of-age narrative, all set against the backdrop of World War II.
As you’re reading the book, watch out for her literary or poetic language, and keep track of the story’s overall mood. These will be important considerations for text study, particularly if you are to write a creative response on this text for your SAC. With this in mind, I’ve included writing exercises throughout this blog post for you to practise writing creatively on this text.
If you are writing analytically on this text, either for your SAC or for your exam, you may still complete the exercises—each one should still be insightful for your writing in some way. Also, feel free to check the video below; it breaks down an analytical prompt for this text.
Historical Context
This novel is set in Perth during the early 1940s, which gives rise to a couple of interesting historical elements all intersecting in the book.
Crucially, the events of the novel take place for the most part while World War II is raging in Europe. This is important for understanding the backstory of the Gold family: they are Hungarian Jews who have escaped their war-torn home of Budapest to seek safety in Australia. In particular, we know that at some stage, Meyer had been taken away to a labour camp, and that Frank had had to hide himself in an attic.
Their Hungarian heritage, however, is something that distances them from other Australians, and they never really get a good chance to settle in, always feeling like they just weren’t on the same wavelength as the locals. In many ways, the story of the Golds is underpinned by tragedy—not only are they war refugees, but young Frank then contracts poliomyelitis (known to us just as polio), which forces the family to reassess all the plans they had for him to settle into an ordinary, Australian life.
However, Frank was far from the only victim of polio at the time—the entire nation was rocked by a wave of polio , with major outbreaks during the 1930s-40s. This was quite a nerve-wracking, and causing great fear for our country and its active, outdoors-y culture. The prospects of death, paralysis and permanent disability were understandably terrifying. About 70,000 people were affected, and almost half of them eventually died as a result. Almost every Australian at the time knew or knew of someone who had polio.
Task: You are Ida, composing a letter to Julia Marai after Frank’s diagnosis. Convey succinctly (in 250 words or less) what you think and how you feel.
Key themes & implications.
I like to think that a lot of the themes in this book exist in diametric or opposing pairs. For instance, London gives Frank a voice that is wise beyond his years, yet uses it to tell a tender story of first love. She also plays on the paradox that while some characters have become isolated due to the unfortunate events that have befallen them, these very events end up becoming the thing that unite them.
Essentially, London plays with a lot of these thematic tensions, showing us that life isn’t really ever black and white, but there are whole lot of grey areas in every day life.
Central to the novel are ideas of innocence or childhood . These ideas are really explored in the friendship between Frank and Elsa, who are both on the cusp of adolescence. While they are set up as young lovers in the eyes of readers, we know that they are far too young to truly have romantic feelings for each other. In actual fact, their interactions are permeated by a sense of innocence.
However, these interactions are also punctuated by a sense of maturity , a desire for more. This is evident to the extent where nurses are getting hesitant about leaving them alone with each other (even though their parents still trust them entirely). In actual fact, these parents serve as an important point of contrast. Some manage to recapture the magic of youth even as adults—consider Ida reigniting her love for the piano, or Meyer jumping on opportunities to start anew. In this sense, innocence and maturity are a pair of themes that are interestingly not always found where one might expect.
Another key thematic element of the novel is tragedy or adversity , which are relevant to a far wider gamut of characters. Considering the story’s geographical and historical setting, it seems evident that these ideas will play a major role in the story. A particularly poignant example lies in Sullivan, who contracts polio right on the cusp of adulthood, and readers can’t help but feel a sense of loss for what might have been.
However, on the other end of this spectrum is the strength required to cope with their suffering. While Sullivan had his indefatigable sense of humour, other characters have developed different mechanisms to stay strong in the face of adversity. In some cases, you might say that they’ve transcended or risen above their tragedies, and become stronger for it.
Finally, London also tackles the idea of isolation , which can be seen as a consequence of tragedy—characters become isolated because they lose their ability to relate to others, and others feel unable to relate to them. Symbolically, the Golden Age hospital is surrounded by four roads and therefore cut off from the world, almost as if quarantined. However, the solidarity and unity of patients inside becomes a great source of strength—I’ll leave it to you to think about what London was trying to say with this!
Task: Selecting one of the above themes, write a poem from the POV of an imaginary spectator in the novel, outlining how you perceive/experience these themes in other characters. Use all five senses(how you see it, hear it, smell it, taste it, and touch/feel it)
Major characters.
I haven’t written too extensively about characters for a range of reasons: on one hand, it’s important for you to form your own interpretations about what they’re like and why they do the things they do, but on the other hand, I wanted to leave you with some key points to consider and/or some essential points about their characters to incorporate into your writing. This will allow you to hopefully feel like you’re capturing them accurately when writing your creatives, but without feeling restricted by an extensive set of traits that you have to invoke.
- the central character, he is cerebral, intelligent and mature (which we can tell from his narrative voice, or how he ‘sounds’)
- he is, however, still very young, wide-eyed, inquisitive in spite of the tragedies which have befallen him (consider how he sees his relationship with Elsa)
- also significant is the motif of his poetry; not only does it highlight his maturity, but it also acts as a way for him to voice or articulate his feelings and experiences in the hospital—you could try incorporating some poetry in your writing (either original poems or quoted from the novel)
Elsa Briggs
- another central character who becomes quite attached to Frank (they are the two eldest children in the Golden Age)
- she is warm, caring and selfless, demonstrating an emotional maturity beyond her years (because of having to bear the metaphorical albatross of polio)
- a lot of what we know about Elsa comes from Frank’s perspective (though we do get some insight from her own, and some from her mother’s)—how does this shape the way we see her? Consider London’s use of imagery, portraying her as an angelic figure.
Ida & Meyer
- Frank’s parents, Hungarian Jews, and war refugees who come to Australia to cleanse them of their pasts and to have a fresh start; some of this is purely by circumstance, but there are parts of their past that they willingly and actively eschew e.g. Ida’s piano
- note that Hungary is a landlocked country in the midst of European hustle and bustle with easy access to other nations/cultures/peoples, but Australia is an island on the other side of the world—consider how this affects their sense of isolation
- on the other hand, they do form new connections with people here and in their own individual ways; Ida by reclaiming her pianist talents and Meyer by taking up a new job
Task: You are Elsa, Ida, or Meyer and you’ve just discovered Frank’s poem book. What are your thoughts and feelings towards his writing? Consider the context of your chosen character’s own experiences
Minor characters.
I’m sure you’ve heard it by now, but any piece of text-based writing (creative or analytical) can be strengthened by diversifying the range of characters that you write about. Even though you’ve already differentiated yourself from most VCE students by even doing this text at all (very few people choose it, so props to you!), some inclusion of more minor characters might help to distinguish yourself further. I’ve picked some that I think are interesting to talk about, but feel free to experiment with others as well!
- a young man who contracts a severe strand of polio right on the cusp of adulthood, thereby exemplifying the theme of tragedy—however, his sense of humour remains active in spite of his immobility, so perhaps he not only exemplifies this theme but subverts it as well
- London poses the complex question of whether or not he’s actually unhappy or defeated as a result of polio; there’s no clear answer, since there’s many ways to interpret his humour (is it a sign of strength or is it a front for inner turmoils expressed through poetry?)
- in addition to his humour and poetry, his relationship with his family could also be an interesting point of discussion to address some of these questions
- a young girl in the hospital who is quite close to Elsa (almost in a sisterly way)—how have they developed this relationship, and how does this relate to the theme of unity/companionship/human connection?
- notably, she wanted to rehabilitate herself after polio took away her ability to feed the brumbies in her desert town—think about how this might represent strength as well
Julia Marai & Hedwiga
- Ida’s former piano teacher and her flatmate/partner who live at the top of an apartment block in Budapest; they shelter Frank in their attic under no obligation whatsoever, but purely out of the kindness and selflessness of their hearts
- again, there’s this subversion of what it means to be isolated: on one hand, their apartment is so cut off from the rest of the world below, and they lead a largely self-sufficient life together, but on the other hand, the fact that they’re together means that they’re not entirely isolated consider the power of human connection in this context as well
Task: Pick a minor character from this list and a character from the above list of major characters, and write about them meeting each other for the first time. Pick two that do not already interact closely within the novel e.g. Elsa meeting Sullivan
I hope this gives you some ideas or starting points about writing creatively on this text!
Download the PDF version of The Golden Age study guide here .
Dissecting an A+ Essay using 'The Golden Age'
Picture this: you’re sitting down at your desk, fumbling your fingers, inspecting the new stationary that you convinced yourself you needed for year 12, resisting the urge to check your phone. Your text response SAC is in two weeks. You’re freaking out because you want, no, need an A+. You decide to write a practice essay for your English teacher. Practice makes perfect, right? You stay up for hours, pouring your heart and soul into this essay. The result? B+. Where did I go wrong?
That’s where I come in! Writing an A+ essay can be really tough without examples and specific advice. Before reading on, make sure you've read our Ultimate Guide to VCE Text Response so you are up to scratch.
I will be explaining some basic dos and don’ts of writing an essay on The Golden Age , providing a model essay as an example.
The following prompt will be referenced throughout the post;
‘The Golden Age’ shows that everyone needs love and recognition. Discuss.
Planning: the silent killer of A+ essays
I’m sure your teachers have emphasised the importance of planning. In case they haven’t, allow me to reiterate that great planning is compulsory for a great essay . However, flimsy arguments aren’t going to get you an A+. The examiners are looking for complex arguments , providing a variety of perspectives of the themes at hand. From the above prompt, the key word is, ‘discuss’. This means that you should be discussing the prompt, not blindly agreeing with it . Make sure you don’t write anything that wouldn’t sit right with London.
Don’t plan out basic arguments that are one-dimensional. This may give you a pass in English, but won’t distinguish you as a top-scoring student.
For example:
- Paragraph 1: The children at TGA need love and recognition.
- Paragraph 2: Ida and Meyer need love and recognition
- Paragraph 3: Sister Penny needs love and recognition.
The above paragraphs merely agree with the statement, but don’t delve into the many aspects of the novel that could contribute to a sophisticated essay.
Do create complex arguments, or paragraphs with a twist! If you can justify your argument and it makes sense, include it in your essay. There are many ways that you could answer this question, but my plan looks like this:
- Paragraph 1: Frank Gold yearns for mature, adult love, not recognition from onlookers or outsiders
- Paragraph 2: Ida Gold does not seek recognition from Australia, but love and validation from herself
- Paragraph 3: Albert requires love from a specific kind of relationship – family, and Sullivan may view love from his father as pity which he rebukes
See the difference?
The introduction: how to start your essay off with a BANG!
Personally, I always struggled with starting an introduction. The examiners will be reading and marking thousands of essays, so if possible, starting your introduction with something other than Joan London’s ‘The Golden Age’… is a great way to make you stand out from the crowd. Having a strong start is essential to pave the way for a clear and concise essay. You could start with a quote/scene from the text! This is not essential, but it’s a great way to mix things up. This is my start:
Perhaps nothing exemplifies the power of love and recognition more than the bond between Albert Sutton and his older sister, Lizzie, in Joan London’s ‘The Golden Age’. Many of London’s characters exhibit suffering that requires compassion and support to heal and grow, to distinguish present from past. However, London explores the perspectives of such characters from different aspects of trauma, and emphasise that love and recognition do not always work to heal and mature. Frank Gold, the novel’s resident “sneaky” boy who adjusts to newfound life in the Golden Age Convalescent Home seeks love as an adult, rather than eliciting sympathy as a supposed victim. Here love and recognition are unsuccessful in amending Frank’s troubles when given from the perspective of an outsider, a judgemental onlooker. In a similar sense, Ida Gold seeks recognition not from Australia, who she views as a ‘backwater’, but validation in herself after having been ousted from her Hungarian identity. London, however, makes sure to emphasise the impact that Sullivan has on Frank Gold’s life. Sullivan, a boy only a few years older than Frank, seems content with his future, with his fate, despite his sacrifice of rugby and conventional life. There is a lacking sense of urgency for love and recognition in Sullivan’s life, rather, it appears that Sullivan accepts his fate, regardless of his father’s sympathy or support. Thus, London explores a myriad of ways in which love and recognition may or may not heal wounds inflicted upon individuals.
Remember, there are many other ways you could start your essay.
The body paragraphs: To TEEL or not to TEEL?
I’m sure you’ve heard of TEEL countless times since year 7. Topic sentence, evidence, explanation, link. The truth is that these elements are all very important in a body paragraph. However, following a rigid structure will render your essay bland and repetitive. It is also extremely important to note that you should be using evidence from multiple points in the text , and you should be making sure that your paragraphs are directly answering the question . Write what feels natural to you, and most importantly, don’t abuse a thesaurus . If you can’t read your essay without rummaging for a dictionary every second sentence, you should rewrite it. If vocabulary isn’t your strong point (it definitely isn’t mine!), focus on clean sentence structure and solid arguments. There’s nothing worse than you using a fancy word incorrectly.
Don’t overuse your thesaurus in an attempt to sound sophisticated, and don’t use the same structure for every sentence. For example:
Prematurely in the paperback London makes an allusion to Norm White, the denizen horticulturalist of The Golden Age Convalescent Home…
That was an exaggerated example generated by searching for synonyms. As you can see, it sounds silly, and some of the words don’t even make sense. I mean, “denizen horticulturalist”…really?
Do mix up your paragraph structure! If vocabulary is your weak point, focus on clean language.
Here’s mine:
Early in the novel, London makes reference to Norm White, the resident groundskeeper of The Golden Age Convalescent Home. Norm White hands Frank Gold a cigarette, “as if to say a man has the right to smoke in peace”. Here, there is a complete disregard for rule and convention, an idea that London emphasises throughout the text. This feature provides a counter-cultural experience for Frank, pushing him to realise that he is a strong human being rather than a mere victim. This is a clear contrast to the “babyishness” of the home, and is used as evidence of true humanity in an era where society judged upon the unconventional. Frank yearns for a traditional Australian life after his trauma in Hungary; “his own memory…lodged like an attic in the front part of his brain”. Hedwiga and Julia Marai’s caring of him pushed him towards fear and reluctance to trust, yet also pressured him to seek acceptance in a world that ostracises him for his Jewish heritage and polio diagnosis. This here is why Frank desires a mature, adult connection – love that regards him as an equal human being. Frank seeks Elsa’s love and company as she too loathes being reduced to a victim, an object of pity. Frank thereafter uses humour to joke of his wounds; “we Jews have to be on the lookout”. Elsa sees “a look in his eyes that she recognised”, thus their bond enables both characters to heal. London alludes that Frank requires love and recognition not from the perspective of a sorrowful onlooker, rather he longs to be recognised as a mature adult.
To learn more about using the right vocabulary, read 'Why using big words in VCE essays can make you look dumber'.
The conclusion: closing the deal
I firmly believe in short and sharp conclusions. Your body paragraphs should be thoroughly explaining your paragraphs, so don’t include any new information here. A few sentences is enough. Once again, write what feels natural, and what flows well.
Don’t drag out your conclusion. Short and concise is the key to finishing well.
Do write a sharp finish! Sentence starters such as, “Ultimately…” or “Thus, London…” are great.
To learn more about A+ essays, you should also have a read of 10 easy English points you're missing out on .
I'll finish off by giving you an exercise: brainstorm and write up a plan for the essay topic shown in the video below. I'd recommend you do this before watching Lisa's brainstorm and plan. That way, you can see which of your ideas overlapped, but also potentially see which ideas you may have missed out on. Good luck!
The Golden Age Essay Topic Brainstorm
[Video Transcript]
The takeaway message for this video will be to utilise minor characters here and there to deepen your argument. London has really developed all her characters to feel three-dimensional and real, so it’s important not to just write about Frank and Elsa when there are so many others worth touching on.
Let's head straight into background information:
Joan London’sThe Golden Age is a novel about children recovering from polio in a convalescent home in Perth. She tells the stories of these various children, their families, and their caretakers, focusing on FrankGold and Elsa Briggs, the young protagonists who are just starting to develop romantic feelings for each other. Though they, and many of the other children, have faced much hardship and misfortune, London tells a story of hope and human connection in times of misery.
On that note, today’s essay topic is:
The Golden Age is primarily a tragic tale of isolation. Discuss.
Let’s break this prompt down and define some keywords. The keywords we’ll be looking at first are isolation and tragic. We’ll be defining them quite briefly, but be sure to think about these in terms of how they relate to the novel. In particular, see if any scenes, passages or characters jump to mind.
Isolation is a state of being alone or away from others and can be associated with a sense of powerlessness or insignificance. Tragic can simply just mean sad, depressing and loaded with sorrow or ‘pathos’, but there are also literary implications to this word: you might’ve done a tragic Shakespeare play and learned this before, but in general, a tragic story centres on a hero who encounters misfortune, and treats their demise in a serious or solemn way. Note that a good essay will discuss both these terms, and will address not only isolation but also the question of whether or not it is treated tragically.
The other important word is ‘primarily’. This word in the prompt suggests that The Golden Age is for the most part about these ideas - for you, that means you should ask yourself how central you think they are, and make a call on whether they are the most central.
Well, it’s definitely true that elements of isolation and separation do exist in The Golden Age, but these themes are not primarily tragic ideas in the novel -London explores the way in which hope can shine through in times of hardship. In fact, the novel overall has a message of kinship and hope, and this would be the primary thematic focus, as well as the main treatment of otherwise tragic ideas. So how might this look in paragraphs?
Paragraph 1: Let’s concede that the novel does evoke sadness through its frequently sombre tone and treatment of isolation
We see this through characters such as Ida and Meyer, who have been cut off from the world in their escape from their war-torn home, and forced to transition from their landlocked Hungary to an island on the other side of the globe. Their struggle to adjust is evoked through symbols - for instance, black cockatoos, which represent a “homely, comforting” omen to locals, sound “melancholy [and] harsh” to Ida. In particular, London’s solemn characterisation of Ida as constantly “frowning”, and as having a “bitter little mouth that usually gripped a cigarette ”works to emphasise her ennui or her dissatisfaction with being cut off from the world. Their homesickness is evoked through this constant longing for home, though sometimes much more literally: Meyer feels that “never again on this earth…would, he feel at home as he once had.”
Similarly, the story of Sullivan Backhouse, confined in an “iron lung” and physically isolated from outside contact, is also primarily tragic. London develops this character and gives him a backstory - he has “just turned eighteen” and had been the “prefect [and] captain of the rowing team.” This gives readers an idea of the life he might have had if not for the tragedy of his condition. Even in spite of his “good-humoured nature”, his poetry belies the pessimism within - his book, morbidly entitled “on my last day on earth”, closes with the line “in the end, we are all orphans.” We can thus see how lonely he must have felt when he tragically passed away.
In this paragraph, we’ve considered three different characters, whereas a lot of people writing on this text might just do a character per paragraph, so this is a good way to really show the examiners that you’ve considered the full extent of what the book offers. Let’s continue this as we move onto…
Paragraph 2: We disagree, however, since the novel includes various other moods and thematic material - in particular, London explores notions of resolve and hope in times of hardship
Now, the first character that comes to mind would have to be Elsa - London uses particularly powerful imagery, such as her “translucent”, “golden wave” of hair or even her “profile, outlined in light”, to portray her as angelic or elysian. For the children, Elsa evidently represents hope - even in her state of isolation, her “graceful and dignified” demeanour and her quiet acceptance that polio “was part of her” is courageous and worthy of admiration.
Moving onto a minor character who was perhaps inspired by Elsa - the young Ann Lee, who was quite close to Elsa, also has a story which is more inspiring than tragic. When polio first crippled her, she found herself unable to give water to the brumbies in her desert town. As a result, she perseveres, “step after painstaking step” so as to be able to return home and “give a drink to thirsty creatures.” Her compassion and determination to work against her isolation become the focus of her tale.
Paragraph 3: In fact, the novel ’s focus is on hope rather than tragedy
A range of other characters demonstrate the power of love and human connection in the face of adversity, and London seems to be focusing on these ideas instead. Plus, it’s not just the children who are brave in the face of tragedy, but ordinary people prove themselves to have the potential for strength and courage. Take Julia Marai and Hedwiga, who hide Frank in their attic during the Nazi invasion of Hungary. Even though their apartment is “on the top” of the block, and isolated in its height, suspended from the world, they become “provider[s]” for Frank. London writes that in difficult times, “kindness and unselfishness were as unexpected, as exhilarating, as genius,” and it’s easy to see how these qualities form a counterpoint to the tragedies that permeate the novel, allowing hope to shine through.
And that’s the end of the essay! Being able to explore minor characters like we did here is a really good way to show examiners that you have a deeper understanding of a text, that you’ve considered it beyond just the main characters on the surface. The Golden Age is a really great one for this because London has done so much with her cast.
Essay topics
1. “Being close made them stronger.” In The Golden Age , adversities are tempered by camaraderie. Do you agree?
2. Despite the grim context, The Golden Age highlights and celebrates the potential of life. Discuss.
3. Memories of past successes and failures have significant lingering effects on characters in The Golden Age . Is this an accurate assessment?
4. “[I would be] a fox, following a Palomino.” How do animals such as these contribute symbolically to The Golden Age ?
5. It is largely loneliness which defines the struggles of the children in The Golden Age . Discuss.
6. In what ways is The Golden Age a novel of displacement?
7. Fear of the unknown is something which permeates The Golden Age . Is this true?
8. What is the role of family in Joan London’s The Golden Age ?
9. Isolation in The Golden Age exists in many oppressive forms. Discuss.
10. Throughout The Golden Age , London draws attention to beauty rather than to suffering. Discuss.
11. In spite of their youth, it is the children of The Golden Age who understand best what it means to be an individual in the world. Do you agree?
12. How do characters from The Golden Age learn, grow and mature as the novel takes its course?
13. Due to the range of different onset stories, each of the children and their families in The Golden Age face a different struggle with their identity. Discuss.
14. “Home. She hadn’t called Hungary that for years.” In spite of all their struggle, the Golds never truly feel any sense of belonging in Australia. To what extent do you agree?
15. Explore the factors which drive Joan London’s characters to persevere.
The Ultimate guide to VCE Text Response
How To Write A Killer Text Response Study Guide
How to embed quotes in your essay like a boss
How to turn your Text Response essays from average to A+
5 Tips for a mic drop worthy essay conclusion
Stories We Tell is a different beast to anything many of you will have encountered previously in your English studies. This blog is a continuation of the above Stories We Tell YouTube video so make sure you watch it first!
With interviews, archival footage, extradiegetic film and sound elements alongside recreated scenes, the documentary can seem very overbearing and convoluted upon first viewing. However, once you have a holistic understanding of the text a plethora of opportunity for high-level analysis and discussion presents itself. Stories We Tell is usually studied in the Australian curriculum under Text Response. For a detailed guide on Text Response, check out our Ultimate Guide to VCE Text Response .
To begin, watch our introduction covering background and themes below:
Video Transcription
Stories We Tell centres around director Sarah Polley attempting to piece together her family history. While she endeavours to understand who her mother Diane was and finally learn the identity of her biological father, Director Polley also poses a number of questions to viewers surrounding the nature of the truth and the importance of stories in our lives. The film is comprised of interviews with Diane’s loved ones, home movies from the Polley family, extra-diegetic newspaper clippings, recreated Super 8 footage and excerpts from other productions - all of which contribute to Sarah’s inquisition into the notion of truth, and demonstration that how a story is told can shape how it is received.
NB: I have used ‘Sarah’ when discussing Sarah Polley as a character, and ‘Polley’ when describing her as the director.
The idea of the truth, and what comprises it is a constant question being answered through the documentary. Before exploring Polley’s depiction of the truth, it’s important that we fully understand what the truth is. One definition characterises it as the burden of confirming with fact or reality, and with this in mind it becomes easier to appreciate and analyse the intricacies of Stories We Tell . Polley creates a distinction between universal truths - which are accepted by all as fact, and subjective truths which can vary on individual interpretations. For example, Michael conflicts with the rest of the family while discussing his relationship with Sarah after Diane’s passing. Mark details Michael’s obsession with “playing solitaire” , Susy depicts the house as one of “complete and utter disuse” , while Joanna observed him “smoking all day” and perceived Sarah as “just a little kid who nobody was looking after.” Michael, however, has fond memories of his time spent with Sarah - he believed he was “lucky to have her to look after as well as himself” , called their time together a “great period” - eventuating in him feeling “closer to [Sarah] than any of the other children.”
Individual recollections of Michael’s actions and demeanor during this period belong to each storyteller, and form the basis for what they consider to be the ‘truth’ regarding Michael and Sarah’s relationship. By presenting contrasting accounts of the same event, Polley reveals her stance on the idea of truth - being that it is entirely subjective and open to interpretation, centred around the perceptions of each individual at any moment in time. It is entirely possible that Michael did “smoke all day” and feel a sense of increased “close[ness]” with Sarah, but due to the variability of the human memory, this is impossible to state with any certainty - illustrating the fallible nature of universal truths.
Storytelling
Stories and how they are told are a constant factor during the documentary - beginning with the title, ‘ Stories We Tell’ and concluding with Geoff’s admission that he and Diane did sleep together during their days acting in Montreal. For example, Polley’s use of the inclusive ‘we’ signifies her interest in storytelling on a grand scale; not merely the stories she unravels onscreen. As a result, one can argue that her purpose for the documentary extends far beyond the action captured onscreen and in fact involves Polley encouraging others to share their own stories - enabling them to “create shape out of mess” as she has done through the presentation of her own family story.
By placing Geoff’s confession at the conclusion of the documentary (and casting doubt on all of the discoveries she has made throughout Stories We Tell) Polley emphasises how storytelling allows a “clearer picture” of the past to develop - as he had previously denied any sexual history with Diane, labelling them just friends. As such his admission of a relationship with her symbolises the manner in which the truth can be “refracted” over time, leading to many “shifts and fictions” while clouding “what really happened.” Therefore, Polley reveals how storytelling can provide some semblance of closure to us, in a world where the truth is “ephemeral” and “difficult to pin down.”
While Polley undoubtedly utilises Stories We Tell to express her views on truth and storytelling, fundamentally it remains a story of the Polley family, and what holds it together. The narrative begins with the ‘storytellers’ providing loving, yet somewhat conflicting recollections of Diane as Polley seeks to understand who she was. Family members buoyantly describe her as “infectious” and “enthusiastic” , while friends paint a more mysterious picture of Diane as a “woman of secrets” , alluding to her alleged infidelity. The closeness of the Polley family is evident throughout their discussion of Diane’s first marriage, universally criticising the outcome of the court case in which she was labeled “ unrepentant ” for “ allow[ing] her desire for a career to overtop her “domestic duties” - resulting in Diane losing custody of John and Susy, which proved to be a major strain on Diane and the family.
Despite this closeness, Mark expresses his disappointment in Diane following the confirmation of Harry being Sarah’s father - detailing the she “broke the rules” and “broke a kind of taboo” when she had the affair. This is the only real example of any member of the family disapproving of Diane’s past - indicating Polley’s desire to demonstrate that families are not perfect, and bring their own faults and shortcomings. In spite of this, however, their care the family shows for one another is clearly demonstrated through their interviews with Polley, highlighting to the audience that by staying close, families can better cope with the trauma of losing a loved one and in time, be able to honour their memory by sharing their stories.
Putting it all together
While analysing the themes in isolation can provide a good foundation for success studying Stories We Tell , looking at how they interact and interrelate enables students to demonstrate their higher-order skills. Truth, storytelling and family are intrinsically linked - for example: Polley’s presentation of conflicting accounts and recollections of Diane demonstrates the complexity of her family, while showcasing her stance on the inability of individuals to find universal truths. As a result of this, the importance of storytelling is highlighted as a means to provide some understanding of our past - and how it affects us in the present and shapes who we are. Including different interpretations of the text and the context in which Polley grew up and created the text can also help to improve your writing to A+ standard - and this will be covered in the blog post that acts as a continuation of this video! *end video*
Following on from the video, the content below is an expansion upon Stories We Tell .
Author views and values
One of the golden rules of A+ essay writing is to understand that everything contained within the text is seen to be a deliberate choice by the author. With this in mind, we can start considering how Polley’s choice to include certain snippets or position footage in a particular way highlights her views.
The truth is ephemeral - can it ever be known?
Throughout Stories We Tell , Polley continually emphasises the impossibility of knowing a truth with absolute certainty. Her stance is shaped by the clouded nature of her paternity and family history, exemplified within the text by the varying accounts of Diane’s personality. Portraying her as “infectious” and “enthusiastic”, Polley captures Diane dancing - cleverly lighting up her face, thus symbolising her warm nature. However, juxtaposing this is Deidre’s assertion that Diane was a “woman of secrets” - bolstered by Polley’s recreation of a covert phone call in which Diane ponders the identity of Sarah’s biological father. Through her presentation of contrasting recollections of her mother, Director Polley showcases the relativity of truth within her own family, inviting the audience to question the meaning of truth in their own lives, highlighting that “you can never get to an answer.” As a result, Stories We Tell predominantly displays the impossibility of one knowing a singular truth.
Subjective truths can be found
Continuing the theme of ambiguity within her synthetic documentary, Sarah Polley demonstrates that individuals can develop their own interpretations of the truth, in spite of her stance on the validity of singular truths. Within Stories We Tell, Polley illustrates this by depicting the contrasting recollections of Michael’s relationship with Sarah as a child. Supporting Joanna’s assertion that Sarah was “just a little kid that nobody was looking after”, Polley ironically captures a full shot of Michael in the middle of the couch, portraying him as a distinctive presence in the scene in spite of Joanna’s belief that Michael isn’t present in Sarah’s life. Conversely, Michael recalls his time with Sarah as “a great period in [his] life” - a claim reinforced by Polley, via recreated Super 8 footage of the pair assembling a snowman, symbolising their construction of a new beginning following Diane’s death. Through this interaction, Polley portrays Michael as a compassionate and loving father - juxtaposing this with Joanna’s description, revealing to her audience the ability of individuals to find subjective truths - encouraging them to do so in their own lives in spite of searching for universal truths.
The importance of stories
Building on her depiction of the truth as fallible, Polley thus emphasises our need to tell stories, illustrating how they allow one to better understand themselves, their families and the world around them. Within Stories We Tell, unearthing the ‘story’ of Diane takes centre stage for a majority of the production, and Polley hints towards this goal via her inclusion of Bon Iver’s folk ballad Skinny Love. The line “pour a little salt, we were never here” plays on the use of salt to heal wounds - implying that the storytellers aim to ‘heal’ their pain felt from Diane’s death via telling “the whole story” they have developed from their memories of her. Moreover, the phrase “who the hell was I” addresses Polley’s attempt to “form [Diane]” by piecing together the various second hand accounts and layers of connected stories from her loved ones - allowing her to ascertain a clearer understanding of her family history. Polley utilises stories to “[clear] up...the smoke” in her past,” praising the idea that such tales shed a light on areas of confusion and uncertainty - while also allowing one to “[cope]” and make sense of their heritage. Through her demonstration that stories enable individuals to move past the “small and large details that vary”, Polley prompts the audience to seek more information about their own families, and relay their own family stories.
Throughout the documentary, Polley demonstrates, both explicitly and implicitly, a number of her inherent values. Drawing upon these, referring to them in your essays and (most importantly!) connecting them to your analysis of the text is a great way to get ahead of the pack and maximise your marks both in your sac and the exam.
NB: Much of the excerpts contained here are analysing specific scenes/motifs, and then linking such thinking to the theories listed below. I found this to be a coherent and structured way of including this deeper level of thinking in the publication of my own essays!
Feminist lens on the social values of 1960’s Canada
.png)
By depicting extradiegetic footage of Diane singing Ain’t Misbehavin, Director Polley provides a feminist commentary on the dominant social values of 1960’s Canada; the lyrics “I walk the streets to balance the sheets” and “what is an honest girl to do” metaphorically representing the perception of Diane by the court and wider society - denied “custody” of her children due to her “adultery.”
.png)
By inserting a newspaper clipping criticising Diane’s choice to let her “desire for a career” to supercede her “domestic duties”, Polley illustrates the difficulties faced by aspirational women in such a restrictive society - condemning the treatment of her mother while calling on female viewers to continually campaign for equality of opportunity in their societies.
Outlining the fact that Diane was not considered “ladylike”, Polley sardonically ridicules the “controlling” nature of such rigid gender stereotypes and their effect on Diane losing her children - exhibiting her desire to empower her female audience to “save [themselves]” from similar situations and “ma[ke] a choice to live.”
Postmodernist interpretation of the truth
As I’ve discussed at length in this blog post, Polley continually reminds us as an audience that the truth is not set in stone and is in fact a flexible, relative concept. Such a line of thinking directly correlates to the postmodernism literary theory - notable for being hostile to absolutes such as truth, and not creating a text in isolation.
Polley continually blurs the line between fact and fiction within Stories We Tell - an ode to the postmodernist school of thought she is following. Depicting recreated Super-8 footage capturing herself directing the actress Rebecca Jenkins who ‘plays’ the ‘role’ of the younger Diane, Polley seeks to somewhat deceive her audience as to what is real and what is derivative - prompting the audience to “consider what was real and what wasn’t… in their own minds.” As a result, she seeks to promote the validity of the postmodernist critical theory, prompting philosophical discussions between individuals about the variability of memory and whether any absolute truths can ever be truly known.
Intertextuality
Another feature of postmodernism in literature is the relationship between one text to another. In her creation of Stories We Tell , Sarah Polley exacerbates this relationship, including a number of extradiegetic elements such as newspaper clippings, emails, songs and segments from other productions in order to add greater meaning to the documentary. For example, Polley presents her email exchange with Harry, illustrating her desire for the story to include “everyone’s point of view”, as it is only then that the “whole picture” can be established. While reciting the email aloud, Polley delicately pauses when articulating that the story must include “[her] experience, [Harry’s] experience” and her “family’s [experience]”, emphasising her desire to give “equal weight” to all versions of the story.
Different Interpretations
In my experience studying the text, this documentary can be interpreted two ways:
1. as a self-reflective memoir following the journey of Sarah finding her father and gaining a more mature understanding of her mother, or;
2. A philosophical and, at-times political commentary on the way stories are told and the nature of truth. Both interpretations (and others you find or develop through your own viewing) are great to use in your writing, just ensure that they are relevant to the specific prompt/idea you are discussing!
Let's dive into each a little further:
1. Stories We Tell is a commentary on how stories are told - specifically, how the way a story is told can shape how it is received and the meaning one can draw from it
Upon first glance this point may seem rather convoluted, and several viewings of the text are necessary to fully engage with this line of thinking. Essentially, this centres around the idea that the different forms, mediums and extradiegetic elements present in the documentary can significantly influence how we as an audience react to the story that is being told.
The best way to explain this is to acknowledge the level of credibility and the associations attached to each individual medium used to tell the story.
For example, what impact does the newspaper clipping (detailing her custody battle and fight for equality in a restrictive society) have on our sympathy for Diane? Does the sense of credibility and validity drawn from an upstanding publication such as a newspaper elicit a greater sense of trust and acceptance of fact from viewers - therefore making us as an audience more inclined to view her in a positive light? Conversely, are viewers more accepting of Diane’s affair with Harry following testimony from those who witnessed her unhappiness with Michael first hand - her friends and family?
Moreover, in spite of her declaration that “equal weight” will be given to all experiences, does Polley’s use of Michael as narrator and his constant presence in the formal setting of a recording studio provide his version greater significance than Harry’s - who notwithstanding his involvement in the story as Sarah’s biological father, is resigned to providing his interview somewhat informally in a home setting, in the same vein as the rest of the storytellers?
Feel free to apply this line of thinking to other aspects of the text - such a deeper engagement with the philosophical ideas of the text are far more likely to score highly, as opposed to shallow pieces that merely discuss the storytellers in isolation - and not what they represent.
2. Stories We Tell is a commentary on the ephemeral nature of truth
The notion of truth seems to be just as much of a theme through this blog as it is in the documentary!
This is for good reason, however, as I found this to be the primary theme running through Stories We Tell , through the journey to discover Sarah’s paternity, the affair and conflict over whose story it is to tell. Truth affects a number of other ideas within the texts, such as storytelling, intertextuality, the variability of memory, production and identity - thus, using the ephemeral nature of the truth to explain why certain ambiguities exist in Harry’s “faulty” recollections, for example is an excellent way to show a greater depth of understanding of the interrelationships in the documentary.
Essay Topic Breakdown
Essay topic from the 2018 vcaa exam:.
“To save all hurt, why not leave things as they are?”
Why does Sarah not “leave things as they are?”
Initial thoughts:
This prompt does not ask you to discuss a specific theme or character - instead it guides you toward providing an analysis on Sarah Polley’s purpose for creating Stories We Tell. While authorial intent should always be included in any text response essay, it is essential that the purpose is central in response to this type of prompt - essentially, providing points of discussion as to why Sarah is unable to “leave things as they are.”
Essay Plan:
1. Unable to leave things as they are - wanted to question the concept of traditional family structures, by contrasting the influence of biological connections and emotional relationships on her development.
I discussed the effect of both Harry and Michael on Sarah’s development - concluding that while both of them had a significant role to play in her becoming the woman she is today, Michael’s influence was significantly stronger. Polley implies this by giving him a greater voice in the documentary through his role as the narrator.
2. Unable to leave things as they are - wanted to comment on the ephemeral nature of the truth in our lives.
Central to this paragraph is Polley’s use of recreated Super-8 footage. Using three prime examples (the opening scene with Diane and Michael crossing the bridge, Polley directing the actress that ‘plays the role’ of Diane in recreated footage, and the staging of Diane’s funeral) I aim to display Polley’s postmodern perspective on the truth and how this is conveyed through her deliberate creation of Stories We Tell.
3. Unable to leave things as they are - Emphasise the importance of storytelling in our lives to gain some understanding of the past.
Due to her depiction of the truth as a “mystery of nothingness”, Polley highlights the role that stories play in our lives. Within Stories We Tell, Polley attempts to understand herself by recreating Diane’s story on screen - allowing her to create “shape out of mess” and form a clearer picture of how she became who she is. Moreover, Polley also reveals how stories enable individuals to maneuver through the “wreckage” of the truth and “recreate the past.”
[Modified Video Transcription]
What's up everyone! So, I want to get a new segment started and it's pretty much the ‘essay questions with Lisa Tran’ segment. And basically, what this includes is every now and then I will choose a topic on one of your suggestions of whatever book, or film you’re studying, and break that down together with you on camera, on YouTube. So, if you like the idea of that, then make sure you give this video a thumbs up so that I know that this is something that you're super keen on and that you'll find helpful.
So, I've taken liberties (since this is the first one that we've ever done) of choosing my own essay topic that I was interested in doing. It's based on The Handmaid's Tale , and if any of you have read this or watched it (it's a TV series on Hulu) I have read and watched both and it has just been sensational, so I wanted to basically break down this prompt with you. If it's something that you haven't watched, or if you haven't read it, that's not a problem at all because the skills that I will be teaching you when it comes to breaking down an essay topic will be invaluable when it comes to actually applying it to your own studies. So, let's get started.
The Handmaid's Tale Quick Summary
Just as a really quick summary (that will probably butcher the overall meaning and the experience that you get from the book, but I don't want to really spoil it for you either), The Handmaid’s Tale is set in this future world where America, or the United States, has become a dystopian society, and women in particular are reduced to nothing more than just a child bearing species. Men are in charge and these women, who are deemed to be people who can give birth, are kept alive and kept around in these rich people's homes or people who are higher up in the hierarchy, and they basically have to have sex with the male leader of the home and just create children, and that is their purpose. If they're no longer fertile, then they'll pretty much be out-casted from society and rejected.
As a book, it's very thought-provoking because it's set in the future. Of course, this is something that we cannot guarantee won't actually happen. It's really scary to see how a world that was progressive (because they lived in modern American society, there was a lot of free movement happening, there were same-sex relationships that were out in the open, people were taking contraceptives) regressed, and it went back to a lot of old values that we had moved on from. It really opens up a pot of questions that you can ask about where we’re going as a society, where we think we're going as a society and where we'll actually end up.
That's just my quick two minute spiel. If you wanted to get your hands on the book then I highly recommend it - I'll pop it down in the description box below (on Youtube).
Part 1: Brainstorm
The question here is ‘Atwood’s concerns in The Handmaid's Tale go beyond women's freedom’ Discuss.
So, the first thing I always do is I look at the keywords; we've got ‘Atwood’s concerns’ , ‘go beyond ’ and ‘women's freedom’ .
The reason why we look at keywords is because we want to confirm to ourselves (as the writer of this essay), that we are going to stay focused and not go off topic with the essay topic, and the keywords will ensure that not only we stay on topic, but they emphasize the ideas that we really need to focus on. So, let's break down each of the keywords individually.
‘Atwood’s concerns’
This means that we have to focus on the author's intention or message in writing The Handmaid's Tale . We'd be thinking about ‘what ideas does she criticize or condemn?’, or ‘what does she endorse on the other hand?’
‘go beyond’
So, ‘go beyond’ is a very straightforward way of saying that an essay that is only focused on women's freedom probably won't be holistic or well-rounded enough. We have to look beyond the obvious.
‘women’s freedom’
The third one is ‘women's freedom’ . So, what does this mean? To live in a patriarchal society, to be constantly monitored by guards and potential eyes.
It's very easy to slip into just speaking about handmaids. Like I mentioned before, there's a male lead in the house who is the highest up in the hierarchy. He has a wife as well. Serena Joy is a perfect example of someone who on the surface ranks as the highest in female roles, because she is the wife of the commander. So, we see things from her perspective.
Part 2: Main Arguments
From this exploration of the key words, I can come up with two main body paragraphs. The two ideas are one:
‘To live in a chilling, post-modernism dystopia, Atwood showcases the evils of the patriarchy ’
My second one is:
‘Moreover, Atwood reveals how, despite being at the top of the female hierarchy as commander’s wives, even they suffer’
Let's have a look at both of these ideas individually.
‘To live in a chilling, post-modernism dystopia, Atwood showcases the evils of the patriarchy’
Some of my rationale behind this idea include one: Offred, who is our protagonist. Offred is actually not her real name, and because Offred is not her real name, she therefore represents any type of handmaid. She's just another one of them with a name assigned to her. Our identity is connected with our name, so her identity, which is what makes her feel human, is completely shredded from her. She has trouble remembering what she even used to look like.
The second thing is that it's dehumanizing. It doesn't matter whether Offred is intelligent, educated or even beautiful, what matters are viable ovaries and therefore, she's classified as a handmaid, and this is her last chance at being able to survive in this type of society.
The third one is that she isn't even given the freedom to take her own life. Suicide is almost impossible, “I know why there was no glass in front of the watercolor picture of the blue irises, and why the window opens only partly and why the glass in it is shatter-proof. It isn’t running away they're afraid of. We wouldn't get that far. It's those other escapes, the ones you can open in yourself, given a cutting edge”. For us as humans, we get the opportunity to do things that we want, but even to take her own life away, to save herself from the world that she's living in, is impossible.
Onto our second idea.
The first example I have for this is how Serena Joy, the commander’s wife, actually used to have her own television show. She used to be really popular, she was a celebrity, and yet she's been reduced to basically just being the commander's wife, where she lurks around in the house. She really doesn't do that much anymore, she's just there to support her husband and that is her role.
The second example is that she's forced to partake in a ritual where her husband has sex with a handmaid, “Which of us is it worse for, her or me?” (her meaning Offred). So, you can see that even for a commander’s wife, somebody who is in a high position in this society (she's the elite basically of what women could be), even she is suffering.

Going back to our keyword of ‘go beyond’
This means that in fact, we should speak about other major issues in the novel and not just about female concerns. Our first two ideas revolve around female concern, but let's see what else we could discuss. To me, another major issue revolving around freedom that's important to talk about is ‘has the Gilliad society actually influenced men and men's freedom?’ It's super easy to just target men and say that, you know, men are in power now and so it's all about the women, but there are ample examples that show that even the men are suffering.
Of course there are heaps of other issues that are brought forward in The Handmaid's Tale , but the ideas that I’ve discussed here are the ones that personally interest me the most, meaning that I've got a lot more to say and a lot more opinion to offer in my discussion.
At this point, I'll leave it up to you guys. If you have read or watched The Handmaid's Tale , tell me what you think or ask me any questions you have about how you would structure this essay. I'd really love to have a productive discussion with you that includes some critical thinking on your part. So, let's get it started.
If you like this type of advice, you may like joining my mailing list . Basically I send out weekly emails to you where I answer student questions and give you more advice, tips and resources that I don't give anywhere else.
And, if you're in need of a more detailed guide on Text Response, check out our Ultimate Guide to VCE Text Response .
It's 32 degrees today for the first time in Melbourne, in like forever, so I'm going to the beach and I'm going to spoil myself right now. I'll see you guys next week. Bye!
Updated 24/12/2020
Ransom is usually studied in the Australian curriculum under Area of Study 1 - Text Response. For a detailed guide on Text Response, check out our Ultimate Guide to VCE Text Response .
- Plot, Analysis, Important Passages and Quotes
1. Characters
Priam is an elderly king of Troy. As a child, his sister Hesione saved him from slavery, and had his named changed from Podarces to Priam, the name meaning ‘the ransomed one’ or ‘the price paid'. After the death of his son Hector, Priam envisions himself in plain clothing, riding a plain cart to Achilles who is effectively holding Hector ransom. His vision is the catalyst for the novel’s events, for his journey is one of learning and self-development. Though the royal family is doubtful of his plan to save Hector, Priam is resolute and insists that he needs to try his best to confront Achilles as a father, rather than as king. After many decades as king of Troy, Priam is determined to reinvent how he will be remembered; as a king who performed an extraordinary act of heroism in order to save his beloved son.
Achilles is known as the greatest warrior of the Greeks. The death of Patroclus, his closest companion and hinted lover, drives Achilles to insanity. Hector murdered Patroclus and, as a result, Achilles takes revenge by killing Hector. He then drags Hector’s dead body along the walls of Troy for the next 11 days. Achilles loses his sense of humanity as he is possessed by his rage, hatred and grief.
Somax is representative of the ‘common man’ in Ransom . He is chosen to escort Priam to Achilles. His simple and plain presence is contrasted with Priam’s royal status. He often engages in useless chatter and performs daily activities in a way that is foreign to the king. Although Somax is far from royalty, his great deal of affection for his daughter-in-law and granddaughter teaches Priam about love, family and life.
Beauty is Somax’s favourite mule. She accompanies Priam and Somax on their journey to the Greek camp where Achilles resides.
Somax’s other mule who carries the cart to Achilles’ camp.
Hecuba is Priam’s beloved wife and mother of Hector. She is initially uncertain of Priam’s vision to save Hector. However, after hearing Priam’s sentimental reasons, she shows support and urges him to first share his plan with their family and the kingdom’s council before he departs.
Hector is Priam’s son and also the leader of the Trojan army. He is kind, brave and noble without any cruel intentions, unlike his rival Achilles. During a battle between the Trojans and the Greeks, Hector kills Patroclus. This results in Achilles challenging Hector to a battle, resulting in Hector’s death and Achilles’ triumph.
Neoptolemus
Neoptolemus is Achilles’ son. Although he is mentioned throughout Ransom , he makes his first appearance at the end of the novel where he savagely slaughters an old and defenseless Priam in an effort to avenge his father’s death.
By the way, to download a PDF version of this blog for printing or offline use, click here !
2. Themes
Ransom explores who we are and what it means to have an identity. As the leader of Troy for many decades, Priam has always viewed himself as a king. It appears as though Priam has been unhappy with his identity for quite some time, is physically weak, and feels as though he cannot protect his kingdom as efficiently as he used to. However, the death of Hector is a catalyst for Priam as he realises that he needs to become a ‘father’ rather than the ‘king’ he had become so accustomed to. His search for Hector is also a search for himself, to reinvent who he is and how he wishes others to remember him.
Meanwhile, Somax is designated as the king’s herald, with the name Idaeus. He secretly notes his unhappiness with this name appointment, since he is ‘Somax, not Idaeus'. The name ‘Somax’ is associated with many significant events in his life including his marriage and family, yet the new unfamiliar name strips him of this identity. Somax’s confidence and pride in his identity is starkly contrasted with Priam’s pursuit for an identity transformation.
Malouf demonstrates that it is never too late to change one’s ways. Priam’s determination to change how he is remembered – from just another king leading a regal life to a hero who went to extraordinary lengths to regain his child – demonstrates that change is within our grasp. Even though his beautiful wife Hecuba and the rest of his family have reservations about his desire to confront Achilles, Priam is resolved in taking a ‘chance', rather than achieving nothing by remaining within the walls of his home. Unexpectedly, this one idea propels Priam into a multitude of other changes. His journey with Somax teaches Priam a far greater deal than he had anticipated, for he learns to appreciate the value of the human connection and other daily simplicities in life.
Although Achilles is driven by hatred and anger after Patroclus’ death, as with Priam, he manages to change his ways. He is touched by Priam’s pleas and consequently accepts the ransom and returns Hector’s body. He is able to reach this state of peace by releasing his immoral intentions and even offers to hold a ritual for Hector’s body in the Greek walls that very night. This transformation, from a human who responds to grief with vengeance to someone who releases and forgives, demonstrates the benefits we can gain from amending our ways.
Revenge, Guilt and Peace
Revenge is portrayed as a never-ending vicious cycle until both parties reach a negotiation or peace. After Patroclus’ death, Achilles hunts down Hector in order to avenge his best friend’s early death. Although he is successful in murdering Hector, Achilles does not follow the custom of leaving the body for the grieving family to bury. Instead, Achilles feels the need to mutilate the body day after day without any sense of remorse or regret. His additional need to inflict harm on Hector’s body indicates that revenge will not bring closure. His sense of loss is shown as he reflects feeling empty inside, to the point where he no longer feels like himself, but someone else altogether.
Although Achilles and Priam ultimately find peace within themselves, many years later Achilles’ son Neoptolemus murders Priam, bounded by the same hatred and pain depicted by Achilles. Neoptolemus’ subsequent guilt and regret is carried with him throughout the rest of his life, demonstrating that again, revenge is not the answer to any problem.
Chance and Fate
The role of the gods is heavily woven into the events that unfold in Ransom. Priam only begins his transition and journey after envisioning the goddess Iris, who suggests that he take a ‘chance’ and try to save Hector from Achilles’ camp. During his journey, a jovial young man who joins the travellers is revealed as Hermes, a god who has come to safely guide the elderly men to Achilles. The power of the gods in controlling human fate is illustrated during the scene where Hermes saves the travellers from being swept away by a stream.
Nevertheless, it can also be argued that it is the characters’ decisions that lead them to their fate. Although the gods may have instilled in Priam the idea that he should rescue Hector, it is the king’s determination which is a main driving force for the journey. Even when confronted with doubt and hesitancy from his family, it is Priam who pushes onwards to fulfil his vision. Whether his actions were already predestined or of his own agency is up to you to decide.
Nature Versus Man
Man’s presence on earth is shown to have little significance in comparison to the power of nature. While the events in Ransom teach the characters many valuable lessons, ultimately these meaningful moments in the humans’ lives disappear as one reaches their fate – death. Time moves on beyond our lives as we are forgotten over decades and centuries while nature prevails. Priam’s desire to be remembered by others highlights how little significance a life possesses unless one behaves extraordinarily. Malouf demonstrates that in the end, life just is – we are granted by nature to have a brief existence, yet in the end, nature and time will move forward without us.
Commoners Versus Royalty
Although royalty is portrayed to be blessed with power and authority, it is ironically the commoners in Ransom who appear to have the ‘richest’ (and more fulfilling) lives. For the first time, Priam is exposed to the different interests and values of the common man and is intrigued by the simplicities of life. It is Somax, a mere old man from the marketplace, who teaches Priam more about life than he had imagined possible.
Jove’s Eagle
Jove’s eagle is a representation of a bird renowned for its keen sight. The presence of Jove’s eagle during Priam and Somax’s departure hints that the gods will safely guide their journey as the bird behaves as a lookout. Furthermore, the symbol of the eagle’s powerful vision is contrasted with Priam’s ‘blindness’ at the beginning of the journey since he is yet to experience the outside world. It is during the journey that he learns about himself and others, and thus, improves his ‘sight.’ Coincidently, Jove’s eagle is no longer mentioned when Priam is endowed with his new insight.
The royal cart is ‘a fine new one, the marks of the adze still visible on its timbers. The twelve-spoked wheels are elaborately carved and painted, a wickerwork canopy covers the tray'. On all occasions, the king had used this elegant cart to alert others that royalty was present. The use of this cart demonstrates how Priam has been encapsulated in his own royal sphere since everything is meticulously chosen and designed specifically for the king. Nevertheless, his demand for a ‘common work cart’ depicts his determination for a simple approach to Achilles, as a father to another father. This simplicity highlights Priam’s desire to become just another man and father, anonymous in the plain cart with the hopes of retrieving Hector.
Priam as a Child
At the beginning of the journey, Priam is characterised with childish traits. When Somax urges Priam to dabble his feet in the stream, words such as ‘obedient toddler', ‘three uncertain steps', and ‘happy smile’ reflect the actions of a young child trying new experiences. This childish nature is contrasted with Priam’s old and frail age, which demonstrates that although he has lived a life in royalty, his lack of exposure to ‘real life’ has left him crippled of the simplest experiences such as the cooling effect of feet in water and eating delicious homemade cookies.
The cakes Somax brings along during the journey highlight Priam’s lack of knowledge of even the simplest things. For Somax, the little griddlecakes are a regular and delectable snack, yet Priam 'ha[s] never seen them before'. Priam’s unfamiliarity with the cakes represents his isolation from the ‘real world’ since he has been deprived from things that even commoners view as ordinary.
Futhermore, Somax’s lengthy chatter about his daughter-in-law cooking the cakes with the ‘batter bubbling and setting and turning a golden brown’ prompts Priam to think about the activities in his kingdom that occur behind closed doors. He had previously never noticed that there was so much preparation and work that went into the food that appeared at his table, let alone the ingredients and thickness of a batter. These matters had been of little concern to Priam, yet he realises that even the ‘common and low…activities and facts of life, had an appeal'.
Hector’s Body
Although Achilles drags Hector’s body across the walls of Troy for eleven days, each morning he would return to find Hector’s body healed of any wounds, and absent of any physical damage to his body. This is a cruel reminder of the god’s ability to ‘toy around’ with the Ancient Greeks’ lives. Hector’s body also symbolises how revenge is not the answer to any conflict, since dealing with a tragic loss through revenge does not gain anything but more pain and suffering.
Although Priam initially believes he understands the distress of losing a son, Somax’s experience of losing his son is driven with emotions that Priam had never previously experienced. When sharing the story of his son’s death, Somax sniffles, an ‘odd habit’ according to Priam. The use of ‘odd habit’ to describe Somax’s sadness demonstrates how Priam has never truly felt the loss of his son, but only the loss of a royal relationship between king and prince.
Later on, Somax once again ‘snuffles’ and ‘rubs his nose’ at the thought of the ending to their journey. Similarly, Priam makes ‘small sounds', presumably crying as well. The transformation of Priam from someone who failed to empathise with Somax’s tears at the beginning of the journey to a man filled with emotions demonstrates that Priam undergoes both a physical and metaphysical journey where he undergoes self-development and appreciation of the world around him.
4. Plot, Analysis, Important Passages and Quotes
Achilles, the greatest warrior of the Greeks, stands next to the sea while reminiscing about the past. After his mother’s death he had ‘entered the rough world of men’ (p. 6) where wars and battles prevail. Every morning, he feels the need to ‘tramp to shore’ (p. 10) since he is haunted by the death of his ‘soulmate and companion’ Patroclus, and his raging hatred towards Hector, killer of Patroclus and thus, the ‘implacable enemy'.
When Achilles was a child, his cousin Patroclus came to live with the young Achilles since the former had killed the son of a high official of the royal court due to a ‘quarrel over a game of knucklebones’ (p. 11). In need of asylum, Patroclus came to live with Achilles’ family. As the years passed, the pair grew closer to the extent where Achilles believes that ‘he had mated with Patroclus’ (p. 15).
When the tide of the battle was against the Greeks, Patroclus disguises himself in Achilles’ armour in order to instill fear in the Trojans and cause them to return to the safety of their walls, thus providing temporary relief for the Greeks. In his last act for his closest friend, Patroclus is killed in battle*. The death of Patroclus left Achilles with an overwhelming sense of loss and also burning animosity. Achilles whispers that he will join Patroclus soon, but firstly, he has to avenge Patroclus’ killer, Hector.
Hector, the son of Trojan king Priam and leader of the Trojan army, wore Achilles' armour as a sign of triumph and disrespect for the Greeks. In a dramatic battle between Hector and himself, Achilles was successful in killing his enemy. Achilles’ Myrmidons then stripped Hector of his armour and ‘without pity…plunged their swords into Hector’s unprotected flesh’ (p. 24). For Achilles however, this was not enough. Still fuelled by his pain, Achilles ties Hector’s body to a chariot and drags it ‘up and down under the walls of Troy’ (p. 26) as the dead warrior’s royal family devastatingly watches on. Achilles feels like a ‘dead man…feeling nothing’ (p. 26), unable to seal the void left by his beloved friend.
The next day, Achilles is furious to find Hector’s body ‘smoothly sealed and the torn flesh made whole again'. His men cannot bear to look at him as he drives the chariot with Hector’s body along the walls of the Trojans once again. Afterwards he quickly falls asleep, into ‘oblivion’ (p. 35) as he struggles with the shame and guilt of his actions. He is ‘waiting for a break…something new and unimaginable’ in his life.
The Human Side
Along with the conflict between Greece and Troy, Ransom also delves into the consequences of those affected by the war. As the greatest warrior of all Greeks, Achilles has lived his life as a fighter. Nevertheless, his pathway in life has led him to believe that ‘such a life is death to the warrior spirit’ (p. 7). While warriors are known for sacrificing their lives in the battlefield, Achilles does not literally refer to warriors confronting death each time they fight for their team. In fact, ‘death to the warrior spirit’ means to metaphorically lose what it means to ‘live’ when one experiences bloodshed in each war. Growing up surrounded by ‘the rough world of men’ (p. 6), Achilles develops traits of aggression, cruelty and vengefulness in order to become an implacable man of war. As a consequence, Achilles only knows how to deal with Patroclus’ death with a fighter’s mindset. Instead of grieving openly, ‘he never permit[s] himself to betray to others what he [feels]’ (p. 5), thus detaching himself from the natural human process of grieving. In order to deal with his friend’s tragic ending, Achilles' ‘soul chang[es] colour’ as drags Hector’s body for eleven days without any sense of regret or remorse, and thus, is referred to as ‘death to his human spirit’ since he was no longer ‘a living man’ (p. 27). He faces Patroclus’ death with the same warrior traits of aggression, cruelty and vengefulness, depriving himself of any ability to humanely mourn his close friend’s death.
Furthermore, Achilles grieves for his mother in the opening passages of Ransom . During this time of loss, his mother symbolises Achilles’ need to be nurtured. The imagery of the sea surface as a ‘belly’ and ‘a membrane stretched to a fine transparency’ (p. 3) represents his mother’s pregnancy where he ‘had hung curled in a dream of pre-existence’ for ‘nine changes of the moon’ – or in other words, nine months of pregnancy. Achilles is characterised as a foetus, for his position is ‘chin down, shoulders hunched’ as though he is inside a womb. Although Achilles is a fighter, he hides the fact that he wishes to be ‘rocked and comforted’ by his mother, thus demonstrating that even beneath the surface of a cold-hearted warrior, the current of human emotions can cripple a man’s confident veneer.
If you'd like to read more of my analysis, feel free to access a sample of our ebook A Killer Text Guide: Ransom . In this ebook, I cover Plot, Analysis, Important Passages and Quotes so you can prepare for your SAC and exam. I've also included 5 Sample A+ English essays on Ransom , complete with annotations so you know exactly what you need to do in your next essay to achieve an A+.
All the best for your studies in Ransom!
Download a PDF version of this blog for printing or offline use
If you’ve been studying John Donne’s metaphysical poetry, you’ve probably noticed that his works are riddled with different symbols and motifs. Embedded throughout his poetry, these literary devices may seem slightly abstruse to the reader. You may find yourself asking: What do they mean? And in relation to what? Even Donne’s contemporaries failed to appreciate his poetry. The neoclassical poet John Dryden rejected Donne’s works because it “affects the metaphysics” and “perplexes the minds of the fair sex with nice speculations of philosophy, when he should engage their hearts, and entertain them with the softnesses of love”.
One thing that you should understand about Donne’s romantic poetry, is that while his stark images of compasses and spheres may seem foreign to you, they were also alien to his predecessors too. So, if you’re struggling to comprehend his enigmatic poetry, not to fear! Because John Donne’s poetic peers didn’t initially get it either.
The reason for this is because Donne refused to conform to the poetic conventions of the time. The poet emerged as an idiosyncratic in the Elizabethan era, the Renaissance. Unlike his contemporaries, he didn’t employ elaborate descriptions of symbol natural landscapes, classical myths and female beauty. The reason for this was because Donne did not believe in the one-sided love and emotional frustrations that his contemporaries tried so hard to convey in such imagery.
Donne’s poetry was so different because he rejected and even openly mocked the idea of such a high-minded religious worship in literary romance. In “A Valediction Forbidding Mourning,” Donne criticises the “tear-floods” and “sigh-tempests” of the “dull sublunary lovers.”. In a similar vein, Donne satirises the “sighs” and “tears” (The Canonisation) so prevalent in Petrarchan works.
Instead, Donne advocated for a different kind of love. He espoused a love that comprised of the Body and the Soul, which was a dominant intellectual issue in the literary treatment of love in the 1590s. More specifically, Donne embraced the balance between Platonic love and the Ovidian love.
Platonic: Platonic love is essentially love that surpasses the mere sensual and physical. It is a very spiritual concept and is based on reason, affection, respect, intellect and compatibility.
Ovidian: Ovidian love
The idea of balance derived from discoveries being made about the human body during the Elizabethan era. The Renaissance was fundamentally a time of discovery (particularly in the area of science). Elizabethans believed that elements in the body needed to be balanced,
Top Tip: When you’re analysing John Donne’s poetry and writing essays, be aware of Donne’s overarching message in his romantic poetry. Most explanations about his use transcendent relationship with his lover is thus determined by obtaining a balance between the spiritual and earthly pleasures. Most examination questions will leave room for to discuss the connection between the material and the divine world! Make sure to understand this, because this is a huge component to his poetry.
For a deep dive into the Creative and what it entails, check out our blog post: VCE English Unit 3, Area Of Study 2: Creating Texts - What Is It?
Leo Tolstoy wrote his magnum opus, War and Peace , over the span of six years. It took Harper Lee two and a half years to write To Kill A Mockingbird . Anthony Doerr’s All the Light We Cannot See took ten years to complete.
The incredibly intricate and complex nature of stories means that it often takes time to fit all the elements in harmony. But for those of you studying VCE English Units 1 and 3 , you don’t have the luxury of two or six, let alone ten years to write your Creative. The time constraints you face can mean that it’s harder to put the metaphorical puzzle pieces together.
Luckily, we can simplify the process for you by breaking down what makes a good story (using Cinderella to demonstrate).
The Skeleton of a Good Story (With Steps!)
In primary school, we were all taught the “beginning-middle-end“ approach to stories. Aside from being kind of vague, this overused approach doesn’t ensure a clear transformation between the “beginning” and the “end“. If nothing changes between the beginning and the end of your story, you have no story.
The skeleton approach is an effective alternative to other forms of story writing because it guarantees that your character has fundamentally changed by the end. Think of the following as criteria when you write your Creative - if you have (even slightly) addressed all of the following aspects, you can be sure you’ve written a story worth telling (and a Creative that’s going to score highly).
1) The Status Quo
Most stories feature a main protagonist, and your Creative piece should too! This is the main character who is in a zone of comfort/familiarity with some obvious shortcoming. This shortcoming can be a character flaw or something in the setting. This is Cinderella: she is used to her ordinary life in her small house, with her shortcoming being that she’s a servant to her evil stepsisters.
2) The Want
Additionally, your character has to want something (or at least, think that they want that thing). Since your time is limited, keep the desire simple. For instance, Cinderella’s main desire is to escape her life of servitude and be supported.
3) The New Situation
After you have established the character’s “want”, your character has to enter an unfamiliar situation that addresses their shortcoming. Continuing the example of Cinderella, this unfamiliar situation is the royal ball, which offers her the chance to marry the prince and live with him instead.
4) The Plan
After the new situation is presented, the character must carry out a plan to get what they want, be it explicitly or subconsciously. This plan can either succeed or fail in getting them what they want. Cinderella plans to present herself as a viable option for the prince by ensuring she is well-groomed and presentable - a plan she fulfils.
However, the character must pay a very heavy price for it - mentally, physically or emotionally. This is the climax of the story, where the character is challenged and maybe even forced to change. For Cinderella, the clock striking midnight signals a limit on the amount of time she can maintain the princess persona and interact with the prince.
5) The “Eureka” Moment
This part of the story is potentially the most vital: when the character is forced to look within and reflect on who they are, what they actually need and want, and who they must be to achieve these things. Cinderella's initial reluctance to claim ownership of the shoe suggests her acceptance of a life of servitude, implying that she views the "aristocratic dream" as unachievable.
6) The Resolution
Finally, the character either returns to their familiar situation or a new situation is born. In Cinderella , a new situation arises when Cinderella marries the prince and escapes her previous life. This is when the situation has been “resolved ”, not “ended”.
Experiment!
The other benefit of the skeleton approach is that you have the room to experiment with your Creative piece. For instance, you can do an allegorical text (like Animal Farm ) or maybe even a cyclical structure ( Gone Girl , film). Your Creative piece is inspired by your experiences and no one else’s so have fun with your creative control!
For a step-by-step explanation of everything you need to know to ace your SAC or exam, check out our How To Write A Killer Language Analysis ebook.
For many students, Language Analysis is their downfall. Here is the main reason why: Lots of students don’t think about how language is used to persuade , instead they rely on lists of language techniques to tell them the answer. These sheets are usually distributed by teachers when you first start language analysis – see below.

Whether or not you’ve seen that particular document before, you’ve probably got something similar. You’ve also probably thought, ‘this sheet is absolutely amazing – it has everything I need and it tells me how language persuades!’ – I know I did. Unfortunately, this mindset is wrong. Don’t fall into the trap like so many other students have over the years. For a detailed guide on Language Analysis including how to prepare for your SAC and exam, check out our Ultimate Guide to VCE Language Analysis .
The following comes from VCAA 2009 English Assessment Report:
…some students presented a simple summary [when analysing]…with little development. These responses did not score well as they did not fulfil the task as required.
The ‘simple summary’ refers to students who rely on those technique sheets to paraphrase the explanations regarding how language persuades. There is ‘little development’ because copying the explanations provided on these sheets doesn’t demonstrate enough insight into the article you’re analysing. Let’s have a look at the VCAA English Practice Exam published in 2009, ‘Chickens Range Free’ so that we can demonstrate this point. We will look at two students, both analysing the same technique. Compare the two and determine who you believe provides the better analysis.
Student 1: Emotive language such as “abominably cruel” and “dire plight” is intended to stimulate strong emotional reactions that manipulate readers’ responses.
Student 2: The use of emotive language such as “abominably cruel” and “dire plight” intends to appeal to people’s instinctive compassion for the chickens by describing their dreadful treatment, hence causing readers to agree with Smith that urgent action is required to save these animals.
It should be clear that Student 2’s example is best. Let’s see why.
Student 1 has determined the correct language technique and found suitable evidence from the article. This is a good start. However, Student 1 goes on to merely reiterate the explanations provided by language technique sheets and as a result, their analysis is too broad and non-specific to the article.
Student 2 conversely, understands that this last step – the analysing part – is the most important and vital component that will distinguish themselves from others. Instead of merely quoting that the article ‘manipulates the reader response’ like student 1, they provide an in-depth analysis of how and why reader feelings are manipulated because of this technique. Student 2 was able to use the information to illustrate the author’s contention that we should feel sorry for these caged chickens – and we do because of our ‘instinctive compassion.’ They explain that the sympathy expressed from readers encourages them to agree that some action needs to be taken to help the chickens. As you can see, Student 2 has gone beyond identifying that ‘strong emotional reactions’ will be displayed by readers, to establishing what emotions are involved, and the consequences of those emotions.
This is why it’s best to avoid paraphrasing language technique sheets. By all means, don’t totally disregard them altogether. They’re definitely great for learning new language techniques – just be mindful of the explanations given. The part regarding how the author persuades is the downfall of many students because even though teachers tell you to analyse more, they often don’t show you the difference between what you’re doing wrong and what you should be doing right.
For a detailed guide on Language Analysis, what you're expected to cover, how to prepare for your SAC and Exam and more, check out our Ultimate Guide to VCE Language Analysis .
Analyse the VCAA 2020 Article With Me
I'm so excited to be doing the VCAA 2020 English Exam with you. I have done these Analysing Argument pieces before on YouTube, but this is the first time that I'm doing one live. I wanted to do one live with you guys because I wanted to interact with you, for you to be able to ask me questions and for you to see how my brain works in a live setting. When it comes to analysing - and you know I've got an edited version for you - you don't see me thinking through and understanding what's happening in the article itself. So, I think it will be really handy for you to see my thought processes because sometimes, yeah, you can see somebody's analysis, but if you don't quite understand HOW they arrived at that analysis, then it's not that helpful for you. It's like reading an essay that's already been done by an A+ student and you go, yeah, okay, I kind of get that, but how did they get there? How did they find that language technique to begin with? How did they find that argument? So that's what I want to work with you guys today.
You can download VCAA 2020 English past exam HERE , which is what we're going through today. If you've already read it before, even if you've done it before, I'm confident I'll still be able to give you some new, interesting perspectives and to pick out some new language techniques for you guys. So, go ahead and make sure you download that and print it out. I think printing things out is usually a better option than trying to annotate online, unless you've got an iPad or equivalent. The exam is absolutely free - it's the last few pages of the exam, starting at page 11.
Let's just get into it. I don't think I have any other housekeeping pointers except that throughout this live stream, I'm going to direct you to where you can actually go and get the A+ completed essay I've got for this article. While we're going to be analysing this together now, I think it's handy for you to be able to see an A+ completed version of everything that we've talked about. Then you can take it from the very beginning (the analysis), then the annotations and then you can finally see the written-up version. Being able to take you through that entire process from start to finish is going to be so wholesome, so fabulous.
Pay Attention to the Background Information
Whenever you look at section C, which is Analysing Argument also called Language Analysis (I'm going to interchange these two terms), you really need to ensure that you read the background information. I know it's super obvious, but background information is there for a reason, do not skip over it!
They didn't just give you an entire extra page just for the sake of it. Usually, the background information is a really great place for you to understand conceptually what is going on in this article. If we didn't have this background and therefore context to the article, there's a chance that you might accidentally come up with the wrong contention. You might misinterpret the arguments as something else. The background information is really just there for backup. It's a great place for you to ensure that what you're understanding from the article is actually correct because usually the background information is filled with facts and these facts will help shape your understanding of the article.
Let’s Read the Background Information Together
‘The shire of Byways in regional Victoria depends on both farmers and tourists for its prosperity. The local community is concerned about the increased recreational use of drones by many of the tourists visiting the area. The following is the transcript of a speech’
Ah! Interesting - 'transcript of a speech' is something that makes me go already yep, I need to make sure I note this because as soon as I recognise that it's a speech, it means that my audience, I don't call them readers, I call them listeners .
Simple things, small things will help differentiate you from other students. Someone else might not pick up that this is a speech and they'll just say readers the entire time. And no, you're not really going to get marks deducted for it, but there's an element of finesse I suppose. If you just notice that small nuance and you're able to present that in your essay, it makes the examiner or assessor more confident that you know what you're doing.
'by young farmer Warwick Bandle at a public meeting'
Interesting, ‘public meeting’.
'called by the Byways Shire Council to discuss the community’s concerns.'
It's interesting because I'm already getting this community vibe from this background information. The fact that it's regional Victoria, the fact that it's actually a very specific council, the fact that he's at a public meeting. People have taken time out of their day to go to the council meeting. Who goes to the council meeting? People who care. This is just something that I'm kind of noting for myself as I go into my analysis because then I'll be able to develop my analysis in a particular way.
'Bandle provided two images to be projected on a screen to accompany his speech.'
Okay, cool, all this does is tell me that I just need to be wary that there are two images and that I, as a student, need to talk about them .
Analysing Paragraph One
He says, 'Good evening, everyone', already indicative of a speech, I'm just going to write that down. Remember that it's a speech!
'Drones and their inexperienced users are proving to be a costly problem for us farmers. Drones are not toys. What happens when a drone flies out of range? What happens when the battery runs out? A drone being flown out of control, or crashing out of the sky, can be lethal.'
Wow. Okay, this is what I think when I read an article, I genuinely think about my own personal response. I mean, I am actually the audience of this article. No, I'm not there at the council listening to him live, but I'm still a person who's absorbing what he's saying. I trust my instinct and my gut feeling, and that kind of leads me to develop my own unique interpretations. The reason why I said 'Wow' is because he uses the word 'lethal'. To me, it's a little bit of an exaggeration. I mean I'm sure drones have killed people before, but I guess it's like an I'm serious about this, we're not joking around and he's making it seem like this is a serious problem and that we need to address it seriously. So in that sense, I guess we could talk a little bit about tone. What tone do you think he's using?
Viewers from our live stream suggested:
Nice! I like all of these. I don't think there's anything wrong with them. When it comes to English, it's a matter of your own interpretation. As long as you can back it up, then you've got yourself straight. You can go and find my 195 Tones PDF , which you can download for free. You can use that whenever you analyse an article, it has a bunch of tones listed there for you so that you never run out of tones!
He's already set this tone for the remainder of the article. I'm interested in what he's going to say next. Otherwise, I think the fact that he's serious or alarmist is reaffirmed by what he's saying. He says, 'drones are not toys'. Okay. This is not a game, we're not playing around, we're not fooling around. And I suppose that's important for him to establish because drones are kind of seen as toys, at least for me anyway. When drones first came out, it was kind of like a toy aeroplane that you drive around with your remote control. So, I think he's dispelling that idea or that conception or perception of drones immediately so that we can be on board with whatever he's saying next.
LSG’s Specificity and Simplicity Strategy
I just wanted to point out, this is pretty obvious, but rhetorical questions. There's not necessarily much I would say at this point in time with rhetorical questions, and that's because of my SPECIFICITY and SIMPLICITY strategy . If you don't know much about that - I haven't talked much about it on my YouTube channel - it's a strategy that I developed for myself in Year 12 when I couldn't figure out why I wasn't getting full marks in English and yeah, okay, I was a nerd, I was already getting 17 or 18 out of 20, but you know, the high achiever in me was kind of like, why am I not getting 19 out of 20? Why am I not getting 20 out of 20? Why am I losing these one or two marks?
I realised later on that it's because I wasn't being SPECIFIC enough with my analysis. So, when it comes to some of the comments (referring to comments from live stream) you guys have written, one of you wrote down 'emotive language'. If you're one of my students, you know that you don't use emotive language. Emotive language is way too broad. It's way too general to really mean anything. Instead of saying emotive language, why don't you say exactly what emotion they're appealing to. You're then taking that general vagueness of whatever emotive language means and replacing it with something very specific, and therefore, it's going to be more meaningful for you to write about, but also for your assessor to understand what you're going on about.
So in case you don't know, I have study guides (it is called Lisa's Study Guides after all). In How To Write A Killer Language Analysis I actually go through this golden strategy of SIMPLICITY and SPECIFICITY . This is what helped me get an A+ in my Analysing Argument and in my end of year exam. If you're interested, then I'd highly recommend that you go and check out the study guide. It's a world of value I promise.
More Analysis of Paragraph One
We're still only on the introduction, which is crazy, there's just so much to say when it comes to this stuff.
‘Just imagine the damage that can be done by a falling drone. Imagine, then, these drone users, realising that they have lost their drone, searching, crashing through crops, or leaving gates open and letting livestock out. And finally, when they don’t find the drone, it’s just left to rust away in the field until harvest time, when it’s swept up, damaging the harvester.’
I guess there's this idea of 'imagine'. He's building upon that alarmist attitude, which I'll pull from what you guys are saying, and by asking us to 'imagine' the worst-case scenario, it's making us feel more and more concerned, right? Just by reading this, I go ew, I don't want these drone users to be losing their drones in my farm space, in my land .
One other point for you to think about is, I was talking before about how I am part of the audience too, right? But the next step from that, for a more advanced analysis, is to think about who is HE talking to? If we go back to the prior page, he's at a public meeting to address the community's concerns. You could say that part of the audience would be farmers, people who care about their livestock, people who care about the invasion of privacy and people stepping on their property. Remember this as you analyse, because it's going to make your analysis way more specific, and bonus tip, assessors, teachers, examiners - they love it when you can be specific with who the audience is. It shows that you're capable and you get it.
Even just in this first paragraph, we've managed to talk about quite a bit.
Let's Look at Your Questions:
- I think my target audience is probably farmers. I say probably just because I want to keep reading to understand exactly who he's talking about, these are just my assumptions, just from reading the first part of the article.
- In terms of how you can incorporate tone into a body paragraph, you can do it as simple as actually just talking about the tone or you can integrate it with another language technique. Remember just before we were talking about rhetorical questions and how the repetitive use of 'imagine' kind of builds upon that sense of concern in the audience? You could link that back to his tone and say, 'By building up this concern, he's using his serious tone in order to persuade the audience to...' .
Analysing the Photograph
You absolutely need to talk about it. We've got this photograph of this girl who seems to be a bit of a dark shadow and because she's a dark shadow I'd say that it's like she is an anonymous person. The sense is that this could be anyone and by making the person anonymous, like a blank face, it's easier for us to hate on them because it kind of takes the humanity away. If you don't know who it is, they're just drone invaders. They're people who don't respect our land. That's one point that I would talk about.
Then you've got that really focused point of view of the drone itself. It makes sense because the drone is the topic of this conversation, so it's the focal point you could say, and it reconfirms or reaffirms that idea of it just crashing out of the sky, crashing through crops or being left to rust away. Remember, imagine that we're in the council meeting, he's put this image up for us and he's saying this. I think about it as how does having the photograph there on a presenter with him talking about it, how does that change how I respond? I think about how I feel and what I think, which is something that we talked about in one of my previous videos, called How to write a Language Analysis (Analysing Argument) - we talk about the TEE rule. In my opinion, when I have that photograph right there in front of me, it definitely makes me angrier. It's more confronting because it's in your face and it definitely riles me up more. So, you could include that in your analysis as well.
Pay Attention to the Structure of Articles/Arguments
The way that he has structured his argument, in the sense that he's structured where he positions his photograph (which is basically right after his introduction), makes me feel more inclined to agree with him. Whereas, if it was just him saying it (without an image as proof), then I'd actually have to just take his word for it. But, here's proof people are doing this!
A viewer says ‘she's dressed for the city and outside of, not part of the community’ - I love it, well done!
Another viewer says ‘the camera angle gives the allusion that she's dominant’ - interesting.
I think to extrapolate what you're saying, that dominance, as somebody who's part of the local community, I don't want that. I don't want somebody else to be dominating over my crib, my place! So it's kind of making me really deterred and making me want to steer clear. It makes me want these people to steer clear of my space.
A viewer says ‘the lack of crop suggests that drones have destroyed the normal way of farming’ - yeah, absolutely! Not only is there rubbish in their plot of land, but if anything, the drone has added to the destruction.
She's dominant, therefore she's a threat.
A viewer says ‘she believes that the black and white makes it gloomy and sad’ - a hundred percent. This is actually a really good point. Sometimes you can get so absorbed in the analysis that you only think about what's there in front of you, but a great way to create contrast and to understand what's there when it's so obvious is by considering what things would be like if it were otherwise. Basically, what I'm saying is, think about why it is black and white. Why is it not in colour? If it was in colour, how would that change your perception of what's happening here? Thinking about what's NOT there helps you understand what IS there.
You can talk about how it's good versus evil.
I wanted to just share with you guys because I won't be able to go through all of this today, but I did mention before that I do want to show you the A+ sample essay. It's in my How To Write A Killer Language Analysis study guide in Chapter 16, Section 10. We've actually recently updated it with the 2020, 2019 & 2017 past English Exams, so it's all A+ essays for you. Plus we have several A+ essays for single articles, double articles and triple articles with images as well.
We've talked a little bit about the photograph, which by the way, we could keep finding more and more, but I think it gets to a certain point where you kind of have to figure out what's valuable for you to talk about and what's not so much. Once you get good enough at Analysing Argument, you should have an excess of language techniques to choose from and then it's just a matter of deciding which ones are going to give you that advantage and which ones are going to help you stand out from the rest of the cohort.
Analysing Paragraph Two
‘It’s time our council started to defend the farmers rather than the tourists’
That's juicy - ‘our council’
What I'm thinking about here is, he's saying 'our council', but he's using inclusive language - 'our'. There's this sense of ownership, this is our space, this is our community.
'Defend farmers rather than the tourists'
Now he's creating a dichotomy between farmers and tourists. I love the word dichotomy; essentially, it just means a true opposition - farmers versus tourists. The way that I remember the word is di as a prefix usually means divide or division, to split things in half. So it's creating this dichotomy of us versus them. And the way that I build upon this - I'm just thinking ahead with an essay - is I'd probably connect it to this girl; there's this sense of ‘us’ and ‘them’. ‘Them’ is a threat. ‘Them’ is an outsider. ‘Them’ is all the things that we mentioned before, but ‘us’, he hasn't said too much about ‘us’ yet. So maybe he's going to build upon that here.
'The farmers are the backbone of this community'.
Okay. He is building upon it. This paragraph seems like it's more about the farmers and building the 'us'
'farmers are the backbone of this community, many of us having lived in this area for generations.'
This has been our space forever and look at these intruders coming in now. How rude!
‘While we understand the importance to our town of visitors supporting businesses and, indeed, have welcomed the holiday-makers, when they start causing havoc while searching for their wayward drones it’s time to say, ‘Enough!’’
'when they' - there's that dichotomy again - ‘start causing havoc’.
Another word that kind of adds to that sense of them being a threat, them being intruders while searching for their wayward drones is ‘it’s time to say, ‘Enough!’’.
Build Your Vocabulary
I actually don't know what wayward means, so if this happens, and this stuff happens all the time, what I do is actually look it up in the dictionary and understand it because I know that if I don't know what this word means, it probably means that the majority of other people also don't know what this word means. It, therefore, gives me a potential advantage, because if I'm able to analyse it, there's something that not as many people would have analysed.
So, wayward means difficult to control or predict because of willful or perverse behaviour.
In my own interpretation, I guess it's unpredictable. If I build upon this idea more, I guess there's a sense of loss of control and this builds upon that idea that farmers are losing control of their plot of land and their privacy. You can kind of see this is how my mind works and I just try to sync everything back up to the contention and to what he's saying essentially. That's actually quite a bit that we went through in that little bit there.
I'm just going to have a look at your comments now.
A viewer says 'dichotomy simplifies a debate for an audience to make it seem a neutral position is not possible and consequently one must pick a side.' Thank you, that's actually really helpful.
Analysing Paragraph Three
'Don’t get me wrong! I’m not just another technophobe'
Oh, quickly. I just want to go back while we understand the importance of our town, of visitors supporting businesses, I think there's this acknowledging the opposition, acknowledging that there are benefits in having visitors. He's not completely tunnel-visioned. He is being fairer, or at least that's how he's portraying himself, and that makes me at least more inclined to side with him because I'm seeing that he's a little bit more rational and he's not just saying, oh, screw them . It's not just his way or the highway, there is some give or take, so that kind of makes him more credible in a sense.
The reason why I thought about that just then is because this next part, ‘Don’t get me wrong! I’m not just another technophobe’, builds to this idea as well. I'm just going to say acknowledging the opposition . There, you can finesse that by replacing the word opposition with something else. That's fine.
‘I'm not just another technophobe’
He's kind of anticipating people's reactions to what he's saying and he's going no, no, no, I'm not like that. It's all good, not just another person complaining about technology.
As a young farmer’
I just find that hilarious. He's young guys, okay?! He's not some old person, I guess that’s the stereotype, that old people don't fare well with technology, which I don't think is true by the way. I think everyone's getting on board with technology these days. But, he's kind of reaffirming, I'm young guys, I'm a cool guy, I'm not anti-tech at all. He literally says it 'I'm introducing new tech'. I'm on board with that, you know, ‘we’re using drones’.
Shifts in Tone
Now he's kind of talking about the benefits of drones, the time and the money they save.
‘There is absolutely no way we want to ban drones.’
I think this is a really interesting way he's structuring his argument. He's kind of started off going, drones, they're so bad for you . Then he's showing this picture, which is kind of like drones, they suck. And then in this paragraph here, he differentiates farmers from outsiders, and then he kind of takes a turn and goes, no, I love drones, don’t get me wrong. I think there's this analysis there for you and I'd actually love for you guys to write down in the comments section what you think is going on? Why is he structuring his argument like this?
A viewer says 'there's a shift in tone' Absolutely! Love it. Great pickup.
Here's a tip for you guys. A shift in tone usually means that there's a new argument coming. They usually tie in together pretty well, so if you see a shift in tone, you can kind of hedge the bet that it's a new argument. This is particularly helpful if it's an article that's really hard. Usually for SACs, teachers will choose articles from newspapers and we all know that newspaper articles are way tougher than VCAA articles. If you don't know, it's true.
Another viewer says 'it may be the start of rebuttal' Interesting.
A viewer asks 'will these annotations be provided for our personal use at the end?' - I'm only actually uploading the annotations into my study guide . So, they will be accessible there. Otherwise, it's just access through the live stream video (linked at top of page), which will be posted up afterwards as well.
A viewer says 'By stating he's young and uses drones, it showcases his argument isn't based on personal bias towards young people or drones, but is a legitimate problem.' - Hmm. With your analysis, I'm not a hundred percent sure what you're saying. I think it could be a little bit clearer. Give that a go. Just try rewriting it, see if you can make it even more concise.
Let’s Recap What We’ve Analysed So Far
So we've managed to annotate the background information, paragraph one, the photograph, paragraph two and paragraph three. We still have one more paragraph left and this next page with the image.
Unfortunately, I have to wrap it up there, but if you want to see me annotate and analyse the rest of this article, head over to Part 2 on Youtube where I finish this off.
Have a go at analysing the rest of the article yourself though!
Don't forget that I've got my How To Write A Killer Language Analysis study guide. If you want to head over there you can access/download the annotations + a complete A+ essay based on this article.
For a detailed guide on Comparative, check out our Ultimate Guide to VCE Comparative.
Why Is the Context Important?
Understanding the context of the texts you are studying is essential if you are to satisfactorily respond to any prompt ( learn about the 5 types of prompts here ). Not only does it provide an insight into the society of the time and their views and values , it also allows for greater awareness of the characters’ motivations, resulting in a richer discussion in your essays. Discussing the context of the texts also makes for an ideal comparison which can be incorporated in the introduction as well as the body paragraphs. Moreover, context paragraphs are a great tool to have up your sleeves, as they can easily be adapted to almost every essay question, a real asset when attempting to write an essay in an hour.
In this blog post, I will be giving a brief overview of the contexts of the play The Crucible by Arthur Miller and Rosalie Ham’s The Dressmaker . Further down , I have also provided a sample paragraph as an example of a way in which I would go about writing a context paragraph in response to an essay prompt concerning the two texts. Both of these texts are set in fascinating and significant eras of human history so I invite you to conduct your own research after reading this!
At first glance, the town of Salem, Massachusetts in 1692 and Dungatar, Victoria in 1950s Australia have little in common; however, both towns exist in stifling geographical isolation, allow myopic and parochial outlooks to flourish, and maintain an irrational but overwhelming fear of ‘the other.’
The Crucible, Arthur Miller
The Crucible is set in 1692 in Salem. The provincial, conservative town was established by English Puritans who, fearing persecution, fled from a Britain dominated by The Church of England. The first Puritans to arrive in Salem faced brutal conditions, including 'marauding Indians' and living on a 'barbaric frontier' that lay close to the 'dark and threatening…virgin forest' that they believed to be the 'devil’s last preserve'. In order to overcome these challenges, the people of Salem were forced to unify and remain diligent. In order to ensure efficiency, a strict and rigid way of life was adopted, where work and prayer were championed and individual freedoms and pleasures abhorred. Though this harsh way of life did allow the Salemites to stay alive, it forced them to suppress various natural human emotions such as joy and anger, so as to not detract from work and prayer. Further, the town had limited their interaction with the outside world, compelling them to instead be constantly surrounded by each other. This hazardous combination of repression of emotions and interaction with only a small pool of people spurred private jealousies and vengeance within the townspeople, and it is here that the play commences.
The Dressmaker, Rosalie Ham
In contrast, Ham’s novel takes place in 1950s rural Australia, in the fictional town of Dungatar. Despite being set centuries after The Crucible , Dungatar is rife with the same parochialism (great word to use for both texts, referring to a limited/ narrow outlook), resentment and gossip as Salem. The town’s physical isolation - it is surrounded by 'wheat, yellow plains' and seems to be a 'dark blot shimmering on the edge of flatness' - corresponded with their metaphoric isolation from global events, creating an intense fear of ‘the other’. Further, similarly to The Crucible , the stark physical isolation ensures that each individual’s social interactions are limited to the town’s small population, fostering a breeding ground for narrow-mindedness and prejudice. Ham’s description of the way 'the crowd screamed with lust, revenge, joy, hate and elation' after a local football match win reveals the underlying emotions of the town, repressed behind a veneer of respectability and perceived moral propriety. All it takes is a stimulus, which arrives in the form of outcast Tilly Dunnage, to uncover the malicious undertones of the provincial town.
Example Context Paragraph
During VCE, I tended to use my first paragraph (in response to an essay prompt) as a way to explore the context of the texts I was studying, and relate the context to the essay prompt being addressed ( learn more about the different types of essay prompts here ). In this case, the prompt I have responded to is:
Compare the ways in which The Crucible and The Dressmaker portray divided societies.
I was able to adapt much of this paragraph below to whatever essay prompts I came across.
The geographical isolation of rural, parochial towns can breed a kind of myopia amongst inhabitants and promote binary thinking. Salem is situated on the 'edge of wilderness’, with the 'American continent stretching endlessly West’. The 'dark and threatening' forest which ominously surrounds the town is believed to be 'the last place on earth not paying homage to God’, inciting the irrational fear that 'the virgin’s forest was the Devil’s last preserve' (1) . To combat the imminent threat of the 'marauding Indians' upon their arrival in Salem, the Salemites maintained that 'in unity…lay the best promise of safety’, and hence were governed as 'an autocracy by consent' (2) . Similarly, in The Dressmaker , the town of Dungatar 'stretches as far as the silos' and is described as a 'dark blot shimmering on the edge of flatness’. 'The green eye of the oval' is a physical representation of the town’s predilection for prejudice and endorsement of slyly watching others (3) . The stifling insularity experienced by both towns perpetuates a paucity of culture and 'parochial snobbery’, as well as fostering austere social expectations (4) . The totalitarian regime that governed Salem and their 'strict and sombre way of life' conditioned the people of Salem to repress natural human emotions so as to conform to the conservative and rigid values of society. Indeed, Miller’s description of the 'small windowed dark houses struggling against the raw Massachusetts winter' alludes to the Salemites’ dogmatically narrow-minded outlook and their repression of any individuality. Hence, despite the veneer of propriety upheld by Salem’s 'sect of fanatics’, the town is rife with hidden resentments and 'long-held hatreds of neighbours' (5) . Whilst moral respectability and piety conceal the true sentiments of the people of Salem, clothing is the mask for the 'liars, sinners and hypocrites' of Dungatar (6) . Though on the surface the town appears respectable, the true desires of 'the sour people of Dungatar' are revealed through their desire 'to look better than everybody else’. Their lack of connection with the outside world forces their constant interaction with one another and means that 'everybody knows everything about everyone' (7) . Thus, Miller and Ham postulate that geographical isolation inevitably forges unyielding social norms that repress human emotions and pits individuals against each other (8) .
Annotations (1) In these two sentences, I’ve provided the geographical context of Salem. (2) My description of the geographical location is followed quickly by describing the town’s beliefs and values, which have a large impact on the social context. (3) Here, I’ve used the geographical context as a metaphor to explain the social context of Dungatar. (4) I’ve described a similarity between the two towns - remember to use lots of meaningful comparisons in all paragraphs ( LSG’s CONVERGENT and DIVERGENT strategy is a useful strategy for this). (5) I’ve detailed how the societal expectations and values of the Salemites (the people of Salem) can impact the behaviour of the characters. (6) Here, I’ve outlined a subtle difference (or divergence ) between Dungatar and Salem. (7) Once again, I’ve related the townspeople’s values and beliefs, as well as the physical context, to their behaviour. (8) I’ve ended with a meaningful comparison between the intent of the two authors.
Looking for more? Check out our other blog posts on The Crucible and The Dressmaker :
The Crucible by Arthur Miller
The Dressmaker by Rosalie Ham
Comparing The Crucible and The Dressmaker
1. 'The fantasy never got beyond that—I didn't let it—and though the tears rolled down my face, I wasn't sobbing or out of control. I just waited a bit, then turned back to the car, to drive off to wherever it was I was supposed to be.'
Compare how a perceived sense of control shapes characters in both Never Let Me Go and Stasiland .
2. Compare how the texts explore the importance of memory in defining identity.
3. 'To conform is to be safe and to survive.'
Compare how this idea is examined in both texts.
4. 'I'll have Hailsham with me, safely in my head, and that'll be something no one can take away.' (Never Let Me Go)
Compare how these texts explore the consequences of denying history for affected individuals.
5. Compare how Never Let Me Go and Stasiland examine what it means to be human.
6. Compare how both texts explore the influence of being an outsider on one's understanding of society and their place in the world.
7. 'This society, it was built on lies – lie after lie after lie.' ( Stasiland )
Compare what the two texts say about wilful ignorance in society.
8. 'It is impossible to be free when you are unaware of your confines.'
Compare how the two texts explore freedom and confinement.
9 . 'When I got out of prison, I was basically no longer human.' ( Stasiland )
'Poor creatures. What did we do to you?' ( Never Let Me Go )
Compare how Never Let Me Go and Stasiland explore how humanity can be irreparably broken.
10. Compare how these texts examine the sacrifices required for societal progression and change.
11. Compare what the two texts say about the inevitability of change and being forgotten.
12. Compare the ways these texts explore the influence of different types of human relationships on the individual.
13. 'Things have been put behind glass, but they are not yet over.' ( Stasiland )
Compare how Never Let Me Go and Stasiland demonstrate differing attitudes towards reality and the past.
14. Compare what the two texts suggest about the factors which shape an individual's world view.
15. 'We took away your art because we thought it would reveal your souls. Or to put it more finely, we did it to prove you had souls at all.' ( Never Let Me Go )
'...a soul buckled out of shape, forever.' ( Stasiland )
Compare how Never Let Me Go and Stasiland explore the concept of souls in relation to one's identity.
We all love hacks. Life hacks, game hacks, Netflix hacks (wait, what) ? They're all fabulous. Even better is when we can use English study hacks - because who doesn't want to make English just that much simpler?
Watched the video above already? Awesome! Keep reading for extra life hacks:
Extra hack #11 - don’t just write essays..
There is a massive difference between writing an essay for the sake of writing an essay, as opposed to actively learning when applying your skills. If you feel yourself slipping into the dreaded ‘reusing the same evidence for every essay’, or you’ve somehow ended up doing 5 essay prompts based on the same character – STOP RIGHT THERE. Be proactive. You have to keep switching things up. This means constantly trying new prompts that are more challenging than the last and always trying to find new evidence you can use. Yes, there will always be our go-to pieces of evidence we like to use, like our favourite quote or symbol, but change it up often so that you don’t become complacent.
Extra hack #12 – Unique interpretations
The purpose of develop a unique interpretation of a text or film is so that you can demonstrate originality in your thinking and bring something new to the table that teachers have never come across before. After all, if you’re marking 30 essays in a row, you’d get pretty bored reading the same arguments again and again, wouldn’t you? Try to view the text from different lenses – feminist, Marxist, post-colonial perspective – and these will offer you new ways of interpreting the story.
Extra hack #13 – FOCUS
Some books can be very long (and no, we’re not talking about don’t need to go into detail with every single passage. Instead, have a selection of passages throughout the book that you know really well. It’s much better having an in-depth understanding of fewer passages, but produce a sound essay than to have a superficial overview of the book and struggle to write much at all!
English is not easy, but it doesn’t need to be hard either. Adopt only a few of these hacks and see your improvement in English – they really do work! Keep it up!
Get exclusive weekly advice from Lisa, only available via email.
Power-up your learning with free essay topics, downloadable word banks, and updates on the latest VCE strategies.
latest articles
Check out our latest thought leadership on enterprise innovation., walkthrough of a full scoring vce oral presentation.

How To Incorporate Sunset Boulevard's Cinematic Features Into Your VCE Essay

VCE Creative Writing: How To Structure Your Story

Keep in touch
Have questions? Get in touch with us here - we usually reply in 24 business hours.
Unfortunately, we won't be able to answer any emails here requesting personal help with your study or homework here!

Copyright © Lisa's Study Guides. All Rights Reserved. The VCAA does not endorse and is not affiliated with Lisa's Study Guides or vcestudyguides.com. The VCAA provides the only official, up to date versions of VCAA publications and information about courses including the VCE. VCE® is a registered trademark of the VCAA.
03 9028 5603 Call us: Monday to Friday between 3pm - 6pm or leave us a message and we'll call you back! Address: Level 2 Little Collins St Melbourne 3000 VIC

How to Write a VCE Argument Analysis for English

Are you unsure where to begin with the VCE argument and language analysis? If so, you’ve come to the right place.
The argument analysis essay is usually introduced in Year 11 English, and a part of your final exam in VCE English. Unlike your analytical or comparative pieces you are unlikely to have had much practice writing this type of essay in earlier years.
To get you started on how to write your argument analysis response, we have compiled everything you need to know right here!
Let’s get started!
What is the VCE Argument Analysis? Types of Pieces for Argument Analysis What Makes a Good Argument Analysis? Consider the Following Before Writing Your Response How to Write Your VCE Argument Analysis
What is the VCE Argument Analysis?
The VCE Argument and language Analysis is one of three types of responses you are assessed on in Year 11 and 12 VCE English .
You are presented with an article from a source such as a newspaper and you are then asked to analyse the language that the writer has used, as well as how they convince an audience of their stance on an issue.
Make sure you’re ready for everything in the VCE English Language Study Design and read our guide !
Access our sample VCE Argument and Language Analysis
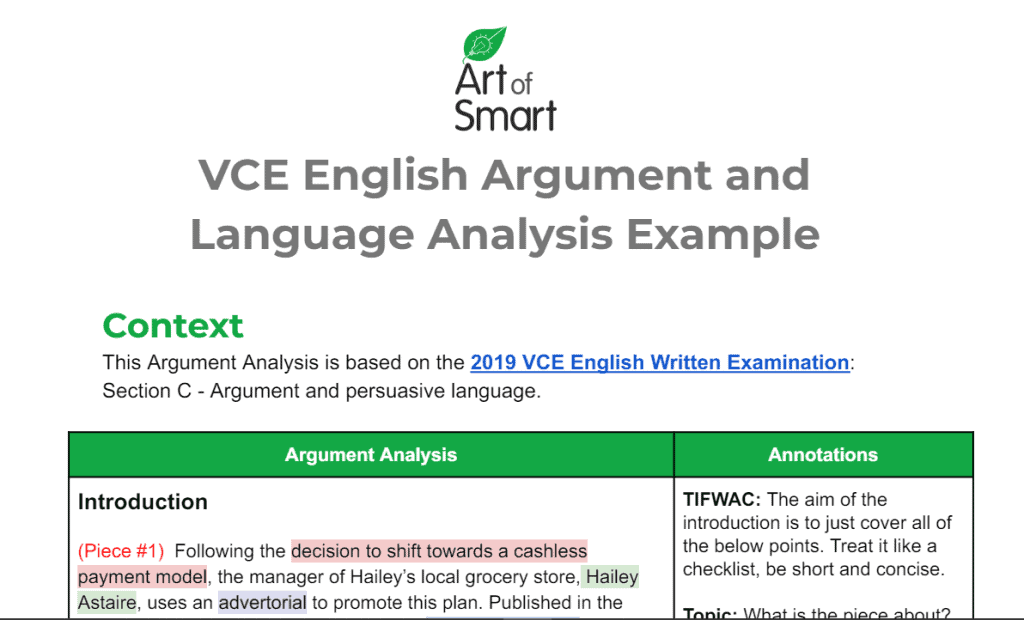
Types of Articles for Argument Analysis

An editorial has the insignia of the newspaper in which it is published, and does not have the name of the writer . This type of article should be referred to as an editorial, an article or with the name of the newspaper when referred to in your response.
Want a deeper dive on the different types of feature articles? Check out our complete guide to writing feature articles !
Letter to The Editor

A letter to the editor has the name of the writer and the place from which they have come . These articles are typically shorter in length and should be referred to with the writer’s last name, as a letter or an article.
Opinion Article

An opinion article has the name of the writer and their credentials . These are generally longer articles . Can be referred to as an opinion article or by the last name of the writer.

The cartoonist’s name should be found on or near the illustration . Watch for what occupies much of the cartoon to show impactful analysis. Make sure to analyse what is presented in the foreground as well as the background.
Note: Not every article you will be asked to analyse will be from a newspaper, they may also be from a blogpost or a post from an online forum. It is important to identify precisely what type of article you have been presented with , so you can gauge why the article has used specific language and the specific audience they are targeting. Additionally, you also tackle some non-written texts in your SACs:

The alternative pieces you need to analyse require a different approach. For audio pieces, you need to take note of everything you notice throughout the piece . This can range from tone, talking speed, volume, language techniques, argument techniques and so on.
After the audio has been played, try organise your notes chronologically: beginning, middle and end . Just like with an article, you want to discuss everything in order. This will be your structure for the analytical piece.
Outside of that, everything else is the same, you write the same way, discuss the same components, and have the same analytical structure.
My biggest tip is to not overcomplicate it ! If you can write an analysis for an article you definitely can do one for a visual piece!
Audio Visual

In these pieces, on top of analysing speech, you need to analyse what you see. This means taking note of imagery, so you’ll need to find some imagery techniques for use in your analysis. Some imagery techniques could include:
English Visual Techniques Example
English visual techniques help convey a message in the form of an image. They may be used in many forms of still media like photos, picture books, book covers and photos.
| Techniques | Definition |
|---|---|
| Allusions | Sometimes in the form of a parody (referencing another image but making it humorous), these usually recontextualise or “change the meaning” of the original media. |
| Angles/lines | The ‘direction’ of an image based on the angles or lines within it. Horizontals create a sense of calm, verticals a sense of structure and diagonals a mood of unease or being off balance. |
| Body Language | . Often focussed on overall body movement and positioning. |
| Close-up Shot | When the frame is mostly or entirely filled with a character’s face, an important object, etc. Used to create viewer focus and show that whatever is being shown is important. Often used on character’s faces in highly emotional images. |
| Colour (Hue/Tones) | . Purple is a colour of royalty, wealth and luxury whereas red symbolises lust, passion, anger and so on. Also consider how saturated colours are (are they bright and vivid or dull and desaturated?). |
| Composition | What an image is made up of – , etc. This generally refers to the image as a whole. |
| Contrast | Placing things that are considered opposite close to each other. Contrasts can be (black and white), (large and small), (rough and smooth), etc. to create interest and complexity. One small contrasting colour/size/shape in an image is also usually highly salient because it stands out. |
| Framing | The camera shots and angles used in images/films to create different audience reactions and emotions. E.g. close-up, extreme close-up, mid shots, aerial shots, etc. |
| Gaze | Where a character looks, which then directs viewer’s eyes. A ‘demand’ gaze involves direct eye contact between a character and the viewer, an ‘offer’ has the character look at something within the image, drawing the viewer’s eyes there too. Can also be used to express emotion/intent. |
| High Angle Shot | A shot taken from slightly above something/someone, looking down on it/them. Creates a sense of the character being weak, helpless, intimidated, etc. May also be used to represent someone literally looking down at an object/scene (point of view). |
| Law of Thirds | By dividing an image into equal thirds along the horizontal, the vertical axis you can break it into 9 equal sections which each have different connotations, Movement is expected to from the left thirds to the right thirds, otherwise it’s read as moving backwards (literally or figuratively). Characters in the top right third are seen as powerful or in control, while those in the bottom left thirds are weaker or being controlled. |
| Lighting | How a shot is lit or not lit. This includes natural lighting (the sun, open windows, etc.) and man-made lighting (lamps, torches, etc.) as well as feature lighting such as coloured lights, spotlights, moving lights, etc. Lighting has a major impact on the mood and atmosphere of an image (low light is seedy, harsh light is unnerving, soft light is intimate, etc.). |
| Long/Wide | A shot that is made up of a large landscape, cityscape or other kind of scene, Generally these are used to get across lots of information at once, such as the layout of a room, the location of an event, the number of people around, etc. |
| Low Angle Shot | A shot taken from slightly below someone/something, used to present them/it as being in a position of power, dominance or control. It may also be used to have someone literally look up at someone/something (point of view) |
| Mid Shot | A shot that is approximately half-filled with a figure, object, etc. Usually these are ‘regular’ shots and are very common for character conversations/interactions or showing a select area or object within an area (a desk, chair, etc.). |
| Point of View | . Does the shot take the character’s point of view (a shot of a character leaning out a window cutting to an aerial shot looking down from a window) or is the audience placed level with, above or below the characters/objects/action? |
| Positioning | Where have objects and characters been placed in the shot? What is in the foreground, middle ground and background and why have they been placed there? |
| Salience | How much any section of an image draws the viewer’s eyes – the most salient feature of an image is whatever/wherever the viewer’s eyes are first drawn when they look at it. Salience is always deliberate and usually created through contrast, colour, framing and layout. |
| Symbolism | . Religious symbolism, pop culture symbolism and animal symbolism are all very common. |
| Text | Words used within images to convey a literal or figurative message. Consider the font, colour, size, weight, etc. of the text, where and how often it has been used and the connotations of the words actually used. |
| Vectors | The lines or paths viewer’s eyes follow when looking at an image, usually vectors are deliberately created to lead the eyes to a focal point or important feature. Because we read left to right we tend to follow vectors in the same direction across an image. |
Film-specific Techniques Example
Film-specific techniques are visual tools used to convey messages in film, television episodes, documentaries and other forms of video.
| Technique | Desfinition |
|---|---|
| Aerial Shot | A shot usually taken from a crane or helicopter to show a landscape, city, or many other elements within a single moving shot. Usually these are used to establish settings, large spaces/areas or a sense of scale. |
| Costuming | The clothes, makeup, hairstyles, accessories, etc. designed to be worn by characters to represent their personality, status, heritage, culture, etc. Often characters clothes will fit within one or two similar colour palettes or tones and use fabrics of similar textures. Colour symbolism often comes into play here (a character wearing earthy colours may be associated with gardening, plants and nature). |
| Cut | The splicing of two shots together so that one seems to instantly move to the other. There are many different types of cuts – jump cuts are more jagged and create a sense of fast pace or deliberately poor editing, match cuts involve cutting between two very visually similar shots to create a more seamless flow. |
| Dialogue | The words spoken by characters. (metaphor, simile, personification, etc.) but also consider etc. as well as their vocal range (does the character have a deep voice? A high, feminine voice?). |
| Diegetic Sound | The ‘literal sound’ created by the objects and people within a shot – sounds that the character is presumed to be hearing as well. This includes; character dialogue, fabric rustling, animals, background noise/voices, sounds made by objects (doors closing, rain), etc. |
| Digital Effects | . Remember that all digital effects are deliberate and have been added for a reason – to change the mood of a shot, change character gesture, etc. |
| Establishing Shot | The shot at the beginning of a film or scene that gives the basic or introductory information to viewers. Generally includes or introduces the location, characters, etc. |
| Fade In/Out | A transition device whereby a shots fades into or out of black (or another image) at the end or beginning of the shot respectively. These are generally used to create a sense of slow movement, intimacy or ‘trailing off’ in a shot/scene. |
| Montage | The cutting together or several shots that show small pieces of a larger scene or idea to create an overall sense of time passing/something occurring. Most commonly used in training sequences where a character must become skilled in a task over time, so many shots of them completing different training exercises are cut together to create a sense of them improving over time. |
| Non-diegetic Sound | The ‘non-literal sound’ that has been added into a shot that the characters cannot hear. This includes; narration/voice-over, added sound effects, music (that isn’t shown to be produced from an onscreen source such as a tv, dance party, etc.) and the film score/soundtrack. |
| Props | . Generally the most important props are those used or seen as important by characters, as well as recurring props that feature in several different scenes/shots throughout the film. |
| Voice-over | Audio narration laid over the top of a shot’s regular soundtrack. . |
Tip: Don’t try to use and understand all of these techniques. Just use the ones that work best for you!
What Makes a Good Argument Analysis?
The concept and structure of an argument and language analysis are fairly simple to get your head around, therefore it is important to pay attention to some close details that will make your analysis of a particular article stand out.
Here are some tips!
Check out our definitive guide to each VCE English SAC text response !

Tip #1: Have a Good Understanding of the Issue
Before you begin to analyse the writer’s persuasive techniques, it’s important that you have a thorough grasp on what they are trying to persuade the audience of .
This helps you better understand their techniques thereby resulting in better quality analysis. To achieve this make sure that you read the article slowly instead of rushing through it and take note of the title , as it is a good indicator for what you are going to read.
Tip #2: Plan Your Response
Argument analysis essays are very structural , and so there are certain aspects that you should be including in every single one of your responses.
By taking advantage of this ‘ticking the boxes’ approach , you can assure that you will receive marks by including certain things in your response. This includes the contention of the writer, target audience and the tone of the writer.
Tip: To make sure you include all of these points in your final essay, you should use the VCE Argument Analysis template for each response until it becomes intuitive.
Tip #3: Vary Your Sentence Structure
Whilst having a structure is necessary, you should also consider the flow of your piece .
It is easy to fall into using repetitive sentence structures , with a pattern of bringing out the evidence from the article, followed by the persuasive technique that the writer is using, and then the impact it has on the reader.
Whilst it is important to include these in your essay, it should not be written in a choppy and disjointed manner .
Tip: In some parts of your essay, you could start by highlighting how the readers are positioned and then expand on how the writer has done this, in order to provide some variation .
This requires a bit of practice, so be patient and keep trying!
Tip #4: Don’t Quote Everything in Your Essay
It’s normal to feel overwhelmed by the amount of text that you are presented with in an article, as well the short amount of time you have to analyse it. As surprising as it may sound, to write a good VCE argument analysis you do not need to analyse everything .
Instead, it is about how you pick out good pieces of evidence and show quality analysis .
A good way to choose the best evidence is to imagine you’re presenting a speech. Check out our guide to Acing Your VCE English Oral Presentation !
When you find a piece of evidence that you’re planning to use in your essay, don’t quote the entire thing . Instead, you should pick the few words that really make an impac t and show deep analysis of those. For example :
‘From the outset, Gill criticises the long-standing “intransigence of political leaders” towards pill testing. Through utilising the term “intransigence,” the health officials are led to feel attacked having been labelled unyielding and stubborn, reflecting Gill’s earlier claim that they are incapable of looking beyond their own limited experience.’
Tip #5: Use Specific Vocabulary for Tones and Persuasive Words
Of the details that sets apart an excellent analysis from an average one, the use of specific and varied vocabulary is a major distinguisher.
But, vice versa, don’t use extravagant and lengthy words if you are unsure of their exact meanings and relevance — most likely, the examiner can sense when you don’t know the actual meaning of a certain word.
Tip : You should memorise a list of persuasive words and tones as well as their definitions, so that you have an ingrained bank of terms to choose from as you are actively writing your analysis.
Check out our list of persuasive words and tones that we’ve compiled for you!
Persuasive Words
| For | Against | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Discusses | Voices | Attacks | Implicates |
| Accentuates | Overstates | Doubts | Provokes |
| Advances | Understates | Criticises | Mocks |
| Advocates | Concurs | Denigrates | Derogates |
| Asserts | Responds | Dismisses | Contradicts |
| Condones | Contributes | Disputes | Divides |
| Contends | Links | Rebuts | Protests |
| Magnifies | Demonstrates | Refutes | Exposes |
| Promotes | Signposts | Retorts | Challenges |
| Positive | Neutral | Negative |
|---|---|---|
| Amused | Authoritative | Accusing |
| Assertive | Bemused | Admonishing |
| Confident | Considered | Antagonistic |
| Earnest | Controlled | Condescending |
| Encouraging | Measured | Contemptuous |
| Enthusiastic | Pragmatic | Cynical |
Might need some help crafting a VCE Argument and language Analysis? Work with a tutor from our English tutoring Melbourne team !
Consider the Following Before Writing Your Argument Analysis
When you are handed an article and once you’ve read through it, i t’s not the best idea to begin writing your VCE argument analysis straight away . Instead, try and identify the following points :
Points to consider for the introduction:
What issue has the article come as a response to? What is the name of the writer (if applicable), article type, and the title of the article? What are the credentials of the writer? where applicable. Find the main contention of the writer and write it out in your own words
Points to consider for the body paragraphs:
Identify the tone and the target audience of the writer Summarise the main arguments that are used to support the contention Consider the impact of headlines, captions and visuals and decide which argument they belong to Locate and identify words that illustrate the persuasive techniques that are used to support an argument Remember not to judge the quality of the argument, nor give your opinion of it – you are only assessing what intended effect the language is meant to have on the reader.
Access our comprehensive VCE Argument and Language Analysis Structure and Template !
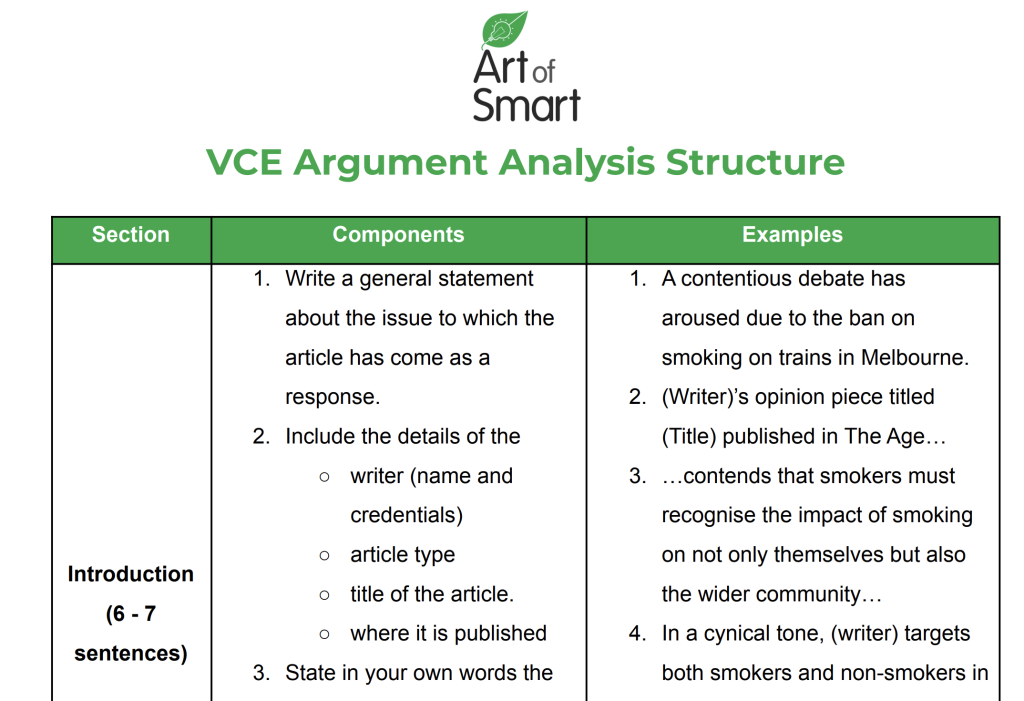
Did you know that you can swap Year 11 English out for English Language in Year 12, or any subject in that case? Check out our guide to selecting VCE subjects!
How to Write Your VCE Argument Analysis
Introduction .
Write a general statement about the issue to which the article has come as a response, this could be as large as a global issue such as the COVID-19 pandemic, or as small as implementing local infrastructure.
Usually, students like to use one of the following acronyms to structure their response:
The TIFWAC acronym gives you a comprehensive template for your introduction.
With TIFWAC, just follow the acronym chronologically in your introduction, one sentence per point of the acronym, and you’ll have your introduction!
There’s no need to add any detail, or summarise your body paragraphs, just follow TIFWAC.

CDFASTCAT is a more detailed version of TIFWAC.
Just like with TIFWAC, you should go through CDFASTCAT in your introduction chronologically. This will ensure you have a perfect introduction structure!
Although, one key consideration with this acronym is that students can fall into the trap of writing too much for the introduction .
So, be very careful with how much you write. Keep it short and concise .

Both acronyms are highly effective and recommended . There is not a better choice of acronym, so just choose the one that suits you best.
You should go through each point of the acronym – one point a sentence – chronologically . If you do this, you’ll have a really nice introduction paragraph.
Now, it’s important to note that you should write the introduction as concisely as possible. No need to elaborate and go on tangents like in an essay.
Just address each point of your chosen acronym structure , make sure it’s clear and concise , then move on to the body paragraphs. Your introduction should take you at most 5 minutes!
Body Paragraphs
What should each body paragraph cover.
Body paragraphs are just as easy. Try and have a BME body paragraph structure, which means:
B: Your first paragraph covers the beginning of the piece. M: Your second paragraph covers the middle of the piece. E: Your final paragraph covers the end of the piece.
Going chronologically works well in the language analysis because you can show how the writer progresses and builds upon their argument throughout the piece.
Also, you can write 3-5 body paragraphs for an argument or language analysis. But try not to write more than 3 pages .
Why? Because occasionally you will have to analyse multiple pieces in one analysis. Here you will have to pivot and make a decision: how many body paragraphs do I use for each piece?
For example, if you need to analyse two articles, you could do two body paragraphs on each, split it to one and three paragraphs or two and one.
Wheras, if you needed to analyse three or four article (which has happened in a VCE exam before) you may have to analyse each piece with a single paragraph!
Additionally, here are some other points to consider:
- Each paragraph addresses only one argument . The arguments should begin with a topic sentence — this can be related to something the writer agrees or disagrees with or is proposing as a solution.
- Analyse how the writer uses the piece of evidence by identifying the underlying persuasive technique. However, there is no need to write out the actual technique that is being used such as simile or hyperbole, instead you should talk about how it is being used.
- Ensure you comment on what effect the language has on the reader and how it positions them to feel.
Ready to smash your VCE Argument and language Analysis? Check out our master list of VCE English Past Papers !
How should each body paragraph be structured?
Body paragraphs for an argument and language analysis should utilise the following structure.
What: what is the writer doing? How: how is the writer doing it? Why: why is the writer doing it? What is their intended effect on the audience.
Think of this as your TEEL structure for essays.
However, you’ll need to repeat the what how why structure 3 to 4 times a paragraph to ensure there is sufficient detail.
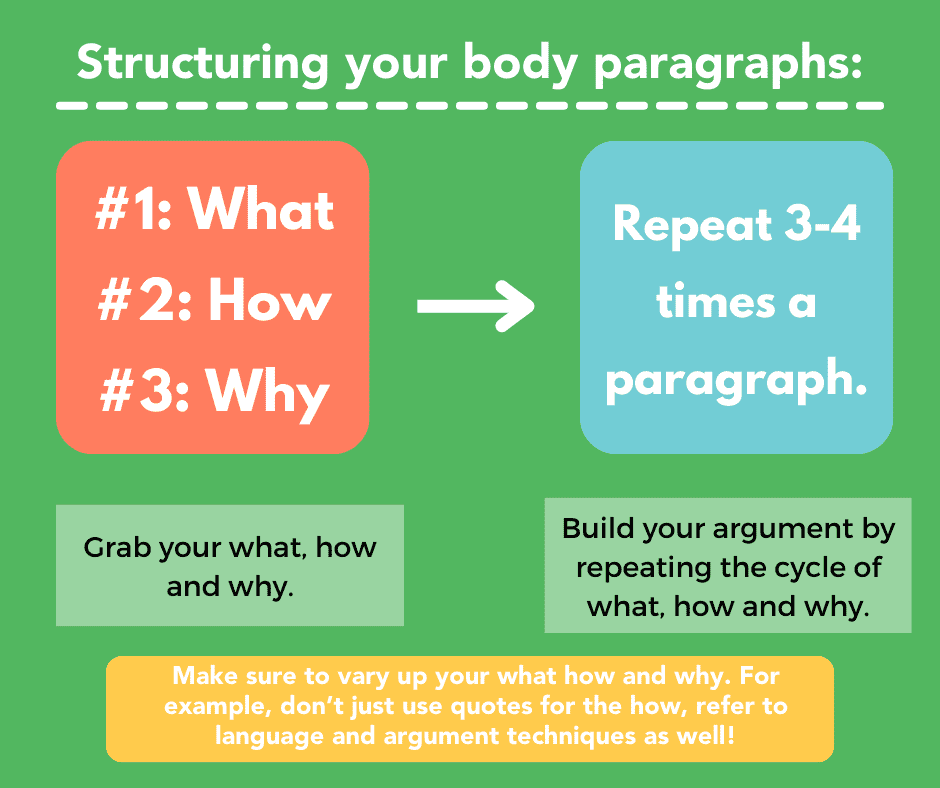
Think of this as the TEEL structure but for an argument analysis . Keep in mind though that you want to repeat the what, how, why cycle at least 3-4 times per paragraph.
This cycle ensures you are identifying how the piece is making arguments and what their arguments intend to do.
Try to place a lot of emphasis on the ‘why’ section of the analysis . This is because showing the marker that you understand how the audience is being effected, and why the writer is trying to effect them in that way, is the most important part of the whole analysis .
Each ‘why’ discussion should have at least 2-3 sentences!
Conclusions are really not that important in an argument or language analysis.
Just outline a brief summary of the argument presented by the writers . Then address how they argued , then finish your piece.
Honestly, most top students don’t use one at all.
Are you looking for some extra help with preparing for your VCE Argument Analysis for English?
We have an incredible team of VCE tutors and mentors!
We can help you master the VCE Argument Analysis and ace your upcoming VCE assessments with personalised lessons conducted one-on-one in your home or online! For Melbourne locals, we’ve got a Melbourne tutoring team that can support you with your English assessments.
We’ve supported over 8,000 students over the last 11 years , and on average our students score mark improvements of over 20%!
To find out more and get started with an inspirational VCE tutor and mentor, get in touch today or give us a ring on 1300 267 888!
Abhisha Vaheesan completed her VCE in 2021 and is currently an undergraduate student studying Bachelor of Radiography and Medical Imaging (Honours) at Monash University. As much as she is invested in Biology and putting together the building blocks of life, she is equally immersed in debating the conflicts of modern literature. Aside from this, she loves listening to music, is an avid writer and K-drama fanatic.
- Topics: ✏️ English , ✍️ Learn
Related Articles
How to write a captivating feature article (examples + structure), the comprehensive guide to acing your vce english oral presentation, everything you need to know from the vce english language study design, 45,861 students have a head start....
Get exclusive study content & advice from our team of experts delivered weekly to your inbox!

Looking for English Support?
Discover how we can help you!

We provide services in

Please login to system to use all resources
Search the forums now!
We have moved.
We want to extend a heartfelt thanks to everyone who has made the original ATAR Notes forum such a helpful, warm and welcoming place. Your contributions are appreciated and we will be leaving the forum in archive mode for posterity.
Please visit our new website and discussion area .
Welcome, Guest . Please login or register.
- ATAR Notes: Forum »
- VCE Stuff »
- VCE Subjects + Help »
- VCE English Studies »
- VCE English & EAL »
- VCE English Premier Award - Free Resources - Creative Essay
Author Topic: VCE English Premier Award - Free Resources - Creative Essay (Read 8859 times) Tweet Share
0 Members and 1 Guest are viewing this topic.
- Respect: +7
Re: VCE English Premier Award - Ask me anything
Stormbreaker-x.
- Forum Leader
- Respect: +31
Hi all, My name is Julian and I was fortunate enough to receive a Premier's Award for VCE English. I know it's been a tough year for everyone, so I want to help by going over some common questions and my sample essays in a video format (all FREE of charge)? Would anyone be interested? Thanks, and feel free to ask me anything J (mods, if this post doesn't belong here, feel free to move it)
How did you revise for English exams?
Can you share some sentence stems you used for section C?
SmartWorker
- Forum Obsessive
- Wake determined. Sleep Satisfied.
- Respect: +79
Had a few questions: 1) How do you suggest to compare two texts in comparative? Do you compare throughout the body paragraphs or is more like the first half the body paragraph is text 1, linking sentence, 2nd half: text 2? Can you also share an example? 2) How do you come up with arguments? 3) How many body paragraphs did you write for each section? Thanks!
Thank you for your reply! I was also wondering how you come up with arguments for Section A/B?
woahjustjkingchill
can we see your comparative essay(s), on the longest memory and the 7 stages of grieving? also thanks for the thread <3
Re: VCE English Premier Award - Free Resources - Ask me anything
- Forum Regular
- Respect: +3
Recent Posts
A Step-by-Step Approach to Crafting High-Scoring Comparative Essays
Comparative essays might seem daunting, but this article is here to help. Let’s unpack exactly what is required, break down the structure, and aim for those top marks!
9 months ago • 5 min read
Comparative writing is mostly relevant for English subjects, especially at the ATAR level. Comparatives vary between states – in VCE, the Comparative SAC asks a question specific to the texts studied. In WACE English, comparatives are simply a type of question offered under Responding and are broadly applicable across texts. In the HSC comparative writing is imbedded into Mod A - textual conversations and even in short response questions.
Nevertheless, the general premise of the Comparative Essay is universal and this article is for all English students ; no matter the year level or state syllabus.
What is a comparative?
A comparative is just like any other analytical literary essay, but with a catch – instead of analysing one text, you compare two.
You will need to craft an argument which addresses what makes the two texts similar and what is different. You will need to read the essay question carefully and work out what the two texts have in common , and for which concept you should argue there is a difference .
Let’s look at some examples:
Q. Compare how two texts of different genres endorse a similar perspective.
Similar : Perspective
Different : Genre/generic conventions used
Example thesis: Texts A and B both endorse a pacifist, anti-war perspective, however, Text A achieves this through lighting and sound effects, whereas Text B employs poetic structure and rhyme scheme.
Q. Analyse how two texts employ characterisation to encourage different reader responses.
Similar: Characterisation
Different: Reader Response
Example thesis: Text A employs vivid characterisation of its protagonist to evoke readers’ empathy and affection, whereas Text B’s intense characterisation encourages a response of tension and discomfort.
Q. Compare the representation of the ‘ideal man’ in Text A and Text B
Similar: Ideal Man
Different: Representation
Example Thesis: Whilst both texts provide vivid constructions of the ‘ideal man’, Text A’s representation is an adaptable intellectual, whereas Text B represents the ideal man as stubborn and brawny.
Q. Discuss how two texts’ differing contexts of production affect their perspective on an issue.
Similar : Issue
Different : Perspective, context
Example thesis : Text A (1950), influenced by a restrictively patriarchal climate, presents a dismissive perspective that violence towards women is peripheral and harmless, whereas Text B (2018), created during the #MeToo movement, suggests that it is urgent and devastating.
For some comparatives, it might also make sense for your thesis to include the extent to which the texts are similar/different.
Writing your Comparative: Step-by-Step
1. understand your texts and why they work together.
There’s no point comparing apples and oranges! It’s important to know why your texts complement each other for a comparative essay. What do they have in common?
2. Deconstruct the question.
Try colour-coding key terms – for example, command words, similarities and differences. E.g. Compare how two texts employ conventions of the same genre, to explore different ideas.
3. Write your thesis/contention.
This should answer every aspect of the question. If you’ve colour-coded your question, make sure each colour is addressed.
4. Gather evidence.
It’s to find relevant evidence and quotes to back up your argument! This should be a rough 50/50 split between each text.
5. Have a list of comparative language handy!
Your reader/marker shouldn’t become confused about which text you’re talking about. Here’s some great comparative language for clarity and flow:
SIMILARITIES:
- Similarly
- Likewise
- In a similar vein/fashion/manner/way
- In parallel
- Additionally
- Equally
- Comparably
- Correspondingly
- Also, as well, too
- Just as
DIFFERENCES:
- Conversely
- Contrarily
- In contrast
- As opposed to
- Otherwise
- However
- Alternatively
- Instead
- Yet, but
- On the other hand
- Whereas
- Differently
- Unlike
- Although
- Compared to
- Meanwhile
6. Organise points and paragraphing.
A comparative should have an introduction and conclusion, just like any other textual analysis essay. They’re the bread holding your essay together.
Introduction:
- Hook or global statement
- Introduce your texts (brief synopses/plot summaries, relevant contextual information)
- Thesis / Contention / Central Argument
- Roadmap of your essay (i.e. signpost what your body paragraphs are each going to cover)
Conclusion:
- Reiterate argument
- Summarise points
- Final remarks about potential relevance of argument, significance, extent of similarity of the texts, etc.
But what about the middle of the sandwich? Usually, you will have four body paragraphs, but there are a couple of different ways to structure them:
Comparative Essay Structure

The point-by-point method is usually regarded as more sophisticated and will award you better marks.
This is because the comparison is better integrated into the analysis and demonstrates a more nuanced expression. However, the block is suitable for earlier stages (e.g. Year 9/10 level), or the texts you are comparing do not align precisely per point.
If you want to reach for those very top marks, you can take the point-by-point method even further, alternating more frequently between evidence from Texts A and B for even more specific comparison. This is sometimes called…
THE RAINBOW METHOD:
My final tips for top marks (from a 99.95 graduate)
- Maintain your 50/50 text balance
- Use specific evidence
- Use terminology from the question
- Ensure your discussion of the two texts interacts – it shouldn’t feel like two separate essays awkwardly glued together
- Consider why the texts are different, particularly in your conclusion. What is the significance?
Good luck, and happy comparative writing!

Want more personalised tips to drastically improve your English mark? A private tutor can make the biggest difference!
Written by KIS Academics Tutor from WA, Poppy Bell. Poppy received a 99.95 ATAR and is currently studying Arts/Law at the University of Melbourne (Chancellor’s Scholar). Poppy tutors English, Literature, Mathematics, Modern History, and French. You can view Poppy’s profile and glowing reviews here and request her as a tutor.
- High School
Spread the word
Cracking the code: achieving a perfect ib english score, navigating naplan: strategies for year 5 achievement., keep reading, how to write a band 6 module b critical study of literature essay, how to respond to short answer questions in vce english language, how to craft a band 6 mod a textual conversations essay, subscribe to our newsletter.
Stay updated with KIS Academics Blog by signing up for our newsletter.
🎉 Awesome! Now check your inbox and click the link to confirm your subscription.
Please enter a valid email address
Oops! There was an error sending the email, please try later
1300 914 329
- ★ ★ ★ ★ ★ 5 star rating from 5000+ verified reviews

How to write a VCE comparative essay
- by The Alchemy Team
Comparative essays are an important part of the VCE English syllabus. Also known as ‘Reading and Comparing’, and ‘Compare and Contrast’ questions, these essays involve analysing and comparing the similarities and differences between two texts.
Lots of students worry about writing a comparative essay because putting two texts into the mix seems complex. Thankfully, there are lots of ways you can tackle this ‘beast’, and hopefully even pick up a top band mark in doing so.
Understand what’s being asked
First and foremost, you need to be crystal clear about what’s being asked of you. You’ll know you’re being asked to write a comparative essay if the topic contains key verbs like ‘compare’.
The topic might require a detailed comparison of the way the texts construct their respective settings, or the ways that named characters are developed. It could even be that you’re asked to provide a much broader thematic comparison that compares and contrasts how a certain theme is explored and discussed by the texts.
Why not also read: How to analyse an HSC English text
You should also be ready to face a topic that focusses on a few quotes from the texts. For these questions, you’ll need to have a complete knowledge of your subject matter, since you’ll need to recognise the context of the relevant quotes.
As with most things in VCE English, knowing your texts is the key to scoring high marks in a comparative essay.
Give equal attention to the texts
Students often fall into the trap of focussing too heavily on one text over another, so be careful not to limit the scope of your essay.
Keep in mind that you’re being asked to compare the texts for similarities and differences – and you can’t do that effectively unless you maintain a balance between your discussion of them. Make sure that every point you make references and provides evidence for both texts.
Keep your essay structured
Comparative essays can seem daunting to start with, but the good news is that they follow a broadly similar structure to any other academic essay. This means that you’ll need to work in an introduction, several body chapters full of analysis, and an insightful conclusion.
You should be sure to set the tone of the essay from the beginning – which means summarising the point you’re going to make. Remember, the most effective essays follow a similar rule: tell them what you’re going to say, say it (with evidence), and then tell them what you’ve said.
It’s in the body paragraphs that comparative essays most obviously differ from other formats. This is because you need to find a way of comparing two texts in a fairly even-handed way. You can achieve this by using one of two methods – the block approach or the woven approach .
Why not also read: How to Study for the HSC English Exam
The block approach involves addressing each text in turn, with a few paragraphs for each. This might seem simple, but the challenge with this approach is to maintain the connection between the texts as you make your point. You’ll need to be very careful to use plenty of linking words (more on that later) and should avoid any lengthy passages that simply recount the events or techniques found in one text or another.
The woven approach , in contrast, is a way to provide a more direct comparison between the texts – with your analysis and evidence for each sitting side by side in the same paragraphs. It’s best to look at this approach as a fluid analysis with each paragraph making an individual point before going on to illustrate how the two texts achieve a similar (or altogether different) result.
How you write your comparative essay is up to you, but you absolutely must keep the focus on both texts whichever route you choose.
Draw attention to similarities and differences
It’s easy enough to recognise similarities between different texts, but the very best marks are reserved for students who draw attention to the key differences too.
By bringing in the factors that separate two texts, you can demonstrate your wider knowledge whilst having even more literary techniques and devices to talk about. If you can balance the ideas contained within the two texts, you’ll stand a good chance of impressing the examiners.
Link your discussion of the texts
All too often, students get drawn into recounting the relevant texts when they should be comparing them. Remember, you’re being asked to draw parallels and explore the differences between texts, so you should always be careful to avoid writing about them separately.
To help the examiner understand that the ideas you’re discussing are connected, be sure to use plenty of linking words and phrases. These might include:
Similarly, in contrast, conversely, in the same way, X distinguishes text A from text B
Don’t ignore the wider context
The topic for your comparative essay will probably focus in on a particular character or theme, but that doesn’t mean that you have to limit your answer to those elements alone. The highest-scoring essays have depth, and that means drawing on other textual elements to make and evidence your point.
If you can bring in other areas of comparison (for instance, the way another theme is treated by the texts) then there’s a good chance your essay will be more compelling and attract higher marks. Just make sure that any other literary techniques or textual elements you reference don’t steal the spotlight from the focus of the topic.
VCE English tutoring – a crash course on comparatives
Since 2005, Alchemy Tuition has worked with thousands of students – many of which needed help to get to grips with writing comparative essays.
Our friendly and knowledgeable private English tutors are surprisingly affordable, and having completed the same exams and assignments, they really know their stuff.

Search our archive:

Recent posts:
- What to do when your child fails an exam
- How to do active learning
- How can tutoring nurture smart kids more
- How tutoring can develop life-essential skills for kids
- Benefits of tutoring for primary school students

- Selective School
- Uncategorised

Get in touch
Let's create gold together.
Our office is closed from the 17th of December and will re-open on Wednesday the 4th of January 2023.
During this time you can still book a tutor here and we will get in touch to confirm when we re-open!
Office hours: Monday–Friday | 9AM–9PM AEST
We come to you
All suburbs of Sydney, Melbourne and Brisbane or online everywhere.
AN ELITE EDUCATION AUSTRALIA PTY LTD COMPANY Level 36/1 Farrer Place, Sydney NSW 2000 ABN: 88606073367 | ACN: 606073367


IMAGES
COMMENTS
Below are the VCE criteria for Comparative essays (sourced from the VCAA English examination page). Note: Some schools may express the following points differently, however, they should all boil down to the same points - what is necessary in a Comparative essay. ... Juxtaposed with Blair's introduction is the stoic Queen Elizabeth II, residing ...
The comparative essay, in only its second year of being on the VCE English syllabus, is a cause for confusion for many students and teachers alike. Read on for one simple way to structure a comparative essay. Comparative essay structure How to write an introduction for a comparative essay. This can be structured in much the same way as a text ...
Introduction and Key Themes of Reckoning and The Namesake. Families. Love them or hate them, everybody has a family in some shape or form. ... Topics for comparative essays are usually pretty ... Authorial intent is without a doubt one of the most important parts of any analytical essay in VCE English because talking about it is what offers the ...
Comparative Essay Structure - VCE - 2020 EditionThings to mention, ways to sequence it. All that stuff, eh?🌎 My website: http://www.stevenkolber.com📱 Twitt...
Step 2: Introduction. Now that you've got all the planning out of the way, next comes beginning the essay and writing up your introduction. Having a top notch introduction not only sets the standard for the rest of your language analysis, but it gives you a chance to set yourself apart from the crowd.
The comparative essay is still a relatively new element of VCE English, only becoming part of the Study Design in 2016. However, while the Area of Study is new, your essay should still have a clear and largely familiar structure, with an introduction, body and conclusion.
Introduction to Writing a VCE Comparative Essay The Importance of Comparative Essays in VCE When tackling the VCE English curriculum, one quickly realizes the significance of comparative essays.
Just when you thought you had finally become accustomed to the complicated art of essay writing, VCE decides to throw you a curveball in the form of a reading and comparing essay that addresses not just one, but two texts. Being introduced to a comparative essay for the first time, it is not surprising that many students encounter difficulties in structuring their writing.
Reading and Comparing essays. Lisa Tran. August 29, 2016. To elaborate further on the example using Macbeth and Animal Farm: Avoid simply drawing connections between the texts which are immediately obvious. It is clear that both Napoleon and Macbeth are powerful leaders. The questions below start to delve into a more insightful comparison ...
It usually goes: 1 - Introduction using OUTCAST structure, if your SAC has two texts, it's OUTCASTCAST, 3 texts would be OUTCASTCASTCAST and so on. 2 - Analysis of text A 3 - Comparison of text A to B 4 - Analysis of text B 5 - Comparison of text B to C 6 - Analysis of text C 7 - Conclusion. 1. Reply.
In this article, we will teach you how to write a comparative essay, including Y12 Module A Textual Conversations requirements, different comparative essay structures, dos and don'ts, and an exemplar paragraph of both structures.
Yo yo yo! It's time for a fun-filled-caffeine-fuelled-crash-course in the Comparing Texts Area of Study! Since everyone in Year 12 seems be hitting this delightful brick wall of confusion at the same time, what follows is an overview of the most optimal ways to structure your essays to achieve high marks in your Unit 4 SAC, and in the exam Of course, there are different ways of approaching ...
The VCE Comparative Text Response (reading and comparing) is the assessment that makes up the most marks for school assessed work, and so it is essential to ...
Like its name, Text Response is when you respond to a text. The most popular texts are novels and films; however plays, poetry and short stories are also common. Your response will be in the form of an essay, in which you discuss themes, ideas and characters. Recall all the novels and films you've studied since Year 7 (there'll be quite a few!). You should be very familiar with the process of ...
Section A - Your Analytical Interpretation of a Text. The first text response within your VCE English examination will require you to pick a text in which you have studied thoroughly in Unit 3 and write your own analytical interpretation of the text. The exam will provide two essay questions for each text and you will choose one to respond to.
Tip #4: Don't Quote Everything in Your Essay. It's normal to feel overwhelmed by the amount of text that you are presented with in an article, as well the short amount of time you have to analyse it. As surprising as it may sound, to write a good VCE argument analysis you do not need to analyse everything.
A Kolber introduction to writing the comparative text response essay in VCE English. Some hints and tips to help you succeed from 2 very experienced VCE Engl...
I found this section the most difficult.Essay:https://1drv.ms/w/s!AjziWiBP3e6shBj0acMxljSnmFl7Remember to comment 'I will ace the UCAT' in my previous video ...
My name is Julian and I was fortunate enough to receive a raw 50 and a Premier's Award for VCE English in 2020. I know it's been a tough year for everyone, so I want to help by going over some common questions and my sample essays in the format of Youtube Videos (all FREE of charge) I've attached my full sample essays and an introduction video ...
A Step-by-Step Approach to Crafting High-Scoring Comparative Essays. Comparative essays might seem daunting, but this article is here to help. Let's unpack exactly what is required, break down the structure, and aim for those top marks! Comparative writing is mostly relevant for English subjects, especially at the ATAR level.
Comparative essays are an important part of the VCE English syllabus. Also known as 'Reading and Comparing', and 'Compare and Contrast' questions, these essays involve analysing and comparing the similarities and differences between two texts. Lots of students worry about writing a comparative essay because putting two texts into the mix seems complex. Thankfully, there […]