

Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving (8D)
– Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving –
⇓ Introduction to 8D
⇓ What is 8D
⇓ Why Apply 8D
⇓ When to Apply 8D
⇓ How to Apply 8D

Introduction to Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving (8D)
The Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving (8D) is a problem solving methodology designed to find the root cause of a problem, devise a short-term fix and implement a long-term solution to prevent recurring problems. When it’s clear that your product is defective or isn’t satisfying your customers, an 8D is an excellent first step to improving Quality and Reliability.
Ford Motor Company developed this problem solving methodology, then known as Team Oriented Problem Solving (TOPS), in the 1980s. The early usage of 8D proved so effective that it was adopted by Ford as the primary method of documenting problem solving efforts, and the company continues to use 8D today.
8D has become very popular among manufacturers because it is effective and reasonably easy to teach. Below you’ll find the benefits of an 8D, when it is appropriate to perform and how it is performed.
What is Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving (8D)
The 8D problem solving process is a detailed, team oriented approach to solving critical problems in the production process. The goals of this method are to find the root cause of a problem, develop containment actions to protect customers and take corrective action to prevent similar problems in the future.
The strength of the 8D process lies in its structure, discipline and methodology. 8D uses a composite methodology, utilizing best practices from various existing approaches. It is a problem solving method that drives systemic change, improving an entire process in order to avoid not only the problem at hand but also other issues that may stem from a systemic failure.
8D has grown to be one of the most popular problem solving methodologies used for Manufacturing, Assembly and Services around the globe. Read on to learn about the reasons why the Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving may be a good fit for your company.
Why Apply Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving (8D)
The 8D methodology is so popular in part because it offers your engineering team a consistent, easy-to-learn and thorough approach to solving whatever problems might arise at various stages in your production process. When properly applied, you can expect the following benefits:
- Improved team oriented problem solving skills rather than reliance on the individual
- Increased familiarity with a structure for problem solving
- Creation and expansion of a database of past failures and lessons learned to prevent problems in the future
- Better understanding of how to use basic statistical tools required for problem solving
- Improved effectiveness and efficiency at problem solving
- A practical understanding of Root Cause Analysis (RCA)
- Problem solving effort may be adopted into the processes and methods of the organization
- Improved skills for implementing corrective action
- Better ability to identify necessary systemic changes and subsequent inputs for change
- More candid and open communication in problem solving discussion, increasing effectiveness
- An improvement in management’s understanding of problems and problem resolution
8D was created to represent the best practices in problem solving. When performed correctly, this methodology not only improves the Quality and Reliability of your products but also prepares your engineering team for future problems.
When to Apply Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving (8D)
The 8D problem solving process is typically required when:
- Safety or Regulatory issues has been discovered
- Customer complaints are received
- Warranty Concerns have indicated greater-than-expected failure rates
- Internal rejects, waste, scrap, poor performance or test failures are present at unacceptable levels
How to Apply Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving (8D)
The 8D process alternates inductive and deductive problem solving tools to relentlessly move forward toward a solution. The Quality-One approach uses a core team of three individuals for inductive activities with data driven tools and then a larger Subject Matter Expert (SME) group for the deductive activities through brainstorming, data-gathering and experimentation.
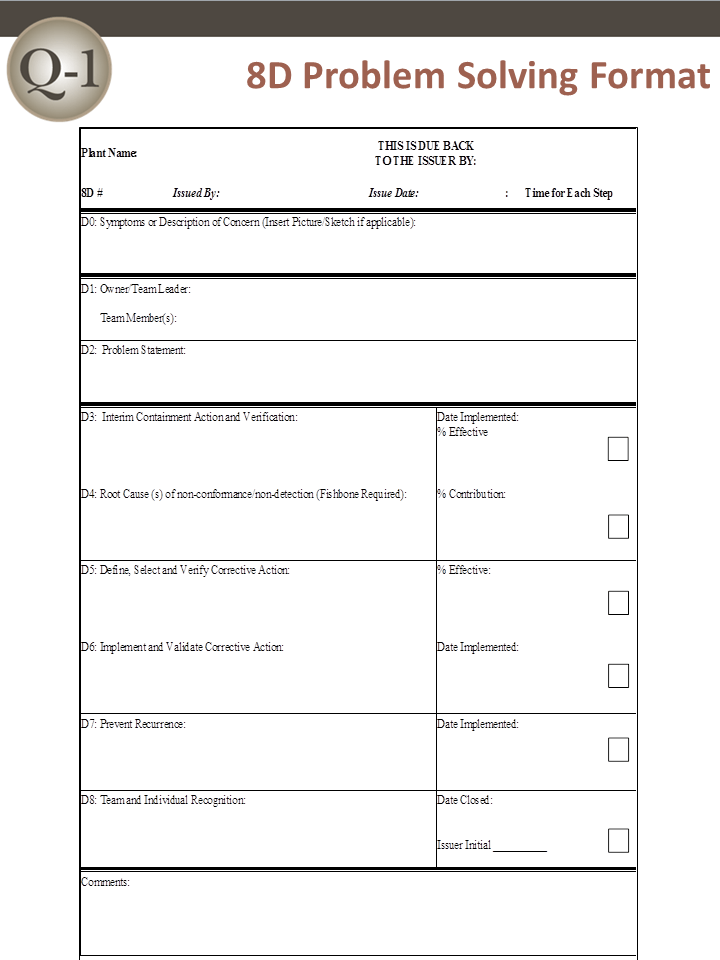
D0: Prepare and Plan for the 8D
Proper planning will always translate to a better start. Thus, before 8D analysis begins, it is always a good idea to ask an expert first for their impressions. After receiving feedback, the following criterion should be applied prior to forming a team:
Collect information on the symptoms
Use a Symptoms Checklist to ask the correct questions
Identify the need for an Emergency Response Action (ERA), which protects the customer from further exposure to the undesired symptoms
D1: Form a Team
A Cross Functional Team (CFT) is made up of members from many disciplines. Quality-One takes this principle one step further by having two levels of CFT:
- The Core Team Structure should involve three people on the respective subjects: product, process and data
- Additional Subject Matter Experts are brought in at various times to assist with brainstorming, data collection and analysis
Teams require proper preparation. Setting the ground rules is paramount. Implementation of disciplines like checklists, forms and techniques will ensure steady progress. 8D must always have two key members: a Leader and a Champion / Sponsor:
- The Leader is the person who knows the 8D process and can lead the team through it (although not always the most knowledgeable about the problem being studied)
- The Champion or Sponsor is the one person who can affect change by agreeing with the findings and can provide final approval on such changes
D2: Describe the Problem
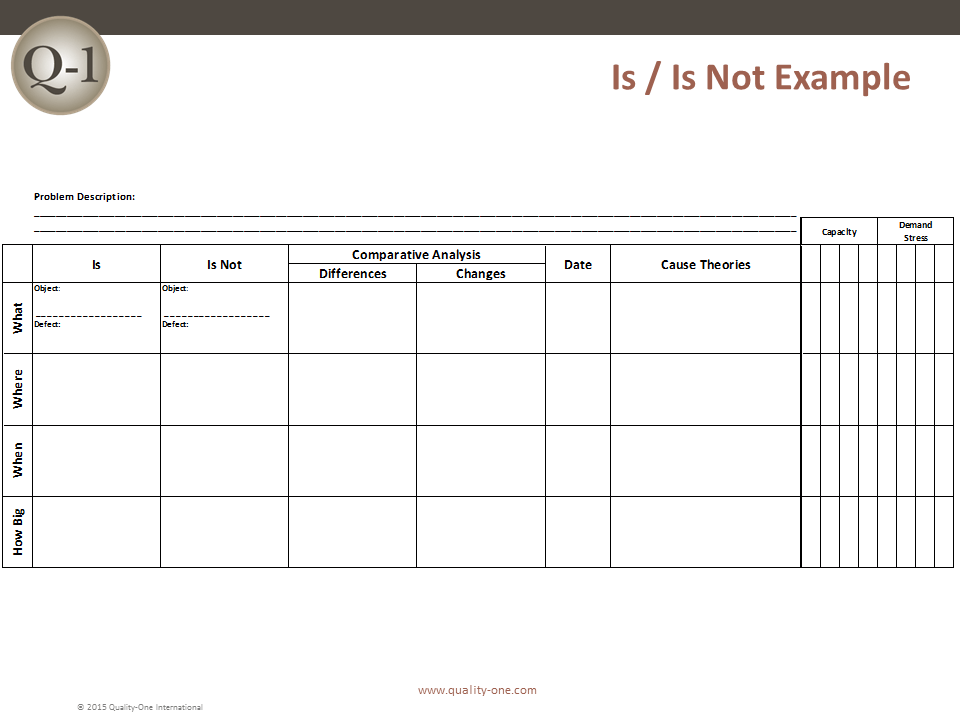
The 8D method’s initial focus is to properly describe the problem utilizing the known data and placing it into specific categories for future comparisons. The “Is” data supports the facts whereas the “Is Not” data does not. As the “Is Not” data is collected, many possible reasons for failure are able to be eliminated. This approach utilizes the following tools:
- Problem Statement
- Affinity Diagram (Deductive tool)
- Fishbone/Ishikawa Diagram (Deductive tool)
- Problem Description
D3: Interim Containment Action
In the interim, before the permanent corrective action has been determined, an action to protect the customer can be taken. The Interim Containment Action (ICA) is temporary and is typically removed after the Permanent Correct Action (PCA) is taken.
- Verification of effectiveness of the ICA is always recommended to prevent any additional customer dissatisfaction calls
D4: Root Cause Analysis (RCA) and Escape Point
The root cause must be identified to take permanent action to eliminate it. The root cause definition requires that it can be turned on or off, at will. Activities in D4 include:
- Comparative Analysis listing differences and changes between “Is” and “Is Not”
- Development of Root Cause Theories based on remaining items
- Verification of the Root Cause through data collection
- Review Process Flow Diagram for location of the root cause
- Determine Escape Point, which is the closest point in the process where the root cause could have been found but was not
D5: Permanent Corrective Action (PCA)
The PCA is directed toward the root cause and removes / changes the conditions of the product or process that was responsible for the problem. Activities in D5 include:
- Establish the Acceptance Criteria which include Mandatory Requirements and Wants
- Perform a Risk Assessment / Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) on the PCA choices
- Based on risk assessment, make a balanced choice for PCA
- Select control-point improvement for the Escape Point
- Verification of Effectiveness for both the PCA and the Escape Point are required
D6: Implement and Validate the Permanent Corrective Action
To successfully implement a permanent change, proper planning is essential. A project plan should encompass: communication, steps to complete, measurement of success and lessons learned. Activities in D6 include:
- Develop Project Plan for Implementation
- Communicate the plan to all stakeholders
- Validation of improvements using measurement
D7: Prevent Recurrence
D7 affords the opportunity to preserve and share the knowledge, preventing problems on similar products, processes, locations or families. Updating documents and procedures / work instructions are expected at this step to improve future use. Activities in D7 include:
- Review Similar Products and Processes for problem prevention
- Develop / Update Procedures and Work Instructions for Systems Prevention
- Capture Standard Work / Practice and reuse
- Assure FMEA updates have been completed
- Assure Control Plans have been updated
D8: Closure and Team Celebration
Teams require feedback to allow for satisfactory closure. Recognizing both team and individual efforts and allowing the team to see the previous and new state solidifies the value of the 8D process. Activities in D8 include:
- Archive the 8D Documents for future reference
- Document Lessons Learned on how to make problem solving better
- Before and After Comparison of issue
- Celebrate Successful Completion
8D and Root Cause Analysis (RCA)
The 8D process has Root Cause Analysis (RCA) imbedded within it. All problem solving techniques include RCA within their structure. The steps and techniques within 8D which correspond to Root Cause Analysis are as follows:
- Problem Symptom is quantified and converted to “Object and Defect”
- Problem Symptom is converted to Problem Statement using Repeated Whys
- Possible and Potential Causes are collected using deductive tools (i.e. Fishbone or Affinity Diagram)
- Problem Statement is converted into Problem Description using Is / Is Not
- Problem Description reduces the number of items on the deductive tool (from step 3)
- Comparative Analysis between the Is and Is Not items (note changes and time)
- Root Cause theories are developed from remaining possible causes on deductive tool and coupled with changes from Is / Is Not
- Compare theories with current data and develop experiments for Root Cause Verification
- Test and confirm the Root Causes
Example: Multiple Why Technique
The Multiple / Repeated Why (Similar to 5 Why) is an inductive tool, which means facts are required to proceed to a more detailed level. The steps required to determine problem statement are:
- Problem Symptom is defined as an Object and Defect i.e. “Passenger Injury”
- Why? In every case “SUV’s Roll Over”
- Why? In every case, it was preceded by a “Blown Tire”
- Why? Many explanations may be applied, therefore the team cannot continue with another repeated why past “Blown Tire”
- Therefore, the Problem Statement is “Blown Tire”
- Why? Low (Air) Pressure, Tire Defect (Degradation of an Interface) and High (Ambient) Temperature
- Counter measures assigned to low pressure and tire defect
This example uses only 4 of the 5 Whys to determine the root causes without going further into the systemic reasons that supported the failure. The Repeated Why is one way to depict this failure chain. Fault Tree Analysis (FTA) could also be used.
Learn More About Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving (8D)
Quality-One offers Quality and Reliability Support for Product and Process Development through Consulting, Training and Project Support. Quality-One provides Knowledge, Guidance and Direction in Quality and Reliability activities, tailored to your unique wants, needs and desires. Let us help you Discover the Value of 8D Consulting , 8D Training or 8D Project Support .
Contact Us | Discover the Value!
(248) 280-4800 | [email protected]
Remember Me
Guide: 8D Problem Solving
Author: Daniel Croft
8D Problem Solving is regarded as robust methodology that has proven its worth across multiple industries and manufacturing in particular. The methodology was Initially developed within the automotive industry, it has since been widely adopted in manufacturing, logistics and health care to name a few. The 8D approach goes beyond helping team just identify the root cause of problem but also provides a structured approach for implementing and verifying corrective actions.
What is 8D Problem Solving?
8D is also encourages collaborative team based approach to addressing issues in the workplace This methodology was purposefully designed to be a cross-functional effort, ensuring to bring together expertise from different departments or disciplines to comprehensively address an issue by looking at it from all point of view. Here are the key components:
Team Establishment : A cross-functional team is assembled, each member having a specific role and responsibility.
Root Cause Analysis : Various tools and methods are used to identify the real cause of the problem.
Prevent Recurrence : Measures are taken to ensure that the problem does not occur again.
How does 8D Compare to over Problem-Solving Methods?
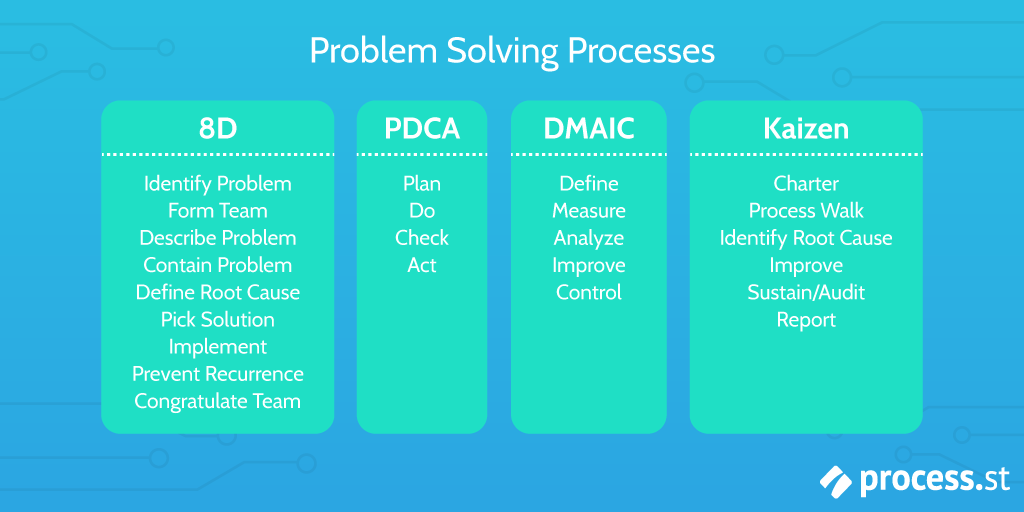
Between quality management systems and lean six sigma there are several problem-solving methodologies such as PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act), DMAIC (Define-Measure-Analyze-Improve-Control), and A3 . However the combination of the 8D steps results in a comprehensive frame work that is:
Structured Framework : 8D provides a very detailed, step-by-step guide for solving complex problems, by breaking it down in to logical steps making it easier to manage and track progress.
Broad Applicability : While some methodologies like DMAIC are closely tied to Six Sigma, 8D can be applied in various contexts without being tied to a particular quality management system.
The 8 Disciplines Explained
D0: prepare for the process.
Before you start 8D you should prepare for the 8D process. This phase sets the foundation for the entire methodology, ensuring that the team is able to tackle the problem effectively. Therefore, effective preparation helps in avoiding unnecessary delays and ensures that you’re not solving the wrong problem.
Within the initial preparation step you should also the time to think about what knowledge, expertise and experience you need within the team. Cross-functional teams are important, as they bring alternative perspectives and skills to the table rather than everyone looking at the problem from one point of view. Make sure you consider expertise, availability, and interest when selecting team members.
D1: Establish the Team
In D1 you should establish the team by clearly defining the roles and responsibilities for each team member. This includes assigning a team leader, subject matter experts, and roles for data collection , analysis, and communication this helps to provide the team members clarity on how they will be involved and contribute to the success of the problems solving activity.
Team Composition
Communication, d2: describe the problem.
In D2 it is time to create a well formed problem statement. This step is key as it provides a foundation for understanding the problem which will lead to generally more successful problem-solving. It ensures that everyone clearly understands what needs to be addressed, setting the scope for the entire process. Ensure that the problem is clearly understood by everyone in the team at this stage to prevent confusion later on in the process.
5W1H Method of creating a Problem Definition
Problem Definition – is / is not template
D3: Implement and Verify Interim Actions
In this step you should identify, plan, and execute short-term fixes that can quickly contain the problem. This could include quarantining the product to ensure it is not sent out to the customer or even pausing production lines that continue to product defects. Ensure these actions are documented for future reference.
D4: Root Cause Analysis
D5: choose and verify permanent corrective actions, d6: implement permanent corrective actions.
Once verified, implement the corrective actions across all relevant departments or processes. This can involved documenting the new process and training out to all stakeholders involved to ensure the new process is followed and that the stakeholders understand the reason for the change.
D7: Prevent Recurrence
It is important to conduct regular reviews to continuously monitor the process and ensure procedures are being followed but also to identify further opportunities for process improvement.
D8: Congratulate the Team
Finally it is always important to conduct a lessons-learned session and document the insights gained during the process for future reference. This can be used as a future point of reference for problem solving activities.
Q: What is 8D problem solving?
Q: why is it called "8d" problem solving, q: what are the eight disciplines (8d) in problem solving.
A: The eight disciplines in problem solving, often abbreviated as 8D, are as follows:
Q: What is the purpose of forming a team in the 8D problem-solving process?
A: Forming a team at the beginning of the 8D problem-solving process helps ensure that the right individuals with the necessary expertise are involved in addressing the problem. The team collaboratively works towards understanding the issue, analyzing data, and developing effective solutions.
Q: How is the root cause determined in the 8D problem-solving process?
Q: can the 8d problem-solving methodology be applied to any type of problem, daniel croft.
Hi im Daniel continuous improvement manager with a Black Belt in Lean Six Sigma and over 10 years of real-world experience across a range sectors, I have a passion for optimizing processes and creating a culture of efficiency. I wanted to create Learn Lean Siigma to be a platform dedicated to Lean Six Sigma and process improvement insights and provide all the guides, tools, techniques and templates I looked for in one place as someone new to the world of Lean Six Sigma and Continuous improvement.
Download Template
Free lean six sigma templates.
Improve your Lean Six Sigma projects with our free templates. They're designed to make implementation and management easier, helping you achieve better results.
Was this helpful?

Advisory boards aren’t only for executives. Join the LogRocket Content Advisory Board today →

- Product Management
- Solve User-Reported Issues
- Find Issues Faster
- Optimize Conversion and Adoption
An overview of the 8D problem-solving method
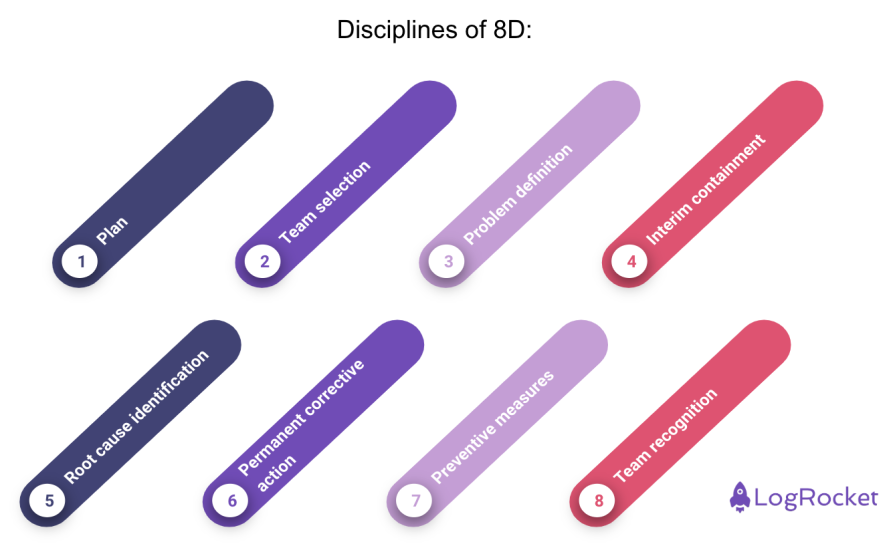
The 8D problem-solving method is a powerful tool in product management. It’s designed to help product managers tackle issues systematically and enhance product quality. This method follows eight steps in total, hence the name 8D.
The steps range from identifying problems to implementing long-term solutions. Today you’ll explore how you can effectively apply 8D to your products. You’ll also learn about the benefits of using this approach and analyze some real case studies.
What is 8D?
The 8D problem-solving method is designed to address and resolve problems by identifying, correcting, and eliminating recurring issues.
It involves eight different steps:
- Plan — Prepare for the problem-solving process
- Team selection — Assemble a team with the necessary knowledge and skills
- Problem definition — Clearly define the problem and its impact
- Interim containment action — Implement temporary measures to contain the problem
- Root cause identification — Identify the underlying cause(s) of the problem
- Permanent corrective action — Develop and implement a solution to address the root cause
- Preventive measures — Take steps to prevent the recurrence of the problem
- Team recognition — Acknowledge and reward the team’s efforts in resolving the issue
These steps focus on root cause analysis, preventive measures, and long-term solution implementation. The end goal is to improve product quality and operational efficiency.
The eight disciplines of 8D
The eight disciplines of the 8D method represent a comprehensive approach to solve problems within an organization. Each discipline is designed to guide teams through the process at each stage. Here’s a deeper look into each stage:
This initial step involves preparing for the problem-solving process. The goal here is to understand the problem’s magnitude and set up objectives. It’s about getting ready to tackle the issue systematically.
Team selection
In this step, a cross-functional team is formed. The team should consist of individuals with the necessary knowledge, skills, and experience to address the problem effectively. The team works together throughout the 8D process.
Problem definition
Next, the team has to describe the issue in specific terms. The goal here is to understand the impact and scope of the complication. A well-defined problem is easier to solve.
Interim containment
In the process of finding a solution, temporary measures are taken to contain the problem and prevent it from worsening. This reduces further damage or impact to the involved operations.
Root cause identification
In this phase, the team uses various tools and techniques to identify the underlying cause of the problem. An understanding of the root cause is essential for developing an effective, lasting solution.
Permanent corrective action
With the root cause identified, the team moves to develop a permanent corrective action plan to resolve the issue. Now, the team needs to choose the best solution, implement it, and monitor its effectiveness. This analysis will ensure that the problem is truly resolved.

Over 200k developers and product managers use LogRocket to create better digital experiences
Preventive measures
With such vast processes, there is always a possibility of the problem recurring. To resolve this, the team identifies and implements measures that address the root cause. There might be a need for changes to different aspects of the overall approach.
Team recognition
The final stage focuses on acknowledging and rewarding the team’s efforts. Recognizing the team’s hard work and success in resolving the issue is important for morale. It also promotes a culture of continuous improvement.
By following these eight disciplines, product managers can solve problems more effectively. The other benefit is that it builds a proactive culture that addresses issues before they escalate.
Applying 8D in product management
Applying the 8D problem-solving method in product management involves leveraging its structured approach. This helps you eliminate problems and process improvement initiatives.
Problem identification
The 8D process begins with gathering data and feedback to quickly identify potential issues. After that, a diverse team from various departments works together to uncover issues. And finally, the team solves the problems efficiently.
Once a problem is spotted, quick fixes are applied to limit its impact. Simultaneously, you explore root causes of an issue using methods like the Five Whys . The final step is to implement the solution based on these insights. Occasionally, redesigns or process upgrades are also used to resolve the issue thoroughly.
Elimination
To eliminate recurring problems, it’s crucial to establish preventive measures. Several steps support the main goal of elimination including process adjustments, quality control improvements, and updates to design standards.
The insights gathered from each 8D cycle help with continuous improvement. It also aids in formulating strategies to avert future issues.
Benefits of the 8D method
The main benefit of using the 8D method is its impact on teamwork and continuous improvement. The more obvious benefits focus on root cause analysis and prevention of issues:
- Enhanced quality control
- Efficient problem resolution
- Systematic and thorough approach
- Teamwork and knowledge sharing
- Focus on root cause analysis
- Reduced recurrence of issues
- Cost reduction
- Improved customer satisfaction
The systematic approach to address issues ensures that no effort goes to waste. Eventually, it helps the teams to quickly propose long-term solutions to a range of problem patterns.
Challenges in implementing 8D
The 8D problem-solving method is extremely valuable when used in the right manner. However, there can be challenges at every stage of this process. Because of this, it’s beneficial for you to have an understanding of how to quickly identify these challenges.
These include:
- Resistance to change among team members
- Insufficient teamwork and collaboration
- Lack of training on the 8D methodology
- Difficulties in data collection and analysis
How to solve them?
- Clearly communicate benefits to overcome resistance
- Foster collaboration and teamwork among participants
- Provide targeted training on the 8D process
- Encourage data analysis for effective problem-solving
For a deeper understanding, let’s take a look at two case studies of how the 8D process can enhance the product management workflow.
Real-life examples of 8D
A leading tech company, (similar to Apple) faced public backlash over smartphones overheating and reduced battery life. In this context, the 8D method helped to quickly identify and contain the issues.
The root cause analysis helped it track the problem back to a battery design flaw. Collaborative efforts with the battery supplier led to a redesigned battery and an update to the operating system. This not only resolved the issue but also restored consumer trust. Eventually, the brand’s reputation for quality was restored.
Similarly, a major automaker found a software glitch in its driver-assistance systems. This issue was risking driver safety. Using the 8D method, it pinpointed outdated algorithms as the root cause. The solution was simple, it issued a software update and enhanced its development processes.
Both of these examples are evidence of how the 8D method can be utilized to prevent complications efficiently.
Key takeaways
In wrapping up, it’s clear that this approach is more than just a procedure. Think of it as a strategic framework designed for the product manager. The 8D method equips you with a robust toolkit for addressing and preempting issues, systematically.
On top of that it helps you to:
- Promote teamwork and continuous improvement
- Reduce problem recurrence through root cause analysis
- Overcome implementation challenges with effective communication
Feel free to comment with any questions you may have!
Featured image source: IconScout
LogRocket generates product insights that lead to meaningful action
Get your teams on the same page — try LogRocket today.
Share this:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- #agile and scrum
- #project management

Stop guessing about your digital experience with LogRocket
Recent posts:.
Product management for microservices architecture
Microservices architecture transforms how we build applications, but what does that mean for a product manager? In this blog, I talk about why mastering microservices is essential for modern product management.

Leader Spotlight: The evolution of customer expectations, with Erica Randerson
Erica Randerson, Vice President of Ecommerce at Edible, talks about how Edible Brands has evolved pricing, delivery, and customization.

Utilizing a 2×2 matrix for effective decision-making
Prioritizing can be time-consuming. This not only fosters stress and anxiety, but brings productivity and morale to a standstill.
Leader Spotlight: Driving demand with the digital shelf, with Marianna Zidaric
Marianna Zidaric, Senior Director of Ecommerce at Spin Master, talks about how digital might have changed the way we can reach the shopper.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply

Designorate
Design thinking, innovation, user experience and healthcare design
What is the 8D Problem Solving? And How to use the 8D Report?
The 8D problem-solving process (also known as the 8 Disciplines) is very different from previous processes we explored previously, such as the Double Diamond process or the IBM Design Thinking. The 8D process works in a rigid standardised nature to address the crisis caused by problems. The 8D process aims to walk with the team to highlight the problem, its root causes and propose a long-term solution. The process is documented in an 8D report which includes details of each of the eight stages. At the end of this article, we will explore an example report, and you can find a free 8D report template to download.
In times of crisis, companies face the challenge of analysing and solving problems efficiently in a short time to save developed projects. Problem-solving techniques such as the TRIZ method and Hurson’s Production Thinking Model allow companies to overcome crises and solve problems using less effort and time.
- Stage Gate Process: The Complete Practice Guide
- The Double Diamond Design Thinking Process and How to Use it
- A Guide to the SCAMPER Technique for Creative Thinking
- Design Thinking Tools: Reverse Brainstorming
Brief History of the 8D Problem Solving
The 8D method was first implemented by the US government during WW II as a military standard and was referred to as the Army Directive 1520, “Remedies and disposal of nonconforming materials.” In 1987, the demand for a team-oriented problem-solving method increased among the management organisation in the automotive industry to find a way to eliminate recurring issues.
Ford Motor Company published their manual, Team Oriented Problem Solving (TOPS), which includes their 8 Disciplines of the problem-solving process. The process was initially used to deal with quality control and safety issues inside the company but later expanded its role to a team approach problem-solving method. The 8D process is employed by engineers and designers to identify, analyse, and correct problems by eliminating the primary source that caused the problem.
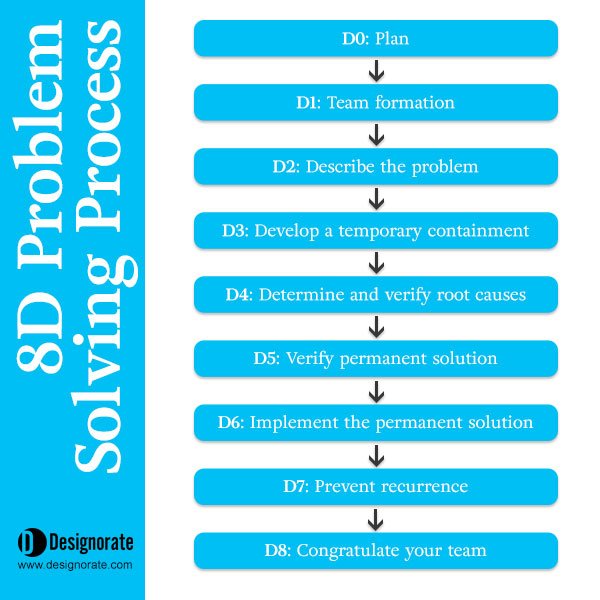
So, what are the eight steps in the 8D methodology? The 8D problem solving process includes 8 Disciplines. In the mid-90s, a D0 step for planning was added to the process. The 8D steps include the following:
- D1: Team formation
- D2: Describe the problem
- D3: Develop a temporary containment plan
- D4: Determine and verify root causes
- D5: Verify the permanent solution
- D6: Implement the permanent solution
- D7: Prevent recurrence
- D8: Congratulate your team
The 8 Disciplines aim to achieve the following targets while solving the specified problem:
- Think as a team while solving the problem
- Isolate the situation and understand its causes
- Identify the factors that contribute to the problem
- Provide a temporary solution to halt the impact of the problem
- Eliminate the causes of the problem and the factors contributing to it
- Prevent the problem from recurring
When Should the 8D Problem Solving be Used?
Based on the above targets, the 8D problem solving process is designed for complex problems whose solution exceeds the ability of one expert. Also, it aims to establish communication for problem resolution through different levels inside the company. In some situations, the consumer or the management team requests the application of the 8D process through several forms or documentation.
While 8D problem solving is suitable for recurring problems that may repeatedly occur within a project or company, it is not ideal for simple issues that can be solved quickly by individual efforts. The process is unsuitable for a problem that can be solved with a straightforward solution. The 8D process is designed for complex issues, which require several weeks to solve and the involvement of at least four people.
8D problem solving provides a systematic process to find and solve problems. Therefore, if the situation requires choosing between alternative solutions, 8D acknowledges that other tools may help solve the problem better than the 8D process.
How to Apply the 8D Problem Solving Process?
The steps below form the 8 Discipline process to achieve targeted problem solving through the eight steps.
This discipline is also known as the Pre 8D because it aims to understand the problem and determine if the 8D process is the correct method to use. At this stage, the team aims to answer general questions such as:
- Is this a new problem, or has it happened before?
- Is this a recurring problem?
- What is the history of this issue?
- What was the method used to solve the problem before?
At this stage, the target is to learn about the problem’s history and decide if the 8D process is the best tool to solve the problem.
D1: Team Formation
Thinking as a team can produce more efficient solutions than trying to solve a problem alone. The team includes all the stakeholders involved in the situation. The team communicates with each other and performs brainstorming to solve the problem (check Design Thinking Tools: Reverse Brainstorming ). If the team does not know each other, the brainstorming time can be used to learn how to teach members to explore ideas together. Methods can be used in brainstorming sessions such as mind mapping , Six Thinking Hats , and Lego Serious Play.
D2: Describe the Problem
After team formation, the second step is to understand the problem and its risks. This stage starts with a risk analysis to identify the situation and how it can affect the project flow. Several methods can be used to analyse the problem from different perspectives, including SWOT analysis , SCAMPER technique , and similar tools. This stage is essential to building a clear vision of the problem and ensuring all stakeholders have the same understanding of the situation.
D3: Develop a Temporary Containment Plan
While solving the problem, there should be a temporary containment plan to prevent the problem from affecting the rest of the project or the final product. This temporary containment solution is a short-term operation such as adding more labour, increasing the quality measurements, applying a risk plan, etc.
It is essential to understand that the containment action is not the real solution and can only be used for the short term. Therefore, this action can be applied internally and not affect the process of reaching a permanent solution.
D4: Determine and Verify Root Causes
This stage aims to investigate the root causes of the problem; it can be considered the core of the 8D problem solving process. In many problems, what we see as causes are symptoms of other root causes. This misunderstanding can lead to inaccurate attempts at solutions that can have negative consequences in the future and leave the underlying problem unsolved.
An intensive investigation should be implemented because, in many cases, the root cause is hidden inside the process and covered by many symptoms, which is confusing. Some tools can be used to define the root causes of the problem, such as brainstorming , statistical analysis, flow charts, audits, etc.
D5: Verify the Permanent Solution
Once the root cause is defined, the solution becomes apparent, and the team better understands how to solve the problem. However, the symptoms and other related factors may create difficulties deciding how best to apply the solution. So, these other factors should be considered when determining the permanent solution to the dilemma.
When choosing the permanent solution to the problem, it should meet the following criteria to ensure it is the ideal solution for the problem:
- The solution should be practical
- The solution should be feasible
- The solution should be cost-effective
- The solution should not fail during production
- The solution should be implemented in all affected facilities in the company
D6: Implement the Permanent Solution
Once the solution is approved, this step tends to work as an action plan. This plan aims to outline the steps to implement the solution. It is common to ask questions in this stage: What should be done? Who should be involved in the correction plan?
More documentation and detailed plans should be created if the solution is complex and needs further procedures. The method may include training the team and checking the plan’s progress for further development and improvement.
D7: Prevent Recurrence
Once the action plan is set and ready to be implemented, the team should establish a plan to prevent the problem from occurring in the future. The action plan should be tested and documented as part of the process to avoid the recurrence of the problem. Some of the tools that can achieve this goal are Control Charts, Capabilities Analysis, and Control Plans.
D8: Congratulate the Team
After completing the task and implementing the solution, the team deserves an acknowledgement of their work and a celebration. This event will positively impact the stakeholders and reflect recognition of employees’ efforts from the management inside the company.
How do you Write an 8D Report?
The primary documentation used in the problem solving process is the 8D report. Korenko et al. (2013) presented an example of the 8D problem-solving application, Application 8D Method For Problems Solving . After this example, you can find a free 8D Report template that you can download and use for both commercial and noncommercial applications. The first part of the report, D0, includes information about the problem and the project details related to the project. D1 section contains details of the team involved in the project, roles, titles and contact information. D2 part of the report includes a detailed description of the problem and possible visual images to show the problem clearly. The report can consist of the type of damage of the failure and the function where the problem occurs (Figure 2).
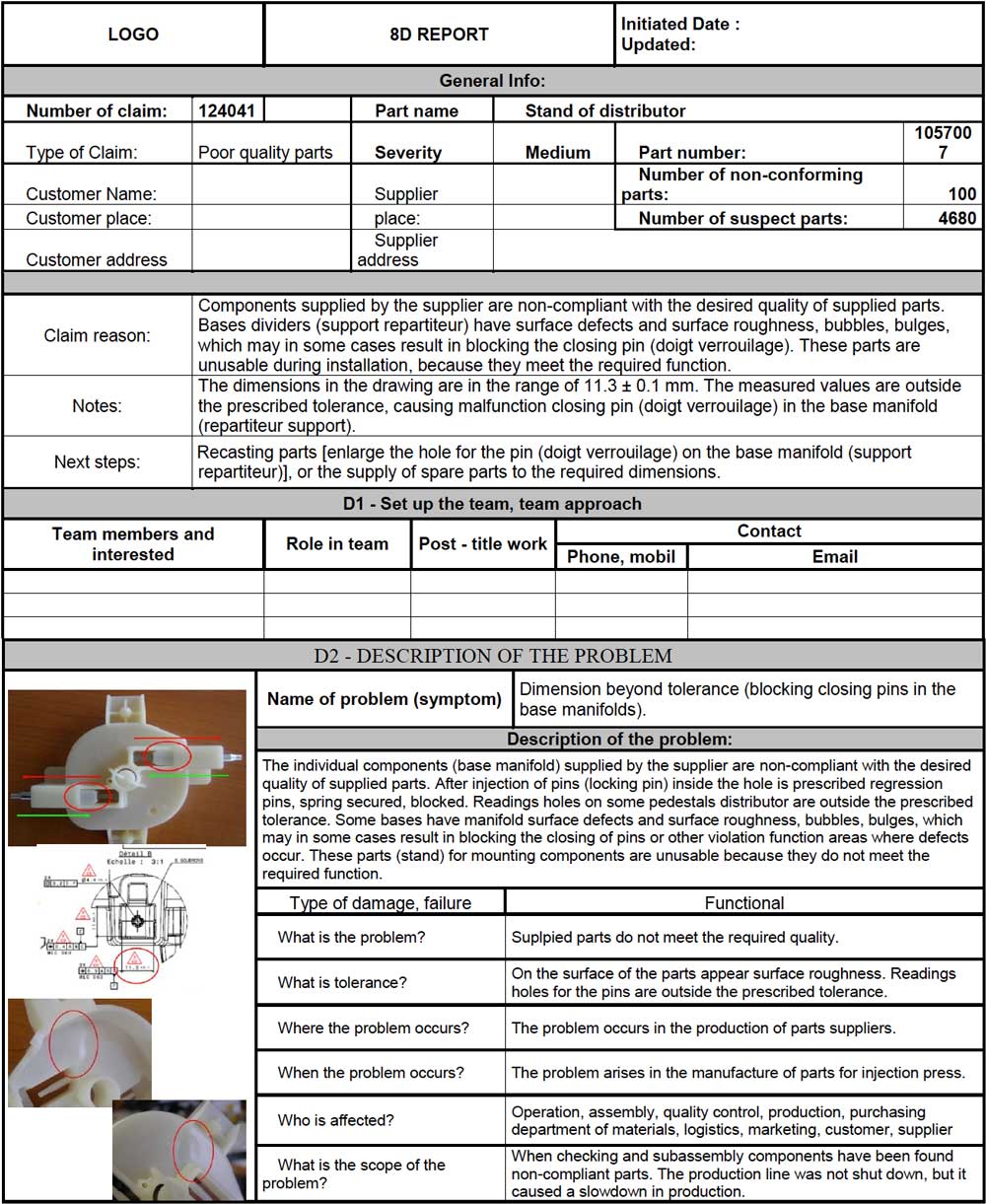
D3 includes details of the temporary solution for the problem required to stop the damage rapidly. In this part, the temporary remedy is described, particularly the symptoms affect, the responsibility, and the validation of the action. In D4, the team uses a root-cause method such as the 5WHYs or the Cause-Effect analysis (Fish Bone method). These methods help the team to identify the root causes of the problem. In Figure 3, the 5WHYs method is used several times to identify the root cause of the problem.
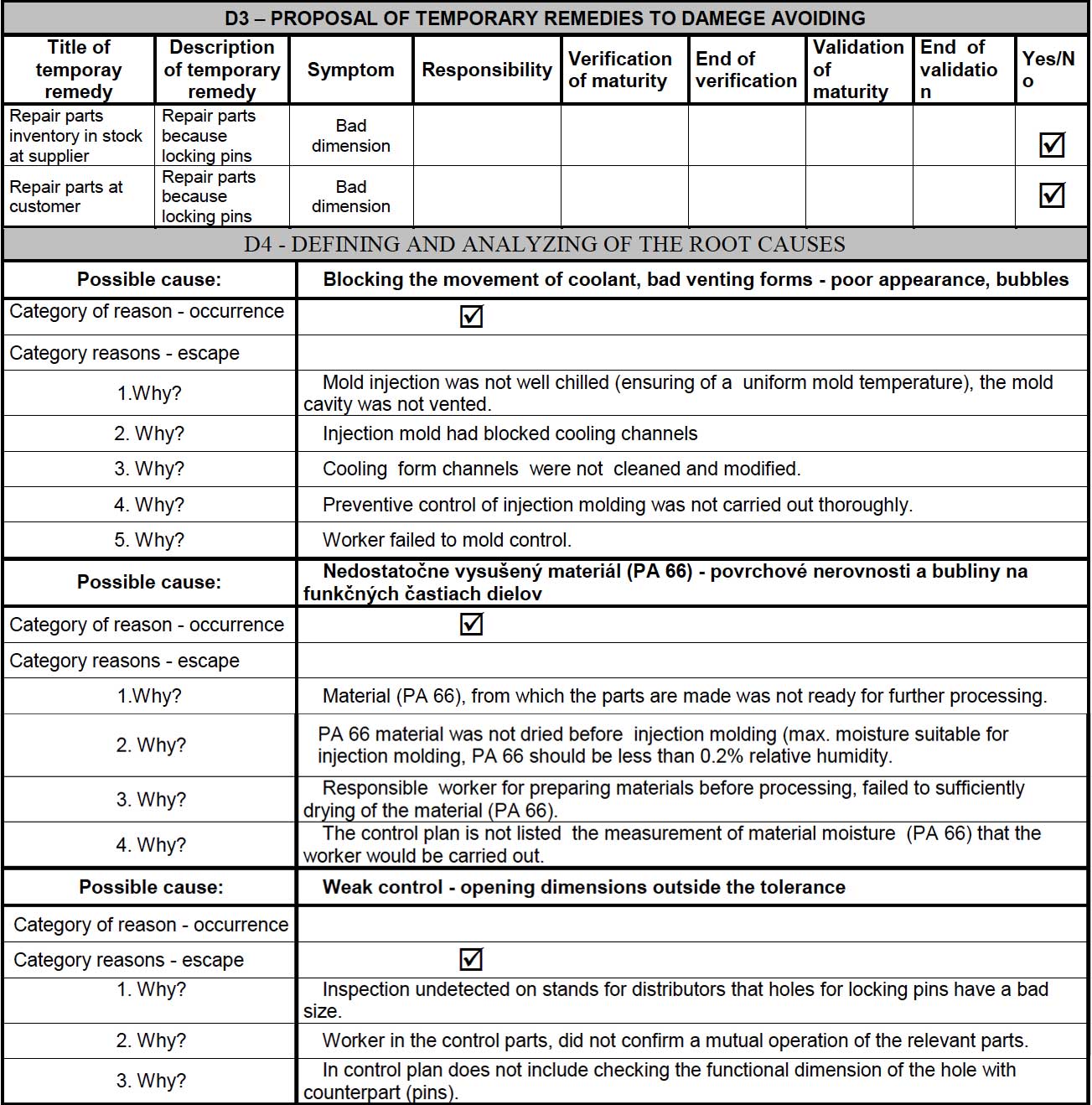
D5 of the report provides details about the permanent solution to fix the problem. Unlike the temporary solution, this aims to element the root causes of the problem. This section includes the procedure’s name, the reason to use it, the responsibility, the management approval to apply it and the expected date of completing the utilisation of the solution, as seen in Figure 4. In the following stage, D6, the team provides details on the implementation and validation of the permanent action.
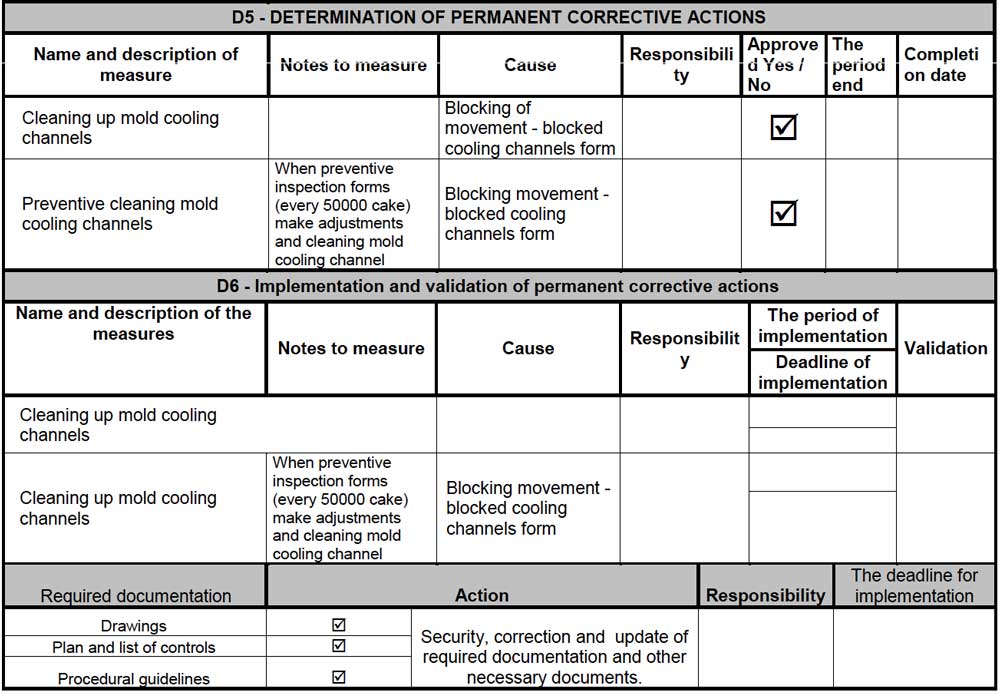
D7 provides details about preventing the recurrent problem, such as the name of the action after the validation process in the previous stage. Also, this stage provides details of the cause behind this action and elements about its responsibility and implementing details. Finally, in D8, the report includes a summary of the procedure and the proper approvals related to the procedure implementation (Figure 5).
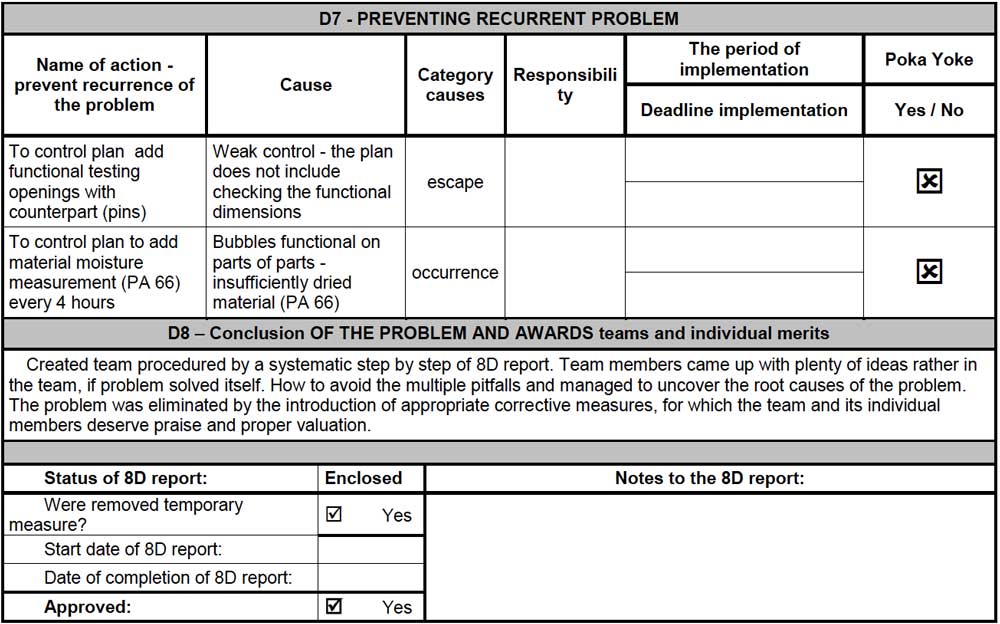
Free 8D Report Template Download

You can download the below 8D report, which you can use for commercial and noncommercial projects. Don’t forget to mention Designorate as the source of this free 8D report.
The 8D Problem Solving process provides a reliable and systematic method that ensures that the problems inside a company or project are solved by eliminating their root causes and preventing recurrence. However, it is most suitable for complex problems that can take weeks or even months to solve. Therefore, the first stage aims to determine if the 8D process is ideal for the problem or if more straightforward tools should be implemented. If the 8D problem solving method is appropriate for your business problem, you have a step-by-step template to guide you through your attempts to find a suitable solution to the obstacle you need to overcome.
Wait, Join my Newsletters!
As always, I try to come to you with design ideas, tips, and tools for design and creative thinking. Subscribe to my newsletters to receive new updated design tools and tips!
Dr Rafiq Elmansy
As an academic and author, I've had the privilege of shaping the design landscape. I teach design at the University of Leeds and am the Programme Leader for the MA Design, focusing on design thinking, design for health, and behavioural design. I've developed and taught several innovative programmes at Wrexham Glyndwr University, Northumbria University, and The American University in Cairo. I'm also a published book author and the proud founder of Designorate.com, a platform that has been instrumental in fostering design innovation. My expertise in design has been recognised by prestigious organizations. I'm a fellow of the Higher Education Academy (HEA), the Design Research Society (FDRS), and an Adobe Education Leader. Over the course of 20 years, I've had the privilege of working with esteemed clients such as the UN, World Bank, Adobe, and Schneider, contributing to their design strategies. For more than 12 years, I collaborated closely with the Adobe team, playing a key role in the development of many Adobe applications.
You May Also Like

4 Service Design Tools to Focus on Consumers’ Needs

30+ Distance Learning Tools And Advices for Design Educators

Top Resources to Learn Design Thinking Online

How to Evaluate Design Ideas

Critical Thinking as a Catalyst of Change in Design
Practice Guide to Run a Google Design Sprint
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Sign me up for the newsletter!
Discover your potential savings with our ROI Calculator
8D Management (8 Disciplines Management)

8D Management & The 8D of Problem Solving
Problems are a part of life and a business is no exception. Even with the best of intentions and systems, some errors can creep in and be hard to detect. It may be nothing serious or can have serious repercussions such as reputation damage, heavy fines, product recall, property loss, and so on. It becomes essential to identify the problem, its consequences on the one hand, and causes on the other to be able to not only resolve it for now but also ensure prevention of its recurrence. One of the methodologies, popular amongst engineers and professionals mainly in the automotive industry but now applied across several industries is the eight disciplines (8D) model. It helps to identify, correct, and eliminate recurring problems, affecting improvement in product and process.
Related Assets
Whenever organizations tackle problems and generate solutions based out of root cause analysis, they tend to generate a lot of…
Key Highlights: 8D is an extremely effective, proven problem-solving framework, especially in the manufacturing and automotive sector. However, to truly…
From a quality management standpoint, a problem may be reported in an organization from one of the following processes: Complaints…

What is 8D?
The 8D is a systematic, holistic and proven methodology designed to identify the root cause of a problem, plan a quick fix, and implement corrective actions and preventive actions to avoid their recurrence. If your product is defective or not meeting your customer requirements, then 8D is an excellent first step to improve Quality and Reliability.
One of the core parts of introducing 8D problem solving, greatly accepted by most disciplines of industries, and having huge effectiveness levels in improving product and process quality, would be 8D (Eight Disciplines). Key steps in the 8D methodology are forming a team, defining the problem, identifying and implementing interim containment, identifying the root causes, implementing and verifying permanent corrective actions, and avoiding future recurrence of problems. The 8D process for root cause analysis concludes by highlighting that the team members not only play a vital role but also recognizes them, hence reinforcing that this approach is a collaborative one. 8D has become very popular among manufacturers, assembly, and services around the globe because it is effective and comparatively easy to teach.
Introduction to 8d Problem Solving
The 8D approach to problem-solving, also known as the 8D methodology, is a systematic and comprehensive method used to address and resolve complex issues, particularly in manufacturing and other industries.
This 8D troubleshooting methodology involves a structured process designed to identify, correct, and prevent issues, ensuring that similar problems do not occur in the future.
By following the 8D process steps, teams can effectively perform root cause analysis and implement corrective actions.
The 8D structured problem-solving process is highly valued for its ability to provide a clear framework for identifying and eliminating the root cause of a problem, thereby enhancing overall operational efficiency.

Why to Apply 8D Problem Solving Methodology?
The 8D methodology , developed to represent the best practices in problem solving, provides the engineering teams with an effective and efficient team-oriented problem solving skill, a better understanding of Root Cause Analysis (RCA) and how to use basic statistical tools required for problem solving. 8D helps the management understand and resolve problems better, identify necessary systemic changes and inputs for change, and facilitate a more candid and open communication in problem solving discussions.
8D improves the Quality and Reliability of your products, and if performed correctly, prepares the engineering team for future problems.
When to Apply 8D Problem Solving Process?
The 8D problem solving process is used to solve major, critical, chronic, and recurring problems. The 8D is typically required during safety or regulatory issues, customer complaints , warranty concerns, poor performance or test failures, internal rejects, and to minimize waste and scrap.

How to Use Root Cause Analysis to Transform Your Safety Program
8d problem solving approach.
The 8D is a systematic process for the introduction and improvement of quality, and elimination of problems. Here we will show you the step by step approach of the problem solving tools that can make you proficient at identifying causes of problems, defining problems, and errors. Additionally, it helps identify root causes and take actions to solve and prevent identified problems in processes. So, let’s take a peep inside:

D0: Planning and preparing for the 8D
Proper planning and preparation are always a good start before taking any action. So, you need to consider the following before forming a team:
- Problem description
- Timeframe for the resolution
- The number of resources to accomplish this

D1: Team establishment
Create a team with people who varied backgrounds and experiences which will lead to the best quality inputs and a complete solution. For the team to function smoothly, define clear roles, and responsibilities for your people, and have a team leader.

D2: Problem description
The 8D method’s primary focus is to describe the problem appropriately and objectively such that it captures all the vital information. During this analysis, repeated 5W1H (why, what, who, where, when, and how) are required to be asked to develop a clear description.

D3: Problem containment plan
A temporary problem containment plan is sometimes needed to minimize the impact of the problem until you develop permanent solutions. On developing the plan based on the hypothetical cases, the resources for addressing the main problem can be released. At times, new processes may be required to work around the problem until you have a permanent fix.

D4: Root Cause Analysis (RCA)
With the problem temporarily contained, you can now turn to identify all of the root causes of the nonconformance . There are several tools to identify the actual root cause of an issue including the 5W1H to understand the problem in-depth, Fishbone diagrams to visually categorize causes, and Pareto charts to identify the vital causes.

D5: Permanent Corrective Action
Once the root cause of the problem is determined, the team can start brainstorming permanent corrections to identify what the best long-term solution will be. Brainstorming sessions combined with tools such as affinity diagrams help organize ideas based on their relationships and determine the best course of action.

D6: Implement and Validate the Permanent Corrective Action
Once the solution is identified, the management needs to implement and verify the corrective action using the PDCA (plan-do-check-act) approach for small-scale testing before large-scale rollout. Thus, the outcomes and corrective actions are tracked to ensure expected results. To successfully implement a permanent change, a project plan should incorporate:
- Development of the project plan for implementation
- Communicating the plan to all stakeholders
- Validating improvements using measurement

D7: Prevent Recurrence
A complete solution of problems means preventing them from occurring. Besides, preventative measures should also be implemented for corrective actions in the 8D methodology. This requires reviewing management processes, operating procedures, and training manuals to ensure that best practices are followed.
At this stage, organizations should consider actions including updating process audit questions and regularly verifying them based on corrective actions to reduce risk in other processes, presenting poka-yoke or error-proofing devices to big-risk processes, and conducting red rabbit tests to see how long it takes poka-yoke devices to detect defective product.

D8: Verification and Team Celebration
Once the problem is solved, the ultimate step is to congratulate the team. It’s important to recognize their efforts and share their success across the organization because teams require feedback to allow for satisfactory closure. This facilitates motivation and employee engagement while helping you improve quality control, execute process improvements, and aid change management as you grow.

Create a team with people who are having varied backgrounds and experiences which will lead to the best quality inputs and a complete solution. For the team to function smoothly, define clear roles, and responsibilities for your people, and have a team leader.

A complete solution of problems means preventing them from occurring initially. Besides, preventative measures should also be implemented for corrective actions in the 8D methodology. This requires reviewing management processes, operating procedures, and training manuals to ensure that best practices are followed.
8D Root Cause Analysis (RCA) and 8D Corrective Action Process
The 8D Root Cause Analysis, as well as the 8D Corrective Action process, is a widely systematic approach in quality management , especially concerning 8D in quality control. This method includes eight comprehensive steps that are devised to problem solving by dealing with root causes of the problems comprehensively. The steps of the 8D process start with the formation of a team, a clear definition of the problem, and move on to interim containment actions. This is then followed by detailed root-cause analysis using the 8D RCA process, development and verification of permanent corrective actions, implementation, and recurrence preventing efforts. Encouraging details in the analysis: the 8D methodology steps encompass collaborative efforts and documentation that ensure durable solutions and continuous improvement in organizational processes. Root Cause Analysis (RCA) is embedded within the 8D process and includes the following steps and techniques:

Problem Symptom is measured and transformed to “Object and Defect”

Problem Symptom is reformed to Problem Statement using the 5W1H process

Potential Causes are gathered using the tools like Fishbone or Affinity Diagram

Problem Statement should fit using both the “is” and the “isn’t” sections of the question

Root Cause concepts are developed from remaining possible causes on the tool and related changes from is/is not

Compare theories with recent data and develop experiments for Root Cause Verification

Test and confirm the Root Causes

Customer Success
3 Women Leaders Making a Powerful Impact in Global Quality and Safety Management
How to use the 8d approach.
8D portrays 8 steps of a structured approach to solve difficult, recurring, or critical problems by providing transparency, driving a team approach, and increasing the chances of solving the problem.
Proper plan for solving the problem and identify the prerequisites.
Team creation
Gather a cross-functional team with product/process knowledge.
Problem description and definition
Use the data and information to specify the problem by identifying in quantifiable terms the who, what, where, when, why, how, and how many (the 5W1H) for the problem.
Problem Containment Plan development
Develop and implement interim actions to eliminate the problem from any customer in the future.
Specify and assess Root Causes
Identify and review all relevant causes and sources of variation that analyze why the problem has occurred and figure out why the problem was not noticed at first using 5W1H or diagrams.
Verify Permanent Solutions
After collecting data confirm that the possible solutions will actually resolve the problem.
Implement and Validate Corrective Actions
Discuss and review results and develop plans to implement the best solutions or countermeasures.
Preventive measures
Transform the operation systems, management systems, procedures, and practices to avoid the recurrence of similar problems.
Compliment your team
Recognize the collective efforts of your team and formally thank them for their involvement.
8D Problem Solving Tools and Techniques
The 8D problem solving methodology is the set of tools and methods aiming for complex quality issues. 8D problem solving techniques are basically comprised of a fishbone diagram, 5 Whys analysis, Pareto charts, process flowcharts, and Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) to come to terms with the 8D framework. Integration with statistical tools and data analysis in every step of 8D analysis is sure to make the most accurate identification of the root cause.
This approach would ensure that cross-functional teams' participation would not only be present in the brainstorming sessions but also in the 8D problem solving process at the problem solving stage.

Training in 8D Methodology
8D training is an inevitable imperative that makes its deployment in organizations effective. The 8D methodology provides all the necessary details that the teams could apply to the skills and knowledge required at every step in 8D of quality control . Training the workforce on 8D methodology will make them able to apply these aspects when dealing with real-world problems, which will better off the quality and efficiency of the entire organization. It ensures that all these measures and strategies have been inducted to make sure that 8D problem solving approaches are not just tools for problem solution but have been inducted to lay down the base for sustainable quality improvement and prevention practices in the organizational processes.
How to Enhance Quality and Efficiency in 8D Manufacturing?
Understand the Basics of the 8D Approach to Problem Solving
- Familiarize yourself with the principles of the 8D methodology.
- Recognize that the 8D process steps include team formation, problem
Form a Cross-Functional Team
- Assemble a team with diverse skills and perspectives.
- Ensure each member understands their role in the 8D structured problem solving process.
- Use precise language to describe the problem.
- Implement tools like the 5 Whys to aid in the root cause analysis 8d problem solving phase.
Implement Interim Containment Actions
- Take immediate steps to prevent the problem from worsening.
- Document these actions as part of the 8D troubleshooting methodology
Identify and Verify Root Causes
- Conduct a thorough root cause analysis to pinpoint the underlying issues.
- Utilize techniques like fishbone diagrams and Pareto charts in the 8D RCA Process.
Develop Permanent Corrective Actions
- Propose solutions that address the root causes identified.
- Ensure these solutions are sustainable and prevent recurrence.
Validate the Corrective Actions
- Test the solutions to ensure they effectively resolve the problem.
- Collect data to confirm the effectiveness of the root cause analysis and the 8Dd corrective action process.
Implement and Monitor Solutions
- Roll out the verified solutions across relevant areas.
- Continuously monitor the impact to ensure long-term success.
Prevent Recurrence
- Update processes and documentation to incorporate the new solutions.
- Train employees on the new procedures to embed them in daily operations.
Recognize and Celebrate Success
- Acknowledge the efforts of the team in solving the problem.
- Use this opportunity to reinforce the importance of the 8D methodology in maintaining quality and efficiency.
Ensuring compliance with FDA regulations is crucial for medical device manufacturers to maintain market access and ensure patient safety. Medical Device Compliance Software plays a pivotal role in helping companies align with these stringent requirements. Here’s how:
Great product, support, and people to work with!
We have rolled-out CQ across our company to automate various elements of QMS requirements such as Document Management, Complaints, Non-conformances, Corrective Action (8D and A3), Supplier Management and Audit Management. We have been using the software for more than 2 years. We are glad to see how well the system is being used across the company. We have several thousand users on the system currently and working to scale the usage further. CQ solution has been configured to meet our needs, works elegantly across languages, across time zones, and business verticals. With integration between CQ and SAP to exchange critical data, the process automation provides a lot of productivity.
CQ configuration team and support have worked hard to ensure that our needs continue to be met. They consistently go above and beyond. We cannot be more pleased with our use of CQ QMS capabilities and would definitely recommend to anyone who is looking for a modern cloud based EQMS solution especially if you want a scalable EQMS solution.
Lia Budiman, Continental Contitech

8D Process Improvement in Different Industries
Automotive Industry
- Application of 8D Methodology : Essential for addressing recurring quality issues and customer complaints.
- Root Cause Analysis 8D Problem Solving : Identifies underlying issues affecting vehicle performance and safety.
- 8D Structured Problem Solving: Used to enhance manufacturing processes and reduce defects.
- 8D Process Steps: Followed rigorously to maintain high safety and quality standards in vehicle production
Aerospace Industry
- 8D Troubleshooting Methodology: Critical for resolving complex technical issues and ensuring compliance with stringent safety regulations.
- 8D RCA Process: Applied to investigate and eliminate root causes of system failures.
- 8D Corrective Action Process: Ensures that preventive measures are implemented to avoid the recurrence of problems.
- 8D Manufacturing: Focuses on precision and reliability in the production of aerospace components.
Electronics Industry
- 8D Approach to Problem Solving: Used to tackle issues related to product design and manufacturing.
- Root Cause Analysis and the 8D Corrective Action Process: Vital for maintaining product quality and reducing warranty claims.
- 8D Process Steps: Helps in identifying and addressing defects in electronic components and assemblies.
- 8D Methodology: Ensures continuous improvement and innovation in electronics manufacturing processes.
Healthcare Industry
- 8D Structured Problem Solving: Applied to improve patient care and operational efficiency in healthcare facilities.
- 8D Problem-Solving Steps: Utilized to address issues related to medical equipment and procedural errors.
- Root Cause Analysis 8D Problem Solving: Enhances patient safety by identifying and eliminating causes of medical errors.
- 8D Troubleshooting Methodology: Ensures that corrective actions are taken to prevent the recurrence of adverse events.
Food and Beverage Industry
- 8D Manufacturing: Ensures product quality and safety throughout the production process.
- 8D Approach to Problem-Solving: Addresses contamination issues and improves production line efficiency.
- Root Cause Analysis and the 8D Corrective Action Process: Essential for maintaining food safety standards.
- 8D Process Steps: Used to investigate and resolve quality issues in food production systematically.
Pharmaceutical Industry
- 8D Methodology: Applied to ensure the consistency and safety of pharmaceutical products.
- 8D RCA Process: Identifies and addresses root causes of deviations in manufacturing processes.
- 8D Corrective Action Process: Implements preventive measures to ensure compliance with regulatory standards.
- 8D Troubleshooting Methodology: Enhances production efficiency and reduces the risk of product recalls.
Consumer Goods Industry
- 8D Structured Problem Solving: Used to resolve product design and manufacturing issues.
- 8D Process Steps: Ensures consistent product quality and customer satisfaction.
- Root Cause Analysis 8D Problem Solving: Identifies and eliminates causes of defects in consumer products.
- 8D Manufacturing: Focuses on improving production processes and reducing waste.
Energy Industry
- 8D Approach to Problem Solving: Applied to address equipment failures and improve operational reliability.
- Root Cause Analysis and the 8D Corrective Action Process: Ensures the continuous improvement of energy production processes.
- 8D Troubleshooting Methodology: Helps resolve complex technical issues in energy plants.
- 8D RCA Process: Identifies and eliminates causes of energy generation and distribution inefficiencies.
8D Process Metrics and KPIs
- Problem Resolution Time: This metric tracks the time taken from problem identification to resolution in the 8D root cause analysis process, ensuring timely corrective actions are implemented to prevent recurrence.
- Recurrence Rate: By measuring how often a similar problem reappears after the 8D corrective action process, this KPI helps assess the effectiveness of the implemented solutions and continuous improvement efforts.
- Root Cause Identification Accuracy: This KPI evaluates the precision and accuracy with which the root causes are identified during the 8D root cause analysis, ensuring that the correct issues are being addressed.
- Corrective Action Implementation Rate: This metric tracks the percentage of corrective actions successfully implemented within the stipulated timeline, indicating the efficiency of the 8D corrective action process.
- Customer Satisfaction Improvement: Monitoring changes in customer satisfaction levels following the 8D corrective action process can highlight the impact of the process on overall product quality and customer perception.

8D Problem Solving Report
8D problem solving reports and templates are useful tools to initiate a problem solving process. These reports are used to explain what 8D is and including information about each step so that one will know what needs to be done by attempting this to solve problems. Keeping these reports easily available can avoid repeating work on the same problems over and over again.
8D reports must be detailed and incorporate information at every step within the 8D process. Those who are working on the problem should provide sufficient information when completing a report so that someone who was not on the current 8D team can pull it out and understand what the problem was and what solutions were implemented.
Improve quality, eliminate problems and identify the root cause of a problem with 8d Methodology
Who can 8d help.
The 8D methodology is universally applicable for every organization that needs solving. Although, there are a few industries and sectors where this 8D approach is successfully used such as manufacturing, the automotive industry , engineering companies that manufacture products or parts, and medium and large-scale enterprises.

Related Checklists

Quality Assurance Checklist – Part A (Project Management)
Checklist | September 7th, 2022

Quality Assurance Checklist – Part B (Project Deliverables)

Quality Control Area Safety Audit Checklist for Pharmaceutical Companies
Checklist | April 22nd, 2022
Implementing the 8D Root Cause Analysis

Establish the Team
- Assemble a cross-functional team: Ensure diverse perspectives and expertise.
- Define roles and responsibilities: Clarify each member's contributions.
- Team leader selection: Choose someone with strong leadership and problem-solving skills.
Describe the Problem
- Problem statement creation: Define the issue clearly and concisely.
- Use of data and evidence: Gather and present data to illustrate the problem.
- Scope and impact: Detail how the problem affects processes, products, or customers.
- Immediate actions: Implement temporary measures to contain the problem.
- Verification of ICAs: Ensure the containment actions are effective.
- Monitoring: Continuously monitor the situation until a permanent solution is found.
Determine Root Causes
- Root cause analysis techniques: Utilize tools like the 5 Whys and Fishbone diagrams.
- Data analysis: Examine data to identify patterns and anomalies.
- Identify multiple root causes: Look beyond the obvious to find all contributing factors.
Develop Permanent Corrective Actions (PCAs)
- Brainstorm solutions: Generate potential corrective actions.
- Evaluate effectiveness: Assess the feasibility and impact of each solution.
- Select the best solution: Choose the most effective and sustainable corrective action.
Implement and Validate PCAs
- Action plan creation: Develop a detailed plan to implement corrective actions.
- Execution: Carry out the corrective actions according to the plan.
- Validation: Verify that the corrective actions resolve the problem effectively.
- Standardization: Update processes, procedures, and documentation to include the new solutions.
- Training: Educate employees on the new procedures to ensure consistent application.
- Monitoring and review: Regularly review the effectiveness of the implemented solutions.
Recognize the Team and Celebrate Success
- Team recognition: Acknowledge the contributions of each team member.
- Celebrate achievements: Celebrate the success of solving the problem.
- Document lessons learned: Record insights and lessons learned for future reference.
Quality-centric Companies Rely on CQ QMS

Frequently Asked Questions
The 8D methodology is often used since it provides a consistent, simple, and thorough approach to solving raised problems at various stages. If properly applied, it gives several advantages such as:
A systematic approach for improving team-oriented problem solving skills
A clear understanding of basic statistical tools needed for problem solving
A practical understanding of the ‘ root cause analysis’ tool
Creating and expanding relative information about past failures and lessons learned to avoid future problems in the organization
Improving skills for corrective action deployment
When the team is trying to find the root cause of the problem and deploy corrective actions, some defective products will continue to be manufactured. To prevent these defective parts from reaching the customer, interim containment ensures that the defects are contained in the facility till the problem is completely solved. If defective parts reach the customer, it may result in warranty claims, field failures, and customer complaints.
To implement the 8D process successfully, the following factors are crucial:
The right team
An accurate description of the problem
Avoiding skipping through steps
Ensuring cooperation within the team and management support
Understanding the difference between real causes and possible causes
Related Insights

5 Dos and Don’ts When Choosing a QMS Solution for Your Enterprise
Every investment a business makes should have a measurable impact. In the case of an EQMS, the ROI is based…
Root Cause Analysis – Definition, Benefits and Process
All Quality and Safety Management Standards emphasize the importance of…
5 Why vs. Pareto Chart vs. Fishbone Diagram – Pros and Cons of Each of These RCA Techniques
All Quality Management Standards emphasize the importance of identifying the…
Automated CAPA with RCA and 5 Why to Make Your Workplace Healthy and Safe
PGT Innovations (PGT), pioneers in the impact-resistant window and door…
Connect with a CQ Expert
Learn about all features of our Product, Quality, Safety, and Supplier suites. Please fill the form below to access our comprehensive demo video.

Please confirm your details
By submitting this form you agree that we can store and process your personal data as per our Privacy Statement. We will never sell your personal information to any third party.
In Need of Smarter Ways Forward? Get in Touch.
Got questions we can help.
Chat with a CQ expert, we will answer all your questions.

8D Chess: How to Use The 8 Disciplines for Problem Solving
Hospitals have developed something of a reputation for being rife with bad processes . When processes aren’t adequate, the result is an abundance of “workarounds”.
For example, when equipment or supplies are missing, a nurse might waste time running around searching for what is needed, and once the item is found, return to their previous duties.
One study indicates that nurses spend 33 minutes of a 7.5-hour shift completing workarounds that are not part of their job description.
This may well “put out the fire” so-to-speak, but really it is just a hastily applied band-aid that does nothing to treat the root cause of the problem.
More time is wasted and more problems will arise in the future because nothing has been done to prevent the initial problem from happening again.
Individual nurses are not at fault here; workplace culture often values expertise in the form of those who “get the job done”, which tends to pull against the notion of spending time building good processes (time in which the job is perhaps not “getting done”).
So how to approach the problem of problem solving ?
In a lean context, problem solving can be distilled into two simple questions:
- What is the problem and how did it happen?
- How can we make sure that it doesn’t happen again?
The 8D, or eight disciplines methodology, is a problem solving process – most likely one of the most widely used problem solving processes out there. It is used by many different countries, in many different industries, and many different organizations.
8D is designed to help you put out those fires, and make sure they don’t happen again.
In this article, I’ll introduce you to the 8D problem solving methodology and provide you with an outline of the basic process that you can hopefully apply in your own business, plus how you can enhance 8D with other tools and methodologies like Six Sigma , FMEA , and Process Street .
Here’s what I hope you’ll take away after reading:
- An understanding of the basics of 8D
- Advantages of using 8D
- The purpose and objectives of each phase of the 8D process
- An understanding of how to use 8D for problem solving
- How 8D works with other problem solving tools
- How you can use Process Street to maximize the potential of the 8D framework
Let’s begin with the origins of 8D – what is it, and where did it come from?
What is 8D?
8D (sometimes Global 8D or G8D) stands for eight disciplines, and is a problem solving methodology. It’s basically a process for understanding and preventing problems.
Much like how risk management seeks to take a proactive, preventative stance, 8D aims to gain insight into the root causes of why the problems happen, so they won’t happen again.
The 8D process involves eight (sometimes nine) steps to solve difficult, recurring problems. It’s a transparent, team-based approach that will help you solve more problems in your business.
8D origins: Where did it come from?

Despite the popular story that 8D originated at Ford, it was in fact developed in 1974 by the US Department of Defence, ultimately taking the form of the military standard 1520 Corrective Action and Disposition System for Nonconforming Material .
Ford took this military standard, which was essentially a process for quality management , and expanded on it to include more robust problem solving methods.
In 1987, Ford Motor Company published their manual, Team Oriented Problem Solving (TOPS) , which included their first iteration of the 8D methodology.
Initially termed Global 8D (or G8D) standard, it is currently used by Ford and many other companies in the automotive supply chain.
8D, PDSA, & other problem solving processes
The disciplines of 8D follow the same logic as the Deming Cycle (also known as PDSA, and sometimes PDCA).
PDSA stands for Plan, Do, Study, Act (or Check, in the case of PDCA).
The similarity lies in the fact that both PDSA and 8D are designed to be used to improve processes. They’re both examples of cycles of continuous improvement.
Whereas 8D may be painted as a more generic problem-solving framework, structurally speaking both 8D and PDSA share a lot in common.
The simple idea of beginning with a clear objective, or desired output, and then testing, analyzing , and iteratively tweaking in a continuous cycle is the basis for both methodologies.
There are, of course, differences. We’ll cover the different applications of both 8D and PDSA in this article.
8D advantages

One of the main strengths of 8D is its focus on teamwork. 8D philosophy encourages the idea that teams, as a whole, are more powerful than the sum of the individual qualities of each team member.
It’s also an empirical methodology; that is to say that it is a fact-based problem solving process.
A branch of continuous improvement, proper use of 8D will help you coordinate your entire team for effective problem solving and improved implementation of just about all of the processes used in your business.
The 8 disciplines for problem solving
As you may have noticed, we’re starting with zero, which makes nine total disciplines. This “zero” stage was developed as an initial planning step.
D0: Plan adequately
Make comprehensive plans for solving the problem including any prerequisites you might determine.
Be sure to include emergency response actions.
D1: Establish your team
Establish your core team with relevant product or process knowledge. This team will provide you with the perspective and ideas needed for the problem solving process.
The team should consist of about five people, from various cross-functional departments. All individuals should have relevant process knowledge.
A varied group will offer you a variety of different perspectives from which to observe the problem.
It is advisable to establish team structure, roles, and objectives as far ahead in advance as possible so that corrective action can begin as quickly and effectively as possible.
D2: Describe the problem
Have your team gather information and data related to the problem or symptom. Using clear, quantifiable terms, unpack the problem by asking:
D3: Contain the problem (temporary damage control)
Depending on the circumstances, you may need to mobilize some kind of temporary fix, or “firefighting”.
The focus of this stage should be on preventing the problem from getting worse, until a more permanent solution can be identified and implemented.
D4: Identify, describe, and verify root causes
In preparation for permanent corrective action, you must identify, describe, and verify all possible causes that could contribute to the problem happening.
You can use various techniques for this, including a Failure Modes and Effects Analysis , or Ishikawa (fishbone) diagram .
It’s important that the root causes are systematically identified, described in detail, and promptly verified (or proved). How each cause is verified will depend on the data type and the nature of the problem.
Take a look at the section towards the end of this article for some more problem solving tools to help you decide the right approach.
D5: Identify corrective actions
You must verify that the corrective action you identified will in fact solve the problem and prevent it from happening again in the future (or whatever is your desired threshold of recurrence).
The best way to do this is to collect as much data as possible and by performing smaller-scale “pilot” tests to get an idea of the corrective action’s impact.
You can’t begin to identify the optimal corrective action until you have identified the root cause(s) of the problem.
D6: Implement and validate corrective actions
Carry out the corrective actions, and monitor short and long term effects. During this stage, you should assess and validate the corrective actions with empirical evidence.
Discuss and review results with your team.
D7: Take preventative measures (to avoid the problem happening again)
Here is where you make any necessary changes to your processes, standard operating procedures , policies , and anything else to make sure the problem does not happen again.
It may not be possible to completely eliminate any chance of the problem recurring; in that case, efforts should focus on minimizing possibility of recurrence as much as possible.
D8: Congratulate your team
It’s important to recognize the joint contribution of each and every one of the individuals that were involved in the process.
Team members should feel valued and rewarded for their efforts; this is crucial and perhaps the most important step – after all, without the team, the problem would not have been fixed.
Providing positive feedback and expressing appreciation helps to keep motivation high, which in turn improves the sense of process ownership and simply increases the likelihood your team will actually want to improve internal processes in the future.
How to use 8D for problem solving
The 8D method above outlines a proven strategy for identifying and dealing with problems. It’s an effective problem solving and problem prevention process.
In addition to avoiding long-term damage from recurring problems, 8D also helps to mitigate customer impact as much as possible.
More than just a problem-solving methodology, 8D sits alongside Six Sigma and other lean frameworks and can easily be integrated with them to minimize training and maximize efficacy.
8D is definitely a powerful framework on its own, but it really shines when combined with other synergistic concepts of lean and continuous improvement.
More problem solving tools that synergize well with 8D
8D has become a leading framework for process improvement, and in many ways it is more prescriptive and robust than other more simplistic Six Sigma approaches.
However, there are many Six Sigma methodologies, and even more frameworks for problem solving and process improvement .
The following improvement tools are often used within or alongside the 8D methodology.
DMAIC: Lean Six Sigma

DMAIC stands for:
The DMAIC process is a data-driven cycle of process improvement designed for businesses to help identify flaws or inefficiencies in processes.
Simply put, the goal with DMAIC is to improve and optimize existing processes.
Interestingly, the development of the DMAIC framework is credited to Motorola , whose work built upon the systems initially developed by Toyota .
In terms of working alongside 8D, you could use DMAIC to identify root causes as in D4; you could also implement the same techniques to better understand prospects for corrective actions as in D5, and D6.
We have a whole article on the DMAIC process, if you’re interested.
SWOT analysis

Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. You can use a SWOT analysis to gain insight into your organization as a whole, or on individual processes.
The main synergy with 8D is in the identification of opportunities, threats, and weaknesses.
These can represent opportunities for process improvements, weaknesses in your process that could produce problems further down the line, and threats, both internal and external, that may be out of your direct control but that could cause problems for you.
Here’s a SWOT analysis checklist you can use to structure your own analysis:
FMEA: Failure Mode and Effects Analysis

FMEA (Failure Mode and Effects Analysis) is a way of understanding the potential for problems and making preemptive preparations in order to avoid them. It is a method of risk management .
It is a type of preventative risk management process, and so works well in the context of identifying causes of problems so you can better deal with them.
FMEA and 8D work well together because:
- 8D can make use of information gathered during an FMEA process, like brainstorming sessions, to identify potential problems and their root causes.
- You can reuse possible cause information gathered during an FMEA process to feed into different representational diagrams like the Ishikawa (fishbone) diagram, which will help in the 8D process.
- 8D brainstorming data is useful for new process design. This allows the FMEA to take actual process failures into account, which produces more effective results.
- FMEA completed in the past can be used as databases of potential root causes of problems to inform 8D process development.
Here’s a free FMEA template for you to get started ASAP:
The Pareto Chart
The Pareto Chart helps us understand the impact of different variations of input on our output.
In relation to 8D, Pareto Charts can help us prioritize which root cause to target, based on which will have the greatest impact on improvement (where improvement is the desired output of the 8D process).
Here’s the Six Sigma Institute’s example Pareto Chart :
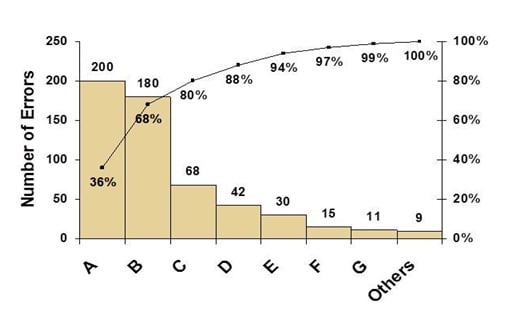
Here we have a simple deductive reasoning technique that asks “why?” five times to dig into the root cause of a problem.
The logic here is that by asking the same question five times, you work progressively “deeper” into the complexity of the problem from a single point of focus.
Ideally, by the fifth question you should have something that has a high likelihood of being a root cause.
This example from Wikipedia does a great job of conveying how the process works:
- The vehicle will not start. (the problem)
- Why? – The battery is dead. (First why)
- Why? – The alternator is not functioning. (Second why)
- Why? – The alternator belt has broken. (Third why)
- Why? – The alternator belt was well beyond its useful service life and not replaced. (Fourth why)
- Why? – The vehicle was not maintained according to the recommended service schedule. (Fifth why, a root cause)
Ishikawa diagrams (fishbone diagrams)
Sometimes called “cause-and-effect diagrams”, they are as such used to visualize the cause and effect of problems.
The approach takes six different categories and places information about the problem into different categories to help you understand what factors could be contributing to the problem.
One advantage over the 5 Whys approach is the way this method forces a more holistic perspective, as opposed to the potentially narrow vantage point offered by zooming in on a single aspect or question.
According to the Six Sigma Institute, the 6 key variables pertaining to root causes of problems are:
- Machine: Root causes related to tools used to execute the process.
- Material: Root causes related to information and forms needed to execute the process.
- Nature: Root causes related to our work environment, market conditions, and regulatory issues.
- Measure: Root causes related to the process measurement.
- Method: Root causes related to procedures, hand-offs, input-output issues.
- People: Root causes related people and organizations.
There’s also this useful illustration of a company using a fishbone diagram to better understand what factors contribute to a company’s high turn around time.
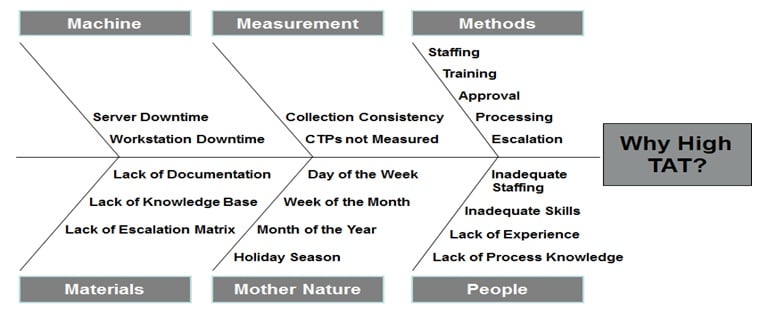
Gap analysis

A gap analysis is concerned with three key elements:
- The current situation, or “performance”
- The ideal situation, or “potential”
- What needs to be done in order to get from performance to potential, or “bridging the gap”
The “gap” is what separates your current situation from your ideal situation.
Businesses that perform a gap analysis can improve their efficiency and better understand how to improve processes and products.
They can help to better optimize how time, money, and human resources are spent in business.
There’s a lot that goes into a gap analysis, and quite a few different ways to approach it. Check out our article for a deeper dive into the gap analysis process.
Superpowered checklists
Checklists can be a great way to simplify a complex process into a series of smaller, easy-to-manage tasks. They’re one of the best ways to start using processes in your business.
By using checklists, you can reduce the amount of error in your workflow , while saving time and money by eliminating confusion and uncertainty.
What’s more, if you’re using Process Street, you have access to advanced features like conditional logic , rich form fields and streamlined template editing .
How to use Process Street for 8D problem solving
Good problem solving relies on good process. If you’re trying to solve problems effectively, the last thing you want is your tools getting in your way.
What you want is a seamless experience from start to finish of the 8D methodology.
The best kinds of processes are actionable. That’s why you should consider using a BPM software like Process Street to streamline recurring tasks and eliminate manual work with automation .
Process Street’s mission statement is to make recurring work fun, fast, and faultless. By breaking down a process into bite-sized tasks , you can get more done and stay on top of your workload.
Sign up today for a free Process Street trial!
Problem solving is an invaluable skill. What’s your go-to process for problem solving? We’d love to know how it compares with the 8D method. Let us know in the comments!
Get our posts & product updates earlier by simply subscribing
Oliver Peterson
Oliver Peterson is a content writer for Process Street with an interest in systems and processes, attempting to use them as tools for taking apart problems and gaining insight into building robust, lasting solutions.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Take control of your workflows today

Mastering the 8D Problem Solving Method: A Comprehensive Guide

It is often said that “a stitch in time saves nine.” Efficient problem-solving is an essential skill , especially in a professional environment.
When it comes to addressing complex issues, the 8D Problem Solving method has gained significant traction across various industries. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the 8D Problem Solving method, its history, and its application across multiple sectors.
History of the 8D Problem Solving Method
The 8D Problem Solving approach has its origins in World War II when the American military was under intense pressure to produce reliable weapons as quickly as feasible.
The military established a methodical approach to problem-solving, focusing on quality control and continual improvement, to ensure that resources were used effectively.
This was the first instance of what would later develop into the 8D technique.
The writings of Walter Shewhart , W. Edwards Deming , and Joseph M. Juran , who set the groundwork for contemporary quality control and continuous improvement ideas, had a substantial impact on the development of the 8D Problem Solving approach.
These guidelines stress the value of data-driven decision-making and the necessity for businesses to take a pro-active approach to problem-solving.
The Ford Motor Company faced intense competition from Japanese automakers in the 1980s, which caused it to struggle.
Ford used quality control and continuous improvement as its guiding principles and included the 8D Problem Solving process into its business practices to regain its footing.
The automobile sector adopted the 8D methodology widely as a result of the initiative’s success.
The 8D Problem Solving approach gained popularity outside of the automobile industry as it showed continuous promise.
The 8D methodology is now being used by businesses in a variety of industries, such as manufacturing, healthcare, and technology, to solve complicated issues, enhance their operations, and guarantee customer happiness.
The 8D Problem Solving approach has attained widespread acceptance throughout a number of industries.
It is a potent tool for businesses looking to improve their problem-solving skills and promote long-term success due to its systematic approach, emphasis on teamwork, and emphasis on continual improvement.
The Eight Disciplines of 8D Problem Solving

D1: Form a Team
Assembling a diverse team with relevant expertise
The first phase in the 8D process is to put together a varied team of people with the necessary knowledge, making sure that all viewpoints and skill sets are represented. This multidisciplinary approach makes it easier to recognize problems and produce creative solutions.
Defining roles and responsibilities
The tasks and responsibilities of each team member must be established once the team has been constituted. Team members can work cooperatively and effectively by setting clear expectations, ensuring that everyone’s abilities are utilized to the utmost extent. It keeps the problem-solving process on track and upholds accountability.
D2: Define the Problem
Accurate problem description
Accurately characterizing the current problem is the second discipline of the 8D technique. In order to do this, the team must acquire pertinent data, analyze it, and create a clear, succinct statement describing the problem. A focused and efficient problem-solving approach is built on a well identified problem.
Gathering data and identifying root causes
To create long-lasting solutions, the problem’s underlying causes must be determined. The team must gather information from a variety of sources, such as consumer feedback, product testing, or process performance measurements, in order to accomplish this. The team is able to uncover patterns, trends, and potential fundamental causes thanks to this data-driven approach, which also ensures that the problem-solving procedure is unbiased and grounded in facts.
D3: Develop an Interim Containment Plan
Quick, temporary solutions
Minimizing the effects of a problem is crucial in the field of problem solving. Creating an interim containment strategy, which offers quick, temporary solutions to the issue, is the third discipline in the 8D technique. These quick fixes aid in limiting the harm, stopping more problems, and buying the team some time while they produce a more long-term fix.
Mitigating damage and preventing further issues
It is essential to keep an eye on the interim containment plan’s efficacy and adjust as necessary as you go. This guarantees that the short-term fix works to contain the harm and stop the issue from getting worse. Any lessons learnt during this phase should also be recorded by the team because they will be helpful in creating the ultimate corrective action.
D4: Identify Root Causes

Root cause analysis techniques
The fourth discipline of the 8D technique entails examining the issue more closely in order to determine its underlying causes. Various root cause analysis methods, including the Five Whys, Fishbone Diagram, and Fault Tree Analysis, must be used in this situation. The team may create focused solutions that address the issue at its source rather than just treating its symptoms by determining the fundamental causes of the problem.
Verifying root causes through data
Verifying potential root causes with data is crucial after the team has discovered them. Taking this step, the team can avoid being misled by assumptions or unrelated elements and instead concentrate on the real core cause. The team may be confident that their suggested remedies will be successful in tackling the problem by validating the main causes using data.
D5: Choose and Verify Permanent Corrective Actions
Developing and evaluating potential solutions
The team can now consider various solutions after determining the root reasons. “Two heads are better than one,” as the saying goes, and this collaborative process frequently produces innovative and useful ideas. The team should assess each alternative after producing a list of potential corrective actions based on elements including feasibility, cost, and potential impact. This makes it more likely that the selected solution will be both workable and efficient.
Implementing and verifying chosen solution
It’s crucial to assess the effectiveness of the chosen solution before fully applying it. A small-scale trial or a pilot program can be used to accomplish this. The team may be certain that their selected corrective action will be successful when used on a bigger scale by confirming the solution’s success in resolving the issue.
D6: Implement Permanent Corrective Actions
Developing a detailed action plan
The team must create a thorough action plan for putting the selected solution into practice when it has been verified. This strategy should specify the actions, materials, and timetable required for a full integration of the solution into the organization’s operations. A comprehensive action plan makes for an effective implementation that minimizes any hiccups or setbacks.
Monitoring implementation and adjusting as needed
It’s essential to keep an eye on the permanent remedial action’s development and adjust, as necessary. The team may make sure that the solution is properly integrated and produces the required results by remaining alert and reacting to any unforeseen obstacles.
D7: Prevent Recurrence
Identifying potential future issues
The 8D method’s seventh discipline focuses on predicting prospective problems that might develop in the future from comparable underlying causes. The team can help to prevent repeat incidences and continuously enhance the organization’s procedures by foreseeing and addressing these possible issues.
Adjusting processes and procedures to prevent recurrence
The team should analyze and make any necessary modifications to the organization’s systems and procedures to stop the issue from happening again. This can entail creating new quality control procedures, updating the documentation, or changing the training materials. Implementing these changes, the company can promote a climate of continuous development and make sure that the lessons discovered throughout the problem-solving procedure are incorporated into every aspect of its day-to-day work.
D8: Congratulate the Team
Recognizing team achievements
It’s important to acknowledge the team’s effort and commitment when the 8D technique has been implemented successfully. Celebrating their accomplishments promotes a sense of ownership, boosts morale, and encourages continuing commitment to ongoing growth.
Sharing lessons learned with the organization
The team should share their lessons learned with the broader organization. Doing so, they can help to disseminate the knowledge gained during the problem-solving process, fostering a culture of learning and improvement throughout the company.
Practical Application of the 8D Problem Solving Method

Numerous industries, including aerospace, automotive, healthcare, manufacturing, and technology, have successfully used the 8D Problem Solving method. These actual instances show how adaptable and successful the system is at solving a variety of challenging issues .
Although the 8D method offers a structured approach to problem-solving, it is crucial to customize the procedure to the particular requirements and context of the current problem.
This could entail modifying the chronology, modifying the root cause analysis methods, or adding new data sources.
The team can ensure the most efficient problem-solving procedure by continuing to be adaptable and flexible.
Tips for Successful 8D Problem Solving Implementation

Emphasizing clear communication
Clear communication is the lifeblood of effective problem-solving.
Throughout the 8D process, the team should prioritize open and honest communication, ensuring that all members have a thorough understanding of the problem, the chosen solution, and their individual responsibilities.
Fostering a culture of collaboration and continuous improvement
A collaborative and improvement-focused culture is key to the success of the 8D method.
Encouraging open dialogue, mutual support, and ongoing learning, the organization can create an environment in which the 8D method can thrive.
Employing project management tools and techniques
Project management tools and techniques can be invaluable in facilitating the 8D process.
Using tools such as Gantt charts, project management software, or Kanban boards, the team can better track progress, allocate resources, and manage timelines.
These tools can help to keep the problem-solving process organized and efficient, ensuring that the team stays on track and achieves their goals.
Final Thoughts
The 8D Problem Solving method is an effective and adaptable way for tackling complicated challenges in a variety of industries.
Organizations may methodically identify and address problems, stop them from happening again, and promote a culture of continuous improvement and adhering to the eight disciplines.
As we’ve seen, the 8D method’s effectiveness depends on putting together a varied team, upholding clear communication, customizing the procedure for particular circumstances, and using efficient project management tools and approaches.
We urge you to use the 8D Problem Solving method inside your organization now that you have a thorough understanding of it.
Doing this, you may not only address issues more quickly, but also unleash the long-term growth potential of your company.
If you can master the 8D approach, your business will have a better future and you’ll be well-equipped to traverse the waters of problem-solving.
Q: What is the 8D Problem Solving method?
A : A systematic strategy for addressing complicated challenges across multiple industries is the 8D Problem Solving method. It consists of eight disciplines that help firms recognize problems, find solutions, stop them from happening again, and promote a continuous improvement culture.
Q: What are the origins of the 8D Problem Solving method?
A : The United States military created a systematic approach to problem-solving during World War II that was centered on quality control and continual improvement, and this is where the 8D technique got its start. The Ford Motor Company later adopted and promoted the technique in the 1980s.
Q: What are the eight disciplines of the 8D Problem Solving method?
A : The eight disciplines of the 8D method are
- Form a Team
- Define the Problem
- Develop an Interim Containment Plan
- Identify Root Causes
- Choose and Verify Permanent Corrective Actions
- Implement Permanent Corrective Actions
- Prevent Recurrence
- Congratulate the Team
Q: How can the 8D method be applied across different industries?
A : The 8D method is adaptable and may be used to solve a wide variety of complicated problems in a number of different industries, including manufacturing, aerospace, automotive, healthcare, and technology. Organizations should modify the process to match the particular requirements and context of the current challenge in order to utilize the 8D technique effectively.
Q : What are some tips for successfully implementing the 8D Problem Solving method?
A : To ensure the success of the 8D method, organizations should
- Emphasize clear communication.
- Foster a culture of collaboration and continuous improvement.
- Employ effective project management tools and techniques .
Q: What is the role of root cause analysis in the 8D method?
A : The 8D method’s key element is root cause analysis, which identifies the root reasons of an issue. Organizations can create focused solutions that solve the issue at its foundation rather than just masking the symptoms by addressing the root causes.
Q: How can the 8D method help prevent the recurrence of problems?
A : By recognizing potential future issues that may result from comparable root causes and modifying processes and procedures accordingly, the 8D technique aids in preventing the recurrence of problems. This proactive strategy assists companies in making continuous improvements and reducing the possibility that similar issues will arise again.

Ronnie Patterson
Ronnie Patterson, founder of MagnÜron, is a multifaceted entrepreneur with a diverse background in music, electronics engineering, and engineering management. Drawing on experience across various industries, He offers expertise in SEO, operations, and strategy to help businesses thrive. Possessing a unique perspective and unwavering commitment to collaboration, and ideal partner for growth and success.
Similar Posts

Virtual Events: A Guide for Businesses
Businesses are increasingly leveraging the power of virtual events to…

What is Production: Defining the Process and Economic Importance
What is Production Production is the process of transforming unfinished…

Unlocking the Game: 15 Impactful Leadership Competencies
Leadership competencies is more critical than ever. Leadership competencies, which…

10 Tips For a Mobile Detailing Business
Mobile detailing is a business that has been growing in…

How to Start a Cleaning Business: Tips for Establishing and Growing Your Cleaning Company
Starting a cleaning business can be a great way to…


7 Tips on How to Start a House Painting Business
If you’re reading this, there’s a good chance you’re interested…
8D Problem Solving: Comprehensive Breakdown and Practical Applications

The 8D problem-solving process stands as a beacon of structured analysis and corrective action within the complexities of operational pitfalls and quality control discrepancies across industries. Originating from the automotive industry and since adopted widely, the methodology offers a meticulous step-by-step approach that fosters team cohesion, addresses problems at their roots, and implements sustainable solutions.
This article seeks to delve into the nuances of the 8D problem-solving framework, presenting a lucid exposition of its origins, a detailed foray into each step enriched by practical examples, and concluding with the unequivocal benefit bouquet it presents to the organization adopting it.
The Origins of the 8D Problem Solving Methodology
The 8D, or "Eight Disciplines," problem-solving approach germinated from the fertile grounds of collaborative efforts to ensure superior quality and reliability in manufacturing. Initially developed by the Ford Motor Company in the 1980s, this systematic method was a response to a confluence of quality and operational issues that were pervasive in the automotive industry. It drew broader appeal as its efficacy became apparent - functioning as an amalgam of logic, analytics, and teamwork to tackle problems methodically.
The wide reach of the 8D methodology is evident in industries ranging from manufacturing to healthcare, aerospace to IT, and beyond. Its universal applicability stems from a foundational adherence to principle over process, transcending the intricacies of industry-specific challenges. By combining reactive and proactive measures, the 8D method helps in not just extinguishing the fire, but also preventing its outbreak, making it an enduring asset in the organizational toolkit.
The 8 Steps of Problem Solving
An incursion into the 8D methodology reveals a framework that is both systematic and flexible. Each step is sequenced to ensure that issues are not merely patched but genuinely resolved, implementing robust preventive measures to curtail recurrences. This section expounds on each disciplinary step and serves as a substrate for practical implementation examples, supplementing theoretical insights with real-world applicability.
Step 1: Establish a Team
The cornerstone of any formidable 8D approach begins with assembling a competent team. The wisdom embedded in this initial phase is the recognition that effective problem-solving is not a solitary venture but a collaborative pursuit. A multidisciplinary team brings diverse perspectives that are critical in diagnosing issues accurately and devising solutions effectively.
When determining team composition, the emphasis should be on a mix of skills and expertise relevant to the problem at hand. Roles within the team should be clearly defined to streamline activities and foster accountability. Each member should be well-versed in their responsibilities, from those leading the problem-solving charge to those executing and tracking actions.
Step 2: Describe the Problem
Clarity is vital in the second step, which necessitates delineating the problem with precision. A meticulous description sets the foundation for targeted analysis and actionable solutions. It involves accruing information that is factual, quantifiable, and devoid of assumptions – the cornerstone of an accurate problem portrayal.
Techniques like '5W2H' (who, what, when, where, why, how, how much) can galvanize teams into crafting detailed problem descriptions. An exemplar of a well-articulated problem statement might state, "Machine X has experienced a 15% decline in output quality, resulting in a monthly loss of 200 units of product Y since January due to recurrent mechanical inaccuracies."
Step 3: Develop Interim Containment Actions
Addressing a problem's immediate impact is pivotal to prevent exacerbation as a root cause analysis is conducted. Interim containment actions can be likened to first aid – essential, though not the definitive cure. These measures should be rigorously designed to quell the problem's spread or intensification without creating new issues.
An interim action for the aforementioned issue with Machine X could involve adjusting the production schedule to mitigate output loss while the machine is under examination. This demonstrates a temperate solution, buying time for a comprehensive fix without severely disrupting the production chain.
Step 4: Define and Verify the Root Cause(s)
Singular in its focus yet pluralistic in its approach, this phase is committed to uncovering the underlying reasons for the problem. Root cause identification is a task of surgical precision, necessitating a deep dive into the problem without the constraints of predetermined notions.
Techniques such as the "5 Whys" and "Fishbone Diagram" guide problem solvers through a structured investigation of potential causes. Verification is as crucial as identification, ensuring that purported root causes stand up to scrutiny and testing.
Step 5: Verify Permanent Corrective Action(s)
Once root causes have been established, attention shifts to devising and validating long-term corrective actions. This step traverses the path from theory to practice. It requires a judicious appraisal of potential solutions with a clear-eyed view of their feasibility, effectiveness, and sustainability.
Best practices in this step incorporate piloting solutions on a smaller scale, enabling refinement before full-scale implementation. A well-considered corrective action for Machine X might involve upgrading mechanical components identified as failure points, subject to cost-benefit analysis and potential disruption to the production line.
Step 6: Implementing and Validating Permanent Corrective Actions
This step transitions the plan into reality, pushing the corrective actions beyond the threshold into the operational environment. Careful implementation is the linchpin, with detailed plans and schedules ensuring that actions are well-executed and efficacious.
The validation process is a keystone in affirming that corrective actions deliver the intended improvements. For Machine X, this could entail monitoring post-repair performance metrics over a defined period against pre-issue levels to authenticate the efficacy of the improvements.
Step 7: Preventive Measures
Armed with insights gleaned, the 7th step propels the methodology into preventative mode. Here, the onus is on forestalling a problem’s resurgence by ingraining the lessons learned into the organizational fabric. The aim is to encapsulate these insights in policies, procedures, or system changes.
This could mean revising maintenance schedules or worker training programs for Machine X to include the specific nuances that led to the mechanical inaccuracies, thereby shielding against repeat episodes.
Step 8: Congratulate Your Team
The final step encompasses a human-centered focus on recognition and commendation. Acknowledgment of the team’s efforts reinforces motivation, fosters a positive culture, and encourages engagement in future problem-solving initiatives.
Celebrating the success could manifest in a ceremonious recognition of the team’s achievements, an internal announcement of their contributions, or a tangible expression of appreciation. This not only cements the accomplishment but also propels a sense of camaraderie and collective purpose.
The Importance of the 8D Problem Solving Process
A mature consideration of the 8D problem-solving process corroborates its contributory significance in unraveling complex issues and instituting consequential improvements. The benefits it confers are manifest in enhanced product quality, heightened customer satisfaction, and the stimulation of a proactive problem-solving culture. Challenges do persist, mainly in the form of resistance to change or insufficient training; nevertheless, with a conscientious implementation, these can be navigated.
Moreover, the 8D approach aligns seamlessly with the pursuit of continuous improvement – a cornerstone of many business philosophies such as Lean and Six Sigma. It thus serves not only as a solution framework but also as a catalyst for organizational growth and learning.
In summary, the 8D problem-solving methodology stands out for its disciplined, team-driven, and methodical approach to tackling complex problems. From its historical roots in the automotive industry to its implementation in modern enterprises, its efficacy in achieving sustainable solutions is undoubted. Online certificate programs and problem-solving courses often feature 8D due to its relevance and value across industries.
As this article delineates each step, with practical applications and advice, the message is clear: mastery of 8D is not just for immediate problem resolution – it is a pathway to building a resilient and adaptive organization capable of facing the challenges of an ever-changing business landscape.
What are the key steps involved in the 8D Problem Solving process and how do they interact with each other?
Introduction to the 8d process.
The 8D Problem Solving process stands tall. It is a structured approach. Businesses use it widely. 8D tackles complex problems effectively. It drives teams towards lasting solutions. It also fosters quality and reliability. The "D" denotes eight disciplined steps. These steps guide teams. They identify, correct, and prevent issues.
8D Steps Explained
D1: establish the team.
Form a skilled team first. Diversity matters here. Each member brings insights. Their combined expertise is crucial. Team formation kicks off the process.
D2: Describe the Problem
Articulate the issue clearly. Use quantifiable data here. Understanding the scope matters. Have accurate problem statements ready. They pave the way forward.
D3: Develop Interim Containment Action
Ensure a temporary fix. It limits the problem's impact. Speed is of the essence. However, ensure the action is effective. The goal is to stabilize the situation.
D4: Determine Root Cause
Dig deep into causes. Use data-driven analysis. Techniques include fishbone diagrams. Five Whys is also popular. Root cause analysis is pivotal. It prepares the team for corrective actions.
D5: Design and Verify Permanent Corrective Actions
Choose the best corrective action. Rigorous selection criteria apply. Effectiveness and efficiency matter. Verify through testing. Make certain the solution fits.
D6: Implement and Validate Permanent Corrective Actions
Roll out the solution. Watch closely for results. Validation takes place here. Use performance indicators for this. They must indicate that the solution works.
D7: Prevent Recurrence
Embed the improvement. Update systems and policies. Training may be necessary. Maintain the gains. This step safeguards the future. Documentation is important here.
D8: Congratulate the Team
Never overlook recognition. Acknowledge everyone's efforts. Celebrate the success achieved. It boosts team morale. It also promotes a culture of quality.
Interplay Between Steps
The interdependence is strong. Each step builds on the previous one. For example, a strong team in D1 enhances problem understanding in D2. Similarly, effective interim actions in D3 set the stage for a thorough root cause analysis in D4.
The verification in D5 ensures the solution from D4 is sound. Implementation in D6 then relies on the verified action. To prevent recurrence (D7), one must understand the root cause. The entire process relies on clear communication. Team recognition (D8) closes the loop neatly. It paves the way for future problem-solving success.
In essence, the 8D steps are interlinked. Each step informs the next. Teams achieve the best results by following the sequence. They also adapt as needed. 8D enforces a discipline that leads to high-quality results. The interaction between steps ensures problems do not just disappear. They stay solved. This is the power of an integrated problem-solving approach.

Can you provide some practical examples of the effective application of 8D Problem Solving strategies in real-life settings?
Understanding 8d problem solving.
8D problem solving stands for Eight Disciplines. It involves steps that teams must follow. Starting from identifying problems , it goes until preventing reoccurrences . Companies use 8D to tackle complex issues. Its main goal remains quality improvement.
Here are practical examples where 8D shines.
Example 1: Automotive Industry
D0: Plan - An auto manufacturer formed a team. Their goal was clear: resolve brake failures.
D1: Team Formation - They gathered experts from diverse fields. Collaboration was key here.
D2: Describe the Problem - They identified specific issues. Customers reported brakes failing at high speeds.
D3: Develop Interim Containment - They distributed quick-fix kits to dealerships. This ensured immediate customer safety.
D4: Determine Root Causes - A deep dive ensued. The team discovered a faulty brake fluid line.
D5: Choose and Verify Permanent Corrective Actions (PCAs) - They redesigned the brake line. Then they tested it under rigorous conditions.
D6: Implement and Validate PCAs - The new design went into production. Ongoing assessments confirmed its effectiveness.
D7: Take Preventive Measures - They updated their design guidelines. Thus, they eliminated the possibility of similar failures.
D8: Congratulate Your Team - Management recognized the team's effort. This promoted a culture of problem-solving.
Example 2: Electronics Manufacturer
D0: Plan - A sudden surge in returned gadgets prompted action.
D1: Team Formation - A cross-functional team took charge. They had one aim: find the flaw.
D2: Describe the Problem - Devices were overheating during usage. Anxiety among customers grew.
D3: Develop Interim Containment - They halted the production line. Assessing risks was necessary.
D4: Determine Root Causes - Detailed analysis revealed a substandard battery component.
D5: Choose and Verify PCAs - They sourced a higher quality component. Subsequent tests showed promising results.
D6: Implement and Validate PCAs - They integrated the new component into production. Monitoring phases ensured it was a fix.
D7: Take Preventive Measures - They revamped their quality control protocols. Now they could avoid similar issues.
D8: Congratulate Your Team - The team's innovative approach earned praise. They set new standards in their processes.
Example 3: Food Packaging Company
D0: Plan - Reports of packaging leaks triggered an 8D.
D1: Team Formation - Experts from production to distribution joined forces. They understood the stakes were high.
D2: Describe the Problem - The leaks were sporadic but damaging. Food safety concerns escalated.
D3: Develop Interim Containment - They removed compromised products from shelves. Protecting the consumer was paramount.
D4: Determine Root Causes - Investigation exposed a sealing machine defect.
D5: Choose and Verify PCAs - Engineers redesigned the sealing mechanism. Trials followed, proving success.
D6: Implement and Validate PCAs - The updated machines replaced the old ones. Continuous evaluations followed to assure quality.
D7: Take Preventive Measures - They introduced more rigorous maintenance routines. They aimed to preempt future failures.
D8: Congratulate Your Team - The swift and thorough response earned accolades. They reinforced trust in their brand.
8D's Practical Value
Each example showcases 8D's potential. This problem-solving framework adapts to various scenarios. Through structured teamwork and analysis, it guides toward sustainable solutions. It helps in ensuring the same problem does not occur twice. Businesses across different sectors find 8D crucial for their continuous improvement efforts. It underlines that a methodical approach to problem-solving can yield significant long-term benefits.

How is the effectiveness and success of the 8D Problem Solving approach measured in practical applications?
Introduction to 8d problem solving.
The 8D Problem Solving approach stands as a structured methodology. It aims to address and resolve critical issues within an organization. Rooted in the team-oriented approach, 8D follows eight disciplined steps. These steps ensure a comprehensive and effective resolution process. The process includes identifying the problem, implementing interim controls, defining root causes, developing a corrective action plan, taking corrective actions, validating those actions, preventing recurrence, and finally congratulating the team.
Measuring Effectiveness and Success
Quantitative metrics.
Timeliness of Response
The promptness of the initial response is critical. It alerts stakeholders to the emergence and acknowledgment of the issue.
Problem Recurrence Rates
A key success indicator is the frequency of problem recurrence. A declining trend signifies effective corrective actions.
Financial Impact
Cost savings or avoidance measures the fiscal efficiency of the resolution. It counts both direct and indirect factors.
Cycle Time Reduction
Improvements in processes can lead to shorter cycle times. This reflects efficiency gains from the 8D implementation.
Qualitative Metrics
Quality of Documentation
Comprehensive documentation ensures thorough issue analysis. It captures the nuances of the problem-solving journey.
Stakeholder Satisfaction
Feedback from affected parties gauges the outcome’s acceptability. Satisfaction levels can direct future interventions.
Knowledge Transfer
Disseminating learnings enhances organizational capability. Sharing insights leads to broader, preventive measures.
Team Cohesion and Growth
Personal and team development signal process benefits. Such growth provides intangible value to the organization.
Practical Application and Continuous Improvement
In practical applications, tailoring metrics to contexts is vital. Unique business environments demand specific success criteria. Therefore, adapting the approach and its measurement system is necessary.
Organizations may employ a combination of tangible and intangible metrics. Aligning these to strategic goals ensures relevance. The 8D Process receives fine-tuning through iterative cycles. Each cycle offers an opportunity for enhanced problem-solving efficacy.
The Importance of Measure Standardization
Standardizing the measurement process ensures consistency. It aids in comparing and benchmarking against best practices. Homogeneity in measures facilitates clearer communication. It enhances the understanding of successes and areas for improvement.
Revisiting and Refining the 8D Process
Upon completion, a rigorous review of the 8D process is crucial. It ensures learnings lead to process refinement. Alterations in measures might follow to better reflect evolving business needs. This ongoing evolution drives the sustained value of the 8D methodology.
The 8D Problem Solving approach, with its disciplined steps, delivers a robust framework. Measuring its effectiveness requires a blend of quantitative and qualitative metrics. These metrics, when standardized and continually refined, offer a clear lens to assess the 8D process's success. They help organizations not just to solve problems but to evolve in their problem-solving capabilities.

He is a content producer who specializes in blog content. He has a master's degree in business administration and he lives in the Netherlands.

Decision Tree: A Strategic Approach for Effective Decision Making

Lateral Thinking for Problem-Solving: Find the Haystack!

Unlocking Problem Solving Skills: Where Do Problems Come From?

Developing Problem Solving Skills Since 1960s WSEIAC Report
- Product overview
- All features
- Latest feature release
- App integrations
- project icon Project management
- Project views
- Custom fields
- Status updates
- goal icon Goals and reporting
- Reporting dashboards
- asana-intelligence icon Asana AI
- workflow icon Workflows and automation
- portfolio icon Resource management
- Capacity planning
- Time tracking
- my-task icon Admin and security
- Admin console
- Permissions
- list icon Personal
- premium icon Starter
- briefcase icon Advanced
- Goal management
- Organizational planning
- Project intake
- Resource planning
- Product launches
- View all uses arrow-right icon

- Work management resources Discover best practices, watch webinars, get insights
- Customer stories See how the world's best organizations drive work innovation with Asana
- Help Center Get lots of tips, tricks, and advice to get the most from Asana
- Asana Academy Sign up for interactive courses and webinars to learn Asana
- Developers Learn more about building apps on the Asana platform
- Community programs Connect with and learn from Asana customers around the world
- Events Find out about upcoming events near you
- Partners Learn more about our partner programs
- Asana for nonprofits Get more information on our nonprofit discount program, and apply.
- Project plans
- Team goals & objectives
- Team continuity
- Meeting agenda
- View all templates arrow-right icon
- Project management |
- What is 8D? A template for efficient pr ...
What is 8D? A template for efficient problem-solving
How you respond when problems arise is one of the most defining qualities of a manager. Luckily, there are tools you can use to master problem-solving. The 8D method of problem-solving combines teamwork and basic statistics to help you reach a logical solution and prevent new issues from arising.
You’ve spent months overseeing the development of your company's newest project. From initiation, planning, and execution, you’re confident this may be your best work yet.
Until the feedback starts rolling in.
There’s no sugar-coating it—things don’t always go as planned. But production or process issues are hardly a signal to throw in the towel. Instead, focus on honing your problem-solving skills to find a solution that keeps it from happening again.
The 8D method of problem solving emphasizes the importance of teamwork to not only solve your process woes but prevent new ones from occurring. In this guide, we’ll break down what 8D is, how to use this methodology, and the benefits it can give to you and your team. Plus, get an 8D template to make solving your issue easier.
What is 8D?
The eight disciplines (8D) method is a problem-solving approach that identifies, corrects, and eliminates recurring problems. By determining the root causes of a problem, managers can use this method to establish a permanent corrective action and prevent recurring issues.
How do you use the 8D method?
The 8D method is a proven strategy for avoiding long-term damage from recurring problems. If you’re noticing issues in your workflow or processes, then it’s a good time to give this problem-solving method a try.
To complete an 8D analysis, follow “the eight disciplines” to construct a statistical analysis of the problem and determine the best solution.
The eight disciplines of problem-solving
8D stands for the eight disciplines you will use to establish an 8D report. As you may notice, this outline starts with zero, which makes nine total disciplines. The “zero stage” was developed later as an initial planning stage.
To illustrate these steps, imagine your organization experienced a decline in team innovation and productivity this past year. Your stakeholders have noticed and want to see changes implemented within the next six months. Below, we’ll use the 8D process to uncover a morale-boosting solution.
![8d method of problem solving [inline illustration] D8 problem solving approach (infographic)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/6ab7c188-3258-4d2e-afe6-9a4a084cc09f/inline-productivity-8d-template-1-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
D0: Prepare and plan
Before starting the problem-solving process, evaluate the problem you want to solve. Understanding the background of the problem will help you identify the root cause in later steps.
Collect information about how the problem has affected a process or product and what the most severe consequences may be. Planning can include:
Gathering data
Determining the prerequisites for solving the problem
Collecting feedback from others involved
![8d method of problem solving [inline illustration] D0 Planning (example)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/abc3621d-e1ae-47ff-b731-0ee38cff99e9/inline-productivity-8d-template-2-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
If we look back at our example, you may want to figure out whether this decline in morale is organization-wide or only applies to a few departments. Consider interviewing a few employees from different departments and levels of management to gain some perspective. Next, determine what knowledge and skills you will need to solve this lapse in productivity.
D1: Form your team
Create a cross-functional team made up of people who have knowledge of the various products and workflows involved. These team members should have the skills needed to solve the problem and put corrective actions in place.
Steps in this discipline may include:
Appointing a team leader
Developing and implementing team guidelines
Determining team goals and priorities
Assigning individual roles
Arranging team-building activities
![8d method of problem solving [inline illustration] D1 Team members (example)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/51986017-5150-4dd4-940c-252cd0eb8ba5/inline-productivity-8d-template-3-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
From our example, a solid team would consist of people with first-hand experience with the issues—like representatives from all departments and key people close to workshop-level work. You may also want to pull someone in from your HR department to help design and implement a solution. Most importantly, make sure the people you choose want to be involved and contribute to the solution.
D2: Identify the problem
You may have a good understanding of your problem by now, but this phase aims to break it down into clear and quantifiable terms by identifying the five W’s a and two H’s (5W2H):
Who first reported the problem?
What is the problem about?
When did it occur and how often?
Where did it occur (relating to the sector, supplier, machine, or production line involved)?
Why is solving the problem important?
How was the problem first detected?
How many parts/units/customers are affected?
![8d method of problem solving [inline illustration] D2 Problem statement & description (example)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/9825ecd6-2bd3-4559-a68c-b1ae8aca2e52/inline-productivity-8d-template-4-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
Use your team’s insights to answer these questions. From our example, your team may conclude that:
Employees feel overwhelmed with their current workload.
There is no real structure or opportunity to share new ideas.
Managers have had no training for meetings or innovation settings.
Disgruntled employees know they can achieve more—and want to achieve more—even if they seem disengaged.
Once you answer these questions, record an official problem statement to describe the issue. If possible, include photos, videos, and diagrams to ensure all parties have a clear understanding of the problem. It may also help to create a flowchart of the process that includes various steps related to the problem description.
D3: Develop an interim containment plan
Much like we can expect speedy first aid after an accident, your team should take immediate actions to ensure you contain the problem—especially if the problem is related to customer safety.
An interim containment plan will provide a temporary solution to isolate the problem from customers and clients while your team works to develop a permanent corrective action. This band-aid will help keep your customers informed and safe—and your reputation intact.
![8d method of problem solving [inline illustration] D3 Interim containment action (example)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/d6279c36-ccc6-4de3-89d2-f221632a1059/inline-productivity-8d-template-5-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
Because your findings revealed workers were overworked and managers lacked training, your team suggests scheduling a few mandatory training sessions for leaders of each department covering time and stress management and combating burnout . You may also want to have a presentation outlining the topics of this training to get key managers and stakeholders interested and primed for positive upcoming changes.
D4: Verify root causes and escape points
Refer back to your findings and consult with your team about how the problem may have occurred. The root cause analysis involves mapping each potential root cause against the problem statement and its related test data. Make sure to test all potential causes—fuzzy brainstorming and sloppy analyses may cause you to overlook vital information.
![8d method of problem solving [inline illustration] D4 Root cause & escape points (example)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/301717c6-0434-4c88-addf-d500dc23ae87/inline-productivity-8d-template-6-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
In our example, focus on the “why” portion of the 5W2H. You and your team identify six root causes:
Managers have never had any training
There is a lack of trust and psychological safety
Employees don’t understand the objectives and goals
Communication is poor
Time management is poor
Employees lack confidence
In addition to identifying the root causes, try to pinpoint where you first detected the problem in the process, and why it went unnoticed. This is called the escape point, and there may be more than one.
D5: Choose permanent corrective actions
Work with your team to determine the most likely solution to remove the root cause of the problem and address the issues with the escape points. Quantitatively confirm that the selected permanent corrective action(s) (PCA) will resolve the problem for the customer.
Steps to choosing a PCA may include:
Determining if you require further expertise
Ensuring the 5W2Hs are defined correctly
Carrying out a decision analysis and risk assessment
Considering alternative measures
Collecting evidence to prove the PCA will be effective
![8d method of problem solving [inline illustration] D5 Permanent corrective action (example)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/53509966-18dd-4bb4-88a1-c7ca940fde3f/inline-productivity-8d-template-7-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
Your team decides to roll out the training used in the interim plan to all employees, with monthly company-wide workshops on improving well-being. You also plan to implement meetings, innovation sessions, and team-coaching training for managers. Lastly, you suggest adopting software to improve communication and collaboration.
D6: Implement your corrective actions
Once all parties have agreed on a solution, the next step is to create an action plan to remove the root causes and escape points. Once the solution is in effect, you can remove your interim containment actions.
After seeing success with the training in the interim phase, your stakeholders approve all of your team’s proposed PCAs. Your representative from HR also plans to implement periodic employee wellness checks to track employee morale .
![8d method of problem solving [inline illustration] D6 PCA implementation plan (example)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/ca68af4a-afa7-4be4-93cb-8a8321eb5172/inline-productivity-8d-template-8-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
To ensure your corrective action was a success, monitor the results, customer, or employee feedback over a long period of time and take note of any negative effects. Setting up “controls” like employee wellness checks will help you validate whether your solution is working or more needs to be done.
D7: Take preventive measures
One of the main benefits of using the 8D method is the improved ability to identify necessary systematic changes to prevent future issues from occurring. Look for ways to improve your management systems, operating methods, and procedures to not only eliminate your current problem, but stop similar problems from developing later on.
![8d method of problem solving [inline illustration] D7 Preventive measure (example)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/cdd7b133-fb80-4db7-8935-1285a6b62b69/inline-productivity-8d-template-9-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
Based on our example, the training your team suggested is now adopted in the new manager onboarding curriculum. Every manager now has a “meeting system” that all meetings must be guided by, and workloads and projects are managed as a team within your new collaboration software . Innovation is improving, and morale is at an all-time high!
D8: Celebrate with your team
The 8D method of problem-solving is impossible to accomplish without dedicated team members and first-class collaboration. Once notes, lessons, research, and test data are documented and saved, congratulate your teammates on a job well done! Make an effort to recognize each individual for their contribution to uncovering a successful solution.
![8d method of problem solving [inline illustration] 8D Team congratulations & reward (example)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/d2055965-bf3d-4bf4-a1ea-a0a7c4bf8a32/inline-productivity-8d-template-10-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
8D report template and example
Check out our 8D report template below to help you record your findings as you navigate through the eight disciplines of problem solving. This is a formal report that can be used as a means of communication within companies, which makes for transparent problem-solving that you can apply to the entire production or process chain.
Benefits of using the 8D method
The 8D method is one of the most popular problem-solving strategies for good reason. Its strength lies in teamwork and fact-based analyses to create a culture of continuous improvement —making it one of the most effective tools for quality managers. The benefits of using the 8D method include:
Improved team-oriented problem-solving skills rather than relying on an individual to provide a solution
Increased familiarity with a problem-solving structure
A better understanding of how to use basic statistical tools for problem-solving
Open and honest communication in problem-solving discussions
Prevent future problems from occurring by identifying system weaknesses and solutions
Improved effectiveness and efficiency at problem-solving
Better collaboration = better problem solving
No matter how good a manager you are, production and process issues are inevitable. It’s how you solve them that separates the good from the great. The 8D method of problem solving allows you to not only solve the problem at hand but improve team collaboration, improve processes, and prevent future issues from arising.
Try Asana’s project management tool to break communication barriers and keep your team on track.
Related resources

Gartner® Magic Quadrant™ for Adaptive Project Management and Reporting

How Asana drives impactful product launches in 3 steps
Waterfall, Agile, Kanban, and Scrum: What’s the difference?

New site openings: How to reduce costs and delays

Home > Quality Management > The 8D Problem-Solving Method: What is it And How To Use It
The 8D Problem-Solving Method: What is it And How To Use It
Free Counselling :
IN +91 9899577620
US +1 2093823469
Table of Contents
The 8D ( 8D Problem-Solving Method ) method, also known as 8 disciplines, first appeared in Ford’s 1987 “Team-Oriented Problem Solving” manual. It is a tool that has stood the test of time and has become the first solution used by the company known today as Global 8D. Although the 8D method has been around for years, many companies still face the problem of low resolution and poor use of fixes.
Eight Laws of Problem-Solving ( 8D Problem-Solving Method ) are an efficient, effective, and proven way to identify the root cause of a problem, plan a quick solution, and prevent a solution, treatment, and recurrence of the problem. If your product is faulty or does not meet customer expectations, the 8D is a great first step toward improving quality and reliability. The 8D has become very popular with manufacturers, installers, and workshops worldwide due to its efficiency and ease.

Organizations can benefit from improving their production processes and preventing problems that can hinder productivity. This approach provides businesses with the necessary and practical tools to increase efficiency and take action when necessary.
The 8D Problem-Solving Method is the process of teaching and improving quality and eliminating problems. Here we will show you a step-by-step troubleshooting tool to help you identify the problem and identify issues and errors. It also helps identify root causes and take steps to resolve and prevent problems identified in the process. So, let us look at the steps:
1. D0: Planning and Preparation-
Planning and proper planning is a good start before taking action. The process begins with devising a plan and analyzing the problems the organization wants to solve. In this step, company leaders combine information from different sources and generate ideas. In general, at this stage, they identify the problem that needs urgent attention, the main resources that can be used to solve the problem, and the parties involved in the resolution process. The planning phase forms the basis for the next step.
Therefore, before building a team, you should consider:
- Problem description
- The time frame for resolution
- Resources needed to complete the job.
2. D1: Formation of a Team-
This process is based on the creation of groups that will be part of the problem-solving process. During teamwork, the team leader will usually select someone with experience on the job and identify areas to consider in hiring professionals with skills in these areas. The group may also choose a leader to lead its efforts in the problem-solving process.
Building teams to do the 8D Problem-Solving Method is a weak spot for many organizations. Collaborating with people from relevant organizations is important because you cannot solve the problem without first-hand knowledge. If a part problem, the engineer responsible for the design should be in the team. If a production problem, it should be walked around by the staff from the special work area. Do not make the mistake of thinking that the 8D is a job only a competent person can do at their desk.
3. D2: Describing Problem-
The main purpose of the 8D approach is to accurately and objectively describe the problem so that all important information is captured. This step involves writing down detailed information and information to describe the problem, and this is another area where people run into a lot of trouble. Problem definition may mean walking the field to observe the problem on the production floor, reviewing quality data, and/or confirming/not validating the problem.
Organizations can further identify and solve the problem by identifying the problem. During this time, the team reviews issues that need fixing, and management maintains good communication with everyone on the team. Describe the situation in meaningful terms to help identify the potential and type of problem. Often, at this stage, the team writes problem statements, gathers information, and creates diagrams and charts to add to the project.
4. D3: Problem Containment Planning-
Sometimes it is necessary to develop a temporary problem management plan to reduce the impact of the problem until a permanent solution is found. New methods are needed to fix the problem until a permanent solution is found. Problem-solving is a process that takes time and goes through many stages. It is important to have a contingency plan when dealing with serious and persistent problems. Issue management can help reduce the immediate impact of an incident on a product or customer. Temporary protection plans often use quick, easy, and inexpensive measures that the team can reverse at a later stage if needed. With advice, it is important to analyze the results and monitor the situation carefully to prevent further damage.
Temporary protection minimizes the impact of the problem during a permanent solution, which is especially important when product quality or safety is at risk. Many automakers make the mistake of stopping at this point and causing confusion and correction. Sorting materials or clearing clutter only fixes the symptoms, not the cause. The result: repeated problems, higher costs, and loss of business.
5. D4: The Root Cause Analysis (RCA)-
There are many tools available to identify the true root cause of a problem. With the issue temporarily resolved, you can now begin to identify the cause of the inconsistency.
Once the interim plan is in effect, the next step will be an in-depth analysis of the root of the problem. The team examines each potential resource through in-depth analysis and testing. They bring in all relevant test data and discuss the unidentifiable details of the method. This issue is common and can help organizations better identify problems and prevent their recurrence in the future. Organizations often use marketing and visualization tools such as Five WHYs, the Fishbone diagram to visualize the cause, and the Pareto charts to identify root cause analysis.
6. D5: Analyzing Permanent Corrective Action-
Once the team has identified the source of the problem, we can decide what the best solution is. Networking with tools such as social mapping can help plan ideas and identify best practices through relationships.
After determining the best solution, the team evaluates corrective action against the root cause of the problem and escape points. With this information, they can compare corrections and write their results. At this stage, they can also make a risk assessment of each solution they create and choose the most appropriate one. Brainstorming combined with tools such as affinity diagrams helps organize ideas based on relationships and determine the best course of action.
7. D6: Implementing & Validating Permanent Corrective Action-
Management should be involved in verifying correct operation and this means that they must be present in the workshop to measure performance and in regular reviews of key performance indicators (KPIs). Leadership should be exemplified by examining the process from the paying customer’s perspective. It is worth noting that the 6 steps of the 8D Problem-Solving Method are when you are finally ready to use the correction, demonstrating the critical role of planning in this process.
Once a solution is identified, management should implement corrective actions using the PDCA (Plan Do Check Act) process with small tests before expansion. So, keep track of the results and tweak the fix to get the desired results. To achieve and implement a permanent change, the strategic plan should include:
- Creating an action plan
- Communicating the plan to all stakeholders
- Recognizing improvement using metrics
8. D7: Preventing Recurrence-
Once the best solutions have been identified and tested, it is important to pursue permanent corrective action to eliminate roots and escapes. Generally, the organization pulls back the management plan from time to time, creates an action plan for the right action, and then communicates it to all stakeholders. To implement the plan, organizations monitor instant results and results over time. It also monitors the effectiveness of permanent fixes.
The organization should decide to take steps such as updating the process of checking questions and performing regular preventive maintenance on them, ensuring defect-free products for high-risk processes, and rejecting to avoid risking other processes.
9. D8: Recognizing Team Contributions-
When the problem is solved, the last step is to congratulate the team. Because teams need feedback to achieve great results, it is important to recognize their efforts and share their success across the organization. This increases motivation and employee engagement while helping you develop quality control, implement process improvements, and manage change as you grow.
At the final stage of the process, the team reviews their work and discusses the project and its achievements. Effective communication and comparison before and after the 8D Problem-Solving Method process helps the team. Awareness of personal effort and feedback is important during this period as it can increase job satisfaction.
About Henry Harvin 8D Analysis Course:
Henry Harvin’s 8D Problem-Solving Method Analysis course is designed to identify the root cause of a problem, develop a short-term solution strategy, and implement long-term solutions to prevent the recurrence of the problem and 8D gives you an understanding of Root Cause Analysis. It’s not just about solving problems. However, it can help prepare your engineering team for the future.

Rating: 9.8/10
Learning Benefits:
- Learn and find clear information on 8D analysis courses.
- Learning various 8D Problem-Solving Method analysis principles.
- Understand government processes and products.
- Design advanced knowledge using project management.
- Manage performance, and understand capacity and growth.
Youtube URL: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IX4eMOJC4VE
Other Courses
- LEAN SIX SIGMA IN IT COURSE
- ADVANCED STATISTICS FOR SIX SIGMA COURSE
- POST-GRADUATE PROGRAM IN LEAN SIX SIGMA
Benefits of the 8D Problem-Solving Method include a better way to find the root cause, establish the necessary measures to eliminate the root cause, and apply the right treatment. The 8D method also helps find the control that is causing the problem to escape. The purpose of learning escape points is to improve management’s ability to identify failures or their causes (when and when they occur again). Finally, the prevention cycle examines the sequence of events that allowed the failure and the process that caused it to exist.
The 8D Problem-Solving Method approach is universally applicable to any organization that needs a solution. However, there are some industries and businesses that have been successful using this 8D method, such as manufacturing, the automotive industry, engineering companies that produce products, and large and medium-sized businesses.
Recommended Blogs
- Amazon Lean Management: The Six Sigma Case Study in 2023
- Top 20 Quality Management Tips For Business
- Importance of Six Sigma Quality and Scenarios in 2023
- Quality Function Deployment: An Overview
Youtube URL: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-9MUBLT0DjI
To complete the 8D process, the following are important: i. Good team. ii. A correct description of the problem. iii. Not skipping the 8D Problem-Solving Method steps. iv. Cooperation within the team and management support.
Some errors continued to occur as the team tried to locate the source of the problem and implement the correct solution. To prevent these defective products from reaching consumers, interim containment ensures that the defect remains in place until the problem is completely resolved. If the customer reaches the wrong location, it can lead to liability, failure, and customer dissatisfaction.
The 8D Problem-Solving Method report is a document used to document the 8D process, detailing the implementation of solutions and evaluating the effectiveness of solutions.
The Future of AI: How Will AI Impact Programming Career?

Top 9 Amazing Tally Courses in Delhi
Related posts.

Top 10 Benefits of Quality Management System

Top 15 Quality Management Interview Questions and Answers

Difference Between Quality Assurance and Quality Control

Quality Management Interview Questions and Answers

What Is Quality Planning And Why Is It Important?

Quality Management Tools: A Complete Guide
Join the discussion cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
.webp)
Our Career Advisor will give you a call shortly

Just purchased a course
Type above and press Enter to search. Press Esc to cancel.
Noida Address:
Henry Harvin House, B-12, Sector 6, Noida, Uttar Pradesh 201301
FREE 15min Course Guidance Session:
8D (Eight Disciplines) – The problem Solving tool
In this modern era, to sustain products in the market needs to use advanced manufacturing processes. Modern machinery and cost effective processes for produce quality products with low cost. but as you all know that. It’s difficult to constant manufacturing processes and sustain product quality. Because it is natural that, during the working time unexpected problems can be occurred and that kind of problems must be resolved in respective manner. Some organizations are used outmoded technique that solve the issues on temporary basis. As well those problems can be possible reoccur in processes in future.
So, needs to efficient system that eliminate the possibility of reoccur issues as well as smooth the manufacturing processes. Fortunately, we have some problem solving tools can solve the issue permanently. 8D (Eight disciplines) is one of the popular problem solving tool that in now days, organizations are adopting pleasurably. OK, so let’s see how to implement 8D in organization.
What is 8D (Eight Disciplines)?
“8D (Eight Disciplines) is problem solving tool / methodology used for correctly identified the cause of the problem, fixed and dissipate possibility of recurrence of quality problems.”
8D model is systematic approach popularly used in responding to manufacturing issues. Generally, quality team conduct eight disciplines processes for identify root causes of problem and eliminate it by appropriate actions. The 8D (Eight Discipline) model is correctly identify the cause of the problem. And apply such actions to prevent recurrence of the problem. 8D is perform as preventive and corrective action system by implement step by step process to identify potential and actual problems in processes.
Benefits of 8D (Eight Disciplines)
- The 8D method is very easy for implement in workplace as well as logical method that clearly indicate required steps of problem solution.
- The method is very popular in automotive industry, mean your customer may ask for 8D report for its own application implementation. Because it is reliable and well know problem solving tool for automotive industry.
- An excellent way of reporting non conformance to suppliers and their corrective actions.
- 8D helps to eliminate complicated issues at appropriate locations where defined the causes of the problem incorrect, lack of consequences in implementation and same problem appear again.
- The team approach works best when the problem, and its associated information is labyrinthine. Because 8D is designed and capable for special cause of problems identification and elimination.
8D (Eight Disciplines) Process Chart: Table
| WHAT RESULTS (PROCESS INDICATORS) | INPUTS | BY WHOM | HOW | OUTPUTS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| To identify and eliminate problems. And to Prevent reoccurring problems. | Notification of non-conformity products / process and products return from customer. | CFT (Cross functional team) responsible for performing 8D process. | The process carried out using qualitative analysis in the form of a case study of the 8D method. (Integrated supplementary tools) | Corrective actions and preventive actions on identified causes of problems. Assurance of not being recurrence of such problems. |
8D (Eight Disciplines) Methodology
- D1: Team Establishment
- D2: Problem Description
- D3: Containment Action
- D4: Root cause
- D5: Corrective Action
- D6: Implement and validation corrective actions
- D7: Prevent recurrence
- D8: Verify and congratulate team

The 8D (eight Disciplines) is a process for systematic introduction of quality perfection, improvement and elimination of problems. Here in this article I will show you step by step approach and using several examples of the problem solving tools . When we involve in 8D methodology and its processes using a structured method, we become very effective at identifying cause of problems, defining problems and mistakes. As well as easily establish root causes and taking actions that solve and prevent problem identifying in processes.
So, let’s see 8D (Eight Disciplines) in deep:
As you well know, whenever any problem occurring in the manufacturing processes before you must see some warning sign that indicate the problem. Which is being experience in terms of an undesirable results and can be describe using data to identify the variation as expected and actual results.
Actually, this is the preparation stage that require to be complete before starting the eight disciplines processes in organization. Generally, peoples asking what type of preparation required before 8D process? –
A deep analysis and empathetic of the issues and problems, previous experience with same issues or related issues are necessary to determine. If the eight disciplines (8D) is the correct method to be used for solving the issues.
You have to ask the questions as below as recognizing the problem:
- Describe it is new problem in organization / division? If same problem, occur previously at where? If it is new how long from it were being in process. Or it is unknown cause?
- Has it occurred before? where? and what solutions / actions are applied at on it? What is the history of this problem?
- Why it’s happened again? is there proper solutions are not applied? what causes behind it is occur again?
- What problem solving method was used? It was joint method for one or more problem? if it is separately performed what was defects remained in method?
- To consider warning sign of problems is it really looks very complex to one person cannot resolve the problem?
- To consider above points, does the problem warrant required an eight Disciplines (8D) method? if yes, why and proceed it.
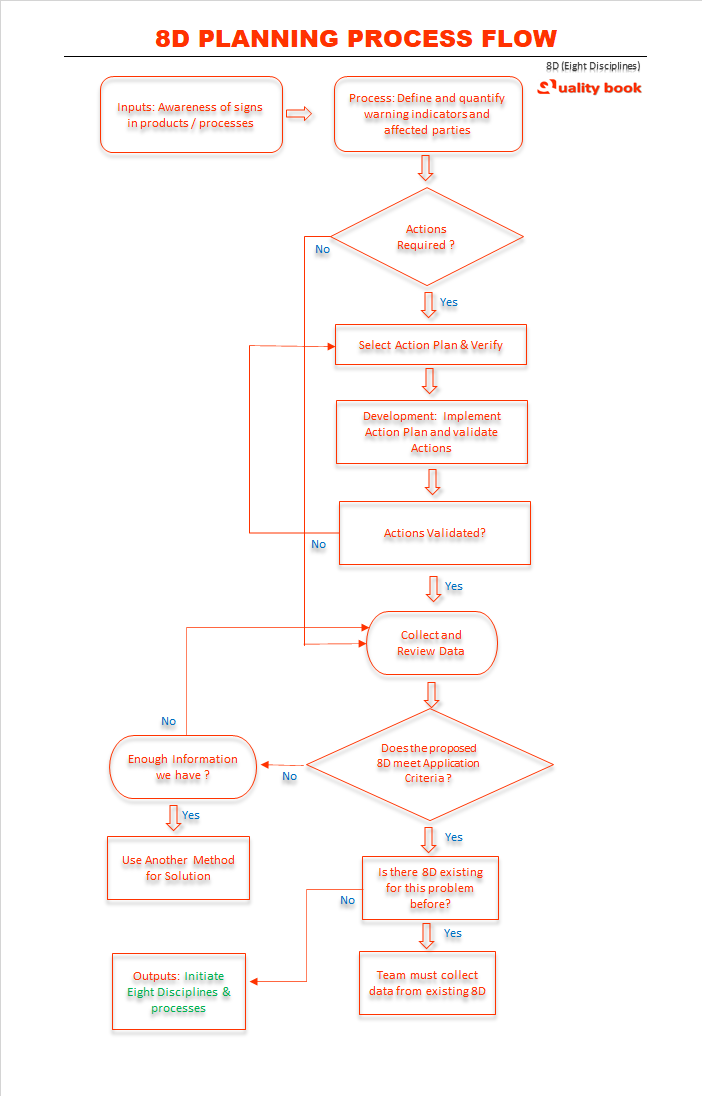
The 8D (eight disciplines) process is a team based problem solving methodology. Hence the team members must be involve for identify, action plan and eliminate issues of appropriate problem. A deeper understanding of the problem & its previous records are required to ensure if the 8D solved issues for raise issue.
D1 » Team Establishment
The team establishment is first step of the 8D (Eight Disciplines) approach. This discipline is significant stage as the eight disciplines is based on the substance of team cooperation. Establishment group of peoples called CFT (Cross Functional Team) where must each one from different department is selected by management, with the production process knowledge, product knowledge, and skill in the required technical disciplines to solve the problem and implement corrective actions.
Why team approach is important?
- CFT (Cross Functional team) build by group of peoples from different department and expertise. So any technical issues can be possible to identify, fix and eliminate problem through it.
- A Cross functional team can perform more effectively than individuals trying to solve problems.
- Cross functional team may have adequate capability to introduce proper solution of the problem.
- A group of people can discuss, focus on negative effects of actions, and can think creatively.
- Brainstorming as a group can stimulate ideas giving the team a better perspective of the problem.
A Cross functional team for eight disciplines consists of more than two people who are closely concern to the problem. Generally, involves peoples form different departments in the organization coming together to solve a problem. The skills that the team members require for this discipline to ensure the proper solution are:
- (A). Team member must knowledge of product / part / item (manufacturing processes, assembly etc.)
- (B). Team member must know the process where the problem has showed itself.
- (C). Team member must have knowledge of the customer application, technical use and end application requirements.
- (D). Team member must have skill about decision making, communication skill , and analysis of the processes and data related to manufacturing processes.
How to define team role & responsibility?
Usually, every team must have leader, here the same team leader has an important role to establish procedures and implement actions accordingly. The team leader must prepare a list defining the team structure as eight disciplines concern. the list is also important to establish role & responsibility in 8D processes. Every team member has its own importance in 8D methodology. Because every single member comes with different expertise. Hence to solve problem multifunction conception and views helpful for appropriate issues.
The role and responsibilities of the individual team member must have allocate by the team and will involve some of the points are:
Data collection and analysis, experimentation, decision making processes, modelling managing resources, planning and implementation of action plans, action plan verification and validation, communications etc.
The common processes and requirements for the 8D processes needed to contribute to the problem solving effort.
D2 » Problem Description
Problem description is a second stage designate for deep into the problem & getting a more complete information and sophisticated understanding of the problem. The problem description indicates, problem clearly identify and the eight discipline problem solving planner activities to take as much actual information as possible. Which organizes the first analysis perform in the problem solving process. You have to describe problem accurately in this stage, clear designed information is foundation to further steps of analysis.
The process of this discipline as below:
Describe The Problem Process Flow: Table
| FLOW DETAILS |
|---|
| Establish the data base that currently exists for the problem description. At this stage of the , you must look to provide brief data about the problem and determine the exact nature of the problem. |
| Prepare a process for all product stages. |
| Collect current and historical data as needed to further quantify the problem. Previous eight disciplines record helpful to accurately describe. |
| The problem be subdivided. |
| Describe the problem in terms of an operational definition. |
| Convention the customer to ensure correct problem description. if the problem description different from the customer or supplier explanation, both shall be documented and recognized accordingly. |
| Have the extent and the distribution of the problem been established for all stratification factors. |
| Established by determining : much huge and uses the is / is not form to drive this part of the process. |
| Prepare problem description. |
A problem description is the results of a practice that uses the is / is not method to magnify the problem statement. The location and nature of the problem have to be describe along with its impacts. Another very important analyzing results of information. To ensure that the problem involves is recurrent or whether it could occur on particular process or product.
See table below help for better understanding:
Describe the problem with Is / Is Not Method: Table
| FUNCTION WORD | IS | IS NOT |
|---|---|---|
| of problem? |
When the describing the problem with 5W + 2H (Who, What, Why, Where, When, how, how many / much) method should be use. Where you get the answered thoroughly and systematically by the questions.
See picture below for problem analysis worksheet:
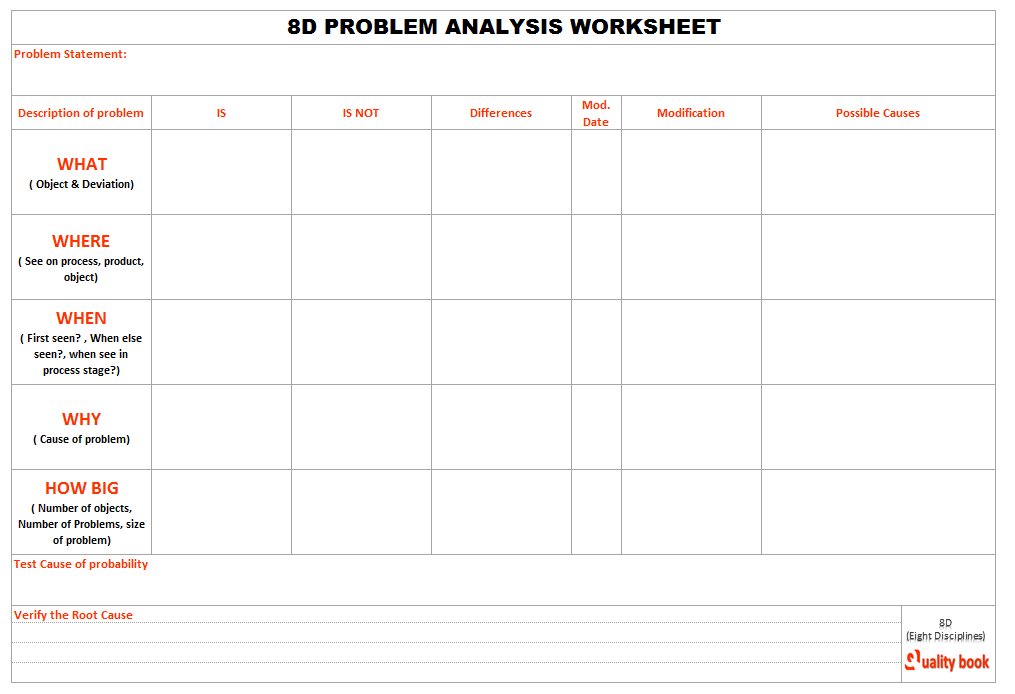
Remember that, you have to specified problem statement been defined, and you have get to know for certain why that is occurring. So Is / Is not analysis must been perform for it. You have to also verify that the similar parts / components displayed the same problem? current process flow identified? does this process flow represent a change.
Once you get the answer you can collect the data and analyze it. The information you collected are evaluated for potential root causes, and identify physical evidence of the problem. The problem description been reviewed for completeness with 8D (Eight disciplines) customer and affected parties, and document the activities.
D3 » Containment Action
This is the stage where are taken correct containment action to prevent escalation of the problem. Or at the worst delivering non-conforming product to the customer. You have to describe the containment action plan to put in place in order to eliminate the effects of the problem. In this stage, immediate correction action should be carrying out in the shortest time possible. The main objective of the implement interim actions / containment actions to isolate issues from parties while a permanent solution is being develop and implement.
Why containment action required?
- When the cross functional team working on identification of the root causes of problem , collecting information and other related processes might possible some defective product produced by manufacturing in tenure. So, it is extremely important containment actions on this condition at appropriate locations.
- To ensure the customer has minimal or no impact felt as a results of the problem identified, as well prevent these defective products from getting the customer.
- In case of any defective lot / product reached to customer, it may not comply requirements to end application, hence customer will claim and complaints as results customer dissatisfaction.
- Due to immediate actions, the similar products and processes must be verified and ensure the risk levels are minimum or not evident.
Through PDCA Cycle
Plan » Prepare the most effective containment action plan and implementation including verifying the containment action effectiveness and concerned activities such as work instructions , resources and equipment available.
Do » The plan must execute as containment action plan prepared, and ensure that the actions should be clearly communicated at processes and management levels.
Check » It is cross function team responsibility that every containment actions prepared during the planning section must be implemented exactly accordingly and ensure that it may continue to be effective. One of the important activity of this section is to verify and ensure that. The activities must not any other side effects raise as a result of the containment actions.
Act » Take the actions to ensure containment action are effective and sustained with all manufacturing and supporting processes. Take the questioners and get the feedback from internal and external customers to implement and make sure is there further containment actions or correction required to rectify other issues.
8D – Containment actions checklist

8D containment action points:
D4 » root cause.
On this stage in Eight disciplines (8D) problem solving process, needs to establish and describing the root causes of a problem is the core of this disciplines. And you will have appraise the team structure and configuration to ensure that all the right skills and experience is available for the upcoming phases or processes in the problem solving effort.
Elimination of the problem should be detecting the real cause of the problem. The objective of the explain and verify root causes is to identify all significant causes which could clarify why this problem happens. An eliminate and confirm the root cause by examine each significant cause against the describe problem and results of tested data.
For define and verify root causes you have to step out as below:
- Establish a process flow and Cause and Effect Diagram to include all the sources of variations.
- Develop a stratification cause and effect diagram, but remember that, the cause and effect diagrams used input from all team members, lack of the information of remains any points or data left, you will not get real cause.
- Establish comparative analysis, by determine critical differences between problem location and non-problem locations.
- You can also use time line analysis. Graphical / visual charts give you better understanding in most cases.
- Index the potential causes of problems by use both the process flow and cause and effect diagram.
- By using the both the tool, you can analyze the potential cause for the most likely cause.
- Determine slot of data, identify the potential cause as a root cause.
- Collect and analyze the appropriate information to identify the potential cause as a root cause.
- Specify causes that permitted the apparent warning sign to occur, are the root causes and often repressed deep in the processes. You can use the tools to help in the whole processes that is problem solving techniques are : (1) Pareto charts (2) 5 Whys analysis (3) Statistical analysis (4) Flow charts (5) Fishbone diagram (6) GR & R study (7) FMEA (8) Frequent audits (9) Fault tree Analysis (10) Brainstorming etc..
The time line is one of the important and useful tool that manage the records at time line of all events in and around the problem.
A company making steel tubes is experiencing a pits on tubes problem identified.
The significant processes / event are recorded on a time line are:
The time line helps to draw processes and events on time. Though it you can get the answer when actually the problem was first seen at which location. Now you can filter out possible causal theories later in the process by identifying what could possibly have caused the problem and what could not have caused the problem.
There are more three important stages you have to concentrate are:
(1) Develop possible causal theories (2) Establish possible root causes (3) Verify possible root causes and define and verify escape point.
You must do deeply thought about the possible causes and documents on separate media. For each of the cause you have to prepare a proper theory that describe how that the possible cause would result in the problem being experienced. You have to do write note of each ideas for develop causal theory for possible root causes.
Ask the simple question to each causal points that answered in “IS” / “IS NOT”. Does this explain the reason why the problem exists on the “IS” and not on the “IS NOT”. For separately of the possible root causes, there now requirements to be useful action to validate the possible root cause. This should be carried out in practical terms wherever possible.
D5 » Corrective Action
On the fifth stage of eight disciplines, the cross functional team must determine which corrective actions should be establishing and implement in the short period of time to ensure that the processes and product quality maintained and controlled. The corrective actions must be requirements that satisfy both the parties internal and external customers. Once the root causes are known, team concentrate on the permanent solutions, by systematic approach is needed to use the root cause analysis to establish actions for proper solution. The points that you need to focused on:
- Empathetic and defining the problem, the eight disciplines (8D) team must be able to defining the problems and implement the solution practically.
- Enclosing the effects of the problem, please note that implementation and using the program for solution must be cost effective.
- Identifying and verifying the root cause of the problem.
- Need to permanently solve the problem, and the solution must be feasible.
- Confirm the potential solutions through testing programs, and remember that the implementation program should not fail during the implement in production so, it is important the solution is a test and essential characteristic such as mistake proof and affordable.
- Verify that the solution eliminates the problem and its effects;
In fifth stage of eight disciplines, the team can introduce the additional control in the processes, and ensure that the solution is properly validated that during the implementation in running production it will not raise any unwanted issues, so trail on the small quantities first to verify the solution is effective is necessary. To ensure that the permanent corrective actions need to establish proper process flow for it, see the example process flow:
Verify Corrective Actions Process Flow: Table
| Conduct Inputs to verified root causes |
| Establish Corrective Action Decision Criteria and Re-evaluate team composition is customer represented. |
| Choose the suitable permanent corrective actions |
| Choose indicators and record baseline data, and plan corrective action feasibility using pre-production test program. |
| Record verification data |
| Has the program been solved and verified using the appropriate statistical method, if yes go ahead otherwise re-arrange the permanent corrective action plan and chose best for appropriate requirements |
| Does the customer agree that the problem has been corrected? if yes go ahead otherwise re-define the customer issues, and identify proper corrective action plan accordingly. |
| will the corrective action when implemented avoid creating problems with the customer? if yes choose verified corrective actions, otherwise follow the selection of corrective actions. |
Verify the corrective actions
It is extremely important that all the established actions and implementation plans for fix the issues must be performed to not leading any further problems. So, cross functional team must well aware of this kind of technicality and must should try out the implementation program with small part of production or small quantities first to verify its effectiveness.
Corrective actions test with pre-production with small quantity can confirm that the identified corrective actions will resolve the problem of the customer, and ensure that will do not any undesirable side effects.
Check points
Somethings that still need to confirm and ensure that corrective action is will properly works at real production. Some points that help you to re-verify the condition such as:
- (1) List and measure all of the indicators related to the program.
- (2) identify which of the indicators are most direct relation to the program.
- (3) Determine intervals to measure the problem.
- (4) identify what cross fictional team prioritized the customer / end user evaluation after the implementation.
- (5) confirm the scientific methods used to verify effectiveness etc.
D6 » Implement and validation corrective actions
On the stage of validation corrective actions, the cross functional team consists of measuring the long term effectiveness of the corrective actions. The purpose of verification of the corrective action is ensure that the actions are implemented are efficient and these are eliminated permanently through effective controls and activities that are embedded in the tasks of the process. Some indicators that you can ensure that the corrective actions are properly works:
- Test and control results display improvement
- Less Rejection or reject ppm (%) in process.
- Measurements such as dimension, units’ appearance are correct according to tolerance and specifications.
- Controls on incoming raw materials for quality improvement.
- Increased satisfaction ratio and feedbacks from customers.
The statistical tools such as process capability, histograms, control charts etc. can used to measured and verify the effectiveness of the implemented corrective actions. The cross functional team must have informed to customer about the results achieved, if the process capability submitted with the requirements the customer validates the corrective measures functional. The 8D team confirms whether the capability complies with internal manufacturing requirements, if the process capability complied the team validates the corrective action.
Checkpoints:
You can use PDCA cycle for implement this stage in manufacturing processes. The implementation of the permanent corrective action conduct to implement to verify the plan for validation of the corrective action. You can plan to withdraw containment (immediate) action as part of implementation of the corrective actions.
There is also important that each resources used in processes must be properly planned as well as all documentation, process instructions and communication implementation for corrective actions. Check that the corrective actions have been implemented and integrated into the appropriate tasks and manufacturing processes. Take the actions on any variation from the plan or expected results.
D7 » Prevent recurrence
On this stage, the cross functional team have to determine what action should be taken to prevent recurrence of the problem. You have to amend those operating systems, regular practices, management system as well as procedures to prevent recurrence of this problem and all similar issues. Because preventing recurrence is a one of the important task of problem’s solution. The general process flow of the prevent recurrent is:
- Input implemented corrective actions and validation
- Review the history / previous record of the problem.
- Analyze how this problem occurred and escaped.
- Identify affected parties and opportunities for similar problems to occur and escape
- Identify the system’s policies, practices and procedures that allowed this problem to occur and escape to the customer.
- Revise the process flow of the management or operating system.
- Analyze how similar problems could be addressed.
- Develop plans to coordinate necessary actions. And verify prevent actions.
- Develop systematic prevent recommendations to process owner.
- Identify and choose prevent actions. And implement preventive actions.
- Make the system changes to prevent recurrence.
- Verify the preventive actions are effectives? If yes, Standardize the new practices.
- Notify all personnel of the resolution actions by using failure mode effects analysis.
In this stage of the 8D (eight disciplines) cross functional team analyses whether the corrective action implemented would prevent or improve the quality of similar products and processes. To ensure the prevent recurrent of the problem, you should verify results of their actions and must validate that the results is on target. To verify the actions, you must check out below points:
D8 » Verify and congratulate team
The last stage of the 8D (Eight Disciplines) Is verification of the introduced actions in previous stages are effective. It is highly recommended that verification be made by comparing the measures of the problem with outcomes from upcoming actions of material or outcomes from rejecting of next lot. Once cross functional team has complete implementation all previous stages and ensure that the actions taken in previous stages are works. All team member deserve to be congratulate as well to know that their efforts are appreciate and that the organization knows about their accomplishments.
The cross functional team must have skills and experience to be able to make progress toward as satisfactory problem resolution, and skills and experiences are base reasons for individual selection. Different skills and experiences will support to be drafted in at various stages throughout the process to get the deep understanding about the symptom of problem, root causes and resolution.
The 8D report
From beginning to end of all 8D (Eight Disciplines) processes, the single document calls 8D report is essential part once complete. Team assume that all things are complete and fix as appropriate actions for appropriate issues. This report serves as a communication tool displaying overall process of the 8D (Eight Disciplines) processes along with actions taken. So, let’s see example format of 8D report:
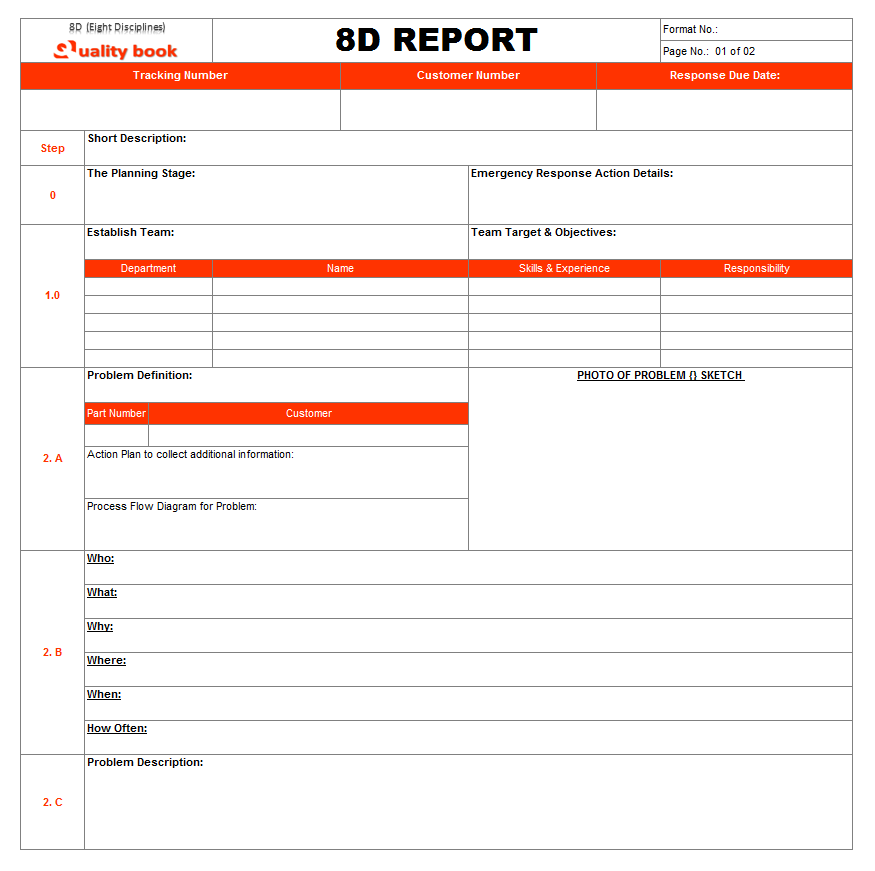
Conclusion:
When the problem has been resolve. The cross functional team should release a final document with stage wise brief description about its experiences. The 8D report give quick and better explanation of how the whole process had handling by team and also 8D serves report as a communication tool displaying overall progress of process.
We can assume that, the successful corrective actions have eliminated repetition of problems and prevention of similar issues. Further, team must ensure that corrective actions will be assess on their ability to help avoiding future problems. If we do not distinguish between major and minor problems, any issue will hold the delivery of customer and that is the reason we must have to categorize by identify systematic issues to eliminate appropriate problems.
Related Posts
Six sigma does not equal total customer satisfaction, quality control circle [qcc] : basic guide, entrepreneurship: navigating challenges and cultivating success, 7s management, enterprises quality management innovation, pre-control charts | pre-control limits | narrow-limit gauging, cost control in production | efficiency and optimization, lean: kanban tools, lean manufacturing optimises enterprise production.

- Lean Six Sigma
8D Problem Solving Report
8D is a problem solving method used globally, mainly in manufacturing industry by Quality Engineers and Operations managers. The purpose of 8D problem solving method is to identify, correct and prevent problems affecting customers and operational efficiency. It is a problem solving approach similar to PDCA cycle (Plan – Do – Check – Act).
8D stands for 8 Disciplines. It is a methodology that emphasizes “No problem should be repeated but fixed permanently”.
8D Problem Solving Method originally evolved during Second World War. But it became an official methodology in 1974, when it was used by US Government for its Military Operations as ‘Military Standard 1520’. Later it was adapted and popularized by Ford Motors with slight modification in the methodology.
As the name indicates 8D has 8 disciplines that any process or operations should follow to solve the problems occurring. The outcome of 8D is a report called ‘8D Report’ that records the problems, root cause(s) and corrective and preventive actions.
The below are the D’s in 8D approach:
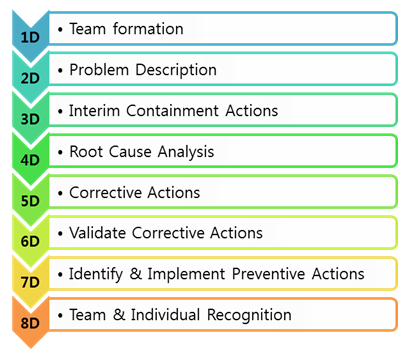
Figure 1: 8D Problem Solving Approach
1D – Team Formation: The first and foremost step not only in 8D but also in any other initiative or project is Team Formation, for any initiative cannot be successful without a right team. The team selected should be committed, competent, co-ordinated, cross-functional with representation from all teams, and should be knowledgeable in 8D methodology.
2D – Problem Description: After selecting the team, our concentration should be on detailing the problem. The team should collect details about the problem, for completely understanding the depth of the problem. All details should be data and fact based.
3D – Interim Containment Actions: Once the problem is described, before heading up to problem solving, the team should fix the effect of the problem, especially on customers. It might involve actions like isolating the items affected, replacing defective parts, before it reaches the customers. This step is mainly to prevent the problem from reaching the market and customers, which might become a competitive disadvantage and reduce customer loyalty.
4D – Root Cause Analysis: After taking containment actions, the team should involve in identifying the root cause(s) for the problem. Methods and tools like 5-Why Analysis , Fishbone diagram , Pareto Analysis , 7 Old QC tools , New QC tools etc. can be used for identifying the root cause. An important point to be noted is: Whatever method is used for RCA , it should be data & fact based.
5D – Formulate Corrective Actions: After successfully arriving at the root cause, the team should formulate corrective actions to be taken to correct the problem. Tools like Brain storming, Affinity diagram etc. can be used.
6D – Validate Corrective Actions: After arriving at the corrective actions, the team should validate whether the solutions are effective. There are several tools like Accelerated life testing , simulation etc. available for this purpose. Then the solution can be implemented in the process. The solution approach from step 4-6 should be repeated until the problem is completely eliminated.
7D – Preventive Action: Identifying and implementing corrective actions is only a temporary solution that keeps the system running or is like ‘Living with the problem by taking counter measures’. The permanent solution is to identify a potential long term solution that will not allow the problem (similar problems) from occurring into the system again. Sometimes corrective action will be a costly, time being measure. Preventive action makes changes in the system, upstream or downstream processes so that the entire system is modified or aligned for ‘Problem Free’ operations.
8D – Team and Individual Recognition: Once the problem is completely solved, the team and the extra-ordinary contributors must be rewarded and recognized appropriately. This will act as a motivation factor for other employees.
These are the steps of 8D methodology. To summarize, 8D is a holistic, systematic and proven methodology for problem solving.
Previous post: Change Management
Next post: Project Portfolio Management
- 10 Things You Should Know About Six Sigma
- Famous Six Sigma People
- Six Sigma Software
Recent Posts
- Control System Expansion
- Energy Audit Management
- Industrial Project Management
- Network Diagram
- Supply Chain and Logistics
- Visual Management
- Utilizing Pareto Charts in Business Analysis
- Privacy Policy

8D Method: Level-Up Your Problem-Solving Skills

- · May 22, 2023
Solving problems is an essential part of industrial daily operations, and the 8D method might just be what you need to optimise your processes and increase the value of your whole chain of production.
Today, we talk about how the 8D process helps you identify, fix, and prevent problems so you don’t have to deal with costly downtime and customer complaints .
What is 8D?
8D is a very robust problem-solving method that follows eight steps to help you identify, fix, and even anticipate recurrent problems.
This process was developed in the 80s by Ford and used to improve its manufacturing process.
Today, it’s a tried-and-tested approach that features in many factories across different industries.
How does 8D work?
As its name suggests, there are eight steps to follow to implement this process successfully :

Step 1 — Establish the team
The first thing to do is to establish a team.
This team should be effective and knowledgeable. It’s important that its members have the skills they need to be able to fix the issue.
To make sure that you’re taking a comprehensive look at the issue, it’s a good idea to include members from other departments too .
When you have your team ready to go, you need to brief them properly on the issue at hand.
Step 2 — Describe the problem
To describe the problem, you need to work with facts. And the best way to get these facts is by gathering data and information .
Some useful information would be where it happened, when, and what impact it had on safety, production, quality, etc.
When you’re describing the problem, you need to be as specific as possible , and let factual data guide you — leave all opinions and emotions out of the process.
Step 3 — Interim containment action
When your team is ready and you’ve described the problem as specifically as possible, it’s time to take interim containment action.
This is a temporary solution you need to implement to prevent the issue from worsening while the team works on a permanent solution .
Some typical interim containment actions are stopping production or isolating the affected area.
Step 4 — Identify the root cause
Here’s where we call on a great method we’ve seen before — Root Cause Analysis .
At this stage, you identify the root cause of the problem using an approach that suits the situation.
If the issue is relatively simple to fix, you can use the 5 Whys method, and leave RCA for more complex problems.
This is the time to i dentify the underlying cause of the problem, and not just treat the symptoms .
Step 5 — Plan, develop and verify corrective actions
After identifying the cause, it’s time to plan, develop, and verify corrective actions.
To do this, you can carry out a brainstorming session with your team members.
Whatever solution you decide to implement, you need to test it first. to make sure that the problem will get solved, and that it won’t happen again.
Step 6 — Implement permanent corrective actions
When the corrective solution has been tried and tested —and it’s clear it works— all you have to do is implement it!
To do this, you need to make sure your solution is fully integrated into your processes and clearly communicated to every relevant stakeholder .
This ensures everybody’s on the same page with the changes you made to implement the solution.
Step 7 — Prevent recurrence
Once everything’s fixed and everybody’s on board with the changes, you need to make sure the problem doesn’t come back .
To do this, you need to implement preventive measures. Some examples are updating standard operating procedures, scheduling training sessions, or auditing certain processes regularly.
Step 8 — Close the problem and celebrate your team
When you close the problem, it’s very important that you thank the team for their effort .
Acknowledging their hard work keeps everybody productive, motivated, and focused.
What does 8D look like in real life?
Imagine a factory just received a factory complaint about a product they received with the wrong characteristics. Let’s say it was the wrong colour. This is the problem we need to solve. Let’s go through the steps:
Step 1 ― Assemble your team and gather information about the problem (why is the colour wrong? Where did things go wrong? Was it a mechanic issue?)
Step 2 ― Secondly, describe the problem as specifically as you can
Step 3 ― Take interim containment measures. In this case, your action is contacting the customer and offering them a replacement product free of charge
Step 4 ― F ind the root cause of the issue. Because it’s fairly simple, you use the 5 Whys and find out that the root cause was a miscommunication between departments
Step 5 ― Your team plans, develops, and verifies corrective action, which in this case, consists of implementing a new communication process. They test it, and it works
Step 6 ― Update the standard operating procedure that the affected departments use to communicate, and let everybody involved know
Step 7 ― P revent the problem from happening again by conducting regular training sessions, and you have your departments perform regular audits of their new standard operating procedures
Step 8 ― The team is recognized for their hard work and dedication to solving the problem and improving customer satisfaction
Advantages of the 8D problem-solving method
The 8D method is a very robust problem-solving tool, but despite the obvious —it solves problems— there are more benefits to this approach than meets the eye:
Structured approach — Because the 8D method always uses the same eight steps, managers can rely on it to solve problems in a methodical, structured, and predictable way. This means no surprises and no downtime having to figure out what the next step is, which allows everybody to focus on the problem at hand and solve it quickly.
Root Cause Analysis — By implementing RCA, you make sure you’re dealing with the root of the problem, and not just treating the symptoms. This means you can also implement preventive measures to prevent the issue from surfacing ever again.
Collaborative environment — This method encourages collaboration and teamwork. The first step is to assemble a team to deal with the problem, fostering cooperation among team members and stakeholders. This translates into more comprehensive ideas and solutions.
Continuous improvement — 8D boosts continuous improvement by implementing permanent corrective actions to prevent the problem from coming back. This leads to increased efficiency, productivity, and quality.
Customer satisfaction — By adopting interim containment measures and focusing on finding the root of the issue, customers are protected from further problems until the issue is dealt with, and overall quality will improve. This leads to increased customer loyalty and repeat business.
Cost reduction — 8D identifies and eliminates waste and inefficiencies in the process, helping factories reduce costs. This translates into a higher bottom line and a competitive advantage in the marketplace.
mlean ® and the 8D method
The 8D method is a great tool to identify, fix, and prevent problems in your factory.
And the best way to implement it is digitally. This means everybody has access to the same information and collaborate better.
Our mlean Production System (mPS) is the most complete and flexible continuous improvement software in the market, and of course, we include 8D problem-solving in our digital toolkit .
Our 8D module gives you access to the full problem lifecycle in one single dashboard . It also allows you to track the issue and create a knowledge database from problems solved so that your processes can be as effective as possible.
With our module, you can escalate your problem directly from our 8D module. This allows you to give access to your data to the right person at the right time.
Our 8D integrates seamlessly with any other modules in the mPS to ensure a more comprehensive and robust problem-solving process .
Get a free demo today and take a look!
Book Your Free Demo Today
Blog category
- Deep dive (20)
- Digital transformation (18)
- How-tos (18)
- Industry Trends (18)
- mlean news (22)
- Solutions (1)

How lean manufacturing software is improving mass production

Factories and the environment: How to make it work

Factory performance: how to level up your game
Seeing is believing.
Book a call to see the full power of the mPS.

Running a factory is hard. We make it easy.
- Standard Work
- Shop Floor Management
- Start of production
- Maintenance
- Improvement Drivers
- mlean Hoshin Kanri
- Who benefits from the mPS?
- mlean product integrations
How we do it
- Success Stories
- Our philosophy
Let´s Work Together
- Become a partner
- 2024 © Mobile Lean S.L. All rights reserved.
- Privacy policy
- Legal Notice
- Information Security Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Complaints Channel
PROGRAMA INVESTIGO Proyecto financiado por el mecanismo de recuperación y resilencia.

MOBILE LEAN SL en el marco del Programa ICEX Next, ha contado con el apoyo de ICEX y con la cofinanciación del fondo europeo FEDER. La finalidad de este apoyo es contribuir al desarrollo internacional de la empresa y de su entorno.

MOBILE LEAN SL en el marco de su Programa de Internacionalización cuenta con el apoyo del Instituto para la Competitividad Empresarial de Castilla y León (ICE) y con la cofinanciación del fondo europeo FEDER.

- Privacy Summary
- Strictly necessary cookies
- Third party cookies
This website uses cookies so that we can offer you the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognizing you when you return to our website or helping our team understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.
Strictly necessary cookies must always be activated so that we can save your cookie settings preferences.
This website uses Google Analytics to collect anonymous information such as the number of visitors to the site, or the most popular pages.
Leaving this cookie active allows us to improve our website.
Please enable strictly necessary cookies first so we can save your preferences.
More information about our Cookies policy
The 8D method: easy and effective problem-solving as a team

The 8D method
Do you want to improve your management, or more specifically your problem-solving processes? With the 8D template, you can learn how to react quickly to a problem, and prevent it from recurring in the future. Follow the eight steps of the 8D process, and you will easily find the most suitable long-term solutions to your problems!
The 8D method: eight steps to find and implement long-term solutions to a problem
Are you looking for an effective problem-solving method? The 8D template uses eight disciplines or specific steps to help teams find suitable long-term responses to a problem. So this is just what you need!
This template comes from the Japanese management approach known as Kaizen , a continuous improvement process based on simple and inexpensive concrete actions. It’s all about working as a team to make small improvements every day .
Follow the 8D method to involve all the teams affected by the problem, and find the appropriate solutions. This way, you promote continuous improvement to eradicate any problems identified in a process or a project:
- Create the working group
- Define the problem
- Fix it in the short term
- Identify its root causes
- Assess the solutions
- Measure the effectiveness of corrective actions
- Standardize improvement actions
- Congratulate the team

What are the benefits of the 8D process?
On a day-to-day basis, team management often makes you choose to not fix small recurring irritants, as long as they don't bring a project to a standstill. However, it’s by addressing these small problems that you will see your productivity, efficiency and long-term project management improve greatly from one day to the next!
Whether you manage one or more teams, working at different times and in different places, the 8D tool can be used in person or even for remote working thanks to the Board , Klaxoon’s whiteboard. This shared space that can be accessed at any time, and on any connected device, helps you to quickly react to a problem in your business. You no longer need to postpone projects or team meetings because setting up a problem-solving process could take too long and slow down your business.
What’s more, with the 8D method you can analyze every aspect of a problem and eradicate it permanently , thanks to the last step, “Standardizing Solutions”. This will save you a lot of time for the rest of your project. Finally, it’s the ideal method to work with because it applies to all types of problems , whatever your project.
How to follow the 8D method with Klaxoon
1. create the working group.
Start by inviting your team to your whiteboard, then create your working group. Everyone has to send their photo in an idea, and add their name as a Dimension .
2. Define the problem
Once you’ve done the first step, you have to correctly define your problem . To do this, use the 5W1H method to ask yourself the right questions:
3. Correct problems in the short term
Next, you need to define together the solutions that you can implement immediately . Ask all the participants to send their ideas to control the situation as quickly as possible in the D3 area. You’ll get a lot of ideas, so ask everyone to like their two favorites, i.e., the ones they think are the easiest to implement and will have the best impact . Finally, apply the one that gets the most likes in the end.
4. Identify the root causes
Now, tackle longer-term solutions that are slower to implement . To do this, go to step 4 of the 8D process, to identify the root causes of the problem: ask yourself “Why?” five times or more, to deep dive into your problem. Here, you can also use Klaxoon's dedicated 5 Whys template to help you.
This step is essential to ensure the long-term solutions to be implemented are set up correctly.
5. Define permanent corrective actions
Once the root cause is discovered, collectively propose long-term solutions in D5 . Use the Dimensions to add two key pieces of information:
- The name(s) of the action owners
- An implementation date for the solution
The first part of the method ends here: at this stage, everyone knows what they have to do and when it needs to be done .
6. Measure the effectiveness of permanent corrective actions
Once the corrective actions have been implemented, bring the team back to this Board after a certain time, for the second part of the method. Copy the actions previously defined in D6, and then launch a Yes/No Poll Question to assess the effectiveness of these actions.
An example of question could be: “Did the action that you implemented solve the problem?” This way, you identify the solutions that you want to keep in the long term , and the ones to modify or abandon.
You can also do this step asynchronously . Contact the participants before the meeting, and ask them to answer the Question and add explanations in comments. So when your meeting starts, you avoid a tedious round table and you’re all set to process the information and act as a team.
7. Standardize improvement actions
This is a crucial step of the 8D method. Now that the effectiveness of the solutions has been assessed, what you have to do in D7 is propose ideas for deploying your long-term solutions on a large scale , for other products or in other teams. Keep in mind that the goal is for the problem never to recur again.
8. Congratulate the group
This step should not to be overlooked! Use D8 to congratulate the team on your progress and your results , and take the opportunity to summarize your improvements and share any photos of the results!
.png)
You too can adopt Klaxoon!
With Templates, innovate in the management of your projects, represent them visually and move forward as a team in a synchronized manner
Get inspired by other templates from the same categories

The GROW model
As a manager, use the GROW coaching model to increase employee engagement and help your team achieve their goals.

Sales Methods
With this Quiz template, consolidate your knowledge of sales methods.

Fresh eyes report
The HR new employee induction tool you can use to identify possible improvements within the company.
Unlock your teamwork potential
Master the 8D method of problem-solving
Related articles, the 8d method was originally the brainchild of the ford motor company. the concept was developed in the 1980s and was initially given the moniker tops (team oriented problem solving) due to its emphasis on a team approach..
This approach proved to be incredibly effective, and the process has now been adopted by other companies to root out their own problems. Now known as Global 8D, the method is ideally suited to manufacturers, but it’s also been effectively used in healthcare, retail, finance and government sectors.
What is the 8D problem-solving method?
‘8D’ stands for the eight disciplines of problem-solving. Each discipline of the tool supports businesses in finding the root cause of a non-conformity and implementing a permanent solution. This detailed and disciplined approach makes it a valuable method for boosting quality and reliability within your business.
Its methodology also puts a great deal of emphasis on what is referred to as the problem-solving team. By bringing different people together, you can take advantage of their diverse experience as well as rapidly develop their individual problem-solving skills.
Other benefits include:
- Greater problem-solving efficiency
- The discovery of any necessary systemic changes
- The creation of a document trail and database outlining non-conformities and their solutions
- Better understanding of non-conformities within the business and their solutions
How do I use the 8D method?
To help you through your problem-solving journey, here is a step-by-step guide through the eight dimensions.
0D: Planning
This stage is not an official part of the eight-step process, but it remains crucial for the method to work.
Before you begin to problem-solve, you need a plan of action. Start gathering evidence on the issue, whether it is a series of customer complaints, a defective product or a process that was not carried out correctly. This will help you decide upon your team and will kick-start the investigation.
1D: Find a team
Now you have an idea of the issue, it’s time to assemble your team.
Try to choose people from different departments within the business but remember to include those who are familiar with the processes linked to the non-conformity/issue. This team can shift as your investigations continue, so be prepared to call in other expertise as you learn more about the events leading up to the issue.
To keep things moving, make sure a leader is elected. Ideally, they should be someone who is familiar with the 8D process.
2D: Problem identification
At this stage you need to set down a description of the problem. This should be fact-based and focused on information taken from business data. By doing this, you can narrow down the issue and start to rule out possible causes of the non-conformity.
To help you create an accurate description, you may like to base it on the 5W2H methodology (who, what, where, when, how and how much?).
3D: Temporary correction
Now that you have a good idea of what the problem is, you may need to put a temporary corrective action in place.
This won’t resolve the root cause of the issue, but it will help to protect your customer from receiving bad products or service from your business.
Interim measures could include stopping production or replacing defective parts, for example.
4D: Root cause analysis
We’re now getting to the business end of this process. At this stage, you can begin to identify the root causes of the non-conformity and verify them using facts gleaned from your data collection.
To help you identify the true cause of the problem, take advantage of other problem-solving techniques, such as the five whys.
The five ways is a very straightforward technique in which you ask the question ‘why’ for every answer you generate.
Here’s an example:
How to use the five whys
Problem: Water spillage in the factory.
1. First why: The water spillage occurred because the factory pipeline was leaking.
2. Second why: The factory pipeline leaked because it was damaged.
3. Third why: The factory pipeline was damaged due to poor maintenance.
4. Fourth why: The pipeline was poorly maintained because it wasn’t checked regularly.
5. Fifth why: It wasn’t checked regularly because there isn’t a maintenance schedule for the pipelines.
Root cause: A missing maintenance schedule
Other techniques include the fishbone diagram, which is illustrated below. In this example, the non-conformity was a late delivery. If using the fishbone method, you won’t necessarily fill every section – it will depend on the type and scale of problem you are investigating.
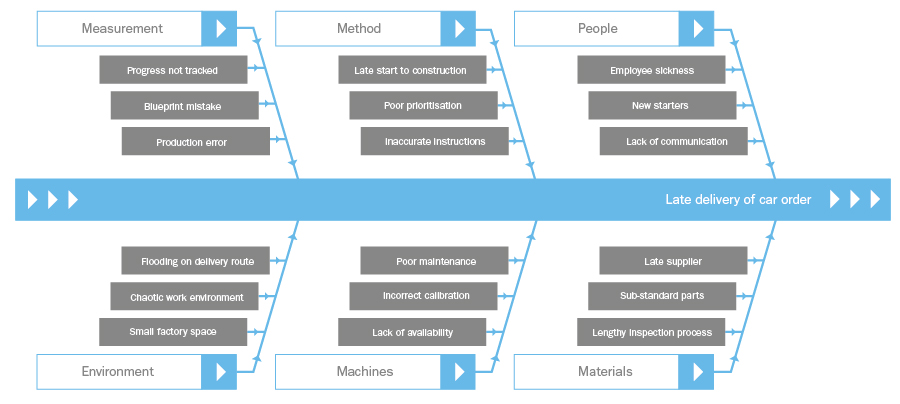
You may also like to walk through your business’ processes to discover the exact location of the root cause. In this case, a process flow diagram may be useful. This is essentially a flowchart that illustrates the relationship between major components.
5D: Permanent correction
Once you are happy that you have found the root cause of your issue, it is time to put together a permanent corrective action. This action will replace the temporary measures you put in place.
In the case of the factory water spillage, the permanent corrective action will be to create a new maintenance schedule to prevent excessive damage.
When you have a plan of what to do, you need to establish its probable effectiveness before you put it into action. Simulations or tools such as Accelerated Life Testing (ALT) can be handy for this. ALT is useful in manufacturing as it tests a product by subjecting it to extreme conditions. Once you’re satisfied that you have found the right solution, it’s time to move to the next stage.
6D: Implementation
It’s now time to implement your chosen permanent corrective action.
To implement it correctly, you need to create a project plan that covers communication to the relevant work teams and overseers as well as the steps to completion. Make sure you also decide how you will measure your success.
7D: Prevention
This stage is dedicated to making sure you prevent the non-conformity from reoccurring.
For example, in the case of the water spillage from the pipeline, the preventative action will be to communicate the new maintenance checks to the relevant team and to issue training on how to check the pipes.
Sharing your knowledge and the lessons learned during the fact-finding process is also key. Make sure the problem and its resolution are communicated to the rest of the business and update documents and your ISO processes.
You may also like to take a look at related products or procedures to see if similar problems are occurring in different parts of the business.
8D: Feedback
The last discipline is dedicated to rewarding your problem-solving team and recognising their efforts. Feed back on their performance and highlight any areas for improvement – this will help them to develop their problem-solving skills and tighten up the process during the next investigation. Once that’s done, it’s time to celebrate!
Need some extra support?
Running a management system and playing detective when it comes to non-conformities can be quite challenging when you’re juggling other business needs.
For more support or guidance, you can reach our team of experts by calling 0333 344 3646 or emailing [email protected] .
Sign up to get the latest in your inbox
- Email address
About the author
Claire Price
Content Marketing Executive
Claire worked for Citation ISO Certification between 2020 and 2022 writing creative and informative content on ISO certification and consultation to help businesses reach their potential.

Looking for some guidance? Join us for one of our upcoming seminars!
QMS International use cookies to provide you with a better site experience, enable features and to help us understand how our website is being used.
By continuing, you consent to the use of cookies in accordance with our Cookie Policy
Allow All Cookies
Allow Strictly Necessary Cookies Only
Please Wait...

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
What is 8D? Eight Disciplines Problem Solving Process
Eight disciplines problem solving
Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving (8D)
8D Problem Solving is a systematic and structured approach used to solve business related problems. It names has been given by the fact there are 8 steps or 8 disciplines that are followed to identify, correct and eliminate recurring problems. 8D Problem Solving is regarded as robust methodology that has proven its worth across multiple ...
8D Problem Solving Process - Solving Major Problems in a ...
The 8D problem-solving method is designed to address and resolve problems by identifying, correcting, and eliminating recurring issues. It involves eight different steps: Plan — Prepare for the problem-solving process. Team selection — Assemble a team with the necessary knowledge and skills. Problem definition — Clearly define the problem ...
8D (or Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving) is a methodology for solving problems that aims to identify the root cause of the problem and provide a solution. 8D is a great first step in improving quality and reliability. Ford Motor Company created this problem-solving method, which was then called Team Oriented Problem Solving.
The 8D Problem Solving (also known as Eight Disciplines) is used to solve a complex problem using eight steps. It is a team-oriented method. The 8D approach is based on solving the problem through short-term (temporary) saluting to reduce or stop the negative impact of the situation while the team is looking for the problem's root cause to ...
The 8D approach to problem-solving, also known as the 8D methodology, is a systematic and comprehensive method used to address and resolve complex issues, particularly in manufacturing and other industries. This 8D troubleshooting methodology involves a structured process designed to identify, correct, and prevent issues, ensuring that similar ...
Abstract. The 8D problem solving method is a scientific, systematic approach which has similarities to the DMAIC method. The overlap in the two methods is briefly discussed in this overview of the 8D approach. 8D is usually driven by the customer; as the process is meant to resolve a specific customer complaint.
How to use 8D for problem solving. The 8D method above outlines a proven strategy for identifying and dealing with problems. It's an effective problem solving and problem prevention process. In addition to avoiding long-term damage from recurring problems, 8D also helps to mitigate customer impact as much as possible.
The 8D Problem Solving method is an effective and adaptable way for tackling complicated challenges in a variety of industries. Organizations may methodically identify and address problems, stop them from happening again, and promote a culture of continuous improvement and adhering to the eight disciplines.
The 8D, or "Eight Disciplines," problem-solving approach germinated from the fertile grounds of collaborative efforts to ensure superior quality and reliability in manufacturing. Initially developed by the Ford Motor Company in the 1980s, this systematic method was a response to a confluence of quality and operational issues that were pervasive ...
What is 8D? A Template for Efficient Problem-Solving [2024]
The 8D (8D Problem-Solving Method) method, also known as 8 disciplines, first appeared in Ford's 1987 "Team-Oriented Problem Solving" manual.It is a tool that has stood the test of time and has become the first solution used by the company known today as Global 8D. Although the 8D method has been around for years, many companies still face the problem of low resolution and poor use of fixes.
The 8D (eight Disciplines) is a process for systematic introduction of quality perfection, improvement and elimination of problems. Here in this article I will show you step by step approach and using several examples of the problem solving tools.When we involve in 8D methodology and its processes using a structured method, we become very effective at identifying cause of problems, defining ...
The purpose of 8D problem solving method is to identify, correct and prevent problems affecting customers and operational efficiency. It is a problem solving approach similar to PDCA cycle (Plan - Do - Check - Act). 8D stands for 8 Disciplines. It is a methodology that emphasizes "No problem should be repeated but fixed permanently".
The 8D method is a very robust problem-solving tool, but despite the obvious —it solves problems— there are more benefits to this approach than meets the eye: Structured approach — Because the 8D method always uses the same eight steps, managers can rely on it to solve problems in a methodical, structured, and predictable way.
The 8D method: eight steps to find and implement long-term solutions to a problem. Are you looking for an effective problem-solving method? The 8D template uses eight disciplines or specific steps to help teams find suitable long-term responses to a problem. So this is just what you need!
The 8D method was originally the brainchild of the Ford Motor Company. The concept was developed in the 1980s and was initially given the moniker TOPS (Team Oriented Problem Solving) due to its emphasis on a team approach. This approach proved to be incredibly effective, and the process has now been adopted by other companies to root out their ...