Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Academic writing
- Transition Words & Phrases | List & Examples

Transition Words & Phrases | List & Examples
Published on May 29, 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on August 23, 2023.
Transition words and phrases (also called linking words, connecting words, or transitional words) are used to link together different ideas in your text. They help the reader to follow your arguments by expressing the relationships between different sentences or parts of a sentence.
The proposed solution to the problem did not work. Therefore , we attempted a second solution. However , this solution was also unsuccessful.
For clear writing, it’s essential to understand the meaning of transition words and use them correctly.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
When and how to use transition words, types and examples of transition words, common mistakes with transition words, other interesting articles.
Transition words commonly appear at the start of a new sentence or clause (followed by a comma ), serving to express how this clause relates to the previous one.
Transition words can also appear in the middle of a clause. It’s important to place them correctly to convey the meaning you intend.
Example text with and without transition words
The text below describes all the events it needs to, but it does not use any transition words to connect them. Because of this, it’s not clear exactly how these different events are related or what point the author is making by telling us about them.
If we add some transition words at appropriate moments, the text reads more smoothly and the relationship among the events described becomes clearer.
Germany invaded Poland on September 1, 1939. Consequently , France and the United Kingdom declared war on Germany. The Soviet Union initially worked with Germany in order to partition Poland. However , Germany invaded the Soviet Union in 1941.
Don’t overuse transition words
While transition words are essential to clear writing, it’s possible to use too many of them. Consider the following example, in which the overuse of linking words slows down the text and makes it feel repetitive.
In this case the best way to fix the problem is to simplify the text so that fewer linking words are needed.
The key to using transition words effectively is striking the right balance. It is difficult to follow the logic of a text with no transition words, but a text where every sentence begins with a transition word can feel over-explained.
Don't submit your assignments before you do this
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students. Free citation check included.

Try for free
There are four main types of transition word: additive, adversative, causal, and sequential. Within each category, words are divided into several more specific functions.
Remember that transition words with similar meanings are not necessarily interchangeable. It’s important to understand the meaning of all the transition words you use. If unsure, consult a dictionary to find the precise definition.
Additive transition words
Additive transition words introduce new information or examples. They can be used to expand upon, compare with, or clarify the preceding text.
| Function | Example sentence | Transition words and phrases |
|---|---|---|
| Addition | We found that the mixture was effective. , it appeared to have additional effects we had not predicted. | indeed, furthermore, moreover, additionally, and, also, both and , not only but also , , in fact |
| Introduction | Several researchers have previously explored this topic. , Smith (2014) examined the effects of … | such as, like, particularly, including, as an illustration, for example, for instance, in particular, to illustrate, especially, notably |
| Reference | The solution showed a high degree of absorption. , it is reasonable to conclude that … | considering , regarding , in regard to , as for , concerning , the fact that , on the subject of |
| Similarity | It was not possible to establish a correlation between these variables. , the connection between and remains unclear … | similarly, in the same way, by the same token, in like manner, equally, likewise |
| Clarification | The patient suffered several side effects, increased appetite, decreased libido, and disordered sleep. | that is (to say), namely, specifically, more precisely, in other words |
Adversative transition words
Adversative transition words always signal a contrast of some kind. They can be used to introduce information that disagrees or contrasts with the preceding text.
| Function | Example sentence | Transition words and phrases |
|---|---|---|
| Conflict | The novel does deal with the theme of family. , its central theme is more broadly political … | but, however, although, though, equally, by way of contrast, while, on the other hand, (and) yet, whereas, in contrast, (when) in fact, conversely, whereas |
| Concession | Jones (2011) argues that the novel reflects Russian politics of the time. this is correct, other aspects of the text must also be considered. | even so, nonetheless, nevertheless, even though, on the other hand, admittedly, despite , notwithstanding , (and) still, although, , regardless (of ), (and) yet, though, granted |
| Dismissal | It remains unclear which of these hypotheses is correct. , it can be inferred that … | regardless, either way, whatever the case, in any/either event, in any/either case, at any rate, all the same |
| Emphasis | The chemical is generally thought to have corrosive properties. , several studies have supported this hypothesis. | above all, indeed, more/most importantly |
| Replacement | The character of Godfrey is often viewed as selfish, self-absorbed. | (or) at least, (or) rather, instead, or (perhaps) even, if not |
Causal transition words
Causal transition words are used to describe cause and effect. They can be used to express purpose, consequence, and condition.
| Function | Example sentence | Transition words and phrases |
|---|---|---|
| Consequence | Hitler failed to respond to the British ultimatum, France and the UK declared war on Germany. | therefore, because (of ), as a result (of ), for this reason, in view of , as, owing to x, due to (the fact that), since, consequently, in consequence, as a consequence, hence, thus, so (that), accordingly, so much (so) that, under the/such circumstances, if so |
| Condition | We qualified survey responses as positive the participant selected “agree” or “strongly agree.” , results were recorded as negative. | (even/only) if/when, on (the) condition that, in the case that, granted (that), provided/providing that, in case, in the event that, as/so long as, unless, given that, being that, inasmuch/insofar as, in that case, in (all) other cases, if so/not, otherwise |
| Purpose | We used accurate recording equipment our results would be as precise as possible. | to, in order to/that, for the purpose of, in the hope that, so that, to the end that, lest, with this in mind, so as to, so that, to ensure (that) |
Sequential transition words
Sequential transition words indicate a sequence, whether it’s the order in which events occurred chronologically or the order you’re presenting them in your text. They can be used for signposting in academic texts.
| Function | Example sentence | Transition words and phrases |
|---|---|---|
| Enumeration | This has historically had several consequences: , the conflict is not given the weight of other conflicts in historical narratives. , its causes are inadequately understood. , … | first, second, third… |
| Initiation | , I want to consider the role played by women in this period. | in the first place, initially, first of all, to begin with, at first |
| Continuation | , I discuss the way in which the country’s various ethnic minorities were affected by the conflict. | subsequently, previously, eventually, next, before , afterwards, after , then |
| Conclusion | , I consider these two themes in combination. | to conclude (with), as a final point, eventually, at last, last but not least, finally, lastly |
| Resumption | my main argument, it is clear that … | to return/returning to , to resume, at any rate |
| Summation | Patel (2015) comes to a similar conclusion. , the four studies considered here suggest a consensus that the solution is effective. | as previously stated/mentioned, in summary, as I have argued, overall, as has been mentioned, to summarize, briefly, given these points, in view of , as has been noted, in conclusion, in sum, altogether, in short |
Transition words are often used incorrectly. Make sure you understand the proper usage of transition words and phrases, and remember that words with similar meanings don’t necessarily work the same way grammatically.
Misused transition words can make your writing unclear or illogical. Your audience will be easily lost if you misrepresent the connections between your sentences and ideas.
Confused use of therefore
“Therefore” and similar cause-and-effect words are used to state that something is the result of, or follows logically from, the previous. Make sure not to use these words in a way that implies illogical connections.
- We asked participants to rate their satisfaction with their work from 1 to 10. Therefore , the average satisfaction among participants was 7.5.
The use of “therefore” in this example is illogical: it suggests that the result of 7.5 follows logically from the question being asked, when in fact many other results were possible. To fix this, we simply remove the word “therefore.”
- We asked participants to rate their satisfaction with their work from 1 to 10. The average satisfaction among participants was 7.5.
Starting a sentence with also , and , or so
While the words “also,” “and,” and “so” are used in academic writing, they are considered too informal when used at the start of a sentence.
- Also , a second round of testing was carried out.
To fix this issue, we can either move the transition word to a different point in the sentence or use a more formal alternative.
- A second round of testing was also carried out.
- Additionally , a second round of testing was carried out.
Transition words creating sentence fragments
Words like “although” and “because” are called subordinating conjunctions . This means that they introduce clauses which cannot stand on their own. A clause introduced by one of these words should always follow or be followed by another clause in the same sentence.
The second sentence in this example is a fragment, because it consists only of the “although” clause.
- Smith (2015) argues that the period should be reassessed. Although other researchers disagree.
We can fix this in two different ways. One option is to combine the two sentences into one using a comma. The other option is to use a different transition word that does not create this problem, like “however.”
- Smith (2015) argues that the period should be reassessed, although other researchers disagree.
- Smith (2015) argues that the period should be reassessed. However , other researchers disagree.
And vs. as well as
Students often use the phrase “ as well as ” in place of “and,” but its usage is slightly different. Using “and” suggests that the things you’re listing are of equal importance, while “as well as” introduces additional information that is less important.
- Chapter 1 discusses some background information on Woolf, as well as presenting my analysis of To the Lighthouse .
In this example, the analysis is more important than the background information. To fix this mistake, we can use “and,” or we can change the order of the sentence so that the most important information comes first. Note that we add a comma before “as well as” but not before “and.”
- Chapter 1 discusses some background information on Woolf and presents my analysis of To the Lighthouse .
- Chapter 1 presents my analysis of To the Lighthouse , as well as discussing some background information on Woolf.
Note that in fixed phrases like “both x and y ,” you must use “and,” not “as well as.”
- Both my results as well as my interpretations are presented below.
- Both my results and my interpretations are presented below.
Use of and/or
The combination of transition words “and/or” should generally be avoided in academic writing. It makes your text look messy and is usually unnecessary to your meaning.
First consider whether you really do mean “and/or” and not just “and” or “or.” If you are certain that you need both, it’s best to separate them to make your meaning as clear as possible.
- Participants were asked whether they used the bus and/or the train.
- Participants were asked whether they used the bus, the train, or both.
Archaic transition words
Words like “hereby,” “therewith,” and most others formed by the combination of “here,” “there,” or “where” with a preposition are typically avoided in modern academic writing. Using them makes your writing feel old-fashioned and strained and can sometimes obscure your meaning.
- Poverty is best understood as a disease. Hereby , we not only see that it is hereditary, but acknowledge its devastating effects on a person’s health.
These words should usually be replaced with a more explicit phrasing expressing how the current statement relates to the preceding one.
- Poverty is best understood as a disease. Understanding it as such , we not only see that it is hereditary, but also acknowledge its devastating effects on a person’s health.
Using a paraphrasing tool for clear writing
With the use of certain tools, you can make your writing clear. One of these tools is a paraphrasing tool . One thing the tool does is help your sentences make more sense. It has different modes where it checks how your text can be improved. For example, automatically adding transition words where needed.
If you want to know more about AI for academic writing, AI tools, or writing rules make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
Academic Writing
- Avoiding repetition
- Effective headings
- Passive voice
- Taboo words
- Deep learning
- Generative AI
- Machine learning
- Reinforcement learning
- Supervised vs. unsupervised learning
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, August 23). Transition Words & Phrases | List & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved September 9, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-writing/transition-words/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, using conjunctions | definition, rules & examples, transition sentences | tips & examples for clear writing, how to write topic sentences | 4 steps, examples & purpose, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser or activate Google Chrome Frame to improve your experience.
Connectors in English: How to Use Them
Are your essays in English marked poorly despite your grammatically correct sentences?
Have you ever been told that your paragraphs don’t connect to each other even though they talk about the same topic?
This is where English connectors come in—a.k.a., the words I’ve marked in bold above!
Today, I’m going to talk about what connectors in English are, the most common ones you’ll come across and how to practice them.
Once you’re done with this article, I hope you’ll agree that these words and phrases are simply magical!
What Are English Connectors?
English connectors for cause and effect, english connectors for illustration, english connectors for emphasis, english connectors for comparison, english connectors for contrast, english connectors for sequence, english connectors for conclusion, tips for practicing english connectors, and one more thing....
Download: This blog post is available as a convenient and portable PDF that you can take anywhere. Click here to get a copy. (Download)
English connectors are little words and phrases that help you connect sentences, paragraphs and ideas. Used both in spoken and written English, they help make your English sound more logical and structured.
You can think of connectors as like the thread that holds a necklace’s beads (i.e. sentences, paragraphs and ideas) together.
In fact, you probably already use them without even realizing it!
Note that English connectors are different from English conjunctions . While conjunctions link two or more words or clauses within a sentence, connectors establish that two separate sentences or ideas are related to each other.
To help you understand further, I’m going to walk you through some of the most common connectors in English and how they’re used. Some are used formally, while others are more casual. Some are even interchangeable —that is, you can use them in place of similar words.
In everyday conversations , we often need to explain things.
Perhaps you were late for school because your car ran out of gas. Or you want to buy chocolates because you want to surprise your mother on her birthday.
Explaining things will be much easier if you throw in these important English connectors.
Let’s take a look at them!
| English Connectors for Cause and Effect | Usage | Context | Example Sentences |
|---|---|---|---|
| -Indicates cause -Placed in the middle of a sentence -Used in writing and conversations | Formal and informal | her car ran out of gas. I didn't eat breakfast. | |
| -Indicates cause -Placed at the beginning of a sentence -Often used in writing | Usually formal | Jack's sickness, he missed two weeks of work. our budget, we can't go on vacation this year. | |
| -Indicates effect -When followed by "of," indicates cause -Placed at the beginning of a sentence -Used in writing and conversations | Formal and informal | of her bad behavior, she wasn't allowed to go to the party. , our profit was less than normal. | |
| -Indicates outcome or conclusion -Used at the end or beginning of new paragraphs -Often used in writing | Usually formal (but can also be used informally) | , they aren't the same. , she's had lots of practice cooking. | |
| -Similar to "therefore" -Used at the end or beginning of new paragraphs -Also often used in writing | Usually formal | , you have to be consistent. , he continued to play in college. | |
| -Indicates effect (comes from the word "consequence") -Similar to "as a result" -Typically used in writing | Usually formal | , he received a bad grade. , she's very bad at it. |
Giving illustrations or examples helps us prove our point and convince other people to believe us. These words help people understand what you’re trying to say and can help them see why you believe what you believe.
| English Connectors for Cause and Effect | Usage | Context | Example Sentences |
|---|---|---|---|
| | -Used in everyday conversations and in writing -Most popular ways to give examples | Formal and informal | , she was able to solve a difficult math problem in half the time that everyone else did. , I spent four hours trying to learn how to use the . |
| | -Used in everyday conversations and in writing -Can be used to give examples and list things | Formal and informal | teaching, journalism, advertising and so on. pizza, pasta and ravioli. |
| -Similar to "for example" -Often used in writing | Usually formal | , he killed six women before being tracked down by the police. |
While discussing an issue or idea, you may want to focus on a particular point or example. To make the listener understand the importance of that specific idea, you can use the following connectors.
| English Connectors for Emphasis | Usage | Context | Example Sentences |
|---|---|---|---|
| -Used quite often -Used at the beginning, middle or even the end of sentences -Used in writing and conversations | Formal and informal | , I think learning English was one of the best decisions I've ever made. , it's more common than you think. | |
| -Used in writing and conversations -Used to indicate a fact supporting an opinion stated beforehand | Formal and informal | , there are 57 million speakers! , I don't miss meat at all! | |
| -Similar to "as a matter of fact" -Used in writing and conversations | Formal and informal | , I don't think it'll work this time either. , I make them every day. | |
| -As the phrase suggests, it's used to highlight or emphasize a point that's more important than the others already stated -Often used in writing -May be used in everyday conversations as well | Usually formal | , without sunlight, there would be no life on this planet. , you have to be clear about what you want to say. | |
| -Used to highlight a point or several points -Used in writing and conversations | Formal and informal | since she's upset right now. rock and roll! | |
| -Used to emphasize that a point (or several points) is important -Usually appears in writing | Usually formal | the invention of the light bulb. for his book "Adventures of Huckleberry Finn." | |
| -Only used in writing -Used to say that something is worth noting (compared to others) | Formal | is his work on child psychology. to the field of biology. |
Sometimes, we need to draw attention to certain similarities to make a point or explain something. This is especially important in writing!
To make better comparisons, use the following English connectors.
| English Connectors for Comparison | Usage | Context | Example Sentences |
|---|---|---|---|
| -Used to say that the next point is similar to the previous one -Used in writing and conversations | Formal and informal | , dogs love chasing after balls. , squirrels use holes in trees to protect their babies. | |
| | -Can be interchangeable with "similarly" -Used in writing and conversations | Formal and informal | , my brother loves playing sports. , animals need a variety of foods, too. |
| | -Used to add to a point made previously -Usually appear in writing -Used at the beginning of new paragraphs to ensure they're connected to the overall topic -Used as (that is, these words make new sentences and paragraphs flow with others) | Usually formal | , it explores racism in America in the 20th century. , it's great for remembering everything you've learned! |
| -Can be used instead of "and" -Used in writing and conversations | Formal and informal | an excellent dancer. math. | |
| -Used to give examples -Used to show how two things are alike -Used in writing and conversations | Mostly informal | his cousin. we're strangers. | |
| -Similar to "also" and "similarly" -Used in writing | Usually formal | , her best friend also favors tea. studied English. |
Sometimes, we need to express different or contradicting ideas side-by-side. Doing this helps the listener or reader focus on important differences and makes them aware of the many sides of a topic.
| English Connectors for Contrast | Usage | Context | Example Sentences |
|---|---|---|---|
| -Similar to "while" -Used in writing and conversations | Formal and informal | Maria is good at speaking. Chinese doesn't. | |
| | -Used in writing and conversations | Formal and informal | Rose was a hard-working student, she failed the entrance exam. you're young, you're very mature. |
| -Similar to "but" -Used in writing and conversations | Formal and informal | , you still need to exercise. , they can be expensive. | |
| -Used in writing and conversations | Formal and informal | , my friend prefers rainy seasons. , eating chocolate every day is bad for your health. | |
| -Similar to "even though" or "although" -Used in writing and conversations | Formal and informal | the rain, we went for a walk and enjoyed the fresh air. their different personalities. | |
| -More common way to say "in spite of" -Used in writing and conversations | Formal and informal | being warned, she still went into the scary woods. being tired. | |
| -Mostly used in writing | Usually formal | , I think he's quite innocent and deserves a chance to explain himself. , I believe in aliens. |
These connectors are useful when you’re giving step-by-step instructions or listing points.
| English Connectors for Sequence | Usage | Context | Example Sentences |
|---|---|---|---|
| -Used in writing and conversations | Formal and informal | , you need to mix the flour, baking soda and cocoa powder together. , you need to carefully add the milk. , there's no evidence to support it. , the logic used isn't strong enough. | |
| -Similar to "firstly... secondly..." -Used in writing and conversations | Formal and informal | , it only takes a few minutes a day. , anyone can do it. , I check my emails. , I reply to important messages. | |
| -Used in writing and conversations | Formal and informal | , it's delicious. Also, it cools me down on hot days. , it expands your communication skills. In the second place, it opens up new opportunities. | |
| -Used to state the last point of a topic -Used in writing and conversations | Formal and informal | , the effects of the chemicals must be taken into consideration. , I organize my desk before leaving the office. | |
| -When used in writing, it's an excellent way to begin the last or the second to the last paragraph -When used in speech, you can use it to give the final instructions or end a conversation | Formal and informal | , mix all the ingredients well. , after editing the document, I proofread for any errors. |
Finally , how do you let your reader know that you’ve reached the end? (See what I did there?)
There are certain connectors that we usually use during conclusions or when we’ve reached the end of what we wanted to say. When writing or stating conclusions, you usually repeat the most important points.
| English Connectors for Conclusion | Usage | Context | Example Sentences |
|---|---|---|---|
| Used in formal writing as a way to begin the last or "concluding" paragraph in an essay or report | Formal | , we can't ignore the role modern science plays in our everyday lives. , it's crucial for everyone to be on the same page moving forward. | |
| Used in writing and conversations | Formal and informal | , you need to directly confront Kevin about the matter we've just discussed. , the story revolves around a young detective solving a mysterious case. | |
| Used in writing and conversations | Formal and informal | , I think Kayla should go to the party. , bilingualism enhances cognitive abilities and opens up cultural opportunities. | |
| Used in conversations (though may also be used in writing) | Mostly informal | , organizing a surprise birthday party for Josh was certainly worth it. , I'd say the science fair was a success. |
Here are some quick tips that’ll help you learn English connectors more efficiently.
Make Your Own Sentences
To explain the meanings and uses of different connectors, I’ve provided example sentences for each. However, you’ll remember them much better if you come up with your own examples.
You can start by using connectors in your diary entries, notebooks, essays and the like. Soon, you’ll find yourself using these connectors in everyday speech as well!
Write a Short Story or Essay
To see the huge difference English connectors can make, try writing a paragraph without any connectors and then rewrite it using some of the connectors above. You’ll quickly realize that your sentences will flow better, sound more logical and become easier to understand.
Learn English with Authentic Content
You probably want to speak English like a native (or at least try to). So why not learn from natives? Try watching a speech in English to get a good idea of how these fit together. Look for the ones with transcripts that you can write notes in, maybe even circling all of the connecting terms as you see them.
FluentU takes authentic videos—like music videos, movie trailers, news and inspiring talks—and turns them into personalized language learning lessons.
You can try FluentU for free for 2 weeks. Check out the website or download the iOS app or Android app.
P.S. Click here to take advantage of our current sale! (Expires at the end of this month.)
Try FluentU for FREE!
Do Online Exercises
Finally, to check whether you’ve understood how to use connectors correctly, you can try online exercises from websites that cover English grammar .
For example, the ones on English Daily and English Grammar are pretty short and can be completed in a few minutes.
There’s also ToLearnEnglish , which provides a brief list of common connectors before you solve the exercise, making it a great resource for review.
Now that you know the most commonly-used English connectors, you can use them in sentences and paragraphs with great confidence. Try your hand at some of the exercises I’ve suggested for practice.
So what are you waiting for?
Get out there and start incorporating these useful English connectors into your everyday life!
If you like learning English through movies and online media, you should also check out FluentU. FluentU lets you learn English from popular talk shows, catchy music videos and funny commercials , as you can see here:
If you want to watch it, the FluentU app has probably got it.
The FluentU app and website makes it really easy to watch English videos. There are captions that are interactive. That means you can tap on any word to see an image, definition, and useful examples.
FluentU lets you learn engaging content with world famous celebrities.
For example, when you tap on the word "searching," you see this:
FluentU lets you tap to look up any word.
Learn all the vocabulary in any video with quizzes. Swipe left or right to see more examples for the word you’re learning.
FluentU helps you learn fast with useful questions and multiple examples. Learn more.
The best part? FluentU remembers the vocabulary that you’re learning. It gives you extra practice with difficult words—and reminds you when it’s time to review what you’ve learned. You have a truly personalized experience.
Start using the FluentU website on your computer or tablet or, better yet, download the FluentU app from the iTunes or Google Play store. Click here to take advantage of our current sale! (Expires at the end of this month.)
Related posts:
Enter your e-mail address to get your free pdf.
We hate SPAM and promise to keep your email address safe

50 Linking Words (Logical Connectors) in English Classified by Theme
Updated on 27 August 2024
- Linking words, also known as logical connectors, are adverbs or conjunctions used to structure your English sentences. They are important for connecting different ideas and avoiding repetition.
- You will need it to: start a text, express a cause and effect, link an opposition, state a condition, add or list ideas, indicate a consequence, or summarize an idea.
Here are some examples:
- First of all
In this course, you will find the 50 most useful English logical connectors , along with examples, videos, and exercises to test your knowledge. The course is also available in PDF format.
Understanding how to use linking words is an essential vocabulary and grammar concept to improve your writing and speaking skills. Indeed, they help you write better essays, stories, and arguments and organize your thoughts more clearly in speech.
Table of contents →
To start a sentence
These English linking words are useful for introducing an idea, a first point, or a complete argument that you will develop further in a paragraph.
| Use this to introduce the first idea or point. | ||
| Emphasizes that this is the very first point. | ||
| Beginning a discussion or series of arguments; introducing the first idea. |
To express a condition
When you need to establish a condition between two sets of ideas in a conversation or writing, the following expressions are very useful.
| Indicates that one thing will happen only if another condition is met. | ||
Introduces a possible situation and its consequence. | ||
| Similar to , indicating a specific condition that must be true for something else to happen. | ||
| Expresses an exception to a situation; the opposite of . | ||
| Commonly used when making a choice between two options or alternatives. |
To express argument (cause, consequence)
The following logical connectors are used to express because, as a result, therefore, etc . These linking words are useful for showing a logical cause-and-effect relationship between different elements , especially when making an argument.
| Indicates the consequence of a previous action or situation. | ||
| Shows that something happened due to a specific cause. | ||
| Refers to something happening immediately after another event. | ||
| Indicates the reason for something. | ||
| Used to link a reason directly to its effect. | ||
| Used to show the effect of a previous statement. | ||
| Often used to explain why something occurred. | ||
| Indicates the purpose or goal of an action. | ||
| Introduces a reason or explanation. | ||
| Used to explain the goal of an action. | ||
| Indicates a result or conclusion. | ||
| Shows intent while avoiding something specific. | ||
| Indicates a positive cause for something. | ||
| Explains why something happened. | ||
| Often used to conclude an argument or show a consequence. | ||
| Used to explain the cause of a situation or action. | ||
| Used to show a difference or opposition between ideas. | ||
| Presents two contrasting ideas or points of view. | ||
| Often used to show what happens next or to conclude. |
Note: It’s important to carefully distinguish between purpose, cause, and consequence . The purpose is the reason for performing an action, while the consequence is the result of that action.
To continue a discussion
To expand on your thoughts or arguments , you’ll need some additional vocabulary. With the following linking words, you’ll be able to say in addition, furthermore, for example, indeed , etc.
| Connects two similar ideas or points. | ||
| Used to continue a sequence or list of ideas. | ||
| Used after to introduce the second point or idea. | ||
| Adds another point or idea. | ||
Introduces an example to support the previous statement. | ||
| Adds extra information or reinforces a point. | ||
| Used to add extra information that strengthens the argument. | ||
| Used to clarify or explain a previous statement in simpler terms. | ||
| Used to explain or define something in more detail. | ||
| Introduces specific examples to illustrate a point. | ||
| Emphasizes or confirms a previous statement. | ||
| Used to provide more accurate or relevant information. | ||
| Adds extra information to what has already been said. |
To compare and contrast
Need to contrast two ideas or viewpoints? Express opposition in English with the following list of conjunctions.
| Adds another point or idea. | ||
| Introduces a contrasting idea, despite what was mentioned earlier. | ||
| Compares one thing with another; shows opposition. | ||
| Suggests something is true in a hypothetical or imaginary way. | ||
| Introduces an opposing idea or viewpoint. | ||
| Shows that something is true irrespective of something else might suggest otherwise. | ||
| Used to emphasize that something happens regardless of another factor. | ||
| Introduces a contradicting statement or an opposing point. | ||
| Shows contrast, similar to . | ||
| Introduces a comparison by showing similarity. | ||
| Used to contrast two actions occurring simultaneously. | ||
| Used to present a different option or outcome if a condition is not met. | ||
| Used to highlight differences between two things or ideas. | ||
| Compares two contrasting ideas or situations. | ||
| Introduces a contrast or simultaneous action. | ||
| Used to introduce an unexpected contrast or outcome. |
To suppose (conditional)
| Introduces a possible situation or condition. | ||
| Used to express what might happen as a precaution. | ||
| Suggests something is true for the sake of argument. | ||
| Indicates an exception or a situation where something won’t happen. | ||
| Used to show a decision between two options. |
To end a speech
Concluding your speech effectively is crucial for clear communication. The following phrases can be used to conclude a speech, summarize your main points, or add a final thought to your text.
| Signals the end of a speech or writing, summarizing the key points. | ||
| Used to give a brief overview of what was discussed. | ||
| Introduces the final point or remark. |
Note: The Case of For and Since
Pay attention to the meaning of for and since when you encounter them.
- For = Indicates duration of time
| Expresses that the speaker hasn’t visited the US over a period of time. |
Since = Refers to a starting point in time (date or precise moment).
| Indicates the beginning of the knee pain. |
For = Because → This usage is rare and rather literary, but you can come across its usage.
| Indicates the reason for getting lost. |
Since = As → Can be replaced by As ; used when explaining a reason.
| Indicates the reason for being able to help. |
Adrien’s Tip 💡
You will find a lot of different names for linking words:
- Logical connectors
- Adverb (of cause, consequence, etc.)
- Adverbial phrases
- Preposition
- Coordinating conjunction
- Subordinating conjunction
- Conjunctive phrase
To keep things simple, focus on how to use these words instead of their definitions. Just remember:
These are words that help organize your ideas in a logical way, either across multiple paragraphs or by connecting sentences to express a complex idea clearly.

50 sentences to learn how to use them
Here are more than 50 concrete examples to help you understand how to use logical connectors in English. Each example is provided with a brief explanation and audio to guide your learning.
To start a text
| introduces the first point. | ||
| , it is not the first time it happened to me … | introduces the initial part of an explanation. |
Express a condition
| tells that a condition must be met for something to be true. | ||
| you pick me up. | indicates that an action will happen only if a specific condition is met. | |
| you want me to. | shows that something will not happen except under a specific condition. |
Justify your point in an argument
| , many will lose their jobs. | shows the effect of the crisis. | |
| our efforts, we were granted a quality award. | explains the outcome of efforts made. | |
| I arrived, people stopped talking. | indicates that one event follows another immediately. | |
| I studied for my English test all night. | explains the reason for being tired. | |
| the noise. | gives the cause of not being able to sleep. | |
| I’m exhausted. | shows the consequence of continuous work. | |
| the bad weather. | explains the reason for postponement. | |
| explains the purpose of not ringing. | ||
| you’re home early, you can give me a hand. | gives the reason for being able to help. | |
| the skin gets crispy. | explains the purpose of grilling. | |
| he won’t come. | explains the reason for not coming. | |
| spread your germs everywhere. | shows the purpose of washing hands. | |
| this vocabulary sheet. | indicates what helped with understanding. | |
| I’ve decided to quit my job. | explains the decision to leave. | |
| the meeting is cancelled. | shows the reason for canceling the meeting. | |
| I always get bad grades on essays. | explains the cause of bad grades. |
To continue the discussion
| , the weather made me feel so depressed. | adds another reason or point to support the main idea. | |
| in a fiction movie not to miss the bus. , he would have been fired if he had not managed to take it. | shows comparison and emphasizes the seriousness of the situation. |
Logical connectors for comparing and contrasting
| impacted by the crisis. | shows a similarity between the two situations. | |
| the people were against it, the government decided to implement the law. | introduces a contrast between public opinion and government action. | |
| his 250K. | compares two different incomes. | |
| nothing happened. | introduces a hypothetical situation that is not true. | |
| I’m always criticizing her. | suggests a false impression or perception. | |
| what you said, Billy didn’t turn up last night. | highlights a difference between what was said and what actually happened. | |
| the rain? | introduces an action taken in opposition to a condition (rain). | |
| a minority of people voted for him. | indicates a contrast between the election outcome and voter support. | |
| we can participate again any time we want. | contrasts the loss with the possibility of participating again. | |
| my sister’s new boyfriend is really stupid, I quite like him. | introduces a contradiction between opinion and personal feelings. | |
| the ones in the other room. | indicates that the same action applies to another situation. | |
| I will do the cleaning. | shows that two actions happen at the same time. | |
| I never want to do something like that again. | contrasts success with reluctance to repeat the experience. | |
| she is actually really exuberant. | shows a contrast between initial thoughts and reality. | |
| we’re going to be late. | presents a consequence of not leaving on time. | |
| his brother, Luke doesn’t eat meat. | compares two people with opposite habits. | |
| I just had a tiny sandwich. | highlights a difference in what two people had for lunch. | |
| Sue was playing on her phone. | indicates two actions happening simultaneously. | |
| I didn’t get a good grade. | contrasts effort with the disappointing result. |
| possible. | indicates a condition for the request. | |
| you get thirsty. | suggests preparing for a potential situation (thirst). | |
| you win the lottery, what would you do with all the money? | introduces a hypothetical scenario for discussion. | |
| you contact the customer service. | indicates a condition that must be met for the refund. | |
| I should come or not. | presents a choice or uncertainty between two options. |
Linking words to end a speech
| I was afraid of Peter. I got to know him, and I like him. | show the progression of feelings over time. | |
| , I would say that he is a brilliant student. , every teacher appreciates his investment. , I think he should not be fired. | introduces the first point, adds information, and summarizes the argument. |
4 Exercises on English Linking Words

1. Complete the sentences using the following connectors. Only one word can fit in each blank.
Linking Words to Use: WHEREAS – THANKS TO – SO AS TO – SINCE – HOWEVER – DUE TO – AS LONG AS – ALTHOUGH.
- I don’t mind going there ________ it’s not too far.
- ________a problem in our computer system, the online assistance is temporarily not available.
- Can you pick up the kids from school ________ you’re not working today?
- Please check all your equipment every morning ________ make sure it’s fully operational.
- We managed to solve our problem ________ the help of a technician.
- ________ many people congratulated him, he didn’t seem satisfied.
- He was exhausted halfway through the game; ________, he didn’t give up.
- I would like to watch an action movie ________she wants to watch a romantic comedy.
| 1. | it’s not too far | |
| 2. | a problem in our computer system, the online assistance is temporarily not available. | |
| 3. | you’re not working today? | |
| 4. | make sure it’s fully operational. | |
| 5. | the help of a technician. | |
| 6. | many people congratulated him, he didn’t seem satisfied. | |
| 7. | , he didn’t give up. | |
| 8. | she wants to watch a romantic comedy. |
2. Read the two sentences and use the given linking word to create one sentence. Make any necessary changes.
- Bring a snack.
- You might get hungry.
- Connector: IN CASE
- Result: Bring a snack in case you get hungry.
Now, construct sentences using the following pairs of sentences and connectors:
- I will do it.
- If you tell me not to, I won’t do it.
- Connector: UNLESS
- We need to leave now.
- If we don’t leave now, we’ll be late.
- Connector: OTHERWISE
- You said I would like it.
- I didn’t like it.
- Connector: CONTRARY TO
- Jim likes fishing.
- Paul doesn’t.
- Connector: UNLIKE (2 possibilities)
- We made a financial gesture.
- They didn’t accept our offer.
- Connector: DESPITE (2 possibilities)
| 1. | you tell me not to | |
| 2. | we’ll be late | |
| 3. | what you said, I didn’t like it | |
| 4. | Paul, Jim likes fishing. / Jim likes fishing unlike Paul. Jim, Paul doesn’t like fishing. / Paul doesn’t like fishing unlike Jim. | |
| 5.1 | our financial gesture, they didn’t accept our offer. They didn’t accept our offer despite our financial gesture. | |
| 5.2 | the financial gesture we made, they didn’t accept our offer. They didn’t accept our offer despite the financial gesture we made. |
3. Complete the sentences using the linking words below to match the beginning and end of each sentence. There is only one correct combination for each one.
Linking words to use: YET – THEREFORE – SO THAT – FOR – AS SOON AS – AS A RESULT OF.
| of the bad weather, the competition was cancelled. | ||
| she had lost the keys. | ||
| , he got fired. | ||
| it faces the entrance. | ||
| she doesn’t understand anything. | ||
| I have my own car, he won’t have to drive me around anymore. |
4. Complete the following sentences using FOR or SINCE .
- I haven’t seen Mark ____ ages.
- Paul has been sick ____ his birthday.
- I’ve worked in this building ____ 2010.
- I haven’t heard of him ____ months.
- Lucy’s had a headache ____ this morning.
- We’ve been married ____ two years.
- What have you been doing ____ last summer?
- Can I stay at your place ____ a couple of days?
| 1. | ages. | |
| 2. | his birthday. | |
| 3. | 2010. | |
| 4. | months. | |
| 5. | this morning. | |
| 6. | two years. | |
| 7. | last summer? | |
| 8. | a couple of days? |
Ce cours vous a aidé ? Partagez votre avis !
Leave a comment cancel reply, apprendre l'anglais.
Apprendre l'anglais facilement
Tests de niveau
Expression écrite
Expression orale
Les formations
Formations CPF
Conjugaison
Auxiliaires
Tableaux de conjugaison
Concordance des temps
Liste des verbes irréguliers
Les nombres
L'orthographe
Difficultés
Vocabulaire
Listes de fréquence
Vocabulaire de base
Vocabulaire général
Vocabulaire professionnel
Vocabulaire du voyage
ISpeakSpokeSpoken
Adrien Jourdan
Témoignages
Liens utiles
Index des cours
Se connecter
ISpeakSpokeSpoken est situé à Tallinn, en Estonie (Vesivärava tänav 50-201)
Mentions légales
Conditions générales de vente
Confidentialité
Copyright 2024 - Tous droits réservés | ISpeakSpokeSpoken | Have fun learning English!
Quel est votre votre VRAI niveau en anglais: le test
Le plan précis pour parler anglais dans les semaines qui viennent

Comment ENFIN parler ET comprendre l’anglais sans bloquer ni chercher vos mots

How to Use Transition Sentences: Definition, Tips, and Examples

Transition sentences are crucial components of written and spoken language that serve as bridges between different ideas, paragraphs, or sections within a piece of writing. These sentences smoothly guide the reader from one point to another, ensuring coherence and logical progression in the narrative. Transition sentences play a vital role in maintaining the flow of a text, helping readers navigate through complex information or arguments with ease.
The primary function of transition sentences is to establish connections and relationships between different text parts, creating a sense of unity and coherence. By using transitional words or phrases, writers create a cohesive and well-organized structure, enhancing the overall readability and comprehension of their work. They can take various forms, including words like "however," "meanwhile," or phrases like "on the other hand." Students who use our essay writing service receive their papers where transitional words and sentences are used on point.
What Are Transition Sentences Explained
Transitional sentences are crucial links within a written or spoken discourse, aiding in the seamless connection between ideas, paragraphs, or sections. These sentences play a pivotal role in ensuring a cohesive narrative flow and logical progression, enhancing the overall clarity and comprehension of the text. Here are several examples:
- Addition Transition: “Building on this idea, the next section delves into…”
- Contrast Transition: “While the previous paragraph discussed the benefits, it is essential to examine the drawbacks…”
- Causation Transition: “The initial steps in the process set the foundation; consequently, the final stages produce tangible results…”
- Time Transition: “As the narrative unfolds, the protagonist's journey takes unexpected turns, ultimately leading to a surprising climax…”
- Comparison Transition: “In contrast to the traditional approach, the modern methodology offers a more efficient and streamlined solution…”
These transitional sentences exemplify how authors seamlessly guide readers through shifts in thought, emphasize relationships between ideas, and ensure a coherent and engaging narrative structure. Remember that before you learn how to use transitions, we recommend you read this guide on how to write an essay introduction .
What Are Good Transition Sentences
Good transition sentences are the linchpin of effective writing, ensuring a seamless flow of ideas and maintaining the reader's engagement. These sentences serve as roadways, connecting one thought to the next and guiding the audience through the narrative. Achieving a balance between cohesion and variety is essential for crafting effective transitions, which can be seen in the examples of transition sentences below.
Consider the transition from one paragraph to another. Instead of abruptly shifting topics, a good transition sentence introduces the upcoming idea while connecting it to the previous one. For example, "Having explored the historical context of the Industrial Revolution, we now delve into its profound socio-economic impacts."
Another critical function of transition sentences is to indicate contrasts or contradictions in ideas. By using words like "however," "on the contrary," or "in contrast," writers signal a shift. For instance, "The benefits of renewable energy are undeniable. However, it is crucial to acknowledge the challenges associated with its widespread implementation."
Time transitions are indispensable for chronological order. "In the following years" or "Meanwhile" are cues that seamlessly guide the reader through the timeline of events. For instance, "The initial phase of the project laid the groundwork. Meanwhile, unforeseen challenges arose during the implementation stage."
To highlight similarities or draw comparisons between ideas, phrases like "similarly," "in the same vein," or "likewise" prove valuable. For example, "Just as the scientific method revolutionized research in the natural sciences, applying a similar empirical approach can advance social sciences."
Good transition sentences are versatile tools that elevate writing by ensuring coherence, progression, and reader understanding. A thoughtful integration of transitions contributes to the overall rhythm and clarity of the narrative, enhancing the impact of the written work. If you are just about to write your paper and want to know the difference between Metaphors and Analogies, we suggest you take a look at our guide to help you find a good topic ideas example.
How to Write a Transition Sentence
When writing a transition sentence, there are three very important aspects to consider: The logical relationship between the ideas, Wording, and Placement. Use this as a rule of thumb; you will always write good transition sentences.
Start with identifying the relationship between the key point and the ideas. Ask yourself whether to contrast them, make a smooth connection, summarize the point, or bring in a new idea. Once you know why you need an effective transition, consider half of the job done.
The wording of transitions is equally important. You must choose words that express the relationship between the previous paragraph and a new one. Every language has common transitional words that smoothly make logical connections between the ideas. There are so many that you can easily avoid overusing the same transition words and phrases. The following examples of transition sentences will give you a clearer understanding of the concept: 'In conclusion…', 'On the other hand…' 'Previously mentioned…' and so on.
The right placement helps you outline the logical connections more effortlessly. You should put the transition words where they fit naturally. Usually, it's either at the beginning of a new paragraph or at the end to let the reader know you are about to draw conclusions.
All the above is an ABC of how to write a transition sentence. Follow our guide; you will master the art of transitional devices in no time.
You can be interested: Metaphors and Analogies: How to Use Them in Your Academic Life

Looking for Professional Help with Your Essay Writing?
Our team of expert writers will get you a cohesive essay with timely transitional sentences. Become the top student in your class!
Transition Sentences Between Paragraphs
Transition sentences between paragraphs play a pivotal role in weaving a cohesive tapestry of ideas, guiding readers through the narrative with fluidity and clarity. These sentences act as connective tissue, smoothly transitioning from one paragraph to the next, enhancing the overall readability of the text.
Consider the scenario where a narrative shifts from introducing a problem to presenting a solution. A well-crafted transition sentence can bridge this gap seamlessly. For instance, "Having identified the challenges, let's now explore viable solutions that can pave the way for meaningful change."
Similarly, when delving into a contrasting idea, a transition sentence becomes the compass that guides readers through the shift in perspective. "While the benefits of technology are evident, it is imperative to acknowledge the potential drawbacks that accompany such rapid advancements."
Time transitions are indispensable when narrating a sequence of events. "As the story unfolds" or "In the subsequent years" serve as cues, allowing readers to effortlessly follow the chronological progression of the narrative. For example, "The initial experiments yielded promising results. In the subsequent years, researchers encountered unforeseen challenges that reshaped the trajectory of their investigations."
Furthermore, comparison transitions help draw parallels between concepts. "In a similar vein" or "Likewise" act as highways, linking one idea to another for a smoother transition. "Just as the characters in the novel undergo personal growth, the storyline also evolves, creating a nuanced exploration of human experiences."
In general, transition words and sentences are the architects of narrative coherence, ensuring that readers navigate through the text seamlessly. By strategically placing these transitions, writers can guide their audience through shifts in ideas, perspectives, and timelines, creating a harmonious and engaging reading experience. If you are just about to write your paper and want to know how to write a hypothesis, we suggest you take a look at our guide to help you find a good example of topic ideas.
You can be interested: How to Write a Hypothesis

Where to Place Transition Sentences
Transition sentences are powerful tools, but their effectiveness depends on strategic placement within a text. Correct usage enhances coherence, while incorrect placement can disrupt the flow. Let's explore where to appropriately position these sentences with examples.
.webp)
Placing a transition sentence at the start of a new paragraph signals a shift in focus, preparing the reader for what lies ahead. This ensures a logical progression.
- Correct: "Having examined the historical context, we now shift our focus to the societal impacts of the Industrial Revolution."
- Incorrect: "The Industrial Revolution, a turning point in history. Its impacts on society were profound."
Within a paragraph, transitions can signal a shift in perspective, introducing contrast or contradiction smoothly without abrupt interruptions.
- Correct: "The advantages of renewable energy are evident; however, challenges in infrastructure remain significant."
- Incorrect: "Renewable energy has numerous benefits. The challenges in infrastructure are, however, significant."
Transition sentences guide readers through time, indicating progression. Placing them at natural breakpoints helps readers follow the chronological sequence effortlessly.
- Correct: "The project's initiation marked a period of excitement. Subsequently, unforeseen challenges altered the course."
- Incorrect: "The project's initiation marked a period of excitement. However, unforeseen challenges altered the course."
When comparing ideas, transitions can smoothly connect concepts, creating a link that aids in understanding relationships.
- Correct: "The scientific method revolutionized natural sciences. In a similar vein, applying empirical approaches can advance social sciences."
- Incorrect: "The scientific method revolutionized natural sciences. Likewise, empirical approaches can advance social sciences."
Concluding with a transition sentence summarizes key points, guiding readers out of the main discussion gracefully.
- Correct: "In conclusion, the evidence supports the hypothesis. However, further research is needed to explore long-term effects."
- Incorrect: "The evidence supports the hypothesis. In conclusion, further research is needed to explore long-term effects."
By placing transition sentences strategically, writers guide readers through the narrative, creating a coherent and engaging reading experience. Incorrect usage disrupts the flow, making it essential to consider the context and purpose when incorporating these transitions.
Transition Sentences Between Sections
Transition sentences serve as pathways, seamlessly connecting different segments of your text and ensuring a cohesive and logical flow. These sentences play a pivotal role in guiding readers through shifts in themes, perspectives, chronological progressions, or comparative analyses. For instance, when transitioning from an exploration of historical context to an in-depth analysis of the economic ramifications of the Industrial Revolution, the text might gracefully progress: "Having delved into the historical backdrop, the narrative now shifts focus to the economic repercussions of the Industrial Revolution, shedding light on its profound impact on commerce and societal structures."
Similarly, in contrasting perspectives, a transition sentence such as "While the benefits of renewable energy are evident, a closer examination reveals potential challenges in its widespread implementation. This nuanced perspective prompts a deeper exploration of the complexities inherent in adopting sustainable practices on a global scale."
In cases of chronological progression, a transition like "With the foundation laid, the narrative progresses to the crucial developments during the implementation phase. This chronological shift allows readers to follow the evolution of ideas, connecting past events to present implications and fostering a comprehensive understanding."
Likewise, during comparative analyses, a transition sentence such as "In contrast to traditional methodologies, the discussion now centers on the innovative approaches that have reshaped the field. This shift in focus invites readers to critically evaluate the transformative impact of progressive strategies and their implications for future practices."
In conclusion, transition sentences between sections are indispensable for maintaining coherence and guiding readers through different thematic or analytical shifts. The strategic use of these sentences provides clarity and ensures a seamless reading experience, allowing readers to navigate through diverse ideas with ease. Keep in mind that you can always order an essay online if anything seems too difficult or you don’t have time to deal with the assignment personally.
Transition Sentences Within Paragraphs
Let’s find out how to use transition sentences to connect ideas, ensuring a seamless flow of thoughts. They are like subtle guides that help readers navigate through the evolving narrative. For instance, when introducing additional information, consider a transition like: "Moreover, the data suggests a clear correlation between regular exercise and improved mental well-being." This transition smoothly leads the reader to a deeper understanding by introducing supporting evidence.
In cases of contrasting ideas, a transition sentence can gracefully shift the focus. Imagine exploring technological advancements and social inequality, with a transition like: "On the contrary, some argue that technological advancements may exacerbate social inequality rather than alleviate it." This transition introduces an opposing viewpoint without causing abrupt disruption, encouraging a more nuanced examination of the topic.
For sequential progression, a transition sentence paves the way for the next step in reasoning. Visualize transitioning from theoretical discussions to practical implications: "Following this line of reasoning, the next logical step is to examine the practical implications of these theoretical frameworks in real-world scenarios." This transition guides the reader through the logical progression of ideas within the paragraph, enhancing overall comprehension.
As you can see, transition sentences within paragraphs are subtle tools that enhance readability by smoothly connecting thoughts and ideas. These examples illustrate how these transitions create a cohesive and engaging reading experience.
Transition Words and Phrases
What transforms ordinary sentences into transition sentences? The answer lies in transition words that serve as the guiding signposts, steering your writing's flow from one thought to the next.
The choice of a transition word in a sentence is crucial to your reader's ability to comprehend your writing, as seemingly identical sentences can take on vastly different meanings with different transition words. Let's delve into quick examples illustrating how the selection of words can reshape an idea:
Consider the following sentences:
- We love to try different local restaurants and explore new cuisines. Recently, we tried two new restaurants downtown.
- We love to try different local restaurants and explore new cuisines. Hence, we tried two new restaurants downtown.
- We love to try different local restaurants and explore new cuisines. On the whole, we tried two new restaurants downtown.
Observe how the foodies' point undergoes a dramatic shift simply by substituting various transition words and phrases. This exemplifies the profound impact of word choice on the overall meaning of a sentence. While working on short assignments like essays, this information might seem easy. But when longer papers are due, one may easily get lost in the abundance of transition words and phrases scattered around the document. That’s why we have a professional coursework writing service that can help you with this matter.
Explore the following list of commonly used transition words and phrases tailored for specific transitions:
Transition Words and Phrases to Communicate Similarities
When highlighting similarities between ideas, events, or concepts in your writing, the careful use of transition words is essential. These linguistic tools serve as bridges, guiding your readers through parallel thoughts seamlessly.
- In the same vein
- Correspondingly
- Similarly to
- Analogously
Transition Words and Phrases to Express Emphasis
Adding emphasis to key points in your writing can significantly impact the reader's understanding and engagement. Transition words designed for emphasis play a crucial role in signaling the importance of specific ideas.
- Undoubtedly
- Unquestionably
Transition Words and Phrases to Demonstrate Cause and Effect
Unraveling the cause-and-effect relationship in your writing requires the strategic use of transition words. These words guide readers through the logical progression of events and help them understand the connections between actions.
- Consequently
- As a result
Transition Words and Phrases to Denote Position
When conveying the spatial or logical arrangement of ideas, transition words indicating position become invaluable. They provide clarity and structure, allowing readers to follow the sequential or spatial organization of your content.
- Adjacent to
- Furthermore
- In the background
- In the foreground
Transition Words and Phrases to Illustrate a Sequence
Sequencing ideas in your writing demands a smooth flow to keep readers engaged. Transition words that denote sequence act as navigational tools, guiding your audience through a logical progression of events.
- Subsequently
- In the meantime
Transition Words and Phrases to Show Examples
Providing examples enhances the clarity and credibility of your writing. Transition words tailored for illustrating examples help seamlessly integrate supporting details into your narrative.
- For example
- For instance
- In particular
- To illustrate
- Specifically
Logical Connectors Examples
When it comes to logical connectors English grammar offers a wide range of words and phrases you can use to enrich your text. Below you will find a logical connectors table full of logical connectors examples from our dissertation writing services .
Incorporating transition sentences and phrases is an indispensable skill for any proficient writer. These linguistic tools act as the adhesive that binds individual thoughts, creating a seamless and coherent narrative. The strategic use of transitional elements ensures readers can effortlessly follow the flow of ideas, enhancing comprehension and engagement. Through the judicious selection of transition words, writers wield the power to guide their audience through a logical journey, connecting concepts and building a narrative that is both compelling and easily digestible.
Moreover, the importance of employing transitional sentences extends beyond mere stylistic finesse. It is a fundamental aspect of effective communication, whether in academic writing, professional documents, or creative pieces. As seen in the examples of transition sentences, they not only facilitate the smooth progression of ideas but also serve as cues for readers, signaling shifts in tone, perspective, or logical structure. Our dissertation writing service can help you with smooth transitions between paragraphs and sections of text in complex documents such as theses and capstones.
Too Busy and Need Help from a Writing Assistant?
No worries! Our writing assistants know how to get you that A+

Daniel Parker
is a seasoned educational writer focusing on scholarship guidance, research papers, and various forms of academic essays including reflective and narrative essays. His expertise also extends to detailed case studies. A scholar with a background in English Literature and Education, Daniel’s work on EssayPro blog aims to support students in achieving academic excellence and securing scholarships. His hobbies include reading classic literature and participating in academic forums.

is an expert in nursing and healthcare, with a strong background in history, law, and literature. Holding advanced degrees in nursing and public health, his analytical approach and comprehensive knowledge help students navigate complex topics. On EssayPro blog, Adam provides insightful articles on everything from historical analysis to the intricacies of healthcare policies. In his downtime, he enjoys historical documentaries and volunteering at local clinics.

Mathematical Proof and the Principles of Mathematics/Logic/Logical connectives
In the previous section we made clear what mathematical statement is. In this section we talk about how mathematical statements can be combined to make more complex statements. This is done using what are called 'logical connectives' or 'logical operators'. You can think of these as functions of one or more variables, where the variables can be either True or False and the value of the function can be either True or False. The logical connectives commonly used in mathematics are negation, conjunction, disjunction, implication, and equivalence, which are fancy words for things you encounter in everyday English.

- 2 Conjunction
- 3 Disjunction
- 4 Implication
- 5 Equivalence
- 6 Complex expression
| Statement | Negation |
|---|---|
| It rained on 1 September 2005. | It did not rain on 1 September 2005. |
| All teachers are female. | Not all teachers are female. |
| Mike's dog has a black tail. | Mike's dog does not have a black tail. |
| 2 + 2 = 4 | 2 + 2 ≠ 4. |
| Triangle ABC is equilateral. | Triangle ABC is not equilateral. |
| Not | |
|---|---|
| True | False |
| False | True |

Even though "Not" is the simplest logical operator, the negation of statements is important when trying to prove that certain objects have or do not have certain properties. It makes the skill of being able to correctly negate statements an important one.
Conjunction
Note that phrasing in English can sometimes include meaning that is not captured by the word 'and'. For example the statement
captures the idea that the fact that it rained would lead you to expect that it would be difficult to have a good time. Logically though, the statement is equivalent to
since both combine the statements
| First statement | Second statement | Conjunction |
|---|---|---|
| The hall was long. | The hall was dark. | The hall was long and dark. |
| All teachers are female. | All teachers are humans. | All teachers are female humans. |
| Mike's dog has a black tail. | Mike's dog has a wet nose. | Mike's dog does has a black tail and a wet nose. |
| 4 is even. | 6 is odd. | 4 is even and 6 is odd. |
| Triangle ABC is equilateral. | Triangle ABC is equiangular. | Triangle ABC is equilateral and equiangular. |
| and | ||
|---|---|---|
| True | True | True |
| True | False | False |
| False | True | False |
| False | False | False |

Disjunction
In mathematics the exclusive or is never used, so
always means
This contrasts with English where the exclusive or is often implied by context, as in
In the rare cases where exclusive or is needed in mathematics, the phrase "but not both" can be added to make it clear.
| First statement | Second statement | Disjunction |
|---|---|---|
| The hall was long. | The hall was dark. | The hall was either long or dark. |
| Mike's dog has a black tail. | Dave's dog has a black tail. | Either Mike's dog or Dave's dog has a black tail. |
| 4 is even. | 6 is odd. | 4 is even or 6 is odd. |
| Triangle ABC is isosceles. | Triangle ABC is scalene. | Triangle ABC is either isosceles or scalene. |
| or | ||
|---|---|---|
| True | True | True |
| True | False | True |
| False | True | True |
| False | False | False |

Implication
Implication is perhaps the most important, but also the most confusing of the logical connectives. In fact it even has a paradox named after it.
When we use the phrase "If ... then ..." in English it usually means there is some sort of causality going on. For example the statement
is logically true even though whether the moon is made of cheese has nothing to do with whether 0 is equal to 1.
This is an implication between the two statements
Now suppose you want to prove your dentist wrong and say "Ha! You don't know what you're talking about. I shall seek dental care elsewhere." If you stay away from sugar and don't get cavities then your dentist will be right. If you stay away from sugar but get cavities anyway then your dentist can ask "Did you brush after eating?" and you'll say "No," and your dentist will say "There you go!" and will still be right. The only way you can prove your dentist wrong is to eat a lot of sugar but not get cavities.
This fact is actually useful in some situations and since it's logically valid there's nothing wrong with using it in a proof.
| First statement | Second statement | Implication |
|---|---|---|
| The hall was long. | The hall had many doors. | If the hall was long then it had many doors. |
| Mike's dog has a wet nose. | Mike's dog is healthy. | If Mike's dog has a wet nose then he/she is healthy. |
| 4 is even. | 6 is odd. | If 4 is even then 6 is odd. |
| Triangle ABC is equilateral. | Triangle ABC is isosceles. | If Triangle ABC is equilateral then it is isosceles. |
| or | ||
|---|---|---|
| True | True | True |
| True | False | False |
| False | True | True |
| False | False | True |

is not always the same as
The two statements are related though and we call the statement
the 'converse' of
Implication plays an important role since most theorems take on the form of an implication.
Equivalence
The last connective we'll be talking about is equivalence. This one does not occur in English very often, so some of the ways of stating an equivalence may be unfamiliar. But it is important enough in mathematics that it gets its own terminology.
Some ways to phrase this are
| First statement | Second statement | Equivalence |
|---|---|---|
| 4 is even. | 6 is odd. | 4 is even iff 6 is odd. |
| Triangle ABC is equilateral. | Triangle ABC is equiangular. | Triangle ABC is equilateral exactly when it is equiangular. |
| or | ||
|---|---|---|
| True | True | True |
| True | False | False |
| False | True | False |
| False | False | True |

The statement
states that the implication
and its converse are both true.
Complex expression
With the connectives given above we can build up more complex expressions. For example

So, for example, the first example above can be written more simply as
but the second example can't be simplified.
- Book:Mathematical Proof and the Principles of Mathematics
- Pages that use a deprecated format of the math tags
Navigation menu
200+ Linking Words – Full List, Examples
| Candace Osmond
Candace Osmond
Candace Osmond studied Advanced Writing & Editing Essentials at MHC. She’s been an International and USA TODAY Bestselling Author for over a decade. And she’s worked as an Editor for several mid-sized publications. Candace has a keen eye for content editing and a high degree of expertise in Fiction.

Worried that your essay lacks structure and coherence? Perhaps you should use linking words, transition words, or connectors to give it a boost.
Linking words join separate sentences to improve writing flow. You can also find them mid-sentence to connect clauses.
Read on as I show you the definition and types of linking words in English. I also list examples of linking words under every category, and I whipped up a helpful worksheet to test your skills.
What Are Linking Words?

Linking words, transition words, or connecting words in the English language help connect ideas and sentences when speaking or writing.
Linking words and phrases are connectors or transitional phrases. They are also part of formal language, so you’ll find them in academic writing, opinion writing, critical essays, dialectic essays , journalism, and business documents.
Some linking verbs link clauses within a sentence, such as although, in case, and whatever. That means you can find them in the middle of sentences from time to time. Others link two complete sentences, such as besides, as a result, and however.
List of Transition Words

Now that you know the meaning of transition words, let’s look at the usage of transition words in sentences and clauses. Don’t worry, I’ll break it all down for you!
Below, I’ve got a list of linking words and phrases to serve as alternative choices for connecting ideas in writing. Note that there are several types of transition words which we will discuss later.
Agreement/Addition/Similarity
Linking words may help the reader understand additional comments or ideas in a statement. They may also express agreement or similarities. These words are also called additive transition words, commonly found in expository essays and narrative essays.
- In the first place
- As a matter of fact
- In like manner
- In addition
- Not only, but also
- Coupled with
- In the same way
- In the same manner
- First, second, third
- Not to mention
- In the light of
- By the same token
- Additionally
- Correspondingly
- Furthermore
- Comparatively
- At the same time
- Together with
- Identically
Here are some examples of additive linking words in a sentence.
- The group found that a constructivist approach leads to higher test scores. Moreover, essay examinations show higher levels of learning.
- The resort has tennis courts. Furthermore, it has an Olympic pool.
Negative Ideas
Some linking words come in pairs to join negative ideas.
- Not, neither
- Neither, nor
Here are sentence examples of linking words showing negative ideas.
- I haven’t seen Lory, neither have I talked to her friend.
- I neither drink nor smoke.
Opposition/Limitation/Contradiction
Whereas some linking words show an extra idea, these transition phrases and words express contrasting ideas in writing.
- Although this may be true
- In contrast
- (and) still
- Notwithstanding
- Different from
- Of course…, but
- On the other hand
- On the contrary
- Be that as it may
- Nonetheless
- Even so/though
- Nevertheless
- In spite of
Here are some sentences with linking words of opposition.
- The short story can be analyzed using a functionalist lens. However, its historical theme is better understood with a critical perspective.
- As much as I want to go, I must take care of my sister.
Some linking words show relationships between ideas by accepting an idea with reservation instead of showing complete opposition. Here are some examples.
- All the same
- Regardless of this
- Up to a point
Here are some sentence examples.
- Many citizens opposed this unfair policy, which the president nevertheless enacted.
- I like him even if we have different views in life.
Cause/Condition/Purpose
You may also use linking words in your writing piece to show conditions and purpose for a logical flow of ideas. Words like reason get the reader ready to understand why. These words are commonly found in hypothesis essays.
- In the event that
- Granted (that)
- Provided that
- On (the) condition (that)
- For the purpose of
- With this intention
- With this in mind
- In the hope that
- Inasmuch as
- To the end that
- For fear that
- In order to
- Seeing/being that
- The researchers used this method so that the results would be valid, reliable, and aligned with the objectives.
- I will not be attending the seminar due to a high fever.
Examples/Support/Emphasis
You can also use transition words in your piece of writing that show examples or support of an idea.
- In other words
- To put it differently
- For one thing
- In particular
- As an illustration
- In this case
- For example
- For instance
- For this reason
- To put it another way
- To demonstrate
- That is to say
- With attention to
- By all means
- To emphasize
- To enumerate
- Particularly
- Significantly
- Specifically
- Surprisingly
- Important to realize
- Another key point
- On the negative side
- First thing to remember
- Must be remembered
- To point out
- Point often overlooked
- She visited several cities, namely Portland, Jacksonville, Charleston, and Hartford.
- Transition words improve writing flow. For instance, we use further to add extra ideas related to the previous statement.
Effect/Consequence/Result

You might also spot transitional devices for essays that show consequences, results, and effects.
- As a result
- In that case
- Under those circumstances
- Accordingly
- Consequently
Consider the examples below.
- We watered the plant for seven days. In effect, it grew three inches taller.
- Because she didn’t study for the test, Anna failed and had to retake it.
Conclusion/Summary/Restatement
These words and phrases show transitions between sentences to show conclusions. You’ll find these words in essay conclusions of different essay types.
- In simple language
- In explanation
- In lay terms
- In a nutshell
- As can be seen
- In simple terms
- Generally speaking
- All things considered
- As shown above
- In the final analysis
- In the long run
- In either case
- Given these points
- As has been noted
- In any event
- On the whole
- By and large
- For the most part
- In conclusion
- To summarize
Note that in lay terms and in explanation are formal alternative choices to “ in a nutshell.”
Here are some examples.
- Matter is a material that occupies space and has mass. In simple language, it is any physical substance.
- I don’t want to climb the corporate ladder. After all, money isn’t everything.
Time/Chronology/Sequence
Linking words’ other role in writing is to show sequence or chronology. Under the time category, these phrases add a meaning of time. You can find these words in an essay introduction when the writer explains how the paper is structured.
- In due time
- From time to time
- At the present time
- Sooner or later
- Up to the present time
- To begin with
- Straightaway
- In the meantime
- In a moment
- Without delay
- All of a sudden
- At this instant
- First, second
- By the time
- Immediately
- Occasionally
- I watched the movie on television. Eventually, I fell asleep.
- First, fill the pan with water. Then, bring it to a boil.
Space/Location/Place
The following transition words are famous adverbial expressions that limit or modify space. Some of these words and phrases are also transition words of time.
- In the middle of
- To the left/right
- In front of
- On this side
- In the distance
- In the foreground
- In the background
- In the center of
- Adjacent to
- Opposite to
Below are sentence examples using transition words of space.
- My house is located behind the building.
- To the left of the supermarket is a flower shop.
Common Mistakes With Transition Words
Transition words help you create a flow of arguments for readers to understand what you’re saying. But misused transition words and phrases will make your writing unclear. Avoid these mistakes to give your readers a better experience.
Starting a Sentence With So, And, and Also
Both so and and are coordinating conjunctions, which means they can start independent clauses that stand on their own. But it’s not recommended to use these words and also as sentence starters in formal writing. For example:
- Incorrect: Also, there are unauthorized charges on my credit card account.
- Correct: Furthermore, there are unauthorized charges on my credit card account.
Combination of Transition Words And/Or
When writing an essay, avoid English transition words and/or because it makes your paper look messy. Instead, consider whether you need both connectors or only one of them. If you need them both, try this alternative.
- Incorrect: boat and/or plane.
- Correct: boat, plane, or both.
Using As Well As as Alternative to And
As well as has a different meaning from the transition word and. And means you’re listing something of equal importance. Meanwhile, as well as is for additional, less essential information. Here’s an example.
- Incorrect: In this paper, I discuss my movie analysis as well as provide recommendations for improvement.
- Correct: In this paper, I discuss my movie analysis and provide recommendations for improvement.
Archaic Words
Your writing may not make any sense to readers if you overuse archaic transition words like therewith .
For example, hereby means as a result. We can replace it with more modern and explicit phrasing expressing how the current statement is connected to the previous statement.
Linking Words Summary
A linking word is a term that connects different ideas in your text, whether they are contrasting, supporting, or adding. They can improve your writing and help it flow better, I promise!
Regardless of the style of writing, every piece of writing contains linking words to show perfect transitions. I hope my guide on the definition and list of transitions helps you use these words and phrases correctly. Memorize each category, and don’t overuse them in essays.
Grammarist is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon.com. When you buy via the links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission at no cost to you.
2024 © Grammarist, a Found First Marketing company. All rights reserved.
- DOI: 10.1016/J.SBSPRO.2010.07.406
- Corpus ID: 58214156
Quantitative usage of logical connectors in Iranians’ EFL Essay writing and logical and linguistic intelligences
- A. Rahimi , Jamal-addin Qannadzadeh
- Published 2010
- Linguistics, Education
- Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences
29 Citations
Linguistic intelligence and logical intelligence: which is determinant for logical connector (lc) comprehension by efl readers.
- Highly Influenced
Variation of Sentence Connectors as Logical Devices in Abstracts
A contrastive study of the variation of sentence connectors in academic english, the correlation between linguistic intelligent and students ability in writing descriptive text, the effects of explicit and implicit teaching of connectors on the reading comprehension performance of iranian efl learners, the relationship between multiple intelligences and iranian high school students' l2 writing achievement, the relevance of multiple intelligence theory to narrative performance: a study of iranian undergraduates of english, comparative study of conjunctive adverbials (cas) in native researchers' (nrs) and non-native researchers' (nnrs) experimental articles, the effectiveness of think talk write model in english essay writing, comparative study of conjunctive adverbials (cas) in experimental articles, 13 references, nagoya university, the use of conjunctive adverbials in the academic papers of advanced taiwanese efl learners, connector usage in the english essay writing of native and non‐native efl speakers of english, a corpus-based study of connectors in student writing: research from the international corpus of english in hong kong (ice-hk), the grammar book: an esl/efl teacher's course.
- Highly Influential
Frames of Mind: The Theory of Multiple Intelligences
A multiple intelligences inventory., calculating, interpreting, and reporting cronbach’s alpha reliability coefficient for likert-type scales, multiple intelligences: voices from an efl writing class.
- 11 Excerpts
A corpus-based study of logical connectors in EFL students' writing : directions for future research
Related papers.
Showing 1 through 3 of 0 Related Papers

Logical Connectors Examples

Have you ever heard the term “ conjunction “? If you have, then you must know some examples of conjunction, such as “ and , or , though , then , if ” and so on. In English, conjunction is one of the subjects discussed in the Logical Connector chapter.
Table of Contents
Logical Connectors Definition
Logical Connector is a conjunction that connects a word in other words, a clause with another clause, a sentence with another sentence, or a paragraph with another paragraph.
In other words, logical connectors are conjunctions that connect two ideas that have a certain relationship, which are related to time (sequential), reason & purpose, condition, or adversative.
Types of Logical Connectors
There are several types of logical connectors you should know, which are:
Subordinating Conjunctions
Subordinating Conjunctions are useful for starting adverb clauses.In addition, they are commonly used in compound sentences where the dependent clause or independent clause can exchange positions without any change in meaning. For example:
Before he came, we did not have a physical education teacher. We did not have a physical education teacher before he came.
Prepositions
Prepositions are usually followed by a noun and noun phrase. We also use prepositions in compound sentences where the dependent clause or independent clause can exchange positions without any change in meaning, just same as subordinating conjunctions. For example:
The new student did not come to class due to his illness.
Transitions and Conjunctive Adverbs
Transitions and Conjunctive Adverbs combine two sentences separated by periods (.), or two clauses separated by commas (,). We also use transitions and conjunctive adverbs in sentences that only have one sentence arrangement, but if the two clauses exchange their positions then the meaning will change.
The transition word can be in the form of an initial clause, final clause, or between subject and verb. For example:
He was sick. Nevertheless , he came to class.
Conjunctions
Conjunctions are often used in sentences that only have one sentence arrangement and if the two clauses exchange their positions then the meaning will change.
In academic writing, don’t use conjunction to start a sentence. Also, use a comma (,) before the conjunction.
She always did not do her homework, so she did not pass the class.
Following are some logical connectors examples along with the classifications.
| Sequential | Reason & Purpose | Adversative | Condition |
| Until After Before When While Since Once Whenever As soon as As long as By the time | Because As Since As much as Now that As long as So that In order that | Even though Although Though In spite of the fact that Whereas Where | If Unless Even if Providing + that Provided + that In case Whether or not Only if |
| Sequential | Reason & Purpose | Adversative | Condition |
| During After Before Since Until Upon | Because of Due to In order to | Despite In spine of |
| Sequential | Reason & Purpose | Adversative | Condition |
| Then Next After that Following that Before that Afterwards Meanwhile Beforehand | Therefore Consequently | However Otherwise Nonetheless Nevertheless On the other hand In contrast On the contrary |
| Sequential | Reason & Purpose | Adversative | Condition |
| And then | So | But … anyway But … still Yet … still But | Or + else |
A Few Things to Note
Many conjunctions have the same meaning but different structures, such as the use of the words “ despite ” and “ in spite of “. Please pay attention to our brief explanation below.
1. The word “ despite ” is followed by a noun. For example:
I went out despite the heavy rains.
2. The word “ in spite of ” is followed by the form – ing . For example:
I went to work in spite of feeling ill.
That was the definition of logical connectors along with the types and examples. Make sure to keep yourself updated with our English lessons and exercises to improve your skills. See you on the next lesson!
Share this:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Tumblr (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
Notify me of new posts by email.
Connectors of Cause and Effect (Definition and Examples)

We all know what it feels like when one thing happens after another. But what exactly is causing these events? And how do we identify them?
In this blog post, we’ll explore the definition and examples of connectors of cause and effect. We’ll also discuss how to identify these connectors in your own writing. So let’s get started!
List of Connectors of Cause and Effect in Detail
1) As a Result Of
These connectors are used to identify a clear cause-and-effect relationship between two events. The phrase “as a result of” can be used to introduce either the cause or the effect, but it is typically used to introduce the cause.
e.g. She was very happy as a result of her marriage.
This connector is used to introduce the cause of an event. It can be used with or without the phrase “of.”
e.g. I’m going to bed because I’m exhausted.
3) Caused By
This connector is used to introduce the effect of an event. It can be used with or without the phrase “by.”
e.g. His death was caused by a heart attack.
4) Consequently
This connector is used to introduce the effect of an event. This connector is very similar to “as a result of,” but it typically has a more negative connotation.
e.g. The company went bankrupt as a consequence of the recession.
e.g. The accident was due to driver error.
This connector is used to introduce a hypothetical situation. It can be used with or without the phrase “then.”
e.g. If I were taller, I would be able to reach the top shelf.
7) In Order To
e.g. He was running in order to get fit.
This connector is typically used to introduce the cause of an event that has been happening for a while.
e.g. We’ve been having trouble with our internet connection since last week.
This connector is used to introduce the effect of an event. It can be used with or without the phrase “that.”
e.g. I’m going to bed so that I can wake up early tomorrow.
10) Supposed To
e.g. You’re supposed to call me when you get there.
This connector is typically used to introduce the cause of an event that happens immediately before another event.
e.g. When I got home, I saw that my car was gone.
Related Posts

Connectors of Contrast (Definition and Example Sentences)

Gerund: Types of Gerunds, Examples of Verbs Followed By Gerund

Sentence Connectors in English (Definition and Examples)

Using However in English (Rules and Examples)
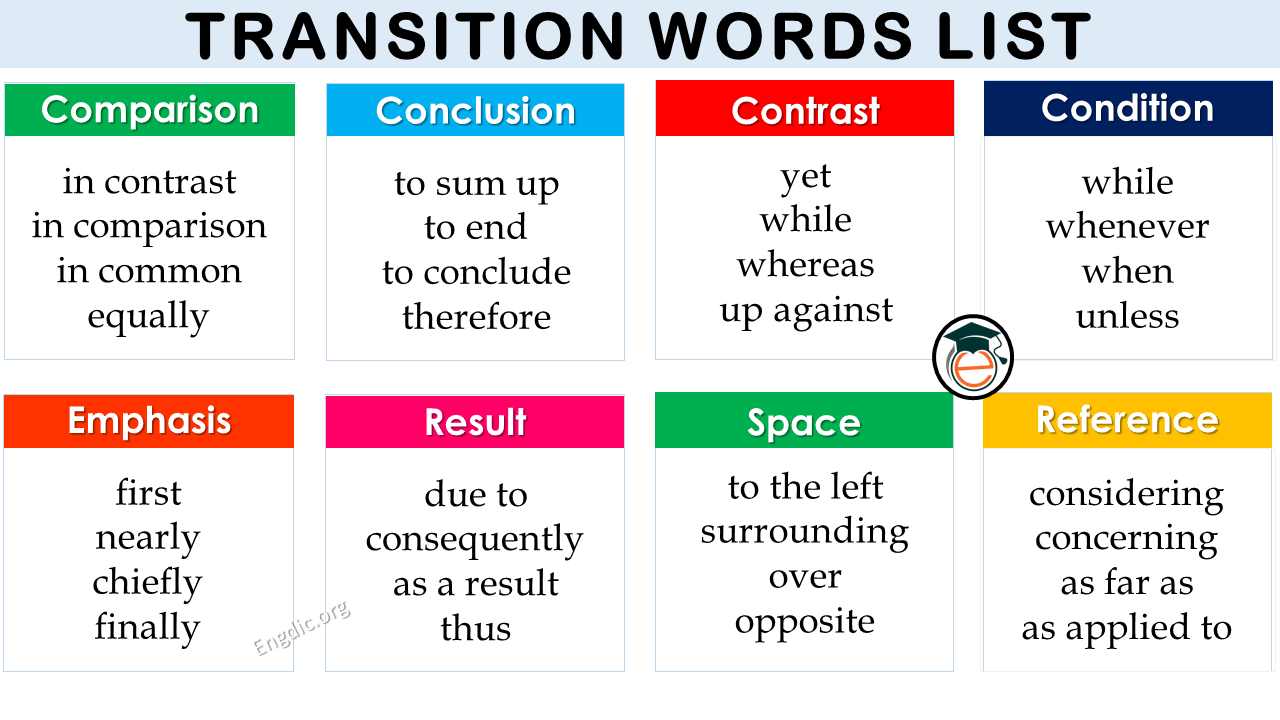
Different Types of Transition Words in a List Pdf
Noun Verb Adjective Adverb List in English
About the author.
Hi, I'm USMI, engdic.org's Author & Lifestyle Linguist. My decade-long journey in language and lifestyle curation fuels my passion for weaving words into everyday life. Join me in exploring the dynamic interplay between English and our diverse lifestyles. Dive into my latest insights, where language enriches every aspect of living.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
LOGICAL CONNECTORS
Transition Words & Phrases | List & Examples
Connectors in English: How to Use Them
4 Exercises on English Linking Words. 1. Complete the sentences using the following connectors. Only one word can fit in each blank. Linking Words to Use: WHEREAS - THANKS TO - SO AS TO - SINCE - HOWEVER - DUE TO - AS LONG AS - ALTHOUGH.
Using connectors in essays requires a few steps: Choose the connector that best suits your needs. Connect the two sentences with the connector. Make sure the sentences are logically connected. Here's an example: Result: I didn't get a good grade on my test. Contrast: However, I got a good score on the practice test.
Transition sentences are crucial components of written and spoken language that serve as bridges between different ideas, paragraphs, or sections within a piece of writing. These sentences smoothly guide the reader from one point to another, ensuring coherence and logical progression in the narrative. Transition sentences play a vital role in ...
A1: Connectors and linkers are words or phrases that help link ideas and sentences together, establishing logical relationships between them. They are essential for structuring arguments ...
The logical connectives commonly used in mathematics are negation, conjunction, disjunction, implication, and equivalence, which are fancy words for things you encounter in everyday English. In this section the symbols P {\displaystyle P} and Q {\displaystyle Q} denote mathematical statements.
Sentence connectors are words, phrases, clauses, or symbols that are used to ensure a sentence transitions smoothly. Moving from one sentence to the next without using proper words to connect them makes a piece of writing seem abrupt. To ensure seamless sentence transitions, different types of sentence connectors are used in the English language.
This paper explores the use of English logical connectors in the academic writing of twenty-. six Macedonian learners of English. Logical connectors are dened as types of cohesive. devices ...
Linking Words - Full List, Examples & Worksheet
Concessives. The concessives- although, even though, though, and while- fall within the class of inferential. connectors. The use of concessive expressions involves a functional sort. of contrast ...
Semantic Scholar extracted view of "A corpus-based study of logical connectors in EFL students' writing : directions for future research" by J. Milton et al. ... examines the use of discourse markers by Saudi English learners who struggle to master them when they write English essays. The hypothesis is, and based on previous studies of ...
DOI: 10.1016/J.SBSPRO.2010.07.406 Corpus ID: 58214156; Quantitative usage of logical connectors in Iranians' EFL Essay writing and logical and linguistic intelligences @article{Rahimi2010QuantitativeUO, title={Quantitative usage of logical connectors in Iranians' EFL Essay writing and logical and linguistic intelligences}, author={Ali Rahimi and Jamal-addin Qannadzadeh}, journal={Procedia ...
In this paper we report on our quantitative analysis of 25 logical connectors in advanced Japanese university students' essay writing and compare it with the use in comparable types of native ...
2.1.1 The First-Pattern Usage of Logical Connectors Logical connectors in L2 writers' English texts often displayed an informal and speech-like nature. Chen (2006) noticed an extensive usage of informal logical connectors in Taiwan students' essays and asserted that the non-native-English writers were probably unaware of stylistic ...
The required data was supplied from a corpus of 300 essay-type compositions written by 100 sophomore English major students, as well as an intelligence questionnaire. The findings revealed that EFL students with higher logical/mathematical intelligence tend to use more logical-connectors in their essay writing.
four proficiency levels use more logical connectors in their essays (72, 72, 76, 86)than the NS do (63).This means that the EFL learners relatively overus e . connectors in comparison to NS.
Visit my website: SpeakEnglishPodcast.com. And look for episode #042. I'll just go ahead and start talking about connectors. But don't worry, I'm not gonna give any grammatical theory here :) As usual, I'll give you some examples, and then you'll practice the connectors in context with the point of view story.
Logical Connector is a conjunction that connects a word in other words, a clause with another clause, a sentence with another sentence, or a paragraph with another paragraph. In other words, logical connectors are conjunctions that connect two ideas that have a certain relationship, which are related to time (sequential), reason & purpose ...
e.g. His death was caused by a heart attack. 4) Consequently. This connector is used to introduce the effect of an event. This connector is very similar to "as a result of," but it typically has a more negative connotation. e.g. The company went bankrupt as a consequence of the recession. 5) Due To.
Students with higher Logical-Mathematical Intelligence tend to use more logical connectors in their essay writing [27], there is a significant positive correlation between learning achievement in ...
Table 1: Semantic Classification of Logical Connectors Examined in this Study As comparable essay writing data, we selected two sub-corpora of the ICLE project with permission to use them for our research purposes: (1) the Japanese component of the ICLE corpus and (2) the Louvain Corpus of Native English Essays (LOCNESS).