

The 7 Types of Dissertations Explained: Which One is Right for You?
Your dissertation is a pretty big deal and likely represents years of hard slog studying your subject of expertise.
But did you know there are 7 different types of dissertation ?

The purpose of this article is to demystify the various types of dissertations you might encounter or choose to undertake during your advanced studies. Armed with this knowledge, you can select the most appropriate methodology and framework for your research interests and academic requirements.
Each type of dissertation serves a different academic purpose and requires a unique approach and structure. In this article, we’ll take a look at these differences in detail, providing clear explanations and examples from a range of academic disciplines. By the end of this article, you should have a thorough understanding of the options available for your dissertation and be better prepared to select a path that aligns with your research goals and academic ambitions.
Remember, regardless of what type of dissertation you ultimately decide to pursue, best dissertation proofreading can make all the difference between a pass and a fail.
7 Types of Dissertation
| Type of Dissertation | Key Features | Typical Disciplines | Primary Focus |
|---|---|---|---|
| Empirical | Data collection through experiments, surveys, observations | Sciences, Social Sciences | Gathering new data |
| Theoretical | Focuses on existing theories and literature | Philosophy, Literature, Sociology, Psychology | Developing or expanding theories |
| Case Study | In-depth study of a particular case | Business, Education, Psychology, Social Sciences | Detailed analysis of a specific instance |
| Comparative | Compares and contrasts two or more entities | Law, Education, Political Science, International Relations | Identifying patterns or discrepancies |
| Project-Based | Centers around a practical project | Engineering, Computer Science, Applied Arts | Application of theoretical knowledge to real-world problems |
| Narrative | Uses narrative techniques to convey research | Creative Arts, Literature, Education | Personal or creative exploration of topics |
| Systematic Review | Structured review of literature | Healthcare, Psychology, Social Sciences | Synthesizing existing research |
Empirical Dissertations
So, let’s dive right in with empirical dissertations—arguably the most hands-on type of dissertation out there. If you’re studying a field like psychology, biology, or social sciences, you’re probably going to become very familiar with this approach.
What exactly is an empirical dissertation?
It’s all about gathering data. You’ll be conducting your own experiments, surveys, or observations, making this type extremely engaging (and a bit daunting). Essentially, you’re collecting new data from the world or from people, rather than relying on existing data from other studies.
The structure of an empirical dissertation is pretty straightforward but involves rigorous methodology. Typically, it will include an introduction to set up your SMART research question , a literature review to justify why this question needs answering, a methodology section that details how you’ve gone about your data collection, a results chapter presenting your findings, and a discussion that ties everything back to your research question and explores the implications.
This type of dissertation not only tests your ability to conduct research and analyze data but also challenges you to apply theoretical knowledge in practical scenarios. By the end of an empirical dissertation, you should not only have answers to your original questions but also a solid chunk of real-world experience under your belt.
Best suited to: Students who are ready to roll up their sleeves and get their hands dirty.
Theoretical Dissertations
Now, shifting gears, let’s talk about theoretical dissertations. If the empirical dissertation is the hands-on, muddy boots kind of research, the theoretical dissertation is its more contemplative, indoor cousin. Perfect for those of you in fields like philosophy, literature, or certain branches of sociology and psychology, where concrete data might not be the main focus.
What’s the deal with theoretical dissertations? They revolve around developing, exploring, or expanding on existing theories. Instead of collecting new data, you invest your time and effort studying existing research and theoretical frameworks to build an argument or propose a new theory or perspective on an old one.
The structure of a theoretical dissertation generally includes a comprehensive introduction where you lay out your thesis or theory, followed by a detailed literature review that supports and provides the foundation for your thesis. After this, you’ll move into a discussion or analysis section, where you critically analyze your thesis in the light of existing theories and literature. The aim here is to offer a fresh or refined perspective that contributes to the existing body of knowledge.
This type of dissertation is a test of your analytical skills and your ability to synthesize complex ideas into a coherent argument. It’s less about creating new paths and more about mapping the ones already laid out in new ways.
Best suited to: Students who love theory and thrive on crafting arguments.
Case Study Dissertations
Next up, it’s case study dissertations. This type of dissertation is especially attractive if you’re someone who loves storytelling with a purpose or is drawn to in-depth analysis of specific events, individuals, or organizations. It’s a favorite in disciplines like business, education, psychology, and social sciences, where a single case can lead to the development of new theories and concepts.
A case study dissertation involves an intensive investigation of a particular individual, group, organization, or event. You’ll get to the nitty gritty of the specifics, examining various aspects of the case to understand its implications and applications. This method allows you to apply theoretical concepts in a real-world context, providing rich insights that aren’t always accessible through broader surveys or experiments.
The structure of a case study dissertation usually starts with an introduction to the chosen case, followed by a literature review that sets the theoretical framework. You then proceed to a detailed methodology section explaining how you collected and analyzed your data. The core of your dissertation will likely be the case analysis chapter, where you dissect the case in relation to your research question. Finally, you’ll conclude with a discussion of how the case impacts the wider field and what new understandings it brings to the fore.
Best suited to: Those who are meticulous and have a keen eye for detail, a case study dissertation allows you to explore the intricacies of a specific example while contributing to broader academic debates.
Comparative Dissertations
Next up is the comparative dissertation. This type is tailor-made for the analytically minded who love drawing connections and distinctions between different elements. It’s particularly prevalent in fields like law, education, political science, and international relations, where understanding differences and similarities across cases, laws, or educational methods can provide critical insights.
Essentially, a comparative dissertation involves systematically comparing and contrasting two or more entities. These could be policies, theories, populations, or even historical periods, depending on your study area. The goal is to identify patterns or discrepancies that reveal underlying principles or suggest new interpretations of data.
The structure of a dissertation of this nature typically includes a dissertation abstract followed by an introduction that defines the entities being compared and poses your research question. This is followed by a literature review that frames the theoretical bases for comparison. The methodology section should clearly outline the criteria and methods for comparison, ensuring transparency and replicability. The subsequent chapters will then detail the comparative analysis, discussing each entity individually before bringing them together for a comprehensive comparison. Finally, the conclusion synthesizes the findings, highlighting the significance of the differences and similarities discovered.
Best suited to: Those who can juggle multiple themes and variables without losing sight of the overarching question, a comparative dissertation challenges you to remain objective and balanced in your analysis.
Project-Based Dissertations
Project-based dissertations are more practical in nature. This type of dissertation is particularly appealing if you’re inclined towards applying your theoretical knowledge to create something tangible or solve a real-world problem. It’s a common choice in fields like engineering, computer science, and applied arts, where the end product can be a piece of software, an engineering prototype, or a design project.
What makes a project-based dissertation stand out? It centers around a project that you will plan, execute, and manage through the duration of your dissertation process. This could involve designing a new gadget, developing a software program, or creating a marketing plan for a startup. The focus is on applying the skills and knowledge you’ve acquired through your studies to produce a project that has practical and theoretical implications.
The structure of a project-based dissertation generally includes an introduction to the project, its objectives, and its relevance to your field. Following this, you’ll provide a literature review that supports the theories and methodologies you intend to use. The methodology section should detail your project plan, resources, and the processes you will follow. The main body of the dissertation will describe the project development and implementation phases in detail. Finally, the conclusion will evaluate the project’s success, its impact, and potential future developments or applications.
Best suited to: The innovative and the practical, a project-based dissertation allows you to showcase your ability to deliver a concrete outcome that demonstrates your professional capabilities.
Narrative Dissertations
If you’re drawn to writing and storytelling, a narrative dissertation might be right up your alley. This type is particularly popular in fields such as creative arts, literature, and education, where personal narratives or creative elements can be used to explore and communicate complex ideas.
What does a narrative dissertation involve? It’s about crafting a dissertation that primarily uses narrative techniques to convey research findings or explore scholarly questions. This could mean writing in a first-person perspective, incorporating fictional elements, or structuring the dissertation like a series of interconnected stories or essays.
The structure of a narrative dissertation often deviates from the traditional format. It begins with an introduction that sets the stage for the narrative journey. The literature review might be woven into the narrative itself, providing contextual background as the story unfolds. The methodology section explains how narrative methods will be used to explore the research question. The main body is where the narrative takes center stage, presenting research through personal reflections, storytelling, or hypothetical scenarios. The conclusion then ties all narrative threads together, reflecting on the insights gained and their broader implications.
Best suited to: those who think and express themselves best through stories, a narrative dissertation allows you to engage with your topic in a deeply personal and creative way.
Systematic Review Dissertations
Systematic review dissertations are perfect if you’re keen on synthesizing existing research to draw comprehensive conclusions about a specific topic. This type is particularly valuable in fields like healthcare, psychology, and social sciences, where summarizing and evaluating existing studies can provide powerful insights and inform practice and policy.
A systematic review dissertation involves a rigorous and structured approach to reviewing literature. You’ll gather all relevant data from previously published studies to answer a specific research question. The focus is on transparency and reproducibility, employing predefined methods to minimize bias and provide reliable results.
The structure of a systematic review dissertation typically begins with an introduction that outlines the research question and its significance. This is followed by a methodologically detailed section that explains the criteria for selecting studies, the search strategy used, and the methods for data extraction and synthesis. The results section then presents a detailed analysis of the studies included in the review, often using quantitative methods like meta-analysis. The discussion interprets these findings, considering their implications for the field and any limitations. The conclusion suggests areas for further research and summarizes the contributions made by the review.
Best suited to: Those with a keen eye for detail and a systematic approach to research, a systematic review dissertation can significantly impact by clarifying and summarizing existing knowledge.
Methodological Considerations
Choosing the right type of dissertation is an important decision in your academic journey, and several factors should guide your selection. This section aims to help you navigate these choices, ensuring that the methodology and framework you choose align perfectly with your research goals, available resources, and time constraints.
First, consider your discipline’s requirements and norms. Different fields favor different types of dissertations, so understanding what is expected and respected in your area of study is crucial. Next, think about your own strengths and interests. Choose a dissertation type that not only meets academic criteria but also excites you and plays to your strengths, whether they lie in empirical research, theoretical exploration, practical application, or creative expression.
Resource availability is another critical factor. Some types of dissertations, like empirical and project-based, may require access to specific equipment, software, or locations, which can be a deciding factor. Time constraints are also essential to consider; some dissertations, particularly those involving extensive data collection and analysis, may require more time than others.
Finally, discuss your ideas with your advisor or mentor. They can provide valuable insights and feedback that can help you refine your choice and ensure that you are prepared to tackle the challenges ahead. With the right preparation and understanding of what each type of dissertation entails, you can make an informed decision that sets the stage for a successful and rewarding research endeavor.
Leave a Comment
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
What Is a Dissertation? | Guide, Examples, & Template
A dissertation is a long-form piece of academic writing based on original research conducted by you. It is usually submitted as the final step in order to finish a PhD program.
Your dissertation is probably the longest piece of writing you’ve ever completed. It requires solid research, writing, and analysis skills, and it can be intimidating to know where to begin.
Your department likely has guidelines related to how your dissertation should be structured. When in doubt, consult with your supervisor.
You can also download our full dissertation template in the format of your choice below. The template includes a ready-made table of contents with notes on what to include in each chapter, easily adaptable to your department’s requirements.
Download Word template Download Google Docs template
- In the US, a dissertation generally refers to the collection of research you conducted to obtain a PhD.
- In other countries (such as the UK), a dissertation often refers to the research you conduct to obtain your bachelor’s or master’s degree.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

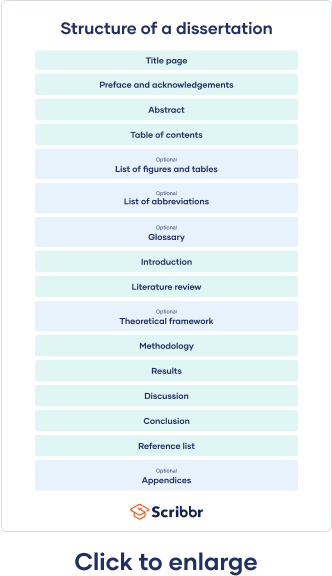
Table of contents
Dissertation committee and prospectus process, how to write and structure a dissertation, acknowledgements or preface, list of figures and tables, list of abbreviations, introduction, literature review, methodology, reference list, proofreading and editing, defending your dissertation, free checklist and lecture slides.
When you’ve finished your coursework, as well as any comprehensive exams or other requirements, you advance to “ABD” (All But Dissertation) status. This means you’ve completed everything except your dissertation.
Prior to starting to write, you must form your committee and write your prospectus or proposal . Your committee comprises your adviser and a few other faculty members. They can be from your own department, or, if your work is more interdisciplinary, from other departments. Your committee will guide you through the dissertation process, and ultimately decide whether you pass your dissertation defense and receive your PhD.
Your prospectus is a formal document presented to your committee, usually orally in a defense, outlining your research aims and objectives and showing why your topic is relevant . After passing your prospectus defense, you’re ready to start your research and writing.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
The structure of your dissertation depends on a variety of factors, such as your discipline, topic, and approach. Dissertations in the humanities are often structured more like a long essay , building an overall argument to support a central thesis , with chapters organized around different themes or case studies.
However, hard science and social science dissertations typically include a review of existing works, a methodology section, an analysis of your original research, and a presentation of your results , presented in different chapters.
Dissertation examples
We’ve compiled a list of dissertation examples to help you get started.
- Example dissertation #1: Heat, Wildfire and Energy Demand: An Examination of Residential Buildings and Community Equity (a dissertation by C. A. Antonopoulos about the impact of extreme heat and wildfire on residential buildings and occupant exposure risks).
- Example dissertation #2: Exploring Income Volatility and Financial Health Among Middle-Income Households (a dissertation by M. Addo about income volatility and declining economic security among middle-income households).
- Example dissertation #3: The Use of Mindfulness Meditation to Increase the Efficacy of Mirror Visual Feedback for Reducing Phantom Limb Pain in Amputees (a dissertation by N. S. Mills about the effect of mindfulness-based interventions on the relationship between mirror visual feedback and the pain level in amputees with phantom limb pain).
The very first page of your document contains your dissertation title, your name, department, institution, degree program, and submission date. Sometimes it also includes your student number, your supervisor’s name, and the university’s logo.
Read more about title pages
The acknowledgements section is usually optional and gives space for you to thank everyone who helped you in writing your dissertation. This might include your supervisors, participants in your research, and friends or family who supported you. In some cases, your acknowledgements are part of a preface.
Read more about acknowledgements Read more about prefaces
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
The abstract is a short summary of your dissertation, usually about 150 to 300 words long. Though this may seem very short, it’s one of the most important parts of your dissertation, because it introduces your work to your audience.
Your abstract should:
- State your main topic and the aims of your research
- Describe your methods
- Summarize your main results
- State your conclusions
Read more about abstracts
The table of contents lists all of your chapters, along with corresponding subheadings and page numbers. This gives your reader an overview of your structure and helps them easily navigate your document.
Remember to include all main parts of your dissertation in your table of contents, even the appendices. It’s easy to generate a table automatically in Word if you used heading styles. Generally speaking, you only include level 2 and level 3 headings, not every subheading you included in your finished work.
Read more about tables of contents
While not usually mandatory, it’s nice to include a list of figures and tables to help guide your reader if you have used a lot of these in your dissertation. It’s easy to generate one of these in Word using the Insert Caption feature.
Read more about lists of figures and tables
Similarly, if you have used a lot of abbreviations (especially industry-specific ones) in your dissertation, you can include them in an alphabetized list of abbreviations so that the reader can easily look up their meanings.
Read more about lists of abbreviations
In addition to the list of abbreviations, if you find yourself using a lot of highly specialized terms that you worry will not be familiar to your reader, consider including a glossary. Here, alphabetize the terms and include a brief description or definition.
Read more about glossaries
The introduction serves to set up your dissertation’s topic, purpose, and relevance. It tells the reader what to expect in the rest of your dissertation. The introduction should:
- Establish your research topic , giving the background information needed to contextualize your work
- Narrow down the focus and define the scope of your research
- Discuss the state of existing research on the topic, showing your work’s relevance to a broader problem or debate
- Clearly state your research questions and objectives
- Outline the flow of the rest of your work
Everything in the introduction should be clear, engaging, and relevant. By the end, the reader should understand the what, why, and how of your research.
Read more about introductions
A formative part of your research is your literature review . This helps you gain a thorough understanding of the academic work that already exists on your topic.
Literature reviews encompass:
- Finding relevant sources (e.g., books and journal articles)
- Assessing the credibility of your sources
- Critically analyzing and evaluating each source
- Drawing connections between them (e.g., themes, patterns, conflicts, or gaps) to strengthen your overall point
A literature review is not merely a summary of existing sources. Your literature review should have a coherent structure and argument that leads to a clear justification for your own research. It may aim to:
- Address a gap in the literature or build on existing knowledge
- Take a new theoretical or methodological approach to your topic
- Propose a solution to an unresolved problem or advance one side of a theoretical debate
Read more about literature reviews
Theoretical framework
Your literature review can often form the basis for your theoretical framework. Here, you define and analyze the key theories, concepts, and models that frame your research.
Read more about theoretical frameworks
Your methodology chapter describes how you conducted your research, allowing your reader to critically assess its credibility. Your methodology section should accurately report what you did, as well as convince your reader that this was the best way to answer your research question.
A methodology section should generally include:
- The overall research approach ( quantitative vs. qualitative ) and research methods (e.g., a longitudinal study )
- Your data collection methods (e.g., interviews or a controlled experiment )
- Details of where, when, and with whom the research took place
- Any tools and materials you used (e.g., computer programs, lab equipment)
- Your data analysis methods (e.g., statistical analysis , discourse analysis )
- An evaluation or justification of your methods
Read more about methodology sections
Your results section should highlight what your methodology discovered. You can structure this section around sub-questions, hypotheses , or themes, but avoid including any subjective or speculative interpretation here.
Your results section should:
- Concisely state each relevant result together with relevant descriptive statistics (e.g., mean , standard deviation ) and inferential statistics (e.g., test statistics , p values )
- Briefly state how the result relates to the question or whether the hypothesis was supported
- Report all results that are relevant to your research questions , including any that did not meet your expectations.
Additional data (including raw numbers, full questionnaires, or interview transcripts) can be included as an appendix. You can include tables and figures, but only if they help the reader better understand your results. Read more about results sections
Your discussion section is your opportunity to explore the meaning and implications of your results in relation to your research question. Here, interpret your results in detail, discussing whether they met your expectations and how well they fit with the framework that you built in earlier chapters. Refer back to relevant source material to show how your results fit within existing research in your field.
Some guiding questions include:
- What do your results mean?
- Why do your results matter?
- What limitations do the results have?
If any of the results were unexpected, offer explanations for why this might be. It’s a good idea to consider alternative interpretations of your data.
Read more about discussion sections
Your dissertation’s conclusion should concisely answer your main research question, leaving your reader with a clear understanding of your central argument and emphasizing what your research has contributed to the field.
In some disciplines, the conclusion is just a short section preceding the discussion section, but in other contexts, it is the final chapter of your work. Here, you wrap up your dissertation with a final reflection on what you found, with recommendations for future research and concluding remarks.
It’s important to leave the reader with a clear impression of why your research matters. What have you added to what was already known? Why is your research necessary for the future of your field?
Read more about conclusions
It is crucial to include a reference list or list of works cited with the full details of all the sources that you used, in order to avoid plagiarism. Be sure to choose one citation style and follow it consistently throughout your dissertation. Each style has strict and specific formatting requirements.
Common styles include MLA , Chicago , and APA , but which style you use is often set by your department or your field.
Create APA citations Create MLA citations
Your dissertation should contain only essential information that directly contributes to answering your research question. Documents such as interview transcripts or survey questions can be added as appendices, rather than adding them to the main body.
Read more about appendices
Making sure that all of your sections are in the right place is only the first step to a well-written dissertation. Don’t forget to leave plenty of time for editing and proofreading, as grammar mistakes and sloppy spelling errors can really negatively impact your work.
Dissertations can take up to five years to write, so you will definitely want to make sure that everything is perfect before submitting. You may want to consider using a professional dissertation editing service , AI proofreader or grammar checker to make sure your final project is perfect prior to submitting.
After your written dissertation is approved, your committee will schedule a defense. Similarly to defending your prospectus, dissertation defenses are oral presentations of your work. You’ll present your dissertation, and your committee will ask you questions. Many departments allow family members, friends, and other people who are interested to join as well.
After your defense, your committee will meet, and then inform you whether you have passed. Keep in mind that defenses are usually just a formality; most committees will have resolved any serious issues with your work with you far prior to your defense, giving you ample time to fix any problems.
As you write your dissertation, you can use this simple checklist to make sure you’ve included all the essentials.
Checklist: Dissertation
My title page includes all information required by my university.
I have included acknowledgements thanking those who helped me.
My abstract provides a concise summary of the dissertation, giving the reader a clear idea of my key results or arguments.
I have created a table of contents to help the reader navigate my dissertation. It includes all chapter titles, but excludes the title page, acknowledgements, and abstract.
My introduction leads into my topic in an engaging way and shows the relevance of my research.
My introduction clearly defines the focus of my research, stating my research questions and research objectives .
My introduction includes an overview of the dissertation’s structure (reading guide).
I have conducted a literature review in which I (1) critically engage with sources, evaluating the strengths and weaknesses of existing research, (2) discuss patterns, themes, and debates in the literature, and (3) address a gap or show how my research contributes to existing research.
I have clearly outlined the theoretical framework of my research, explaining the theories and models that support my approach.
I have thoroughly described my methodology , explaining how I collected data and analyzed data.
I have concisely and objectively reported all relevant results .
I have (1) evaluated and interpreted the meaning of the results and (2) acknowledged any important limitations of the results in my discussion .
I have clearly stated the answer to my main research question in the conclusion .
I have clearly explained the implications of my conclusion, emphasizing what new insight my research has contributed.
I have provided relevant recommendations for further research or practice.
If relevant, I have included appendices with supplemental information.
I have included an in-text citation every time I use words, ideas, or information from a source.
I have listed every source in a reference list at the end of my dissertation.
I have consistently followed the rules of my chosen citation style .
I have followed all formatting guidelines provided by my university.
Congratulations!
The end is in sight—your dissertation is nearly ready to submit! Make sure it's perfectly polished with the help of a Scribbr editor.
If you’re an educator, feel free to download and adapt these slides to teach your students about structuring a dissertation.
Open Google Slides Download PowerPoint
Is this article helpful?
Other students also liked.
- How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates
- Dissertation Table of Contents in Word | Instructions & Examples
- How to Choose a Dissertation Topic | 8 Steps to Follow
More interesting articles
- Checklist: Writing a dissertation
- Dissertation & Thesis Outline | Example & Free Templates
- Dissertation Binding and Printing | Options, Tips, & Comparison
- Example of a dissertation abstract
- Figure and Table Lists | Word Instructions, Template & Examples
- How to Write a Discussion Section | Tips & Examples
- How to Write a Dissertation or Thesis Proposal
- How to Write a Results Section | Tips & Examples
- How to Write a Thesis or Dissertation Conclusion
- How to Write a Thesis or Dissertation Introduction
- How to Write an Abstract | Steps & Examples
- How to Write Recommendations in Research | Examples & Tips
- List of Abbreviations | Example, Template & Best Practices
- Operationalization | A Guide with Examples, Pros & Cons
- Prize-Winning Thesis and Dissertation Examples
- Purpose and structure of an advisory report
- Relevance of Your Dissertation Topic | Criteria & Tips
- Research Paper Appendix | Example & Templates
- Shorten your abstract or summary
- Theoretical Framework Example for a Thesis or Dissertation
- Thesis & Dissertation Acknowledgements | Tips & Examples
- Thesis & Dissertation Database Examples
- Thesis & Dissertation Title Page | Free Templates & Examples
- What is a Dissertation Preface? | Definition & Examples
- What is a Glossary? | Definition, Templates, & Examples
- What Is a Research Methodology? | Steps & Tips
- What Is a Theoretical Framework? | Guide to Organizing
- What Is a Thesis? | Ultimate Guide & Examples
What is your plagiarism score?

Dissertation Structure & Layout 101: How to structure your dissertation, thesis or research project.
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) Reviewed By: David Phair (PhD) | July 2019
So, you’ve got a decent understanding of what a dissertation is , you’ve chosen your topic and hopefully you’ve received approval for your research proposal . Awesome! Now its time to start the actual dissertation or thesis writing journey.
To craft a high-quality document, the very first thing you need to understand is dissertation structure . In this post, we’ll walk you through the generic dissertation structure and layout, step by step. We’ll start with the big picture, and then zoom into each chapter to briefly discuss the core contents. If you’re just starting out on your research journey, you should start with this post, which covers the big-picture process of how to write a dissertation or thesis .

*The Caveat *
In this post, we’ll be discussing a traditional dissertation/thesis structure and layout, which is generally used for social science research across universities, whether in the US, UK, Europe or Australia. However, some universities may have small variations on this structure (extra chapters, merged chapters, slightly different ordering, etc).
So, always check with your university if they have a prescribed structure or layout that they expect you to work with. If not, it’s safe to assume the structure we’ll discuss here is suitable. And even if they do have a prescribed structure, you’ll still get value from this post as we’ll explain the core contents of each section.
Overview: S tructuring a dissertation or thesis
- Acknowledgements page
- Abstract (or executive summary)
- Table of contents , list of figures and tables
- Chapter 1: Introduction
- Chapter 2: Literature review
- Chapter 3: Methodology
- Chapter 4: Results
- Chapter 5: Discussion
- Chapter 6: Conclusion
- Reference list
As I mentioned, some universities will have slight variations on this structure. For example, they want an additional “personal reflection chapter”, or they might prefer the results and discussion chapter to be merged into one. Regardless, the overarching flow will always be the same, as this flow reflects the research process , which we discussed here – i.e.:
- The introduction chapter presents the core research question and aims .
- The literature review chapter assesses what the current research says about this question.
- The methodology, results and discussion chapters go about undertaking new research about this question.
- The conclusion chapter (attempts to) answer the core research question .
In other words, the dissertation structure and layout reflect the research process of asking a well-defined question(s), investigating, and then answering the question – see below.

To restate that – the structure and layout of a dissertation reflect the flow of the overall research process . This is essential to understand, as each chapter will make a lot more sense if you “get” this concept. If you’re not familiar with the research process, read this post before going further.
Right. Now that we’ve covered the big picture, let’s dive a little deeper into the details of each section and chapter. Oh and by the way, you can also grab our free dissertation/thesis template here to help speed things up.
The title page of your dissertation is the very first impression the marker will get of your work, so it pays to invest some time thinking about your title. But what makes for a good title? A strong title needs to be 3 things:
- Succinct (not overly lengthy or verbose)
- Specific (not vague or ambiguous)
- Representative of the research you’re undertaking (clearly linked to your research questions)
Typically, a good title includes mention of the following:
- The broader area of the research (i.e. the overarching topic)
- The specific focus of your research (i.e. your specific context)
- Indication of research design (e.g. quantitative , qualitative , or mixed methods ).
For example:
A quantitative investigation [research design] into the antecedents of organisational trust [broader area] in the UK retail forex trading market [specific context/area of focus].
Again, some universities may have specific requirements regarding the format and structure of the title, so it’s worth double-checking expectations with your institution (if there’s no mention in the brief or study material).

Acknowledgements
This page provides you with an opportunity to say thank you to those who helped you along your research journey. Generally, it’s optional (and won’t count towards your marks), but it is academic best practice to include this.
So, who do you say thanks to? Well, there’s no prescribed requirements, but it’s common to mention the following people:
- Your dissertation supervisor or committee.
- Any professors, lecturers or academics that helped you understand the topic or methodologies.
- Any tutors, mentors or advisors.
- Your family and friends, especially spouse (for adult learners studying part-time).
There’s no need for lengthy rambling. Just state who you’re thankful to and for what (e.g. thank you to my supervisor, John Doe, for his endless patience and attentiveness) – be sincere. In terms of length, you should keep this to a page or less.
Abstract or executive summary
The dissertation abstract (or executive summary for some degrees) serves to provide the first-time reader (and marker or moderator) with a big-picture view of your research project. It should give them an understanding of the key insights and findings from the research, without them needing to read the rest of the report – in other words, it should be able to stand alone .
For it to stand alone, your abstract should cover the following key points (at a minimum):
- Your research questions and aims – what key question(s) did your research aim to answer?
- Your methodology – how did you go about investigating the topic and finding answers to your research question(s)?
- Your findings – following your own research, what did do you discover?
- Your conclusions – based on your findings, what conclusions did you draw? What answers did you find to your research question(s)?
So, in much the same way the dissertation structure mimics the research process, your abstract or executive summary should reflect the research process, from the initial stage of asking the original question to the final stage of answering that question.
In practical terms, it’s a good idea to write this section up last , once all your core chapters are complete. Otherwise, you’ll end up writing and rewriting this section multiple times (just wasting time). For a step by step guide on how to write a strong executive summary, check out this post .
Need a helping hand?
Table of contents
This section is straightforward. You’ll typically present your table of contents (TOC) first, followed by the two lists – figures and tables. I recommend that you use Microsoft Word’s automatic table of contents generator to generate your TOC. If you’re not familiar with this functionality, the video below explains it simply:
If you find that your table of contents is overly lengthy, consider removing one level of depth. Oftentimes, this can be done without detracting from the usefulness of the TOC.
Right, now that the “admin” sections are out of the way, its time to move on to your core chapters. These chapters are the heart of your dissertation and are where you’ll earn the marks. The first chapter is the introduction chapter – as you would expect, this is the time to introduce your research…
It’s important to understand that even though you’ve provided an overview of your research in your abstract, your introduction needs to be written as if the reader has not read that (remember, the abstract is essentially a standalone document). So, your introduction chapter needs to start from the very beginning, and should address the following questions:
- What will you be investigating (in plain-language, big picture-level)?
- Why is that worth investigating? How is it important to academia or business? How is it sufficiently original?
- What are your research aims and research question(s)? Note that the research questions can sometimes be presented at the end of the literature review (next chapter).
- What is the scope of your study? In other words, what will and won’t you cover ?
- How will you approach your research? In other words, what methodology will you adopt?
- How will you structure your dissertation? What are the core chapters and what will you do in each of them?
These are just the bare basic requirements for your intro chapter. Some universities will want additional bells and whistles in the intro chapter, so be sure to carefully read your brief or consult your research supervisor.
If done right, your introduction chapter will set a clear direction for the rest of your dissertation. Specifically, it will make it clear to the reader (and marker) exactly what you’ll be investigating, why that’s important, and how you’ll be going about the investigation. Conversely, if your introduction chapter leaves a first-time reader wondering what exactly you’ll be researching, you’ve still got some work to do.
Now that you’ve set a clear direction with your introduction chapter, the next step is the literature review . In this section, you will analyse the existing research (typically academic journal articles and high-quality industry publications), with a view to understanding the following questions:
- What does the literature currently say about the topic you’re investigating?
- Is the literature lacking or well established? Is it divided or in disagreement?
- How does your research fit into the bigger picture?
- How does your research contribute something original?
- How does the methodology of previous studies help you develop your own?
Depending on the nature of your study, you may also present a conceptual framework towards the end of your literature review, which you will then test in your actual research.
Again, some universities will want you to focus on some of these areas more than others, some will have additional or fewer requirements, and so on. Therefore, as always, its important to review your brief and/or discuss with your supervisor, so that you know exactly what’s expected of your literature review chapter.

Now that you’ve investigated the current state of knowledge in your literature review chapter and are familiar with the existing key theories, models and frameworks, its time to design your own research. Enter the methodology chapter – the most “science-ey” of the chapters…
In this chapter, you need to address two critical questions:
- Exactly HOW will you carry out your research (i.e. what is your intended research design)?
- Exactly WHY have you chosen to do things this way (i.e. how do you justify your design)?
Remember, the dissertation part of your degree is first and foremost about developing and demonstrating research skills . Therefore, the markers want to see that you know which methods to use, can clearly articulate why you’ve chosen then, and know how to deploy them effectively.
Importantly, this chapter requires detail – don’t hold back on the specifics. State exactly what you’ll be doing, with who, when, for how long, etc. Moreover, for every design choice you make, make sure you justify it.
In practice, you will likely end up coming back to this chapter once you’ve undertaken all your data collection and analysis, and revise it based on changes you made during the analysis phase. This is perfectly fine. Its natural for you to add an additional analysis technique, scrap an old one, etc based on where your data lead you. Of course, I’m talking about small changes here – not a fundamental switch from qualitative to quantitative, which will likely send your supervisor in a spin!
You’ve now collected your data and undertaken your analysis, whether qualitative, quantitative or mixed methods. In this chapter, you’ll present the raw results of your analysis . For example, in the case of a quant study, you’ll present the demographic data, descriptive statistics, inferential statistics , etc.
Typically, Chapter 4 is simply a presentation and description of the data, not a discussion of the meaning of the data. In other words, it’s descriptive, rather than analytical – the meaning is discussed in Chapter 5. However, some universities will want you to combine chapters 4 and 5, so that you both present and interpret the meaning of the data at the same time. Check with your institution what their preference is.
Now that you’ve presented the data analysis results, its time to interpret and analyse them. In other words, its time to discuss what they mean, especially in relation to your research question(s).
What you discuss here will depend largely on your chosen methodology. For example, if you’ve gone the quantitative route, you might discuss the relationships between variables . If you’ve gone the qualitative route, you might discuss key themes and the meanings thereof. It all depends on what your research design choices were.
Most importantly, you need to discuss your results in relation to your research questions and aims, as well as the existing literature. What do the results tell you about your research questions? Are they aligned with the existing research or at odds? If so, why might this be? Dig deep into your findings and explain what the findings suggest, in plain English.
The final chapter – you’ve made it! Now that you’ve discussed your interpretation of the results, its time to bring it back to the beginning with the conclusion chapter . In other words, its time to (attempt to) answer your original research question s (from way back in chapter 1). Clearly state what your conclusions are in terms of your research questions. This might feel a bit repetitive, as you would have touched on this in the previous chapter, but its important to bring the discussion full circle and explicitly state your answer(s) to the research question(s).

Next, you’ll typically discuss the implications of your findings . In other words, you’ve answered your research questions – but what does this mean for the real world (or even for academia)? What should now be done differently, given the new insight you’ve generated?
Lastly, you should discuss the limitations of your research, as well as what this means for future research in the area. No study is perfect, especially not a Masters-level. Discuss the shortcomings of your research. Perhaps your methodology was limited, perhaps your sample size was small or not representative, etc, etc. Don’t be afraid to critique your work – the markers want to see that you can identify the limitations of your work. This is a strength, not a weakness. Be brutal!
This marks the end of your core chapters – woohoo! From here on out, it’s pretty smooth sailing.
The reference list is straightforward. It should contain a list of all resources cited in your dissertation, in the required format, e.g. APA , Harvard, etc.
It’s essential that you use reference management software for your dissertation. Do NOT try handle your referencing manually – its far too error prone. On a reference list of multiple pages, you’re going to make mistake. To this end, I suggest considering either Mendeley or Zotero. Both are free and provide a very straightforward interface to ensure that your referencing is 100% on point. I’ve included a simple how-to video for the Mendeley software (my personal favourite) below:
Some universities may ask you to include a bibliography, as opposed to a reference list. These two things are not the same . A bibliography is similar to a reference list, except that it also includes resources which informed your thinking but were not directly cited in your dissertation. So, double-check your brief and make sure you use the right one.
The very last piece of the puzzle is the appendix or set of appendices. This is where you’ll include any supporting data and evidence. Importantly, supporting is the keyword here.
Your appendices should provide additional “nice to know”, depth-adding information, which is not critical to the core analysis. Appendices should not be used as a way to cut down word count (see this post which covers how to reduce word count ). In other words, don’t place content that is critical to the core analysis here, just to save word count. You will not earn marks on any content in the appendices, so don’t try to play the system!
Time to recap…
And there you have it – the traditional dissertation structure and layout, from A-Z. To recap, the core structure for a dissertation or thesis is (typically) as follows:
- Acknowledgments page
Most importantly, the core chapters should reflect the research process (asking, investigating and answering your research question). Moreover, the research question(s) should form the golden thread throughout your dissertation structure. Everything should revolve around the research questions, and as you’ve seen, they should form both the start point (i.e. introduction chapter) and the endpoint (i.e. conclusion chapter).
I hope this post has provided you with clarity about the traditional dissertation/thesis structure and layout. If you have any questions or comments, please leave a comment below, or feel free to get in touch with us. Also, be sure to check out the rest of the Grad Coach Blog .

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
36 Comments
many thanks i found it very useful
Glad to hear that, Arun. Good luck writing your dissertation.
Such clear practical logical advice. I very much needed to read this to keep me focused in stead of fretting.. Perfect now ready to start my research!
what about scientific fields like computer or engineering thesis what is the difference in the structure? thank you very much
Thanks so much this helped me a lot!
Very helpful and accessible. What I like most is how practical the advice is along with helpful tools/ links.
Thanks Ade!
Thank you so much sir.. It was really helpful..
You’re welcome!
Hi! How many words maximum should contain the abstract?
Thank you so much 😊 Find this at the right moment
You’re most welcome. Good luck with your dissertation.
best ever benefit i got on right time thank you
Many times Clarity and vision of destination of dissertation is what makes the difference between good ,average and great researchers the same way a great automobile driver is fast with clarity of address and Clear weather conditions .
I guess Great researcher = great ideas + knowledge + great and fast data collection and modeling + great writing + high clarity on all these
You have given immense clarity from start to end.
Morning. Where will I write the definitions of what I’m referring to in my report?
Thank you so much Derek, I was almost lost! Thanks a tonnnn! Have a great day!
Thanks ! so concise and valuable
This was very helpful. Clear and concise. I know exactly what to do now.
Thank you for allowing me to go through briefly. I hope to find time to continue.
Really useful to me. Thanks a thousand times
Very interesting! It will definitely set me and many more for success. highly recommended.
Thank you soo much sir, for the opportunity to express my skills
Usefull, thanks a lot. Really clear
Very nice and easy to understand. Thank you .
That was incredibly useful. Thanks Grad Coach Crew!
My stress level just dropped at least 15 points after watching this. Just starting my thesis for my grad program and I feel a lot more capable now! Thanks for such a clear and helpful video, Emma and the GradCoach team!
Do we need to mention the number of words the dissertation contains in the main document?
It depends on your university’s requirements, so it would be best to check with them 🙂
Such a helpful post to help me get started with structuring my masters dissertation, thank you!
Great video; I appreciate that helpful information
It is so necessary or avital course
This blog is very informative for my research. Thank you
Doctoral students are required to fill out the National Research Council’s Survey of Earned Doctorates
wow this is an amazing gain in my life
This is so good
How can i arrange my specific objectives in my dissertation?
Trackbacks/Pingbacks
- What Is A Literature Review (In A Dissertation Or Thesis) - Grad Coach - […] is to write the actual literature review chapter (this is usually the second chapter in a typical dissertation or…
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly

- Subject Guides
Academic writing: a practical guide
Dissertations.
- Academic writing
- The writing process
- Academic writing style
- Structure & cohesion
- Criticality in academic writing
- Working with evidence
- Referencing
- Assessment & feedback
- Reflective writing
- Examination writing
- Academic posters
- Feedback on Structure and Organisation
- Feedback on Argument, Analysis, and Critical Thinking
- Feedback on Writing Style and Clarity
- Feedback on Referencing and Research
- Feedback on Presentation and Proofreading
Dissertations are a part of many degree programmes, completed in the final year of undergraduate studies or the final months of a taught masters-level degree.
Introduction to dissertations
What is a dissertation.
A dissertation is usually a long-term project to produce a long-form piece of writing; think of it a little like an extended, structured assignment. In some subjects (typically the sciences), it might be called a project instead.
Work on an undergraduate dissertation is often spread out over the final year. For a masters dissertation, you'll start thinking about it early in your course and work on it throughout the year.
You might carry out your own original research, or base your dissertation on existing research literature or data sources - there are many possibilities.

What's different about a dissertation?
The main thing that sets a dissertation apart from your previous work is that it's an almost entirely independent project. You'll have some support from a supervisor, but you will spend a lot more time working on your own.
You'll also be working on your own topic that's different to your coursemate; you'll all produce a dissertation, but on different topics and, potentially, in very different ways.
Dissertations are also longer than a regular assignment, both in word count and the time that they take to complete. You'll usually have most of an academic year to work on one, and be required to produce thousands of words; that might seem like a lot, but both time and word count will disappear very quickly once you get started!
Find out more:

Key dissertation tools
Digital tools.
There are lots of tools, software and apps that can help you get through the dissertation process. Before you start, make sure you collect the key tools ready to:
- use your time efficiently
- organise yourself and your materials
- manage your writing
- be less stressed
Here's an overview of some useful tools:
Digital tools for your dissertation [Google Slides]
Setting up your document
Formatting and how you set up your document is also very important for a long piece of work like a dissertation, research project or thesis. Find tips and advice on our text processing guide:

University of York past Undergraduate and Masters dissertations
If you are a University of York student, you can access a selection of digitised undergraduate dissertations for certain subjects:
- History
- History of Art
- Social Policy and Social Work
The Library also has digitised Masters dissertations for the following subjects:
- Archaeology
- Centre for Eighteenth-Century Studies
- Centre for Medieval Studies
- Centre for Renaissance and Early Modern Studies
- Centre for Women's Studies
- English and Related Literature
- Health Sciences
- History of Art
- Hull York Medical School
- Language and Linguistic Science
- School for Business and Society
- School of Social and Political Sciences
Dissertation top tips
Many dissertations are structured into four key sections:
- introduction & literature review
There are many different types of dissertation, which don't all use this structure, so make sure you check your dissertation guidance. However, elements of these sections are common in all dissertation types.
Dissertations that are an extended literature review do not involve data collection, thus do not have a methods or result section. Instead they have chapters that explore concepts/theories and result in a conclusion section. Check your dissertation module handbook and all information given to see what your dissertation involves.
Introduction & literature review
The Introduction and Literature Review give the context for your dissertation:
- What topic did you investigate?
- What do we already know about this topic?
- What are your research questions and hypotheses?
Sometimes these are two separate sections, and sometimes the Literature Review is integrated into the Introduction. Check your guidelines to find out what you need to do.
Literature Review Top Tips [YouTube] | Literature Review Top Tips transcript [Google Doc]

The Method section tells the reader what you did and why.
- Include enough detail so that someone else could replicate your study.
- Visual elements can help present your method clearly. For example, summarise participant demographic data in a table or visualise the procedure in a diagram.
- Show critical analysis by justifying your choices. For example, why is your test/questionnaire/equipment appropriate for this study?
- If your study requires ethical approval, include these details in this section.
Methodology Top Tips [YouTube] | Methodology Top Tips transcript [Google Doc]
More resources to help you plan and write the methodology:
The Results tells us what you found out .
It's an objective presentation of your research findings. Don’t explain the results in detail here - you’ll do that in the discussion section.
Results Top Tips [YouTube] | Results Top Tips transcript [Google Doc]

The Discussion is where you explain and interpret your results - what do your findings mean?
This section involves a lot of critical analysis. You're not just presenting your findings, but putting them together with findings from other research to build your argument about what the findings mean.
Discussion Top Tips [YouTube] | Discussion Top Tips transcript [Google Doc]
Conclusions are a part of many dissertations and/or research projects. Check your module information to see if you are required to write one. Some dissertations/projects have concluding remarks in their discussion section. See the slides below for more information on writing conclusions in dissertations.
Conclusions in dissertations [Google Slides]
The abstract is a short summary of the whole dissertation that goes at the start of the document. It gives an overview of your research and helps readers decide if it’s relevant to their needs.
Even though it appears at the start of the document, write the abstract last. It summarises the whole dissertation, so you need to finish the main body before you can summarise it in the abstract.
Usually the abstract follows a very similar structure to the dissertation, with one or two sentences each to show the aims, methods, key results and conclusions drawn. Some subjects use headings within the abstract. Even if you don’t use these in your final abstract, headings can help you to plan a clear structure.
Abstract Top Tips [YouTube] | Abstract Top Tips transcript [Google Doc]
Watch all of our Dissertation Top Tips videos in one handy playlist:
Research reports, that are often found in science subjects, follow the same structure, so the tips in this tutorial also apply to dissertations:
Other support for dissertation writing
Online resources.
The general writing pages of this site offer guidance that can be applied to all types of writing, including dissertations. Also check your department guidance and VLE sites for tailored resources.
Other useful resources for dissertation writing:

Appointments and workshops
There is a lot of support available in departments for dissertation production, which includes your dissertation supervisor, academic supervisor and, when appropriate, staff teaching in the research methods modules.
You can also access central writing and skills support:

- << Previous: Reports
- Next: Reflective writing >>
- Last Updated: Jul 31, 2024 1:38 PM
- URL: https://subjectguides.york.ac.uk/academic-writing

- Harvard Library
- Research Guides
- Harvard Graduate School of Design - Frances Loeb Library
Write and Cite
- Theses and Dissertations
- Academic Integrity
- Using Sources and AI
- Academic Writing
- From Research to Writing
- GSD Writing Services
- Grants and Fellowships
- Reading, Notetaking, and Time Management
What is a thesis?
What is a dissertation, getting started, staying on track.
A thesis is a long-term project that you work on over the course of a semester or a year. Theses have a very wide variety of styles and content, so we encourage you to look at prior examples and work closely with faculty to develop yours.
Before you begin, make sure that you are familiar with the dissertation genre—what it is for and what it looks like.
Generally speaking, a dissertation’s purpose is to prove that you have the expertise necessary to fulfill your doctoral-degree requirements by showing depth of knowledge and independent thinking.
The form of a dissertation may vary by discipline. Be sure to follow the specific guidelines of your department.
- PhD This site directs candidates to the GSAS website about dissertations , with links to checklists, planning, formatting, acknowledgments, submission, and publishing options. There is also a link to guidelines for the prospectus . Consult with your committee chair about specific requirements and standards for your dissertation.
- DDES This document covers planning, patent filing, submission guidelines, publishing options, formatting guidelines, sample pages, citation guidelines, and a list of common errors to avoid. There is also a link to guidelines for the prospectus .
- Scholarly Pursuits (GSAS) This searchable booklet from Harvard GSAS is a comprehensive guide to writing dissertations, dissertation-fellowship applications, academic journal articles, and academic job documents.
Finding an original topic can be a daunting and overwhelming task. These key concepts can help you focus and save time.
Finding a topic for your thesis or dissertation should start with a research question that excites or at least interests you. A rigorous, engaging, and original project will require continuous curiosity about your topic, about your own thoughts on the topic, and about what other scholars have said on your topic. Avoid getting boxed in by thinking you know what you want to say from the beginning; let your research and your writing evolve as you explore and fine-tune your focus through constant questioning and exploration.
Get a sense of the broader picture before you narrow your focus and attempt to frame an argument. Read, skim, and otherwise familiarize yourself with what other scholars have done in areas related to your proposed topic. Briefly explore topics tangentially related to yours to broaden your perspective and increase your chance of finding a unique angle to pursue.
Critical Reading
Critical reading is the opposite of passive reading. Instead of merely reading for information to absorb, critical reading also involves careful, sustained thinking about what you are reading. This process may include analyzing the author’s motives and assumptions, asking what might be left out of the discussion, considering what you agree with or disagree with in the author’s statements and why you agree or disagree, and exploring connections or contradictions between scholarly arguments. Here is a resource to help hone your critical-reading skills:
http://writing.umn.edu/sws/assets/pdf/quicktips/criticalread.pdf
Conversation
Your thesis or dissertation will incorporate some ideas from other scholars whose work you researched. By reading critically and following your curiosity, you will develop your own ideas and claims, and these contributions are the core of your project. You will also acknowledge the work of scholars who came before you, and you must accurately and fairly attribute this work and define your place within the larger discussion. Make sure that you know how to quote, summarize, paraphrase , integrate , and cite secondary sources to avoid plagiarism and to show the depth and breadth of your knowledge.
A thesis is a long-term, large project that involves both research and writing; it is easy to lose focus, motivation, and momentum. Here are suggestions for achieving the result you want in the time you have.
The dissertation is probably the largest project you have undertaken, and a lot of the work is self-directed. The project can feel daunting or even overwhelming unless you break it down into manageable pieces and create a timeline for completing each smaller task. Be realistic but also challenge yourself, and be forgiving of yourself if you miss a self-imposed deadline here and there.
Your program will also have specific deadlines for different requirements, including establishing a committee, submitting a prospectus, completing the dissertation, defending the dissertation, and submitting your work. Consult your department’s website for these dates and incorporate them into the timeline for your work.
Accountability
Sometimes self-imposed deadlines do not feel urgent unless there is accountability to someone beyond yourself. To increase your motivation to complete tasks on schedule, set dates with your committee chair to submit pre-determined pieces of a chapter. You can also arrange with a fellow doctoral student to check on each other’s progress. Research and writing can be lonely, so it is also nice to share that journey with someone and support each other through the process.
Common Pitfalls
The most common challenges for students writing a dissertation are writer’s block, information-overload, and the compulsion to keep researching forever.
There are many strategies for avoiding writer’s block, such as freewriting, outlining, taking a walk, starting in the middle, and creating an ideal work environment for your particular learning style. Pay attention to what helps you and try different things until you find what works.
Efficient researching techniques are essential to avoiding information-overload. Here are a couple of resources about strategies for finding sources and quickly obtaining essential information from them.
https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/subject_specific_writing/writing_in_literature/writing_in_literature_detailed_discussion/reading_criticism.html
https://students.dartmouth.edu/academic-skills/learning-resources/learning-strategies/reading-techniques
Finally, remember that there is always more to learn and your dissertation cannot incorporate everything. Follow your curiosity but also set limits on the scope of your work. It helps to create a folder entitled “future projects” for topics and sources that interest you but that do not fit neatly into the dissertation. Also remember that future scholars will build off of your work, so leave something for them to do.
Browsing through theses and dissertations of the past can help to get a sense of your options and gain inspiration but be careful to use current guidelines and refer to your committee instead of relying on these examples for form or formatting.
DASH Digital Access to Scholarship at Harvard.
HOLLIS Harvard Library’s catalog provides access to ProQuest Dissertations & Theses Global .
MIT Architecture has a list of their graduates’ dissertations and theses.
Rhode Island School of Design has a list of their graduates’ dissertations and theses.
University of South Florida has a list of their graduates’ dissertations and theses.
Harvard GSD has a list of projects, including theses and professors’ research.
- << Previous: Reading, Notetaking, and Time Management
- Next: Publishing >>
- Last Updated: Jul 26, 2024 9:44 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.harvard.edu/gsd/write
Harvard University Digital Accessibility Policy
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
What Is a Dissertation? | 5 Essential Questions to Get Started
Published on 26 March 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on 5 May 2022.
A dissertation is a large research project undertaken at the end of a degree. It involves in-depth consideration of a problem or question chosen by the student. It is usually the largest (and final) piece of written work produced during a degree.
The length and structure of a dissertation vary widely depending on the level and field of study. However, there are some key questions that can help you understand the requirements and get started on your dissertation project.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
When and why do you have to write a dissertation, who will supervise your dissertation, what type of research will you do, how should your dissertation be structured, what formatting and referencing rules do you have to follow, frequently asked questions about dissertations.
A dissertation, sometimes called a thesis, comes at the end of an undergraduate or postgraduate degree. It is a larger project than the other essays you’ve written, requiring a higher word count and a greater depth of research.
You’ll generally work on your dissertation during the final year of your degree, over a longer period than you would take for a standard essay . For example, the dissertation might be your main focus for the last six months of your degree.
Why is the dissertation important?
The dissertation is a test of your capacity for independent research. You are given a lot of autonomy in writing your dissertation: you come up with your own ideas, conduct your own research, and write and structure the text by yourself.
This means that it is an important preparation for your future, whether you continue in academia or not: it teaches you to manage your own time, generate original ideas, and work independently.
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
During the planning and writing of your dissertation, you’ll work with a supervisor from your department. The supervisor’s job is to give you feedback and advice throughout the process.
The dissertation supervisor is often assigned by the department, but you might be allowed to indicate preferences or approach potential supervisors. If so, try to pick someone who is familiar with your chosen topic, whom you get along with on a personal level, and whose feedback you’ve found useful in the past.
How will your supervisor help you?
Your supervisor is there to guide you through the dissertation project, but you’re still working independently. They can give feedback on your ideas, but not come up with ideas for you.
You may need to take the initiative to request an initial meeting with your supervisor. Then you can plan out your future meetings and set reasonable deadlines for things like completion of data collection, a structure outline, a first chapter, a first draft, and so on.
Make sure to prepare in advance for your meetings. Formulate your ideas as fully as you can, and determine where exactly you’re having difficulties so you can ask your supervisor for specific advice.
Your approach to your dissertation will vary depending on your field of study. The first thing to consider is whether you will do empirical research , which involves collecting original data, or non-empirical research , which involves analysing sources.
Empirical dissertations (sciences)
An empirical dissertation focuses on collecting and analysing original data. You’ll usually write this type of dissertation if you are studying a subject in the sciences or social sciences.
- What are airline workers’ attitudes towards the challenges posed for their industry by climate change?
- How effective is cognitive behavioural therapy in treating depression in young adults?
- What are the short-term health effects of switching from smoking cigarettes to e-cigarettes?
There are many different empirical research methods you can use to answer these questions – for example, experiments , observations, surveys , and interviews.
When doing empirical research, you need to consider things like the variables you will investigate, the reliability and validity of your measurements, and your sampling method . The aim is to produce robust, reproducible scientific knowledge.
Non-empirical dissertations (arts and humanities)
A non-empirical dissertation works with existing research or other texts, presenting original analysis, critique and argumentation, but no original data. This approach is typical of arts and humanities subjects.
- What attitudes did commentators in the British press take towards the French Revolution in 1789–1792?
- How do the themes of gender and inheritance intersect in Shakespeare’s Macbeth ?
- How did Plato’s Republic and Thomas More’s Utopia influence nineteenth century utopian socialist thought?
The first steps in this type of dissertation are to decide on your topic and begin collecting your primary and secondary sources .
Primary sources are the direct objects of your research. They give you first-hand evidence about your subject. Examples of primary sources include novels, artworks and historical documents.
Secondary sources provide information that informs your analysis. They describe, interpret, or evaluate information from primary sources. For example, you might consider previous analyses of the novel or author you are working on, or theoretical texts that you plan to apply to your primary sources.
Dissertations are divided into chapters and sections. Empirical dissertations usually follow a standard structure, while non-empirical dissertations are more flexible.
Structure of an empirical dissertation
Empirical dissertations generally include these chapters:
- Introduction : An explanation of your topic and the research question(s) you want to answer.
- Literature review : A survey and evaluation of previous research on your topic.
- Methodology : An explanation of how you collected and analysed your data.
- Results : A brief description of what you found.
- Discussion : Interpretation of what these results reveal.
- Conclusion : Answers to your research question(s) and summary of what your findings contribute to knowledge in your field.
Sometimes the order or naming of chapters might be slightly different, but all of the above information must be included in order to produce thorough, valid scientific research.
Other dissertation structures
If your dissertation doesn’t involve data collection, your structure is more flexible. You can think of it like an extended essay – the text should be logically organised in a way that serves your argument:
- Introduction: An explanation of your topic and the question(s) you want to answer.
- Main body: The development of your analysis, usually divided into 2–4 chapters.
- Conclusion: Answers to your research question(s) and summary of what your analysis contributes to knowledge in your field.
The chapters of the main body can be organised around different themes, time periods, or texts. Below you can see some example structures for dissertations in different subjects.
- Political philosophy
This example, on the topic of the British press’s coverage of the French Revolution, shows how you might structure each chapter around a specific theme.

This example, on the topic of Plato’s and More’s influences on utopian socialist thought, shows a different approach to dividing the chapters by theme.

This example, a master’s dissertation on the topic of how writers respond to persecution, shows how you can also use section headings within each chapter. Each of the three chapters deals with a specific text, while the sections are organised thematically.

Like other academic texts, it’s important that your dissertation follows the formatting guidelines set out by your university. You can lose marks unnecessarily over mistakes, so it’s worth taking the time to get all these elements right.
Formatting guidelines concern things like:
- line spacing
- page numbers
- punctuation
- title pages
- presentation of tables and figures
If you’re unsure about the formatting requirements, check with your supervisor or department. You can lose marks unnecessarily over mistakes, so it’s worth taking the time to get all these elements right.
How will you reference your sources?
Referencing means properly listing the sources you cite and refer to in your dissertation, so that the reader can find them. This avoids plagiarism by acknowledging where you’ve used the work of others.
Keep track of everything you read as you prepare your dissertation. The key information to note down for a reference is:
- The publication date
- Page numbers for the parts you refer to (especially when using direct quotes)
Different referencing styles each have their own specific rules for how to reference. The most commonly used styles in UK universities are listed below.
| & | An author–date citation in brackets in the text… | …corresponding to an entry in the alphabetised reference list at the end. |
|---|---|---|
| A superscript or bracketed reference number in the text… | …corresponding to an entry in the numbered reference list at the end. | |
| A footnote in the text that gives full source information… | …and an alphabetised bibliography at the end listing all sources. |
You can use the free APA Reference Generator to automatically create and store your references.
APA Reference Generator
The words ‘ dissertation ’ and ‘thesis’ both refer to a large written research project undertaken to complete a degree, but they are used differently depending on the country:
- In the UK, you write a dissertation at the end of a bachelor’s or master’s degree, and you write a thesis to complete a PhD.
- In the US, it’s the other way around: you may write a thesis at the end of a bachelor’s or master’s degree, and you write a dissertation to complete a PhD.
The main difference is in terms of scale – a dissertation is usually much longer than the other essays you complete during your degree.
Another key difference is that you are given much more independence when working on a dissertation. You choose your own dissertation topic , and you have to conduct the research and write the dissertation yourself (with some assistance from your supervisor).
Dissertation word counts vary widely across different fields, institutions, and levels of education:
- An undergraduate dissertation is typically 8,000–15,000 words
- A master’s dissertation is typically 12,000–50,000 words
- A PhD thesis is typically book-length: 70,000–100,000 words
However, none of these are strict guidelines – your word count may be lower or higher than the numbers stated here. Always check the guidelines provided by your university to determine how long your own dissertation should be.
At the bachelor’s and master’s levels, the dissertation is usually the main focus of your final year. You might work on it (alongside other classes) for the entirety of the final year, or for the last six months. This includes formulating an idea, doing the research, and writing up.
A PhD thesis takes a longer time, as the thesis is the main focus of the degree. A PhD thesis might be being formulated and worked on for the whole four years of the degree program. The writing process alone can take around 18 months.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2022, May 05). What Is a Dissertation? | 5 Essential Questions to Get Started. Scribbr. Retrieved 30 July 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/what-is-a-dissertation/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, how to choose a dissertation topic | 8 steps to follow, how to write a dissertation proposal | a step-by-step guide, what is a literature review | guide, template, & examples.
)
How to Write a Dissertation
Published September 27, 2020. Updated May 4, 2022.
Dissertation Definition
A dissertation is a long work of original research.
Overview of a Dissertation
The dissertation is one of many requirements for a PhD. It is also one of the most demanding. The word “dissertation” comes from the Latin root word “dissertare,” which means “to debate.” The reference to a “debate” points to how students must “defend” their arguments before a committee of professors after writing a dissertation.
Students arrange dissertations differently depending on their discipline. Regardless, creating an outline beforehand ensures a well-structured paper.
A dissertation demonstrates that you are not simply another entry-level student. Rather, a dissertation shows you are a scholar meaningfully contributing new ideas and sound research to the academic community .
This page covers the following points:
Key Takeaways
What is a dissertation, what is the difference between a dissertation and an essay, why are dissertations important, planning your dissertation, writing your dissertation, additional tips for writing your dissertation, examples of good dissertations.
- PhD programs require students to write dissertations to complete the graduate program. Dissertations are long original research papers written by PhD candidates.
- Choose a dissertation topic you are passionate and knowledgeable about and that makes a meaningful contribution to scholarship in your subject.
- Writers structure dissertations differently depending on the discipline. Regardless, creating an outline beforehand ensures a well-structured paper.
- The main components of most dissertations include an introduction, a literature review or theoretical framework, research methods, results, discussion, conclusions, and references.
A dissertation is a long work of original research. Graduate students submit a dissertation to fulfill one of the requirements for a doctoral degree at most North American universities. Once admitted to a doctoral program, a PhD candidate must propose a topic for their dissertation. Candidates form a committee of faculty to oversee the project. They then choose a dissertation advisor who will work closely with them on each chapter.
The dissertation is one of many requirements for a PhD, and it’s one of the most demanding. The word “dissertation” comes from the Latin root word “dissertare,” which means “to debate.” This alludes to how students must “defend” their arguments before a committee of their professors after finishing the dissertation.
Worried about your writing? Submit your paper for a Chegg Writing essay check , or for an Expert Check proofreading . Both can help you find and fix potential writing issues.
Essays are typically shorter papers assigned by professors as part of a class. Undergraduate and graduate students often write essays in a similar style. However, graduate students pursuing a PhD typically write dissertations.
Dissertations focus on a topic you propose. Faculty qualified in your area of research must approve the dissertation topic. The approval process can be lengthy and complex, differing according to academic discipline and institution.
A dissertation demonstrates that you’re not simply another entry-level student. Rather, you are a scholar who is meaningfully contributing new ideas and sound research to the academic community.
A well-written dissertation is important for many reasons:
- Highlights your knowledge of a given subject and your ability to conduct rigorous, original research.
- Gives you the opportunity to show off your critical analysis skills.
- Introduces a new idea and opinion to the scholarly community.
Finally, a dissertation is important because it’s the only way to earn your doctoral (or “terminal”) degree. Without a dissertation under your belt, you’re considered “ABD” (all but dissertation). Approximately 50% of doctoral students complete their dissertation, though this percentage varies according to discipline .
The Initial Stages
One of the first steps is to find funding. Writing your dissertation is essentially a full-time job, so you need a source of income while you focus on this task. Try applying for grants, scholarships, and fellowships instead. Many universities offer internal funding opportunities for their graduate students.
Next, choose a topic for your dissertation. The best dissertations open up an entirely new line of thought, ideally leading to the creation of 3-4 other dissertations by future students.
Choose a topic that you have experience with. You should also choose a subject that you personally find interesting, as you’ll be spending countless hours on it.
Think about problems within your field and whether new lines of research can solve these problems. Aim to make a strong impact on your area of study. Provide evidence on topics lacking strong evidence.
If you’re not exactly sure which topic to choose, don’t worry. The first step is to create a general idea in your mind and begin your research. As you delve deeper into your research, you’ll start to narrow down your idea and hopefully discover an argument never made in your field.
Another important initial step is to form a committee of experts within your field of study. Your committee must accept your dissertation’s topic and agree to work with you throughout the approval process. Committee members may also provide you with a reading list related to your topic before you start writing your dissertation.
Finally, it’s important to choose a good advisor. Your advisor is the committee member who works with you most closely as you research and write your dissertation. Advisors guide you every step of the way and ensure you stay on track.
Don’t ignore the advice of your advisor and committee. Allow them to play a role in shaping your dissertation during these initial stages. You can benefit from their expertise.
Create an Outline
Creating an outline is another crucial first step when planning your dissertation. If you figure out the structure of your work beforehand, writing the main chapters becomes easier.
Be aware that not all dissertations are structured the same way. Different disciplines require different information (a dissertation for English vs. chemistry would be very different). Universities and schools within universities may also have their own requirements. Consult your advisor or school for their specific dissertation details.
Here are some main sections of a standard dissertation. Some are essential to every dissertation. (Again, note that your outline will vary depending on your program’s requirements.)
Acknowledgments
- Table of contents
- List of figures and tables (sometimes split into separate sections)
- List of abbreviations
Introduction
- Literature review or theoretical framework
- Research methods
Conclusion(s)
The general structure of a dissertation in the sciences or social sciences is as follows:
- Literature review
- Methodology
To further illustrate the structure above, here is a dissertation paper template .
Conducting Research
Consult your advisor before starting research. Advisors usually give you some tips about where to begin. A solid first step is to skim the titles of research papers related to your chosen topic and see where that takes you. Carefully review the reading list provided by your committee.
You will also need to collect data during the research phase. Make sure to carefully define the extent and limitations of your research before collecting data. If you’re too hasty, you risk collecting data that is irrelevant to your dissertation. Create a system that allows for easy and accurate storing of data. Don’t be afraid to speak to your advisor about the best methods for recording data.
As you research your topic, take plenty of notes and jot down any ideas that come to mind. Keep a notebook or laptop handy and refer back to these ideas while you write.
You’ll need to come up with a title for your dissertation. Choose something catchy and interesting—but also consider how easy your paper will be to find on Google or in academic databases. Your title page must adhere to strict formatting guidelines set forth by your institution. Requirements usually include your name, department, institution, and degree program. An ideal title should state the overall result of your research in fewer than eight words.
The acknowledgments page is optional, but it’s a great opportunity to thank anyone who helped you along the way. This might include certain professors, your advisor, or even family and friends.
Although the abstract usually comes first in the reading order of your dissertation, write this section last. The abstract is a short summary of your dissertation, usually between 150 and 300 words. The abstract contains a short summary of the following:
- Conclusions
Table of Contents
The first “official” page of your dissertation is the table of contents. Every section should be included in your table of contents, so readers can easily navigate the document.
List of Figures and Tables
Separate from the table of contents are the lists of tables and figures. This page is only necessary if you have included a multitude of figures, tables, and graphs in your dissertation.
List of Abbreviations
Including a list of abbreviations makes your dissertation easier to read. A list is especially helpful for readers who are unfamiliar with your field.
A glossary allows the reader to easily discover the definitions of specialized terms they may not be familiar with. List each term alphabetically and include a brief definition.
The introduction should lay out your topic and let the reader know what to expect throughout the dissertation. The introduction should accomplish the following:
- Describe your research topic
- Define the extent and limitations of your research
- Mention existing research on your topic and its impact
- Lay out your research objectives
- Let the reader know how the paper is structured
- Mention the “what,” “how,” and “why” of your topic
The main goal of the introduction is to “hook” the reader and get them interested. You can easily intimidate readers with overly complex language, so keep it simple to encourage them to keep reading.
Literature Review or Theoretical framework
The literature review or theoretical framework highlights research you’ve done to prepare for your dissertation. However, a literature review isn’t just a list of books and articles you read while researching. Instead, it focuses on the most relevant sources. You need to establish connections between different lines of research and evaluate the existing literature related to your topic.
If you discovered gaps in existing research, now’s the time to mention them. Always connect your research back to your topic or argument. How do these sources support your claims? Does the existing literature provide a foundation for your new ideas?
Research Methods
Research methods are all about how you conducted your research. The reader should be able to determine whether your research is reliable based on this section. Methods should include the following:
- The type of research you conducted
- How you collected data
- How you analyzed the data
- What materials, tools, and devices you used to conduct research
- Problems you encountered in your research
- A self-evaluation of your methods and whether they were reliable
When laying out results in this section, only include data relevant to your hypotheses, questions, or overall topic. Results often include graphs, tables, and charts. In some disciplines, the results section and the discussion section are combined.
The discussion section is one of the most important parts of your dissertation, as you’ll be exploring the implications of your results. How do the results relate to your topic? Were any of the results unexpected?
Instead of interpreting your results in one way, explore all the possible ways someone could draw conclusions from the data. In addition, highlight the limitations of your results.
The conclusion is a concise, clear answer to the original question posed in the introduction. Finalize your argument and leave the reader with a clear understanding of how the research has impacted your point of view.
The conclusion also highlights your contribution to existing knowledge within your field. How has your research impacted the subject you chose to explore? Why was this line of research important in the first place?
This section may also include recommendations, or “Recommendations” may also be its own section.
Also known as a “works cited” or bibliography, the reference list contains all cited sources. Make sure to closely follow your discipline’s citation style.
Only use relevant data and information in the main body of your dissertation. That being said, you need to include the data, tables, interviews, etc. in their entirety within the appendices section.
- Edit and proofread the dissertation
- Write in the correct tense and voice (different disciplines use different tenses)
- Use decisive language. You are arguing your point of view, so be confident and professional
- Cite your sources
- Eliminate passive voice and excessive adverbs and adjectives
- Get tons of feedback from others
- Stick to the formatting requirements
- Avoid plagiarism at all costs
Before you turn in that paper, don’t forget to cite your sources in APA format , MLA format , or a style of your choice.
Dissertation example from the liberal arts/humanities:
Albarran, Louis. “The Face of God at the End of the Road: The Sacramentality of Jack Kerouac in Lowell, America, and Mexico.” Electronic Thesis or Dissertation. University of Dayton, 2013. OhioLINK Electronic Theses and Dissertations Center. 10 Aug 2020.
Full Text: https://etd.ohiolink.edu/!etd.send_fileaccession=dayton1375235381&disposition=inline
Dissertation example from the social sciences:
Simon, L. S. (2011). From Negative Act to Negative Relationship: Understanding How Patterns of Abusive Supervision Emerge and Develop over Time. (Doctoral Dissertation). University of Florida. Retrieved from https://ufdc.ufl.edu/UFE0042895
https://ufdc.ufl.edu/UFE0042895/00001
There are numerous online resources for searching dissertation topics, titles, and examples. If you are interested in browsing these resources, most college or university libraries provide access to students to at least one or more of these databases.
In addition, you could try searching a free, open-sourced database, like these two:
- EBSCO Open Dissertations Project: https://biblioboard.com/opendissertations/
- Open Access Theses and Dissertations archive: https://oatd.org/
Example Dissertation Template
By Andy Block. Andy received his B.A. in English from the University of South Carolina and his M.A. in comparative literature from the University of New Mexico. After teaching ESL in Asia and Europe as well as public school in New York City, Andy taught writing at a community college for more than a decade before transitioning to a new career in EdTech.
Common Writing Assignments, Apps & Tests
- Analytical Essay
- AP synthesis Essay
- Argumentative Essay
- Book Report
- Compare and Contrast Essay
- Cause and Effect Essay
- College Admissions Essay
- Critical Analysis Essay
- Definition Essay
- Descriptive Essay
- Dissertation
- Explanatory Essay
- Expository Essay
- Informative Essay
- Narrative Essay
- Opinion Essay
- Personal Essay
- Persuasive Essay
- Reflective Essay
- Research Paper
- Rhetorical Analysis
- Scholarship Essay
- Short Essay
- Thesis Paper

What’s included with a Chegg Writing subscription
- Unlimited number of paper scans
- Plagiarism detection: Check against billions of sources
- Expert proofreading for papers on any subject
- Grammar scans for 200+ types of common errors
- Automatically create & save citations in 7,000+ styles
- Cancel subscription anytime, no obligation
- Resources Home 🏠
- Try SciSpace Copilot
- Search research papers
- Add Copilot Extension
- Try AI Detector
- Try Paraphraser
- Try Citation Generator
- April Papers
- June Papers
- July Papers

What is a thesis | A Complete Guide with Examples

Table of Contents
A thesis is a comprehensive academic paper based on your original research that presents new findings, arguments, and ideas of your study. It’s typically submitted at the end of your master’s degree or as a capstone of your bachelor’s degree.
However, writing a thesis can be laborious, especially for beginners. From the initial challenge of pinpointing a compelling research topic to organizing and presenting findings, the process is filled with potential pitfalls.
Therefore, to help you, this guide talks about what is a thesis. Additionally, it offers revelations and methodologies to transform it from an overwhelming task to a manageable and rewarding academic milestone.
What is a thesis?
A thesis is an in-depth research study that identifies a particular topic of inquiry and presents a clear argument or perspective about that topic using evidence and logic.
Writing a thesis showcases your ability of critical thinking, gathering evidence, and making a compelling argument. Integral to these competencies is thorough research, which not only fortifies your propositions but also confers credibility to your entire study.
Furthermore, there's another phenomenon you might often confuse with the thesis: the ' working thesis .' However, they aren't similar and shouldn't be used interchangeably.
A working thesis, often referred to as a preliminary or tentative thesis, is an initial version of your thesis statement. It serves as a draft or a starting point that guides your research in its early stages.
As you research more and gather more evidence, your initial thesis (aka working thesis) might change. It's like a starting point that can be adjusted as you learn more. It's normal for your main topic to change a few times before you finalize it.
While a thesis identifies and provides an overarching argument, the key to clearly communicating the central point of that argument lies in writing a strong thesis statement.
What is a thesis statement?
A strong thesis statement (aka thesis sentence) is a concise summary of the main argument or claim of the paper. It serves as a critical anchor in any academic work, succinctly encapsulating the primary argument or main idea of the entire paper.
Typically found within the introductory section, a strong thesis statement acts as a roadmap of your thesis, directing readers through your arguments and findings. By delineating the core focus of your investigation, it offers readers an immediate understanding of the context and the gravity of your study.
Furthermore, an effectively crafted thesis statement can set forth the boundaries of your research, helping readers anticipate the specific areas of inquiry you are addressing.
Different types of thesis statements
A good thesis statement is clear, specific, and arguable. Therefore, it is necessary for you to choose the right type of thesis statement for your academic papers.
Thesis statements can be classified based on their purpose and structure. Here are the primary types of thesis statements:
Argumentative (or Persuasive) thesis statement
Purpose : To convince the reader of a particular stance or point of view by presenting evidence and formulating a compelling argument.
Example : Reducing plastic use in daily life is essential for environmental health.
Analytical thesis statement
Purpose : To break down an idea or issue into its components and evaluate it.
Example : By examining the long-term effects, social implications, and economic impact of climate change, it becomes evident that immediate global action is necessary.
Expository (or Descriptive) thesis statement
Purpose : To explain a topic or subject to the reader.
Example : The Great Depression, spanning the 1930s, was a severe worldwide economic downturn triggered by a stock market crash, bank failures, and reduced consumer spending.
Cause and effect thesis statement
Purpose : To demonstrate a cause and its resulting effect.
Example : Overuse of smartphones can lead to impaired sleep patterns, reduced face-to-face social interactions, and increased levels of anxiety.
Compare and contrast thesis statement
Purpose : To highlight similarities and differences between two subjects.
Example : "While both novels '1984' and 'Brave New World' delve into dystopian futures, they differ in their portrayal of individual freedom, societal control, and the role of technology."
When you write a thesis statement , it's important to ensure clarity and precision, so the reader immediately understands the central focus of your work.
What is the difference between a thesis and a thesis statement?
While both terms are frequently used interchangeably, they have distinct meanings.
A thesis refers to the entire research document, encompassing all its chapters and sections. In contrast, a thesis statement is a brief assertion that encapsulates the central argument of the research.
Here’s an in-depth differentiation table of a thesis and a thesis statement.
Aspect | Thesis | Thesis Statement |
Definition | An extensive document presenting the author's research and findings, typically for a degree or professional qualification. | A concise sentence or two in an essay or research paper that outlines the main idea or argument. |
Position | It’s the entire document on its own. | Typically found at the end of the introduction of an essay, research paper, or thesis. |
Components | Introduction, methodology, results, conclusions, and bibliography or references. | Doesn't include any specific components |
Purpose | Provides detailed research, presents findings, and contributes to a field of study. | To guide the reader about the main point or argument of the paper or essay. |
Now, to craft a compelling thesis, it's crucial to adhere to a specific structure. Let’s break down these essential components that make up a thesis structure
15 components of a thesis structure
Navigating a thesis can be daunting. However, understanding its structure can make the process more manageable.
Here are the key components or different sections of a thesis structure:
Your thesis begins with the title page. It's not just a formality but the gateway to your research.

Here, you'll prominently display the necessary information about you (the author) and your institutional details.
- Title of your thesis
- Your full name
- Your department
- Your institution and degree program
- Your submission date
- Your Supervisor's name (in some cases)
- Your Department or faculty (in some cases)
- Your University's logo (in some cases)
- Your Student ID (in some cases)
In a concise manner, you'll have to summarize the critical aspects of your research in typically no more than 200-300 words.

This includes the problem statement, methodology, key findings, and conclusions. For many, the abstract will determine if they delve deeper into your work, so ensure it's clear and compelling.
Acknowledgments
Research is rarely a solitary endeavor. In the acknowledgments section, you have the chance to express gratitude to those who've supported your journey.

This might include advisors, peers, institutions, or even personal sources of inspiration and support. It's a personal touch, reflecting the humanity behind the academic rigor.
Table of contents
A roadmap for your readers, the table of contents lists the chapters, sections, and subsections of your thesis.

By providing page numbers, you allow readers to navigate your work easily, jumping to sections that pique their interest.
List of figures and tables
Research often involves data, and presenting this data visually can enhance understanding. This section provides an organized listing of all figures and tables in your thesis.

It's a visual index, ensuring that readers can quickly locate and reference your graphical data.
Introduction
Here's where you introduce your research topic, articulate the research question or objective, and outline the significance of your study.

- Present the research topic : Clearly articulate the central theme or subject of your research.
- Background information : Ground your research topic, providing any necessary context or background information your readers might need to understand the significance of your study.
- Define the scope : Clearly delineate the boundaries of your research, indicating what will and won't be covered.
- Literature review : Introduce any relevant existing research on your topic, situating your work within the broader academic conversation and highlighting where your research fits in.
- State the research Question(s) or objective(s) : Clearly articulate the primary questions or objectives your research aims to address.
- Outline the study's structure : Give a brief overview of how the subsequent sections of your work will unfold, guiding your readers through the journey ahead.
The introduction should captivate your readers, making them eager to delve deeper into your research journey.
Literature review section
Your study correlates with existing research. Therefore, in the literature review section, you'll engage in a dialogue with existing knowledge, highlighting relevant studies, theories, and findings.

It's here that you identify gaps in the current knowledge, positioning your research as a bridge to new insights.
To streamline this process, consider leveraging AI tools. For example, the SciSpace literature review tool enables you to efficiently explore and delve into research papers, simplifying your literature review journey.
Methodology
In the research methodology section, you’ll detail the tools, techniques, and processes you employed to gather and analyze data. This section will inform the readers about how you approached your research questions and ensures the reproducibility of your study.

Here's a breakdown of what it should encompass:
- Research Design : Describe the overall structure and approach of your research. Are you conducting a qualitative study with in-depth interviews? Or is it a quantitative study using statistical analysis? Perhaps it's a mixed-methods approach?
- Data Collection : Detail the methods you used to gather data. This could include surveys, experiments, observations, interviews, archival research, etc. Mention where you sourced your data, the duration of data collection, and any tools or instruments used.
- Sampling : If applicable, explain how you selected participants or data sources for your study. Discuss the size of your sample and the rationale behind choosing it.
- Data Analysis : Describe the techniques and tools you used to process and analyze the data. This could range from statistical tests in quantitative research to thematic analysis in qualitative research.
- Validity and Reliability : Address the steps you took to ensure the validity and reliability of your findings to ensure that your results are both accurate and consistent.
- Ethical Considerations : Highlight any ethical issues related to your research and the measures you took to address them, including — informed consent, confidentiality, and data storage and protection measures.
Moreover, different research questions necessitate different types of methodologies. For instance:
- Experimental methodology : Often used in sciences, this involves a controlled experiment to discern causality.
- Qualitative methodology : Employed when exploring patterns or phenomena without numerical data. Methods can include interviews, focus groups, or content analysis.
- Quantitative methodology : Concerned with measurable data and often involves statistical analysis. Surveys and structured observations are common tools here.
- Mixed methods : As the name implies, this combines both qualitative and quantitative methodologies.
The Methodology section isn’t just about detailing the methods but also justifying why they were chosen. The appropriateness of the methods in addressing your research question can significantly impact the credibility of your findings.
Results (or Findings)
This section presents the outcomes of your research. It's crucial to note that the nature of your results may vary; they could be quantitative, qualitative, or a mix of both.

Quantitative results often present statistical data, showcasing measurable outcomes, and they benefit from tables, graphs, and figures to depict these data points.
Qualitative results , on the other hand, might delve into patterns, themes, or narratives derived from non-numerical data, such as interviews or observations.
Regardless of the nature of your results, clarity is essential. This section is purely about presenting the data without offering interpretations — that comes later in the discussion.
In the discussion section, the raw data transforms into valuable insights.
Start by revisiting your research question and contrast it with the findings. How do your results expand, constrict, or challenge current academic conversations?
Dive into the intricacies of the data, guiding the reader through its implications. Detail potential limitations transparently, signaling your awareness of the research's boundaries. This is where your academic voice should be resonant and confident.
Practical implications (Recommendation) section
Based on the insights derived from your research, this section provides actionable suggestions or proposed solutions.
Whether aimed at industry professionals or the general public, recommendations translate your academic findings into potential real-world actions. They help readers understand the practical implications of your work and how it can be applied to effect change or improvement in a given field.
When crafting recommendations, it's essential to ensure they're feasible and rooted in the evidence provided by your research. They shouldn't merely be aspirational but should offer a clear path forward, grounded in your findings.
The conclusion provides closure to your research narrative.
It's not merely a recap but a synthesis of your main findings and their broader implications. Reconnect with the research questions or hypotheses posited at the beginning, offering clear answers based on your findings.

Reflect on the broader contributions of your study, considering its impact on the academic community and potential real-world applications.
Lastly, the conclusion should leave your readers with a clear understanding of the value and impact of your study.
References (or Bibliography)
Every theory you've expounded upon, every data point you've cited, and every methodological precedent you've followed finds its acknowledgment here.

In references, it's crucial to ensure meticulous consistency in formatting, mirroring the specific guidelines of the chosen citation style .
Proper referencing helps to avoid plagiarism , gives credit to original ideas, and allows readers to explore topics of interest. Moreover, it situates your work within the continuum of academic knowledge.
To properly cite the sources used in the study, you can rely on online citation generator tools to generate accurate citations!
Here’s more on how you can cite your sources.
Often, the depth of research produces a wealth of material that, while crucial, can make the core content of the thesis cumbersome. The appendix is where you mention extra information that supports your research but isn't central to the main text.

Whether it's raw datasets, detailed procedural methodologies, extended case studies, or any other ancillary material, the appendices ensure that these elements are archived for reference without breaking the main narrative's flow.
For thorough researchers and readers keen on meticulous details, the appendices provide a treasure trove of insights.
Glossary (optional)
In academics, specialized terminologies, and jargon are inevitable. However, not every reader is versed in every term.
The glossary, while optional, is a critical tool for accessibility. It's a bridge ensuring that even readers from outside the discipline can access, understand, and appreciate your work.

By defining complex terms and providing context, you're inviting a wider audience to engage with your research, enhancing its reach and impact.
Remember, while these components provide a structured framework, the essence of your thesis lies in the originality of your ideas, the rigor of your research, and the clarity of your presentation.
As you craft each section, keep your readers in mind, ensuring that your passion and dedication shine through every page.

Thesis examples
To further elucidate the concept of a thesis, here are illustrative examples from various fields:
Example 1 (History): Abolition, Africans, and Abstraction: the Influence of the ‘Noble Savage’ on British and French Antislavery Thought, 1787-1807 by Suchait Kahlon.
Example 2 (Climate Dynamics): Influence of external forcings on abrupt millennial-scale climate changes: a statistical modelling study by Takahito Mitsui · Michel Crucifix
Checklist for your thesis evaluation
Evaluating your thesis ensures that your research meets the standards of academia. Here's an elaborate checklist to guide you through this critical process.
Content and structure
- Is the thesis statement clear, concise, and debatable?
- Does the introduction provide sufficient background and context?
- Is the literature review comprehensive, relevant, and well-organized?
- Does the methodology section clearly describe and justify the research methods?
- Are the results/findings presented clearly and logically?
- Does the discussion interpret the results in light of the research question and existing literature?
- Is the conclusion summarizing the research and suggesting future directions or implications?
Clarity and coherence
- Is the writing clear and free of jargon?
- Are ideas and sections logically connected and flowing?
- Is there a clear narrative or argument throughout the thesis?
Research quality
- Is the research question significant and relevant?
- Are the research methods appropriate for the question?
- Is the sample size (if applicable) adequate?
- Are the data analysis techniques appropriate and correctly applied?
- Are potential biases or limitations addressed?
Originality and significance
- Does the thesis contribute new knowledge or insights to the field?
- Is the research grounded in existing literature while offering fresh perspectives?
Formatting and presentation
- Is the thesis formatted according to institutional guidelines?
- Are figures, tables, and charts clear, labeled, and referenced in the text?
- Is the bibliography or reference list complete and consistently formatted?
- Are appendices relevant and appropriately referenced in the main text?
Grammar and language
- Is the thesis free of grammatical and spelling errors?
- Is the language professional, consistent, and appropriate for an academic audience?
- Are quotations and paraphrased material correctly cited?
Feedback and revision
- Have you sought feedback from peers, advisors, or experts in the field?
- Have you addressed the feedback and made the necessary revisions?
Overall assessment
- Does the thesis as a whole feel cohesive and comprehensive?
- Would the thesis be understandable and valuable to someone in your field?
Ensure to use this checklist to leave no ground for doubt or missed information in your thesis.
After writing your thesis, the next step is to discuss and defend your findings verbally in front of a knowledgeable panel. You’ve to be well prepared as your professors may grade your presentation abilities.
Preparing your thesis defense
A thesis defense, also known as "defending the thesis," is the culmination of a scholar's research journey. It's the final frontier, where you’ll present their findings and face scrutiny from a panel of experts.
Typically, the defense involves a public presentation where you’ll have to outline your study, followed by a question-and-answer session with a committee of experts. This committee assesses the validity, originality, and significance of the research.
The defense serves as a rite of passage for scholars. It's an opportunity to showcase expertise, address criticisms, and refine arguments. A successful defense not only validates the research but also establishes your authority as a researcher in your field.
Here’s how you can effectively prepare for your thesis defense .
Now, having touched upon the process of defending a thesis, it's worth noting that scholarly work can take various forms, depending on academic and regional practices.
One such form, often paralleled with the thesis, is the 'dissertation.' But what differentiates the two?
Dissertation vs. Thesis
Often used interchangeably in casual discourse, they refer to distinct research projects undertaken at different levels of higher education.
To the uninitiated, understanding their meaning might be elusive. So, let's demystify these terms and delve into their core differences.
Here's a table differentiating between the two.
Aspect | Thesis | Dissertation |
Purpose | Often for a master's degree, showcasing a grasp of existing research | Primarily for a doctoral degree, contributing new knowledge to the field |
Length | 100 pages, focusing on a specific topic or question. | 400-500 pages, involving deep research and comprehensive findings |
Research Depth | Builds upon existing research | Involves original and groundbreaking research |
Advisor's Role | Guides the research process | Acts more as a consultant, allowing the student to take the lead |
Outcome | Demonstrates understanding of the subject | Proves capability to conduct independent and original research |
Wrapping up
From understanding the foundational concept of a thesis to navigating its various components, differentiating it from a dissertation, and recognizing the importance of proper citation — this guide covers it all.
As scholars and readers, understanding these nuances not only aids in academic pursuits but also fosters a deeper appreciation for the relentless quest for knowledge that drives academia.
It’s important to remember that every thesis is a testament to curiosity, dedication, and the indomitable spirit of discovery.
Good luck with your thesis writing!
Frequently Asked Questions
A thesis typically ranges between 40-80 pages, but its length can vary based on the research topic, institution guidelines, and level of study.
A PhD thesis usually spans 200-300 pages, though this can vary based on the discipline, complexity of the research, and institutional requirements.
To identify a thesis topic, consider current trends in your field, gaps in existing literature, personal interests, and discussions with advisors or mentors. Additionally, reviewing related journals and conference proceedings can provide insights into potential areas of exploration.
The conceptual framework is often situated in the literature review or theoretical framework section of a thesis. It helps set the stage by providing the context, defining key concepts, and explaining the relationships between variables.
A thesis statement should be concise, clear, and specific. It should state the main argument or point of your research. Start by pinpointing the central question or issue your research addresses, then condense that into a single statement, ensuring it reflects the essence of your paper.
You might also like

Boosting Citations: A Comparative Analysis of Graphical Abstract vs. Video Abstract

The Impact of Visual Abstracts on Boosting Citations

Introducing SciSpace’s Citation Booster To Increase Research Visibility
- FindAMasters
- Researching and Writing a Masters Dissertation
Written by Mark Bennett
All Masters programmes include some form of extended individual project. Research-focussed programmes, such as an MRes , may include multiple independent research components. Taught courses usually culminate with a substantial research task, referred to as the Masters dissertation or thesis.
This article talks about how long a Masters dissertation is and the structure it follows.Before you get started on your dissertation, you'll usually need to write a proposal. Read our full guide to Masters dissertation proposals for more information on what this should include!
| Length | 15,000 - 20,000 words |
| Structure | Abstract (300 words) Introduction (1,000 words) Literature review (1,000 words) Research methodology (1,500 words) Results Discussion (12,000 words) Conclusion (1,500 words) References/Bibliography Appendices |
| Supervision | Yes, you’ll be paired with an academic from your own university |
| Assessment | External examiner along with additional members of faculty. There is not usually a viva at Masters level. |
On this page
What’s the difference between a masters dissertation and an undergraduate dissertation.
The Masters thesis is a bridge between undergraduate study and higher level postgraduate degrees such as the PhD .
A postgraduate dissertation may not look that different to its undergraduate equivalent. You’ll likely have to produce a longer piece of work but the foundations remain the same.
After all, one of the purposes of an undergraduate dissertation or final year project is to prepare you for more in-depth research work as a postgraduate. That said, there are some important differences between the two levels.
So, how long is a Masters dissertation? A Masters dissertation will be longer than the undergraduate equivalent – usually it’ll be somewhere between 15,000 and 20,000 words, but this can vary widely between courses, institutions and countries.
To answer your overall research question comprehensively, you’ll be expected to identify and examine specific areas of your topic. This can be like producing a series of shorter pieces of work, similar to those required by individual modules. However, there’s the additional requirement that they collectively support a broader set of conclusions.
This more involved Masters dissertation structure will:
- Give you the scope to investigate your subject in greater detail than is possible at undergraduate level
- Challenge you to be effective at organising your work so that its individual components function as stages in a coherent and persuasive overall argument
- Allow you to develop and hone a suitable research methodology (for example, choosing between qualitative and quantitative methods)
If the individual topics within your overall project require you to access separate sources or datasets, this may also have an impact on your research process.
As a postgraduate, you’ll be expected to establish and assert your own critical voice as a member of the academic community associated with your field .
During your Masters thesis you’ll need to show that you are not just capable of analysing and critiquing original data or primary source material. You should also demonstrate awareness of the existing body of scholarship relating to your topic .
So, if you’ll excuse the pun, a ‘Masters’ degree really is about achieving ‘mastery’ of your particular specialism and the dissertation is where you’ll demonstrate this: showing off the scholarly expertise and research skills that you’ve developed across your programme.
What’s the difference between a dissertation and a thesis?
A dissertation is a long piece of (usually) written work on the same topic. A thesis is a little more specific: it usually means something that presents an original argument based on the interpretation of data, statistics or content.
So, a thesis is almost always presented as a dissertation, but not all dissertations present a thesis.
Masters dissertation structure
As you can probably imagine, no two dissertations follow the exact same structure, especially given the differences found between Masters programmes from university to university and country to country .
That said, there are several key components that make up the structure of a typical Masters dissertation
How long is a Masters dissertation?
Most dissertations will typically be between 15,000 and 20,000 words long, although this can vary significantly depending on the nature of the programme.
You should also check with your university exactly which sections of the dissertation count towards the final word count (the abstract, bibliography and appendices won’t usually be included in the total).
Usually around 300 words long, the abstract is meant to be a concise summary of your dissertation. It should briefly cover the question(s) you aim to answer, your primary argument and your conclusion.
Introduction
The purpose of the introduction is to provide context for the rest of the dissertation, setting out your aims and the scope of what you want to achieve with your research. The introduction should give a clear overview of the dissertation’s chapters and will usually be around 1,000 words long.
Literature review
This part of the dissertation should examine the scholarship that has already been published in your field, presenting various arguments and counter-arguments while situating your own research within this wider body of work.
You should analyse and evaluate other publications and explain how your dissertation will contribute to the existing literature in your subject area. The literature review sometimes forms part of the introduction or follows immediately on from it. Most literature reviews are up to 1,000 words long.
Research methodology
Not all dissertations will require a section covering research methodology (Arts and Humanities dissertations won’t normally undertake the kind of research that involves a set methodology). However, if you are using a particular method to collect information for your dissertation, you should make sure to explain the rationale behind your choice of methodology. The word count for this part of the dissertation is usually around the 1,500 mark.
Those in the Arts and Humanities will usually outline their theoretical perspectives and approaches as part of the introduction, rather than requiring a detailed explanation of the methodology for their data collection and analysis.
Results / findings
If your research involves some form of survey or experiment, this is where you’ll present the results of your work. Depending on the nature of the study, this might be in the form of graphs, tables or charts – or even just a written description of what the research entailed and what the findings were.
This section forms the bulk of your dissertation and should be carefully structured using a series of related chapters (and sub-chapters). There should be a logical progression from one chapter to the next, with each part building on the arguments of its predecessor.
It can be helpful to think of your Masters dissertation as a series of closely interlinked essays, rather than one overwhelming paper. The size of this section will depend on the overall word count for your dissertation. However, to give you a rough idea for a 15,000-word dissertation, the discussion part will generally be about 12,000 words long.
Here you should draw together the threads of the previous discussion chapters and make your final concluding statements, drawing on evidence and arguments that you’ve already explored over the course of the dissertation. Explain the significance of your findings and point towards directions that future research could follow. This section of the Masters thesis will be around 1,500 words long.
References / bibliography
While planning and writing your dissertation, you should keep an extensive, organised record of any papers, sources or books you’ve quoted (or referred to). This will be a lot easier than leaving all of it until the end and struggling to work out where a particular quotation is from!
Appendices won’t be necessary in many dissertations, but you may need to include supplementary material to support your argument. This could be interview transcripts or questionnaires. If including such content within the body of the dissertation won’t be feasible – i.e. there wouldn’t be enough space or it would break the flow of your writing – you should consult with your supervisor and consider attaching it in an appendix.
It’s worth bearing in mind that these sections won’t always be discretely labelled in every dissertation. For example, everything up to ‘discussion’ might be covered in introductory chapter (rather than as distinct sections). If you’re unsure about the structure of your Masters dissertation, your supervisor will be able to help you map it out.
How does supervision work for a Masters dissertation?
As a Masters student at the dissertation stage you’ll usually be matched with an academic within your institution who will be tasked with guiding your work. This might be someone who has already taught you, or it may be another scholar whose research interests and expertise align well with what you want to do. You may be able to request a particular supervisor, but taught postgraduates are more likely to be assigned them by their department.
Specific arrangements with your supervisor will vary depending on your institution and subject area. They will usually meet with you at the beginning of the dissertation period to discuss your project and agree a suitable schedule for its undertaking. This timetable will probably set dates for:
- Subsequent discussions and progress checks
- The submission of draft chapters or sections
- Feedback appointments
Though your supervisor is there to help and advise you, it is important to remember that your dissertation is a personal research project with associated expectations of you as an independent scholar.
As a rule of thumb, you can expect your supervisor to read each part of your dissertation once at the draft stage and to offer feedback. Most will not have time to look at lots of subsequent revisions, but may respond favourably to polite requests for exceptions (provided their own workload permits it).
Inundating your supervisor with emails or multiple iterations of draft material is best avoided; they will have their own research to manage (as well as other supervision assignments) and will be able to offer better quality feedback if you stick to an agreed schedule.
How is a Masters dissertation assessed and examined?
On most courses your dissertation will be assessed by an external examiner (as well as additional members of faculty within your university who haven’t been responsible for supervising you), but these will read and critique the work you submit without personally questioning and testing you on it.
Though this examination process is not as challenging as the oral defence or ‘ viva voce ’ required for a PhD thesis, the grading of your Masters dissertation is still a fundamental component of your degree.
On some programmes the result awarded to a student’s dissertation may determine the upper grade-band that can be awarded to their degree.
Search for a Masters
Ready to start looking for your ideal postgraduate opportunity? Browse and compare Masters degrees on FindAMasters.com.
Our postgrad newsletter shares courses, funding news, stories and advice
You may also like....

Applying for a Masters can feel a bit daunting. Here is a checklist of all the things you need to do to make sure you have everything covered in your Masters application.

Postgraduate study is often very flexible, with the option to study a Masters degree or other qualification part-time, online or through blended learning.

How do Bachelors and Masters courses differ? We’ve covered the main differences you’ll encounter when making the transition from undergrad to postgrad study.

Our guide explains how online Masters degree work, what the benefits of online learning are and how to choose what to study online.

Our guide tells you everything about the application process for studying a Masters in Italy.

Our guide tells you everything about the application process for studying a Masters in the USA.
FindAMasters. Copyright 2005-2024 All rights reserved.
Unknown ( change )
Have you got time to answer some quick questions about Masters study?
Select your nearest city
- Aberystwyth
- Beaconsfield
- Bishop Burton
- Bournemouth
- Bridlington
- Chatham Maritime
- Cirencester
- East Malling
- Hemel Hempstead
- High Wycombe
- Huddersfield
- Isle of Man
- Jordanstown
- London Central
- London East
- London South
- London West
- Londonderry
- Loughborough
- Middlesbrough
- Milton Keynes
- Musselburgh
- Northampton
- Potters Bar
- Saffron Waldon
- Scarborough
- Southampton
- St Leonards on Sea
- Stoke on Trent
- Wolverhampton
You haven’t completed your profile yet. To get the most out of FindAMasters, finish your profile and receive these benefits:
- Monthly chance to win one of ten £10 Amazon vouchers ; winners will be notified every month.*
- Access to our £6,000 scholarship competition
- Weekly newsletter with funding opportunities, application tips and much more
- Early access to our physical and virtual postgraduate study fairs
Or begin browsing FindAMasters.com
or begin browsing FindAMasters.com
*Offer only available for the duration of your active subscription, and subject to change. You MUST claim your prize within 72 hours, if not we will redraw.

Do you want hassle-free information and advice?
Create your FindAMasters account and sign up to our newsletter:
- Find out about funding opportunities and application tips
- Receive weekly advice, student stories and the latest Masters news
- Hear about our upcoming study fairs
- Save your favourite programmes, track enquiries and get personalised subject updates

Create your account
Looking to list your Masters programmes? Log in here .

Let us help you find a Masters
Never miss a course
Enter our ambassador competition
Get funding news, tips and advice
Hear about upcoming events
Sign up to our newsletter today
We've been helping students find the right postgraduate course for over a decade.
Login to your account
Enter your username below to login to your account.
Article Categories
Book categories, collections.
- Academics & The Arts Articles
- Language & Language Arts Articles
- Writing Articles
Different Types of Dissertation
Writing a dissertation for dummies.

Sign up for the Dummies Beta Program to try Dummies' newest way to learn.
In writing your dissertation, you’re likely to be taking a practical or a theoretical approach, even though both practical and theoretical considerations are of the utmost importance in social science research. For an undergraduate dissertation, your examiner is going to expect you to choose a largely theoretical or a mainly practical look at your chosen subject.
Any useful practical research you carry out requires a sound theoretical basis, and any theoretical study you do needs to link to what’s happening in the world around you. A theoretical study can be mainly abstract with an emphasis on the philosophical, ethical and cultural considerations of the subject, or your subject can be an applied theoretical study with an emphasis on political, social or economic issues, for example.
More practical research studies in social science are usually about exploring issues through surveys, action research, observations, case-studies or a review of existing studies.
The type of dissertation you end up writing depends on the topic you’re researching. The following table gives a few examples of different ways of approaching a topic just to get you thinking:
| Concern | Method | Type of Study |
|---|---|---|
| Theory/hypothesis | Analysis | Non-empirical |
| Strategy | Analysis | Non-empirical with examples |
| Issue | Question people | Empirical |
| Type of behaviour | Observation | Empirical |
| Personal viewpoint | Reporting / reflection | Narrative |
Empirical dissertations
An empirical dissertation involves collecting data. For example, to gather the views of patients at a GP’s surgery, volunteers in a police service, children in a play centre or translators in a refugee centre, you have to find ways of asking the individuals involved what they think or review what they’re doing. You can collect your data in many ways: from questionnaires and observations to interviews and focus groups.
Or, you may prefer to collect your data by taking another approach such as looking at and analysing existing data from new angles, making useful comparisons or drawing interesting parallels.
Even if the focus of your dissertation is on using data, don’t forget that you’re still going to need a sound theoretical basis for your work.
Non-empirical dissertations
Making the choice to do a non-empirical dissertation shouldn’t be taken lightly. Sustaining an argument over the length of your whole dissertation is a distinct challenge. If you enjoy spending time in the library, reading, thinking and discussing theory, this is likely to be the right choice for you.
If you know that making the university library your home for weeks on end is going to be difficult, you may be better off choosing a more empirical research question to explore.
Key theories in your discipline such as feminism or pragmatism can be the basis of an abstract discussion in your dissertation. Subjects such as sociology have this type of theory at their centre and so it’s perfectly valid, for example, to discuss aspects of the theory of pragmatism as your dissertation topic.
A dissertation that draws upon major theories, such as in education more often takes an applied route, but can also be exclusively theoretical, for example, some work in the philosophy of education.
Narrative dissertations
You’re more than likely to choose doing an empirical or a non-empirical dissertation. However, in other disciplines you may come across different methods of producing a dissertation.
Dissertations in many science subjects include or even focus around a laboratory report describing all the aspects of setting up, carrying out and analysing a complex experiment. In physical geography, time is spent somewhere wild and windswept collecting data needed for analysis. Laboratory work and field trips are a key part of the student experience of writing a dissertation. It’s possible you may even use a passage from the classics or biography as an illustration or example in your dissertation.
About This Article
This article is from the book:.
- Writing a Dissertation For Dummies ,
About the book author:
Dr Carrie Winstanley is a Principal Lecturer in Education at Roehampton University, London, where she works with both undergraduate and postgraduate students. Carrie was recently named one of the Top 50 university teachers in the UK by the Higher Education Academy, for which she was awarded a national teaching fellowship.
This article can be found in the category:
- Essential Networking when Writing a Dissertation
- Obeying the Dissertation Rules and Regulations<b> </b>
- Optimising Your Dissertation Writing
- Organising Your Working Methods while Writing a Dissertation
- Settling on Your Dissertation Research Question
- View All Articles From Book
- 1-888-SNU-GRAD
- Daytime Classes

The Top 3 Types of Dissertation Research Explained

Preparing for your doctoral dissertation takes serious perseverance. You’ve endured years of studies and professional development to get to this point. After sleepless nights and labor-intensive research, you’re ready to present the culmination of all of your hard work. Even with a strong base knowledge, it can be difficult — even daunting — to decide how you will begin writing.
By taking a wide-lens view of the dissertation research process , you can best assess the work you have ahead of you and any gaps in your current research strategy. Subsequently, you’ll begin to develop a timeline so you can work efficiently and cross that finish line with your degree in hand.
What Is a Dissertation?
A dissertation is a published piece of research on a novel topic in your chosen field. Students complete a dissertation as part of a doctoral or PhD program. For most students, a dissertation is the first substantive piece of academic research they will write.
Because a dissertation becomes a published piece of academic literature that other academics may cite, students must defend it in front of a board of experts consisting of peers in their field, including professors, their advisor, and other industry experts.
For many students, a dissertation is the first piece of research in a long career full of research. As such, it’s important to choose a topic that’s interesting and engaging.
Types of Dissertation Research
Dissertations can take on many forms, based on research and methods of presentation in front of a committee board of academics and experts in the field. Here, we’ll focus on the three main types of dissertation research to get you one step closer to earning your doctoral degree.
1. Qualitative
The first type of dissertation is known as a qualitative dissertation . A qualitative dissertation mirrors the qualitative research that a doctoral candidate would conduct throughout their studies. This type of research relies on non-numbers-based data collected through things like interviews, focus groups and participant observation.
The decision to model your dissertation research according to the qualitative method will depend largely on the data itself that you are collecting. For example, dissertation research in the field of education or psychology may lend itself to a qualitative approach, depending on the essence of research. Within a qualitative dissertation research model, a candidate may pursue one or more of the following:
- Case study research
- Autoethnographies
- Narrative research
- Grounded theory
Although individual approaches may vary, qualitative dissertations usually include certain foundational characteristics. For example, the type of research conducted to develop a qualitative dissertation often follows an emergent design, meaning that the content and research strategy changes over time. Candidates also rely on research paradigms to further strategize how best to collect and relay their findings. These include critical theory, constructivism and interpretivism, to name a few.
Because qualitative researchers integrate non-numerical data, their methods of collection often include unstructured interview, focus groups and participant observations. Of course, researchers still need rubrics from which to assess the quality of their findings, even though they won’t be numbers-based. To do so, they subject the data collected to the following criteria: dependability, transferability and validity.
When it comes time to present their findings, doctoral candidates who produce qualitative dissertation research have several options. Some choose to include case studies, personal findings, narratives, observations and abstracts. Their presentation focuses on theoretical insights based on relevant data points.
2. Quantitative
Quantitative dissertation research, on the other hand, focuses on the numbers. Candidates employ quantitative research methods to aggregate data that can be easily categorized and analyzed. In addition to traditional statistical analysis, quantitative research also hones specific research strategy based on the type of research questions. Quantitative candidates may also employ theory-driven research, replication-based studies and data-driven dissertations.
When conducting research, some candidates who rely on quantitative measures focus their work on testing existing theories, while others create an original approach. To refine their approach, quantitative researchers focus on positivist or post-positivist research paradigms. Quantitative research designs focus on descriptive, experimental or relationship-based designs, to name a few.
To collect the data itself, researchers focus on questionnaires and surveys, structured interviews and observations, data sets and laboratory-based methods. Then, once it’s time to assess the quality of the data, quantitative researchers measure their results against a set of criteria, including: reliability, internal/external validity and construct validity. Quantitative researchers have options when presenting their findings. Candidates convey their results using graphs, data, tables and analytical statements.

3. Mixed-Method
Many PhD candidates also use a hybrid model in which they employ both qualitative and quantitative methods of research. Mixed dissertation research models are fairly new and gaining traction. For a variety of reasons, a mixed-method approach offers candidates both versatility and credibility. It’s a more comprehensive strategy that allows for a wider capture of data with a wide range of presentation optimization.
In the most common cases, candidates will first use quantitative methods to collect and categorize their data. Then, they’ll rely on qualitative methods to analyze that data and draw meaningful conclusions to relay to their committee panel.
With a mixed-method approach, although you’re able to collect and analyze a more broad range of data, you run the risk of widening the scope of your dissertation research so much that you’re not able to reach succinct, sustainable conclusions. This is where it becomes critical to outline your research goals and strategy early on in the dissertation process so that the techniques you use to capture data have been thoroughly examined.
How to Choose a Type of Dissertation Research That’s Right for You
After this overview of application and function, you may still be wondering how to go about choosing a dissertation type that’s right for you and your research proposition. In doing so, you’ll have a couple of things to consider:
- What are your personal motivations?
- What are your academic goals?
It’s important to discern exactly what you hope to get out of your doctoral program . Of course, the presentation of your dissertation is, formally speaking, the pinnacle of your research. However, doctoral candidates must also consider:
- Which contributions they will make to the field
- Who they hope to collaborate with throughout their studies
- What they hope to take away from the experience personally, professionally and academically
Personal Considerations
To discern which type of dissertation research to choose, you have to take a closer look at your learning style, work ethic and even your personality.
Quantitative research tends to be sequential and patterned-oriented. Steps move in a logical order, so it becomes clear what the next step should be at all times. For most candidates, this makes it easier to devise a timeline and stay on track. It also keeps you from getting overwhelmed by the magnitude of research involved. You’ll be able to assess your progress and make simple adjustments to stay on target.
On the other hand, maybe you know that your research will involve many interviews and focus groups. You anticipate that you’ll have to coordinate participants’ schedules, and this will require some flexibility. Instead of creating a rigid schedule from the get-go, allowing your research to flow in a non-linear fashion may actually help you accomplish tasks more efficiently, albeit out of order. This also allows you the personal versatility of rerouting research strategy as you collect new data that leads you down other paths.
After examining the research you need to conduct, consider more broadly: What type of student and researcher are you? In other words, What motivates you to do your best work?
You’ll need to make sure that your methodology is conducive to the data you’re collecting, and you also need to make sure that it aligns with your work ethic so you set yourself up for success. If jumping from one task to another will cause you extra stress, but planning ahead puts you at ease, a quantitative research method may be best, assuming the type of research allows for this.
Professional Considerations
The skills you master while working on your dissertation will serve you well beyond the day you earn your degree. Take into account the skills you’d like to develop for your academic and professional future. In addition to the hard skills you will develop in your area of expertise, you’ll also develop soft skills that are transferable to nearly any professional or academic setting. Perhaps you want to hone your ability to strategize a timeline, gather data efficiently or draw clear conclusions about the significance of your data collection.
If you have considerable experience with quantitative analysis, but lack an extensive qualitative research portfolio, now may be your opportunity to explore — as long as you’re willing to put in the legwork to refine your skills or work closely with your mentor to develop a strategy together.
Academic Considerations
For many doctoral candidates who hope to pursue a professional career in the world of academia, writing your dissertation is a practice in developing general research strategies that can be applied to any academic project.
Candidates who are unsure which dissertation type best suits their research should consider whether they will take a philosophical or theoretical approach or come up with a thesis that addresses a specific problem or idea. Narrowing down this approach can sometimes happen even before the research begins. Other times, candidates begin to refine their methods once the data begins to tell a more concrete story.
Next Step: Structuring Your Dissertation Research Schedule
Once you’ve chosen which type of dissertation research you’ll pursue, you’ve already crossed the first hurdle. The next hurdle becomes when and where to fit dedicated research time and visits with your mentor into your schedule. The busyness of day-to-day life shouldn’t prevent you from making your academic dream a reality. In fact, search for programs that assist, not impede, your path to higher levels of academic success.
Find out more about SNU’s online and on-campus education opportunities so that no matter where you are in life, you can choose the path that’s right for you.

Want to learn more about SNU's programs?
Request more information.
Have questions about SNU, our program, or how we can help you succeed. Fill out the form and an enrollment counselor will reach out to you soon!
Subscribe to the SNU blog for inspirational articles and tips to support you on your journey back to school.
Recent blog articles.

Adult Education
Discover Southern Nazarene University's Graduate Programs in Business

How Passion & Dedication Pave the Way for Success in Special Education

How an Instructional Design Degree Helps You Shape the Future of Education

Change Lives with a Degree in Family Studies & Gerontology
Have questions about SNU or need help determining which program is the right fit? Fill out the form and an enrollment counselor will follow-up to answer your questions!
Text With an Enrollment Counselor
Have questions, but want a faster response? Fill out the form and one of our enrollment counselors will follow-up via text shortly!
Thesis/Dissertation Support

Writing and Format Consultations
Individual 60 or 30-minute sessions with Thesis/Dissertation consultants to help you write your chapters and navigate the organization, structure, and formatting of your document.
Thesis/dissertation toolkits that contain format templates, planning tools, and everything else you need to get your document submitted correctly and on time.
Format Requirements and Resources
Graduate College's new and continuing requirements for thesis/dissertation formatting.
Canvas Community
Graduate student community aimed at helping you at any stage of your thesis/dissertation writing process.
Additional Thesis/Dissertation Opportunities
- 3MT at Iowa State
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Types of writing assignments for engineering courses

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Writing assignments in engineering courses can take many forms, ranging from a couple of sentences of in-class writing to formal reports.
Conceptual Writing
Ask students to write about technical definitions, assumptions, or terminology. They can rephrase easily found definitions and assumptions in their own words, which allows them to articulate basic knowledge that they have learned in the course.
Explain-a-Problem
Take an existing “calculator problem” and have students explain their answers. The format of their explanations can range from a few clarifying sentences to a solution manual-type description. This is the simplest type of writing question to apply, and it dovetails perfectly with already-developed homework questions.
How Stuff Works
Ask students to use newly-learned concepts and terminology in an explanation of how something works in the real world. This question forces students to apply new concepts and equations to an actual situation.
Real-world Example
Advise students to seek out and explain a real-world example of a concept in action. This type of writing prompt is great at promoting student appreciation for the real-world importance of what they are learning.
Design-a-Problem
Assign students to design their own homework problem and write a detailed solution to that problem. This approach lets students be creative and encourages deep understanding of technical concepts and procedures.
Open-ended Design
Challenge students to design a device or solution associated with a stated design objective. The writing component of the assignment lies in the explanation of the design. This writing task allows students to create their own design and further engage with technical concepts and procedures as they explain how their design works.
Harvey Cushing/John Hay Whitney Medical Library
Thesis support: your research question.
- Describe the importance of a strong research question
- Identify methods for exploring existing literature
- Understand the difference between keywords and controlled vocabulary
- Produce a basic concept chart from your research question
- How it works

Writing a Methodology for your Dissertation | Complete Guide & Steps
What is a methodology.
The methodology is perhaps the most challenging and laborious part of the dissertation . Essentially, the methodology helps in understanding the broad, philosophical approach behind the methods of research you chose to employ in your study. The research methodology elaborates on the ‘how’ part of your research.
This means that your methodology chapter should clearly state whether you chose to use quantitative or qualitative data collection techniques or a mix of both.
Your research methodology should explain the following:
- What was the purpose of your research?
- What type of research method was used?
- What were the data-collecting methods?
- How did you analyse the data?
- What kind of resources were used in your research?
- Why did you choose these methods?
You will be required to provide justifications as to why you preferred a certain method over the others. If you are trying to figure out exactly how to write methodology or the structure of a methodology for a dissertation, this article will point you in the right direction.
Students must be sure of why they chose a certain research method over another. “I figured out” or “In my opinion” statements will not be an acceptable justification. So, you will need to come up with concrete academic reasons for your selection of research methods.
What are the Standard Contents of a Research Methodology?
The methodology generally acts as a guideline or plan for exactly how you intend to carry out your research. This is especially true for students who must submit their methodology chapter before carrying out the research.
Your methodology should link back to the literature review and clearly state why you chose certain data collection and analysis methods for your research/dissertation project.
The methodology chapter consists of the following:
- Research Design
- Philosophical Approach
- Data Collection Methods
- Research Limitations
- Ethical Considerations (If Any)
- Data Analysis Methods
For those who are submitting their dissertation as a single paper, their methodology should also touch on any modifications they had to make as their work progressed.
However, it is essential to provide academic justifications for all choices made by the researcher.
How to Choose your Dissertation Methodology and Research Design?
The theme of your research methodology chapter should be related to your literature review and research question (s).
You can visit your college or university library to find textbooks and articles that provide information about the commonly employed research methods .
An intensive reading of such books can help you devise your research philosophy and choose the appropriate methods. Any limitations or weaknesses of your chosen research approach should also be explained, as well as the strategies to overcome them.
To research well, you should read well! Read as many research articles (from reputed journals) as you can. Seeing how other researchers use methods in their studies and why will help you justify, in the long run, your own research method(s).
Regardless of the chosen research approach, you will find researchers who either support it or don’t. Use the arguments for and against articulated in the literature to clarify why you decided to choose the selected research design and why the research limitations are irrelevant to your research.
How to Structure your Dissertation Methodology?
The typical structure of the methodology chapter is as follows:
- Research Design And Strategy
- Methods Of Data Collection And Data Analysis
- Ethical Considerations, Reliability , Limitations And Generalisability
In research jargon, generalisability is termed external validity . It means how generalisable your research findings are to other contexts, places, times, people, etc. External validity is expected to be significantly high, especially in quantitative studies.
According to USC-Research Guides (2017) , a research design’s primary function is to enable the researcher to answer the research questions through evidence effectively. Generally, this section will shed light on how you collected your data.
The researcher will have to justify their choice of data collection methods, such as the one that was reviewed, the use of data tools (interviews, phone surveys, questionnaires, observation, online surveys , etc.) and the like.
Moreover, data sampling choice should also be clearly explained with a focus on how you chose the ethnicity, group, profession and age of the participants.
- What type of questions do you intend to ask the respondents?
- How will they help to answer your research questions ?
- How will they help to test the hypothesis of the dissertation?
It is recommended to prepare these questions at the start of your research. You should develop your research problem and questions. This approach can allow the room to change or modify research questions if your data collection methods do not give the desired results.
It’s a good practice to keep referring to your research questions whilst planning or writing the research design section. This will help your reader recall what the research is about; why you have done what you did. Even though this technique is recommended to be applied at the start of every section within a dissertation, it’s especially beneficial in the methodology section.
In short, you will need to make sure that the data you are going to collect relates to the topic you are exploring. The complexity and length of the research design section will vary depending on your academic subject and the scope of your research, but a well-written research design will have the following characteristics:
- It sheds light on alternative research design options and justifies why your chosen design is the best to address the research problem.
- Clearly specifies the research questions that the research aims to address or the hypothesis to validate.
- Explain how the collected data will help address the research problem and discusses your research methodology to collect the data.
Philosophical Approach Behind Writing a Methodology
This will discuss your chosen philosophy to strengthen your research and the research model. Commonly employed philosophies in academia are
- Interpretivism,
- Positivism/Post-Positivism
- Constructivism
There are several other research philosophies that you could adopt.
The choice of philosophy will depend on many factors, including your academic subject and the type and complexity of the research study. Regardless of which philosophy is used, you will be required to make different assumptions about the world.
Once you have chosen your research philosophy, the next step will describe your research context to answer all the questions, including when, where, why, how and what of your research.
Essentially, as a researcher, you will be required to decide whether you will be using a qualitative method, a quantitative method or a mix of both.
Did you know?
Using both qualitative and quantitative methods leads to the use of a mixed-methods approach. This approach also goes by another seldom-used name: eclectic approach.
The process of data collection is different for each method. Typically, you would want to decide whether you will adopt the positivist approach, defining your hypothesis and testing it against reality.
If this is the case, you will be required to take the quantitative approach, collecting numerical data at a large scale (from 30 or more respondents) and testing your hypotheses with this data.
Collecting data from at least 30 respondents/participants ensures reliable statistical analysis . This is especially true for quantitative studies. If the data contains less than 30 responses, it won’t be enough to carry out reliable statistical analyses on such data.
The other option for you would be to base your research on a qualitative approach, which will point you in a direction where you will be investigating broader areas by identifying people’s emotions and perceptions of a subject.
With a qualitative approach, you will have to collect responses from respondents and look at them in all their richness to develop theories about the field you are exploring.
Finally, you can also use a mix of qualitative and quantitative methods (which is becoming increasingly popular among researchers these days). This method is beneficial if you are interested in putting quantitative data into a real-world context or reflecting different perspectives on a subject.
Research philosophy in the ‘research onion.’
Methods of Data Collection and Data Analysis
This section will require you to clearly specify how you gathered the data and briefly discuss the tools you used to analyse it. For example, you may choose to conduct surveys and/or interviews as part of the data collection process.
Similarly, if you used software such as Excel or SPSS to process the data , you will have to justify your software choice. In this section of your methodology chapter , you will also have to explain how you arrived at your findings and how reliable they are.
It is important to note that your readers or supervisor would want to see a correlation between your findings and the hypothesis/research questions you based your study on at the very beginning.
Your supervisor or dissertation research assistant can play a key role in helping you write the methodology chapter according to established research standards. So, keep your supervisor in the loop to get their contributions and recommendations throughout the process.
In this section, you should briefly describe the methods you’ve used to analyse the data you’ve collected.
Qualitative Methods
The qualitative method includes analysing language, images, audio, videos, or any textual data (textual analysis). The following types of methods are used in textual analysis .
Discourse analysis:
Discourse analysis is an essential aspect of studying a language and its uses in day-to-day life.
Content analysis:
It is a method of studying and retrieving meaningful information from documents Thematic analysis:
It’s a method of identifying patterns of themes in the collected information, such as face-to-face interviews, texts, and transcripts.
Example: After collecting the data, it was checked thoroughly to find the missing information. The interviews were transcribed, and textual analysis was conducted. The repetitions of the text, types of colours displayed, and the tone of the speakers was measured.
Quantitative Methods
Quantitative data analysis is used for analysing numerical data. Include the following points:
- The methods of preparing data before analysing it.
- Which statistical test you have used? (one-ended test, two-ended test)
- The type of software you’ve used.
Ethical Considerations, Reliability and Limitations of a Dissertation Methodology
Other important sections of your methodology are:
Ethical Considerations
Always consider how your research will influence other individuals who are beyond the scope of the study. This is especially true for human subjects. As a researcher, you are always expected to make sure that your research and ideas do not harm anyone in any way.Discussion concerning data protection, data handling and data confidentiality will also be included in this brief segment.
- How did you ensure your participants’/respondents’ anonymity and/or confidentiality?
- Did you remove any identifiable markers after conducting the study (post-test stage) so that readers wouldn’t be able to guess the identity of the participant/respondent?
- Was personal information collected according to the purpose of the research? (For instance, asking respondents their age when it wasn’t even relevant in the study). All such ethical considerations need to be mentioned.
Even though there is no established rule to include ethical considerations and limitations within the methodology section, it’s generally recommended to include it in this section, as it makes more sense than including it, say, after the discussions section or within the conclusion.
This is mainly because limitations almost always occur in the methodology stage of research. And ethical considerations need to be taken while sampling, an important aspect of the research methodology.
Here are some examples of ethical issues that you should be mindful of
- Does your research involve participants recalling episodes of suffering and pain?
- Are you trying to find answers to questions considered culturally sensitive either by participants or the readers?
- Are your research, analysis and findings based on a specific location or a group of people?
All such issues should be categorically addressed and a justification provided for your chosen research methodology by highlighting the study’s benefits.
Reliability
Is your research study and findings reliable for other researchers in your field of work? To establish yourself as a reliable researcher, your study should be both authentic and reliable.
Reliability means the extent to which your research can yield similar results if it was replicated in another setting, at a different time, or under different circumstances. If replication occurs and different findings come to light, your (original) research would be deemed unreliable.
Limitations
Good dissertation writers will always acknowledge the limitations of their research study. Limitations in data sampling can decrease your results’ reliability.
A classic example of research limitation is collecting responses from people of a certain age group when you could have targeted a more representative cross-section of the population.Be humble and admit to your own study’s limitations. Doing so makes your referees, editors, supervisors, readers and anyone else involved in the research enterprise aware that you were also aware of the things that limited your study.
Limitations are NOT the same as implications. Sometimes, the two can be confused. Limitations lead to implications, that is, due to a certain factor being absent in the study (limitation) for instance, future research could be carried out in a setting where that factor is present (implication).
Dissertation Methodology Example
At this point, you might have a basic understanding of how to craft a well-written, organised, accurate methodology section for your dissertation. An example might help bring all the aforementioned points home. Here is a dissertation methodology example in pdf to better understand how to write methodology for a dissertation.
Sample Dissertation Methodology
Does your Research Methodology Have the Following?
- Great Research/Sources
- Perfect Language
- Accurate Sources
If not, we can help. Our panel of experts makes sure to keep the 3 pillars of Research Methodology strong.

Types of Methodologies
A scientific or lab-based study.
A methodology section for a scientific study will need to elaborate on reproducibility and meticulousness more than anything else. If your methods have obvious flaws, the readers are not going to be impressed. Therefore, it is important to ensure that your chosen research methodology is vigorous in nature.
Any information related to the procedure, setup and equipment should be clearly stated so other researchers in your field of study can work with the same method in the future if needed.
Variables that are likely to falsify your data must be taken into the equation to avoid ambiguities. It is recommended to present a comprehensive strategy to deal with these variables when gathering and analysing the data and drawing conclusions.
Statistical models employed as part of your scientific study will have to be justified, and so your methodology should include details of those statistical models.
Another scholar in the future might use any aspect of your methodology as the starting point for their research. For example, they might base their research on your methodology but analyse the data using other statistical models. Hence, this is something you should be mindful of.
Behavioural or Social Sciences-Based Dissertation
Like scientific or lab-based research, a behavioural and social sciences methodology needs to be built along the same lines. The chosen methodology should demonstrate reproducibility and firmness so other scholars can use your whole dissertation methodology or a part of it based on their research needs.
But there are additional issues that the researcher must take into consideration when working with human subjects. As a starting point, you will need to decide whether your analysis will be based on qualitative data, quantitative data or mixed-method of research, where qualitative data is used to provide contextual background to quantitative data or the other way around.
Here are some questions for you to consider:
- Will you observe the participants undertaking some activity, ask them to fill out a questionnaire, or record their responses during the interviews ?
- Will you base your research on existing evidence and datasets and avoid working with human subjects?
- What are the length, width, and reach of your data? Define its scope.
- Is the data highly explicit to the location or cultural setting you carried your study in, or can it be generalised to other situations and frameworks (reliability)? What are your reasons and justifications?
While you will be required to demonstrate that you have taken care of the above questions, it is equally important to make sure that you address your research study’s ethical issues side-by-side.
Of course, the first step in that regard will be to obtain formal approval for your research design from the ethics bodies (such as IRBs – institutional review boards), but still, there will be many more issues that could trigger a sense of grief and discomfort among some of the readers.
Humanities and Arts Dissertation Project
The rigour and dependability of the methods of research employed remain undisputed and unquestionable for humanities and arts-based dissertations as well. However, the way you convince your readers of your dissertation’s thoroughness is slightly different.
Unlike social science dissertation or a scientific study, the methodology of dissertations in arts and humanities subjects needs to be directly linked to the literature review regardless of how innovative your dissertation’s topic might be.
For example, you could demonstrate the relationship between A and B to discover a new theoretical background or use existing theories in a new framework.
The methodology section of humanities and arts-based dissertations is less complex, so there might be no need to justify it in detail. Students can achieve a seamless transition from the literature review to the analysis section.
However, like with every other type of research methodology, it is important to provide a detailed justification of your chosen methodology and relate it to the research problem.
Failing to do so could leave some readers unconvinced of your theoretical foundations’ suitability, which could potentially jeopardise your whole research.
Make sure that you are paying attention to and giving enough information about the social and historical background of the theoretical frameworks your research methodology is based on. This is especially important if there is an essential difference of opinion between your research and the research done on the subject in the past.
A justification of why opposing schools of thought disagree and why you still went ahead to use aspects of these schools of thought in your methodology should be clearly presented for the readers to understand how they would support your readings.
A Dissertation in Creative Arts
Some degree programs in the arts allow students to undertake a portfolio of artworks or creative writing rather than produce an extended dissertation research project.However, in practice, your creative research will be required to be submitted along with a comprehensive evaluative paper, including background information and an explanation that hypothesises your innovative exercise.
While this might seem like an easy thing to do, critical evaluation of someone’s work is highly complex and notorious in nature. This further reinforces the argument of developing a rigorous methodology and adhering to it.
As a scholar, you will be expected to showcase the ability to critically analyse your methodology and show that you are capable of critically evaluating your own creative work.Such an approach will help you justify your method of creating the work, which will give the readers the impression that your research is grounded in theory.
What to Avoid in Methodology?
All chapters of a dissertation paper are interconnected. This means that there will undoubtedly be some information that would overlap between the different chapters of the dissertation .
For example, some of the text material may seem appropriate to both the literature review and methodology sections; you might even end up moving information from pillar to post between different chapters as you edit and improve your dissertation .
However, make sure that you are not making the following a part of your dissertation methodology, even though it may seem appropriate to fit them in there:
A Long Review of Methods Employed by Previous Researchers
It might seem relevant to include details of the models your dissertation methodology is based on. However, a detailed review of models and precedents used by other scholars and theorists will better fit in the literature review chapter, which you can link back to. This will help the readers understand why you decided to go in favour of or against a certain tactic.
Unnecessary Details Readers Might Not be Interested In
There is absolutely no need to provide extensive details of things like lab equipment and experiment procedures. Having such information in the methodology chapter would discourage some readers who might not be interested in your equipment, setup, lab environment, etc.
Your aim as the author of the document will be to retain the readers’ interest and make the methodology chapter as readable as possible.
While it is important to get all the information relating to how others can reproduce your experiment, it is equally important to ensure your methodology section isn’t unnecessarily long. Again, additional information is better to be placed within the appendices chapter.
The methodology is not the section to provide raw data, even if you are only discussing the data collection process. All such information should be moved to the appendices section.
Even if you feel some finding or numerical data is crucial to be presented within the methodology section, you can, at most, make brief comments about such data. Its discussion, however, is only allowed in the discussions section .
What Makes your Methodology Stand Out?
The factors which can determine if your dissertation methodology is ‘great’ depend on many factors, including the level of study you are currently enrolled in.
Undergraduate dissertations are, of course, less complex and less demanding. At most universities in the UK, undergraduate students are required to exhibit the ability to conduct thorough research as they engage for the first time with theoretical and conceptual frameworks in their chosen research area.
As an undergraduate student, you will be expected to showcase the capacity to reproduce what you have learnt from theorists in your academic subject, transform your leanings into a methodology that would help you address the research problem, and test the research hypothesis, as mentioned in the introduction chapter.
A great undergraduate-level dissertation will incorporate different schools of thought and make a valuable contribution to existing knowledge. However, in general, undergraduate-level dissertations’ focus should be to show thorough desk-based and independent research skills.
Postgraduate dissertation papers are much more compound and challenging because they are expected to make a substantial contribution to existing knowledge.
Depending on the academic institute, some postgraduate students are even required to develop a project published by leading academic journals as an approval of their research skills.
It is important to recognise the importance of a postgraduate dissertation towards building your professional career, especially if your work is considered impactful in your area of study and receives citations from multiple scholars, enhancing your reputation in academic communities.
Even if some academics cite your literature review and conclusion in their own work, it is a well-known fact that your methodology framework will result in many more citations regardless of your academic subject.
Other scholars and researchers in your area of study are likely to give much more value to a well-crafted methodology, especially one they can use as the starting point for their own research.
Of course, they can alter, refine and enhance your methodology in one way or another. They can even apply your methodological framework to a new data set or apply it in a completely new situation that is irrelevant to your work.
Finally, postgraduate dissertations are expected to be highly convincing and demonstrate in-depth engagement. They should be reproducible and show rigour, so the findings and conclusions can be regarded as authentic and reliable among scientific and academic communities.
The methodology is the door to success when it comes to dissertation projects. An original methodology that takes into consideration all aspects of research is likely to have an impact on the field of study.
As a postgraduate student, you should ask yourself, Is my dissertation methodology reproducible and transferable? Producing a methodology that others can reproduce in the future is as important as answering research questions .
The methodology chapter can either make or break the grade of your research/dissertation paper. It’s one of the research elements that leave a memorable impression on your readers. So, it would help if you took your time when it comes to choosing the right design and philosophical approach for your research.
Always use authentic academic sources and discuss your plans in detail with your supervisor if you believe your research design or approach has flaws in it.
Did this article help you learn how to write a dissertation methodology and how to structure a dissertation methodology? Let us know in your comments.
Are you struggling to create a thorough and well-rounded dissertation methodology?
Avail of our dissertation writing services ! At ResearchProspect, we have Master’s and PhD qualified dissertation writers for all academic subjects, so you can be confident that the writer we will assign to your dissertation order will be an expert in your field of study. They can help you with your whole dissertation or just a part of it. You decide how much or how little help you need.
You May Also Like
Are you looking for intriguing and trending dissertation topics? Get inspired by our list of free dissertation topics on all subjects.
Looking for an easy guide to follow to write your essay? Here is our detailed essay guide explaining how to write an essay and examples and types of an essay.
Learn about the steps required to successfully complete their research project. Make sure to follow these steps in their respective order.
More Interesting Articles
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works
- First-Year Admissions
- Transfer Admissions
- Financial Aid
- Graduate Admissions
- Medical Education Admissions
- International Admissions
- Tours & Open Houses
- Online Learning
- Degree Completion
- Colleges & Schools
- Degrees & Programs
- Courses, Schedules & Registration
- Student Success
- International
- Winter & Summer Sessions
- Camden Campus
- Rowan University Libraries
- The Arts at Rowan
- Athletics & Sports Recreation
- Health & Safety
- Housing & Dining
- Technology on Campus
- Entertainment & Culture
- Rowan Thrive
- Cooper Medical School of Rowan University (MD)
- Virtua Health College of Medicine & Life Sciences (DO)
- Shreiber School of Veterinary Medicine (DVM)
- Office of Research
- Research Centers & Institutes
- South Jersey Technology Park
- Research News
- Military/Veterans
- Our Past, Present & Future
- Visiting Rowan
- Working at Rowan
- Rowan Fast Facts
- Giving to Rowan
- News & Events
Job Postings
Welcome to rowan university’s career site.
A top 100 national public research institution, Rowan University offers bachelor’s through doctoral and professional programs in person and online to 22,000 students through its main campus in Glassboro, N.J., its medical school campuses in Camden and Stratford, and five others. The University has earned national recognition for innovation, commitment to high-quality, affordable education, and developing public-private partnerships. A Carnegie-classified R2 (high research activity) institution, Rowan has been recognized as the fourth fastest-growing public research university, as reported by The Chronicle of Higher Education. For more information on Rowan University, click here
All positions are contingent upon budget appropriations.
Please send any inquiries to [email protected]
Assistant Teaching Professor, Department of Writing Arts - Temporary
Apply now Job no: 499768 Work type: Temporary Full-Time Location: Glassboro, New Jersey Categories: Faculty - Ric Edelman College of Communication & Creative Arts
The Department of Writing Arts at Rowan University is seeking to fill two temporary assistant teaching professor positions to begin Fall 2024. The positions are 10-month, with the appointment of 2 years, and include benefits. Successful candidates will teach a total of 24 credits over two semesters, with the option to teach overload and summer classes for additional compensation. Assignments are determined by departmental need and based on the faculty member's experience and expertise. Candidates should anticipate teaching at the undergraduate level, primarily in the First-Year Writing Program, which includes specialized, discipline-specific sections for Engineering, Computer Science, and/or Business students. Faculty are eligible to teach overloads during the academic year and also are eligible to teach during summer sessions. Candidates must be available to teach five days per week.
In service to the department, faculty in this position are expected to serve on committees, including, but not limited to, curriculum development, assessment, and outreach. Faculty may also pursue other service responsibilities as sought or assigned. In addition, faculty are expected to engage in professional development.
The successful candidate will join a thriving department that offers a BA in Writing Arts, multiple minors and certificates of undergraduate study, and an MA in Writing. Our faculty pursue diverse scholarly and creative agendas and publish in national and international forums. Located in the Ric Edelman College of Communication and Creative Arts, we are one of the few standalone writing departments in the nation. More information can be found on the department’s official webpage at http://www.rowan.edu/wa .
A top 100 national public research institution, Rowan University offers bachelor’s through doctoral and professional programs in person and online to 22,000 students through its main campus in Glassboro, N.J., its medical school campuses in Camden and Stratford, and five others. The University has earned national recognition for innovation, commitment to high-quality, affordable education, and developing public-private partnerships. A Carnegie-classified R2 (high research activity) institution, Rowan has been recognized as the fourth fastest-growing public research university, as reported by The Chronicle of Higher Education.
Qualifications:
Three years of experience teaching writing at the college level preferred; experience teaching Engineering students is especially desirable, but not required.
MA in composition and rhetoric, creative writing, technical and professional writing, or a related field is required. Ph.D. is expected.
Starting Date:
September 1, 2024
Application Package:
Applications will be reviewed starting August 6th until the positions are filled.
Submissions must be a single PDF file containing the following:
A cover letter/statement, addressing how you apply your teaching philosophy through specific examples of teaching practices (such as course/assignment design, assigned readings, class activities, and/or response to student writing). The cover letter should also discuss your relevant teaching experience in first-year writing courses and/or discipline-specific writing courses.
A C.V. or resume
A statement of your teaching philosophy
An assignment sheet for a writing project representative of your primary teaching experience
One set of recent student evaluations
Contact information for three professional references
- Candidates must be legally authorized to work in the US and the university will not sponsor an applicant for a work visa for this position.
Advertised: Jul 29 2024 Eastern Daylight Time Applications close:
Back to search results Apply now Refer a friend
We will email you new jobs that match this search.
Great, we can send you jobs like this, if this is your first time signing up, please check your inbox to confirm your subscription.
The email address was invalid, please check for errors.
You must agree to the privacy statement
Search results
| Position | Location | Closes |
|---|---|---|
| Glassboro, New Jersey | ||
| The Department of Writing Arts at Rowan University is seeking to fill two temporary assistant teaching professor positions to begin Fall 2024. These temporary full-time positions come with 10-month contracts with benefits for academic years 2024-2025 and 2025-2026. Faculty in these positions will teach 12 credits per semester in both fall and spring, with assignments determined by departmental need and based on the faculty member's experience and expertise. | ||
Current Opportunities
| Position | Location | Closes |
|---|---|---|
| Glassboro, New Jersey |
Powered by PageUp
About Rowan University
A top 100 national public research institution, Rowan University offers bachelor’s through doctoral and professional programs in person and online to 22,000 students through its main campus in Glassboro, N.J., its medical school campuses in Camden and Stratford, and five others. Rowan University is home to eight colleges and nine schools. For more information on these colleges, please click here .
Now celebrating its Centennial, Rowan focuses on practical research at the intersection of engineering, medicine, science, and business while ensuring excellence in undergraduate education. The University has earned national recognition for innovation, commitment to high-quality and affordable education, and developing public-private partnerships. A Carnegie-classified R2 (high research activity) institution, Rowan has been recognized as the fourth fastest-growing public research university, as reported by The Chronicle of Higher Education.
Non-Discrimation at Rowan University
Rowan University celebrates diversity and is committed to creating an inclusive environment for all employees. All qualified applicants will receive consideration for employment without regard to age, ethnicity, race, religion, sex, gender identity or expression, genetic information, marital status, national origin, (dis)ability status, military status, and other NJ protected classes. Rowan University does not discriminate on the basis of sex in its educational programs and activities, including employment as required by Title IX. Rowan is committed to providing access, equal opportunity, and reasonable accommodation for individuals with (dis)abilities.
To request reasonable accommodation, contact Christy Mroz, Administrative Assistant, [email protected], 856-256-5494. Rowan strongly encourages applicants from underrepresented groups to apply.
Pursuant to Title IX of the Education Amendments of 1972 and supporting regulations, Rowan does not discriminate on the basis of sex in the education programs or activities that it operates; this extends to admission and employment. Inquiries about the application of Title IX and its supporting regulations may be directed to the Assistant Secretary for Civil Rights, Office for Civil Rights, U.S. Department of Education, or to the University’s Title IX Coordinator, Office of Student Equity & Compliance, Rowan University, Hawthorne Hall, Suite 312, 201 Mullica Hill Rd, Glassboro, NJ 08028, [email protected] , 856-256-5440.
For information on the Title IX Sexual Harassment/Sexual Assault policy and grievance procedures, please click here .
More Information
Rowan University is subject to the residency requirements of the NJ First Act (N.J.S.A. 52:14-7, P.L. 2011, Chapter 70). Any person hired to a non-exempt position shall either have their principal residence in New Jersey or have one (1) year from the date of employment to establish, and then maintain, principal residence in the State of New Jersey. Any person hired to an exempt position shall either have their principal residence in New Jersey, Delaware, Pennsylvania, or New York or have ninety (90) days from the date of employment to establish, then maintain, principal residence in the State of New Jersey, Delaware, Pennsylvania, or New York.
Rowan University is committed to assisting all members of the Rowan community in providing for their own safety and security. The Annual Security and Fire Safety Report is available on the Department of Public Safety website at: https://sites.rowan.edu/publicsafety/_docs/annual_security_report.pdf
If you would like to receive a hard copy of the Annual Security and Fire Safety Report which contains this information, you can stop by the Department of Public Safety Office, located at Bole Hall Annex, 201 Mullica Hill Road, Glassboro, NJ 08028 or you can request that a copy be mailed to you by calling (856) 256-4562 or 4506.
The report contains information regarding campus security and personal safety including topics such as: crime prevention, public safety authority, crime reporting policies, fire safety, disciplinary procedures and other matters of importance related to security on campus. The report also contains information about fire statistics in Rowan University Residential Facilities and crime statistics for the three previous calendar years concerning reported crimes that occurred on campus; in certain off-campus buildings or property owned or controlled by the University; and on public property within, or immediately adjacent to and accessible from the campus. This information is required by federal law, Jeanne Clery Disclosure of Campus Security Policy and Campus Crime Statistics Act or "Clery Act" and is provided by the Rowan University Department of Public Safety.
Position Search
Filter results.
- Temporary Full-Time 1
- Glassboro, New Jersey 1
- Faculty - Ric Edelman College of Communication & Creative Arts 1
- Rowan on Twitter
- Rowan on Facebook
- Rowan on Instagram
- Rowan on YouTube
- Rowan on Flickr
Rowan University • 201 Mullica Hill Road • Glassboro, New Jersey 08028 • 856-256-4000
©2024 Rowan University. Consumer Disclosures .
Read the Notice of Availability of Rowan’s Annual Security & Fire Safety Report

University of Dar es Salaam Library Journal Journal / University of Dar es Salaam Library Journal / Vol. 19 No. 1 (2024) / Articles (function() { function async_load(){ var s = document.createElement('script'); s.type = 'text/javascript'; s.async = true; var theUrl = 'https://www.journalquality.info/journalquality/ratings/2408-www-ajol-info-udslj'; s.src = theUrl + ( theUrl.indexOf("?") >= 0 ? "&" : "?") + 'ref=' + encodeURIComponent(window.location.href); var embedder = document.getElementById('jpps-embedder-ajol-udslj'); embedder.parentNode.insertBefore(s, embedder); } if (window.attachEvent) window.attachEvent('onload', async_load); else window.addEventListener('load', async_load, false); })();
Article sidebar.

Article Details
Copyright for articles published in this journal is retained by the journal.
The content is licensed unader a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs (CC BY-NC-ND) License.
Main Article Content
Postgraduate students’ common errors in writing education studies dissertations lessons from the university of dar es salaam in tanzania, george kahangwa.
The purpose of this study was to investigate common mistakes that postgraduates make in writing dissertation chapters at the University of Dar es Salaam in Tanzania, then propose corrective measures. Using a desk research design, the study reviewed 200 randomly selected master’s degree dissertations. The document review guidelines also facilitated the study’s review of examiners’ reports on the dissertations under review. The information collected was subjected to content analysis. The study found that postgraduate students struggled in stating explicitly the research problems and ended up with vague problem statements. In the limitations section, most of the postgraduates mention trivial issues that the researcher could otherwise address during the planning of logistics. Moreover, the students struggled to critically review literature and, instead, simply described the details or provided summaries of findings from other empirical studies. As a result, the literature review is usually devoid of their respective voices. Students also found difficulties in describing the relationship between the proposed methodology and their study specifically by failing to explain adequately the coherence between the methodology and the nature of the study. Furthermore, some postgraduates failed to analyse data with the required precision; for instance, they use codes and themes interchangeably. Based on the findings, the study recommends intensive and adequate orientation and training of postgraduate students both theoretically and practically on fundamental academic skills for effective writing of quality dissertations.
AJOL is a Non Profit Organisation that cannot function without donations. AJOL and the millions of African and international researchers who rely on our free services are deeply grateful for your contribution. AJOL is annually audited and was also independently assessed in 2019 by E&Y.
Your donation is guaranteed to directly contribute to Africans sharing their research output with a global readership.
- For annual AJOL Supporter contributions, please view our Supporters page.
Journal Identifiers


COMMENTS
How To Write A Dissertation: 8 Steps. Clearly understand what a dissertation (or thesis) is; Find a unique and valuable research topic; Craft a convincing research proposal; Write up a strong introduction chapter; Review the existing literature and compile a literature review; Design a rigorous research strategy and undertake your own research; Present the findings of your research
Empirical Dissertations. So, let's dive right in with empirical dissertations—arguably the most hands-on type of dissertation out there. If you're studying a field like psychology, biology, or social sciences, you're probably going to become very familiar with this approach.
Whether you're considering a doctoral program or you recently passed your comprehensive exams, you've probably wondered how to write a dissertation. Researching, writing, and defending a dissertation represents a major step in earning a doctorate. But what is a dissertation exactly?
A dissertation is a long-form piece of academic writing based on original research conducted by you. It is usually submitted as the final step in order to finish a PhD program. Your dissertation is probably the longest piece of writing you've ever completed.
Abstract or executive summary. The dissertation abstract (or executive summary for some degrees) serves to provide the first-time reader (and marker or moderator) with a big-picture view of your research project. It should give them an understanding of the key insights and findings from the research, without them needing to read the rest of the report - in other words, it should be able to ...
Many dissertations are structured into four key sections: introduction & literature review; methods; results; discussion; There are many different types of dissertation, which don't all use this structure, so make sure you check your dissertation guidance.
Before you begin, make sure that you are familiar with the dissertation genre—what it is for and what it looks like. Purpose. Generally speaking, a dissertation's purpose is to prove that you have the expertise necessary to fulfill your doctoral-degree requirements by showing depth of knowledge and independent thinking.
Dissertation is a lengthy and detailed academic document that presents the results of original research on a specific topic or question....
Dissertation Methodology. In any research, the methodology chapter is one of the key components of your dissertation. It provides a detailed description of the methods you used to conduct your research and helps readers understand how you obtained your data and how you plan to analyze it.
What Is a Dissertation? | 5 Essential Questions to Get Started. Published on 26 March 2020 by Jack Caulfield.Revised on 5 May 2022. A dissertation is a large research project undertaken at the end of a degree.
Dissertations focus on a topic you propose. Faculty qualified in your area of research must approve the dissertation topic. The approval process can be lengthy and complex, differing according to academic discipline and institution.
A thesis is a comprehensive academic paper based on your original research that presents new findings, arguments, and ideas of your study. It's typically submitted at the end of your master's degree or as a capstone of your bachelor's degree.
Abstract. Usually around 300 words long, the abstract is meant to be a concise summary of your dissertation. It should briefly cover the question(s) you aim to answer, your primary argument and your conclusion. Introduction. The purpose of the introduction is to provide context for the rest of the dissertation, setting out your aims and the scope of what you want to achieve with your research.
A dissertation is a paper explaining the individual research that a student has conducted to earn a degree. It usually consists of several sections or chapters.
USC was at the forefront in distinguishing the EdD dissertation (i.e., the purpose of the degree) from that of the PhD. We see the EdD as being about the preparation of scholarly education leaders - "scholarly" here referring to having the ability to translate educational research into practical applications to improve outcomes.
The Cambridge dictionary states that a dissertation is a long piece of writing on a particular subject, especially one that is done to receive a degree at college or university, but that is just the tip of the iceberg because a dissertation project has a lot more meaning and context.
Empirical dissertations. An empirical dissertation involves collecting data. For example, to gather the views of patients at a GP's surgery, volunteers in a police service, children in a play centre or translators in a refugee centre, you have to find ways of asking the individuals involved what they think or review what they're doing.
Table of Contents. Table of contents is the section of a dissertation that guides each section of the dissertation paper's contents. Depending on the level of detail in a table of contents, the most useful headings are listed to provide the reader the page number on which said information may be found at.
Preparing for your doctoral dissertation takes serious perseverance. You've endured years of studies and professional development to get to this point.
Research methods are the techniques and procedures used for conducting research. Choosing the right research method for your writing is an important aspect of the research process. You need to either collect data or talk to the people while conducting any research.
Thesis. Definition: Thesis is a scholarly document that presents a student's original research and findings on a particular topic or question. It is usually written as a requirement for a graduate degree program and is intended to demonstrate the student's mastery of the subject matter and their ability to conduct independent research.
Understand how to develop content or subject matter in ways that meet the expectations of your research community. Our trained consultants will help you p lan, write, revise or format your thesis or dissertation to better articulate the significance of your research.
Free, individual consultations with trained thesis/dissertation writing and formatting consultants who help you navigate the organization, structure, and formatting of your document.
This set of OWL resources aims to help engineering instructors and TAs create and assess a variety of short, low-overhead writing exercises for use in engineering courses. The primary focus here is on "writing to learn" assignments, which leverage writing to improve students' conceptual understanding of technical concepts. Writing exercises can be used in engineering courses to promote ...
Describe the importance of a strong research question; Identify methods for exploring existing literature; Understand the difference between keywords and controlled vocabulary
Writing a Methodology for your Dissertation | Complete Guide & Steps What is a Methodology? The methodology is perhaps the most challenging and laborious part of the dissertation.Essentially, the methodology helps in understanding the broad, philosophical approach behind the methods of research you chose to employ in your study.
This guide explains the focus, rigor, and relevance of qualitative research, highlighting its role in dissecting complex social phenomena and providing in-depth, human-centered insights. The guide ...
Many individuals dread taking a public speaking class in college. As many as 77% of Americans say they suffer from a fear of public speaking. 1 If you are one of the individuals that shares this fear, you can still benefit from this practice in college. By building your confidence and understanding the purpose behind your speech, you can apply the skills from this class to your life after college.
Rowan University is subject to the residency requirements of the NJ First Act (N.J.S.A. 52:14-7, P.L. 2011, Chapter 70). Any person hired to a non-exempt position shall either have their principal residence in New Jersey or have one (1) year from the date of employment to establish, and then maintain, principal residence in the State of New Jersey.
The purpose of this study was to investigate common mistakes that postgraduates make in writing dissertation chapters at the University of Dar es Salaam in Tanzania, then propose corrective measures. Using a desk research design, the study reviewed 200 randomly selected master's degree dissertations. The document review guidelines also facilitated the study's review of examiners' reports ...