- Skip to secondary menu
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
Statistics By Jim
Making statistics intuitive

Null Hypothesis: Definition, Rejecting & Examples
By Jim Frost 6 Comments
What is a Null Hypothesis?
The null hypothesis in statistics states that there is no difference between groups or no relationship between variables. It is one of two mutually exclusive hypotheses about a population in a hypothesis test.

- Null Hypothesis H 0 : No effect exists in the population.
- Alternative Hypothesis H A : The effect exists in the population.
In every study or experiment, researchers assess an effect or relationship. This effect can be the effectiveness of a new drug, building material, or other intervention that has benefits. There is a benefit or connection that the researchers hope to identify. Unfortunately, no effect may exist. In statistics, we call this lack of an effect the null hypothesis. Researchers assume that this notion of no effect is correct until they have enough evidence to suggest otherwise, similar to how a trial presumes innocence.
In this context, the analysts don’t necessarily believe the null hypothesis is correct. In fact, they typically want to reject it because that leads to more exciting finds about an effect or relationship. The new vaccine works!
You can think of it as the default theory that requires sufficiently strong evidence to reject. Like a prosecutor, researchers must collect sufficient evidence to overturn the presumption of no effect. Investigators must work hard to set up a study and a data collection system to obtain evidence that can reject the null hypothesis.
Related post : What is an Effect in Statistics?
Null Hypothesis Examples
Null hypotheses start as research questions that the investigator rephrases as a statement indicating there is no effect or relationship.
| Does the vaccine prevent infections? | The vaccine does not affect the infection rate. |
| Does the new additive increase product strength? | The additive does not affect mean product strength. |
| Does the exercise intervention increase bone mineral density? | The intervention does not affect bone mineral density. |
| As screen time increases, does test performance decrease? | There is no relationship between screen time and test performance. |
After reading these examples, you might think they’re a bit boring and pointless. However, the key is to remember that the null hypothesis defines the condition that the researchers need to discredit before suggesting an effect exists.
Let’s see how you reject the null hypothesis and get to those more exciting findings!
When to Reject the Null Hypothesis
So, you want to reject the null hypothesis, but how and when can you do that? To start, you’ll need to perform a statistical test on your data. The following is an overview of performing a study that uses a hypothesis test.
The first step is to devise a research question and the appropriate null hypothesis. After that, the investigators need to formulate an experimental design and data collection procedures that will allow them to gather data that can answer the research question. Then they collect the data. For more information about designing a scientific study that uses statistics, read my post 5 Steps for Conducting Studies with Statistics .
After data collection is complete, statistics and hypothesis testing enter the picture. Hypothesis testing takes your sample data and evaluates how consistent they are with the null hypothesis. The p-value is a crucial part of the statistical results because it quantifies how strongly the sample data contradict the null hypothesis.
When the sample data provide sufficient evidence, you can reject the null hypothesis. In a hypothesis test, this process involves comparing the p-value to your significance level .
Rejecting the Null Hypothesis
Reject the null hypothesis when the p-value is less than or equal to your significance level. Your sample data favor the alternative hypothesis, which suggests that the effect exists in the population. For a mnemonic device, remember—when the p-value is low, the null must go!
When you can reject the null hypothesis, your results are statistically significant. Learn more about Statistical Significance: Definition & Meaning .
Failing to Reject the Null Hypothesis
Conversely, when the p-value is greater than your significance level, you fail to reject the null hypothesis. The sample data provides insufficient data to conclude that the effect exists in the population. When the p-value is high, the null must fly!
Note that failing to reject the null is not the same as proving it. For more information about the difference, read my post about Failing to Reject the Null .
That’s a very general look at the process. But I hope you can see how the path to more exciting findings depends on being able to rule out the less exciting null hypothesis that states there’s nothing to see here!
Let’s move on to learning how to write the null hypothesis for different types of effects, relationships, and tests.
Related posts : How Hypothesis Tests Work and Interpreting P-values
How to Write a Null Hypothesis
The null hypothesis varies by the type of statistic and hypothesis test. Remember that inferential statistics use samples to draw conclusions about populations. Consequently, when you write a null hypothesis, it must make a claim about the relevant population parameter . Further, that claim usually indicates that the effect does not exist in the population. Below are typical examples of writing a null hypothesis for various parameters and hypothesis tests.
Related posts : Descriptive vs. Inferential Statistics and Populations, Parameters, and Samples in Inferential Statistics
Group Means
T-tests and ANOVA assess the differences between group means. For these tests, the null hypothesis states that there is no difference between group means in the population. In other words, the experimental conditions that define the groups do not affect the mean outcome. Mu (µ) is the population parameter for the mean, and you’ll need to include it in the statement for this type of study.
For example, an experiment compares the mean bone density changes for a new osteoporosis medication. The control group does not receive the medicine, while the treatment group does. The null states that the mean bone density changes for the control and treatment groups are equal.
- Null Hypothesis H 0 : Group means are equal in the population: µ 1 = µ 2 , or µ 1 – µ 2 = 0
- Alternative Hypothesis H A : Group means are not equal in the population: µ 1 ≠ µ 2 , or µ 1 – µ 2 ≠ 0.
Group Proportions
Proportions tests assess the differences between group proportions. For these tests, the null hypothesis states that there is no difference between group proportions. Again, the experimental conditions did not affect the proportion of events in the groups. P is the population proportion parameter that you’ll need to include.
For example, a vaccine experiment compares the infection rate in the treatment group to the control group. The treatment group receives the vaccine, while the control group does not. The null states that the infection rates for the control and treatment groups are equal.
- Null Hypothesis H 0 : Group proportions are equal in the population: p 1 = p 2 .
- Alternative Hypothesis H A : Group proportions are not equal in the population: p 1 ≠ p 2 .
Correlation and Regression Coefficients
Some studies assess the relationship between two continuous variables rather than differences between groups.
In these studies, analysts often use either correlation or regression analysis . For these tests, the null states that there is no relationship between the variables. Specifically, it says that the correlation or regression coefficient is zero. As one variable increases, there is no tendency for the other variable to increase or decrease. Rho (ρ) is the population correlation parameter and beta (β) is the regression coefficient parameter.
For example, a study assesses the relationship between screen time and test performance. The null states that there is no correlation between this pair of variables. As screen time increases, test performance does not tend to increase or decrease.
- Null Hypothesis H 0 : The correlation in the population is zero: ρ = 0.
- Alternative Hypothesis H A : The correlation in the population is not zero: ρ ≠ 0.
For all these cases, the analysts define the hypotheses before the study. After collecting the data, they perform a hypothesis test to determine whether they can reject the null hypothesis.
The preceding examples are all for two-tailed hypothesis tests. To learn about one-tailed tests and how to write a null hypothesis for them, read my post One-Tailed vs. Two-Tailed Tests .
Related post : Understanding Correlation
Neyman, J; Pearson, E. S. (January 1, 1933). On the Problem of the most Efficient Tests of Statistical Hypotheses . Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A . 231 (694–706): 289–337.
Share this:

Reader Interactions
January 11, 2024 at 2:57 pm
Thanks for the reply.
January 10, 2024 at 1:23 pm
Hi Jim, In your comment you state that equivalence test null and alternate hypotheses are reversed. For hypothesis tests of data fits to a probability distribution, the null hypothesis is that the probability distribution fits the data. Is this correct?
January 10, 2024 at 2:15 pm
Those two separate things, equivalence testing and normality tests. But, yes, you’re correct for both.
Hypotheses are switched for equivalence testing. You need to “work” (i.e., collect a large sample of good quality data) to be able to reject the null that the groups are different to be able to conclude they’re the same.
With typical hypothesis tests, if you have low quality data and a low sample size, you’ll fail to reject the null that they’re the same, concluding they’re equivalent. But that’s more a statement about the low quality and small sample size than anything to do with the groups being equal.
So, equivalence testing make you work to obtain a finding that the groups are the same (at least within some amount you define as a trivial difference).
For normality testing, and other distribution tests, the null states that the data follow the distribution (normal or whatever). If you reject the null, you have sufficient evidence to conclude that your sample data don’t follow the probability distribution. That’s a rare case where you hope to fail to reject the null. And it suffers from the problem I describe above where you might fail to reject the null simply because you have a small sample size. In that case, you’d conclude the data follow the probability distribution but it’s more that you don’t have enough data for the test to register the deviation. In this scenario, if you had a larger sample size, you’d reject the null and conclude it doesn’t follow that distribution.
I don’t know of any equivalence testing type approach for distribution fit tests where you’d need to work to show the data follow a distribution, although I haven’t looked for one either!
February 20, 2022 at 9:26 pm
Is a null hypothesis regularly (always) stated in the negative? “there is no” or “does not”
February 23, 2022 at 9:21 pm
Typically, the null hypothesis includes an equal sign. The null hypothesis states that the population parameter equals a particular value. That value is usually one that represents no effect. In the case of a one-sided hypothesis test, the null still contains an equal sign but it’s “greater than or equal to” or “less than or equal to.” If you wanted to translate the null hypothesis from its native mathematical expression, you could use the expression “there is no effect.” But the mathematical form more specifically states what it’s testing.
It’s the alternative hypothesis that typically contains does not equal.
There are some exceptions. For example, in an equivalence test where the researchers want to show that two things are equal, the null hypothesis states that they’re not equal.
In short, the null hypothesis states the condition that the researchers hope to reject. They need to work hard to set up an experiment and data collection that’ll gather enough evidence to be able to reject the null condition.
February 15, 2022 at 9:32 am
Dear sir I always read your notes on Research methods.. Kindly tell is there any available Book on all these..wonderfull Urgent
Comments and Questions Cancel reply

LEARN STATISTICS EASILY
Learn Data Analysis Now!

What is: Null Hypothesis
What is the null hypothesis.
The null hypothesis, often denoted as H0, is a fundamental concept in statistics and hypothesis testing. It serves as a default or baseline assumption that there is no effect or no difference in a given situation. In the context of statistical analysis, the null hypothesis posits that any observed differences in data are due to random chance rather than a specific cause. This hypothesis is crucial for researchers as it provides a framework for testing the validity of their claims and determining whether the evidence supports an alternative hypothesis, known as H1 or Ha, which suggests that there is a significant effect or difference.
Ad description. Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit.
Importance of the Null Hypothesis in Statistical Testing
The null hypothesis plays a pivotal role in the scientific method and statistical inference. By establishing a clear statement that can be tested, researchers can apply statistical techniques to determine whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis. This process is essential for drawing conclusions from data and making informed decisions based on empirical evidence. The significance of the null hypothesis lies in its ability to provide a structured approach to evaluating claims, ensuring that conclusions are not drawn prematurely or based on anecdotal evidence.
Formulating the Null Hypothesis
When formulating a null hypothesis, researchers must clearly define the variables involved and the expected relationship between them. For example, in a clinical trial testing a new medication, the null hypothesis might state that the medication has no effect on patient recovery compared to a placebo. This formulation allows for a straightforward statistical test, where the goal is to determine whether the data collected provides sufficient evidence to reject the null hypothesis in favor of the alternative hypothesis. The clarity and specificity of the null hypothesis are crucial for the integrity of the research.
Testing the Null Hypothesis
Testing the null hypothesis typically involves the use of statistical tests, such as t-tests, chi-square tests, or ANOVA, depending on the nature of the data and the research question. These tests calculate a p-value, which indicates the probability of observing the data, or something more extreme, if the null hypothesis is true. A low p-value (commonly set at a threshold of 0.05) suggests that the observed data is unlikely under the null hypothesis, leading researchers to reject H0. Conversely, a high p-value indicates insufficient evidence to reject the null hypothesis, implying that any observed differences may be attributed to random variation.
Types of Null Hypotheses
There are various types of null hypotheses, each tailored to specific research contexts. A simple null hypothesis asserts that there is no difference between two groups, while a composite null hypothesis may involve multiple parameters or conditions. In some cases, researchers may also formulate directional null hypotheses, which specify the direction of the expected effect, such as stating that one treatment is not only different from another but specifically worse. Understanding the type of null hypothesis being tested is essential for selecting the appropriate statistical methods and interpreting the results accurately.
Common Misconceptions about the Null Hypothesis
One common misconception about the null hypothesis is that it represents a statement of “no effect” or “no difference” in an absolute sense. In reality, the null hypothesis is a statistical tool used to assess the likelihood of observing the data under a specific assumption. It does not imply that there is no effect in the real world; rather, it serves as a benchmark against which evidence can be evaluated. Additionally, failing to reject the null hypothesis does not prove that it is true; it merely indicates that there is not enough evidence to support the alternative hypothesis.
Null Hypothesis in the Context of Data Science
In data science, the null hypothesis is integral to various analytical techniques, including A/B testing, regression analysis, and machine learning model evaluation. Data scientists often use the null hypothesis to assess the effectiveness of interventions, compare model performance, and validate assumptions about data distributions. By systematically testing the null hypothesis, data scientists can derive insights that inform decision-making processes and contribute to the development of robust predictive models.
Limitations of the Null Hypothesis
Despite its widespread use, the null hypothesis has limitations that researchers must consider. One significant limitation is the potential for Type I and Type II errors. A Type I error occurs when the null hypothesis is incorrectly rejected, suggesting a false positive result, while a Type II error happens when the null hypothesis is not rejected despite a true effect being present, leading to a false negative result. Additionally, the binary nature of hypothesis testing can oversimplify complex phenomena, as it does not account for the nuances and variability inherent in real-world data.
Conclusion: The Role of the Null Hypothesis in Research
The null hypothesis is a cornerstone of statistical reasoning and hypothesis testing, providing a structured approach for evaluating claims and drawing conclusions from data. Its formulation, testing, and interpretation are critical for ensuring the validity of research findings across various fields, including statistics, data analysis, and data science. Understanding the nuances of the null hypothesis enables researchers to conduct rigorous analyses and make informed decisions based on empirical evidence.
9.1 Null and Alternative Hypotheses
The actual test begins by considering two hypotheses . They are called the null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis . These hypotheses contain opposing viewpoints.
H 0 , the — null hypothesis: a statement of no difference between sample means or proportions or no difference between a sample mean or proportion and a population mean or proportion. In other words, the difference equals 0.
H a —, the alternative hypothesis: a claim about the population that is contradictory to H 0 and what we conclude when we reject H 0 .
Since the null and alternative hypotheses are contradictory, you must examine evidence to decide if you have enough evidence to reject the null hypothesis or not. The evidence is in the form of sample data.
After you have determined which hypothesis the sample supports, you make a decision. There are two options for a decision. They are reject H 0 if the sample information favors the alternative hypothesis or do not reject H 0 or decline to reject H 0 if the sample information is insufficient to reject the null hypothesis.
Mathematical Symbols Used in H 0 and H a :
| equal (=) | not equal (≠) greater than (>) less than (<) |
| greater than or equal to (≥) | less than (<) |
| less than or equal to (≤) | more than (>) |
H 0 always has a symbol with an equal in it. H a never has a symbol with an equal in it. The choice of symbol depends on the wording of the hypothesis test. However, be aware that many researchers use = in the null hypothesis, even with > or < as the symbol in the alternative hypothesis. This practice is acceptable because we only make the decision to reject or not reject the null hypothesis.
Example 9.1
H 0 : No more than 30 percent of the registered voters in Santa Clara County voted in the primary election. p ≤ 30 H a : More than 30 percent of the registered voters in Santa Clara County voted in the primary election. p > 30
A medical trial is conducted to test whether or not a new medicine reduces cholesterol by 25 percent. State the null and alternative hypotheses.
Example 9.2
We want to test whether the mean GPA of students in American colleges is different from 2.0 (out of 4.0). The null and alternative hypotheses are the following: H 0 : μ = 2.0 H a : μ ≠ 2.0
We want to test whether the mean height of eighth graders is 66 inches. State the null and alternative hypotheses. Fill in the correct symbol (=, ≠, ≥, <, ≤, >) for the null and alternative hypotheses.
- H 0 : μ __ 66
- H a : μ __ 66
Example 9.3
We want to test if college students take fewer than five years to graduate from college, on the average. The null and alternative hypotheses are the following: H 0 : μ ≥ 5 H a : μ < 5
We want to test if it takes fewer than 45 minutes to teach a lesson plan. State the null and alternative hypotheses. Fill in the correct symbol ( =, ≠, ≥, <, ≤, >) for the null and alternative hypotheses.
- H 0 : μ __ 45
- H a : μ __ 45
Example 9.4
An article on school standards stated that about half of all students in France, Germany, and Israel take advanced placement exams and a third of the students pass. The same article stated that 6.6 percent of U.S. students take advanced placement exams and 4.4 percent pass. Test if the percentage of U.S. students who take advanced placement exams is more than 6.6 percent. State the null and alternative hypotheses. H 0 : p ≤ 0.066 H a : p > 0.066
On a state driver’s test, about 40 percent pass the test on the first try. We want to test if more than 40 percent pass on the first try. Fill in the correct symbol (=, ≠, ≥, <, ≤, >) for the null and alternative hypotheses.
- H 0 : p __ 0.40
- H a : p __ 0.40
Collaborative Exercise
Bring to class a newspaper, some news magazines, and some internet articles. In groups, find articles from which your group can write null and alternative hypotheses. Discuss your hypotheses with the rest of the class.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute Texas Education Agency (TEA). The original material is available at: https://www.texasgateway.org/book/tea-statistics . Changes were made to the original material, including updates to art, structure, and other content updates.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/statistics/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: Barbara Illowsky, Susan Dean
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Statistics
- Publication date: Mar 27, 2020
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/statistics/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/statistics/pages/9-1-null-and-alternative-hypotheses
© Apr 16, 2024 Texas Education Agency (TEA). The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.
How Does the Null Hypothesis Work?
Last updated: June 2, 2024
- Math and Logic
- Probability and Statistics
Baeldung Pro comes with both absolutely No-Ads as well as finally with Dark Mode , for a clean learning experience:
>> Explore a clean Baeldung
Once the early-adopter seats are all used, the price will go up and stay at $33/year.
1. Introduction
In this tutorial, we’ll explain the role of null hypotheses in standard statistical tests.
2. Statistical Tests
Let’s say we want to check how a new, recently proposed teaching method using generative AI affects students’ quiz results. To do this, we teach one class using the new AI-powered method and another using the good old presentation slides. To ensure a fair comparison, we choose the classes with equally talented students and instruct them to use the same textbook.
After scoring the quiz, we can be tempted to compute the mean scores in both classes to see which one is better. However, if we want to generalize the conclusions, we need to use statistics . The two classes we scored in this experiment are just two samples of the entire student population. So, the results might differ if the same experiment was conducted with different students. Statistical tests help us quantify this uncertainty and draw general conclusions with high confidence (if we conduct them correctly).
Usually, statistical tests have two hypotheses: the null and the alternative.
The null hypothesis is the hypothesis of “no effect,” i.e., the hypothesis opposite to the effect we want to test for. In contrast, the alternative hypothesis is the one positing the existence of the effect of interest.
3. Effects and Null Hypothesis
The effect depends on our research question. In our example, we want to check the efficacy of a new method, so we’re interested in the score difference. We must formulate the effect using quantifiable and measurable parameters to test it statistically.
3.1. The Special Role of the Null Hypothesis
3.2. the nature of scientific proofs.
The asymmetry between the null and alternative is evident in how we act depending on the test results. We’re usually interested in proving an effect. However, we behave as if that’s true only if the results are highly incompatible with the null hypothesis, as it isn’t sufficient that they are compatible with the alternative.
This means that the null acts as our default reality model , which is the one already in place or of lower risk . For instance, if we have a well-tested and very efficient teaching method, we don’t have much incentive to change it unless the new one is substantially better. Similarly, there’s more risk in erroneously recommending the use of an inefficient or harmful drug than not detecting the efficacy of an efficient one, so having a no-effect hypothesis as a default makes sense.
Therefore, we don’t need convincing to behave as if the null is true. It’s the job of the alternative hypothesis to convince us to act otherwise.
3.3. Effect Formulation
There’s more than one way to formulate the effect of interest. The choice of formulation implicitly defines assumptions about the populations. For instance, we defined the effect as a non-zero difference of means. However, the score distributions need to have the same shape for the difference in means to indicate the distributions are different:
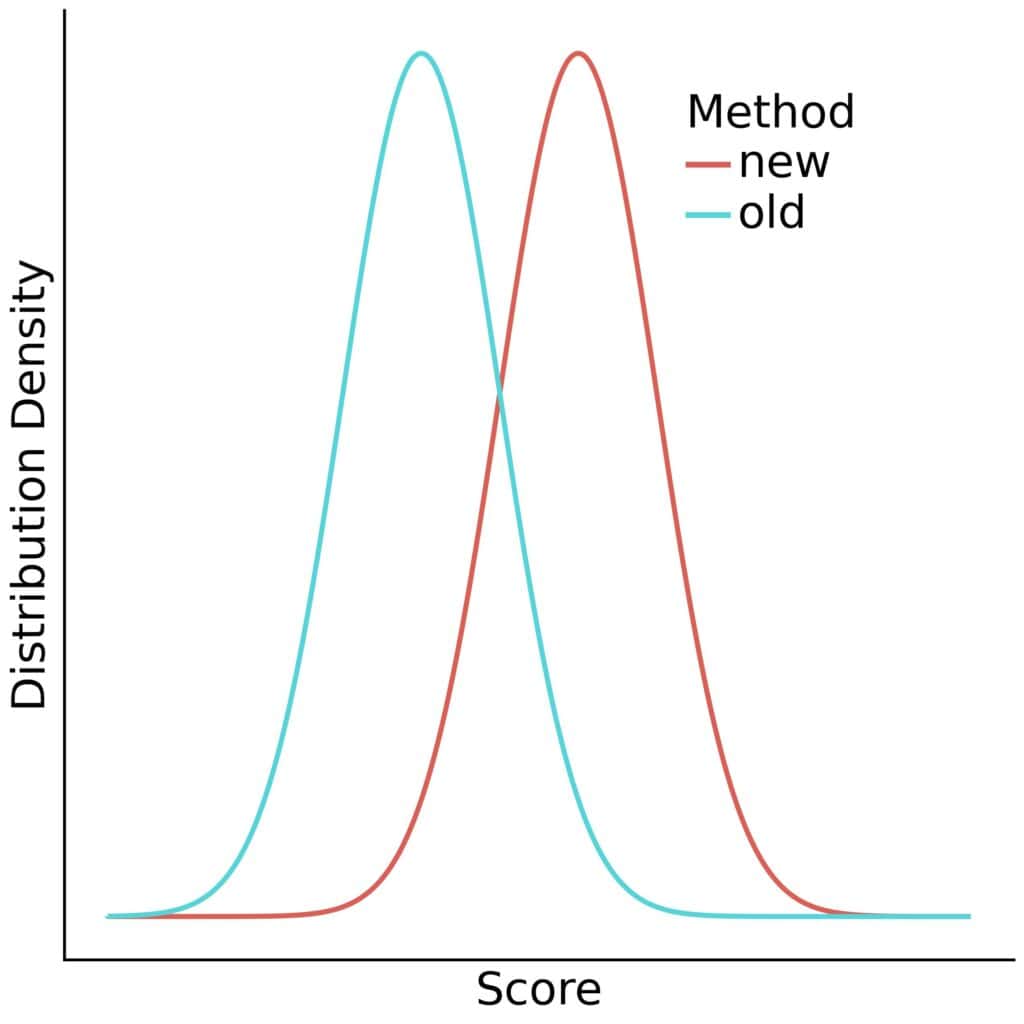
In this case, most values likely under the new method will be unlikely under the old one, and vice versa, because the distributions have the same shape. If they don’t, different means may have little to no practical significance. So, we always have to consider our implicit assumptions and formulate the effects so that they make sense.
4. Simple vs. Composite Null
4.1. the p-value.
assuming that higher values of the test statistic are less compatible with the null.
5. Conclusion
In this article, we explained the null hypothesis in statistics. It corresponds to the no-effect state of the world. We reject it in favor of the alternative hypothesis if the observed effect is unlikely under the null.
Null hypothesis
The null hypothesis (H 0 ) is the basis of statistical hypothesis testing. It is the default hypothesis (assumed to be true) that states that there is no statistically significant difference between some population parameter (such as the mean), and a hypothesized value. It is typically based on previous analysis or knowledge.
The null hypothesis is used for various purposes, such as to verify statistical assumptions, to verify that multiple experiments are producing consistent results, to directly advance theories, and more.
Most commonly, the null hypothesis is used to state the equality between two or more variables, such as a drug and a placebo. This equality is then tested in a statistical hypothesis test. Generally, the null hypothesis is the hypothesis that the researcher is attempting to disprove, though this is not necessarily always the goal. It is contrasted with the alternative hypothesis (H a ), which is a statement that there is some difference (value is greater than, less than, or not the same), and seeks to provide evidence that any observed differences are statistically significant, rather than due to random variation.
For example, the null hypothesis may state that the GPA of students at a given high school is not better than the state average. The corresponding alternative hypothesis may state that the GPA of students at a given high school is better than the state average, and a hypothesis test would then be conducted to determine whether there is sufficient evidence to reject the null hypothesis in favor of the alternative hypothesis.
Mathematically, the null hypothesis is denoted as H 0 , and is stated as
H 0 : μ = μ 0
where μ 0 is the assumed or hypothesized population mean, and μ is the mean of the population from which samples are drawn. Since the null hypothesis is a statement that there is no difference between these population parameters,
μ - μ 0 = 0
The alternative hypothesis generally takes one of three forms:
| H : μ > μ |
| H : μ |
| H : μ ≠ μ |
H 0 can also be stated as an inequality:
H 0 : μ > μ 0
The corresponding alternative hypothesis is stated as:
H a : μ ≤ μ 0
Statistical hypothesis testing
A statistical hypothesis test adheres to the following general procedure:
- State the null and alternative hypotheses.
- Select a significance level, α (the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis when the null hypothesis is true), and the appropriate test statistic.
- chi-squared test
- Reject the null hypothesis in favor of the alternative hypothesis if the observed value lies within the critical region. Otherwise, do not reject the null hypothesis.
Alternatively, instead of using critical regions, it is possible to calculate the p-value and compare it to the chosen significance level:
- If the p-value is less than or equal to the significance level, reject the null hypothesis in favor of the alternative hypothesis.
- If the p-value is greater than the significance level, do not reject the null hypothesis.
Note that the aim of this type of hypothesis test is to determine whether there is evidence to reject the null hypothesis in favor of the alternative hypothesis at a given significance level. This is not the same as proving or accepting an alternative hypothesis, since there may be evidence for the alternative hypothesis at one significance level, but not another. Also, if there is insufficient evidence for the alternative hypothesis, we fail to reject the null hypothesis, rather than accepting it; it is not possible to accept the null hypothesis.
The national average SAT score, calculated for all juniors, was 1150 with a standard deviation of 75. A sample of 35 juniors from a given high school had an average score of 1250. Assuming a significance level of 0.05, use a Z-test to determine whether the difference between the average score of the class of 35 and the national average is statistically significant.
1. State the null and alternative hypotheses:
H 0 : μ = 1150
H a : μ ≠ 1150
2. The selected significance level is 0.05, and test scores follow a normal distribution, so it is appropriate to calculate the Z-score of the test statistic and conduct a Z-test.
3. Since we want to determine if any difference exists, a two-tailed test is appropriate, which means that the 0.05 critical region is broken up into two critical regions comprising an area of 0.025 each; the critical regions for a two-tailed Z-test given a 0.05 significance level are:
4. Calculate the Z-score of the observed value:
5. Since the Z-score of the observed value does not lie within the critical region (as shown in the figure below), we fail to reject the null hypothesis.
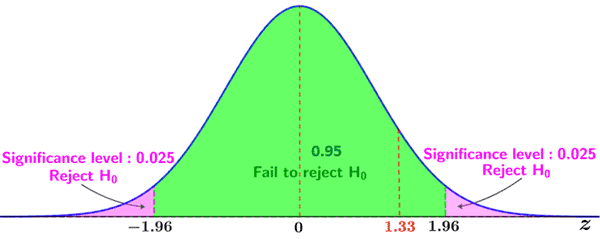
Failing to reject the null hypothesis suggests that there is not a statistically significant difference between the average scores of the class of 35 and the national average at a significance level of 0.05.
A significance level α of 0.05 means that there is a 5% chance of rejecting the null hypothesis when the null hypothesis is true. When this occurs, the error is referred to as a type I error, or a false positive. In cases where the opposite occurs, and we fail to reject the null hypothesis when it is false, it is referred to as a type II error, as summarized in the table below:
| H is true | H is false | |
|---|---|---|
| Reject H | Type I error | Correct inference |
| Fail to reject H | Correct inference | Type II error |
What is The Null Hypothesis & When Do You Reject The Null Hypothesis
Julia Simkus
Editor at Simply Psychology
BA (Hons) Psychology, Princeton University
Julia Simkus is a graduate of Princeton University with a Bachelor of Arts in Psychology. She is currently studying for a Master's Degree in Counseling for Mental Health and Wellness in September 2023. Julia's research has been published in peer reviewed journals.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Saul McLeod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul McLeod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
On This Page:
A null hypothesis is a statistical concept suggesting no significant difference or relationship between measured variables. It’s the default assumption unless empirical evidence proves otherwise.
The null hypothesis states no relationship exists between the two variables being studied (i.e., one variable does not affect the other).
The null hypothesis is the statement that a researcher or an investigator wants to disprove.
Testing the null hypothesis can tell you whether your results are due to the effects of manipulating the dependent variable or due to random chance.
How to Write a Null Hypothesis
Null hypotheses (H0) start as research questions that the investigator rephrases as statements indicating no effect or relationship between the independent and dependent variables.
It is a default position that your research aims to challenge or confirm.
For example, if studying the impact of exercise on weight loss, your null hypothesis might be:
There is no significant difference in weight loss between individuals who exercise daily and those who do not.
Examples of Null Hypotheses
| Research Question | Null Hypothesis |
|---|---|
| Do teenagers use cell phones more than adults? | Teenagers and adults use cell phones the same amount. |
| Do tomato plants exhibit a higher rate of growth when planted in compost rather than in soil? | Tomato plants show no difference in growth rates when planted in compost rather than soil. |
| Does daily meditation decrease the incidence of depression? | Daily meditation does not decrease the incidence of depression. |
| Does daily exercise increase test performance? | There is no relationship between daily exercise time and test performance. |
| Does the new vaccine prevent infections? | The vaccine does not affect the infection rate. |
| Does flossing your teeth affect the number of cavities? | Flossing your teeth has no effect on the number of cavities. |
When Do We Reject The Null Hypothesis?
We reject the null hypothesis when the data provide strong enough evidence to conclude that it is likely incorrect. This often occurs when the p-value (probability of observing the data given the null hypothesis is true) is below a predetermined significance level.
If the collected data does not meet the expectation of the null hypothesis, a researcher can conclude that the data lacks sufficient evidence to back up the null hypothesis, and thus the null hypothesis is rejected.
Rejecting the null hypothesis means that a relationship does exist between a set of variables and the effect is statistically significant ( p > 0.05).
If the data collected from the random sample is not statistically significance , then the null hypothesis will be accepted, and the researchers can conclude that there is no relationship between the variables.
You need to perform a statistical test on your data in order to evaluate how consistent it is with the null hypothesis. A p-value is one statistical measurement used to validate a hypothesis against observed data.
Calculating the p-value is a critical part of null-hypothesis significance testing because it quantifies how strongly the sample data contradicts the null hypothesis.
The level of statistical significance is often expressed as a p -value between 0 and 1. The smaller the p-value, the stronger the evidence that you should reject the null hypothesis.
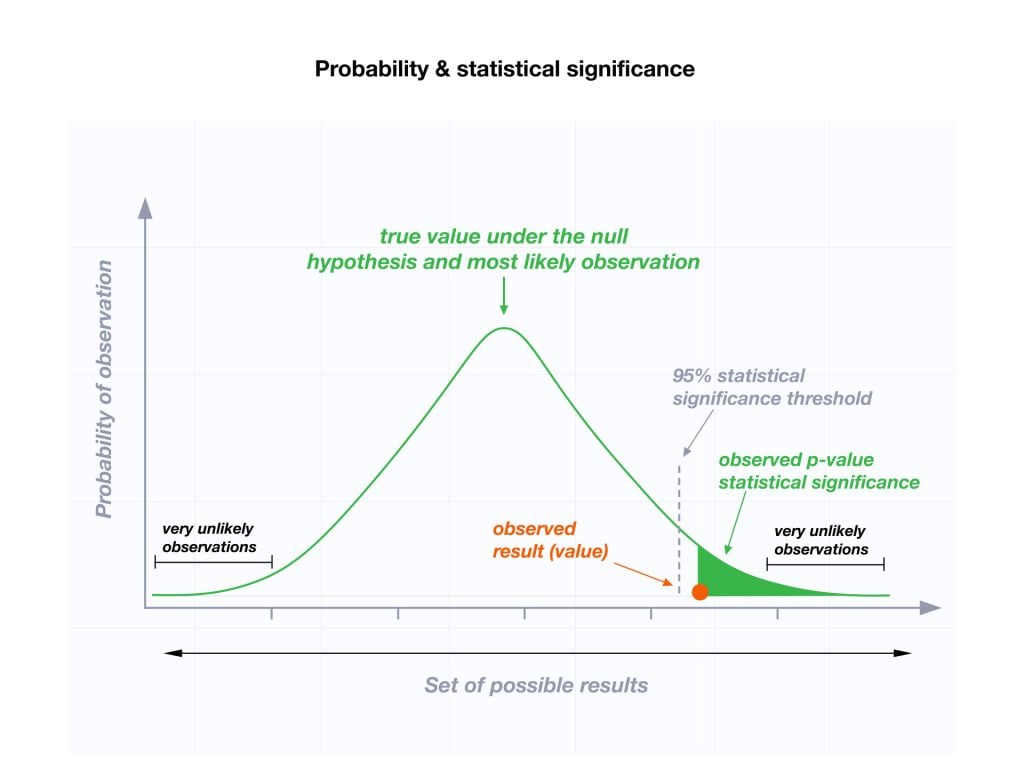
Usually, a researcher uses a confidence level of 95% or 99% (p-value of 0.05 or 0.01) as general guidelines to decide if you should reject or keep the null.
When your p-value is less than or equal to your significance level, you reject the null hypothesis.
In other words, smaller p-values are taken as stronger evidence against the null hypothesis. Conversely, when the p-value is greater than your significance level, you fail to reject the null hypothesis.
In this case, the sample data provides insufficient data to conclude that the effect exists in the population.
Because you can never know with complete certainty whether there is an effect in the population, your inferences about a population will sometimes be incorrect.
When you incorrectly reject the null hypothesis, it’s called a type I error. When you incorrectly fail to reject it, it’s called a type II error.
Why Do We Never Accept The Null Hypothesis?
The reason we do not say “accept the null” is because we are always assuming the null hypothesis is true and then conducting a study to see if there is evidence against it. And, even if we don’t find evidence against it, a null hypothesis is not accepted.
A lack of evidence only means that you haven’t proven that something exists. It does not prove that something doesn’t exist.
It is risky to conclude that the null hypothesis is true merely because we did not find evidence to reject it. It is always possible that researchers elsewhere have disproved the null hypothesis, so we cannot accept it as true, but instead, we state that we failed to reject the null.
One can either reject the null hypothesis, or fail to reject it, but can never accept it.
Why Do We Use The Null Hypothesis?
We can never prove with 100% certainty that a hypothesis is true; We can only collect evidence that supports a theory. However, testing a hypothesis can set the stage for rejecting or accepting this hypothesis within a certain confidence level.
The null hypothesis is useful because it can tell us whether the results of our study are due to random chance or the manipulation of a variable (with a certain level of confidence).
A null hypothesis is rejected if the measured data is significantly unlikely to have occurred and a null hypothesis is accepted if the observed outcome is consistent with the position held by the null hypothesis.
Rejecting the null hypothesis sets the stage for further experimentation to see if a relationship between two variables exists.
Hypothesis testing is a critical part of the scientific method as it helps decide whether the results of a research study support a particular theory about a given population. Hypothesis testing is a systematic way of backing up researchers’ predictions with statistical analysis.
It helps provide sufficient statistical evidence that either favors or rejects a certain hypothesis about the population parameter.
Purpose of a Null Hypothesis
- The primary purpose of the null hypothesis is to disprove an assumption.
- Whether rejected or accepted, the null hypothesis can help further progress a theory in many scientific cases.
- A null hypothesis can be used to ascertain how consistent the outcomes of multiple studies are.
Do you always need both a Null Hypothesis and an Alternative Hypothesis?
The null (H0) and alternative (Ha or H1) hypotheses are two competing claims that describe the effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable. They are mutually exclusive, which means that only one of the two hypotheses can be true.
While the null hypothesis states that there is no effect in the population, an alternative hypothesis states that there is statistical significance between two variables.
The goal of hypothesis testing is to make inferences about a population based on a sample. In order to undertake hypothesis testing, you must express your research hypothesis as a null and alternative hypothesis. Both hypotheses are required to cover every possible outcome of the study.
What is the difference between a null hypothesis and an alternative hypothesis?
The alternative hypothesis is the complement to the null hypothesis. The null hypothesis states that there is no effect or no relationship between variables, while the alternative hypothesis claims that there is an effect or relationship in the population.
It is the claim that you expect or hope will be true. The null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis are always mutually exclusive, meaning that only one can be true at a time.
What are some problems with the null hypothesis?
One major problem with the null hypothesis is that researchers typically will assume that accepting the null is a failure of the experiment. However, accepting or rejecting any hypothesis is a positive result. Even if the null is not refuted, the researchers will still learn something new.
Why can a null hypothesis not be accepted?
We can either reject or fail to reject a null hypothesis, but never accept it. If your test fails to detect an effect, this is not proof that the effect doesn’t exist. It just means that your sample did not have enough evidence to conclude that it exists.
We can’t accept a null hypothesis because a lack of evidence does not prove something that does not exist. Instead, we fail to reject it.
Failing to reject the null indicates that the sample did not provide sufficient enough evidence to conclude that an effect exists.
If the p-value is greater than the significance level, then you fail to reject the null hypothesis.
Is a null hypothesis directional or non-directional?
A hypothesis test can either contain an alternative directional hypothesis or a non-directional alternative hypothesis. A directional hypothesis is one that contains the less than (“<“) or greater than (“>”) sign.
A nondirectional hypothesis contains the not equal sign (“≠”). However, a null hypothesis is neither directional nor non-directional.
A null hypothesis is a prediction that there will be no change, relationship, or difference between two variables.
The directional hypothesis or nondirectional hypothesis would then be considered alternative hypotheses to the null hypothesis.
Gill, J. (1999). The insignificance of null hypothesis significance testing. Political research quarterly , 52 (3), 647-674.
Krueger, J. (2001). Null hypothesis significance testing: On the survival of a flawed method. American Psychologist , 56 (1), 16.
Masson, M. E. (2011). A tutorial on a practical Bayesian alternative to null-hypothesis significance testing. Behavior research methods , 43 , 679-690.
Nickerson, R. S. (2000). Null hypothesis significance testing: a review of an old and continuing controversy. Psychological methods , 5 (2), 241.
Rozeboom, W. W. (1960). The fallacy of the null-hypothesis significance test. Psychological bulletin , 57 (5), 416.
Null Hypothesis Definition and Examples
PM Images / Getty Images
- Chemical Laws
- Periodic Table
- Projects & Experiments
- Scientific Method
- Biochemistry
- Physical Chemistry
- Medical Chemistry
- Chemistry In Everyday Life
- Famous Chemists
- Activities for Kids
- Abbreviations & Acronyms
- Weather & Climate
- Ph.D., Biomedical Sciences, University of Tennessee at Knoxville
- B.A., Physics and Mathematics, Hastings College
In a scientific experiment, the null hypothesis is the proposition that there is no effect or no relationship between phenomena or populations. If the null hypothesis is true, any observed difference in phenomena or populations would be due to sampling error (random chance) or experimental error. The null hypothesis is useful because it can be tested and found to be false, which then implies that there is a relationship between the observed data. It may be easier to think of it as a nullifiable hypothesis or one that the researcher seeks to nullify. The null hypothesis is also known as the H 0, or no-difference hypothesis.
The alternate hypothesis, H A or H 1 , proposes that observations are influenced by a non-random factor. In an experiment, the alternate hypothesis suggests that the experimental or independent variable has an effect on the dependent variable .
How to State a Null Hypothesis
There are two ways to state a null hypothesis. One is to state it as a declarative sentence, and the other is to present it as a mathematical statement.
For example, say a researcher suspects that exercise is correlated to weight loss, assuming diet remains unchanged. The average length of time to achieve a certain amount of weight loss is six weeks when a person works out five times a week. The researcher wants to test whether weight loss takes longer to occur if the number of workouts is reduced to three times a week.
The first step to writing the null hypothesis is to find the (alternate) hypothesis. In a word problem like this, you're looking for what you expect to be the outcome of the experiment. In this case, the hypothesis is "I expect weight loss to take longer than six weeks."
This can be written mathematically as: H 1 : μ > 6
In this example, μ is the average.
Now, the null hypothesis is what you expect if this hypothesis does not happen. In this case, if weight loss isn't achieved in greater than six weeks, then it must occur at a time equal to or less than six weeks. This can be written mathematically as:
H 0 : μ ≤ 6
The other way to state the null hypothesis is to make no assumption about the outcome of the experiment. In this case, the null hypothesis is simply that the treatment or change will have no effect on the outcome of the experiment. For this example, it would be that reducing the number of workouts would not affect the time needed to achieve weight loss:
H 0 : μ = 6
Null Hypothesis Examples
"Hyperactivity is unrelated to eating sugar " is an example of a null hypothesis. If the hypothesis is tested and found to be false, using statistics, then a connection between hyperactivity and sugar ingestion may be indicated. A significance test is the most common statistical test used to establish confidence in a null hypothesis.
Another example of a null hypothesis is "Plant growth rate is unaffected by the presence of cadmium in the soil ." A researcher could test the hypothesis by measuring the growth rate of plants grown in a medium lacking cadmium, compared with the growth rate of plants grown in mediums containing different amounts of cadmium. Disproving the null hypothesis would set the groundwork for further research into the effects of different concentrations of the element in soil.
Why Test a Null Hypothesis?
You may be wondering why you would want to test a hypothesis just to find it false. Why not just test an alternate hypothesis and find it true? The short answer is that it is part of the scientific method. In science, propositions are not explicitly "proven." Rather, science uses math to determine the probability that a statement is true or false. It turns out it's much easier to disprove a hypothesis than to positively prove one. Also, while the null hypothesis may be simply stated, there's a good chance the alternate hypothesis is incorrect.
For example, if your null hypothesis is that plant growth is unaffected by duration of sunlight, you could state the alternate hypothesis in several different ways. Some of these statements might be incorrect. You could say plants are harmed by more than 12 hours of sunlight or that plants need at least three hours of sunlight, etc. There are clear exceptions to those alternate hypotheses, so if you test the wrong plants, you could reach the wrong conclusion. The null hypothesis is a general statement that can be used to develop an alternate hypothesis, which may or may not be correct.
- Kelvin Temperature Scale Definition
- Independent Variable Definition and Examples
- Theory Definition in Science
- Hypothesis Definition (Science)
- de Broglie Equation Definition
- Law of Combining Volumes Definition
- Chemical Definition
- Pure Substance Definition in Chemistry
- Acid Definition and Examples
- Extensive Property Definition (Chemistry)
- Radiation Definition and Examples
- Valence Definition in Chemistry
- Atomic Solid Definition
- Weak Base Definition and Examples
- Oxidation Definition and Example in Chemistry
- Definition of Binary Compound
Best Practices in Science
The Null Hypothesis
Show Topics
Publications
- Journals and Blogs
The null hypothesis, as described by Anthony Greenwald in ‘Consequences of Prejudice Against the Null Hypothesis,’ is the hypothesis of no difference between treatment effects or of no association between variables. Unfortunately in academia, the ‘null’ is often associated with ‘insignificant,’ ‘no value,’ or ‘invalid.’ This association is due to the bias against papers that accept the null hypothesis by journals. This prejudice by journals to only accept papers that show ‘significant’ results (also known as rejecting this ‘null hypothesis’) puts added pressure on those working in academia, especially with their relevance and salaries often depend on publications. This pressure may also be correlated with increased scientific misconduct, which you can also read more about on this website by clicking here . If you would like to read publication, journal articles, and blogs about the null hypothesis, views on rejecting and accepting the null, and journal bias against the null hypothesis, please see the resources we have linked below.
Most scientific journals are prejudiced against papers that demonstrate support for null hypotheses and are unlikely to publish such papers and articles. This phenomenon leads to selective publishing of papers and ensures that the portion of articles that do get published is unrepresentative of the total research in the field.
Anderson, D. R., Burnham, K. P., & Thompson, W. L. (2000). Null hypothesis testing: problems, prevalence, and an alternative. The journal of wildlife management , 912-923.
Benjamini, Y., & Hochberg, Y. (1995). Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. Journal of the royal statistical society . Series B (Methodological), 289-300.
Berger, J. O., & Sellke, T. (1987). Testing a point null hypothesis: The irreconcilability of p values and evidence. Journal of the American statistical Association , 82 (397), 112-122.
Blackwelder, W. C. (1982). “Proving the null hypothesis” in clinical trials. Controlled clinical trials , 3 (4), 345-353.
Dirnagl, U. (2010). Fighting publication bias: introducing the Negative Results section. Journal of cerebral blood flow and metabolism: official journal of the International Society of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism , 30 (7), 1263.
Dickersin, K., Chan, S. S., Chalmersx, T. C., Sacks, H. S., & Smith, H. (1987). Publication bias and clinical trials. Controlled clinical trials , 8 (4), 343-353.
Efron, B. (2004). Large-scale simultaneous hypothesis testing: the choice of a null hypothesis. Journal of the American Statistical Association , 99 (465), 96-104.
Fanelli, D. (2010). Do pressures to publish increase scientists’ bias? An empirical support from US States Data. PloS one , 5 (4), e10271.
Fanelli, D. (2011). Negative results are disappearing from most disciplines and countries. Scientometrics , 90 (3), 891-904.
Greenwald, A. G. (1975). Consequences of Prejudice Against the Null Hypothesis. Psychological Bulletin , 82 (1).
Hubbard, R., & Armstrong, J. S. (1997). Publication bias against null results. Psychological Reports , 80 (1), 337-338.
I’ve Got Your Impact Factor Right Here (Science, February 24, 2012)
Johnson, R. T., & Dickersin, K. (2007). Publication bias against negative results from clinical trials: three of the seven deadly sins. Nature Clinical Practice Neurology , 3 (11), 590-591.
Keep negativity out of politics. We need more of it in journals (STAT, October 14, 2016)
Knight, J. (2003). Negative results: Null and void. Nature , 422 (6932), 554-555.
Koren, G., & Klein, N. (1991). Bias against negative studies in newspaper reports of medical research. Jama , 266 (13), 1824-1826.
Koren, G., Shear, H., Graham, K., & Einarson, T. (1989). Bias against the null hypothesis: the reproductive hazards of cocaine. The Lancet , 334 (8677), 1440-1442.
Krantz, D. (2012). The Null Hypothesis Testing Controversy in Psychology. Journal of American Statistical Association .
Lash, T. (2017). The Harm Done to Reproducibility by the Culture of Null Hypothesis Significance Testing. American Journal of Epidemiology .
Mahoney, M. J. (1977). Publication prejudices: An experimental study of confirmatory bias in the peer review system. Cognitive therapy and research , 1 (2), 161-175.
Matosin, N., Frank, E., Engel, M., Lum, J. S., & Newell, K. A. (2014). Negativity towards negative results: a discussion of the disconnect between scientific worth and scientific culture.
Nickerson, R. S. (2000). Null hypothesis significance testing: a review of an old and continuing controversy. Psychological methods , 5 (2), 241.
No result is worthless: the value of negative results in science (BioMed Central, October 10, 2012)
Negative Results: The Dark Matter of Research (American Journal Experts)
Neil Malhotra: Why No News Is Still Important News in Research (Stanford Graduate School of Business, October 27, 2014)
Null Hypothesis Definition and Example (Statistics How To, November 5, 2012)
Null Hypothesis Glossary Definition (Statlect Digital Textbook)
Opinion: Publish Negative Results (The Scientist, January 15, 2013)
Positives in negative results: when finding ‘nothing’ means something (The Conversation, September 24, 2014)
Rouder, J. N., Speckman, P. L., Sun, D., Morey, R. D., & Iverson, G. (2009). Bayesian t tests for accepting and rejecting the null hypothesis. Psychonomic bulletin & review , 16 (2), 225-237.
Unknown Unknowns: The War on Null and Negative Results (social science space, September 19, 2014)
Valuing Null and Negative Results in Scientific Publishing (Scholastica, November 4, 2015)
Vasilev, M. R. (2013). Negative results in European psychology journals. Europe’s Journal of Psychology , 9 (4), 717-730
Where have all the negative results gone? (bioethics.net, December 4, 2013)
Where to publish negative results (BitesizeBio, November 27, 2013)
Why it’s time to publish research “failures” (Elsevier, May 5, 2015)
Woolson, R. F., & Kleinman, J. C. (1989). Perspectives on statistical significance testing. Annual review of public health , 10 (1), 423-440.
Would you publish your negative results? If no, why? (ResearchGate, October 26, 2012)
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is a Null Hypothesis?
The alternative hypothesis.
- Additional Examples
- Null Hypothesis and Investments
The Bottom Line
- Corporate Finance
- Financial Ratios
Null Hypothesis: What Is It, and How Is It Used in Investing?
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master's in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/adam_hayes-5bfc262a46e0fb005118b414.jpg)
A null hypothesis is a type of statistical hypothesis that proposes that no statistical significance exists in a set of given observations. Hypothesis testing is used to assess the credibility of a hypothesis by using sample data. Sometimes referred to simply as the “null,” it is represented as H 0 .
The null hypothesis, also known as “the conjecture,” is used in quantitative analysis to test theories about markets, investing strategies, and economies to decide if an idea is true or false.
Key Takeaways
- A null hypothesis is a type of conjecture in statistics that proposes that there is no difference between certain characteristics of a population or data-generating process.
- The alternative hypothesis proposes that there is a difference.
- Hypothesis testing provides a method to reject a null hypothesis within a certain confidence level.
- If you can reject the null hypothesis, it provides support for the alternative hypothesis.
- Null hypothesis testing is the basis of the principle of falsification in science.
Alex Dos Diaz / Investopedia
Understanding a Null Hypothesis
A gambler may be interested in whether a game of chance is fair. If it is, then the expected earnings per play come to zero for both players. If it is not, then the expected earnings are positive for one player and negative for the other.
To test whether the game is fair, the gambler collects earnings data from many repetitions of the game, calculates the average earnings from these data, then tests the null hypothesis that the expected earnings are not different from zero.
If the average earnings from the sample data are sufficiently far from zero, then the gambler will reject the null hypothesis and conclude the alternative hypothesis—namely, that the expected earnings per play are different from zero. If the average earnings from the sample data are near zero, then the gambler will not reject the null hypothesis, concluding instead that the difference between the average from the data and zero is explainable by chance alone.
A null hypothesis can only be rejected, not proven.
The null hypothesis assumes that any kind of difference between the chosen characteristics that you see in a set of data is due to chance. For example, if the expected earnings for the gambling game are truly equal to zero, then any difference between the average earnings in the data and zero is due to chance.
Analysts look to reject the null hypothesis because doing so is a strong conclusion. This requires evidence in the form of an observed difference that is too large to be explained solely by chance. Failing to reject the null hypothesis—that the results are explainable by chance alone—is a weak conclusion because it allows that while factors other than chance may be at work, they may not be strong enough for the statistical test to detect them.
An important point to note is that we are testing the null hypothesis because there is an element of doubt about its validity. Whatever information that is against the stated null hypothesis is captured in the alternative (alternate) hypothesis (H 1 ).
For the examples below, the alternative hypothesis would be:
- Students score an average that is not equal to seven.
- The mean annual return of a mutual fund is not equal to 8% per year.
In other words, the alternative hypothesis is a direct contradiction of the null hypothesis.
Null Hypothesis Examples
Here is a simple example: A school principal claims that students in her school score an average of seven out of 10 in exams. The null hypothesis is that the population mean is not 7.0. To test this null hypothesis, we record marks of, say, 30 students ( sample ) from the entire student population of the school (say, 300) and calculate the mean of that sample.
We can then compare the (calculated) sample mean to the (hypothesized) population mean of 7.0 and attempt to reject the null hypothesis. (The null hypothesis here—that the population mean is not 7.0—cannot be proved using the sample data. It can only be rejected.)
Take another example: The annual return of a particular mutual fund is claimed to be 8%. Assume that the mutual fund has been in existence for 20 years. The null hypothesis is that the mean return is not 8% for the mutual fund. We take a random sample of annual returns of the mutual fund for, say, five years (sample) and calculate the sample mean. We then compare the (calculated) sample mean to the (claimed) population mean (8%) to test the null hypothesis.
For the above examples, null hypotheses are:
- Example A: Students in the school don’t score an average of seven out of 10 in exams.
- Example B: The mean annual return of the mutual fund is not 8% per year.
For the purposes of determining whether to reject the null hypothesis (abbreviated H0), said hypothesis is assumed, for the sake of argument, to be true. Then the likely range of possible values of the calculated statistic (e.g., the average score on 30 students’ tests) is determined under this presumption (e.g., the range of plausible averages might range from 6.2 to 7.8 if the population mean is 7.0).
If the sample average is outside of this range, the null hypothesis is rejected. Otherwise, the difference is said to be “explainable by chance alone,” being within the range that is determined by chance alone.
How Null Hypothesis Testing Is Used in Investments
As an example related to financial markets, assume Alice sees that her investment strategy produces higher average returns than simply buying and holding a stock . The null hypothesis states that there is no difference between the two average returns, and Alice is inclined to believe this until she can conclude contradictory results.
Refuting the null hypothesis would require showing statistical significance, which can be found by a variety of tests. The alternative hypothesis would state that the investment strategy has a higher average return than a traditional buy-and-hold strategy.
One tool that can determine the statistical significance of the results is the p-value. A p-value represents the probability that a difference as large or larger than the observed difference between the two average returns could occur solely by chance.
A p-value that is less than or equal to 0.05 often indicates whether there is evidence against the null hypothesis. If Alice conducts one of these tests, such as a test using the normal model, resulting in a significant difference between her returns and the buy-and-hold returns (the p-value is less than or equal to 0.05), she can then reject the null hypothesis and conclude the alternative hypothesis.
How Is the Null Hypothesis Identified?
The analyst or researcher establishes a null hypothesis based on the research question or problem they are trying to answer. Depending on the question, the null may be identified differently. For example, if the question is simply whether an effect exists (e.g., does X influence Y?), the null hypothesis could be H 0 : X = 0. If the question is instead, is X the same as Y, the H 0 would be X = Y. If it is that the effect of X on Y is positive, H 0 would be X > 0. If the resulting analysis shows an effect that is statistically significantly different from zero, the null can be rejected.
How Is Null Hypothesis Used in Finance?
In finance , a null hypothesis is used in quantitative analysis. It tests the premise of an investing strategy, the markets, or an economy to determine if it is true or false.
For instance, an analyst may want to see if two stocks, ABC and XYZ, are closely correlated. The null hypothesis would be ABC ≠ XYZ.
How Are Statistical Hypotheses Tested?
Statistical hypotheses are tested by a four-step process . The first is for the analyst to state the two hypotheses so that only one can be right. The second is to formulate an analysis plan, which outlines how the data will be evaluated. The third is to carry out the plan and physically analyze the sample data. The fourth and final step is to analyze the results and either reject the null hypothesis or claim that the observed differences are explainable by chance alone.
What Is an Alternative Hypothesis?
An alternative hypothesis is a direct contradiction of a null hypothesis. This means that if one of the two hypotheses is true, the other is false.
A null hypothesis states there is no difference between groups or relationship between variables. It is a type of statistical hypothesis and proposes that no statistical significance exists in a set of given observations. “Null” means nothing.
The null hypothesis is used in quantitative analysis to test theories about economies, investing strategies, and markets to decide if an idea is true or false. Hypothesis testing assesses the credibility of a hypothesis by using sample data. It is represented as H 0 and is sometimes simply known as “the null.”
Correction—July 23, 2024: This article was corrected to state accurate examples of null hypothesis in the Null Hypothesis Examples section.
Sage Publishing. “ Chapter 8: Introduction to Hypothesis Testing ,” Page 4.
Sage Publishing. “ Chapter 8: Introduction to Hypothesis Testing ,” Pages 4 to 7.
Sage Publishing. “ Chapter 8: Introduction to Hypothesis Testing ,” Page 7.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/businessperson-calculating-invoice-949219374-5258a9aa6bcd48c5b7af835a15a3935c.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Math Article
Null Hypothesis

In mathematics, Statistics deals with the study of research and surveys on the numerical data. For taking surveys, we have to define the hypothesis. Generally, there are two types of hypothesis. One is a null hypothesis, and another is an alternative hypothesis .
In probability and statistics, the null hypothesis is a comprehensive statement or default status that there is zero happening or nothing happening. For example, there is no connection among groups or no association between two measured events. It is generally assumed here that the hypothesis is true until any other proof has been brought into the light to deny the hypothesis. Let us learn more here with definition, symbol, principle, types and example, in this article.
Table of contents:
- Comparison with Alternative Hypothesis
Null Hypothesis Definition
The null hypothesis is a kind of hypothesis which explains the population parameter whose purpose is to test the validity of the given experimental data. This hypothesis is either rejected or not rejected based on the viability of the given population or sample . In other words, the null hypothesis is a hypothesis in which the sample observations results from the chance. It is said to be a statement in which the surveyors wants to examine the data. It is denoted by H 0 .
Null Hypothesis Symbol
In statistics, the null hypothesis is usually denoted by letter H with subscript ‘0’ (zero), such that H 0 . It is pronounced as H-null or H-zero or H-nought. At the same time, the alternative hypothesis expresses the observations determined by the non-random cause. It is represented by H 1 or H a .
Null Hypothesis Principle
The principle followed for null hypothesis testing is, collecting the data and determining the chances of a given set of data during the study on some random sample, assuming that the null hypothesis is true. In case if the given data does not face the expected null hypothesis, then the outcome will be quite weaker, and they conclude by saying that the given set of data does not provide strong evidence against the null hypothesis because of insufficient evidence. Finally, the researchers tend to reject that.

Null Hypothesis Formula
Here, the hypothesis test formulas are given below for reference.
The formula for the null hypothesis is:
H 0 : p = p 0
The formula for the alternative hypothesis is:
H a = p >p 0 , < p 0 ≠ p 0
The formula for the test static is:
Remember that, p 0 is the null hypothesis and p – hat is the sample proportion.
Also, read:
Types of Null Hypothesis
There are different types of hypothesis. They are:
Simple Hypothesis
It completely specifies the population distribution. In this method, the sampling distribution is the function of the sample size.
Composite Hypothesis
The composite hypothesis is one that does not completely specify the population distribution.
Exact Hypothesis
Exact hypothesis defines the exact value of the parameter. For example μ= 50
Inexact Hypothesis
This type of hypothesis does not define the exact value of the parameter. But it denotes a specific range or interval. For example 45< μ <60
Null Hypothesis Rejection
Sometimes the null hypothesis is rejected too. If this hypothesis is rejected means, that research could be invalid. Many researchers will neglect this hypothesis as it is merely opposite to the alternate hypothesis. It is a better practice to create a hypothesis and test it. The goal of researchers is not to reject the hypothesis. But it is evident that a perfect statistical model is always associated with the failure to reject the null hypothesis.
How do you Find the Null Hypothesis?
The null hypothesis says there is no correlation between the measured event (the dependent variable) and the independent variable. We don’t have to believe that the null hypothesis is true to test it. On the contrast, you will possibly assume that there is a connection between a set of variables ( dependent and independent).
When is Null Hypothesis Rejected?
The null hypothesis is rejected using the P-value approach. If the P-value is less than or equal to the α, there should be a rejection of the null hypothesis in favour of the alternate hypothesis. In case, if P-value is greater than α, the null hypothesis is not rejected.
Null Hypothesis and Alternative Hypothesis
Now, let us discuss the difference between the null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis.
|
|
| |
| 1 | The null hypothesis is a statement. There exists no relation between two variables | Alternative hypothesis a statement, there exists some relationship between two measured phenomenon |
| 2 | Denoted by H | Denoted by H |
| 3 | The observations of this hypothesis are the result of chance | The observations of this hypothesis are the result of real effect |
| 4 | The mathematical formulation of the null hypothesis is an equal sign | The mathematical formulation alternative hypothesis is an inequality sign such as greater than, less than, etc. |
Null Hypothesis Examples
Here, some of the examples of the null hypothesis are given below. Go through the below ones to understand the concept of the null hypothesis in a better way.
If a medicine reduces the risk of cardiac stroke, then the null hypothesis should be “the medicine does not reduce the chance of cardiac stroke”. This testing can be performed by the administration of a drug to a certain group of people in a controlled way. If the survey shows that there is a significant change in the people, then the hypothesis is rejected.
Few more examples are:
1). Are there is 100% chance of getting affected by dengue?
Ans: There could be chances of getting affected by dengue but not 100%.
2). Do teenagers are using mobile phones more than grown-ups to access the internet?
Ans: Age has no limit on using mobile phones to access the internet.
3). Does having apple daily will not cause fever?
Ans: Having apple daily does not assure of not having fever, but increases the immunity to fight against such diseases.
4). Do the children more good in doing mathematical calculations than grown-ups?
Ans: Age has no effect on Mathematical skills.
In many common applications, the choice of the null hypothesis is not automated, but the testing and calculations may be automated. Also, the choice of the null hypothesis is completely based on previous experiences and inconsistent advice. The choice can be more complicated and based on the variety of applications and the diversity of the objectives.
The main limitation for the choice of the null hypothesis is that the hypothesis suggested by the data is based on the reasoning which proves nothing. It means that if some hypothesis provides a summary of the data set, then there would be no value in the testing of the hypothesis on the particular set of data.
Frequently Asked Questions on Null Hypothesis
What is meant by the null hypothesis.
In Statistics, a null hypothesis is a type of hypothesis which explains the population parameter whose purpose is to test the validity of the given experimental data.
What are the benefits of hypothesis testing?
Hypothesis testing is defined as a form of inferential statistics, which allows making conclusions from the entire population based on the sample representative.
When a null hypothesis is accepted and rejected?
The null hypothesis is either accepted or rejected in terms of the given data. If P-value is less than α, then the null hypothesis is rejected in favor of the alternative hypothesis, and if the P-value is greater than α, then the null hypothesis is accepted in favor of the alternative hypothesis.
Why is the null hypothesis important?
The importance of the null hypothesis is that it provides an approximate description of the phenomena of the given data. It allows the investigators to directly test the relational statement in a research study.
How to accept or reject the null hypothesis in the chi-square test?
If the result of the chi-square test is bigger than the critical value in the table, then the data does not fit the model, which represents the rejection of the null hypothesis.

Put your understanding of this concept to test by answering a few MCQs. Click ‘Start Quiz’ to begin!
Select the correct answer and click on the “Finish” button Check your score and answers at the end of the quiz
Visit BYJU’S for all Maths related queries and study materials
Your result is as below
Request OTP on Voice Call
| MATHS Related Links | |
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
Null hypothesis
Null hypothesis n., plural: null hypotheses [nʌl haɪˈpɒθɪsɪs] Definition: a hypothesis that is valid or presumed true until invalidated by a statistical test
Table of Contents
Null Hypothesis Definition
Null hypothesis is defined as “the commonly accepted fact (such as the sky is blue) and researcher aim to reject or nullify this fact”.
More formally, we can define a null hypothesis as “a statistical theory suggesting that no statistical relationship exists between given observed variables” .
In biology , the null hypothesis is used to nullify or reject a common belief. The researcher carries out the research which is aimed at rejecting the commonly accepted belief.
What Is a Null Hypothesis?
A hypothesis is defined as a theory or an assumption that is based on inadequate evidence. It needs and requires more experiments and testing for confirmation. There are two possibilities that by doing more experiments and testing, a hypothesis can be false or true. It means it can either prove wrong or true (Blackwelder, 1982).
For example, Susie assumes that mineral water helps in the better growth and nourishment of plants over distilled water. To prove this hypothesis, she performs this experiment for almost a month. She watered some plants with mineral water and some with distilled water.
In a hypothesis when there are no statistically significant relationships among the two variables, the hypothesis is said to be a null hypothesis. The investigator is trying to disprove such a hypothesis. In the above example of plants, the null hypothesis is:
There are no statistical relationships among the forms of water that are given to plants for growth and nourishment.
Usually, an investigator tries to prove the null hypothesis wrong and tries to explain a relation and association between the two variables.
An opposite and reverse of the null hypothesis are known as the alternate hypothesis . In the example of plants the alternate hypothesis is:
There are statistical relationships among the forms of water that are given to plants for growth and nourishment.
The example below shows the difference between null vs alternative hypotheses:
Alternate Hypothesis: The world is round Null Hypothesis: The world is not round.
Copernicus and many other scientists try to prove the null hypothesis wrong and false. By their experiments and testing, they make people believe that alternate hypotheses are correct and true. If they do not prove the null hypothesis experimentally wrong then people will not believe them and never consider the alternative hypothesis true and correct.
The alternative and null hypothesis for Susie’s assumption is:
- Null Hypothesis: If one plant is watered with distilled water and the other with mineral water, then there is no difference in the growth and nourishment of these two plants.
- Alternative Hypothesis: If one plant is watered with distilled water and the other with mineral water, then the plant with mineral water shows better growth and nourishment.
The null hypothesis suggests that there is no significant or statistical relationship. The relation can either be in a single set of variables or among two sets of variables.
Most people consider the null hypothesis true and correct. Scientists work and perform different experiments and do a variety of research so that they can prove the null hypothesis wrong or nullify it. For this purpose, they design an alternate hypothesis that they think is correct or true. The null hypothesis symbol is H 0 (it is read as H null or H zero ).
Why is it named the “Null”?
The name null is given to this hypothesis to clarify and explain that the scientists are working to prove it false i.e. to nullify the hypothesis. Sometimes it confuses the readers; they might misunderstand it and think that statement has nothing. It is blank but, actually, it is not. It is more appropriate and suitable to call it a nullifiable hypothesis instead of the null hypothesis.
Why do we need to assess it? Why not just verify an alternate one?
In science, the scientific method is used. It involves a series of different steps. Scientists perform these steps so that a hypothesis can be proved false or true. Scientists do this to confirm that there will be any limitation or inadequacy in the new hypothesis. Experiments are done by considering both alternative and null hypotheses, which makes the research safe. It gives a negative as well as a bad impact on research if a null hypothesis is not included or a part of the study. It seems like you are not taking your research seriously and not concerned about it and just want to impose your results as correct and true if the null hypothesis is not a part of the study.
Development of the Null
In statistics, firstly it is necessary to design alternate and null hypotheses from the given problem. Splitting the problem into small steps makes the pathway towards the solution easier and less challenging. how to write a null hypothesis?
Writing a null hypothesis consists of two steps:
- Firstly, initiate by asking a question.
- Secondly, restate the question in such a way that it seems there are no relationships among the variables.
In other words, assume in such a way that the treatment does not have any effect.
| Questions | Null Hypothesis |
|---|---|
| Are adults doing better at mathematics than teenagers? | Mathematical ability does not depend on age. |
| Does the risk of a heart attack reduce by daily intake of aspirin? | A heart attack is not affected by the daily dose of aspirin. |
| Are teenagers using cell phones to access the internet more than elders? | Age does not affect the usage of cell phones for internet access. |
| Are cats concerned about their food color? | Cats do not prefer food based on color. |
| Does pain relieve by chewing willow bark? | Pain is not relieved by chewing willow bark. |
The usual recovery duration after knee surgery is considered almost 8 weeks.
A researcher thinks that the recovery period may get elongated if patients go to a physiotherapist for rehabilitation twice per week, instead of thrice per week, i.e. recovery duration reduces if the patient goes three times for rehabilitation instead of two times.
Step 1: Look for the problem in the hypothesis. The hypothesis either be a word or can be a statement. In the above example the hypothesis is:
“The expected recovery period in knee rehabilitation is more than 8 weeks”
Step 2: Make a mathematical statement from the hypothesis. Averages can also be represented as μ, thus the null hypothesis formula will be.
In the above equation, the hypothesis is equivalent to H1, the average is denoted by μ and > that the average is greater than eight.
Step 3: Explain what will come up if the hypothesis does not come right i.e., the rehabilitation period may not proceed more than 08 weeks.
There are two options: either the recovery will be less than or equal to 8 weeks.
H 0 : μ ≤ 8
In the above equation, the null hypothesis is equivalent to H 0 , the average is denoted by μ and ≤ represents that the average is less than or equal to eight.
What will happen if the scientist does not have any knowledge about the outcome?
Problem: An investigator investigates the post-operative impact and influence of radical exercise on patients who have operative procedures of the knee. The chances are either the exercise will improve the recovery or will make it worse. The usual time for recovery is 8 weeks.
Step 1: Make a null hypothesis i.e. the exercise does not show any effect and the recovery time remains almost 8 weeks.
H 0 : μ = 8
In the above equation, the null hypothesis is equivalent to H 0 , the average is denoted by μ, and the equal sign (=) shows that the average is equal to eight.
Step 2: Make the alternate hypothesis which is the reverse of the null hypothesis. Particularly what will happen if treatment (exercise) makes an impact?
In the above equation, the alternate hypothesis is equivalent to H1, the average is denoted by μ and not equal sign (≠) represents that the average is not equal to eight.
Significance Tests
To get a reasonable and probable clarification of statistics (data), a significance test is performed. The null hypothesis does not have data. It is a piece of information or statement which contains numerical figures about the population. The data can be in different forms like in means or proportions. It can either be the difference of proportions and means or any odd ratio.
The following table will explain the symbols:
| P-value | |
| Probability of success | |
| Size of sample | |
| Null Hypothesis | |
| Alternate Hypothesis |
P-value is the chief statistical final result of the significance test of the null hypothesis.
- P-value = Pr(data or data more extreme | H 0 true)
- | = “given”
- Pr = probability
- H 0 = the null hypothesis
The first stage of Null Hypothesis Significance Testing (NHST) is to form an alternate and null hypothesis. By this, the research question can be briefly explained.
Null Hypothesis = no effect of treatment, no difference, no association Alternative Hypothesis = effective treatment, difference, association
When to reject the null hypothesis?
Researchers will reject the null hypothesis if it is proven wrong after experimentation. Researchers accept null hypothesis to be true and correct until it is proven wrong or false. On the other hand, the researchers try to strengthen the alternate hypothesis. The binomial test is performed on a sample and after that, a series of tests were performed (Frick, 1995).
Step 1: Evaluate and read the research question carefully and consciously and make a null hypothesis. Verify the sample that supports the binomial proportion. If there is no difference then find out the value of the binomial parameter.
Show the null hypothesis as:
H 0 :p= the value of p if H 0 is true
To find out how much it varies from the proposed data and the value of the null hypothesis, calculate the sample proportion.
Step 2: In test statistics, find the binomial test that comes under the null hypothesis. The test must be based on precise and thorough probabilities. Also make a list of pmf that apply, when the null hypothesis proves true and correct.
When H 0 is true, X~b(n, p)
N = size of the sample
P = assume value if H 0 proves true.
Step 3: Find out the value of P. P-value is the probability of data that is under observation.
Rise or increase in the P value = Pr(X ≥ x)
X = observed number of successes
P value = Pr(X ≤ x).
Step 4: Demonstrate the findings or outcomes in a descriptive detailed way.
- Sample proportion
- The direction of difference (either increases or decreases)
Perceived Problems With the Null Hypothesis
Variable or model selection and less information in some cases are the chief important issues that affect the testing of the null hypothesis. Statistical tests of the null hypothesis are reasonably not strong. There is randomization about significance. (Gill, 1999) The main issue with the testing of the null hypothesis is that they all are wrong or false on a ground basis.
There is another problem with the a-level . This is an ignored but also a well-known problem. The value of a-level is without a theoretical basis and thus there is randomization in conventional values, most commonly 0.q, 0.5, or 0.01. If a fixed value of a is used, it will result in the formation of two categories (significant and non-significant) The issue of a randomized rejection or non-rejection is also present when there is a practical matter which is the strong point of the evidence related to a scientific matter.
The P-value has the foremost importance in the testing of null hypothesis but as an inferential tool and for interpretation, it has a problem. The P-value is the probability of getting a test statistic at least as extreme as the observed one.
The main point about the definition is: Observed results are not based on a-value
Moreover, the evidence against the null hypothesis was overstated due to unobserved results. A-value has importance more than just being a statement. It is a precise statement about the evidence from the observed results or data. Similarly, researchers found that P-values are objectionable. They do not prefer null hypotheses in testing. It is also clear that the P-value is strictly dependent on the null hypothesis. It is computer-based statistics. In some precise experiments, the null hypothesis statistics and actual sampling distribution are closely related but this does not become possible in observational studies.
Some researchers pointed out that the P-value is depending on the sample size. If the true and exact difference is small, a null hypothesis even of a large sample may get rejected. This shows the difference between biological importance and statistical significance. (Killeen, 2005)
Another issue is the fix a-level, i.e., 0.1. On the basis, if a-level a null hypothesis of a large sample may get accepted or rejected. If the size of simple is infinity and the null hypothesis is proved true there are still chances of Type I error. That is the reason this approach or method is not considered consistent and reliable. There is also another problem that the exact information about the precision and size of the estimated effect cannot be known. The only solution is to state the size of the effect and its precision.
Null Hypothesis Examples
Here are some examples:
Example 1: Hypotheses with One Sample of One Categorical Variable
Among all the population of humans, almost 10% of people prefer to do their task with their left hand i.e. left-handed. Let suppose, a researcher in the Penn States says that the population of students at the College of Arts and Architecture is mostly left-handed as compared to the general population of humans in general public society. In this case, there is only a sample and there is a comparison among the known population values to the population proportion of sample value.
- Research Question: Do artists more expected to be left-handed as compared to the common population persons in society?
- Response Variable: Sorting the student into two categories. One category has left-handed persons and the other category have right-handed persons.
- Form Null Hypothesis: Arts and Architecture college students are no more predicted to be lefty as compared to the common population persons in society (Lefty students of Arts and Architecture college population is 10% or p= 0.10)
Example 2: Hypotheses with One Sample of One Measurement Variable
A generic brand of antihistamine Diphenhydramine making medicine in the form of a capsule, having a 50mg dose. The maker of the medicines is concerned that the machine has come out of calibration and is not making more capsules with the suitable and appropriate dose.
- Research Question: Does the statistical data recommended about the mean and average dosage of the population differ from 50mg?
- Response Variable: Chemical assay used to find the appropriate dosage of the active ingredient.
- Null Hypothesis: Usually, the 50mg dosage of capsules of this trade name (population average and means dosage =50 mg).
Example 3: Hypotheses with Two Samples of One Categorical Variable
Several people choose vegetarian meals on a daily basis. Typically, the researcher thought that females like vegetarian meals more than males.
- Research Question: Does the data recommend that females (women) prefer vegetarian meals more than males (men) regularly?
- Response Variable: Cataloguing the persons into vegetarian and non-vegetarian categories. Grouping Variable: Gender
- Null Hypothesis: Gender is not linked to those who like vegetarian meals. (Population percent of women who eat vegetarian meals regularly = population percent of men who eat vegetarian meals regularly or p women = p men).
Example 4: Hypotheses with Two Samples of One Measurement Variable
Nowadays obesity and being overweight is one of the major and dangerous health issues. Research is performed to confirm that a low carbohydrates diet leads to faster weight loss than a low-fat diet.
- Research Question: Does the given data recommend that usually, a low-carbohydrate diet helps in losing weight faster as compared to a low-fat diet?
- Response Variable: Weight loss (pounds)
- Explanatory Variable: Form of diet either low carbohydrate or low fat
- Null Hypothesis: There is no significant difference when comparing the mean loss of weight of people using a low carbohydrate diet to people using a diet having low fat. (population means loss of weight on a low carbohydrate diet = population means loss of weight on a diet containing low fat).
Example 5: Hypotheses about the relationship between Two Categorical Variables
A case-control study was performed. The study contains nonsmokers, stroke patients, and controls. The subjects are of the same occupation and age and the question was asked if someone at their home or close surrounding smokes?
- Research Question: Did second-hand smoke enhance the chances of stroke?
- Variables: There are 02 diverse categories of variables. (Controls and stroke patients) (whether the smoker lives in the same house). The chances of having a stroke will be increased if a person is living with a smoker.
- Null Hypothesis: There is no significant relationship between a passive smoker and stroke or brain attack. (odds ratio between stroke and the passive smoker is equal to 1).
Example 6: Hypotheses about the relationship between Two Measurement Variables
A financial expert observes that there is somehow a positive and effective relationship between the variation in stock rate price and the quantity of stock bought by non-management employees
- Response variable- Regular alteration in price
- Explanatory Variable- Stock bought by non-management employees
- Null Hypothesis: The association and relationship between the regular stock price alteration ($) and the daily stock-buying by non-management employees ($) = 0.
Example 7: Hypotheses about comparing the relationship between Two Measurement Variables in Two Samples
- Research Question: Is the relation between the bill paid in a restaurant and the tip given to the waiter, is linear? Is this relation different for dining and family restaurants?
- Explanatory Variable- total bill amount
- Response Variable- the amount of tip
- Null Hypothesis: The relationship and association between the total bill quantity at a family or dining restaurant and the tip, is the same.
Try to answer the quiz below to check what you have learned so far about the null hypothesis.
Choose the best answer.
Send Your Results (Optional)
- Blackwelder, W. C. (1982). “Proving the null hypothesis” in clinical trials. Controlled Clinical Trials , 3(4), 345–353.
- Frick, R. W. (1995). Accepting the null hypothesis. Memory & Cognition, 23(1), 132–138.
- Gill, J. (1999). The insignificance of null hypothesis significance testing. Political Research Quarterly , 52(3), 647–674.
- Killeen, P. R. (2005). An alternative to null-hypothesis significance tests. Psychological Science, 16(5), 345–353.
©BiologyOnline.com. Content provided and moderated by Biology Online Editors.
Last updated on June 16th, 2022
You will also like...
Takahē (porphyrio hochstetteri).
Meet the colorful takahē, an extremely rare flightless bird. Find out more about its unique features and why they matte..
Genetic Control – On and Off Genes
Genes are the blueprint of our bodies, a blueprint that creates a variety of proteins essential to any organism's surviv..
A Balanced Vitamin Diet – Vitamins A – K
A balanced diet is essential to a healthy organism. Insufficiency or too much of a particular element or compound, such ..
Biosecurity and Biocontrol
This lesson explores the impact of biosecurity threats, and why they need to be identified and managed. Examples to incl..
Passive and Active Types of Immunity
Lymphocytes are a type of white blood cell capable of producing a specific immune response to unique antigens. In thi..
The Evolution of Cell Organelles
The nucleus containing the genetic material, DNA, and the mitochondria, well-identified as the "powerhouse of the cell",..
Related Articles...
No related articles found
Module 9: Hypothesis Testing With One Sample
Summary: null and alternative hypotheses, key concepts.
- The null hypothesis is a statement of no change or status quo.
- Symbols used for the null hypothesis are =, ≤ and ≥.
- The alternative hypothesis is sometimes referred to as the research hypothesis; it is what the researcher believes to be true based on the data to be collected.
- Symbols used for the alternative hypothesis are ≠, > and <.
Hypothesis: a statement about the value of a population parameter. In the case of two hypotheses, the statement assumed to be true is called the null hypothesis (notation [latex]H_0[/latex]) and the contradictory statement is called the alternative hypothesis (notation [latex]H_a[/latex]).
Hypothesis Testing: Based on sample evidence, a procedure for determining whether the hypothesis stated is a reasonable statement and should not be rejected or is unreasonable and should be rejected.
- Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution
- Introductory Statistics. Authored by : Barbara Illowsky, Susan Dean. Provided by : OpenStax. Located at : https://openstax.org/books/introductory-statistics/pages/9-key-terms . License : CC BY: Attribution . License Terms : Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/introductory-statistics/pages/1-introduction

Privacy Policy
- School Guide
- Mathematics
- Number System and Arithmetic
- Trigonometry
- Probability
- Mensuration
- Maths Formulas
- Integration Formulas
- Differentiation Formulas
- Trigonometry Formulas
- Algebra Formulas
- Mensuration Formula
- Statistics Formulas
- Trigonometric Table
Null Hypothesis
Null Hypothesis , often denoted as H 0, is a foundational concept in statistical hypothesis testing. It represents an assumption that no significant difference, effect, or relationship exists between variables within a population. It serves as a baseline assumption, positing no observed change or effect occurring. The null is t he truth or falsity of an idea in analysis.
In this article, we will discuss the null hypothesis in detail, along with some solved examples and questions on the null hypothesis.
Table of Content
What is Null Hypothesis?
Null hypothesis symbol, formula of null hypothesis, types of null hypothesis, null hypothesis examples, principle of null hypothesis, how do you find null hypothesis, null hypothesis in statistics, null hypothesis and alternative hypothesis, null hypothesis and alternative hypothesis examples, null hypothesis – practice problems.
Null Hypothesis in statistical analysis suggests the absence of statistical significance within a specific set of observed data. Hypothesis testing, using sample data, evaluates the validity of this hypothesis. Commonly denoted as H 0 or simply “null,” it plays an important role in quantitative analysis, examining theories related to markets, investment strategies, or economies to determine their validity.
Null Hypothesis Meaning
Null Hypothesis represents a default position, often suggesting no effect or difference, against which researchers compare their experimental results. The Null Hypothesis, often denoted as H 0 asserts a default assumption in statistical analysis. It posits no significant difference or effect, serving as a baseline for comparison in hypothesis testing.
The null Hypothesis is represented as H 0 , the Null Hypothesis symbolizes the absence of a measurable effect or difference in the variables under examination.
Certainly, a simple example would be asserting that the mean score of a group is equal to a specified value like stating that the average IQ of a population is 100.
The Null Hypothesis is typically formulated as a statement of equality or absence of a specific parameter in the population being studied. It provides a clear and testable prediction for comparison with the alternative hypothesis. The formulation of the Null Hypothesis typically follows a concise structure, stating the equality or absence of a specific parameter in the population.
Mean Comparison (Two-sample t-test)
H 0 : μ 1 = μ 2
This asserts that there is no significant difference between the means of two populations or groups.
Proportion Comparison
H 0 : p 1 − p 2 = 0
This suggests no significant difference in proportions between two populations or conditions.
Equality in Variance (F-test in ANOVA)
H 0 : σ 1 = σ 2
This states that there’s no significant difference in variances between groups or populations.
Independence (Chi-square Test of Independence):
H 0 : Variables are independent
This asserts that there’s no association or relationship between categorical variables.
Null Hypotheses vary including simple and composite forms, each tailored to the complexity of the research question. Understanding these types is pivotal for effective hypothesis testing.
Equality Null Hypothesis (Simple Null Hypothesis)
The Equality Null Hypothesis, also known as the Simple Null Hypothesis, is a fundamental concept in statistical hypothesis testing that assumes no difference, effect or relationship between groups, conditions or populations being compared.
Non-Inferiority Null Hypothesis
In some studies, the focus might be on demonstrating that a new treatment or method is not significantly worse than the standard or existing one.
Superiority Null Hypothesis
The concept of a superiority null hypothesis comes into play when a study aims to demonstrate that a new treatment, method, or intervention is significantly better than an existing or standard one.
Independence Null Hypothesis
In certain statistical tests, such as chi-square tests for independence, the null hypothesis assumes no association or independence between categorical variables.
Homogeneity Null Hypothesis
In tests like ANOVA (Analysis of Variance), the null hypothesis suggests that there’s no difference in population means across different groups.
- Medicine: Null Hypothesis: “No significant difference exists in blood pressure levels between patients given the experimental drug versus those given a placebo.”
- Education: Null Hypothesis: “There’s no significant variation in test scores between students using a new teaching method and those using traditional teaching.”
- Economics: Null Hypothesis: “There’s no significant change in consumer spending pre- and post-implementation of a new taxation policy.”
- Environmental Science: Null Hypothesis: “There’s no substantial difference in pollution levels before and after a water treatment plant’s establishment.”
The principle of the null hypothesis is a fundamental concept in statistical hypothesis testing. It involves making an assumption about the population parameter or the absence of an effect or relationship between variables.
In essence, the null hypothesis (H 0 ) proposes that there is no significant difference, effect, or relationship between variables. It serves as a starting point or a default assumption that there is no real change, no effect or no difference between groups or conditions.
The null hypothesis is usually formulated to be tested against an alternative hypothesis (H 1 or H [Tex]\alpha [/Tex] ) which suggests that there is an effect, difference or relationship present in the population.
Null Hypothesis Rejection
Rejecting the Null Hypothesis occurs when statistical evidence suggests a significant departure from the assumed baseline. It implies that there is enough evidence to support the alternative hypothesis, indicating a meaningful effect or difference. Null Hypothesis rejection occurs when statistical evidence suggests a deviation from the assumed baseline, prompting a reconsideration of the initial hypothesis.
Identifying the Null Hypothesis involves defining the status quotient, asserting no effect and formulating a statement suitable for statistical analysis.
When is Null Hypothesis Rejected?
The Null Hypothesis is rejected when statistical tests indicate a significant departure from the expected outcome, leading to the consideration of alternative hypotheses. It occurs when statistical evidence suggests a deviation from the assumed baseline, prompting a reconsideration of the initial hypothesis.
In statistical hypothesis testing, researchers begin by stating the null hypothesis, often based on theoretical considerations or previous research. The null hypothesis is then tested against an alternative hypothesis (Ha), which represents the researcher’s claim or the hypothesis they seek to support.
The process of hypothesis testing involves collecting sample data and using statistical methods to assess the likelihood of observing the data if the null hypothesis were true. This assessment is typically done by calculating a test statistic, which measures the difference between the observed data and what would be expected under the null hypothesis.
In the realm of hypothesis testing, the null hypothesis (H 0 ) and alternative hypothesis (H₁ or Ha) play critical roles. The null hypothesis generally assumes no difference, effect, or relationship between variables, suggesting that any observed change or effect is due to random chance. Its counterpart, the alternative hypothesis, asserts the presence of a significant difference, effect, or relationship between variables, challenging the null hypothesis. These hypotheses are formulated based on the research question and guide statistical analyses.
Difference Between Null Hypothesis and Alternative Hypothesis
The null hypothesis (H 0 ) serves as the baseline assumption in statistical testing, suggesting no significant effect, relationship, or difference within the data. It often proposes that any observed change or correlation is merely due to chance or random variation. Conversely, the alternative hypothesis (H 1 or Ha) contradicts the null hypothesis, positing the existence of a genuine effect, relationship or difference in the data. It represents the researcher’s intended focus, seeking to provide evidence against the null hypothesis and support for a specific outcome or theory. These hypotheses form the crux of hypothesis testing, guiding the assessment of data to draw conclusions about the population being studied.
Criteria | Null Hypothesis | Alternative Hypothesis |
|---|---|---|
Definition | Assumes no effect or difference | Asserts a specific effect or difference |
Symbol | H | H (or Ha) |
Formulation | States equality or absence of parameter | States a specific value or relationship |
Testing Outcome | Rejected if evidence of a significant effect | Accepted if evidence supports the hypothesis |
Let’s envision a scenario where a researcher aims to examine the impact of a new medication on reducing blood pressure among patients. In this context:
Null Hypothesis (H 0 ): “The new medication does not produce a significant effect in reducing blood pressure levels among patients.”
Alternative Hypothesis (H 1 or Ha): “The new medication yields a significant effect in reducing blood pressure levels among patients.”
The null hypothesis implies that any observed alterations in blood pressure subsequent to the medication’s administration are a result of random fluctuations rather than a consequence of the medication itself. Conversely, the alternative hypothesis contends that the medication does indeed generate a meaningful alteration in blood pressure levels, distinct from what might naturally occur or by random chance.
People Also Read:
Mathematics Maths Formulas Probability and Statistics
Example 1: A researcher claims that the average time students spend on homework is 2 hours per night.
Null Hypothesis (H 0 ): The average time students spend on homework is equal to 2 hours per night. Data: A random sample of 30 students has an average homework time of 1.8 hours with a standard deviation of 0.5 hours. Test Statistic and Decision: Using a t-test, if the calculated t-statistic falls within the acceptance region, we fail to reject the null hypothesis. If it falls in the rejection region, we reject the null hypothesis. Conclusion: Based on the statistical analysis, we fail to reject the null hypothesis, suggesting that there is not enough evidence to dispute the claim of the average homework time being 2 hours per night.
Example 2: A company asserts that the error rate in its production process is less than 1%.
Null Hypothesis (H 0 ): The error rate in the production process is 1% or higher. Data: A sample of 500 products shows an error rate of 0.8%. Test Statistic and Decision: Using a z-test, if the calculated z-statistic falls within the acceptance region, we fail to reject the null hypothesis. If it falls in the rejection region, we reject the null hypothesis. Conclusion: The statistical analysis supports rejecting the null hypothesis, indicating that there is enough evidence to dispute the company’s claim of an error rate of 1% or higher.
Q1. A researcher claims that the average time spent by students on homework is less than 2 hours per day. Formulate the null hypothesis for this claim?
Q2. A manufacturing company states that their new machine produces widgets with a defect rate of less than 5%. Write the null hypothesis to test this claim?
Q3. An educational institute believes that their online course completion rate is at least 60%. Develop the null hypothesis to validate this assertion?
Q4. A restaurant claims that the waiting time for customers during peak hours is not more than 15 minutes. Formulate the null hypothesis for this claim?
Q5. A study suggests that the mean weight loss after following a specific diet plan for a month is more than 8 pounds. Construct the null hypothesis to evaluate this statement?
Summary – Null Hypothesis and Alternative Hypothesis
The null hypothesis (H 0 ) and alternative hypothesis (H a ) are fundamental concepts in statistical hypothesis testing. The null hypothesis represents the default assumption, stating that there is no significant effect, difference, or relationship between variables. It serves as the baseline against which the alternative hypothesis is tested. In contrast, the alternative hypothesis represents the researcher’s hypothesis or the claim to be tested, suggesting that there is a significant effect, difference, or relationship between variables. The relationship between the null and alternative hypotheses is such that they are complementary, and statistical tests are conducted to determine whether the evidence from the data is strong enough to reject the null hypothesis in favor of the alternative hypothesis. This decision is based on the strength of the evidence and the chosen level of significance. Ultimately, the choice between the null and alternative hypotheses depends on the specific research question and the direction of the effect being investigated.
FAQs on Null Hypothesis
What does null hypothesis stands for.
The null hypothesis, denoted as H 0 , is a fundamental concept in statistics used for hypothesis testing. It represents the statement that there is no effect or no difference, and it is the hypothesis that the researcher typically aims to provide evidence against.
How to Form a Null Hypothesis?
A null hypothesis is formed based on the assumption that there is no significant difference or effect between the groups being compared or no association between variables being tested. It often involves stating that there is no relationship, no change, or no effect in the population being studied.
When Do we reject the Null Hypothesis?
In statistical hypothesis testing, if the p-value (the probability of obtaining the observed results) is lower than the chosen significance level (commonly 0.05), we reject the null hypothesis. This suggests that the data provides enough evidence to refute the assumption made in the null hypothesis.
What is a Null Hypothesis in Research?
In research, the null hypothesis represents the default assumption or position that there is no significant difference or effect. Researchers often try to test this hypothesis by collecting data and performing statistical analyses to see if the observed results contradict the assumption.
What Are Alternative and Null Hypotheses?
The null hypothesis (H0) is the default assumption that there is no significant difference or effect. The alternative hypothesis (H1 or Ha) is the opposite, suggesting there is a significant difference, effect or relationship.
What Does it Mean to Reject the Null Hypothesis?
Rejecting the null hypothesis implies that there is enough evidence in the data to support the alternative hypothesis. In simpler terms, it suggests that there might be a significant difference, effect or relationship between the groups or variables being studied.
How to Find Null Hypothesis?
Formulating a null hypothesis often involves considering the research question and assuming that no difference or effect exists. It should be a statement that can be tested through data collection and statistical analysis, typically stating no relationship or no change between variables or groups.
How is Null Hypothesis denoted?
The null hypothesis is commonly symbolized as H 0 in statistical notation.
What is the Purpose of the Null hypothesis in Statistical Analysis?
The null hypothesis serves as a starting point for hypothesis testing, enabling researchers to assess if there’s enough evidence to reject it in favor of an alternative hypothesis.
What happens if we Reject the Null hypothesis?
Rejecting the null hypothesis implies that there is sufficient evidence to support an alternative hypothesis, suggesting a significant effect or relationship between variables.
What are Test for Null Hypothesis?
Various statistical tests, such as t-tests or chi-square tests, are employed to evaluate the validity of the Null Hypothesis in different scenarios.
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- Geeks Premier League
- School Learning
- Geeks Premier League 2023
- Math-Concepts
- Best Twitch Extensions for 2024: Top Tools for Viewers and Streamers
- Discord Emojis List 2024: Copy and Paste
- Best Adblockers for Twitch TV: Enjoy Ad-Free Streaming in 2024
- PS4 vs. PS5: Which PlayStation Should You Buy in 2024?
- Full Stack Developer Roadmap [2024 Updated]
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
Trending Courses
Course Categories
Certification Programs
- Free Courses
Statistics Guides
- Free Practice Tests
- On Demand Webinars
Null Hypothesis
Published on :
21 Aug, 2024
Blog Author :
Wallstreetmojo Team
Edited by :
Ashish Kumar Srivastav
Reviewed by :
Dheeraj Vaidya
What is Null Hypothesis?
The null-hypothesis is considered an accepted truth. It assumes that the research is false, that the observations are caused by random factors. Researchers must prove the null-hypothesis wrong to prove their alternate hypothesis.
The null-hypothesis presumes that the sampled data and the population data have no difference. It is the opposite of the alternate hypothesis, which says that the sample or claimed data differs from the actual population. The null-hypothesis is denoted by H 0 (pronounced as 'H naught').
Table of contents
Null hypothesis explained, null hypothesis formula, how to find the null-hypothesis, null hypothesis examples, significance, limitations, null hypothesis vs. alternate hypothesis, frequently asked questions (faqs), recommended articles.
- During, Null Hypothesis Significance Testing (NHST), if the level of significance is within the acceptable limit or confidence interval, H0 is accepted; otherwise, it is rejected.
- Hypothesis testing is a form of a mathematical model that is used to accept or reject a hypothesis within a range of confidence levels.
- Null hypothesis is an assumption that is accepted valid unless proven otherwise. It is used for prove or dissprove research statements along with statistical data.
A null-hypothesis can be defined as an accepted fact that may or may not be true. In the initial claim of the null-hypothesis, it is believed that the assumption is valid. The null hypothesis is mainly used for verifying the relevance of Statistical data taken as a sample. This sample is then compared to the characteristics of the whole population from which the sample was taken. Researchers can prove or disprove a statement or assumption by conducting Hypothesis Testing (NHST).
For example, assume that a claim states it takes 30 days to form a habit. Therefore, it will be considered that it is valid until there is some statistical significance to prove that our assumption is wrong, and it does not take 30 days to form a habit. Hypothesis testing is a mathematical model used to accept or reject the hypothesis within the prescribed range of confidence level. It is also used for verifying the difference between alternative procedures.
The null hypothesis serves as a base for prominent scientific research. For example, scientists believe that "there is life on Mars," The statement could be accepted or rejected based on statistical analysis.

Based on the null hypothesis, we need to prove that:

A hypothesis is tested for significance levels level in the observed data. This is done for summarizing theoretical data.
For calculation of deviation from the claimed data, we can use the formula:

Some of the basic steps to determine H 0 are as follows:
- The first step is to assume that the given statement is true.
- Next, find the level of significance or the deviation rate. For this first find the difference between claimed data and the actual data and then divide it by claimed data. The result is multiplied by 100.
- If the result falls within the confidence interval, then the null hypothesis is accepted; however, the hypothesis is rejected if it is outside the confidence interval . Here, we see that the claimed or assumed value has to be equal to or nearly equal to the actual data for the null hypothesis to be true.
Now let us apply the null hypothesis to a few examples.
In an industrial study, it was claimed that on average production of 100 goods, the chance of encountering a faulty product was only 1.5 %. But during the study of a sample taken, it was found that the chances of encountering a faulty product were actually 1.55%. Comment on this condition.
In the case of the Null-Hypothesis Testing, the original claim is assumed to be correct. Here, it is assumed only 1.5 % of 100 goods were faulty products.

In this case, deviation helps ascertain the level of significance.
Calculation of Deviation Rate can be done as follows:

= (1.55%-1.50%) * 100/1.50%
Therefore, the Deviation Rate will be:

Deviation Rate = 3.33%
Explanation
In this example, the standard deviation from the assumed parameter is 3.33 %, which falls within the acceptable range, i.e., 1% to 5%. Thus, the null hypothesis can be accepted even when the actual valuation differs from the assumption. But if such deviation exceeds 5%, the hypothesis will be rejected. Beyond that percentage, the assumption made will have no justification.
There are many ways to verify a presumed statement. For example, with null assumptions, the mean of the sample is compared to the population mean . Here, the term 'mean' could be defined as the average value of the parameter and the number of variables.
While we conduct various statistical tests like P-value , the results can be analyzed by determining the null-hypothesis and alternative hypothesis. Some of the reasons for its importance are discussed below:
- Logic Behind Statistical Significance Testing : Statistics is used to test if the assumptions occur by chance or for particular reasons. It helps in ruling out random factors causing an observation.
- Prove or Disprove Relational Statement : Null-hypothesis proves that there is no relation between two variables; thus, it is used for relational inference.
- Facilitates Alternate Hypothesis Testing : The alternate hypothesis is just one side of the coin. The null-hypothesis is essential for finding and validating its result.
- Confidence Interval : It reflects the same underlying statistical reasoning as P-value in excel .
- Applicable in Different Fields of Study : Whether research, science, psychology, statistics, or investment, everything requires hypothesis testing
The null-hypothesis is based on analysis; therefore, interpretation is critical. Unfortunately, it can be easily misinterpreted and manipulated. In most cases, the significance testing is usually conducted to get rejected; thus, the results often come out false.
Another significant issue is selecting an appropriate sample size for finding the probability or mean. A small sample size fails to provide accurate results. Similarly, a huge sample complicates the calculation.
Null-hypothesis refers to a statistical approach where the sample value deems to be the same as the population data. In this condition, their statistical significance lies somewhere within the confidence level. In contrast, for an alternate hypothesis, the sample value differs from the population data. In such a case, the statistical significance of these two values does not fall within the confidence level.
The null-hypothesis signifies the possibility of observations being caused by chance or random factors. In contrast, the alternate hypothesis highlights that the observations were caused by specific reasons.
The null-hypothesis validates sample data being equivalent to the population data. This means that these two values have no statistical significance. One example is that a doctor states that a human being takes five days on average to recover from viral fever. Based on 50 patients, the average recovery rate is 4.97 days, which is approximately equal to 5 days. Thus, the null assumption is valid. The sample was taken from various states.
The null-hypothesis is accepted when the sample value is equal to or almost identical to the population data. In such a case, the statistical significance falls within the given cut-off confidence interval. Conversely, if the sample data is not equal to the population data or if the statistical significance level is below the confidence interval, the hypothesis is rejected.
Hypothesis testing is essential for the validation of sample data concerning population data. Moreover, it helps draw a meaningful conclusion in medical science, research, psychology, and statistics.
This has been a guide to the What is Null-Hypothesis and its Definition. Here we discuss null-hypothesis' significance, formulas, and calculations using examples. You can learn more about statistics & excel modeling from the following articles –
- ANOVA in Excel
- Z Test in Excel

What Is the Null Hypothesis in Six Sigma?
The null hypothesis refers to the default prediction in research that no significant statistical relationship exists between two variables or two sets of data. The assumption in the null hypothesis is that any measured differences that result from interaction of the two variables are simply the result of randomness.
Six Sigma practitioners typically consider the null hypothesis along with the alternative hypothesis . The alternative hypothesis proposes that interaction between two variables does produce outcomes that are not the result of randomness. It also states that it’s possible to prove this statistically significant relationship through data analysis.
In other words, the alternative hypothesis “rejects the null” and shows evidence of correlation between the two sets of data.
Much of the statistical analysis done in Six Sigma seeks to reject the null hypothesis. That is, it looks to find relationships between variables and identify what action (or lack of action) is leading to unwanted variation and errors. By identifying these relationships, teams can focus on the root cause of a problem.
A Null Hypothesis Example From Sports
The null hypothesis seeks to eliminate assumptions. Rather than look at outcomes and assume an interaction between variables is causing the outcome, the null hypothesis requires the default position that the result is random. Testing then must determine whether it’s possible to reject the null hypothesis and prove some type of correlation.
A simple example involves a hitter on a baseball team. A person might attend many games over the years and make the observation that batters tend to get on base at a higher rate during day games than night games.
To determine if that is true, data analysts would look at two sets of data: one showing the on-base percentage of hitters during day games and one showing the on-base percentage for hitters during night games. This is exactly what researchers at the University of California-Berkeley decided to do .
The null hypothesis calls for a default prediction that any differences in day game vs. night game hitting statistics are generated by randomness. In the case of Berkeley researchers, they constructed a histogram of on-base percentages for batters and other statistical models using 2019 season statistics. They could not find enough statistical evidence to determine that time of day has an impact on a hitter’s ability to make on base.
In this case, data analysis failed to reject the null. The person who saw differences in how often hitters reached based on the games they attended simply witnessed the outcome of statistical randomness in a complex game.
An Example of Null Hypothesis From Business
The steps for a basic hypothesis testing involve identifying the question, determining the significance, choosing the test, interpreting the results and making a decision. In businesses that adhere to Six Sigma, it takes on increased significance because rejecting the null and finding correlation helps to identify challenges that need addressing.
Finding the null hypothesis is relatively easy. Simply take a question and rephrase it as a statement to start with the null.
- Q: Do more website visitors click on the “find out more” when it is blue rather than red or green?
- Null : The color of the “find out more” button has no impact on how often people click on it.
- Q : Does the number of people on a project team impact whether the team achieves its goal?
- Null : The number of people on a project team does not impact the team’s ability to achieve goals.
For the first question, data research would analyze the interaction of one data set (the number of clicks) vs other data sets (the number of clicks when the button is red, blue and green). In the second question, the number of team members would be compared to each team’s rate of success (research in this area suggests it’s five or less ). The results would either reject the null or find no meaningful relationship between the two variables.
A null hypothesis also provides a starting place to determine basic business issues such as the impact of different materials on the quality of the final product, the types of advertising that lead to better sales or the impact of social media postings on website traffic.
Null hypothesis also helps investors make financial decisions, according to Investopedia. For example, they will look at return rates of mutual funds over many years to determine what variables do or do not have an impact on annual returns.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Null hypothesis - Wikipedia ... Null hypothesis
Null Hypothesis: Definition, Rejecting & Examples
That is generally outside the scope of one researcher or a data scientist though. Typically your analysis is with one sample of data — not repeated studies. Unless you're reviewing a broad range of studies from different researchers, you're probably limited to rejecting a null hypothesis, as opposed to claiming a causal relation.
The null hypothesis plays a pivotal role in the scientific method and statistical inference. By establishing a clear statement that can be tested, researchers can apply statistical techniques to determine whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis. This process is essential for drawing conclusions from data and making informed ...
The null hypothesis in a correlational study of the relationship between high school grades and college grades would typically be that the population correlation is 0. This can be written as. H0: ρ = 0 (7.3.2) (7.3.2) H 0: ρ = 0. where ρ ρ is the population correlation, which we will cover in chapter 12. Although the null hypothesis is ...
The actual test begins by considering two hypotheses.They are called the null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis.These hypotheses contain opposing viewpoints. H 0, the —null hypothesis: a statement of no difference between sample means or proportions or no difference between a sample mean or proportion and a population mean or proportion. In other words, the difference equals 0.
Usually, statistical tests have two hypotheses: the null and the alternative. The null hypothesis is the hypothesis of "no effect," i.e., the hypothesis opposite to the effect we want to test for. In contrast, the alternative hypothesis is the one positing the existence of the effect of interest. 3.
The null hypotheses described above imply "no effect" of one sort or another—either no main effect of some independent variable, or no interaction between two independent variables. This kind of "no-effect" null hypothesis is by far the most common null hypothesis to be found in the literature.
The null hypothesis (H 0) is the basis of statistical hypothesis testing. It is the default hypothesis (assumed to be true) that states that there is no statistically significant difference between some population parameter (such as the mean), and a hypothesized value. It is typically based on previous analysis or knowledge.
In statistics, a null hypothesis, often written as , [1] is a statement assumed to be true unless it can be shown to be incorrect beyond a reasonable doubt. [2] The idea is that the null hypothesis generally assumes that there is nothing new or surprising in the population. The most common null hypothesis is the "no-change" or "no-difference ...
What Is The Null Hypothesis & When To Reject It
The Null hypothesis \(\left(H_{O}\right)\) is a statement about the comparisons, e.g., between a sample statistic and the population, or between two treatment groups. The former is referred to as a one-tailed test whereas the latter is called a two-tailed test. The null hypothesis is typically "no statistical difference" between the ...
Null Hypothesis Examples. "Hyperactivity is unrelated to eating sugar " is an example of a null hypothesis. If the hypothesis is tested and found to be false, using statistics, then a connection between hyperactivity and sugar ingestion may be indicated. A significance test is the most common statistical test used to establish confidence in a ...
The null hypothesis, as described by Anthony Greenwald in 'Consequences of Prejudice Against the Null Hypothesis,' is the hypothesis of no difference between treatment effects or of no association between variables. Unfortunately in academia, the 'null' is often associated with 'insignificant,' 'no value,' or 'invalid.'.
Null Hypothesis: What Is It, and How Is It Used in Investing?
For taking surveys, we have to define the hypothesis. Generally, there are two types of hypothesis. One is a null hypothesis, and another is an alternative hypothesis. In probability and statistics, the null hypothesis is a comprehensive statement or default status that there is zero happening or nothing happening.
Null hypothesis - Definition and Examples
The null hypothesis is a statement of no change or status quo. Symbols used for the null hypothesis are =, ≤ and ≥. The alternative hypothesis is sometimes referred to as the research hypothesis; it is what the researcher believes to be true based on the data to be collected. Symbols used for the alternative hypothesis are ≠, > and <.
The null hypothesis generally assumes no difference, effect, or relationship between variables, suggesting that any observed change or effect is due to random chance. Its counterpart, the alternative hypothesis, asserts the presence of a significant difference, effect, or relationship between variables, challenging the null hypothesis. ...
The null-hypothesis is considered an accepted truth. It assumes that the research is false, that the observations are caused by random factors. Researchers must prove the null-hypothesis wrong to prove their alternate hypothesis. The null-hypothesis presumes that the sampled data and the population data have no difference.
The null hypothesis is the complement of the alternative hypothesis. The null hypothesis is what you anticipate through randomness. The alternative hypothesis, sometimes known as the alternate hypothesis is the opposite of that. It is what you would not anticipate by randomness. More often than not you are trying to reject the null because you are trying to see a change in something ...
Null Hypothesis - Know Definition, Functions, Types, And Application Using Examples. A hypothesis may be described as a proposition or set of propositions to explain the relation between occurrences of certain groups of events. A hypothesis may also be expressed solely as a provisional supposition to direct research in light of known facts.
admin — July 14, 2022. The null hypothesis refers to the default prediction in research that no significant statistical relationship exists between two variables or two sets of data. The assumption in the null hypothesis is that any measured differences that result from interaction of the two variables are simply the result of randomness.