

Writing a history essay

An essay is a piece of sustained writing in response to a question, topic or issue. Essays are commonly used for assessing and evaluating student progress in history. History essays test a range of skills including historical understanding, interpretation and analysis, planning, research and writing.
To write an effective essay, students should examine the question, understand its focus and requirements, acquire information and evidence through research, then construct a clear and well-organised response. Writing a good history essay should be rigorous and challenging, even for stronger students. As with other skills, essay writing develops and improves over time. Each essay you complete helps you become more competent and confident in exercising these skills.
Study the question
This is an obvious tip but one sadly neglected by some students. The first step to writing a good essay, whatever the subject or topic, is to give plenty of thought to the question.
An essay question will set some kind of task or challenge. It might ask you to explain the causes and/or effects of a particular event or situation. It might ask if you agree or disagree with a statement. It might ask you to describe and analyse the causes and/or effects of a particular action or event. Or it might ask you to evaluate the relative significance of a person, group or event.
You should begin by reading the essay question several times. Underline, highlight or annotate keywords or terms in the text of the question. Think about what it requires you to do. Who or what does it want you to concentrate on? Does it state or imply a particular timeframe? What problem or issue does it want you to address?
Begin with a plan
Every essay should begin with a written plan. Start constructing a plan as soon as you have received your essay question and given it some thought.
Prepare for research by brainstorming and jotting down your thoughts and ideas. What are your initial responses or thoughts about the question? What topics, events, people or issues are connected with the question? Do any additional questions or issues flow from the question? What topics or events do you need to learn more about? What historians or sources might be useful?
If you encounter a mental ‘brick wall’ or are uncertain about how to approach the question, don’t hesitate to discuss it with someone else. Consult your teacher, a capable classmate or someone you trust. Bear in mind too that once you start researching, your plan may change as you locate new information.
Start researching
After studying the question and developing an initial plan, start to gather information and evidence.
Most will start by reading an overview of the topic or issue, usually in some reliable secondary sources. This will refresh or build your existing understanding of the topic and provide a basis for further questions or investigation.
Your research should take shape from here, guided by the essay question and your own planning. Identify terms or concepts you do not know and find out what they mean. As you locate information, ask yourself if it is relevant or useful for addressing the question. Be creative with your research, looking in a variety of places.
If you have difficulty locating information, seek advice from your teacher or someone you trust.
Develop a contention
All good history essays have a clear and strong contention. A contention is the main idea or argument of your essay. It serves both as an answer to the question and the focal point of your writing.
Ideally, you should be able to express your contention as a single sentence. For example, the following contention might form the basis of an essay question on the rise of the Nazis:
Q. Why did the Nazi Party win 37 per cent of the vote in July 1932? A. The Nazi Party’s electoral success of 1932 was a result of economic suffering caused by the Great Depression, public dissatisfaction with the Weimar Republic’s democratic political system and mainstream parties, and Nazi propaganda that promised a return to traditional social, political and economic values.
An essay using this contention would then go on to explain and justify these statements in greater detail. It will also support the contention with argument and evidence.
At some point in your research, you should begin thinking about a contention for your essay. Remember, you should be able to express it briefly as if addressing the essay question in a single sentence, or summing up in a debate.
Try to frame your contention so that is strong, authoritative and convincing. It should sound like the voice of someone well informed about the subject and confident about their answer.
Plan an essay structure

Once most of your research is complete and you have a strong contention, start jotting down a possible essay structure. This need not be complicated, a few lines or dot points is ample.
Every essay must have an introduction, a body of several paragraphs and a conclusion. Your paragraphs should be well organised and follow a logical sequence.
You can organise paragraphs in two ways: chronologically (covering events or topics in the order they occurred) or thematically (covering events or topics based on their relevance or significance). Every paragraph should be clearly signposted in the topic sentence.
Once you have finalised a plan for your essay, commence your draft.
Write a compelling introduction
Many consider the introduction to be the most important part of an essay. It is important for several reasons. It is the reader’s first experience of your essay. It is where you first address the question and express your contention. It is also where you lay out or ‘signpost’ the direction your essay will take.
Aim for an introduction that is clear, confident and punchy. Get straight to the point – do not waste time with a rambling or storytelling introduction.
Start by providing a little context, then address the question, articulate your contention and indicate what direction your essay will take.
Write fully formed paragraphs
Many history students fall into the trap of writing short paragraphs, sometimes containing as little as one or two sentences. A good history essay contains paragraphs that are themselves ‘mini-essays’, usually between 100-200 words each.
A paragraph should focus on one topic or issue only – but it should contain a thorough exploration of that topic or issue.
A good paragraph will begin with an effective opening sentence, sometimes called a topic sentence or signposting sentence. This sentence introduces the paragraph topic and briefly explains its significance to the question and your contention. Good paragraphs also contain thorough explanations, some analysis and evidence, and perhaps a quotation or two.
Finish with an effective conclusion
The conclusion is the final paragraph of your essay. A good conclusion should do two things. First, it should reiterate or restate the contention of your essay. Second, it should close off your essay, ideally with a polished ending that is not abrupt or awkward.
One effective way to do this is with a brief summary of ‘what happened next’. For example, an essay discussing Hitler’s rise to power in 1933 might close with a couple of sentences about how he consolidated and strengthened his power in 1934-35.
Your conclusion need not be as long or as developed as your body paragraphs. You should avoid introducing new information or evidence in the conclusion.
Reference and cite your sources
A history essay is only likely to succeed if it is appropriately referenced. Your essay should support its information, ideas and arguments with citations or references to reliable sources.
Referencing not only acknowledges the work of others, but it also gives authority to your writing and provides the teacher or assessor with an insight into your research. More information on referencing a piece of history writing can be found here .
Proofread, edit and seek feedback
Every essay should be proofread, edited and, if necessary, re-drafted before being submitted for assessment. Essays should ideally be completed well before their due date then put aside for a day or two before proofreading.
When proofreading, look first for spelling and grammatical errors, typographical mistakes, incorrect dates or other errors of fact.
Think then about how you can improve the clarity, tone and structure of your essay. Does your essay follow a logical structure or sequence? Is the signposting in your essay clear and effective? Are some sentences too long or ‘rambling’? Do you repeat yourself? Do paragraphs need to be expanded, fine-tuned or strengthened with more evidence?
Read your essay aloud, either to yourself or another person. Seek feedback and advice from a good writer or someone you trust (they need not have expertise in history, only in effective writing).
Some general tips on writing
- Always write in the third person . Never refer to yourself personally, using phrases like “I think…” or “It is my contention…”. Good history essays should adopt the perspective of an informed and objective third party. They should sound rational and factual – not like an individual expressing their opinion.
- Always write in the past tense . An obvious tip for a history essay is to write in the past tense. Always be careful about your use of tense. Watch out for mixed tenses when proofreading your work. One exception to the rule about past tense is when writing about the work of modern historians (for example, “Kershaw writes…” sounds better than “Kershaw wrote…” or “Kershaw has written…”).
- Avoid generalisations . Generalisation is a problem in all essays but it is particularly common in history essays. Generalisation occurs when you form general conclusions from one or more specific examples. In history, this most commonly occurs when students study the experiences of a particular group, then assume their experiences applied to a much larger group – for example, “All the peasants were outraged”, “Women rallied to oppose conscription” or “Germans supported the Nazi Party”. Both history and human society, however, are never this clear cut or simple. Always try to avoid generalisation and be on the lookout for generalised statements when proofreading.
- Write short, sharp and punchy . Good writers vary their sentence length but as a rule of thumb, most of your sentences should be short and punchy. The longer a sentence becomes, the greater the risk of it becoming long-winded or confusing. Long sentences can easily become disjointed, confused or rambling. Try not to overuse long sentences and pay close attention to sentence length when proofreading.
- Write in an active voice . In history writing, the active voice is preferable to the passive voice. In the active voice, the subject completes the action (e.g. “Hitler [the subject] initiated the Beer Hall putsch [the action] to seize control of the Bavarian government”). In the passive voice, the action is completed by the subject (“The Beer Hall putsch [the action] was initiated by Hitler [the subject] to seize control of the Bavarian government”). The active voice also helps prevent sentences from becoming long, wordy and unclear.
You may also find our page on writing for history useful.
Citation information Title : ‘Writing a history essay’ Authors : Jennifer Llewellyn, Steve Thompson Publisher : Alpha History URL : https://alphahistory.com/writing-a-history-essay/ Date published : April 13, 2020 Date updated : December 20, 2022 Date accessed : Today’s date Copyright : The content on this page may not be republished without our express permission. For more information on usage, please refer to our Terms of Use.

Steps for Writing a History Paper
Writing a history paper is a process. Successful papers are not completed in a single moment of genius or inspiration, but are developed over a series of steps. When you first read a paper prompt, you might feel overwhelmed or intimidated. If you think of writing as a process and break it down into smaller steps, you will find that paper-writing is manageable, less daunting, and even enjoyable. Writing a history paper is your opportunity to do the real work of historians, to roll up your sleeves and dig deep into the past.
What is a History paper?
History papers are driven by arguments. In a history class, even if you are not writing a paper based on outside research, you are still writing a paper that requires some form of argument. For example, suppose your professor has asked you to write a paper discussing the differences between colonial New England and colonial Virginia. It might seem like this paper is straightforward and does not require an argument, that it is simply a matter of finding the “right answer.” However, even here you need to construct a paper guided by a larger argument. You might argue that the main differences between colonial New England and Virginia were grounded in contrasting visions of colonization. Or you might argue that the differences resulted from accidents of geography or from extant alliances between regional Indian groups. Or you might make an argument that draws on all of these factors. Regardless, when you make these types of assertions, you are making an argument that requires historical evidence. Any history paper you write will be driven by an argument demanding evidence from sources.
History writing assignments can vary widely–and you should always follow your professor’s specific instructions–but the following steps are designed to help no matter what kind of history paper you are writing. Remember that the staff of the History Writing Center is here to assist you at any stage of the writing process.
- Sometimes professors distribute prompts with several sub-questions surrounding the main question they want you to write about. The sub-questions are designed to help you think about the topic. They offer ideas you might consider, but they are not, usually, the key question or questions you need to answer in your paper. Make sure you distinguish the key questions from the sub-questions. Otherwise, your paper may sound like a laundry list of short-answer essays rather than a cohesive argument. A helpful way to hone in on the key question is to look for action verbs, such as “analyze” or “investigate” or “formulate.” Find such words in the paper prompt and circle them. Then, carefully consider what you are being asked to do. Write out the key question at the top of your draft and return to it often, using it to guide you in the writing process. Also, be sure that you are responding to every part of the prompt. Prompts will often have several questions you need to address in your paper. If you do not cover all aspects, then you are not responding fully to the assignment. For more information, visit our section, “Understanding Paper Prompts.”
- Before you even start researching or drafting, take a few minutes to consider what you already know about the topic. Make a list of ideas or draw a cluster diagram, using circles and arrows to connect ideas–whatever method works for you. At this point in the process, it is helpful to write down all of your ideas without stopping to judge or analyze each one in depth. You want to think big and bring in everything you know or suspect about the topic. After you have finished, read over what you have created. Look for patterns or trends or questions that keep coming up. Based on what you have brainstormed, what do you still need to learn about the topic? Do you have a tentative argument or response to the paper prompt? Use this information to guide you as you start your research and develop a thesis.
- Depending on the paper prompt, you may be required to do outside research or you may be using only the readings you have done in class. Either way, start by rereading the relevant materials from class. Find the parts from the textbook, from the primary source readings, and from your notes that relate to the prompt. If you need to do outside research, the UCLA library system offers plenty of resources. You can begin by plugging key words into the online library catalog. This process will likely involve some trial and error. You will want to use search terms that are specific enough to address your topic without being so narrow that you get no results. If your keywords are too general, you may receive thousands of results and feel overwhelmed. To help you narrow your search, go back to the key questions in the essay prompt that you wrote down in Step 1. Think about which terms would help you respond to the prompt. Also, look at the language your professor used in the prompt. You might be able to use some of those same words as search terms. Notice that the library website has different databases you can search depending on what type of material you need (such as scholarly articles, newspapers, books) and what subject and time period you are researching (such as eighteenth-century England or ancient Rome). Searching the database most relevant to your topic will yield the best results. Visit the library’s History Research Guide for tips on the research process and on using library resources. You can also schedule an appointment with a librarian to talk specifically about your research project. Or, make an appointment with staff at the History Writing Center for research help. Visit our section about using electronic resources as well.
- By this point, you know what the prompt is asking, you have brainstormed possible responses, and you have done some research. Now you need to step back, look at the material you have, and develop your argument. Based on the reading and research you have done, how might you answer the question(s) in the prompt? What arguments do your sources allow you to make? Draft a thesis statement in which you clearly and succinctly make an argument that addresses the prompt. If you find writing a thesis daunting, remember that whatever you draft now is not set in stone. Your thesis will change. As you do more research, reread your sources, and write your paper, you will learn more about the topic and your argument. For now, produce a “working thesis,” meaning, a thesis that represents your thinking up to this point. Remember it will almost certainly change as you move through the writing process. For more information, visit our section about thesis statements. Once you have a thesis, you may find that you need to do more research targeted to your specific argument. Revisit some of the tips from Step 3.
- Now that you have a working thesis, look back over your sources and identify which ones are most critical to you–the ones you will be grappling with most directly in order to make your argument. Then, annotate them. Annotating sources means writing a paragraph that summarizes the main idea of the source as well as shows how you will use the source in your paper. Think about what the source does for you. Does it provide evidence in support of your argument? Does it offer a counterpoint that you can then refute, based on your research? Does it provide critical historical background that you need in order to make a point? For more information about annotating sources, visit our section on annotated bibliographies. While it might seem like this step creates more work for you by having to do more writing, it in fact serves two critical purposes: it helps you refine your working thesis by distilling exactly what your sources are saying, and it helps smooth your writing process. Having dissected your sources and articulated your ideas about them, you can more easily draw upon them when constructing your paper. Even if you do not have to do outside research and are limited to working with the readings you have done in class, annotating sources is still very useful. Write down exactly how a particular section in the textbook or in a primary source reader will contribute to your paper.
- An outline is helpful in giving you a sense of the overall structure of your paper and how best to organize your ideas. You need to decide how to arrange your argument in a way that will make the most sense to your reader. Perhaps you decide that your argument is most clear when presented chronologically, or perhaps you find that it works best with a thematic approach. There is no one right way to organize a history paper; it depends entirely on the prompt, on your sources, and on what you think would be most clear to someone reading it. An effective outline includes the following components: the research question from the prompt (that you wrote down in Step 1), your working thesis, the main idea of each body paragraph, and the evidence (from both primary and secondary sources) you will use to support each body paragraph. Be as detailed as you can when putting together your outline.
If you have trouble getting started or are feeling overwhelmed, try free writing. Free writing is a low-stakes writing exercise to help you get past the blank page. Set a timer for five or ten minutes and write down everything you know about your paper: your argument, your sources, counterarguments, everything. Do not edit or judge what you are writing as you write; just keep writing until the timer goes off. You may be surprised to find out how much you knew about your topic. Of course, this writing will not be polished, so do not be tempted to leave it as it is. Remember that this draft is your first one, and you will be revising it.
A particularly helpful exercise for global-level revision is to make a reverse outline, which will help you look at your paper as a whole and strengthen the way you have organized and substantiated your argument. Print out your draft and number each of the paragraphs. Then, on a separate piece of paper, write down each paragraph number and, next to it, summarize in a phrase or a sentence the main idea of that paragraph. As you produce this list, notice if any paragraphs attempt to make more than one point: mark those for revision. Once you have compiled the list, read it over carefully. Study the order in which you have sequenced your ideas. Notice if there are ideas that seem out of order or repetitive. Look for any gaps in your logic. Does the argument flow and make sense?
When revising at the local level, check that you are using strong topic sentences and transitions, that you have adequately integrated and analyzed quotations, and that your paper is free from grammar and spelling errors that might distract the reader or even impede your ability to communicate your point. One helpful exercise for revising on the local level is to read your paper out loud. Hearing your paper will help you catch grammatical errors and awkward sentences.
Here is a checklist of questions to ask yourself while revising on both the global and local levels:
– Does my thesis clearly state my argument and its significance?
– Does the main argument in each body paragraph support my thesis?
– Do I have enough evidence within each body paragraph to make my point?
– Have I properly introduced, analyzed, and cited every quotation I use?
– Do my topic sentences effectively introduce the main point of each paragraph?
– Do I have transitions between paragraphs?
– Is my paper free of grammar and spelling errors?
- Congratulate yourself. You have written a history paper!
Download as PDF

6265 Bunche Hall Box 951473 University of California, Los Angeles Los Angeles, CA 90095-1473 Phone: (310) 825-4601
Other Resources
- UCLA Library
- Faculty Intranet
- Department Forms
- Office 365 Email
- Remote Help
Campus Resources
- Maps, Directions, Parking
- Academic Calendar
- University of California
- Terms of Use
Social Sciences Division Departments
- Aerospace Studies
- African American Studies
- American Indian Studies
- Anthropology
- Archaeology
- Asian American Studies
- César E. Chávez Department of Chicana & Chicano Studies
- Communication
- Conservation
- Gender Studies
- Military Science
- Naval Science
- Political Science

How to write an introduction for a history essay

Every essay needs to begin with an introductory paragraph. It needs to be the first paragraph the marker reads.
While your introduction paragraph might be the first of the paragraphs you write, this is not the only way to do it.
You can choose to write your introduction after you have written the rest of your essay.
This way, you will know what you have argued, and this might make writing the introduction easier.
Either approach is fine. If you do write your introduction first, ensure that you go back and refine it once you have completed your essay.
What is an ‘introduction paragraph’?
An introductory paragraph is a single paragraph at the start of your essay that prepares your reader for the argument you are going to make in your body paragraphs .
It should provide all of the necessary historical information about your topic and clearly state your argument so that by the end of the paragraph, the marker knows how you are going to structure the rest of your essay.
In general, you should never use quotes from sources in your introduction.
Introduction paragraph structure
While your introduction paragraph does not have to be as long as your body paragraphs , it does have a specific purpose, which you must fulfil.
A well-written introduction paragraph has the following four-part structure (summarised by the acronym BHES).
B – Background sentences
H – Hypothesis
E – Elaboration sentences
S - Signpost sentence
Each of these elements are explained in further detail, with examples, below:
1. Background sentences
The first two or three sentences of your introduction should provide a general introduction to the historical topic which your essay is about.
This is done so that when you state your hypothesis , your reader understands the specific point you are arguing about.
Background sentences explain the important historical period, dates, people, places, events and concepts that will be mentioned later in your essay.
This information should be drawn from your background research .
Example background sentences:
Middle Ages (Year 8 Level)
Castles were an important component of Medieval Britain from the time of the Norman conquest in 1066 until they were phased out in the 15 th and 16 th centuries. Initially introduced as wooden motte and bailey structures on geographical strongpoints, they were rapidly replaced by stone fortresses which incorporated sophisticated defensive designs to improve the defenders’ chances of surviving prolonged sieges.
WWI (Year 9 Level)
The First World War began in 1914 following the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand. The subsequent declarations of war from most of Europe drew other countries into the conflict, including Australia. The Australian Imperial Force joined the war as part of Britain’s armed forces and were dispatched to locations in the Middle East and Western Europe.
Civil Rights (Year 10 Level)
The 1967 Referendum sought to amend the Australian Constitution in order to change the legal standing of the indigenous people in Australia. The fact that 90% of Australians voted in favour of the proposed amendments has been attributed to a series of significant events and people who were dedicated to the referendum’s success.
Ancient Rome (Year 11/12 Level)
In the late second century BC, the Roman novus homo Gaius Marius became one of the most influential men in the Roman Republic. Marius gained this authority through his victory in the Jugurthine War, with his defeat of Jugurtha in 106 BC, and his triumph over the invading Germanic tribes in 101 BC, when he crushed the Teutones at the Battle of Aquae Sextiae (102 BC) and the Cimbri at the Battle of Vercellae (101 BC). Marius also gained great fame through his election to the consulship seven times.
2. Hypothesis
Once you have provided historical context for your essay in your background sentences, you need to state your hypothesis .
A hypothesis is a single sentence that clearly states the argument that your essay will be proving in your body paragraphs .
A good hypothesis contains both the argument and the reasons in support of your argument.
Example hypotheses:
Medieval castles were designed with features that nullified the superior numbers of besieging armies but were ultimately made obsolete by the development of gunpowder artillery.
Australian soldiers’ opinion of the First World War changed from naïve enthusiasm to pessimistic realism as a result of the harsh realities of modern industrial warfare.
The success of the 1967 Referendum was a direct result of the efforts of First Nations leaders such as Charles Perkins, Faith Bandler and the Federal Council for the Advancement of Aborigines and Torres Strait Islanders.
Gaius Marius was the most one of the most significant personalities in the 1 st century BC due to his effect on the political, military and social structures of the Roman state.
3. Elaboration sentences
Once you have stated your argument in your hypothesis , you need to provide particular information about how you’re going to prove your argument.
Your elaboration sentences should be one or two sentences that provide specific details about how you’re going to cover the argument in your three body paragraphs.
You might also briefly summarise two or three of your main points.
Finally, explain any important key words, phrases or concepts that you’ve used in your hypothesis, you’ll need to do this in your elaboration sentences.
Example elaboration sentences:
By the height of the Middle Ages, feudal lords were investing significant sums of money by incorporating concentric walls and guard towers to maximise their defensive potential. These developments were so successful that many medieval armies avoided sieges in the late period.
Following Britain's official declaration of war on Germany, young Australian men voluntarily enlisted into the army, which was further encouraged by government propaganda about the moral justifications for the conflict. However, following the initial engagements on the Gallipoli peninsula, enthusiasm declined.
The political activity of key indigenous figures and the formation of activism organisations focused on indigenous resulted in a wider spread of messages to the general Australian public. The generation of powerful images and speeches has been frequently cited by modern historians as crucial to the referendum results.
While Marius is best known for his military reforms, it is the subsequent impacts of this reform on the way other Romans approached the attainment of magistracies and how public expectations of military leaders changed that had the longest impacts on the late republican period.
4. Signpost sentence
The final sentence of your introduction should prepare the reader for the topic of your first body paragraph.
The main purpose of this sentence is to provide cohesion between your introductory paragraph and you first body paragraph .
Therefore, a signpost sentence indicates where you will begin proving the argument that you set out in your hypothesis and usually states the importance of the first point that you’re about to make.
Example signpost sentences:
The early development of castles is best understood when examining their military purpose.
The naïve attitudes of those who volunteered in 1914 can be clearly seen in the personal letters and diaries that they themselves wrote.
The significance of these people is evident when examining the lack of political representation the indigenous people experience in the early half of the 20 th century.
The origin of Marius’ later achievements was his military reform in 107 BC, which occurred when he was first elected as consul.
Putting it all together
Once you have written all four parts of the BHES structure, you should have a completed introduction paragraph.
In the examples above, we have shown each part separately. Below you will see the completed paragraphs so that you can appreciate what an introduction should look like.
Example introduction paragraphs:
Castles were an important component of Medieval Britain from the time of the Norman conquest in 1066 until they were phased out in the 15th and 16th centuries. Initially introduced as wooden motte and bailey structures on geographical strongpoints, they were rapidly replaced by stone fortresses which incorporated sophisticated defensive designs to improve the defenders’ chances of surviving prolonged sieges. Medieval castles were designed with features that nullified the superior numbers of besieging armies, but were ultimately made obsolete by the development of gunpowder artillery. By the height of the Middle Ages, feudal lords were investing significant sums of money by incorporating concentric walls and guard towers to maximise their defensive potential. These developments were so successful that many medieval armies avoided sieges in the late period. The early development of castles is best understood when examining their military purpose.
The First World War began in 1914 following the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand. The subsequent declarations of war from most of Europe drew other countries into the conflict, including Australia. The Australian Imperial Force joined the war as part of Britain’s armed forces and were dispatched to locations in the Middle East and Western Europe. Australian soldiers’ opinion of the First World War changed from naïve enthusiasm to pessimistic realism as a result of the harsh realities of modern industrial warfare. Following Britain's official declaration of war on Germany, young Australian men voluntarily enlisted into the army, which was further encouraged by government propaganda about the moral justifications for the conflict. However, following the initial engagements on the Gallipoli peninsula, enthusiasm declined. The naïve attitudes of those who volunteered in 1914 can be clearly seen in the personal letters and diaries that they themselves wrote.
The 1967 Referendum sought to amend the Australian Constitution in order to change the legal standing of the indigenous people in Australia. The fact that 90% of Australians voted in favour of the proposed amendments has been attributed to a series of significant events and people who were dedicated to the referendum’s success. The success of the 1967 Referendum was a direct result of the efforts of First Nations leaders such as Charles Perkins, Faith Bandler and the Federal Council for the Advancement of Aborigines and Torres Strait Islanders. The political activity of key indigenous figures and the formation of activism organisations focused on indigenous resulted in a wider spread of messages to the general Australian public. The generation of powerful images and speeches has been frequently cited by modern historians as crucial to the referendum results. The significance of these people is evident when examining the lack of political representation the indigenous people experience in the early half of the 20th century.
In the late second century BC, the Roman novus homo Gaius Marius became one of the most influential men in the Roman Republic. Marius gained this authority through his victory in the Jugurthine War, with his defeat of Jugurtha in 106 BC, and his triumph over the invading Germanic tribes in 101 BC, when he crushed the Teutones at the Battle of Aquae Sextiae (102 BC) and the Cimbri at the Battle of Vercellae (101 BC). Marius also gained great fame through his election to the consulship seven times. Gaius Marius was the most one of the most significant personalities in the 1st century BC due to his effect on the political, military and social structures of the Roman state. While Marius is best known for his military reforms, it is the subsequent impacts of this reform on the way other Romans approached the attainment of magistracies and how public expectations of military leaders changed that had the longest impacts on the late republican period. The origin of Marius’ later achievements was his military reform in 107 BC, which occurred when he was first elected as consul.
Additional resources

What do you need help with?
Download ready-to-use digital learning resources.

Copyright © History Skills 2014-2024.
Contact via email
Find your history essay writer
Expert writers.
Choose from our pool of highly qualified writers, selected for their ability to expertly tackle any assignment without using AI.

Additional perks
24/7 support, timely delivery, original content commitment, unlimited edits, get a history essay writer in 3 steps.

Provide your requirements

Pick your expert

Download and finalize
Feedback from our clients.
Naomi was great. Required documents were sent and order was completed prior to the requested date on this essay service. Well written.
i was bombarding him with fine tuning and he handled it professionally
Provided exceptional essay writing help in a short period of time. I plan to work with writer on many more projects!
The assignment was done ahead of schedule and was complete with the details required.
Best and efficient writer on this essay writing service. I am really thankful to him for making my life easy.
Very professional paper, it was submitted before the time, good understanding of the subject provided
Joel always meets the deadline and more time than none is done way before it. He is able to work off the information that is given easily. It is always a very stress-free experience with outstanding work. Thank you!
Very professional: Quick turnaround time , responsive with high quality essay write help.
Do not look for another writer. Mr.Bill will do it for you fast and you will never be disappointed. He is my favorite writing essays service writer
I always ask for Jordan P. because I know the work will be completed way before my deadline and the work is thorough!
Tom does outstanding work. I challenge you to use him...he will not disappoint you.
I absolotely love working with Lillian. She delivers quality work each and every time. I pass with flying colors.
Exceptional writer. Goes above and beyond to produce original paper at any level. will be coming back to this online essay writing service
she is a great writer. I have now used her for multiple assignments and all have turned out great she is one of my favorite writers.
wrote my essay up to a high standard . she listens with patience and delivers what u ask for....
A great writer pays attention to ever bullet point in assignment requirements
wow so fast so good i like the work and the writing that you do please always keep up the good work =)
Wesley got my piece done within 1 week. He is awesome!
Great work! She finished the essay before the deadline and after reading the essay, is very thorough with her work. will definitely be using her again!
He did very well and wrote essay for me in 45 minutes. Great work !!
He wrote my essays, got my paper done early and also great quality
This writer did a fabulous job on the paper and bibliography- exactly what was required and in a very good time. Communication was clear and easy to work with- thank you for high quality work. Highly recommend, would give 10 stars if I could!
Absolutely one of my favs. He helped me with 3 projects all on short notice. I received an "A" on all 3. He is very thorough and pays great attention to detail. I recommend him 100%.
Did an amazing job on an essay. very happy with the work and plan on working again in the near future and ask him to write my essay online again
Thank you Kelvin for the great work. Very fast, this writer delivers work way before the deadline. I highly recommend Kelvin as your writer.
I am in a post Masters program. Anna wrote as if she was an expert in the field! She delivered the paper before it was due, and exceeded my expectations! I would 100% recommend her!
Fair prices
- Writing from $10.80 /page
- Proofreading from $3.24 /page
- Editing from $5.40 /page
- Rewriting from $7.56 /page
- Originality report free
- Unlimited revisions free
- Unlimited sources free
- Title page free
- Formatting free
Frequently asked questions
Who are your experts, how can i pay, how much time is needed to complete my essay, what is the price of your service, who's your history essay writer.
We pride ourselves on working with highly qualified professionals, holding Bachelor's, Master's, or PhD degrees. Our rigorous selection process ensures that we only collaborate with experienced essay writers who excel in academic paper completion, research, and formatting. We have a strict screening process in place and promptly address any violations of our guidelines based on user feedback.
We understand that the quality of your essay is directly linked to the information you provide to a writer. When you ask us to "write my history essay", we encourage you to share as many details and requirements as possible.
We value open communication between you and your assigned writer. You can track the progress of your paper and engage with them directly through our chat feature. Whether you have questions, need to provide additional instructions, or have any concerns about your paper, feel free to communicate with your expert. Consistent communication between you and your expert is vital for the success of your order.
We acknowledge that there might be instances where you forget to specify certain instructions while placing your "do my history essay" order, such as needing proper source citations or other essential details. Not to worry! With EssayHub, you can conveniently send any additional information to your writer at any time after placing your order. This ensures that your paper is completed according to every one of your requirements. Our customer support is available 24/7, so you can reach out to us whenever you need assistance.
At EssayHub, we are committed to delivering high-quality essays for sale and providing excellent customer service. We strive to meet your expectations and ensure your satisfaction throughout the writing process. Say, "Write a history essay for me" and let's get started.
Bonuses I get when you write my history essay
Say goodbye to your stress and let us take the paper-writing burden off your shoulders by letting us craft a history essay for you! Our dedicated service is designed to assist students with all their academic needs, including various types of essays and dissertations. Rest assured that your work will be at least 96% original, as our team works diligently to fulfill your "write my history essay for me" request. With our original content commitment and full refund policy, we stand out from other services. Place an order and let experienced writers help ease your studies.
Experience quick and reliable support with our 24/7 team of experts, who are ready to answer your questions and address any concerns you may have. We prioritize flawless communication to ensure the best possible outcome. When you entrust us with your "do my history essay for me" request, our professionals start working on it immediately, often delivering the final product earlier than expected. Maintaining open communication with your assigned writer is also encouraged, allowing you to provide feedback or promptly request any necessary revisions.
We take the security of your information seriously. Our website utilizes state-of-the-art encryption methods to safeguard your data, ensuring that your "help me write my history essay" request and all your private info are stored securely. Your privacy is our priority, and we observe industry-specific standards to deliver a secure service.
Choose us when you need someone to write essays for money . We're experts at alleviating the pressure of academic tasks while delivering exceptional results. Our team excels at providing the assistance students need to make their academic journey smooth and successful.
What do I have to do for you to do my history essay for me?
We strive to provide you with a seamless experience throughout your journey with us. We understand that students often require essays promptly, leading them to search for services that offer a balance between speed and quality.
Our aim is to satisfy all your academic needs, whether that means offering convenient payment options, a secure document repository, or a one-stop shop for all your history writing requirements. Our modern payment systems ensure the security of both parties involved. When you place a "write my history essay for me" order, your funds are securely deposited in a separate account until the assignment is completed and you confirm your satisfaction. Only then are the funds released to the writer. We accept a wide range of payment methods, including Mastercard, Maestro, Visa, American Express, Discover, JCB, and Diners Club while processing transactions through reliable financial gateways. Enjoy your newfound peace of mind in our partnership. If, for any reason, you're not satisfied with our work, we offer a full refund.
Our user-friendly platform allows you to communicate directly with the writers and make unlimited revisions to your work. With the final product in your hands, you have full control over its appearance. You can also reach out to us via text to expedite the process of finding a suitable expert for your project.
When we write a history essay for you, we prioritize your convenience, security, and satisfaction. Our goal is to provide you with a hassle-free experience, allowing you to receive a well-crafted history essay that meets your expectations.
EssayHub: your perfect academic solution
🏆 Safe payments | Bank-level encryption for your transactions |
✅ Free formatting | Enjoy limitless edits to perfect your assignment |
✍ Original content commitment | We provide papers with a 96-98% original content guarantee |
⏰ Round-the-clock customer service | Count on us for on-time delivery |
🔝 Top-level writers | Our team consists of 750+ expert professionals |
Many students face challenges when it comes to crafting history essays. The demands of studying can be overwhelming, leaving them exhausted and sleep-deprived. Some students juggle part-time jobs alongside their studies, while others struggle with language barriers. At EssayHub, we understand these difficulties and offer the most convenient solution: having your "write my history paper for me" order completed by our professionals. We believe that students deserve some free time to focus on other aspects of their lives.
If you've ever wondered, "Who can do my history essay for me?" the answer is simple: "We can!" With our service, you not only gain valuable free time but also receive a professionally written paper promptly. Students from universities worldwide have already experienced the benefits of our services.
Finding a writer can be a daunting task, especially if you're unsure how to monitor their progress once hired. However, at EssayHub, we provide complete transparency and control over the writing process. Our chat system enables constant communication with your writer, allowing you to request progress updates and provide any necessary clarifications. Effective communication ensures that your order is completed on time and aligns with your expectations.
We are committed to providing you with the best experience, which is why you can request updates or corrections as needed. By working closely with your online helper, you can ensure that your history essay meets your exact requirements. Look no further for a convenient platform – hire us today! With our team of experts and an efficient communication system, you can expect to receive the highest quality work delivered on time.
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Happiness Hub Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- Happiness Hub
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
How to Write a History Essay
Last Updated: December 27, 2022 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Emily Listmann, MA . Emily Listmann is a Private Tutor and Life Coach in Santa Cruz, California. In 2018, she founded Mindful & Well, a natural healing and wellness coaching service. She has worked as a Social Studies Teacher, Curriculum Coordinator, and an SAT Prep Teacher. She received her MA in Education from the Stanford Graduate School of Education in 2014. Emily also received her Wellness Coach Certificate from Cornell University and completed the Mindfulness Training by Mindful Schools. There are 8 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 245,944 times.
Writing a history essay requires you to include a lot of details and historical information within a given number of words or required pages. It's important to provide all the needed information, but also to present it in a cohesive, intelligent way. Know how to write a history essay that demonstrates your writing skills and your understanding of the material.
Preparing to Write Your Essay

- The key words will often need to be defined at the start of your essay, and will serve as its boundaries. [2] X Research source
- For example, if the question was "To what extent was the First World War a Total War?", the key terms are "First World War", and "Total War".
- Do this before you begin conducting your research to ensure that your reading is closely focussed to the question and you don't waste time.

- Explain: provide an explanation of why something happened or didn't happen.
- Interpret: analyse information within a larger framework to contextualise it.
- Evaluate: present and support a value-judgement.
- Argue: take a clear position on a debate and justify it. [3] X Research source

- Your thesis statement should clearly address the essay prompt and provide supporting arguments. These supporting arguments will become body paragraphs in your essay, where you’ll elaborate and provide concrete evidence. [4] X Trustworthy Source Purdue Online Writing Lab Trusted resource for writing and citation guidelines Go to source
- Your argument may change or become more nuanced as your write your essay, but having a clear thesis statement which you can refer back to is very helpful.
- For example, your summary could be something like "The First World War was a 'total war' because civilian populations were mobilized both in the battlefield and on the home front".

- Pick out some key quotes that make your argument precisely and persuasively. [5] X Research source
- When writing your plan, you should already be thinking about how your essay will flow, and how each point will connect together.
Doing Your Research

- Primary source material refers to any texts, films, pictures, or any other kind of evidence that was produced in the historical period, or by someone who participated in the events of the period, that you are writing about.
- Secondary material is the work by historians or other writers analysing events in the past. The body of historical work on a period or event is known as the historiography.
- It is not unusual to write a literature review or historiographical essay which does not directly draw on primary material.
- Typically a research essay would need significant primary material.

- Start with the core texts in your reading list or course bibliography. Your teacher will have carefully selected these so you should start there.
- Look in footnotes and bibliographies. When you are reading be sure to pay attention to the footnotes and bibliographies which can guide you to further sources a give you a clear picture of the important texts.
- Use the library. If you have access to a library at your school or college, be sure to make the most of it. Search online catalogues and speak to librarians.
- Access online journal databases. If you are in college it is likely that you will have access to academic journals online. These are an excellent and easy to navigate resources.
- Use online sources with discretion. Try using free scholarly databases, like Google Scholar, which offer quality academic sources, but avoid using the non-trustworthy websites that come up when you simply search your topic online.
- Avoid using crowd-sourced sites like Wikipedia as sources. However, you can look at the sources cited on a Wikipedia page and use them instead, if they seem credible.

- Who is the author? Is it written by an academic with a position at a University? Search for the author online.
- Who is the publisher? Is the book published by an established academic press? Look in the cover to check the publisher, if it is published by a University Press that is a good sign.
- If it's an article, where is published? If you are using an article check that it has been published in an academic journal. [8] X Research source
- If the article is online, what is the URL? Government sources with .gov addresses are good sources, as are .edu sites.

- Ask yourself why the author is making this argument. Evaluate the text by placing it into a broader intellectual context. Is it part of a certain tradition in historiography? Is it a response to a particular idea?
- Consider where there are weaknesses and limitations to the argument. Always keep a critical mindset and try to identify areas where you think the argument is overly stretched or the evidence doesn't match the author's claims. [9] X Research source

- Label all your notes with the page numbers and precise bibliographic information on the source.
- If you have a quote but can't remember where you found it, imagine trying to skip back through everything you have read to find that one line.
- If you use something and don't reference it fully you risk plagiarism. [10] X Research source
Writing the Introduction

- For example you could start by saying "In the First World War new technologies and the mass mobilization of populations meant that the war was not fought solely by standing armies".
- This first sentences introduces the topic of your essay in a broad way which you can start focus to in on more.

- This will lead to an outline of the structure of your essay and your argument.
- Here you will explain the particular approach you have taken to the essay.
- For example, if you are using case studies you should explain this and give a brief overview of which case studies you will be using and why.

Writing the Essay

- Try to include a sentence that concludes each paragraph and links it to the next paragraph.
- When you are organising your essay think of each paragraph as addressing one element of the essay question.
- Keeping a close focus like this will also help you avoid drifting away from the topic of the essay and will encourage you to write in precise and concise prose.
- Don't forget to write in the past tense when referring to something that has already happened.

- Don't drop a quote from a primary source into your prose without introducing it and discussing it, and try to avoid long quotations. Use only the quotes that best illustrate your point.
- If you are referring to a secondary source, you can usually summarise in your own words rather than quoting directly.
- Be sure to fully cite anything you refer to, including if you do not quote it directly.

- Think about the first and last sentence in every paragraph and how they connect to the previous and next paragraph.
- Try to avoid beginning paragraphs with simple phrases that make your essay appear more like a list. For example, limit your use of words like: "Additionally", "Moreover", "Furthermore".
- Give an indication of where your essay is going and how you are building on what you have already said. [15] X Research source

- Briefly outline the implications of your argument and it's significance in relation to the historiography, but avoid grand sweeping statements. [16] X Research source
- A conclusion also provides the opportunity to point to areas beyond the scope of your essay where the research could be developed in the future.
Proofreading and Evaluating Your Essay

- Try to cut down any overly long sentences or run-on sentences. Instead, try to write clear and accurate prose and avoid unnecessary words.
- Concentrate on developing a clear, simple and highly readable prose style first before you think about developing your writing further. [17] X Research source
- Reading your essay out load can help you get a clearer picture of awkward phrasing and overly long sentences. [18] X Research source

- When you read through your essay look at each paragraph and ask yourself, "what point this paragraph is making".
- You might have produced a nice piece of narrative writing, but if you are not directly answering the question it is not going to help your grade.

- A bibliography will typically have primary sources first, followed by secondary sources. [19] X Research source
- Double and triple check that you have included all the necessary references in the text. If you forgot to include a reference you risk being reported for plagiarism.
Sample Essay

Community Q&A
You Might Also Like

- ↑ http://www.historytoday.com/robert-pearce/how-write-good-history-essay
- ↑ https://www.hamilton.edu/academics/centers/writing/writing-resources/writing-a-good-history-paper
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/the_writing_process/thesis_statement_tips.html
- ↑ http://history.rutgers.edu/component/content/article?id=106:writing-historical-essays-a-guide-for-undergraduates
- ↑ https://guides.lib.uw.edu/c.php?g=344285&p=2580599
- ↑ http://www.hamilton.edu/documents/writing-center/WritingGoodHistoryPaper.pdf
- ↑ http://www.bowdoin.edu/writing-guides/
- ↑ https://www.wgtn.ac.nz/hppi/publications/Writing-History-Essays.pdf
About This Article

To write a history essay, read the essay question carefully and use source materials to research the topic, taking thorough notes as you go. Next, formulate a thesis statement that summarizes your key argument in 1-2 concise sentences and create a structured outline to help you stay on topic. Open with a strong introduction that introduces your thesis, present your argument, and back it up with sourced material. Then, end with a succinct conclusion that restates and summarizes your position! For more tips on creating a thesis statement, read on! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Lea Fernandez
Nov 23, 2017
Did this article help you?
Matthew Sayers
Mar 31, 2019
Millie Jenkerinx
Nov 11, 2017
Oct 18, 2019
Shannon Harper
Mar 9, 2018

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Develop the tech skills you need for work and life
How to Write a History Essay?
04 August, 2020
10 minutes read
Author: Tomas White
There are so many types of essays. It can be hard to know where to start. History papers aren’t just limited to history classes. These tasks can be assigned to examine any important historical event or a person. While they’re more common in history classes, you can find this type of assignment in sociology or political science course syllabus, or just get a history essay task for your scholarship. This is Handmadewriting History Essay Guide - let's start!

Purpose of a History Essay
Wondering how to write a history essay? First of all, it helps to understand its purpose. Secondly, this essay aims to examine the influences that lead to a historical event. Thirdly, it can explore the importance of an individual’s impact on history.
However, the goal isn’t to stay in the past. Specifically, a well-written history essay should discuss the relevance of the event or person to the “now”. After finishing this essay, a reader should have a fuller understanding of the lasting impact of an event or individual.
Need basic essay guidance? Find out what is an essay with this 101 essay guide: What is an Essay?
Elements for Success
Indeed, understanding how to write a history essay is crucial in creating a successful paper. Notably, these essays should never only outline successful historic events or list an individual’s achievements. Instead, they should focus on examining questions beginning with what , how , and why . Here’s a pro tip in how to write a history essay: brainstorm questions. Once you’ve got questions, you have an excellent starting point.
Preparing to Write

Evidently, a typical history essay format requires the writer to provide background on the event or person, examine major influences, and discuss the importance of the forces both then and now. In addition, when preparing to write, it’s helpful to organize the information you need to research into questions. For example:
- Who were the major contributors to this event?
- Who opposed or fought against this event?
- Who gained or lost from this event?
- Who benefits from this event today?
- What factors led up to this event?
- What changes occurred because of this event?
- What lasting impacts occurred locally, nationally, globally due to this event?
- What lessons (if any) were learned?
- Why did this event occur?
- Why did certain populations support it?
- Why did certain populations oppose it?
These questions exist as samples. Therefore, generate questions specific to your topic. Once you have a list of questions, it’s time to evaluate them.
Evaluating the Question

Seasoned writers approach writing history by examining the historic event or individual. Specifically, the goal is to assess the impact then and now. Accordingly, the writer needs to evaluate the importance of the main essay guiding the paper. For example, if the essay’s topic is the rise of American prohibition, a proper question may be “How did societal factors influence the rise of American prohibition during the 1920s? ”
This question is open-ended since it allows for insightful analysis, and limits the research to societal factors. Additionally, work to identify key terms in the question. In the example, key terms would be “societal factors” and “prohibition”.
Summarizing the Argument
The argument should answer the question. Use the thesis statement to clarify the argument and outline how you plan to make your case. In other words. the thesis should be sharp, clear, and multi-faceted. Consider the following tips when summarizing the case:
- The thesis should be a single sentence
- It should include a concise argument and a roadmap
- It’s always okay to revise the thesis as the paper develops
- Conduct a bit of research to ensure you have enough support for the ideas within the paper
Outlining a History Essay Plan

Once you’ve refined your argument, it’s time to outline. Notably, many skip this step to regret it then. Nonetheless, the outline is a map that shows where you need to arrive historically and when. Specifically, taking the time to plan, placing the strongest argument last, and identifying your sources of research is a good use of time. When you’re ready to outline, do the following:
- Consider the necessary background the reader should know in the introduction paragraph
- Define any important terms and vocabulary
- Determine which ideas will need the cited support
- Identify how each idea supports the main argument
- Brainstorm key points to review in the conclusion
Gathering Sources
As a rule, history essays require both primary and secondary sources . Primary resources are those that were created during the historical period being analyzed. Secondary resources are those created by historians and scholars about the topic. It’s a good idea to know if the professor requires a specific number of sources, and what kind he or she prefers. Specifically, most tutors prefer primary over secondary sources.
Where to find sources? Great question! Check out bibliographies included in required class readings. In addition, ask a campus Librarian. Peruse online journal databases; In addition, most colleges provide students with free access. When in doubt, make an appointment and ask the professor for guidance.
Writing the Essay
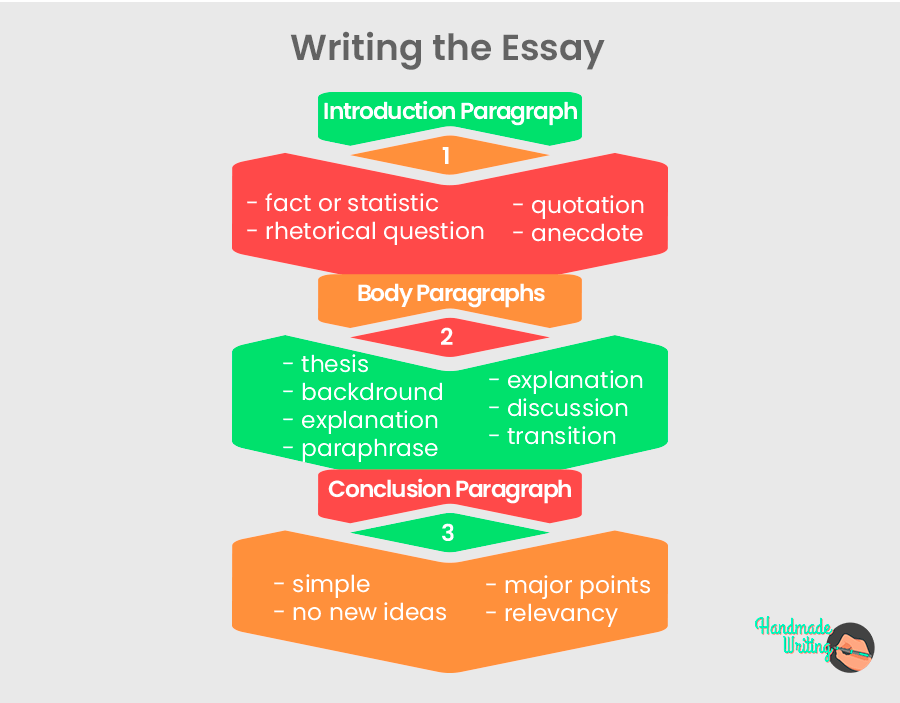
Now that you have prepared your questions, ideas, and arguments; composed the outline ; and gathered sources – it’s time to write your first draft. In particular, each section of your history essay must serve its purpose. Here is what you should include in essay paragraphs.
Introduction Paragraph
Unsure of how to start a history essay? Well, like most essays, the introduction should include an attention-getter (or hook):
- Relevant fact or statistic
- Rhetorical Question
- Interesting quotation
- Application anecdote if appropriate
Once you’ve captured the reader’s interest, introduce the topic. Similarly, present critical historic context. Namely, it is necessary to introduce any key individuals or events that will be discussed later in the essay. At last, end with a strong thesis which acts as a transition to the first argument.
Body Paragraphs
Indeed, each body paragraph should offer a single idea to support the argument. Then, after writing a strong topic sentence, the topic should be supported with correctly cited research. Consequently, a typical body paragraph is arranged as follows:
- Topic sentence linking to the thesis
- Background of the topic
- Research quotation or paraphrase #1
- Explanation and analysis of research
- Research quotation or paraphrase #2
- Transition to the next paragraph
Equally, the point of body paragraphs is to build the argument. Hence, present the weakest support first and end with the strongest. Admittedly, doing so leaves the reader with the best possible evidence.
Conclusion Paragraph
You’re almost there! Eventually, conclusion paragraphs should review the most important points in the paper. In them, you should prove that you’ve supported the argument proposed in the thesis. When writing a conclusion paragraph keep these tips in mind:
- Keep it simple
- Avoid introducing new information
- Review major points
- Discuss the relevance to today
Problems with writing Your History essay ? Try our Essay Writer Service!

Proofreading Your Essay
Once the draft is ready and polished, it’s time to proceed to final editing. What does this process imply? Specifically, it’s about removing impurities and making the essay look just perfect. Here’s what you need to do to improve the quality of your paper:
- Double check the content. In the first place, it’s recommended to get rid of long sentences, correct vague words. Also, make sure that all your paragrahps contain accurate sentences with transparent meaning.
- Pay attention to style. To make the process of digesting your essay easier, focus on crafting a paper with readable style, the one that is known to readers. Above all, the main mission here is to facilitate the perception of your essay. So, don’t forget about style accuracy.
- Practice reading the essay. Of course, the best practice before passing the paper is to read it out loud. Hence, this exercise will help you notice fragments that require rewriting or a complete removal.
History Essay Example
Did you want a history essay example? Take a look at one of our history essay papers.
Make it Shine
An A-level essay takes planning and revision, but it’s achievable. Firstly, avoid procrastination and start early. Secondly, leave yourself plenty of time to brainstorm, outline, research and write. Finally, follow these five tips to make your history essay shine:
- Write a substantial introduction. Particularly, it’s the first impression the professor will have of the paper.
- State a clear thesis. A strong thesis is easier to support.
- Incorporate evidence critically. If while researching you find opposing arguments, include them and discuss their flaws.
- Cite all the research. Whether direct quotations or paraphrases, citing evidence is crucial to avoiding plagiarism, which can have serious academic consequences.
- Include primary and secondary resources. While primary resources may be harder to find, the professor will expect them—this is, after all, a history essay.
History Essay Sample
Ready to tackle the history essay format? Great! Check out this history essay sample from an upper-level history class. While the essay isn’t perfect, the professor points out its many strengths.
Remember: start early and revise, revise, revise . We can’t revise history, but you can revise your ideas until they’re perfect.

A life lesson in Romeo and Juliet taught by death
Due to human nature, we draw conclusions only when life gives us a lesson since the experience of others is not so effective and powerful. Therefore, when analyzing and sorting out common problems we face, we may trace a parallel with well-known book characters or real historical figures. Moreover, we often compare our situations with […]

Ethical Research Paper Topics
Writing a research paper on ethics is not an easy task, especially if you do not possess excellent writing skills and do not like to contemplate controversial questions. But an ethics course is obligatory in all higher education institutions, and students have to look for a way out and be creative. When you find an […]

Art Research Paper Topics
Students obtaining degrees in fine art and art & design programs most commonly need to write a paper on art topics. However, this subject is becoming more popular in educational institutions for expanding students’ horizons. Thus, both groups of receivers of education: those who are into arts and those who only get acquainted with art […]
Writing a Good History Paper
- Top Ten Reasons for Negative Comments
- Making Sure your Paper has Substance
Common Marginal Remarks on Style, Clarity, Grammar, and Syntax
Word and phrase usage problems, analyzing a historical document, writing a book review, writing a term paper or senior thesis, top ten reasons for negative comments on history papers.
(Drawn from a survey of the History Department ) 10. You engage in cheap, anachronistic moralizing . 9. You are sloppy with the chronology . 8. You quote excessively or improperly . 7. You have written a careless “one-draft wonder.” (See revise and proofread) 6. You are vague or have empty, unsupported generalizations . 5. You write too much in the passive voice. 4. You use inappropriate sources . 3. You use evidence uncritically. 2. You are wordy . 1. You have no clear thesis and little analysis.
Making Sure your History Paper has Substance
Get off to a good start..
Avoid pretentious, vapid beginnings. If you are writing a paper on, say, British responses to the rebellion in India in 1857, don't open with a statement like this: “Throughout human history people in all cultures everywhere in the world have engaged in many and long-running conflicts about numerous aspects of government policy and diplomatic issues, which have much interested historians and generated historical theories in many areas.” This is pure garbage, bores the reader, and is a sure sign that you have nothing substantive to say. Get to the point. Here’s a better start: “The rebellion in 1857 compelled the British to rethink their colonial administration in India.” This sentence tells the reader what your paper is actually about and clears the way for you to state your thesis in the rest of the opening paragraph. For example, you might go on to argue that greater British sensitivity to Indian customs was hypocritical.
State a clear thesis.
Whether you are writing an exam essay or a senior thesis, you need to have a thesis. Don’t just repeat the assignment or start writing down everything that you know about the subject. Ask yourself, “What exactly am I trying to prove?” Your thesis is your take on the subject, your perspective, your explanation—that is, the case that you’re going to argue. “Famine struck Ireland in the 1840s” is a true statement, but it is not a thesis. “The English were responsible for famine in Ireland in the 1840s” is a thesis (whether defensible or not is another matter). A good thesis answers an important research question about how or why something happened. (“Who was responsible for the famine in Ireland in the 1840s?”) Once you have laid out your thesis, don’t forget about it. Develop your thesis logically from paragraph to paragraph. Your reader should always know where your argument has come from, where it is now, and where it is going.
Be sure to analyze.
Students are often puzzled when their professors mark them down for summarizing or merely narrating rather than analyzing. What does it mean to analyze? In the narrow sense, to analyze means to break down into parts and to study the interrelationships of those parts. If you analyze water, you break it down into hydrogen and oxygen. In a broader sense, historical analysis explains the origins and significance of events. Historical analysis digs beneath the surface to see relationships or distinctions that are not immediately obvious. Historical analysis is critical; it evaluates sources, assigns significance to causes, and weighs competing explanations. Don’t push the distinction too far, but you might think of summary and analysis this way: Who, what, when, and where are the stuff of summary; how, why, and to what effect are the stuff of analysis. Many students think that they have to give a long summary (to show the professor that they know the facts) before they get to their analysis. Try instead to begin your analysis as soon as possible, sometimes without any summary at all. The facts will “shine through” a good analysis. You can't do an analysis unless you know the facts, but you can summarize the facts without being able to do an analysis. Summary is easier and less sophisticated than analysis—that’s why summary alone never earns an “A.”
Use evidence critically.
Like good detectives, historians are critical of their sources and cross-check them for reliability. You wouldn't think much of a detective who relied solely on a suspect’s archenemy to check an alibi. Likewise, you wouldn't think much of a historian who relied solely on the French to explain the origins of World War I. Consider the following two statements on the origin of World War I: 1) “For the catastrophe of 1914 the Germans are responsible. Only a professional liar would deny this...” 2) “It is not true that Germany is guilty of having caused this war. Neither the people, the government, nor the Kaiser wanted war....” They can’t both be right, so you have to do some detective work. As always, the best approach is to ask: Who wrote the source? Why? When? Under what circumstances? For whom? The first statement comes from a book by the French politician Georges Clemenceau, which he wrote in 1929 at the very end of his life. In 1871, Clemenceau had vowed revenge against Germany for its defeat of France in the Franco-Prussian War. As premier of France from 1917 to 1920, he represented France at the Paris Peace Conference in 1919. He was obviously not a disinterested observer. The second statement comes from a manifesto published by ninety-three prominent German intellectuals in the fall of 1914. They were defending Germany against charges of aggression and brutality. They too were obviously not disinterested observers. Now, rarely do you encounter such extreme bias and passionate disagreement, but the principle of criticizing and cross-checking sources always applies. In general, the more sources you can use, and the more varied they are, the more likely you are to make a sound historical judgment, especially when passions and self-interests are engaged. You don’t need to be cynical as a historian (self-interest does not explain everything), but you do need to be critical and skeptical. Competent historians may offer different interpretations of the same evidence or choose to stress different evidence. You will not find a single historical Truth with a capital “T” on any matter of significance. You can, however, learn to discriminate among conflicting interpretations, not all of which are created equal. (See also: Analyzing a Historical Document )
Be precise.
Vague statements and empty generalizations suggest that you haven't put in the time to learn the material. Consider these two sentences: “During the French Revolution, the government was overthrown by the people. The Revolution is important because it shows that people need freedom.” What people? Landless peasants? Urban journeymen? Wealthy lawyers? Which government? When? How? Who exactly needed freedom, and what did they mean by freedom? Here is a more precise statement about the French Revolution: “Threatened by rising prices and food shortages in 1793, the Parisian sans-culottes pressured the Convention to institute price controls.” This statement is more limited than the grandiose generalizations about the Revolution, but unlike them, it can open the door to a real analysis of the Revolution. Be careful when you use grand abstractions like people, society, freedom, and government, especially when you further distance yourself from the concrete by using these words as the apparent antecedents for the pronouns they and it. Always pay attention to cause and effect. Abstractions do not cause or need anything; particular people or particular groups of people cause or need things. Avoid grandiose trans-historical generalizations that you can’t support. When in doubt about the appropriate level of precision or detail, err on the side of adding “too much” precision and detail.
Watch the chronology.
Anchor your thesis in a clear chronological framework and don't jump around confusingly. Take care to avoid both anachronisms and vagueness about dates. If you write, “Napoleon abandoned his Grand Army in Russia and caught the redeye back to Paris,” the problem is obvious. If you write, “Despite the Watergate scandal, Nixon easily won reelection in 1972,” the problem is more subtle, but still serious. (The scandal did not become public until after the election.) If you write, “The revolution in China finally succeeded in the twentieth century,” your professor may suspect that you haven’t studied. Which revolution? When in the twentieth century? Remember that chronology is the backbone of history. What would you think of a biographer who wrote that you graduated from Hamilton in the 1950s?
Cite sources carefully.
Your professor may allow parenthetical citations in a short paper with one or two sources, but you should use footnotes for any research paper in history. Parenthetical citations are unaesthetic; they scar the text and break the flow of reading. Worse still, they are simply inadequate to capture the richness of historical sources. Historians take justifiable pride in the immense variety of their sources. Parenthetical citations such as (Jones 1994) may be fine for most of the social sciences and humanities, where the source base is usually limited to recent books and articles in English. Historians, however, need the flexibility of the full footnote. Try to imagine this typical footnote (pulled at random from a classic work of German history) squeezed into parentheses in the body of the text: DZA Potsdam, RdI, Frieden 5, Erzgebiet von Longwy-Briey, Bd. I, Nr. 19305, gedruckte Denkschrift für OHL und Reichsleitung, Dezember 1917, und in RWA, Frieden Frankreich Nr. 1883. The abbreviations are already in this footnote; its information cannot be further reduced. For footnotes and bibliography, historians usually use Chicago style. (The Chicago Manual of Style. 15th edition. Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 2003.) On the Writing Center’s website you can find a useful summary of Chicago citation style prepared by a former history major, Elizabeth Rabe ’04 ( Footnotes ). RefWorks (on the library’s website) will convert your citations to Chicago style. Don’t hesitate to ask one of the reference librarians for help if you have trouble getting started on RefWorks.
Use primary sources.
Use as many primary sources as possible in your paper. A primary source is one produced by a participant in or witness of the events you are writing about. A primary source allows the historian to see the past through the eyes of direct participants. Some common primary sources are letters, diaries, memoirs, speeches, church records, newspaper articles, and government documents of all kinds. The capacious genre “government records” is probably the single richest trove for the historian and includes everything from criminal court records, to tax lists, to census data, to parliamentary debates, to international treaties—indeed, any records generated by governments. If you’re writing about culture, primary sources may include works of art or literature, as well as philosophical tracts or scientific treatises—anything that comes under the broad rubric of culture. Not all primary sources are written. Buildings, monuments, clothes, home furnishings, photographs, religious relics, musical recordings, or oral reminiscences can all be primary sources if you use them as historical clues. The interests of historians are so broad that virtually anything can be a primary source. (See also: Analyzing a Historical Document )
Use scholarly secondary sources.
A secondary source is one written by a later historian who had no part in what he or she is writing about. (In the rare cases when the historian was a participant in the events, then the work—or at least part of it—is a primary source.) Historians read secondary sources to learn about how scholars have interpreted the past. Just as you must be critical of primary sources, so too you must be critical of secondary sources. You must be especially careful to distinguish between scholarly and non-scholarly secondary sources. Unlike, say, nuclear physics, history attracts many amateurs. Books and articles about war, great individuals, and everyday material life dominate popular history. Some professional historians disparage popular history and may even discourage their colleagues from trying their hand at it. You need not share their snobbishness; some popular history is excellent. But—and this is a big but—as a rule, you should avoid popular works in your research, because they are usually not scholarly. Popular history seeks to inform and entertain a large general audience. In popular history, dramatic storytelling often prevails over analysis, style over substance, simplicity over complexity, and grand generalization over careful qualification. Popular history is usually based largely or exclusively on secondary sources. Strictly speaking, most popular histories might better be called tertiary, not secondary, sources. Scholarly history, in contrast, seeks to discover new knowledge or to reinterpret existing knowledge. Good scholars wish to write clearly and simply, and they may spin a compelling yarn, but they do not shun depth, analysis, complexity, or qualification. Scholarly history draws on as many primary sources as practical. Now, your goal as a student is to come as close as possible to the scholarly ideal, so you need to develop a nose for distinguishing the scholarly from the non-scholarly. Here are a few questions you might ask of your secondary sources (bear in mind that the popular/scholarly distinction is not absolute, and that some scholarly work may be poor scholarship). Who is the author? Most scholarly works are written by professional historians (usually professors) who have advanced training in the area they are writing about. If the author is a journalist or someone with no special historical training, be careful. Who publishes the work? Scholarly books come from university presses and from a handful of commercial presses (for example, Norton, Routledge, Palgrave, Penguin, Rowman & Littlefield, Knopf, and HarperCollins). If it’s an article, where does it appear? Is it in a journal subscribed to by our library, listed on JSTOR , or published by a university press? Is the editorial board staffed by professors? Oddly enough, the word journal in the title is usually a sign that the periodical is scholarly. What do the notes and bibliography look like? If they are thin or nonexistent, be careful. If they are all secondary sources, be careful. If the work is about a non-English-speaking area, and all the sources are in English, then it's almost by definition not scholarly. Can you find reviews of the book in the data base Academic Search Premier? If the book was published within the last few decades, and it’s not in there, that’s a bad sign. With a little practice, you can develop confidence in your judgment—and you’re on your way to being a historian. If you are unsure whether a work qualifies as scholarly, ask your professor. (See also: Writing a Book Review )
Avoid abusing your sources.
Many potentially valuable sources are easy to abuse. Be especially alert for these five abuses: Web abuse. The Web is a wonderful and improving resource for indexes and catalogs. But as a source for primary and secondary material for the historian, the Web is of limited value. Anyone with the right software can post something on the Web without having to get past trained editors, peer reviewers, or librarians. As a result, there is a great deal of garbage on the Web. If you use a primary source from the Web, make sure that a respected intellectual institution stands behind the site. Be especially wary of secondary articles on the Web, unless they appear in electronic versions of established print journals (e.g., The Journal of Asian Studies in JSTOR). Many articles on the Web are little more than third-rate encyclopedia entries. When in doubt, check with your professor. With a few rare exceptions, you will not find scholarly monographs in history (even recent ones) on the Web. You may have heard of Google’s plans to digitize the entire collections of some of the world’s major libraries and to make those collections available on the Web. Don’t hold your breath. Your days at Hamilton will be long over by the time the project is finished. Besides, your training as a historian should give you a healthy skepticism of the giddy claims of technophiles. Most of the time and effort of doing history goes into reading, note-taking, pondering, and writing. Finding a chapter of a book on the Web (as opposed to getting the physical book through interlibrary loan) might be a convenience, but it doesn’t change the basics for the historian. Moreover, there is a subtle, but serious, drawback with digitized old books: They break the historian’s sensual link to the past. And of course, virtually none of the literally trillions of pages of archival material is available on the Web. For the foreseeable future, the library and the archive will remain the natural habitats of the historian. Thesaurus abuse. How tempting it is to ask your computer’s thesaurus to suggest a more erudite-sounding word for the common one that popped into your mind! Resist the temptation. Consider this example (admittedly, a bit heavy-handed, but it drives the point home): You’re writing about the EPA’s programs to clean up impure water supplies. Impure seems too simple and boring a word, so you bring up your thesaurus, which offers you everything from incontinent to meretricious. “How about meretricious water?” you think to yourself. “That will impress the professor.” The problem is that you don’t know exactly what meretricious means, so you don’t realize that meretricious is absurdly inappropriate in this context and makes you look foolish and immature. Use only those words that come to you naturally. Don’t try to write beyond your vocabulary. Don’t try to impress with big words. Use a thesaurus only for those annoying tip-of-the-tongue problems (you know the word and will recognize it instantly when you see it, but at the moment you just can’t think of it). Quotation book abuse. This is similar to thesaurus abuse. Let’s say you are writing a paper on Alexander Hamilton’s banking policies, and you want to get off to a snappy start that will make you seem effortlessly learned. How about a quotation on money? You click on the index of Bartlett’s Familiar Quotations , and before you know it, you’ve begun your paper with, “As Samuel Butler wrote in Hudibras , ‘For what is worth in anything/ But so much money as ’t will bring?’” Face it, you’re faking it. You don’t know who Samuel Butler is, and you’ve certainly never heard of Hudibras , let alone read it. Your professor is not fooled. You sound like an insecure after-dinner speaker. Forget Bartlett’s, unless you're confirming the wording of a quotation that came to you spontaneously and relates to your paper. Encyclopedia abuse. General encyclopedias like Britannica are useful for checking facts (“Wait a sec, am I right about which countries sent troops to crush the Boxer Rebellion in China? Better check.”). But if you are footnoting encyclopedias in your papers, you are not doing college-level research.
Dictionary Abuse. The dictionary is your friend. Keep it by your side as you write, but do not abuse it by starting papers with a definition. You may be most tempted to start this way when you are writing on a complex, controversial, or elusive subject. (“According to Webster’s Collegiate Dictionary , liberalism is defined as...”). Actually, the dictionary does you little good in such cases and makes you sound like a conscientious but dull high-school student. Save in the rare case that competing dictionary definitions are the subject at hand, keep dictionary quotations out of your paper.
Quote sparingly
Avoid quoting a secondary source and then simply rewording or summarizing the quotation, either above or below the quotation. It is rarely necessary to quote secondary sources at length, unless your essay focuses on a critical analysis of the author’s argument. (See also: Writing a Book Review ) Your professor wants to see your ability to analyze and to understand the secondary sources. Do not quote unless the quotation clarifies or enriches your analysis. When in doubt, do not quote; instead, integrate the author’s argument into your own (though be sure to acknowledge ideas from your sources, even when you are paraphrasing). If you use a lot of quotations from secondary sources, you are probably writing a poor paper. An analysis of a primary source, such as a political tract or philosophical essay, might require lengthy quotations, often in block format. In such cases, you might need to briefly repeat key points or passages as a means to introduce the author’s ideas, but your analysis and interpretation of the text’s meaning should remain the most important aim. (See also: Using primary sources and Use scholarly secondary sources .)
Know your audience
Unless instructed otherwise, you should assume that your audience consists of educated, intelligent, nonspecialists. In fact, your professor will usually be your only reader, but if you write directly to your professor, you may become cryptic or sloppy (oh well, she’ll know what I’m talking about). Explaining your ideas to someone who doesn't know what you mean forces you to be clear and complete. Now, finding the right amount of detail can, admittedly, be tricky (how much do I put in about the Edict of Nantes, the Embargo Act, or President Wilson’s background?). When in doubt, err on the side of putting in extra details. You’ll get some leeway here if you avoid the extremes (my reader’s an ignoramus/my reader knows everything).
Avoid cheap, anachronistic moralizing
Many of the people and institutions of the past appear unenlightened, ignorant, misguided, or bigoted by today’s values. Resist the temptation to condemn or to get self-righteous. (“Martin Luther was blind to the sexism and class prejudice of sixteenth-century German society.”) Like you, people in the past were creatures of their time; like you, they deserve to be judged by the standards of their time. If you judge the past by today’s standards (an error historians call “presentism”), you will never understand why people thought or acted as they did. Yes, Hitler was a bad guy, but he was bad not only by today’s standards, but also by the commonly accepted standards of his own time. Someday you’re going to look pretty foolish and ignorant yourself. (“Early twenty-first century Hamilton students failed to see the shocking inderdosherism [that’s right, you don’t recognize the concept because it doesn’t yet exist] implicit in their career plans.”)
Have a strong conclusion
Obviously, you should not just stop abruptly as though you have run out of time or ideas. Your conclusion should conclude something. If you merely restate briefly what you have said in your paper, you give the impression that you are unsure of the significance of what you have written. A weak conclusion leaves the reader unsatisfied and bewildered, wondering why your paper was worth reading. A strong conclusion adds something to what you said in your introduction. A strong conclusion explains the importance and significance of what you have written. A strong conclusion leaves your reader caring about what you have said and pondering the larger implications of your thesis. Don’t leave your reader asking, “So what?”
Revise and proofread
Your professor can spot a “one-draft wonder,” so don't try to do your paper at the last moment. Leave plenty of time for revising and proofreading. Show your draft to a writing tutor or other good writer. Reading the draft aloud may also help. Of course, everyone makes mistakes, and a few may slip through no matter how meticulous you are. But beware of lots of mistakes. The failure to proofread carefully suggests that you devoted little time and effort to the assignment. Tip: Proofread your text both on the screen and on a printed copy. Your eyes see the two differently. Don’t rely on your spell checker to catch all of your misspellings. (If ewe ken reed this ewe kin sea that a computer wood nut all ways help ewe spill or rite reel good.)
Note: The Writing Center suggests standard abbreviations for noting some of these problems. You should familiarize yourself with those abbreviations, but your professor may not use them.
Remarks on Style and Clarity
Wordy/verbose/repetitive..
Try your hand at fixing this sentence: “Due to the fact that these aspects of the issue of personal survival have been raised by recently transpired problematic conflicts, it is at the present time paramount that the ultimate psychological end of suicide be contemplated by this individual.” If you get it down to “To be or not to be, that is the question,” you’ve done well. You may not match Shakespeare, but you can learn to cut the fat out of your prose. The chances are that the five pages you’ve written for your history paper do not really contain five pages’ worth of ideas.
Misuse of the passive voice.
Write in the active voice. The passive voice encourages vagueness and dullness; it enfeebles verbs; and it conceals agency, which is the very stuff of history. You know all of this almost instinctively. What would you think of a lover who sighed in your ear, “My darling, you are loved by me!”? At its worst, the passive voice—like its kin, bureaucratic language and jargon—is a medium for the dishonesty and evasion of responsibility that pervade contemporary American culture. (“Mistakes were made; I was given false information.” Now notice the difference: “I screwed up; Smith and Jones lied to me; I neglected to check the facts.”) On history papers the passive voice usually signals a less toxic version of the same unwillingness to take charge, to commit yourself, and to say forthrightly what is really going on, and who is doing what to whom. Suppose you write, “In 1935 Ethiopia was invaded.” This sentence is a disaster. Who invaded? Your professor will assume that you don't know. Adding “by Italy” to the end of the sentence helps a bit, but the sentence is still flat and misleading. Italy was an aggressive actor, and your passive construction conceals that salient fact by putting the actor in the syntactically weakest position—at the end of the sentence as the object of a preposition. Notice how you add vigor and clarity to the sentence when you recast it in the active voice: "In 1935 Italy invaded Ethiopia." I n a few cases , you may violate the no-passive-voice rule. The passive voice may be preferable if the agent is either obvious (“Kennedy was elected in 1960”), irrelevant (“Theodore Roosevelt became president when McKinley was assassinated”), or unknown (“King Harold was killed at the Battle of Hastings”). Note that in all three of these sample sentences the passive voice focuses the reader on the receiver of the action rather than on the doer (on Kennedy, not on American voters; on McKinley, not on his assassin; on King Harold, not on the unknown Norman archer). Historians usually wish to focus on the doer, so you should stay with the active voice—unless you can make a compelling case for an exception.
Abuse of the verb to be.
The verb to be is the most common and most important verb in English, but too many verbs to be suck the life out of your prose and lead to wordiness. Enliven your prose with as many action verbs as possible. ( “In Brown v. Board of Education it was the opinion of the Supreme Court that the doctrine of ‘separate but equal’ was in violation of the Fourteenth Amendment.”) Rewrite as “ In Brown v. Board of Education the Supreme Court ruled that the doctrine of ‘separate but equal’ violated the Fourteenth ”
Explain/what’s your point?/unclear/huh?
You may (or may not) know what you’re talking about, but if you see these marginal comments, you have confused your reader. You may have introduced a non sequitur ; gotten off the subject; drifted into abstraction; assumed something that you have not told the reader; failed to explain how the material relates to your argument; garbled your syntax; or simply failed to proofread carefully. If possible, have a good writer read your paper and point out the muddled parts. Reading your paper aloud may help too.
Paragraph goes nowhere/has no point or unity.
Paragraphs are the building blocks of your paper. If your paragraphs are weak, your paper cannot be strong. Try underlining the topic sentence of every paragraph. If your topic sentences are vague, strength and precision—the hallmarks of good writing—are unlikely to follow. Consider this topic sentence (from a paper on Ivan the Terrible): “From 1538 to 1547, there are many different arguments about the nature of what happened.” Disaster looms. The reader has no way of knowing when the arguing takes place, who’s arguing, or even what the arguing is about. And how does the “nature of what happened” differ from plain “what happened”? Perhaps the writer means the following: “The childhood of Ivan the Terrible has provoked controversy among scholars of Russian history.” That's hardly deathless prose, but it does orient the reader and make the writer accountable for what follows in the paragraph. Once you have a good topic sentence, make sure that everything in the paragraph supports that sentence, and that cumulatively the support is persuasive. Make sure that each sentence follows logically from the previous one, adding detail in a coherent order. Move, delete, or add material as appropriate. To avoid confusing the reader, limit each paragraph to one central idea. (If you have a series of supporting points starting with first, you must follow with a second, third , etc.) A paragraph that runs more than a printed page is probably too long. Err on the side of shorter paragraphs.
Inappropriate use of first person.
Most historians write in the third person, which focuses the reader on the subject. If you write in the first person singular, you shift the focus to yourself. You give the impression that you want to break in and say, “Enough about the Haitian revolution [or whatever], now let’s talk about me!” Also avoid the first person plural (“We believe...”). It suggests committees, editorial boards, or royalty. None of those should have had a hand in writing your paper. And don’t refer to yourself lamely as “this writer.” Who else could possibly be writing the paper?
Tense inconsistency.
Stay consistently in the past tense when you are writing about what took place in the past. (“Truman’s defeat of Dewey in 1948 caught the pollsters by surprise.”) Note that the context may require a shift into the past perfect. (“The pollsters had not realized [past perfect] that voter opinion had been [past perfect] changing rapidly in the days before the election.”) Unfortunately, the tense problem can get a bit more complicated. Most historians shift into the present tense when describing or commenting on a book, document, or evidence that still exists and is in front of them (or in their mind) as they write. (“de Beauvoir published [past tense] The Second Sex in 1949. In the book she contends [present tense] that woman....”) If you’re confused, think of it this way: History is about the past, so historians write in the past tense, unless they are discussing effects of the past that still exist and thus are in the present. When in doubt, use the past tense and stay consistent.
Ill-fitted quotation.
This is a common problem, though not noted in stylebooks. When you quote someone, make sure that the quotation fits grammatically into your sentence. Note carefully the mismatch between the start of the following sentence and the quotation that follows: “In order to understand the Vikings, writes Marc Bloch, it is necessary, ‘To conceive of the Viking expeditions as religious warfare inspired by the ardour of an implacable pagan fanaticism—an explanation that has sometimes been at least suggested—conflicts too much with what we know of minds disposed to respect magic of every kind.’” At first, the transition into the quotation from Bloch seems fine. The infinitive (to conceive) fits. But then the reader comes to the verb (conflicts) in Bloch’s sentence, and things no longer make sense. The writer is saying, in effect, “it is necessary conflicts.” The wordy lead-in and the complex syntax of the quotation have tripped the writer and confused the reader. If you wish to use the whole sentence, rewrite as “Marc Bloch writes in Feudal Society , ‘To conceive of...’” Better yet, use your own words or only part of the quotation in your sentence. Remember that good writers quote infrequently, but when they do need to quote, they use carefully phrased lead-ins that fit the grammatical construction of the quotation.
Free-floating quotation.
Do not suddenly drop quotations into your prose. (“The spirit of the Progressive era is best understood if one remembers that the United States is ‘the only country in the world that began with perfection and aspired to progress.’”) You have probably chosen the quotation because it is finely wrought and says exactly what you want to say. Fine, but first you inconvenience the reader, who must go to the footnote to learn that the quotation comes from The Age of Reform by historian Richard Hofstadter. And then you puzzle the reader. Did Hofstadter write the line about perfection and progress, or is he quoting someone from the Progressive era? If, as you claim, you are going to help the reader to judge the “spirit of the Progressive era,” you need to clarify. Rewrite as “As historian Richard Hofstadter writes in the Age of Reform , the United States is ‘the only country in the world...’” Now the reader knows immediately that the line is Hofstadter’s.
Who’s speaking here?/your view?
Always be clear about whether you’re giving your opinion or that of the author or historical actor you are discussing. Let’s say that your essay is about Martin Luther’s social views. You write, “The German peasants who revolted in 1525 were brutes and deserved to be crushed mercilessly.” That’s what Luther thought, but do you agree? You may know, but your reader is not a mind reader. When in doubt, err on the side of being overly clear.
Jargon/pretentious theory.
Historians value plain English. Academic jargon and pretentious theory will make your prose turgid, ridiculous, and downright irritating. Your professor will suspect that you are trying to conceal that you have little to say. Of course, historians can’t get along without some theory; even those who profess to have no theory actually do—it’s called naïve realism. And sometimes you need a technical term, be it ontological argument or ecological fallacy. When you use theory or technical terms, make sure that they are intelligible and do real intellectual lifting. Please, no sentences like this: “By means of a neo-Althusserian, post-feminist hermeneutics, this essay will de/construct the logo/phallo/centrism imbricated in the marginalizing post-colonial gendered gaze, thereby proliferating the subjectivities that will re/present the de/stabilization of the essentializing habitus of post-Fordist capitalism.”
Informal language/slang.
You don’t need to be stuffy, but stay with formal English prose of the kind that will still be comprehensible to future generations. Columbus did not “push the envelope in the Atlantic.” Henry VIII was not “looking for his inner child when he broke with the Church.” Prime Minister Cavour of Piedmont was not “trying to play in the major leagues diplomatic wise.” Wilson did not “almost veg out” at the end of his second term. President Hindenburg did not appoint Hitler in a “senior moment.” Prime Minister Chamberlain did not tell the Czechs to “chill out” after the Munich Conference, and Gandhi was not an “awesome dude.”
Try to keep your prose fresh. Avoid cliches. When you proofread, watch out for sentences like these: “Voltaire always gave 110 percent and thought outside the box. His bottom line was that as people went forward into the future, they would, at the end of the day, step up to the plate and realize that the Jesuits were conniving perverts.” Ugh. Rewrite as “Voltaire tried to persuade people that the Jesuits were cony, step up to the plate and realize that the Jesuits were conniving perverts.” Ugh. Rewrite as “Voltaire tried to persuade people that the Jesuits were conniving perverts.”
Intensifier abuse/exaggeration.
Avoid inflating your prose with unsustainable claims of size, importance, uniqueness, certainty, or intensity. Such claims mark you as an inexperienced writer trying to impress the reader. Your statement is probably not certain ; your subject probably not unique , the biggest, the best, or the most important. Also, the adverb very will rarely strengthen your sentence. Strike it. (“President Truman was very determined to stop the spread of communism in Greece.”) Rewrite as “President Truman resolved to stop the spread of communism in Greece.”
Mixed image.
Once you have chosen an image, you must stay with language compatible with that image. In the following example, note that the chain, the boiling, and the igniting are all incompatible with the image of the cold, rolling, enlarging snowball: “A snowballing chain of events boiled over, igniting the powder keg of war in 1914.” Well chosen images can enliven your prose, but if you catch yourself mixing images a lot, you're probably trying to write beyond your ability. Pull back. Be more literal.
Clumsy transition.
If your reader feels a jolt or gets disoriented at the beginning of a new paragraph, your paper probably lacks unity. In a good paper, each paragraph is woven seamlessly into the next. If you find yourself beginning your paragraphs with phrases such as “Another aspect of this problem...,” then you are probably “stacking note cards” rather than developing a thesis.
Unnecessary relative clause.
If you don’t need to restrict the meaning of your sentence’s subject, then don’t. (“Napoleon was a man who tried to conquer Europe.”) Here the relative clause adds nothing. Rewrite as “Napoleon tried to conquer Europe.” Unnecessary relative clauses are a classic form of wordiness.

Distancing or demeaning quotation marks.
If you believe that a frequently used word or phrase distorts historical reality, don’t put it in dismissive, sneering quotation marks to make your point (“the communist ‘threat’ to the ‘free’ world during the Cold War”). Many readers find this practice arrogant, obnoxious, and precious, and they may dismiss your arguments out of hand. If you believe that the communist threat was bogus or exaggerated, or that the free world was not really free, then simply explain what you mean.
Remarks on Grammar and Syntax
Ideally, your professor will help you to improve your writing by specifying exactly what is wrong with a particular passage, but sometimes you may find a simple awk in the margin. This all-purpose negative comment usually suggests that the sentence is clumsy because you have misused words or compounded several errors. Consider this sentence from a book review:
“However, many falsehoods lie in Goldhagen’s claims and these will be explored.”
What is your long-suffering professor to do with this sentence? The however contributes nothing; the phrase falsehoods lie is an unintended pun that distracts the reader; the comma is missing between the independent clauses; the these has no clear antecedent ( falsehoods? claims? ); the second clause is in the passive voice and contributes nothing anyway; the whole sentence is wordy and screams hasty, last-minute composition. In weary frustration, your professor scrawls awk in the margin and moves on. Buried under the twelve-word sentence lies a three-word idea: “Goldhagen often errs.” When you see awk, check for the common errors in this list. If you don’t understand what’s wrong, ask.
Unclear antecedent.
All pronouns must refer clearly to antecedents and must agree with them in number. The reader usually assumes that the antecedent is the immediately preceding noun. Do not confuse the reader by having several possible antecedents. Consider these two sentences:
“Pope Gregory VII forced Emperor Henry IV to wait three days in the snow at Canossa before granting him an audience. It was a symbolic act.”
To what does the it refer? Forcing the Emperor to wait? The waiting itself? The granting of the audience? The audience itself? The whole previous sentence? You are most likely to get into antecedent trouble when you begin a paragraph with this or it , referring vaguely back to the general import of the previous paragraph. When in doubt, take this test: Circle the pronoun and the antecedent and connect the two with a line. Then ask yourself if your reader could instantly make the same diagram without your help. If the line is long, or if the circle around the antecedent is large, encompassing huge gobs of text, then your reader probably will be confused. Rewrite. Repetition is better than ambiguity and confusion.
Faulty parallelism.
You confuse your reader if you change the grammatical construction from one element to the next in a series. Consider this sentence:
“King Frederick the Great sought to expand Prussia, to rationalize agriculture, and that the state support education.”
The reader expects another infinitive, but instead trips over the that . Rewrite the last clause as “and to promote state-supported education.” Sentences using neither/nor frequently present parallelism problems. Note the two parts of this sentence:
“After 1870 the cavalry charge was neither an effective tactic, nor did armies use it frequently.”
The sentence jars because the neither is followed by a noun, the nor by a verb. Keep the parts parallel.
Rewrite as “After 1870 the cavalry charge was neither effective nor frequently used.”
Sentences with not only/but also are another pitfall for many students. (“Mussolini attacked not only liberalism, but he also advocated militarism.”) Here the reader is set up to expect a noun in the second clause, but stumbles over a verb. Make the parts parallel by putting the verb attacked after the not only .
Misplaced modifier/dangling element.
Do not confuse the reader with a phrase or clause that refers illogically or absurdly to other words in the sentence. (“Summarized on the back cover of the American paperback edition, the publishers claim that...”) The publishers are not summarized on the back cover. (“Upon finishing the book, many questions remain.”) Who finished the book? Questions can’t read. Avoid following an introductory participial clause with the expletives it or there . Expletives are by definition filler words; they can’t be agents. (“Having examined the origins of the Meiji Restoration in Japan, it is apparent that...”) Apparent to whom? The expletive it didn’t do the examining. (“After going on the Long March, there was greater support for the Communists in China.”) Who went on the Long March? There didn’t go on the Long March. Always pay attention to who’s doing what in your sentences.
Run-on sentence.
Run-on sentences string together improperly joined independent clauses. Consider these three sentences:
“Galileo recanted his teaching that the earth moved privately he maintained his convictions.” “Galileo recanted his teaching that the earth moved, privately he maintained his convictions.” “Galileo recanted his teaching that the earth moved, however, privately he maintained his convictions.”
The first fuses two independent clauses with neither a comma nor a coordinating conjunction; the second uses a comma but omits the coordinating conjunction; and the third also omits the coordinating conjunction (however is not a coordinating conjunction). To solve the problem, separate the two clauses with a comma and the coordinating conjunction but. You could also divide the clauses with a semicolon or make separate sentences. Remember that there are only seven coordinating conjunctions ( and, but, or, nor, for, so, yet ).
Sentence fragment.
Write in sentences. A sentence has to have a subject and a predicate. If you string together a lot of words, you may lose control of the syntax and end up with a sentence fragment. Note that the following is not a sentence:
“While in Western Europe railroad building proceeded rapidly in the nineteenth century, and in Russia there was less progress.”
Here you have a long compound introductory clause followed by no subject and no verb, and thus you have a fragment. You may have noticed exceptions to the no-fragments rule. Skilful writers do sometimes intentionally use a fragment to achieve a certain effect. Leave the rule-breaking to the experts.
Confusion of restrictive and nonrestrictive clauses.
Consider these two versions of the same sentence:
1. “World War I, which raged from 1914-1918, killed millions of Europeans.” 2. “World War I that raged from 1914-1918 killed millions of Europeans.”
The first sentence has a nonrestrictive relative clause; the dates are included almost as parenthetical information. But something seems amiss with the second sentence. It has a restrictive relative clause that limits the subject (World War I) to the World War I fought between 1914 and 1918, thus implying that there were other wars called World War I, and that we need to distinguish among them. Both sentences are grammatically correct, but the writer of the second sentence appears foolish. Note carefully the distinction between that (for use in restrictive clauses, with no comma) and which (for use in nonrestrictive clauses, with a comma).
Confusion about who’s doing what.
Remember—history is about what people do, so you need to be vigilant about agency. Proofread your sentences carefully, asking yourself, “Have I said exactly who is doing or thinking what, or have I inadvertently attributed an action or belief to the wrong person or group?” Unfortunately, there are many ways to go wrong here, but faulty punctuation is among the most common. Here’s a sentence about Frantz Fanon, the great critic of European imperialism. Focus on the punctuation and its effect on agency: “Instead of a hierarchy based on class, Fanon suggests the imperialists establish a hierarchy based on race.” As punctuated, the sentence says something absurd: that Fanon is advising the imperialists about the proper kind of hierarchy to establish in the colonies. Surely, the writer meant to say that, in his analysis of imperialism, Fanon distinguishes between two kinds of hierarchy. A comma after suggests fixes the immediate problem. Now look at the revised sentence. It still needs work. Better diction and syntax would sharpen it. Fanon does not suggest (with connotations of both hinting and advocating); he states outright. What’s more, the comparison of the two kinds of hierarchy gets blurred by too many intervening words. The key point of the sentence is, in effect, “instead of A, we have B.” Clarity demands that B follow A as closely as possible, and that the two elements be grammatically parallel. But between the elements A and B, the writer inserts Fanon (a proper noun), suggests (a verb), imperialists (a noun), and establish (a verb). Try the sentence this way: “Fanon says that the imperialists establish a hierarchy based on race rather than class.” Now the agency is clear: We know what Fanon does, and we know what the imperialists do. Notice that errors and infelicities have a way of clustering. If you find one problem in a sentence, look for others.
Confusion about the objects of prepositions.
Here’s another one of those common problems that does not receive the attention it merits. Discipline your prepositional phrases; make sure you know where they end. Notice the mess in this sentence: “Hitler accused Jewish people of engaging in incest and stating that Vienna was the ‘personification of incest.’” The reader thinks that both engaging and stating are objects of the preposition of. Yet the writer intends only the first to be the object of the preposition. Hitler is accusing the Jews of engaging , but not of stating ; he is the one doing the stating . Rewrite as “Hitler accused the Jews of incest; he stated that Vienna was the ‘personification of incest.’” Note that the wordiness of the original encouraged the syntactical mess. Simplify. It can’t be said too many times: Always pay attention to who’s doing what in your sentences.
Misuse of the comparative.
There are two common problems here. The first might be called the “floating comparative.” You use the comparative, but you don’t say what you are comparing. (“Lincoln was more upset by the dissolution of the union.”) More upset than by what? More upset than who? The other problem, which is more common and takes many forms, is the unintended (and sometimes comical) comparison of unlike elements. Consider these attempts to compare President Clinton to President George H. W. Bush. Often the trouble starts with a possessive:
“President Clinton’s sexual appetite was more voracious than President Bush.”
You mean to compare appetites, but you've forgotten about your possessive, so you absurdly compare an appetite to a man. Rewrite as “more voracious than President Bush’s.” A variation of this problem is the unintended comparison resulting from the omission of a verb:
“President Clinton liked women more than President Bush.”
Re-write as “more than did President Bush.”
A misplaced modifier may also cause comparison trouble: “Unlike the Bush administration, sexual scandal nearly destroyed the Clinton administration.” Rewrite as “Unlike the Bush administration, the Clinton administration was nearly destroyed by sexual scandal.” Here the passive voice is better than the misplaced modifier, but you could rewrite as “The Bush administration had been free of sexual scandal, which nearly destroyed the Clinton administration.”
Misuse of apostrophe.
Get control of your apostrophes. Use the apostrophe to form singular or plural possessives (Washington’s soldiers; the colonies’ soldiers) or to form contractions (don’t; it’s). Do not use the apostrophe to form plurals. (“The communists [not communists’] defeated the nationalists [not nationalists’] in China.”)
Comma after although.
This is a new error, probably a carryover from the common conversational habit of pausing dramatically after although . ( “Although , coffee consumption rose in eighteenth-century Europe, tea remained far more popular.”) Delete the comma after although . Remember that although is not a synonym for the word however , so you cannot solve the problem in the sentence by putting a period after Europe . A clause beginning with although cannot stand alone as a sentence.
Comma between subject and verb.
This is a strange new error. (“Hitler and Stalin, agreed to a pact in August 1939.”) Delete the comma after Stalin. Finally, two hints: If your word-processing program underlines something and suggests changes, be careful. When it comes to grammar and syntax, your computer is a moron. Not only does it fail to recognize some gross errors, it also falsely identifies some correct passages as errors. Do not cede control of your writing decisions to your computer. Make the suggested changes only if you are positive that they are correct. If you are having trouble with your writing, try simplifying. Write short sentences and read them aloud to test for clarity. Start with the subject and follow it quickly with an active verb. Limit the number of relative clauses, participial phrases, adjectives, adverbs, and prepositional phrases. You will win no prizes for eloquence, but at least you will be clear. Add complexity only when you have learned to handle it.
An historical/an historian.
The consonant “H” is not silent in historical and historian , so the proper form of the indefinite article is “A.”
Avoid the common solecism of using feel as a synonym for think, believe, say, state, assert, contend, argue, conclude, or write. (“Marx felt that the bourgeoisie exploited the proletariat.” “Emmeline Pankhurst felt that British women should be able to vote.”) The use of feel in these sentences demeans the agents by suggesting undisciplined sentiment rather than carefully formulated conviction. Concentrate on what your historical actors said and did; leave their feelings to speculative chapters of their biographies. As for your own feelings, keep them out of your papers. (“I feel that Lincoln should have freed the slaves earlier.”) Your professor will be delighted that the material engages both your head and your heart, but your feelings cannot be graded. If you believe that Lincoln should have acted earlier, then explain, giving cogent historical reasons.
The fact that.
This is a clumsy, unnecessary construction. ( “The fact that Nixon resigned in disgrace damaged the Republican Party.”) Re-word as “Nixon resigned in disgrace, damaging the Republican Party.” Never use the hideous phrase due to the fact that.
In terms of.
This phrase is filler. Get rid of it. (“Bismarck was a success in terms of uniting Germany.) Rewrite as “Bismarck successfully united Germany.”
Attend carefully to the placement of this limiting word. Note, for example, these three sentences:
“The government only interred Japanese Americans during World War II.” “The government interred only Japanese Americans during World War II.” “The government interred Japanese Americans only during World War II.”
The first limits the action to interring (as opposed to, say, killing); the second limits the group interred (i.e., not Italian Americans); the third limits the time of interring (i.e., not during other wars).
Thus and therefore.
More than likely, you have not earned these words and are implying that you have said more than you actually have. Use them sparingly, only when you are concluding a substantial argument with a significant conclusion.
Misuse of instead.
Instead is an adverb, not a conjunction. Consider this sentence: “Charles Beard argued that the framers of the constitution were not idealists, instead they promoted their economic interests.” Revise as “The framers of the constitution, Charles Beard argued, did not uphold ideals; instead , they promoted their economic interests.” Now the instead appears properly as an adverb. (Note also that the two clauses are now parallel—both contain transitive verbs.)
Essentially and basically.
These are usually either filler words (the written equivalent of “uh” or “um”) or weasel words that merely call attention to your vagueness, lack of conviction, or lazy unwillingness to qualify precisely. (“ Essentially , Churchill believed that Nazi Germany presented a grave danger to Britain.”) Delete essentially and basically unless you are writing about essences or bases.
Both share or both agree.
These are redundant. If two people share or agree , they are both involved by definition. (“Stalin and Mao both agreed that capitalism belonged in the dustbin of history.”) Delete both .
This word means one of a kind. It is an absolute. Something cannot be very unique, more unique, or somewhat unique.
Incredible.
In casual conversation incredible often means extraordinary, astonishing, or impressive (“Yesterday’s storm was incredible.”). To avoid confusion in historical prose, you should stick with the original meaning of incredible : not believable. If you write that “William Jennings Bryan gave incredible speeches,” you’re saying that you don’t believe his speeches, or that his audiences didn’t believe them at the time—in other words, that he appeared to be lying or mistaken. You probably mean that he gave great speeches. If you write that “It’s incredible that Japan attacked Pearl Harbor,” you’re calling into question the very existence of a historical event. You probably mean that the Japanese attack was unwise or reckless. English is rich with adjectives. Finding the best one forces you to think about what you really mean.
As a synonym for subject matter, bone of contention, reservation, or almost anything else vaguely associated with what you are discussing, the word issue has lost its meaning through overuse. (“There were many issues involved with Truman’s decision to use the atomic bomb, and some historians have issues with his decision.”) Stop talking about issues and get to the point.
Beware of the word literally . It’s commonly misused, and you almost never need it in historical prose. Literally means actually, factually, exactly, directly, without metaphor. The careful writer would never say, “Roosevelt literally swamped Landon in the election of 1936.” One imagines Roosevelt (in his wheelchair no less!) dumping the hapless Landon off a pier in the Everglades on election night. The swamping was figurative, strictly a figure of speech. The adverb literally may also cause you trouble by falsely generalizing the coverage of your verb. “London was literally destroyed by the blitz.” This suggests that the whole city was destroyed, when, in fact, only parts were destroyed. Rewrite as “The blitz destroyed parts of London.” Now you’ve qualified properly (and gotten rid of the passive).
When you’re tempted to use this word, resist. Like issue , involve tells the reader too little. (“Erasmus was involved in the Renaissance.”) This statement could mean virtually anything. Delete it and discuss specifically what Erasmus said or did.
This is a fine old word with many precise meanings, but as an overused synonym for feature, side, or part, it is usually a sign of insipid prose (“Another aspect of the issues in this area is the fact that...”). Just get directly to the point.
Most good writers frown on the use of this word as a verb.(“Eisenhower’s military background impacted his foreign policy.”) Affected, influenced, or shaped would be better here. Impacted suggests painfully blocked wisdom teeth or feces. Had an impact is better than impacted , but is still awkward because impact implies a collision.
Here is another beloved but vapid word. (“Many factors led to the Reformation.”) Such a sentence usually opens a vague, boring, weaseling paragraph. If you believe (quite reasonably) that the Reformation had many causes, then start evaluating them.
Meaningful.
Overuse has drained the meaning from meaningful . (“Peter the Great took meaningful steps to westernize Russia.”) Just get to the point.
Interesting.
The adjective interesting is vague, overused, and does not earn its keep. (“Burckhardt had an interesting perspective on the Renaissance.”) This sentence is filler. Delete it and explain and analyze his perspective.
The events that transpired.
Your professor will gag on this one. Events take place or happen by definition, so the relative clause is redundant. Furthermore, most good writers do not accept transpire as a synonym for happen. Again, follow the old rule of thumb: Get right to the point, say what happened, and explain its significance. You don’t need any filler about events and transpiring .
The reason is because.
This phrase is awkward and redundant. Replace it with the reason is, or better still, simply delete it and get right to your reason.
For all intensive purposes.
The phrase is for all intents and purposes , and few good writers use it in formal prose anyway.
Take for granite.
This is an illiteracy. The phrase is “ take for granted .”
Should of/could of.
You mean should have or could have .
Center around.
Good writers frown on this phrase because it’s illogical and jarring. Use center on or center in. Attention to a small detail like this indicates that you’re thinking carefully about what you’re saying, so when the big problems confront you, you’ll be disciplined and ready.
Begs the question.
Recently, many people have started to use this phrase to mean raises, invites, or brings up the question. (“Stalin’s purges beg the question of whether he was paranoid.”) Actually, begging the question is the common logical fallacy of assuming your conclusion as part of your argument. (“In the late nineteenth century, many Americans moved to the cities because of urbanization.”) Note that the use of abstractions (e.g., urbanization) encourages begging the question . Understanding this fallacy is central to your education. The formal Latin term, petitio principii, is too fancy to catch on, so you need to preserve the simple English phrase. If something raises a question, just say so.
Historic/historical confusion.
Everything in the past or relating to the past is historical. Resist the media-driven hype that elevates the ordinary to the historic . (“A three-alarm fire last night destroyed the historic site of the first Portuguese-owned dry cleaners in Cleveland.”) Reserve the word historic for the genuinely important events, persons, or objects of the past. The Norman invasion of England in 1066 was indeed historic . Historically , historians have gathered annually for a historical convention; so far, none of the conventions has been historic .
Affect/effect confusion.
The chances are that the verb you want is affect , which means to have an influence on (“The Iranian hostage crisis affected [not effected] the presidential election of 1980”). Effect as a verb means to bring about or cause to exist ( effect change). Effect as a noun means result or consequence (“The effect of the Iranian hostage crisis on the election...”).
While/whereas confusion.
If you’re stressing contrast, the word you want is whereas . While stresses simultaneity. “Hobbes had a dismal view of human nature, whereas [not while] Rousseau believed that man had a natural sense of pity.”
It’s/its confusion.
This is the classic bonehead error. Note that the spell checker won’t help you. And remember— its’ is not a word at all.
Reign/rein confusion.
A queen reigns during her reign. You rein in a horse with reins.
Their/there/they’re confusion.
You do know the difference. Pay attention.
Everyday/every day confusion.
As an adjective, everyday (one word) means routine. If you wish to say that something happened on every successive day, then you need two words, the adjective every and the noun day . Note the difference in these two sentences: “Kant was famous for going on the same constitutional at the same time every day . For Kant, exercise and thinking were everyday activities.”
Refer/allude confusion.
To allude means to refer to indirectly or to hint at. The word you probably want in historical prose is refer , which means to mention or call direct attention to. “In the first sentence of the ‘Gettysburg Address’ Lincoln refers [not alludes ] to the fathers of the nation [he mentions them directly]; he alludes to the ‘Declaration of Independence’ [the document of four score and seven years earlier that comes to the reader’s mind, but that Lincoln doesn’t directly mention].”
Novel/book confusion.
Novel is not a synonym for book. A novel is a long work of fiction in prose. A historical monograph is not a novel —unless the historian is making everything up.
Than/then confusion.
This is an appalling new error. If you are making a comparison, you use the conjunction than . (“President Kennedy’s health was worse than [not then ] the public realized.”)
Lead/led confusion.
The past tense of the verb to lead is led (not lead ). “Sherman led [not lead ] a march to the sea.”
Lose/loose confusion.
The opposite of win is lose , not loose . “Supporters of the Equal Rights Amendment suspected that they would lose [not loose ] the battle to amend the constitution.”
However/but confusion.
However may not substitute for the coordinating conjunction but. (“Mussolini began his career as a socialist, but [not however ] he later abandoned socialism for fascism.”) The word however has many proper uses; however , [note the semicolon and comma] graceful writers use it sparingly.
Cite/site/sight confusion.
You cited a source for your paper; ancient Britons sited Stonehenge on a plain; Columbus’s lookout sighted land.
Conscience/conscious confusion.
When you wake up in the morning you are conscious , though your conscience may bother you if you’ve neglected to write your history paper.
Tenet/tenant confusion.
Your religion, ideology, or worldview all have tenets —propositions you hold or believe in. Tenants rent from landlords.
All are not/not all are confusion.
If you write, “ All the colonists did not want to break with Britain in 1776,” the chances are you really mean, “ Not all the colonists wanted to break with Britain in 1776.” The first sentence is a clumsy way of saying that no colonists wanted to break with Britain (and is clearly false). The second sentence says that some colonists did not want to break with Britain (and is clearly true, though you should go on to be more precise).
Nineteenth-century/nineteenth century confusion.
Historians talk a lot about centuries, so you need to know when to hyphenate them. Follow the standard rule: If you combine two words to form a compound adjective, use a hyphen, unless the first word ends in ly. (“ Nineteenth-century [hyphenated] steamships cut the travel time across the Atlantic.”) Leave out the hyphen if you’re just using the ordinal number to modify the noun century. (“In the nineteenth century [no hyphen] steamships cut the travel time across the Atlantic.”) By the way, while you have centuries in mind, don’t forget that the nineteenth century is the 1800s, not the 1900s. The same rule for hyphenating applies to middle-class and middle class —a group that historians like to talk about.
Bourgeois/bourgeoisie confusion.
Bourgeois is usually an adjective, meaning characteristic of the middle class and its values or habits. Occasionally, bourgeois is a noun, meaning a single member of the middle class. Bourgeoisie is a noun, meaning the middle class collectively. (“Marx believed that the bourgeoisie oppressed the proletariat; he argued that bourgeois values like freedom and individualism were hypocritical.”)
Your professor may ask you to analyze a primary document. Here are some questions you might ask of your document. You will note a common theme—read critically with sensitivity to the context. This list is not a suggested outline for a paper; the wording of the assignment and the nature of the document itself should determine your organization and which of the questions are most relevant. Of course, you can ask these same questions of any document you encounter in your research.
- What exactly is the document (e.g., diary, king’s decree, opera score, bureaucratic memorandum, parliamentary minutes, newspaper article, peace treaty)?
- Are you dealing with the original or with a copy? If it is a copy, how remote is it from the original (e.g., photocopy of the original, reformatted version in a book, translation)? How might deviations from the original affect your interpretation?
- What is the date of the document?
- Is there any reason to believe that the document is not genuine or not exactly what it appears to be?
- Who is the author, and what stake does the author have in the matters discussed? If the document is unsigned, what can you infer about the author or authors?
- What sort of biases or blind spots might the author have? For example, is an educated bureaucrat writing with third-hand knowledge of rural hunger riots?
- Where, why, and under what circumstances did the author write the document?
- How might the circumstances (e.g., fear of censorship, the desire to curry favor or evade blame) have influenced the content, style, or tone of the document?
- Has the document been published? If so, did the author intend it to be published?
- If the document was not published, how has it been preserved? In a public archive? In a private collection? Can you learn anything from the way it has been preserved? For example, has it been treated as important or as a minor scrap of paper?
- Does the document have a boilerplate format or style, suggesting that it is a routine sample of a standardized genre, or does it appear out of the ordinary, even unique?
- Who is the intended audience for the document?
- What exactly does the document say? Does it imply something different?
- If the document represents more than one viewpoint, have you carefully distinguished between the author’s viewpoint and those viewpoints the author presents only to criticize or refute?
- In what ways are you, the historian, reading the document differently than its intended audience would have read it (assuming that future historians were not the intended audience)?
- What does the document leave out that you might have expected it to discuss?
- What does the document assume that the reader already knows about the subject (e.g., personal conflicts among the Bolsheviks in 1910, the details of tax farming in eighteenth-century Normandy, secret negotiations to end the Vietnam war)?
- What additional information might help you better interpret the document?
- Do you know (or are you able to infer) the effects or influences, if any, of the document?
- What does the document tell you about the period you are studying?
- If your document is part of an edited collection, why do you suppose the editor chose it? How might the editing have changed the way you perceive the document? For example, have parts been omitted? Has it been translated? (If so, when, by whom, and in what style?) Has the editor placed the document in a suggestive context among other documents, or in some other way led you to a particular interpretation?
Your professor may ask you to write a book review, probably of a scholarly historical monograph. Here are some questions you might ask of the book. Remember that a good review is critical, but critical does not necessarily mean negative. This list is not meant to be exhaustive, nor is it a suggested outline. Of course, you can ask these same questions of any secondary historical work, even if you’re not writing a review.
- Who is the author, and what are his or her qualifications? Has the author written other books on the subject?
- When was the book written, and how does it fit into the scholarly debate on the subject? For example, is Smith writing to refute that idiot Jones; to qualify the work of the competent but unimaginative Johnson; or to add humbly to the evidence presented by the redoubtable Brown’s classic study? Be sure not to confuse the author’s argument with those arguments he or she presents only to criticize later.
- What is the book’s basic argument? (Getting this right is the foundation of your review.)
- What is the author’s method? For example, does the author rely strictly on narrative and anecdotes, or is the book analytical in some way?
- What kinds of evidence does the author use? For example, what is the balance of primary and secondary sources? Has the author done archival work? Is the source base substantial, or does it look thin? Is the author up-to-date in the scholarly literature?
- How skillfully and imaginatively has the author used the evidence?
- Does the author actually use all of the material in the bibliography, or is some of it there for display?
- What sorts of explicit or implicit ideological or methodological assumptions does the author bring to the study? For example, does he or she profess bland objectivity? A Whig view of history? Marxism?
- How persuasive is the author’s argument?
- Is the argument new, or is it old wine in new bottles?
- Is the argument important, with wide-ranging implications, or is it narrow and trivial?
- Is the book well organized and skillfully written?
- What is your overall critical assessment of the book?
- What is the general significance, if any, of the book? (Make sure that you are judging the book that the author actually wrote, not complaining that the author should have written a different book.)
Here are some tips for those long, intimidating term papers or senior theses:
- Start early. If you don’t, none of these tips will matter. Big trouble is looming if you don’t have a specific topic by the end of the first week. You should be delving into the sources during the second week.
- Keep in mind all of the dos and don’ts in this booklet.
- Work closely with your professor to assure that your topic is neither too broad nor too narrow.
- Set up a schedule with your professor and check his or her policy about reading rough drafts or parts of rough drafts. Then keep your professor informed about what you’re doing. You don’t want any unpleasant surprises. You certainly don’t want to hear, “I haven’t seen you for weeks, and it sounds like you’re way off base. How can you possibly get this done with only two weeks left in the semester?”
- Make an appointment with Kristin Strohmeyer, the history reference librarian in Burke Library. She will help you to find and use the appropriate catalogs and indexes.
- Use your imagination in compiling a bibliography. Think of all of the possible key words and subjects that may lead you to material. If you find something really good, check the subjects under which it is cataloged. Comb the notes and bibliographies of books and articles you’ve already found.
- Much of what you need will not be in our library, so get to know the friendly folks in the Interlibrary Loan department.
- Start early. This can’t be said too often.
- Use as many primary sources as you can.
- Jot down your ideas as they come to you. You may not remember them later.
- Take careful notes on your reading. Label your notes completely and precisely. Distinguish meticulously and systematically between what you are directly quoting and what you are summarizing in your own words. Unintended plagiarism is still plagiarism. Stay clean as a hound’s tooth. Write down not just the page of the quotation or idea, but also the whole run of pages where the matter is discussed. Reread all of your notes periodically to make sure that you still understand them and are compiling what you will need to write your paper. Err on the side of writing down more than you think you will need. Copious, precise notes won’t come back to haunt you; skimpy, vague notes will. Just accept that there is something anal about good note-taking.
- If you take notes directly into your computer, they will be easy to index and pull up, but there are a couple of downsides. You will not be able to see all of them simultaneously, as you can note cards laid out on a big table. What you gain in ease of access may come at the price of losing the big picture. Also, if your notes are in your computer, you may be tempted to save time and thought by pasting many of them directly into your paper. Note cards encourage you to rethink and to rework your ideas into a unified whole.
- Don’t start to write until you have a good outline.
- Make sure that your paper has a thesis. (See the entry State a clear thesis. )
- Check and recheck your facts.
- Footnote properly. (See the entry Cite sources carefully .)
- Save plenty of time to proofread.
- Start early.
Top Ten Signs that you may be Writing a Weak History Paper
10. You’re overjoyed to find that you can fill the required pages by widening all margins.
9. You haven’t mentioned any facts or cited any sources for several paragraphs.
8. You find yourself using the phrase “throughout history mankind has...”
7. You just pasted in another 100 words of quotations.
6. You haven’t a clue about the content of your next paragraph.
5. You’re constantly clicking on The Britannica, Webster’s, and Bartlett’s.
4. Your writing tutor sneaks another look at her watch as she reminds you for the third time to clarify your thesis.
3. Your main historical actors are this, it, they, the people, and society, and they are all involved with factors, aspects, impacts, and issues.
2. You just realize that you don’t understand the assignment, but it’s 3:00 A.M, the paper is due at 9:00, and you don’t dare call your professor.
1. You’re relieved that the paper counts for only 20 percent of the course grade.
Final Advice
You guessed it — start early.
Studying History at Hamilton
Students will learn to use interdisciplinary methods from the humanities and social sciences to probe the sources of the past for answers to present questions. They will learn to draw comparisons and connections among diverse societies across a range of historical eras. They will further learn to convey their findings through writing that is clearly structured, precise, and persuasive.
Tutor Appointments
Peer tutor and consultant appointments are managed through TracCloud (login required). Find resources and more information about the ALEX centers using the following links.
Office / Department Name
Nesbitt-Johnston Writing Center
Contact Name
Jennifer Ambrose
Writing Center Director

Help us provide an accessible education, offer innovative resources and programs, and foster intellectual exploration.
Site Search
Handbook for Historians Research Guide
- Choosing a Paper Topic
- Thesis Statement
- Find Primary Sources
- Find Secondary Sources
- Formatting References
- Writing an Annotated Bibliography
Sample History Papers
Sample title pages, outlines, & citations.
- Resources for Writing
These are examples of well written, properly cited history papers.
- Sample Paper with Outline
- Judge and Langdon Book Review/Research Paper - Example 1
- Judge and Langdon Book Review/Research Paper - Example 2
- citation presentation
- HST 302 Paper Example example of a paper for upper division History courses
- HST 302 Title Page
- Outline Example Example of an outline for a first year level history paper.
- << Previous: Writing an Annotated Bibliography
- Next: Resources for Writing >>
- Last Updated: Sep 2, 2024 2:55 PM
- URL: https://resources.library.lemoyne.edu/guides/history/handbook
How to Write a History Essay With Tips and Examples
- Icon Calendar 18 May 2024
- Icon Page 4207 words
- Icon Clock 19 min read
When students attend history classes, they need to write many historical essays through their courses. Basically, this article provides a guideline on how to write a history essay, teaching students and anyone passionate about the text what is most important. The guideline begins by defining what is a history essay and its meaning, listing possible topics, showing an outline of such a paper, and giving a practical example of a history essay. Students also learn the technical aspects of writing a historical essay, emphasizing the four steps: preparation, stage setup, writing an initial draft, and wrap-up. Finally, the article provides 20 tips for writing a high-standard history essay, including 10 things to do and 10 things not to do when writing such a paper.
General Aspects of How to Write an Outstanding Essay in History and Examples
Reading and writing are interrelated academic exercises because they develop each other. When students develop a habit of reading different types of essays , they induce their mental faculties of intellect, memory, reason, imagination, and intuition, which are vital in constructing logical academic papers, like essays, reports, and research papers. This guideline on how to write a history essay that offers critical insights into how students can create a high-standard text. The article begins by defining what is a history essay and its meaning, listing possible essay topics students can choose from to write it, the technical steps for creating a document, and 20 tips for producing a high-quality paper. It also provides a sample outline template for writing a historical essay and a practical example. Therefore, reading this guideline is helpful to students because it not only educates them about what is essential but also gives a practical example of how to start writing a history essay.

Definition of What Is a History Essay and Its Meaning
From a simple definition, a history essay is a text that gives a historical account of an issue or topic, such as colonialism, slavery, constitutionalism, human rights activism, or feminism. In this respect, it differs from other types of papers, including an analytical essay, a compare and contrast essay, an argumentative essay, a cause and effect essay, or a report and a research paper. Students write history essays when their instructors require them to examine the origin and evolution of an idea with current and future implications. Ideally, writers interrogate their ideas from different historical perspectives and credible sources to understand how some events began, how they have progressed, the people or entities involved in their developments, and how they affect society currently and may influence it in the future. For example, a history essay about a theory would mean that students need to mention the theorist behind it, its application over time, and any developments, such as incorporating new concepts by contemporary scholars.
Use exceptional writing services that guarantee original and well-researched papers.
Examples of History Essay Topics
Typically, instructors specify essay topics for students in any writing assignment. However, sometimes, students may have to select a topic individually. In the latter case, students should choose history essay topics that are easy to write about, meaning one can easily access materials helpful in creating them, such as books, articles, and videos. The best way to accomplish this task is to read history course content and additional materials to develop and incubate ideas that become rich sources of topics. The following topics are ideal for writing a good history essay because they suggest giving a historical account of an idea.
- Racial Dynamics in the Harlem Renaissance: A Detailed Study
- The Impact of the Printing Press on Renaissance Europe
- Examination of Manifest Destiny’s Influence on Territorial Expansion
- Exploring the Factors that Led to the American Revolutionary War
- Discussing the Development of the United States as a Republic
- Examining the Sentiments that Have Shaped the Abortion Debate
- Explaining How the Republican and Democratic Parties Differ From a Philosophical Perspective
- Discussing the Shift of U.S. Foreign Policy From Isolationism to Interventionism
- Covering the Circumstances That Contributed to the End of the Cold War
- Discussing Religion in the Aztec Era
- Understanding the Role of City-States in Ancient Greece
- Exploring the Cultural Aspects of Immigration
Sample Outline Template for Writing a History Essay
I. Introduction
- Hook: Use a quote, history fact, or question to capture the reader’s attention and trigger their interest to continue reading.
- Brief background: Tell readers about an assigned topic by addressing issues central to this theme that help contextualize a historical discussion.
- Thesis statement: Use a short sentence to tell readers the history essay’s primary objective or ultimate agenda.
Use all body paragraphs with the following:
- A topic sentence that introduces a single idea about an assigned history theme that supports a central claim of an essay.
- Incorporate evidence from reliable sources or primary sources that help back up a single history idea.
- Comment on evidence cited and how it helps readers understand an assigned history topic.
- End with a concluding sentence with a transition or bridge sentence that enhances a logical progression to the next paragraph or section.
Note: The number of body paragraphs depends on the volume of work, essay structure, college essay length, and assignment requirements. For example, for writing a 1000-word history essay (4 double spaced pages or 2 single spaced pages), there should be 3-5 body paragraphs, meaning 100-200 words per one body paragraph. In turn, first and last paragraphs of a history essay must be only 5-10% of the whole word count.
III. Conclusion
- Restate a central thesis in different words.
- Provide a summary of the main ideas discussed in topic sentences.
- Give a final remark about an assigned topic that leaves readers with a lasting impression after reading a history essay.
Example of a Good History Essay
Topic: Discussing the Shift of U.S. Foreign Policy from Isolationism to Interventionism
I. Example of an Introduction in a History Essay
American foreign policy is the most significant in world history for good and bad reasons. The early 20th century saw the United States adopt an isolationist foreign policy under the administration of President Herbert Hoover. The reason behind this stance was the prosperity and high standard of living the country experienced, making it meaningless to meddle in the affairs of Europe. However, the spread of fascism in Europe disturbed this illusion of safety and compelled the country to shift its foreign policy from isolationism to interventionism.
II. Examples of Body Paragraphs in a History Essay
A. isolationism.
The U.S. maintained isolationism in its foreign policy in the early 20th century because, while the nation was developing economically, some issues required internal politicking. As such, the country was increasingly insensitive to the threat of fascism in European democracies. Even if its allies were in trouble created by Adolf Hitler and Benito Mussolini, the U.S. determined to avoid all conflicts at all costs. Ideally, American politicians saw no prospect of European troubles reaching their motherland if the country was not involved. Nonetheless, Americans feared that the instability in Europe could spread to their land. In turn, optimistically naïve politicians began initiatives to protect the country from the threat of war. For example, Frank B. Kellogg created the Kellogg-Briand Pact, which saw 15 countries agree to protect America from the threat of war. Consequently, the Nine Power Treaty affirmed China’s territorial integrity through the Open Door policy. However, Japan’s invasion of Manchuria in 1931 marked the end of the policy. Therefore, while the U.S. was keen to keep the world stable, events were moving too fast to remain aloof and optimistic. The takeover of free countries one by one by the Nazi war machine triggered panic among Americans who realized the folly of optimism in a world under crisis. Besides, politicians began clamoring for the country’s involvement in foreign affairs between 1930 and 1941, when the focus shifted from isolationism to interventionism.
B. Reasons for Moving to Interventionism
The 1940s were instrumental to U.S. foreign policy because the country finally realized that it could no longer be unconcerned about what was happening in Europe. For example, Adolf Hitler and Benito Mussolini, the faces of fascism, were wreaking havoc in the region to create fear among Americans that this idea may reach their shores in no time. As a country with a history with Britain, the U.S. could no longer assume that Britain’s fate was irrelevant. Therefore, support for Britain marked the first sign of the shift of U.S. foreign policy from isolationism to interventionism. However, this shift was minimal because it was based on material support for Britain. It took the Pearl Harbor attack on December 7, 1941, for the U.S. to embrace interventionism fully as Americans anger propelled the country’s immediate revenge against Japan.
C. Adopting Interventionism
The administration of President Franklin D. Roosevelt propelled the U.S. to full interventionism when it agreed to dispatch American troops to aid European allies in repelling fascist forces. For example, the president’s famous “Quarantine Speech” called for ending isolationism because it was dangerous to a free world. In 1940, the U.S. deployed 50 World War I destroyers to Britain, which offered eight defense bases in its colonies in South America and other regions strategic to a global conflict. The U.S. Congress repealed the Neutrality Acts, officially ending isolationism as a foreign policy stance in favor of interventionism. The new perspective saw the country sell weapons to Britain on a ‘cash-and-carry’ basis to avoid the Nazi war machine attacking American ships. America’s dedication to the new policy compelled President Roosevelt to establish the lend-lease system that provided billions of dollars to Britain in American military equipment. The League of Nations gave the U.S. a stage to demonstrate its involvement in foreign affairs because its provisions affirmed people’s right to peace and security. As such, the Pearl Harbor attack gave the U.S. every reason to attack Japan.
III. Example of a Conclusion in a History Essay
The instability in Europe triggered the shift from an isolationist position to an interventionist stance in the U.S. foreign policy. As fascism spread in Europe and the Nazi war machine overran democracies in this part of the world, the U.S. feared that being aloof to these events was dangerous to its citizens and future. As such, politicians and Congress took measures to ensure the country’s involvement in foreign affairs, specifically to end the threat that Hitler and Mussolini presented to the peace and security of free nations.
Receive a high-quality paper without plagiarism from Wr1ter Team.
4 Easy Steps for Writing a Great History Essay
Writing a well-organized history essay is a technical process involving four main steps: preparation, stage setup, writing a first draft of a history essay, and wrap-up. Students should approach each step fully armed with essential details to make the paper meet quality expectations. For example, these details include a topic, background information, thesis statement, topic sentences, evidence, and transitions. Each element must appear in the right section. Therefore, the most crucial factor for students is knowing the basic structure of a history essay because it helps to shape their writing mindset.
Step 1: Preparation
The first step in writing a history essay is preparation, which involves several tasks. The first aspect is to define a specific topic if instructions are not provided. For example, the best approach to selecting a particular topic is using ideas one has generated and incubated over time. In this case, history topics must reflect course content, meaning writers should not define their themes without historical context. The second task is to organize the ideas following the paper’s basic structure, meaning one must determine where each idea falls: introduction, body, or conclusion. In this respect, creating a well-organized essay outline is the third task in the preparation stage. Lastly, writers should consider the audience and the history essay’s purpose, such as assessment or publication. These details determine if one should use simple or technical language. As a result, preparation is where students undertake activities that make it easy to turn ideas into starting a history essay.
Step 2: Stage Setup
Setting the stage is the second step in writing a history essay. In this case, students should research to find evidence to back up their claims about their topics. When doing research, people should make notes of ideas, concepts, statistics, and interesting facts to incorporate into a historical paper. The next task is to match these details with a history essay’s outline, meaning each element must appear in the right section. Since evidence appears in the main section of a history essay, one should ensure all body paragraphs are sufficient for the ideas, concepts, data, and facts from the research process. For example, the best way to collect evidence is to research credible materials, like government reports and primary resources, from key figures involved in the historical development of the idea. As such, libraries and online archives are good places to search for evidence.
Step 3: Writing an Initial Draft
Writing an initial draft is the third step in writing a history essay. For example, students should focus on organizing the ideas into writing the text. People can also search for more information from secondary sources if the ideas are insufficient. However, if there are too many, one should delete some of them and their corresponding sources. The paper’s outline will change whether one adds or deletes some history course sources. Moreover, students must ensure this change does not affect their ability to communicate their ideas logically. In essence, writing a first draft allows people to construct a paper following a history essay’s outline correctly.
Writing an Introduction Paragraph for a History Essay
When writing an introduction paragraph, students must know the expectations. The first thing is to develop a hook, a statement with a quote, data, question, or other interesting fact that grabs the readers’ attention and triggers their interest to continue reading a history essay. The next aspect is to provide a brief background to contextualize an assigned topic and make readers aware of some of the issues central to the main theme. The next activity is to conclude the section with a clear historical thesis, which means a short sentence communicating the writer’s claim and serving the paper’s primary purpose or main agenda. When writing an introduction section, students should know their goal in history is to contextualize a central topic and state a claim demonstrating their thoughts.
Writing Body Paragraphs for a History Essay
A body part of a history essay is the most comprehensive section because it provides substantial details about a specific topic. For example, it is standard for students to construct several body paragraphs depending on the paper’s length and the ideas they wish to use to back up their claim. The first detail in each body paragraph of a history essay is a topic sentence with an idea that links the section to the thesis. The following detail is evidence that establishes a single idea and demonstrates evidence-based writing. In this case, students should use a sandwich rule in each body paragraph, meaning they must comment on evidence cited before proceeding to another history idea. Furthermore, writers should provide a concluding sentence with a transition to allow a logical progression to the next paragraph or section. Hence, students should understand that the body of a history essay is where they must convince the audience that they know an assigned topic well to make a valid claim.
Writing a Conclusion Paragraph for a History Essay
A conclusion paragraph is the part of a history essay that marks the end of writing a paper. As such, students should restate a central thesis from an introduction part using different words, summarize the main ideas discussed in body paragraphs, and give a final remark that leaves a lasting impression on the audience. Moreover, students must refrain from introducing new ideas in this last section because it would be useless and affect the paper’s quality. In turn, this part of a history essay aims to reiterate the ideas covered in body paragraphs and provide the writer’s final remark about their understanding of a particular topic.
Step 4: Wrap-Up
Wrapping up a final paper is the last step in writing a history essay. Because the focus is to perfect an initial draft, students should read and reread their history essays to identify and eliminate mistakes. Therefore, the activities that should define this step are revising a history essay to fix inconsistencies, such as ideas and sentences that do not make sense. Another task is editing a history essay to correct grammatical mistakes like missing punctuation and formatting mistakes like incorrect citations. Then, people need to confirm their outlines by ensuring all the essential elements of the introduction, body, and conclusion are included. In turn, writers should focus on a hook, background, and history thesis statement for the introduction; topic sentences, evidence, and transitions or bridge sentences for body paragraphs; and rewording and restating a central thesis statement, providing a summary of the main ideas, and including a final remark for the conclusion. Lastly, one should confirm the correct formatting (APA, MLA, Harvard, or Chicago/Turabian):
📕 APA Format
If a history essay adopts an APA formatting style, students should provide in-text citations and create a ‘References’ page at the end of the paper to list all the sources used. In turn, in-text citations have two formats:
- The first one has the author’s surname and the source’s publication year in the sentence and the page number at the end of the sentence. An example is:
According to Müller and Mildenberger (2021), college students prefer online classes over physical lecture halls because of convenience and flexibility (p. 6).
- The second format is all the details at the end of the sentence. An example is:
Evidence shows convenience and flexibility make college students prefer online classes over physical lecture halls (Müller & Mildenberger, 2021, p. 6).
- Reference entry example for this article should read:
Müller, C., & Mildenberger, T. (2021). Replacing classroom learning with online learning: A systematic review. Educational Research Review , 34 , 1-16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.edurev.2021.100394
📕 MLA Format
If a history essay follows an MLA formatting style, students should use in-text citations and create a ‘Works Cited’ page to capture all the sources. In this case, in-text citations come in two forms: some details in the sentence and all the details at the end of the sentence.
- An example of the first form is:
Müller and Mildenberger argue that most students in higher learning institutions prefer online over physical learning because of convenience and flexibility (6).
- The second form is:
Scholars suggest most students in colleges and universities prefer online classes over classroom attendance because of convenience and flexibility (Müller and Mildenberger 6).
- Works Cited entry example for this article would read:
Müller, Claude, and Thoralf Mildenberger. “Replacing Classroom Learning With Online Learning: A Systematic Review.” Educational Research Review, vol. 34, 2021, pp. 1-16, doi:10.1016/j.edurev.2021.100394.
📕 Harvard Format
If students adopt a Harvard formatting style for writing a history essay, they should provide in-text citations and create a ‘References List’ at the end of a document.
- The first format of in-text citations is having some details about a source in the sentence:
Müller and Mildenberger (2021) found that students in colleges and universities prefer to study online than attend physical classrooms (p. 6).
- The second format captures all the details about a source at the end:
Research shows most college and university students prefer online classes over classroom learning (Müller & Mildenberger 2021, p. 6).
- References List entry example for this source would read:
Müller, C & Mildenberger, T 2021, ‘Replacing classroom learning with online learning: A systematic review,’ Educational Research Review , vol. 34, pp. 1-16, DOI:10.1016/j.edurev.2021.100394.
📕 Chicago/Turabian Format
If a history essay follows a Chicago/Turabian style, students should use in-text citations and create a ‘Bibliography’ page at the end of a document to list all the sources. In-text citations appear as footnotes and can have the author’s name in the sentence. The uniqueness of this style is that the details in the footnotes reflect all the information on the Bibliography page with minor alterations.
- In-text citation within the text:
Today, people prefer online classes rather than attending physical places. 1
- Example of a footnote for writing a history essay:
1. Claude Müller and Thoralf Mildenberger, “Replacing Classroom Learning With Online Learning: A Systematic Review.” Educational Research Review 34, (2021): p. 6, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.edurev.2021.100394
- Bibliography entry should read:
Müller, Claude, and Thoralf Mildenberger. “Replacing Classroom Learning With Online Learning: A Systematic Review.” Educational Research Review 34, (2021): pp. 1-16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.edurev.2021.100394
20 Tips for Writing a High-Standard History Essay
Since writing a history essay is a technical process that requires students to demonstrate an in-depth understanding of a basic outline and essential details, it is helpful to learn some tips. These recommendations include identifying the purpose of a historical assignment, defining a specific topic, formulating a clear thesis that states a claim, knowing where to get academic sources that provide evidence supporting a single claim, creating a history outline and populating each section with ideas, ensuring an introduction paragraph has all essential details (a hook, background information, and thesis), understanding that all body paragraphs have topic sentences, evidence, and concluding sentences with a transition or a bridge sentence, and finalizing writing a history essay with a conclusion paragraph that summarizes a paper and does not introduce new ideas.
10 things to do when writing a history essay include:
- defining a specific topic that requires one to provide a historical account of an idea or topic;
- researching an assigned topic widely to generate ideas and collect evidence;
- creating a well-organized outline that meets a basic structure of an introduction, body, and conclusion;
- formulating body paragraphs with topic sentences, evidence, and transitions;
- adopting a sandwich rule to demonstrate evidence-based history writing;
- writing a historical essay without grammar or format mistakes;
- providing a conclusion that concludes a history paper;
- following one format style (APA, MLA, Harvard, or Chicago);
- citing all evidence;
- proofreading a history essay.
10 things not to do include:
- including a long, complex history topic;
- having an introduction that does not create a context;
- providing an unclear thesis or stating a biased claim;
- writing an extensive history introduction;
- adding too many headings and subheadings;
- starting body paragraphs without topic sentences that communicate a single idea;
- failing to incorporate evidence in a history essay;
- using outdated evidence;
- creating illogical sentences;
- focusing on too many ideas in one paragraph.
Summing Up on How to Write a Perfect History Essay
- Define a short and clear history topic.
- Use direct quotes or paraphrase information to defend a central claim in a thesis statement.
- Give a historical account of a chosen topic and not an analysis of events.
- Use strong topic sentences that express ideas central to a history thesis.
- Incorporate credible sources, such as speeches, research articles, and government records, to cite evidence.
- Correctly use the proper format (APA, MLA, Harvard, or Chicago/Turabian).
- Read and reread a final draft of a history essay to eliminate all grammar and format mistakes.
- Proofread a final paper to ensure it is logical.
To Learn More, Read Relevant Articles

Classical Music vs. Modern Pop Music: A Historical Perspective
- Icon Calendar 26 August 2023
- Icon Page 777 words

Influence of Colors on Mood and Behavior
- Icon Calendar 25 August 2023
- Icon Page 757 words
Department of History
Primary source essay.
This 3000-word source-based essay focuses on one primary source to shed light on material evaluation in the Enlightenment. To achieve this, the essay will also draw on other primary and secondary sources.
The essay will be marked using the usual history-specific marking criteria for written work . That said, a primary-source essay is a particular type of essay that calls for specific tasks that are not relevant to all other essays.
Like any other essay, this one needs to be an argument--it needs to state a thesis and make a case for that thesis. Unlike other essays, the argument of this essay will centre on a primary source. More details on the task are below.
The thesis. This needs to be related to the theme of the module, namely material evaluation in the Enlightenment. Beyond that, you are free to choose a topic as a function of your own knowledge and interests. It may help to consider some of the theses we have encountered in the secondary readings, such as Emma Spary's thesis that botanical expertise replaced scholarly expertise as the main way of evaluating coffee in France around 1700; or William Ashworth's thesis that the hydrometer was part of the political struggle between producers and the state in eighteenth-century Britain. Your thesis will probably be less ambitious than these, given the constraints of the assignment. But you may find these theses (by Spary, Ashworth, and the other historians we have read) a useful model to follow. The note under 'Contextualise' below may also be useful.
The primary source. This may be any primary source related to material evaluation in the Enlightenment. The one limitation is that it cannot be one of the primary sources we have discussed in detail in seminars, such as Robert Boyle's 1675 article on gold assaying in the Phil. Trans ., or Henry Drax's instructions on the management of a Barbadian sugar plantation. More precisely, you cannot choose the passages from these sources that we discussed in detail in class. For example, you may choose the sections on beer in Leadbetter's Royal Gauger , but not the sections on the distillery. The source may be a written document, but it may also be an object, diagram, painting, or any other historical artefact that sheds light on the past.
Finding a primary source . One way to find the source is through a relevant secondary source. If you are interested in connoisseurship in the fine arts, for example, you might look through the Warwick library catalogue for books on this topic related to the eighteenth century. You might then find, for example, Carol Gibson-Wood's book Jonathan Richardson: Art Theorist of the English Enlightenment , which in turn discusses many relevant primary sources. Another approach is to start with the primary sources themselves by searching through collections of relevant sources. Examples are:
The online archive of the Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London
Early English Books Online , a database of early modern English texts
The online archive of the English East India Company
Eighteenth-century encyclopaedias, such as Chambers' Cyclopaedia , the fourth edition of which has been digitised
The catalogues of public museums, such as the Oxford Museum for the History of Science and the British Museum
Virtual exhibitions, such as the Intoxicating Spaces exhibition or the Sugar and the Visual Imagination exhibition
Analysing the primary source. Analysing primary sources is more an art than a science, and there are no hard-and-fast rules about how to do it. However, for the purpose of this essay you should do at least the following:
Interpret. Decipher the source so that it can be understood by a non-specialist audience. This may mean explaining technical terms, rephrasing complicated sentences, identifying rhetorical devices or figures of speech, or (for long texts) summarising the argument or narrative.
Explain. Get behind the source to understand its conditions of production. Who was the author? Who was the intended audience? Why, when, how, and where was the source made? Which genre does it belong to (encyclopaedia article, scientific article, merchant correspondence...) and how does it fit into the history of that genre?
Contextualise. Relate the source to wider historical developments of the kind that we have covered in the module, such as the the growth of the fiscal-military state, the growth of a consumer culture, and the outbreak of the French Revolution.
The essay could be structured around these three tasks, with one section on each - but it does not need to be. The important thing is to do these three things as part of your research, and to integrate them into your argument.
Other sources. Although the essay should be centred on one primary source, it does not need to be limited to that source. Indeed, you will need to draw on other primary and secondary sources to make sense of the primary source that you focus on. The expectation is that you will draw on five (or more) secondary sources and one (or more) additional primary sources. The secondary sources can be made of books, book chapters, journal articles, or chapters in edited collections.
Meeting with tutor. All students are strongly encouraged to meet the tutor (during office hours ) to discuss their choice of primary source. This meeting can take place any time in term 2 before the essay deadline, but should be around the time you decide upon that source.
History Essay Examples

Top History Essay Examples To Get Inspired By
Published on: May 4, 2023
Last updated on: Jan 31, 2024

Share this article
History essays are a crucial component of many academic programs, helping students to develop their critical thinking, research, and writing skills.
However, writing a great history essay is not always easy, especially when you are struggling to find the right approach. This is where history essay examples come in handy.
By reading and examining samples of successful history essays, you can gain inspiration, learn new ways to approach your topic. Moreover, you can develop a better understanding of what makes a great history essay.
In this blog, you will find a range of history essay examples that showcase the best practices in history essay writing.
Read on to find useful examples.
On This Page On This Page -->
Sample History Essays
Explore our collection of excellent history paper examples about various topics. Download the pdf examples for free and read to get inspiration for your own essay.
History Essay Samples for Middle School
The Impact of Ancient Civilizations on Modern Society
The Rise and Fall of the Roman Empire
The Causes and Consequences of the American Revolution
History Writing Samples for High School Students
The Impact of the Industrial Revolution on Society
Grade 10 History Essay Example: World War 1 Causes and Effects
Grade 12 History Essay Example: The Impact of Technology on World War II
Ancient History Essay Examples
The Societal and Political Structures of the Maya Civilization
The Role of Phoenicians in the Development of Ancient Mediterranean World
The Contributions of the Indus Civilization
Medieval History Essay Examples
The Crusades Motivations and Consequences
The Beginning of Islamic Golden Age
The Black Death
Modern History Essay Examples
The Suez Crisis and the End of British Dominance
The Rise of China as an Economic Powerhouse
World History Essay Examples
The Role of the Silk Road in Shaping Global Trade and Culture
The Rise and Fall of the Ottoman Empire
The Legacy of Ancient Greek Philosophy and Thought

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
American History Essay Examples
The Civil Rights Movement and its Impact on American Society
The American Civil War and its Aftermath
The Role of Women in American Society Throughout History
African History Essay Examples
The Impact of Colonialism on African Societies
The Rise and Fall of the Mali Empire
European History Essay Examples
The Protestant Reformation and the Rise of Protestantism in Europe
The French Revolution and its Impact on European Politics and Society
The Cold War and the Division of Europe
Argumentative History Essay Examples
Was the US Civil War Primarily About Slavery or States
The Effects of British Colonization on Colonies
Art History Essay Examples
The Influence of Greek and Roman Art on Neoclassicism
The Depiction of Women in Art Throughout History
The Role of Art in the Propaganda of Fascist Regimes
How to Use History Essay Examples
History essay examples are a valuable tool for students looking for inspiration and guidance on how to approach their own essays.
By analyzing successful essays, you can learn effective writing techniques that can be expected in a high-quality history essay.
Here are some tips that will help you take full advantage of the samples above.
Tips for Effectively Using History Essay Examples
- Analyze the Structure:
Pay close attention to how the essay is organized, including the introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion. Look for how the author transitions between paragraphs and the use of evidence to support their argument.
- Study the Thesis Statement:
The thesis statement is the backbone of any successful history essay. Analyze how the author crafted their thesis statement, and consider how you can apply this to your own writing.
- Take Note of the Evidence:
Effective history essays rely on using strong evidence to support their arguments. Take note of the sources and types of evidence used in the essay. Consider how you can apply similar evidence to support your own arguments.
- Pay Attention to the Formatting and Other Academic Formalities:
The sample essays also demonstrate how you can incorporate academic formalities and standards while keeping the essay engaging. See how these essays fulfill academic standards and try to follow them in your own writing.
- Practice Writing:
While analyzing history essay examples can be helpful, it is important to also practice writing your own essays. Use the examples as inspiration, but try to craft your own unique approach to your topic.
History essays are an essential aspect of learning and understanding the past. By using history essay examples, students can gain inspiration on how to develop their history essays effectively.
Furthermore, following the tips outlined in this blog, students can effectively analyze these essay samples and learn from them.
However, writing a history essay can still be challenging.
Looking for an online essay writing service that specializes in history essays? Look no further!
Our history essay writing service is your go-to source for well-researched and expertly crafted papers.
And for an extra edge in your academic journey, explore our AI essay writing tool . Make history with your grades by choosing our online essay writing service and harnessing the potential of our AI essay writing tool.
Get started today!
Cathy A. (Law, Marketing)
For more than five years now, Cathy has been one of our most hardworking authors on the platform. With a Masters degree in mass communication, she knows the ins and outs of professional writing. Clients often leave her glowing reviews for being an amazing writer who takes her work very seriously.
Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!

Legal & Policies
- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Terms of Use
- Refunds & Cancellations
- Our Writers
- Success Stories
- Our Guarantees
- Affiliate Program
- Referral Program
- AI Essay Writer
Disclaimer: All client orders are completed by our team of highly qualified human writers. The essays and papers provided by us are not to be used for submission but rather as learning models only.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
If you understand how each part works and fits into the overall essay, you are well on the way to creating a great assessment piece. Most essays will require you to write: 1 Introduction Paragraph. 3 Body Paragraphs. 1 Concluding Paragraph.
om writing in other academic disciplines. As you compose or revise your. history paper, consider t. ese guidelines:s Write in the past tense. Some students have been taught to enliven their prose by wr. ting in the "literary present" tense. Such prose, while acceptable in other discip.
1. Identify the assignment's goals. Have the assignment's goals in mind as you familiarize yourself with your sources/evidence, develop a thesis, outline your main points, and write your essay. *Note: Always follow your professor's specific guidelines before the general suggestions in this handout. Example Essay Prompt: The assignment is ...
In order to demonstrate a knowledge of the six analysis skills, you need to do two things: Carefully read the source to find information that is explicit and implicit. Conduct background research about the creator of the source. After completing these two steps, you can begin to show your understanding about the six features of historical ...
Writing a history paper requires much more than just sitting down at a computer. It involves a lot of early planning, detailed research, critical thinking, skilled organization, and careful writing and rewriting. The first rule of essay writing is to start early so that you have plenty of time to follow these steps.
led instruction.• write in a formal, academic voice. Avoid using the first or second person (e.g., "i" and "you"), and shy away from passive sentence constructions. phrases such as "i think" or. in my opinion" are redundant in. xpository writing.• Proof. for fUrTHer reading. f writing history s.
Historical essay writing is based upon the thesis. A thesis is a statement, an argument which will be presented by the writer. The thesis is in effect, your position, your particular interpretation, your way of seeing a problem. Resist the temptation, which many students have, to think of a thesis as simply "restating" an instructor's question.
As you critically engage with your sources, keep some things in mind: Write in the past tense when discussing history. If a historical event took place in the past, write about it in the past. Be precise. Focus on your thesis and only provide information that is needed to support or develop your argument. Be formal.
Step 1: Understand the History Paper Format. You may be assigned one of several types of history papers. The most common are persuasive essays and research papers. History professors might also ask you to write an analytical paper focused on a particular source or an essay that reviews secondary sources.
For example, an essay discussing Hitler's rise to power in 1933 might close with a couple of sentences about how he consolidated and strengthened his power in 1934-35. ... Reference and cite your sources. A history essay is only likely to succeed if it is appropriately referenced. Your essay should support its information, ideas and arguments ...
Once you are satisfied with your argument, move onto the local level. Put it all together: the final draft. After you have finished revising and have created a strong draft, set your paper aside for a few hours or overnight. When you revisit it, go over the checklist in Step 8 one more time.
Secondary sources interpret or analyze primary sources, and in History & Literature they are used to teach engagement with the intergenerational conversation that is ... with a draft of the Sophomore Essay and the Sophomore Essay itself. Primary Source Analysis The first major assignment for the Sophomore Tutorial is a primary source analysis—a .
1. Background sentences. The first two or three sentences of your introduction should provide a general introduction to the historical topic which your essay is about. This is done so that when you state your hypothesis, your reader understands the specific point you are arguing about. Background sentences explain the important historical ...
Body paragraph 1: Introduction to the Historical Context. Provide background information on the historical context of your topic. Highlight key events, figures, or developments leading up to the main focus of your history essay. Body paragraphs 2-4 (or more): Main Arguments and Supporting Evidence.
Historiographic Essay Manual, updated 17 August 2021 . ... access to primary sources on your topic for History 494 there is no point in doing it for History 394. In pondering topics, most students identify obvious, well-known ... for example the military history of the Civil War or the tension between Martin
Download Article. 1. Have a clear structure. When you come to write the body of the essay it is important that you have a clear structure to your argument and to your prose. If your essay drifts, loses focus, or becomes a narrative of events then you will find your grade dropping.
example, then the thesis statement of any historical work (such as a history exam essay) is the philosophy as yet embellished by example, the analysis as yet buttressed by evidence, the spool of interpretive thread that you will subsequently unravel and weave throughout the body of your essay (for more on weaving your thesis, see #4 below).
Make it Shine. An A-level essay takes planning and revision, but it's achievable. Firstly, avoid procrastination and start early. Secondly, leave yourself plenty of time to brainstorm, outline, research and write. Finally, follow these five tips to make your history essay shine: Write a substantial introduction.
A primary source is one produced by a participant in or witness of the events you are writing about. A primary source allows the historian to see the past through the eyes of direct participants. Some common primary sources are letters, diaries, memoirs, speeches, church records, newspaper articles, and government documents of all kinds.
Finding Sources Toggle Dropdown. Find Primary Sources ; Find Secondary Sources ; Citations & Bibliography Toggle Dropdown. ... Sample Papers. Sample History Papers; Sample Title Pages, Outlines, & Citations; Resources for Writing; Sample History Papers. These are examples of well written, properly cited history papers. Sample Paper with Outline ...
I. Introduction. Hook: Use a quote, history fact, or question to capture the reader's attention and trigger their interest to continue reading. Brief background: Tell readers about an assigned topic by addressing issues central to this theme that help contextualize a historical discussion. Thesis statement: Use a short sentence to tell readers the history essay's primary objective or ...
The essay will be marked using the usual history-specific marking criteria for written work. That said, a primary-source essay is a particular type of essay that calls for specific tasks that are not relevant to all other essays. Like any other essay, this one needs to be an argument--it needs to state a thesis and make a case for that thesis.
Tips for Effectively Using History Essay Examples. Analyze the Structure: Pay close attention to how the essay is organized, including the introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion. Look for how the author transitions between paragraphs and the use of evidence to support their argument. Study the Thesis Statement: