Segment Addition Postulate
The segment addition postulate in geometry is applicable on a line segment containing three collinear points. It states that if there are two given points on a line segment A and C, then point B lies on the same line segment somewhere between A and C only if the sum of AB and BC is equal to AC.
By applying the segment addition postulate, we can precisely determine the length of a line segment when given specific measurements of its parts. Also, this postulate enables us to divide a line segment into different sections and explore the relation (ratios) between their lengths.
| 1. | |
| 2. | |
| 3. |

Segment Addition Postulate Definition
The segment addition postulate states that if a line segment has two endpoints, A and C, a third point B lies somewhere on the line segment AC if and only if the equation AB + BC = AC is satisfied. Look at the image given below to have a better understanding of this postulate.
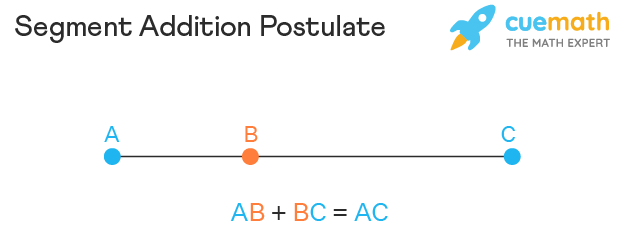
If we carefully look at its name "Segment Addition Postulate", it is very easy to understand.
- A segment, here, means a line segment. It emphasis that this postulate is applicable only on a line segment, and not on a ray or a line . A line segment is part of a line bounded by two defined endpoints. We can have an infinite number of points between the endpoints of a segment.
- The "addition" means that we are adding the distances between points.
- Finally, "postulate" means this axiom is taken as a fact or valid without any proof.
Another way of stating the segment addition postulate is that if point B lies on the line segment AC, then AB + BC = AC.
Segment Addition Postulate Formula
If the end-points of a line segment are denoted as A and C, and there lies a point B on the line segment, then the segment addition postulate formula is given as AB + BC = AC.
Further, extending this theorem to two points, If there are two points B and D on the segment, we will have the formula as AB + BD + DC = AC.
☛ Related Topics:
- Segment Addition Postulate Worksheets
- Difference Between Line and Line Segment
- Line Segment
Segment Addition Postulate Examples
Example 1: In the given figure, if B is the mid-point of line segment AC, find the length of segment AC.

By using the segment addition postulate, we know that the sum of segments AB and BC is equal to AC. It can be written mathematically as AB + BC = AC. Also, B is the midpoint of AC. It implies AB = BC.
⇒ 3x = 4x-6
⇒ 6 = 4x - 3x
Now, put the value of x in the equation AB + BC = AC.
AC = 3x + 4x - 6
⇒ AC = 7x - 6
⇒ AC = 7 × 6 - 6
⇒ AC = 42 - 6
Answer: ∴ The length of the segment AC is 36 units.
Example 2: Find whether Q is the mid-point of segment PR or not, if the length of PR is 45 units. [Refer to the figure below]

Solution: There are three collinear points on the given segment which are points P, Q, and R. By using the segment addition postulate, we know that PQ + QR = PR. Substitute the value of PR as 45 units, we get,
PQ + QR = 45
⇒ 9x + 7 + (-3x+20) = 45
⇒ 9x - 3x + 7 + 20 = 45
⇒ 6x + 27 = 45
Now, let us find the values of PQ and QR.
PQ = 9x + 7 = 9 (3) + 7 = 34 units
QR = -3x+20 = -3 (3) + 20 = 11 units
Answer: ∴ PQ ≠ QR. Q is not the midpoint of segment PR.
Example 3: On a line segment XY, if Z is between X and Y and XY = 25. What will be the expression to find the value of XZ?
Solution: It is given that point Z is between X and Y, so by using the segment addition postulate, we have XZ + ZY = XY. The value of XY is given as 25. So, the expression to find the value of XZ is 25 - ZY.
Answer: ∴ 25 - ZY is the required expression.
go to slide go to slide go to slide

Book a Free Trial Class
Practice Questions on Segment Addition Postulate
go to slide go to slide
FAQs on Segment Addition Postulate
What is segment addition postulate in geometry.
The segment addition postulate in geometry is the axiom which states that the length of a line segment divided into smaller pieces is the sum of the lengths of all those smaller segments. So, if we have three collinear points A, B, and C on segment AC such that B is somewhere between A and C, then AB + BC = AC. It is a mathematical fact that can be accepted without proof.
What are the Two Conditions of the Segment Addition Postulate?
The two conditions of the segment addition postulate are given below:
- A point P lies on a segment MN if and only if points M, P, and N are collinear taken in order.
- The distance between MP and PN must be equal to MN.
What are the Examples of Segment Addition Postulate?
As per the segment addition postulate, if we have an iron rod of length 30 inches that is cut into two parts where the length of one part is 14 inches, it means the length of the other part of the rod is 30 - 14 = 16 inches.
What is a Segment Addition Postulate Used For?
We can apply this postulate in calculating the missing lengths. It can be used to find the sum of the smaller parts of a segment to find the total length. The segment addition postulate has its applications in construction, architecture, design, etc.

How to Solve for x with Segment Addition Postulate?
If we have a missing length, let's say x, and we know the total length and the length of the other part of the segment, then we can apply the segment addition postulate to find x. For example, if AB = 3, BC = x, and AC = 5, then we can find x by subtracting AB from AC. This implies AC - AB = 5 - 3 = 2 = BC. i.e., x = 2.
How to Use the Segment Addition Postulate to Show that ae=ab+bc+cd+de?
If a segment AE has three points on it, marked as B, C, and D in order, then according to the segment addition postulate, their sum is equal. So, AE = AB + BC + CD + DE. This is possible by applying the postulate for more than one time.
What is Segment Addition Postulate in Proofs?
The segment addition postulate does not require any proof. It is accepted as a mathematical fact. But many times, we use this axiom in stating proofs for line segments. One such proof is given as "If two congruent segments are added to the line segments of the same length, then their sum is also equal."
- Kindergarten
- Greater Than Less Than
- Measurement
- Multiplication
- Place Value
- Subtraction
- Punctuation
- 1st Grade Reading
- 2nd Grade Reading
- 3rd Grade Reading
- Cursive Writing
- Alphabet Coloring
- Animals Coloring
- Birthday Coloring
- Boys Coloring
- Buildings Coloring
- Cartoons Coloring
- Christmas Coloring
- Country Flag Coloring
- Country Map Coloring
- Disney Coloring
- Fantasy Coloring
- Food Coloring
- Girls Coloring
- Holidays Coloring
- Music Coloring
- Nature Coloring
- New Year Coloring
- People Coloring
- Religious Coloring
- Sports Coloring
- Toys Coloring
- Transportation Coloring
- US Sports Team Coloring
- Valentine Day Coloring
Unit 1 Geometry Basics Homework 2 Segment Addition Postulate
Displaying top 8 worksheets found for - Unit 1 Geometry Basics Homework 2 Segment Addition Postulate .
Some of the worksheets for this concept are The segment addition postulate date period, Geometry, Geometry unit 1 workbook, Segment addition answers, Geometry chapter 2 reasoning and proof, Identify points lines and planes, 1 introductionto basicgeometry, Infinite geometry.
Found worksheet you are looking for? To download/print, click on pop-out icon or print icon to worksheet to print or download. Worksheet will open in a new window. You can & download or print using the browser document reader options.
1. The Segment Addition Postulate Date Period
2. geometry -, 3. geometry unit 1 workbook, 4. segment addition answers -, 5. geometry chapter 2 reasoning and proof, 6. 1.1 identify points, lines, and planes, 7. 1 introductionto basicgeometry, 8. infinite geometry.
Geometry Basics (Geometry Curriculum - Unit 1) | All Things Algebra®

- Google Apps™
What educators are saying
Also included in.

Description
This Geometry Basics Unit Bundle contains guided notes, homework assignments, three quizzes, dictionary, study guide and a unit test that cover the following topics:
• Points, Lines, and Planes
• Segment Addition Postulate
• The Distance Formula
• The Midpoint Formula
• Partitioning a Segment
• Naming and Classifying Angles
• Angle Addition Postulate
• Angle Relationships (Adjacent, Vertical, Complementary, Supplementary, Linear Pair)
• Solving for Missing Measures using Algebra
• Special Relationships: Perpendicular and Angle Bisectors
• Constructions (Perpendicular bisectors, perpendicular line through a point on the line, perpendicular line through a point not on the line, line parallel to a given line through a given point, angle bisector, congruent angles)
Note: This unit was updated on 8/25/19 to include partitioning a segment. If you do not teach this topic, I included the old unit without this topic in the download as well.
ADDITIONAL COMPONENTS INCLUDED:
(1) Links to Instructional Videos: Links to videos of each lesson in the unit are included. Videos were created by fellow teachers for their students using the guided notes and shared in March 2020 when schools closed with no notice. Please watch through first before sharing with your students. Many teachers still use these in emergency substitute situations. (2) Editable Assessments: Editable versions of each quiz and the unit test are included. PowerPoint is required to edit these files. Individual problems can be changed to create multiple versions of the assessment. The layout of the assessment itself is not editable. If your Equation Editor is incompatible with mine (I use MathType), simply delete my equation and insert your own.
(3) Google Slides Version of the PDF: The second page of the Video links document contains a link to a Google Slides version of the PDF. Each page is set to the background in Google Slides. There are no text boxes; this is the PDF in Google Slides. I am unable to do text boxes at this time but hope this saves you a step if you wish to use it in Slides instead!
This resource is included in the following bundle(s):
Geometry First Semester Notes Bundle
Geometry Curriculum
Geometry Curriculum (with Activities)
More Geometry Units:
Unit 2 – Logic and Proof
Unit 3 – Parallel and Perpendicular Lines
Unit 4 – Congruent Triangles
Unit 5 – Relationships in Triangles
Unit 6 – Similar Triangles
Unit 7 – Right Triangles and Trigonometry Unit 8 – Polygons and Quadrilaterals
Unit 9 – Transformations
Unit 10 – Circles
Unit 11 – Volume and Surface Area Unit 12 – Probability
LICENSING TERMS: This purchase includes a license for one teacher only for personal use in their classroom. Licenses are non-transferable , meaning they can not be passed from one teacher to another. No part of this resource is to be shared with colleagues or used by an entire grade level, school, or district without purchasing the proper number of licenses. If you are a coach, principal, or district interested in transferable licenses to accommodate yearly staff changes, please contact me for a quote at [email protected].
COPYRIGHT TERMS: This resource may not be uploaded to the internet in any form, including classroom/personal websites or network drives, unless the site is password protected and can only be accessed by students.
© All Things Algebra (Gina Wilson), 2012-present
Questions & Answers
All things algebra.
- We're hiring
- Help & FAQ
- Privacy policy
- Student privacy
- Terms of service
- Tell us what you think

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Geometry; Geometry questions and answers; Unit 1: Geometry Basics Homework 2: Segment Addition Postulate age document! ** 1. If LM= 22 and MN = 15, find LN. 2. If LN = 54 and LM = 31, find MN. 4. If DF = 9x - 39, find EF. 47 3x + 10
Final answer: The segment addition postulate states that if three points A, B, and C are collinear, then the sum of the lengths of AB and BC is equal to the length of AC.. Explanation: The segment addition postulate states that if three points A, B, and C are collinear, then the sum of the lengths of AB and BC is equal to the length of AC.. Mathematically, this can be represented as:
Unit 1: Geometry Basics Homework 2: Segment Addition Postulate I * * This is a 2-page document! * * Use the diagram below to answer questions 1 and 2. L M N 1. If LM= 22 and MN= 15, find LN. 22+ 15 ::ŒJJ 2. If LN= 54 and LM= 31, find MN. 5 '4 - 3 I - [2.3 J 3.
Video that talks about the segment addition postulate.
-2- ©l E270 K1E30 QKzu2t GaU PS7o7f Ttsw va 7r 3e e XLKLNC7. B A FAWlMlF er1iQgUh1t3su QrWeGsheLr OvYeBdf. 0 Z uM3aBd4eR vw pi 0t nhM FIYnBfgi LnWi0t ye E vGueso Gmhe utzr2y p.4 Worksheet by Kuta Software LLC
The Segment Addition Postulate in Geometry states that the total length of two contiguous segments is equal to the length of the segment formed by their endpoints. A practical example can be given as points A,B and C on a line, if the distance AB is 3 and BC is 5, then the length of AC must be 8.
Solve for the missing length indicated. 23. Solve for the missing length indicated. 15. Solve for the missing length indicated. 24. Solve for the missing length indicated. Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like 10, 11, 3 and more.
Ruler Postulate: Write an equation for the length of AB. Segment Addition Postulate: Write an equation for the length of AC. Check Your Understanding: 1. Find the length of ST. 2. Write an equation explaining the relationship between Rs, ST, and RT. 3. Use segment addition to write an equation and then solve for x. Click here for more practice ...
Find an answer to your question Unit 1: Geometry Basics homework 2: Segment addition postulate I answered some of these but please help me will mark brainlies ... unit 1 geometry basics homework 2 segment addition postulate answer key. verified. Verified answer. help.? geometry basics homework 2: segment addition postulate . star. 4.3/5. heart. 9.
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Point A, B, and C are collinear. Point B is between A and C. BC = x-7, AB = x-2, and AC = 7. Find x., Point A, B, and C are collinear. Point B is between A and C. Find x if AC = 16, BC = x+6, and AB = x., Point A, B, and C are collinear. Point B is between A and C. Find AB if BC = -2+5x, AB = 2x, and AC = 12. and more.
Geometry 1.2 Homework (Segment Addition Postulate) Name_____ Period____ ©z [2]0_1m7B OKzuBtyag cSCoVfjtYwHamrSet xLxLSCF.J w _AclVlI hrmiQgqhktAsv NrzelsJeWravseFdm. Find the length indicated. 1 ... Infinite Geometry - 1.2 Homework (Segment Addition Postulate) Created Date:
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Point B is between points A and C. The measure of AB is 3x + 4 and the measure of BC is 5x - 6 and the measure of AC is 38., Point B is between points A and C. The measure of AB is 6x + 5 and the measure of BC is 4x and the measure of AC is 45., Point B is between points A and C. The measure of AB is 3x + 4 and the measure of BC ...
Segment Addition Postulate Examples. Example 1: In the given figure, if B is the mid-point of line segment AC, find the length of segment AC. Solution: By using the segment addition postulate, we know that the sum of segments AB and BC is equal to AC. It can be written mathematically as AB + BC = AC. Also, B is the midpoint of AC.
Unit 1 Geometry Basics Homework 2 Answer Key - wiki.drf.com introduction to symplectic geometry for graduate ... Mr. Smith's Mathematics Website Unit 1: Geometry Basics Homework 2: Segment Addition Postulate I * * This is a 2-page document! * * Use the diagram below to answer questions 1 and 2. L M N 1. If LM= 22 and MN= 15, find LN. 22+ 15 ...
Free worksheet at https://www.kutasoftware.com/freeige.htmlGo to ️ https://maemap.com/math/geometry/ ⬅️ for more Geometry information!Please support me: ?...
Unit 1: The Basics of Geometry Learn with flashcards, games, and more — for free. ... Segment Addition Postulate. AB + BC = AC adding two parts of the segment to equal the whole segment ... A point that divides a segment into two congruent segments. Angle Addition Postulate. If P is in the interior of <RST, then m<RSP + m<PST = m<RST. About ...
Displaying top 8 worksheets found for - Unit 1 Geometry Basics Homework 2 Segment Addition Postulate. Some of the worksheets for this concept are The segment addition postulate date period, Geometry, Geometry unit 1 workbook, Segment addition answers, Geometry chapter 2 reasoning and proof, Identify points lines and planes, 1 introductionto basicgeometry, Infinite geometry.
The segment addition postulate states that if we have a line segment AC and there a point B within the line segment AC (The points A, B and C are collinear), then the sum (addition) of individual lengths of each of line segments AB and BC will be equal to the total length of the line segment AC.. What are postulates? Postulates are statements which are also known as axioms that initially might ...
This Geometry Basics Unit Bundle contains guided notes, homework assignments, three quizzes, dictionary, study guide and a unit test that cover the following topics:• Points, Lines, and Planes• Segment Addition Postulate• The Distance Formula• The Midpoint Formula• Partitioning a Segment• Naming an...
It marks a location and is named by a capital letter; it has no thickness and 0 dimension. line. An infinite set of points that goes on forever; it has no thickness and it is one dimensional. plane. A flat surface that goes on forever in two directions; an infinite set of points; it has no thickness and is two dimensional. collinear.
Geometry Basics: Segment Addition Postulate. The Segment Addition Postulate is a concept in geometry which states that if a point B is between points A and C, then the sum of the lengths of segments AB and BC is equal to the length of segment AC. This can be written algebraically as AB + BC = AC. This postulate is foundational in plane geometry ...
The Angle Addition Postulate is a concept in geometry which states that if point B lies in the interior of angle AOC, then the measure of angle AOB + the measure of angle BOC is equal to the measure of angle AOC. To apply this in examples involving vectors, we can consider the analytical methods of vector addition and subtraction.