

Graduate Students
Learn more about our students' research interests and dissertation projects.
CURRENT STUDENTS
Ph.D. Program
Stanford Ph.D. Program in History aims to train world-class scholars.
Every year we admit 10-12 promising students from a large pool of highly selective applicants. Our small cohort size allows more individual work with faculty than most graduate programs in the United States and also enables funding in one form or another available to members of each cohort.
Fields of Study
Our graduate students may specialize in 14 distinct subfields: Africa, Britain, Early Modern Europe, East Asia, Jewish History, Latin America, Medieval Europe, Modern Europe, Ottoman Empire and Middle East, Russia/Eastern Europe, Science, Technology, Environment, and Medicine, South Asia, Transnational, International, and Global History, and United States. Explore each field and their affiliates .
The department expects most graduate students to spend no less than four and no more than six years completing the work for the Ph.D. degree. Individual students' time to degree will vary with the strength of their undergraduate preparation as well as with the particular language and research requirements of their respective Major fields.
Expectations and Degree Requirements
We expect that most graduate students will spend no less than four and no more than six years toward completing their Ph.D. Individual students' time-to-degree vary with the strength of their undergraduate preparation as well as with the particular language and research requirements of their respective subfield.
All History Ph.D. students are expected to satisfy the following degree requirements:
- Teaching: Students who enter on the Department Fellowship are required to complete 4 quarters of teaching experience by the end of their third year. Teaching experience includes teaching assistantships and teaching a Sources and Methods course on their own.
- Candidacy : Students apply for candidacy to the PhD program by the end of their second year in the program.
- Orals: The University Orals Examination is typically taken at the beginning of the 3rd year in the program.
- Languages: Language requirements vary depending on the field of study.
- Residency Requirement : The University requi res 135 units of full-tuition residency for PhD students. After that, students should have completed all course work and must request Terminal Graduate Registration (TGR) status.
Browse the Ph.D. Handbook to learn more .
The History Department offers 5 years of financial support to PhD students. No funding is offered for the co-terminal and terminal M.A. programs. A sample Ph.D. funding package is as follows:
- 1st year: 3 quarters fellowship stipend and 1 summer stipend
- 2nd year: 2 quarters TAships, 1 quarter fellowship stipend, and 1 summer stipend
- 3rd year: 2 quarters TAships, 1 quarter fellowship stipend, and 1 summer stipend
- 4th year: 3 quarters fellowship stipends and 1 summer stipend
- 5th year: 3 quarters fellowship stipends and 1 summer stipend
Knight-Hennessy Scholars
Join dozens of Stanford School of Humanities and Sciences students who gain valuable leadership skills in a multidisciplinary, multicultural community as Knight-Hennessy Scholars (KHS). KHS admits up to 100 select applicants each year from across Stanford’s seven graduate schools, and delivers engaging experiences that prepare them to be visionary, courageous, and collaborative leaders ready to address complex global challenges. As a scholar, you join a distinguished cohort, participate in up to three years of leadership programming, and receive full funding for up to three years of your studies at Stanford. candidates of any country may apply. KHS applicants must have earned their first undergraduate degree within the last seven years, and must apply to both a Stanford graduate program and to KHS. Stanford PhD students may also apply to KHS during their first year of PhD enrollment. If you aspire to be a leader in your field, we invite you to apply. The KHS application deadline is October 9, 2024. Learn more about KHS admission .
How to Apply
Admission to the History Graduate Programs are for Autumn quarter only. Interested applicants can online at https://gradadmissions.stanford.edu/apply/apply-now and submit the following documents:
- Statement of Purpose (included in Application)
- 3 Letters of Recommendation
- Transcripts are required from all prior college level schools attended for at least one year. A scanned copy of the official transcript is submitted as part of the online application. Please do not mail transcripts to the department. We will ask only the admitted students to submit actual copies of official transcripts.
- 1 Writing Sample on a historic topic (10-25 pages; sent via Stanford's online application system only)
- The GRE exam is not required for the autumn 2025 admission cycle
- TOEFL for all international applicants (whose primary language is not English) sent via ETS. Our University code is 4704.
- TOEFL Exemptions and Waiver information
- Application Fee Waiver
- The department is not able to provide fee waivers. Please see the link above for the available fee waivers and how to submit a request. Requests are due 2 weeks before the application deadline.
The Department of History welcomes graduate applications from individuals with a broad range of life experiences, perspectives, and backgrounds who would contribute to our community of scholars. Review of applications is holistic and individualized, considering each applicant’s academic record and accomplishments, letters of recommendation, and admissions essays in order to understand how an applicant’s life experiences have shaped their past and potential contributions to their field.
The Department of History also recognizes that the Supreme Court issued a ruling in June 2023 about the consideration of certain types of demographic information as part of an admission review. All applications submitted during upcoming application cycles will be reviewed in conformance with that decision.
Application deadline for Autumn 2025-26 is Tuesday, December 3, 2024 at 11:59pm EST . This is a hard -not a postmark- deadline.
All application material is available online. No information is sent via snail mail. Interested applicants are invited to view a Guide to Graduate Admissions at https://gradadmissions.stanford.edu/ .
Questions?
Please contact Arthur Palmon (Assistant Director of Student Services).
Department Bookshelf
Browse the most recent publications from our faculty members.

Against Constitutional Originalism: A Historical Critique

Italian Fascism in Rhodes and the Dodecanese Islands, 1922–44

A World Made by Travel: The Digital Grand Tour

The Chinese Computer: A Global History of the Information Age

In the Shadow of Liberty: The Invisible History of Immigrant Detention in the United States

Can You Get a PhD without a Masters?
- Applying to a PhD
Yes, it’s possible to get a PhD without first having a Masters degree .
The conventional route for someone who earns a PhD is to pursue a Bachelor’s degree, followed by a Masters degree and then a PhD. However, several students opt to bypass a Master’s degree by enrolling onto a doctoral programme as soon as they complete their undergraduate degree.
Before we discuss how this can be done, it is worth mentioning the advantages and disadvantages of this route.
Advantages of Applying to a PhD without A Masters
The motivations for undertaking a PhD immediately after an undergraduate course are largely in saving money and time. This is because you will essentially eliminate a year of study. Another advantage of immediately enrolling onto a doctorate degree is project availability. If you find a project that you’re really interested in, it’s unlikely that it will still be available in a years’ time. Therefore, bypassing a Masters and enrolling directly into a PhD will increase your chances of securing the research project before it becomes unavailable.
Disadvantages of Applying to a PhD without A Masters
Although a Masters degree will add a year onto your academic journey, it can be incredibility helpful for your development and can help prepare you for a doctoral degree.
Not having a Master’s degree may prove to be a hindrance during your application process. This is because many other students will also apply to the same research projects, and it’s likely that the majority will hold a Masters. This will put you at a disadvantage to them.
Besides this, the dissertation project you’ll be required to undertake on a Master’s programme will provide you with a taste of what it is like to work on a research-based project. In addition to this, it’s likely that you’ll be able to select your own dissertation topic. As such, you can explore a specific field you’re interested in in further detail. This is a great way to confirm that both research-based work and the specific field you’re interested in are right for you before committing the next few years to it via a PhD.
Another advantage to the dissertation project associated with a Masters degree is the opportunity it provides you with to work closely with a project supervisor. This will help you understand the PhD student-supervisor relationship and communication frequency that works best for you. You can then use this knowledge to find supervisors who would compliment you when it comes time to find a PhD project to apply to. For tips on how to find a great PhD supervisor, check out our supervisor guide .
PhD without a Masters – How Does It Work?
To be considered for a PhD without a Master’s, at a minimum you will be expected to have a Bachelors degree. For students looking to enrol onto a STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths) PhD, a relevant Bachelors in a 3-year undergraduate course is usually expected. However, this is not the case for students looking to apply to non-STEM PhDs. Rather, students looking to apply to doctorates in subjects such as those surrounding Arts and Humanities are usually expected to have a relevant Bachelors from a 4-year course.
In addition to this, you will need to have demonstrated strong academic performance during your undergraduate course. This means that your Bachelors will need to be at least a UK Upper Second-Class Honours (2.1) for nearly all institutions to consider you.
Should you be accepted into a PhD programme without a Masters, the usual process will be to first register you as an MPhil student. You will then have a year to prepare and submit a thesis. Your thesis will need to detail the research you have carried out within that year and outline how you intend to continue it into a full PhD study. There are three outcomes of this MPhil thesis review:
- Failure and you’re not awarded anything.
- You pass, however, the supervisor doesn’t believe you’ve demonstrated strong research skills. You’re awarded an MPhil but they do not upgrade your course to a PhD programme.
- You pass and the supervisor believes you have proven yourself as a capable researcher. Your course is upgraded to a PhD as opposed to you being awarding an MPhil.
For more information on these outcomes, read the outcomes section of our PhD Viva guide .
Integrated PhD
Some universities offer Integrated PhD degree programmes (also known as an Integrated Masters degree). These are four-year programmes comprising of a one-year Masters degree immediately followed by a three-year PhD degree. These can prove a great option for graduate students who are looking to undertake a PhD without a Masters but are struggling to meet the eligibility requirements. You can read about the many benefits of integrated degrees here .
Finding a PhD has never been this easy – search for a PhD by keyword, location or academic area of interest.
PhD without a Bachelors – Is It Possible?
Yes, it is possible to get a PhD without a Bachelor’s, however, this is extremely uncommon.
When this occurs, it is almost always reserved for very mature individuals. For example, an individual may not be in active academia but still may have significantly contributed to their field. This contribution could be through the work they have undertaken as part of their career, or as part of a long-term study project, they have undertaken out of self-interest.
In either case, the individual would need to prove that they have extensive experience in their field and have directly contributed to new knowledge within it. The key factor here is that their work has pushed the boundaries of existing knowledge. It is not enough for an individual to be regarded as an expert in their field – they must have contributed something new and meaningful. It’s common for individuals awarded a PhD through this means to have produced several publications within their lifetime. It’s also common for the individual to have gained several professional accreditations within their field before even being considered suitable for a PhD research degree.
Universities Offering PhD without a Masters
Unfortunately, there is not a centralised list of universities which offer PhDs without a Master’s degree. The reason for this is that the edibility requirements differ from PhD to PhD and from department to department.
Therefore, you will need to check the guidelines for each individual university and the requirements for each specific PhD you’re interested in.
Should you find a PhD programme you can apply to with a Bachelors, make every effort to make your application as strong as possible. This is because you will be competing against other candidates, most of who will have a Master’s degree.
Not only can you strengthen your application by having a Bachelors with a First-Class Honours (1st), but you can also do so by showing the traits of a successful researcher. This includes showing a genuine interest in the project, a high work ethic, and exceptional communication skills.
Additionally, a strong letter of recommendation from a respected university lecturer will prove very beneficial. This is especially true if the lecturer supervisors his or her own PhD students. This is because the lecturer will understand the skills required for an adept research student.
For more advice on how to apply to a PhD degree, check out our Application Process Guide.
Browse PhDs Now
Join thousands of students.
Join thousands of other students and stay up to date with the latest PhD programmes, funding opportunities and advice.
PhD in History
You are here: american university college of arts & sciences history phd in history.

- Request Info
Are you interested in…
Explore more.
Are you interested in...
Contact: Gautham Rao Graduate Director
Battelle-Tompkins Memorial Building on a map
Back to top
Study History Where It Is Made
AU’s PhD in History will prepare you for a career as an educator, researcher, analyst, and writer working in academia, public and institutional history, and other fields requiring investigative and analytical skills. In this program, you will develop a deeper understanding of how historians investigate and interpret the past while you explore the past with your own original research .
You will receive a high level of mentorship and develop close working relationships with your professors. Under the guidance of our award-winning faculty , our students complete strong dissertations and present work at top conferences while making valuable connections and gaining experience in the Washington, DC, area.
This program is ideal for students interested in American and modern European history, including Russian history. Our department also has strengths in a variety of subfields , including public history, African American history, women’s/gender history, politics and foreign relations, and Jewish history. This diversity will open your options for research and allow for specialization without sacrificing breadth of study.
Rigorous Study with a Degree of Flexibility
Our program combines rigorous training in scholarship with the flexibility to pursue your intellectual interests. Our coursework will give you a solid foundation in historical theory and methodology, research methods, and United States or modern European history. Together with your academic advisor, you will design a program of study to match your academic goals . You will acquire and demonstrate mastery of tools of research , such as foreign languages, quantitative research methods, oral history, new media, and other methodologies. Your doctoral examinations will be tailored to fit your individual fields of study. You will then pursue your own research in writing your doctoral dissertation.
The Department will supervise PhD dissertations in the history of Modern Europe (normally for the period 1789 to the present), United States history (including the colonial period), US foreign relations, and modern Jewish history.
See all admissions and course requirements .
Cutting-Edge Faculty Dedicated to Your Success
Our history faculty makes national news, uncovers under-represented areas of history, and guides doctoral students , helping them generate innovative and influential research . From predicting presidential elections to publishing award-winning books and articles, our distinguished professors produce relevant historical scholarship and will train you do the same. With academic and professional mentorship from our faculty, you will you will enter the field as a thoroughly prepared and well-connected scholar.
Endless Opportunities in a Historic City
Pursuing your doctorate in the nation’s capital provides you with unparalleled access to renowned museums, archives, institutions, and resources . From the Library of Congress, Smithsonian Institution and National Archives to the DC Historical Society, our students are only a metro ride away from exceptional local and national repositories. As part of the Washington Consortium , students at American University are able to take courses at colleges and universities throughout the DC metropolitan area, providing the opportunity to work with a variety of faculty in diverse programs and fields of study.
A truly global city, DC, contains hundreds of embassies, cultural organizations, and enclave communities. Brimming with history , the DC area offers Civil War battlefields, the Capitol, Mount Vernon, the White House, and countless landmarks of the colonial period, Revolutionary War, Civil War, and more recent American history. The city is also home to smaller historical organizations like the DC Historical Society and the DC Preservation League. Whether your interest is global, national, or local, this historic city undoubtedly has something for you.
Explore the Possibilities
Our students go on to become university and college faculty and administrators or work in federal and state governments, for museums and archives, and in other exciting fields. Our alumni teach at universities around the world , from the University of Houston in Texas to University of Prince Edward Island in Canada and Ludwig Maximilians Universität in Munich. Our PhDs hold positions with the nation’s most important institutions , including the Library of Congress, Department of State, National Archives and Records Administration, American Historical Association, National Endowment for the Humanities, US Holocaust Memorial Museum, and the National Museum of African American History and Culture.
Recent and Current PhD Dissertation topics
- Auketayeva, Laura : "Gender and Jewish Evacuees in the Soviet Union during the Holocaust"
- Barry, Michael : "Islamophobic & Anti-Islamophobic Ideas in America"
- Brenner, Rebecca : "When Mail Arrived on Sundays, 1810-1912"
- Boose, Donelle : "Black Power and the Organizing Tradition: Work-ing Women of Washington, DC. 1965-1990"
- Chatfield, Andrew : "American Support for India’s Self-Determination from 1915-1920: Progressives, Radicals, and Anti-Imperialists"
- Duval, Lauren : "Landscapes of Allegiance: Space, Gender, and Mili-tary Occupation in the American Revolution"
- Englekirk, Ryan : "The Third Team: Unmasking Fraternity and Mascu-linity Among Major League Baseball Umpires 1970-2010"
- Estess, Jonah : "The People’s Money: The American Revolution, Cur-rency, and the Making of Political Economic Culture in American Life, 1775-1896"
- Frome, Gavin : "American Protestant Service Workers in Viet Nam, 1954-1975"
- Gabor, Ruth : "'Moda' for the Masses: Moscow Fashion’s Appeal at Home and Abroad during the Cold War"
- Gibson, Laura : "It’s Love that Counts: The History of Non-Nuclear Families in American Domestic Sitcoms"
- Grant, Jordan : "Catchers and Kidnappers: Slave Hunting in Early America"
- Grek, Ivan : "Illiberal Civil Society in Russia, 1992-2000"
- Harris, Curtis : "Hardwood Revolution: The NBA's Growth & Player Revolt, 1950-1976"
- Hawks, Julie : "Capital Investments: Engineering American Cold War Culture"
- Jobe, Mary "Allison" : "'We Remember Him for His Character': The Life of James W. Ford and the Communist Party USA"
- Kaplan, Anna : "Left by the Wayside: Memories and Postmemories of the Integration of the University of Mississippi"
- Killian, Linda : "Benjamin Franklin and Thomas Paine: The Shared Political Ideology at the Heart of American Democracy"
- Kitterman, Katherine : "'No Ordinary Feelings': Mormon Women’s Political Activism, 1870-1896"
- Langford, Amy : "Creating a Body Politic: Boundary Crossings and the (Re) Making of Latter-Day Saints on the U.S. Border, 1885-1920"
- Levin, Jeffrey : "Felix Warburg and the Establishment of the Hebrew University"
- MacNeill, Lindsay : "Policing Politics in Austria, 1918-1955"
- Milwicki, Alon : "Baptizing Nazism: An Analysis of the Religious Roots of American Neo-Nazism"
- Rafferty-Osaki, Terumi : "'Strictly Masculine': Reforming and Per-forming Manhood at Tule Lake, 1942-1946"
- Recordati, Maurizio : "Russia Turns Inward: Russian Grand Strategy in the Post-Crimean War Period (1856-78)"
- Sowry, Nathan : "Museums, Native American Representation, & the Public: The Role of Museum Anthropology in Public History, 1873-1929"
- Styrna, Pawel : "Polish-Russian Relations, 1904-1921"
- Vehstedt, Scott : "'Lets Help Finland': The Return of American Relief Aid in the Winter War, 1939-1940"
- Weixelbaum, Jason : "At the Crossroads of Fascism: The Decision of Ford, General Motors, and IBM to do Business with Nazi Germany"
Alumni Job Placements
Graduates of the history PhD program are working as professors, researchers, and directors across the US and at international locations. Here is a list of where select graduates have or are currently working:
- Director, National Coalition for History
- Assistant Professor, University of Prince Edward Island
- Assistant Professor, Towson University
- Assistant Professor of History and Director of American Studies, West Chester University
- Independent historian
- Senior Archivist, National Archives
- Associate Professor, Ryerson University
- Assistant Professor, University of Arkansas at Little Rock
- Historian, US Army
- Senior policy adviser and special assistant to the president of the Humane Society
- Historian, Office of the Historian, Department of State
- Museum Director, Renton History Museum, Oregon
- Public History Coordinator, American Historical Association
- Assistant Professor, Bridgewater State University
- Lecturer in Sociology, California State University at Bakersfield
- Assistant Professor, Delaware State University
- Historian, Global Classroom, US Holocaust Museum
- Director, Digital Archive, Woodrow Wilson Presidential Library
- Assistant Professor, Illinois State University
- Adjunct Professor, University of Maryland at College Park
- Senior Fellow, Carnegie Endowment for International Peace
- Assistant Professor, University of West Florida
- Independent historian and filmmaker
- Adjunct Assistant Professor of History, US Naval Academy
- Administrative Support Specialist at FEMA
- Senior editor and writer, National Endowment for the Humanities
- Instructor, Religion Dept., National Cathedral School (earned Master of Divinity after PhD)
- Curriculum and Publications Coordinator, AU Registrar's Office
- Assistant Professor, Seminole State College
News & Notes
PhD candidate Reza Akbari presented at the Middle East Studies Association's annual conference in Montreal, Canada. His presentation, Etched in Mistrust: Continuity and Change in US-Iran Nuclear Negotiations (1969-1978), argued that America's drive to keep Iran's nuclear program peaceful began decades before the establishment of the Islamic Republic.
PhD candidate Andrew Sperling published " A Halloween Party in Boston Turned Ugly when a Gang Hurled Antisemetic Slurs and Attacked Jewish Teenagers ," detailing the events of an antisemetic attack on Jewish teens at a Halloween party in 1950.
Theresa Runstedtler 's new book on Black ballplayers of the 1970s and '80s setting the NBA up for success: Black Ball: Kareem Abdul-Jabbar, Spencer Haywoof, and the Generation that Saved the Soul of the NBA (2023) .
Doctoral student Maurizio Recordati Koen won first prize in the 2022 Trench Gascoigne Essay Competition for "The Stuff of Strategy: How Sublime Strategics Turned into a Real Thing" in RUSI Journal.
John Schmitz (CAS/PhD '07) published Enemies among Us: The Relocation, Internment, and Repatriation of German, Italian, and Japanese Americans during the Second World War .
Doctoral student Jonah Estess presented his paper, "Mo’ Money, Mo’ Problems: The American Revolution and the National Origins of the Politicization of Money" as part of the panel at this year's Business History Conference.
Andrew Demshuk published Three Cities after Hitler: Redemptive Reconstruction across Cold War Borders .
PhD candidate Katherine Kitterman wrote on women's voting rights in Utah for the Washington Post.

Inaugural Postdoctoral Fellow
Nguyet Nguyen brings new perspective to the Vietnam War.
Discover CAS: The Humanities
Explore our community.
Video Take a Video Tour .
Please send me information about PhD in History
It looks like you already used that name and address to request information for one or more AU graduate program(s).
If you have not previously requested AU graduate program information, create a new request
Department of History
PhD in History (by distance learning)
Join our rich and thriving academic community and deliver research on key research areas in history, with the flexibility to study online.
Year of entry: 2024/25
| Length | Start dates ( ) | |
|---|---|---|
| PhD by distance learning | 3-4 years full-time
| January |
If your passion lies in research, our doctoral degrees give you the independence to focus on a specialism of your choice. You'll have the flexibility to work from anywhere in the world. Study with us and receive expert research guidance from our supportive staff.
Your research
You'll focus on an independent research project on a topic of your choice. Your research will culminate in a dissertation of up to 90,000 words.
Join one of our leading research groups, which bring together historical expertise in various fields. Find out more about our research groups .
Related links
- Research degree funding
- Accommodation
- International students
- Life at York
- How to apply
3rd in the UK for research impact
and 11th overall in the Times Higher Education ranking of the Research Excellence Framework (REF) 2021.
Committed to equality
We are proud to hold an Athena Swan Bronze award in recognition of the work we do to support gender equality in history.
Access to exclusive resources
Our Borthwick Institute for Archives houses one of the most extensive collections of archives in the UK. York Minster Library is the largest cathedral library in the UK and holds material spanning 1000 years of history. We also have strong partnerships and consultancies with museums, archives, heritage sites, the media, artists and community organisations.
.jpg)
Explore funding for postgraduate researchers in the Department of History.

Supervision
We'll help match your research interests to our supervisory expertise. Explore the expertise of our staff.
Training and support
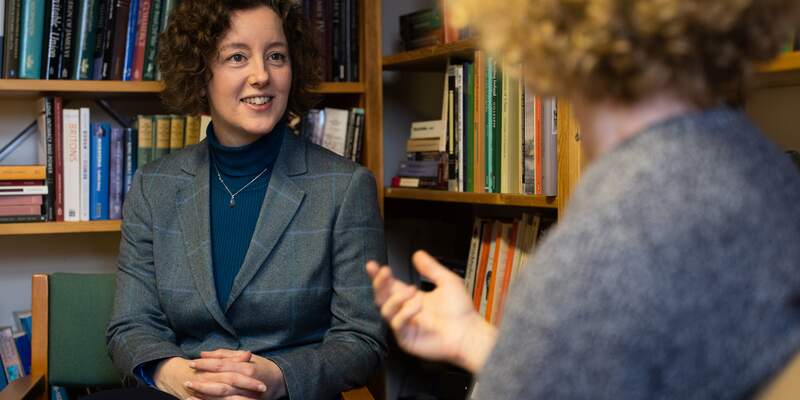
Your progress throughout your degree will be continually guided by your supervisor , who will help you to hone your focus and deliver specialised research. Alongside regular online meetings with your supervisor, you'll attend a Thesis Advisory Panel (TAP), consisting of at least one member of staff in addition to your supervisor. You'll meet twice a year (yearly for part-time students) to discuss your research project, including more general professional development and career training.

Course location
This course is run by the Department of History.
You can study this course from around the world. You must attend a five-day induction programme in York at the beginning of your first year. You'll also visit York in your second and third years (every other year for part-time students).
Entry requirements
You should have, or be about to complete, an MA degree in History or an equivalent subject with a distinction or very high merit.
English language requirements
If English is not your first language you must provide evidence of your ability.
Check your English language requirements
Apply for this course
Take a look at the supporting documents you may need for your application.
Find out more about how to apply .
Identify a supervisor
As part of any application for a research degree you will need to name one or more academic staff who could supervise your research. You should approach them informally to discuss your proposed project before you apply.
Find a supervisor
As part of your application, you'll be interviewed by one or two academic staff members, including your prospective supervisor. The interview will last around 30 minutes to an hour, with plenty of time for you to ask questions and find out what York can offer you. Your interview can be in-person or online.
Careers and skills
Your PhD will help to extend your qualifications, giving you the ability to use research and historical thinking to shed light on historical problems and communicate this knowledge with others. You will become equipped with transferable skills in communication, data analysis, archival research and collaboration, opening the door to a wide range of career opportunities.
Our dedicated careers team offer specific support including a programme of professional researcher development and careers workshops and 1:1 career support sessions. They will help you to build up your employability portfolio and to engage in activities that will build up your skills and experience within and outside of your research work.
Career opportunities
- archives practitioner
- heritage manager
- academic researcher
- museum professional
- historic buildings conservation officer
- lecturer or teacher

Discover York

Distance learning at York
Learn more about the York approach to distance and online learning.

Support and resources
Explore the support and resources we offer for distance and online learners.

Discover more about why York is the perfect choice for your research degree.
Meet us online or on campus
Find out all you need to know about applying to York
Scholarships
Find scholarships to support your studies

- Schools & departments

PhD by Distance
The PhD by Distance programme allows students who are unable to commit to basing themselves in Edinburgh to study for a PhD in a field of History, Classics or Archaeology from their home country or city.

What's involved?
The PhD by Distance mode is available to all applicants for eligible HCA PhD programmes, who will apply via the Postgraduate Degree Finder . Applicants will select between on-campus and distance options, as well as between part-time and full-time options.
PhD by Distance students will receive the same level of support and supervision as on-campus students. The frequency with which students will meet with their supervisors, and method of communication for supervision sessions, will be provisionally agreed at the point of application and confirmed during induction.
Please be aware that some funding bodies do not permit students to study by distance, for example both ESRC and AHRC regulations currently state that students must be residents at the Institution where they are studying.
Entry requirements
The entry requirements for the PhD by Distance are the same as for the School’s on-campus PhD programmes.
In addition, applicants to the PhD by Distance will also be required to complete a PhD by Distance Applicant Admission Form. This form must be emailed to the Postgraduate Research Office ( [email protected] ) who will upload this to your application on your behalf.
Applicants should provide information about previous experience of distance study together with a statement detailing the potential risks and characteristics of distance learning. It is important that student’s applying for this mode of study recognise its particular challenges. While experience of studying at a distance is desirable in applying for the programme, this is not a specific requirement for admission. All of this should be discussed with the potential supervisor(s) prior to application and can be reflected on further during the admissions interview.
Applicants should also use this additional application form to provide details of the access they will have to research facilities at the normal site of study and where the core datasets that they will rely on are located.
Working whilst studying
The School understands that many students will take on paid work alongside their studies. The University’s guidance for full-time PhD students is that they should work no more than an average of 9 hours per week for across the academic year, to ensure they have time for their studies. While there are no specific rules about how many hours part-time students can work, the School recommends that part-time students allocate at least two to three days a week, on average across the year, to their PhD research. You should discuss any working patterns that you have with your proposed supervisor and reflect on the time you are devoting to your studies throughout your programme, particularly if you are struggling to make sufficient progress; this might well be a topic for discussion at annual reviews. Please note that if you need to apply for an extension at the end of your programme, you cannot use the fact that you had a job alongside your studies as a justification for this – an extension request can only be based on unforeseen circumstances. If you need to take on more work for a temporary period of time and this will impact on your studies, you should consider an Authorised Interruption of Studies.
This article was published on 2024-08-01
Share this page
You will work with a stellar faculty in the Department of History and neighboring departments as you acquire advanced skills in historical research, analysis, and writing, as well as teaching.
Nine research centers affiliated with the history program offer further programs in area studies, including The Fairbank Center for Chinese Studies, The David Rockefeller Center for Latin American Studies, and The Davis Center for Russian and Eurasian Studies. You also have access to the largest university library system in the world, consisting of 80 libraries and 17 million volumes.
Examples of dissertations students have worked on include “Cold War Capitalism: The Political Economy of American Military Spending from 1949 to 1989” and “Imperial Schemes: Empire and the Rise of the British Business-State, 1914–1939.”
Graduates of the program have gone on to teach at Yale University, Princeton University, NYU, and the University of Maryland. Others have gone on to positions outside academia as startup founders, lawyers, policy analysts, and museum curators.
Additional information on the graduate program is available from the Department of History , and requirements for the degree are detailed in Policies .
Areas of Study
African History | Ancient History | Byzantine History | Early Modern European History | East Asian History | Environmental History | International and Global History | Latin American History | Medieval History | Middle Eastern History | Modern European History | Russian and Eastern European History | South Asian History | United States History
Admissions Requirements
Please review the admissions requirements and other information before applying. You can find degree program-specific admissions requirements below and access additional guidance on applying from the Department of History .
Writing Sample
A writing sample is required. While there is not a specific length requirement, most writing samples are around 20 to 25 pages. If you are submitting a sample that is part of a larger work (a chapter from a thesis, for instance) you may include a brief abstract situating the piece in the larger work.
Statement of Purpose
Your statement of purpose should include why you want to study history in graduate school, why you want to study at Harvard, and indicate your research interests and potential advisors. The required writing sample should be of remarkable quality and ask historical questions. Reading ability in any languages necessary for the proposed course of study is helpful. Most statements of purpose are around 3 to 5 pages.
Personal Statement
Standardized tests.
GRE General: Optional GRE Subject: Optional
In coordination with Harvard Law School, students may pursue both a PhD in history and a JD at Harvard Law School. To learn more about this course of study, consult the Coordinated JD/PhD program overview.
Theses and Dissertations
Theses & Dissertations for History
See list of History faculty
APPLICATION DEADLINE
Questions about the program.
- Utility Menu
Graduate Program
Graduate program overview .
The goal of the doctoral program is to train students to become both skilled scholars and conscientious teachers. Throughout the program students work with advisors and other faculty members as they engage in coursework , prepare for and take the general exam , work as teaching fellows , and research and write the dissertation . On average it takes seven years to receive the doctoral degree*. Most graduates have pursued academic careers at universities and colleges in the United States and abroad, while others have gone on to successful careers in law and in government.
As a large research university, Harvard offers many resources and opportunities for its students in the form of lectures , conferences , research centers , fellowships, and grants . Students have access to the more than 80 libraries and 15 million volumes that comprise the Harvard University Library, the largest university library in the world.
Additionally, students may take courses offered by other departments in the Faculty of Arts & Sciences, or at other Harvard schools , such as Harvard Divinity School , Harvard Law School , Harvard Graduate School of Education , and Harvard Kennedy School .
In coordination with Harvard Law School, students may pursue both a PhD in history and a JD at the Law School . To learn more about this course of study consult the Coordinated JD/PhD program overview.
* The History Department does not offer a terminal master's program.
- Undergraduate Program
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Program Rules & Requirements
- Financial Aid & Fellowships
- Graduate Program Workshops
- Library Privileges
Graduate Student Resources
Academic Calendar (GSAS)
Recent PhDs
Graduate Program Contacts:
Director of Graduate Studies

Jesse Hoffnung-Garskof
Graduate coordinator.

Dan Bertwell
Department of History
Ph.d. programs.
The Department of History’s doctoral degree program seeks to train talented historians for careers in scholarship, teaching, and beyond the academy. The department typically accepts 22 Ph.D. students per year. Additional students are enrolled through various combined programs and through HSHM. All admitted Ph.D. students receive a full financial aid package from the Graduate School of Arts and Sciences.
History of Science and Medicine
The Program in the History of Science and Medicine (HSHM) is a semi-autonomous graduate track within the Department of History. HSHM students receive degrees in History, with a concentration in the History of Science and Medicine. There is a separate admissions process for students interested in the History of Science and Medicine. For more information, please see the HSHM website .
Combined Doctoral Programs
Joint ph.d. programs.
2024 Best Universities That Offer PhD Without Masters
It may sound like a dream, but universities that offer PhD without a masters do exist.

Imagine fast-tracking your way to becoming a doctor in your field, skipping the traditional master’s step, and diving straight into deep, meaningful research. This article is your guide to understanding this unconventional yet rewarding path.
Editorial Listing ShortCode:
We’ll explore the ins and outs of taking this leap to help you decide if this bold academic journey aligns with your aspirations and goals.
Universities That Offer PhD without a Masters Degree

Can you get a doctorate without a masters? For some, the answer is yes. In PhD programs without masters requirements, you can start working on your PhD right after earning your bachelor’s degree. This means you can focus on intensive research and specialized studies sooner.
It’s a path that may suit you if you’re keen on deepening your knowledge and expertise without the intermediate step of a master’s program. Typical eligibility criteria for these programs include:
- Strong undergraduate academic record
- Research experience
- Recommendation letters
- Well-crafted statement of purpose
- Standardized test scores (if required)
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) , higher education often leads to better job prospects and higher earnings. This route not only saves time but can potentially set you up for promising career opportunities.
You’ll be expected to start your research early. This could be a great fit if you’re already clear about your academic interests and ready to commit to a rigorous research schedule.
Advantages of Fast-Tracking to PhD
Deciding to go straight for a PhD without a master’s degree can be a big step toward your future goals. Here are some potential benefits for considering PhD online programs without masters requirements:
- Speed up your journey : By skipping a master’s program, you may get to your career goals faster.
- Save money : Like any college program, earning a master’s degree can be expensive.
- Immediately deep dive into your interests : Passionate about your field? You may jump straight into advanced studies and research.
- Unique opportunities : These programs can help open doors to rare and exciting research chances, placing you at the forefront of innovation early in your career.
- Stand out : Earning a PhD is a powerful statement about your ambition and skills.
Stepping directly into a PhD program may allow you to fast-track your ambitions and pave the way to a fulfilling future.
Disadvantages and Challenges of Direct PhD Programs

Jumping into a PhD without a master’s degree takes courage. It’s crucial to know the hurdles that might pop up before you start researching PhD programs online without masters requirements.
These are some challenges you may encounter:
- Rapid pace : You’ll likely face a steep learning curve without the preparation a master’s program can provide.
- Immediate research pressure : You’re expected to start producing original research right away.
- Fewer networking opportunities : Skipping a master’s program means missing out on making those crucial academic connections that may be valuable down the line.
- Tougher funding : Funding opportunities often lean toward those with master’s degrees, so securing financial support might be more challenging.
- Self-doubt : Without the stepping stone of a master’s, you might question if you’re ready for this big leap.
According to the NSCRC , with more people pursuing advanced degrees, the academic world is getting more competitive. Navigating these challenges requires resilience and a clear vision of your goals. Choosing a direct PhD route is about weighing these hurdles against your determination and passion for your field.
How to Choose a Doctorate without a Masters Degree

Choosing the right PhD program is key. Here are some important factors to consider:
- Accreditation : Accreditation is like a quality stamp for the program, ensuring that it meets certain academic standards. You can find more information at the S. Department of Education – Accreditation .
- Financial aid and scholarships : Cost can be a big factor, and having financial aid or scholarships can make a huge difference. You can visit the FAFSA website for more information.
- Faculty expertise : You want to learn from the best and ensure they have experience in your area of interest.
- Research opportunities : This is your chance to get hands-on experience in your field.
- Program structure and flexibility : It’s important to consider class schedules, online vs. in-person options, and the balance between coursework and research.
Choosing the right doctorate program is a personal decision that will shape your academic journey. Taking the time to weigh these factors carefully can help you find the best choice to fit your goals and needs.
Applying to Universities That Offer PhD without a Master’s Degree

Applying for a PhD program is like presenting your academic story. Here are some tips to help make each part of your application a testament to your passion and potential:
- Your research proposal : This is a window into your interests. Show your enthusiasm and readiness for the field by making it clear, engaging, and indicative of your ability to bring fresh ideas.
- Letters of recommendation : These are your personal champions, so choose mentors or professors who know your strengths intimately and can confidently vouch for your PhD readiness.
- Showcase your research journey : Research experience is a crucial part of your narrative. Highlight your involvement in projects, papers, or presentations.
- Ace the interview : Be prepared to discuss your motivations, research interests, and how you envision your growth in the program.
Your application is a holistic reflection of your academic identity. It should showcase your achievements and excitement for research and knowledge.
Do You Need a Masters to Get a PhD?

While many paths to a PhD traditionally start with a master’s, there’s a growing trend of programs allowing students to jump straight into doctoral studies from their bachelor’s programs.
This option may be perfect for those who are clear about their research interests and ready to dive into academic exploration. If you’re passionate, determined, and have a clear vision for your research, a direct route to a PhD may be your path forward.
Universities Offering Online PhD Without Masters Degree Programs
Methodology: The following school list is in alphabetical order. To be included, a college or university must be regionally accredited and offer degree programs online or in a hybrid format.

Capitol Technology University offers a PhD in Technology with two pathways for students who may not hold a master’s degree. Applicants may either already hold a doctoral degree or earn an MS in Research Methods while earning their PhD. CapTech’s program is fully online, and residencies are not required.
Capitol Technology University is accredited by the Middle States Commission on Higher Education.

Clemson University offers a PhD in Healthcare Genetics and Genomics. Applicants must hold at least a bachelor’s degree in a related field with a 3.0 cumulative GPA. Applicants who hold a master’s in the field may be given preference. The program is fully online, and courses are in a synchronous format.
Clemson University is accredited by the Southern Association of Colleges and Schools Commission on Colleges.

Indiana University offers a PhD in Music Therapy through the Purdue School of Engineering and Technology at IUPUI. Students who do not already hold a master’s degree can earn a Master’s in Music Therapy through the program. The program requires the completion of 90 credit hours, including a dissertation, and is fully online.
Indiana University is accredited by the Higher Learning Commission.

Students who do not hold a master’s degree may apply for a PhD in Computer Science through Mississippi State University. The program is fully online and does not require campus visits. Courses follow a semester schedule, and there are start dates in the fall and spring. Applicants are not required to submit GRE or GMAT scores.
Mississippi State University is accredited by the Southern Association of Colleges and Schools Commission on Colleges.

Students who do not hold a master’s may earn a PhD in Computer Science through Nova Southeastern University’s bachelor’s track. The program requires the completion of 66 credits and is available fully online or on campus. The program has start dates in August, January, and May and follows a semester schedule. NSU is an NSA-designated school.
Nova Southeastern University is accredited by the Southern Association of Colleges and Schools Commission on Colleges.

Saybrook University offers a PhD in Clinical Psychology program that is fully online. Students who do not hold a master’s degree must complete 103 to 109 credits to graduate, while those who do have a master’s in a related field must complete 100 to 106 credits.
The program can typically be completed in 5 years. It offers several specializations that may be declared, including Applied Psychophysiology, Creativity Studies, and Jungian Studies.
Saybrook University is accredited by the Senior Commission of Western Association of Schools and Colleges.

The University of Arizona offers a PhD in Nursing to students who hold a BSN through its BSN-to-PhD program. The program is mostly online, but short residencies are required. The program can potentially be finished in 4 years when attended full-time. Courses follow a semester schedule, and the completion of 79 credits is required to graduate.
The University of Arizona is accredited by the WASC Senior College and University Commission.

The University of Central Florida offers a BSN-to-PhD in Nursing program for those who do not hold a master’s degree in nursing. All coursework is online, but short intensives on campus are required throughout the program. Applicants are not required to submit GRE scores.
The University of Central Florida is accredited by the Southern Association of Colleges and Schools.

The University of Oklahoma offers a PhD in Nursing with a fast-track to PhD option for students who have a BSN but not a master’s degree. All coursework is fully online. The program can potentially be finished in 36 months, and there are start dates in the fall, spring, and summer. The completion of 78 credits is required to graduate.
The University of Oklahoma is accredited by the Higher Learning Commission.

The University of Wisconsin–Milwaukee offers a fully online program for a PhD in Nursing. Students with only a BSN may apply but must complete 15 additional credits before entering the program. The program starts every other year during the summer semester. It can potentially be completed in 3 years.
UWM is accredited by the Higher Learning Commission.
Advance Your Career: Starting Your PhD without a Masters Degree

Starting your PhD journey without a master’s degree can be a bold step forward in advancing your career, particularly if you pursue some of the highest paying doctorate degrees . It’s a path that speaks to those ready to dive into deep academic waters, driven by passion and a clear vision for their future, with the added potential of high financial rewards in cutting-edge and high-demand areas.
If this resonates with you, you can start exploring accredited universities that offer this opportunity, including those providing online PhD programs for working professionals . These flexible programs are designed to accommodate your busy schedule, allowing you to balance your professional responsibilities with your academic pursuits. Your aspirations and determination may fast-track you on your way to becoming an expert in your field!


- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to secondary sidebar
- Skip to footer
career-advice.jobs.ac.uk
A PhD Without A Masters Degree

The PhD usually came after the Bachelor’s degree for many years in the United Kingdom. There was no real need to successfully gain a Master’s degree before embarking on this mammoth task of empirical research. Whilst some undergraduate degrees still lead to a Master’s qualification, and many people still complete Master degrees, it is possible to do a PhD without a Masters degree .
Firstly, your creative ideas are novel which allows for innovative, fresh approaches, in addition to exerted interest and enthusiasm for an area of study. Secondly, a Master’s degree can be quite expensive and although there are bursaries and schemes available they often still require costly personal financial contributions. Thirdly, pursuing a PhD without a Master’s degree reduces the amount of time on your studies, allowing you to follow a desired career path that motivates and excites you.
Disadvantages
The Master’s degree exists to show that the student can study at a higher level and this qualification allows you to practice the necessary research skills. This also determines if committing to a large research project is right for you. Additionally, the Master’s dissertation forms a part of the PhD in several British universities, so you are potentially gaining one to two extra years to make your original contribution to the field of study.
Applications
As with any PhD application , it is important to check your eligibility with the universities you have chosen to apply to. Different institutions have varying regulations, and in some cases, a Master’s degree might be compulsory. Also, make sure you have lots of evidence in your application about why you would make a good doctoral student by presenting concrete examples of your work at the equivalent of Master’s degree level. Additionally, be clear that you are motivated and determined to add to a body of knowledge through innovative, empirical research that requires stamina, hard work, determination and collaboration.
Coping strategies
The first few months can be overwhelming, but it is important to remember that you have been accepted as a doctoral student. This confirms that a panel of experts believe that you can achieve such a prestigious degree.
In your first term try and reread your research proposal once a week and review it critically. The nature of research is that it changes but it is also useful to remember what you proposed to do. Critical thinking is essential throughout the process.
Avail of the PhD support within the university. Regularly meet with supervisors and other doctoral researchers as support is necessary during this journey, especially in year one. Sign up to university workshops about PhD research – many run one-day skills sessions covering everything from communication to project managing. As a PhD student, you are part of a community of other doctoral researchers and this can be a great source of advice and wisdom, plus a great way of meeting new people.
In your first term, you should have regular and consistent supervision meetings. This allows your research team to set clear time goals and confirm milestones which you can work towards.
And remember, with consistent hard work, dedication, determination, collaboration and a critical mind, you will achieve your PhD .
Find your PhD here .
What is a PhD and Why Should YOU do one?
What did you think of our article? - please rate
Share this article
Dr Denise White FRSA
Dr Denise White FRSA is a multi-award-winning intellectual disability and music expert. Having over 25 years’ experience in the field of early years, primary, post-primary, special educational needs, further and higher education, Denise is known for her innovative and creative teaching methods that transforms lives. She is an advocate for inclusive and community-based ethical learning and teaching models.
She is a passionate education advocate with the talent to develop inspiring hands-on lessons that will capture a student’s imagination and breed success.
Known as ‘The Music Doctor’, Denise is an Author at Bookhub Publishing. Her Music Doctor Series will launch in March 2019. Denise is also a Speaker, Trainer, Consultant, Mentor and Researcher.
Web: www.themusicdoctor.co.uk
Twitter: @_TheMusicDoctor
Reader Interactions
You may also like:.
21st April 2020 at 11:04 am
To whom it concerns. During this enforced Covid Lockdown I explored the possibility of undertaking a Master’s in English Literature by distance learning. My Thesis has explored the topic of “Discrimination of Women in the Literature because of their gender”. As yet I am not affiliated with a University as my exploration is in earl. y stages. I have a Primary Honour’s Degree from my local University in Galway, Ireland. My query is can I bypass the Master’s and undertake a P.H.D in English Literature? I am familiar with the steps necessary to undertake the proposed course of study.
19th December 2020 at 6:03 pm
Good evening. Hope you are doing well inshaAllah. My wife wants to apply for a PHD program nearby london area. Do you have any suggestions on where to apply? She will need to apply for a student visa first in order to enrol into a graduate school. How can she apply for a student visa ? What type of governmental funding is available to her wife? My wife is a USA citizen and she already has her undergraduate degree from New York university. Plz advise me which university will be the best for my wife to enrol into a PhD program.
3rd March 2021 at 5:57 pm
I want to register fie for PHD, i only have law degree, i have no Masters degree
15th January 2022 at 3:30 pm
I want to apply for PhD. I have already have and degree and postgraduate diploma. Please advise
15th January 2022 at 3:32 pm
I have already a degree and a post graduate diploma
11th April 2022 at 10:13 am
Please advice to me where to start. I have degree in Public Administration and Political since graduated 2012 on South East European University in Skopje, in 2012 I make NARIC UK Recognized my foreign degree in UK comparable. In 2018 I have applied on South East European University Master in Business Administration and Management – Sub field Management. And I have finished all my exams on master degree but started this Pandemic Period with covid19 and I have no chance to make defend my master decertation in public defend. I am here in UK more then 10 years I am passion to study. I have EU Settled Status. I was in search for Integrated PhD ( Master and PhD ) in one. Because I have transcript but I don’t hold certificate in Master degree make me break this process. Please advice to me how to continue.
4th February 2023 at 6:47 pm
I am interested in completing a PhD, but only have a Social Science BA 2:1. Is this possible?
14th November 2023 at 2:38 pm
Firstly, you will have to improve your spelling and grammar before you apply for a PhD degree (even more so since you are a lawyer)!!!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Please enter an answer in digits: eighteen − fourteen =
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .

- Chancellor’s Message
Print Options
2024-25 edition, history, ph.d..
The Doctoral Program in History is designed to provide students with advanced historical research skills and a solid grounding in the theory and methodology of history. This combination reflects the Department’s conviction that scholars should approach significant questions about the past with rigor and sophistication. The Department requires that students develop critical abilities in dealing with primary sources, secondary syntheses, and the interrelationship of history and theory. Candidates for the Ph.D. in History are expected to gain teaching experience as an integral part of their graduate training. This is accomplished through work as a teaching assistant.
Doctoral students take a minimum of 15 formal courses to be completed during the first two years of the program. Ten courses must be taken within the History Department.
History and Theory
Required coursework for doctoral students includes two courses in History and Theory. These courses explore a variety of theoretical issues and methodological concerns that have sparked debate in the humanities and social sciences in the past decades and which remain pertinent to 21st century historical writing. Topics may include the relationship between materialist approaches and cultural analysis; subjectivity and governance; gender and sexuality; ethnicity and racial formation; the politics of religion; "the archive" and archival practice; nationalism and postcolonialism; world history and transnational studies.
History Methods
Required coursework for doctoral students includes one course in History Methods. This course introduces graduate students to some of the most foundational ideas and debates that have shaped historiographical practice over the past half century. This course explores fundamental questions about how historians imagine the past as they try to write about it, how they constitute it as a domain of study, and how (and why) they argue about it.
Field Emphases
Doctoral students are required to take a total of five courses satisfying requirements for specialization in two historical fields, in either area studies or thematic fields. Students take three courses in the first field and two courses in the second field. The Department offers area studies fields in Asian History, European History, Latin American History, Middle East and African History, U.S. History, and World History. Thematic fields vary depending on demand. Students may take courses satisfying field requirements in any order.
Research Seminars
Doctoral students are required to take a two-quarter course sequence in research and writing both their first and second year in the graduate program. In the first year, students take a proseminar on historical methodology ( HISTORY 202A ) followed by a second quarter ( HISTORY 202B ) in which they write a research paper that engages the methodologies and questions explored in the previous quarter. Students who enter the doctoral program with a master's may petition to be exempt from the first-year research sequence, pending acceptance of the M.A. thesis as an equivalent to the final research paper of the sequence.
In the second year of study, Ph.D. students take a two-course sequence ( HISTORY 204A and HISTORY 204B ) in which they research and write a paper on a topic of their choice. The second year research paper is required of all doctoral students.
Professional Development Colloquium
Doctoral students are required to take a three quarter long colloquium (HISTORY 210A-HISTORY 210B-HISTORY 210C) on professional development during their first year in the graduate program. The Professional Development Colloquium introduces graduate students in history to career diversity and life as a professional historian both within and outside academia. It addresses topics including finding support for successful and intellectually rewarding on time degree completion, preparing for different kinds of employment searches, and applying skills learned from academic training to a variety of professional settings.
Language Requirement
All students must demonstrate a proficiency in one language other than English prior to taking the Ph.D. candidacy qualifying exam. Competency in a language may be established either by passing a departmental examination (proctored in the department office) or through extensive language use in one of the research seminars. The language used to satisfy this requirement is subject to their advisors' approval.

Summary of Required Course of Study:
- History and Theory - one course
- History Methods – one course
- Research Seminars - four courses
- Professional Development Colloquium – three courses
- First Field - three courses
- Second Field - two courses
- Electives - three courses
- Foreign Language Proficiency
First-Year Review and M.A. Conferral
To continue in the doctoral program, students must satisfactorily pass a departmental evaluation at the end of their first year of study; this includes students who entered with a M.A. from another institution.
Doctoral students can be awarded an M.A. from UCI after fulfilling requirements for residence, one language, and successfully completing 36 units, including 28 units in required courses and one of the following: submitting an approved M.A. thesis, passing a one-hour exam in the primary field, or completing an additional 24 units of approved coursework.
The Candidacy Qualifying Exam and Dissertation Prospectus
In the third year of the doctoral program, students prepare for their candidacy qualifying exam and write the dissertation prospectus. Most third year students enroll in the intensive readings course ( HISTORY 298 ) or directed readings ( HISTORY 291 ) to work closely with faculty in preparing for exams and writing their prospectus.
The candidacy qualifying exam is an oral, two-hour meeting during which a student is examined in their first and second field by a committee of four faculty members, plus an additional faculty referee. Upon successful completion of the exam, the student is officially advance to doctoral candidacy (all but dissertation) and presents the dissertation prospectus in a colloquium including all members of the dissertation committee for formal approval. Both the exam and prospectus colloquium should be completed by the end of the third year.
Dissertation Research and Writing
The dissertation is the most important part of the Department's doctoral program. The dissertation is an original piece of historical scholarship, involving extensive primary research and original analysis of secondary source material. Students spend a year or more engaged in intensive research, and another year or more writing the dissertation. Throughout this period, students work closely with the advisor and the dissertation committee members. The finished dissertation must be approved by all members of the dissertation committee.
Most graduate students begin work as a teaching assistant for the Department or School courses during their second year and continue throughout their tenure in the program, except when dissertation research or writing require their residency away from the university. Students have the opportunity to apply to teach their own courses during summer session once they have advanced to doctoral candidacy. Students beyond their second year are required to also apply for teaching positions outside the department, e.g. in Composition or Humanities Core.
Time to Degree for the Ph.D .
Normative time to degree for the doctoral program is seven years. Maximum time to degree permitted is nine years.
Requirements for Admission to the Ph.D. Program
It is desirable that an applicant have the equivalent of an undergraduate major in History; however, the Department also considers students who have previously specialized in other subject areas and who have strong analytical and writing skills. Many students entering the program hold a Masters degree in History, or an associated field. The Department's required grade-point minimums and English Language Proficiency requirements for international student admission are consistent with university policy. A GRE score is not required for admission. Students are accepted for fall admission only.
Send Page to Printer
Print this page.
Download Page (PDF)
The PDF will include all information unique to this page.
2024-2025 Catalogue
A PDF of the entire 2024-2025 catalogue.
PhD in History
The PhD program in History offers a broad-based, humanistic education that equips you with the research, analytical, and communication skills critical for meaningful careers in the field of History.
The PhD program in History enables you to conduct research at the highest level and begin your career as an academic historian or prepare for a wide range of academic and professional careers. You’ll work alongside CGU faculty-scholars who specialize in U.S. and European history and draw on expert faculty from the highly ranked Claremont Colleges as well. With abundant opportunities to traverse disciplines and bring diverse ideas together, you will engage in first-rate historical scholarship. The result: an in-depth education in history with a breadth of expertise and an instructional environment unmatched by most larger universities.
Program Highlights
- The Libraries of the Claremont Colleges are among the largest collections in California, and the Huntington Library, one of the world’s finest research libraries for English and American history, is nearby.
- You can pursue a PhD in History in conjunction with another degree program at CGU. You receive a diploma for each degree and “double count” some units from one program to the other to decrease your required total units.
Program At-a-glance
required units
degree awarded
Spring, Fall
program start
4 years | full time*
estimated completion time
7 years | part time
Areas of Concentration
American studies.
The American Studies concentration takes a multidisciplinary approach to the study of United States culture, society, civilization, and identity through the curricular lenses of history, literature, critical theory, and more.
Early Modern Studies
The Early Modern Studies concentration undertakes interdisciplinary examination of history, culture, politics, and society within the transitional and transformative period that stretched between Medieval and modern societies, marked especially by the advent of print, Christian confessional war, and the rise of the modern state.
Hemispheric & Transnational Studies
A comparative analysis of culture in the Americas, the concentration in Hemispheric & Transnational Studies explores how scholarship on the Atlantic, borderlands, and diaspora have reshaped U.S. American Studies, Caribbean Studies, and Latin American Studies, emphasizing the topics of empire, race, religion, and revolution.
Media Studies
Situated at the bustling intersection of cultural studies, new media, critical theory, and popular culture, the burgeoning field of Media Studies examines the creative and critical practices of media consumers, producers, artists, and scholars, focusing on questions of representation, power, technology, politics, and economy.
Museum Studies
The Museum Studies concentration investigates the history and political role of museums in society, the interpretation and display of a wide variety of cultural productions, and topics of special concern to museums as cultural organizations, using a multidisciplinary, practice-based approach to understand the historical development of this evolving field.
Featured Students

Where You Can Find Our Alumni
Smith College
Fort Lewis College
CSU Channel Islands
Mount St. Mary's College
Claremont Colleges Libraries
U.S. Department of Commerce
Walla Walla University
The Drucker Institute
Azusa Pacific University

Matthew Bowman
Associate Professor of Religion and History Howard W. Hunter Chair of Mormon Studies
Research Interests
Mormonism, new religious movements, evangelicalism, religion and American politics

Joshua Goode
Professor of Cultural Studies and History Chair, Cultural Studies Department
Modern Spain, 19th- and 20th-century Europe, Genocide and racial thought, Museums and commemoration, Memory

Romeo Guzmán
Assistant Professor of History
Citizenship, Migration, Sport, Public history, Digital humanities

JoAnna Poblete
Professor of History John D. and Lillian Maguire Distinguished Professor in the Humanities Chair, History Department
Colonialism and empire, unincorporated territories, migration and labor, comparative ethnic studies, Asian-American and Pacific Islander studies, 20th-century United States, indigenous issues, environmental history, oral history, U.S. expansionism
Extended Faculty
Shane bjornlie.
Claremont McKenna College
Late Antique history, Roman history
Myriam Chancy
Scripps College
African diaspora with specialization in its literature
Alfred Flores
Harvey Mudd College
U.S. empire in Oceania with an emphasis on diaspora, labor, indigeneity, militarization, oral history and settler colonialism in Guåhan
Lily Geismer
20th century liberalism in the United States, Fair housing, Liberal religion and politics
George Gorse
Pomona College
Italian Renaissance art and architecture; Italian Baroque art and architecture; Medieval art history; history of cities, palaces, villas, and gardens; history of Genoa
Vivien Hamilton
Medical technologies, including x-rays, in the late 19th and early 20th centuries
Daniel Livesay
Early American and Atlantic history; Race, family, and slavery in North America and the Caribbean
Charles Lofgren
American Constitutionalism, American founding, Constitutional law, Military history, War and foreign relations
Char Miller
U.S. environmental policy, U.S. public-lands management, Western water politics, Immigration and border security, Urban politics and development, U.S. intellectual and cultural history
Harmony O’Rourke
Pitzer College
Cultural and social history of early modern and modern Africa, Global diasporas, Gender and sexuality, West Africa, Slavery, Colonialism, Oral history
Albert Park
Design & architecture, East Asian history & political economy, Korean history, Modern Japanese history
Ralph Rossum
American Constitutionalism, American Founding, Constitutional Law, Crime and Criminal Justice, Indian Gaming Issues, Redistricting, Supreme Court, Voting Rights
Victor Silvermam
U.S. History, Alcohol and Drug Studies, History of Sexual/Gender Minorities, The Cold War, Labor Unions, International Labor Movements, U.S. and Britain, San Francisco Bay Area History, California History, Sustainable Development Policy
- History 300 (4 units)
- One Transdisciplinary course (4 units)
- Ten History elective courses (40 units)
- Six elective courses (24 units)
Up to 24 units transfer credit from previous graduate work in History may be substituted for the elective coursework requirements.
Research Tools Requirement
- Two foreign languages ( or one foreign language and one research tool)
Research Papers
- Two substantive research papers
PhD Completion
- PhD qualifying exams
- Dissertation proposal
- Written dissertation and oral defense
Oral History Program
Inaugurated in 1962, the Claremont Graduate University Oral History Program has amassed an impressive collection of interviews with persons whose life experiences merited preservation and special projects, such as China Missionaries Oral History Project, funded by the Henry Luce Foundation. It is a premier resource for research into the history of The Claremont Colleges and California state government and politics.
Application Guidelines
| University Requirements | |
|---|---|
| Application Fee | |
| Official Transcripts | Applicants must submit a sealed, official transcript from every undergraduate and graduate institution that has granted the applicant a degree. Electronic transcripts sent to are also accepted. For undergraduate coursework, applicants are required to submit proof of a completed bachelor’s degree from a regionally accredited college or university. Unofficial copies of transcripts are accepted for review purposes, but official copies will be required upon admission. Applicants currently earning a degree that will be completed prior to attending CGU are required to submit a transcript showing work in progress for evaluation purposes. Once the degree has been granted, a final official transcript documenting the degree conferred must be submitted to CGU. International applicants are advised to review the for additional information on submitting international transcripts. |
| English Proficiency Exam | A valid score on one of the following examinations TOEFL, IELTS, Pearson PTE, Duolingo English Test is required of all non-native English-speaking applicants. The examination is not required for the following applicants: CGU’s school code for the TOEFL exam is . International applicants are encouraged to visit our for more information, including score requirements. |
| Resume | |
| Program Requirements | |
|---|---|
| Statement of Purpose | |
| Academic Prerequisites | |
| Letter of Recommendation | When filling out the online application, please enter references acquainted with your potential for success who will submit a written recommendation on your behalf. In most academic departments, references from faculty members who can speak to your academic ability are preferred; applicants with substantial work experience may request professional references. Please do not enter family members as references. You will be required to input information for your recommenders (whether they are submitting online or not) in the “Recommendations” section of the online application. Please follow the directions in this section carefully before clicking on “Recommendation Provider List” to input the names and contact information for each recommender. You will have an opportunity to indicate if the reference writer will be submitting online. These reference writers will receive an email from CGU with instructions on submitting an online recommendation. .
|
| Standardized Test Scores | For applicants applying to begin in a 2024 term, standardized test scores are not required for this program. Applicants who have taken the Graduate Record Examinations (GRE) General Test are invited to submit scores but are not required to do so. Applicants who feel that their Grade Point Averages do not adequately represent their ability to succeed in a graduate program may find it helpful to submit GRE scores for consideration. CGU’s school code: |
| Writing Sample | |
Key Dates & Deadlines
CGU operates on a priority deadline cycle. Applicants are strongly encouraged to submit complete applications by the priority dates in order to assure maximum consideration for both admission and fellowships.
Once the priority deadlines have passed, the University will continue to review applications for qualified candidates on a competitive, space-available basis. The final deadlines listed are the last date the University can accept an application in order to allow sufficient time to complete the admissions, financial aid, and other enrollment processes.
Spring 2025 Priority Deadline – November 1, 2024 Final Deadline (International) – November 15, 2024 Final Deadline (Domestic) – December 1, 2024 Classes begin – January 21, 2025
Fall 2025 Priority Deadline – February 1, 2025 Final Deadline (International) – July 5, 2025 Final Deadline (Domestic) – August 1, 2025 Classes begin – August 25, 2025
ESTIMATED TUITION (CALIFORNIA RESIDENTS, NON-RESIDENTS, INTERNATIONAL)
| Program | 72 units |
| Tuition per unit* | $2,020 |
*Based on 2024-2025 tuition rates.
STUDENT FEES (PER SEMESTER)
| $245 Student Fee |
| $150 Technology Fee |
| International Student Services Fee*: $661 fall semester, $776 spring semester |
For estimates of room & board, books, etc., please download CGU’s Cost of Attendance 2024-2025 .
Review General Costs
View Concentration
Hemispheric & Transnational Studies
These concentrations are available for students pursuing the following degree programs:
Master’s Degrees
- Applied Gender Studies
- Cultural Studies
- Islamic Studies
Doctoral Degrees
Are you ready to apply?
Request More Info
Contact us for more information, while waiting for our answer, take a look at our faq, maybe you'll find some answers to your questions.
Want to Get your Dissertation Accepted?
Discover how we've helped doctoral students complete their dissertations and advance their academic careers!
Join 200+ Graduated Students

Get Your Dissertation Accepted On Your Next Submission
Get customized coaching for:.
- Crafting your proposal,
- Collecting and analyzing your data, or
- Preparing your defense.
Trapped in dissertation revisions?
Do you need a master’s to get a phd, published by steve tippins on may 12, 2020 may 12, 2020.
Last Updated on: 12th June 2024, 03:27 am
In the traditional academic model, at least in the United States, you get an undergraduate degree, followed by a master’s degree, and then finish your academic journey by getting a PhD. However, that isn’t the only way.
Do you need a master’s degree to get a PhD? The short answer is no; it is possible to get a PhD without a master’s (I did). However, there are some important caveats.
Do You Need a Master’s to Get a PhD? The History
The system of higher education in the United States evolved from the system established in the United Kingdom. Historically in the U.K., a student could get an undergraduate degree and then enroll in a PhD program — no masters degree needed.
In this situation, however, the PhD program was a little different than those found in the U.S. Students came into these programs with a research question or idea and spent their time developing the idea and performing the study under the guidance of a supervisor and a committee. There were very few required courses.
PhDs today remain focused on research (that’s how they differ from professional doctoral designations, like the Ed.D., the Psy.D., or the DBA). Now, though, doctoral programs provide an education in how to do research in the particular field as part of the matriculation process for the PhD, along with courses with program-relevant content for both the professional doctorate and research doctorate.
Today: Professional Master’s Programs

Do you need a master’s to get a PhD today? Not always.
In some disciplines, there are professional master’s programs that are considered terminal degrees. In business, the MBA is thought of as a terminal degree. In accounting, the MS in taxation is similar, as is an MFA for artists.
These degrees are designed for real-world, practical purposes. They are not meant to be a scaffold that provides the underpinning for a PhD.
So it is not unheard of in fields where there are professional master’s degree programs for students to enter a PhD program without a master’s degree.
How I Got a PhD Without a Master’s

In my case, I was about halfway through an MBA when it dawned on me that what I really wanted to do was teach and do research, so I applied for and switched into the PhD program.
(I told myself that I would eventually finish up the last three MBA classes. I never quite got there, because there was no real need or requirement to do so.) For me, this was one of the best decisions that I have ever made.
A recent modification in this area is the rise of the DBA – Doctorate in Business Administration. With the proliferation of the MBA degree, a demand arose for a degree that demonstrated knowledge and dedication beyond the MBA. This brought about the rise of the DBA program. Since a DBA is meant to imply something more than an MBA, most programs will require an MBA for entrance.
Within the field of business, it seems to depend upon which type of doctorate you are looking for. There is a path to a doctorate both with or without a master’s degree.
Should You Get a PhD Without a Master’s?

In most fields, the major distinction of the PhD is the research focus. A master’s in public health will prepare you to be, say, an administrator at a community not-for-profit. A PhD in public health will set you on a course of policy analysis or program evaluation.
It’s similar in most fields, and so what you’d be missing by going directly to the PhD would be the direct services focus that the master’s degree traditionally offers. It’s not just a matter of what you ultimately want to do, it’s a matter of knowing the ins and outs of the field from a service provider perspective.
Getting a PhD Without a Master’s: Humanities Programs
Do you need a master’s to get a PhD in the humanities fields? Here, students don’t have the same opportunities afforded by the professional degree programs.
In traditional liberal arts programs such as history, English, and sociology, the path to a PhD is traditionally through a master’s program. Schools design programs to fit together, so entering a PhD program without a master’s would leave a student at a significant disadvantage. Most social sciences programs would not accept a bachelor-level student into a PhD program without a lot of compelling reasons to do so.
Getting a PhD Without a Master’s: Social Sciences Programs

There are programs designed to go from the BS to the PhD, and one of these is psychology. Many universities admit bachelor-level students into their psychology doctoral programs, intentionally bringing their students through an entire course of study. So you don’t need a master’s degree to get a PhD in these programs.
Such an approach benefits the university by ensuring that the graduate education they receive is consistent; they teach everything from the ground up. That way, their students start from zero and grow together, all on the same page.
While this may sound exciting, the catch is that these programs usually take much longer than other PhD programs, in which students arrive with a master’s degree already in hand. Expect to spend a minimum of five years in such a program; often several more.
Getting a PhD Without Master’s: “Hard” Sciences Programs
Most programs in the hard sciences – disciplines such as chemistry, biology, and physics – require a master’s degree to get into a PhD program. These programs require great amounts of time in a lab, and the basis for lab work is developed in master’s programs.

Even if you could go directly to a PhD program from undergraduate school, most people who have completed programs say that you will get more from your degree if you enter having completed a masters program.
Pros and Cons of Getting a PhD Without a Master’s
As with most opportunities, there are pros and cons to getting a PhD without a master’s degree. Here is a general summary:
Pros of Getting a PhD Without a Master’s
- Less time in school could mean less cost
- You may be able to get to your ultimate profession faster
- Work on your research agenda could begin sooner
Cons of Getting a PhD Without a Master’s
- You will may not have the breadth of understanding needed for graduate work when you initially enter the PhD program
- You may realize in a Master’s program that another direction is better for you, and you will save time and money by switching before you get the terminal degree.
- It may be harder to find faculty members who are ready to mentor you if they suspect you don’t have the expertise in writing or research you would have gained in a master’s program.
Do You Need a Master’s to Get a PhD? Summary

Depending upon your discipline, getting a doctoral degree without a master’s degree is possible.
Before you move forward searching for doctoral programs that do not require a master’s, recognize that there is usually no way around a lot of hard work. Here are some questions to consider as you decide which way to go:
- Do you already have experience in research and writing, even without a master’s degree?
- Are you going into a field that has a tradition of taking students from BS to PhD?
- Is the school you’re interested in open to applicants who do not have a master’s degree?
- Are you prepared to explain (maybe many times) why you chose to skip the master’s degree?
- Are you prone to feelings of inadequacy or “ imposter syndrome ” that will be exacerbated by having less education than your peers in the program?
- What is your ultimate goal? Would a master’s degree get you working in the field quicker and give you experience that might serve you in your doctoral research?
- If you want a job at a university or in a particular field after completing your doctorate, how will your curriculum vitae compare to someone who does have a master’s degree in the field?
- How certain are you that this is the field for you? Might a master’s degree help you decide, before you commit to the rigors of a PhD program?
Most of all, the important thing to know is that getting a PhD is not easy. There are aspects of the research doctorate, particularly the dissertation, that make it a much higher hurdle than the master’s degree. Many people (about half in the U.S.) who begin PhDs drop out, often finishing all but their dissertation . That number is much lower for students in master’s degree programs.
Regardless of how you decide to move forward, you are ready to embark upon an exciting educational process. Good luck!
Steve Tippins
Steve Tippins, PhD, has thrived in academia for over thirty years. He continues to love teaching in addition to coaching recent PhD graduates as well as students writing their dissertations. Learn more about his dissertation coaching and career coaching services. Book a Free Consultation with Steve Tippins
Related Posts

Academic Career
Bipoc academics matter: diversity in academia is long overdue.
We at Beyond PhD Coaching firmly believe that diversifying academia is both necessary and important – and well past overdue. There’s no denying that higher education equals more power in society. This power has been Read more…

Academic Arrogance: Dismantling a Culture of Harm
Academics are like polar bears. We live alone; we hibernate. If you walk down the halls of academic offices, you’ll find that almost all of the doors are shut. We live a solitary existence, occasionally Read more…

How to Be a Good PhD Student
If you’re curious about how to be a good PhD student, this article is a good place to start. As a professor for over 30 years, much of that as a Dissertation Committee Chair, I’ve Read more…

Research Voyage
Research Tips and Infromation
PhD without a Master’s Degree? Exploring Direct PhD Programs
Introduction
What is a direct phd program.
- Pros of Doing a PhD Without a Master's Degree
- Cons of Doing a PhD Without a Master's Degree
- Fields in Which it is More Common to Enter a PhD Program Without a Master's Degree
- Fields in Which a Master's Degree is Often Required for Admission to a PhD Program
- How to Apply for a PhD Program Without a Master's Degree
- Examples of Successful PhD students who did not have a Master's Degree
- Top Universities Offering PhD without Master's Degree
Direct PhD Programmes in United States:
Direct phd programmes in europe:, direct phd programmes in australia:, direct phd programmes in asia:.
During my teaching years at a premier Engineering institute in India, I encountered an intriguing case that shed light on the possibility of pursuing a PhD without a master’s degree.
One day, a former student reached out to me with exciting news. She had successfully cleared the Graduate Aptitude Test in Engineering (GATE), a qualifying exam for admission to postgraduate programs. Even more surprising was her plan to directly join the PhD program at the prestigious Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Delhi.
Initially, I found this puzzling—how could one step into a PhD without completing a master’s degree? It turned out that such programs do indeed exist at IITs and other esteemed institutions in India and abroad.
Intrigued by this revelation, I delved deeper into the details and later shared this valuable information with many students. Little did I know that this piece of knowledge would significantly benefit aspiring scholars aiming for a direct PhD path.
A PhD, or Doctor of Philosophy, is the highest level of academic degree that one can achieve in many fields. It typically involves several years of intensive research and coursework in a specialized area and completing a dissertation that makes an original contribution to the field. A PhD can lead to many career opportunities, including positions in academia, industry, and government.
The traditional path to a PhD usually involves completing a bachelor’s degree in a related field, followed by a master’s degree before starting the PhD program. The bachelor’s degree provides a broad foundation in the field, while the master’s degree provides more specialized training and research experience that prepares students for the rigours of a PhD program.
However, some students may wonder whether it is possible to skip the master’s degree and go straight into a PhD program. This can be an attractive option for students who want to save time and money, or who have extensive research experience that makes them well-prepared for a PhD program.
In this article, we will explore the pros and cons of doing a PhD without a master’s degree, as well as some examples of successful PhD students who took this route.
A direct PhD program, sometimes referred to as an integrated or combined PhD program, is a doctoral-level academic program that allows students to pursue a PhD degree without first obtaining a master’s degree.
In traditional PhD programs, students typically complete a master’s degree before embarking on their doctoral studies. However, in a direct PhD program, students are admitted directly into the PhD program after completing their undergraduate studies.
Direct PhD programs are often structured to be more streamlined, allowing students to move directly into advanced research and coursework related to their field of study. These programs are typically designed for highly motivated and academically strong students who demonstrate exceptional potential for research and scholarly work.
The specific structure and requirements of direct PhD programs can vary depending on the university and the field of study. In some cases, students may be required to complete additional coursework or examinations to ensure they have the necessary background knowledge and skills for doctoral-level research. However, the overall goal of these programs is to accelerate the process of earning a PhD by allowing students to begin their doctoral studies earlier in their academic career.
Pros and Cons of Doing a PhD Without a Master’s Degree
While it is possible to pursue a PhD without completing a master’s degree, there are several potential advantages and disadvantages to consider.
Pros of Doing a PhD Without a Master’s Degree
- Saving time and money: Completing a master’s degree can add two or more years to the time it takes to earn a PhD, as well as significant tuition costs. Skipping the master’s degree can allow students to complete their PhD more quickly and with fewer expenses.
- Gaining more research experience: Some students may already have extensive research experience, either through undergraduate research opportunities or work in a related field. Skipping the master’s degree can allow these students to continue building on their research skills and contribute to the field more quickly.
Cons of Doing a PhD Without a Master’s Degree
- Lack of preparation in research methodology and theory: Master’s degree programs often provide students with more specialized training in research methods and theoretical frameworks, which can be valuable preparation for a PhD program. Skipping the master’s degree can mean missing out on this preparation and potentially struggling to keep up with the demands of a PhD program.
- Potential challenges in meeting admission requirements: Some PhD programs may require applicants to have a master’s degree or equivalent research experience, which can make it difficult for students who have not completed a master’s degree to be accepted into a PhD program. Additionally, some students may need to complete additional coursework or exams to meet the admission requirements for a PhD program.
- A student who completed a bachelor’s degree in computer science and spent several years working in the industry as a software developer may have gained extensive research experience in a specialized area of computer science. This student may be well-prepared to pursue a PhD in computer science without completing a master’s degree.
- A student who completed a bachelor’s degree in psychology and has some research experience through undergraduate research opportunities may struggle to keep up with the demands of a PhD program in psychology without completing a master’s degree that provides more specialized training in research methods and theoretical frameworks.
Fields in Which it is More Common to Enter a PhD Program Without a Master’s Degree
While it is not uncommon for students to pursue a master’s degree before starting a PhD program, there are some fields where it is more common for students to enter a PhD program directly after completing a bachelor’s degree. These fields include:
- Engineering: In many engineering disciplines, it is common for students to enter PhD programs directly after completing a bachelor’s degree. This is because engineering programs often provide students with extensive research experience and specialized training in research methods and theoretical frameworks that prepare them for a PhD program.
- Natural Sciences: In fields such as biology, chemistry, and physics, it is also common for students to enter PhD programs directly after completing a bachelor’s degree. This is because these fields often require extensive research experience and specialized training in laboratory techniques and scientific methods, which students can gain through undergraduate research opportunities and coursework.
In these fields, students who have completed a bachelor’s degree and have extensive research experience may be well-prepared to pursue a PhD program without completing a master’s degree. However, it is important to note that this may not be the case in other fields, such as the social sciences or humanities, where a master’s degree may be more commonly required or preferred for admission to a PhD program.
It is important for students to research the admission requirements and expectations for PhD programs in their chosen field before deciding whether to pursue a master’s degree or apply directly to a PhD program after completing their bachelor’s degree.
Fields in Which a Master’s Degree is Often Required for Admission to a PhD Program
While it is possible to pursue a PhD without completing a master’s degree, there are some fields where a master’s degree is often required or preferred for admission to a PhD program. These fields include:
- Humanities: In fields such as history, philosophy, and literature, it is common for students to complete a master’s degree before applying to a PhD program. This is because these fields often require extensive coursework and training in research methods and theoretical frameworks, which students can gain through a master’s degree program.
- Social Sciences: In fields such as psychology, sociology, and political science, a master’s degree is often required or preferred for admission to a PhD program. This is because these fields often require specialized training in research methods and statistical analysis, which students can gain through a master’s degree program.
In these fields, students who have completed a bachelor’s degree but do not have a master’s degree may find it difficult to gain admission to a PhD program. This is because PhD programs in these fields often have high admission standards and may require applicants to have completed a master’s degree or equivalent research experience.
- A student who completed a bachelor’s degree in English literature and has some research experience through undergraduate research opportunities may need to complete a master’s degree in order to gain admission to a PhD program in literature. This is because PhD programs in literature often require extensive coursework and training in research methods and theoretical frameworks.
- A student who completed a bachelor’s degree in psychology and has some research experience through undergraduate research opportunities may be able to apply directly to a PhD program in psychology. However, some PhD programs in psychology may require applicants to have completed a master’s degree or equivalent research experience, which could make it difficult for this student to gain admission without completing a master’s degree.
How to Apply for a PhD Program Without a Master’s Degree
While it can be challenging to gain admission to a PhD program without a master’s degree, there are some steps that students can take to increase their chances of success. These steps may include:
- Demonstrating exceptional academic qualifications: Students who have completed a bachelor’s degree with exceptional grades and have a strong academic record may be more likely to be considered for admission to a PhD program without a master’s degree.
- Demonstrating research potential: Students with extensive research experiences, such as through undergraduate research opportunities or independent research projects, can demonstrate their potential for success in a PhD program.
- Completing additional coursework or exams: Some PhD programs may require applicants without a master’s degree to complete additional coursework or exams to demonstrate their readiness for PhD-level work. This may include completing additional courses in research methods, statistics, or theory, or taking qualifying exams to demonstrate mastery of the field.
- A student who completed a bachelor’s degree in physics with exceptional grades and extensive research experience may be able to gain admission to a PhD program in physics without completing a master’s degree. This is because the student has demonstrated exceptional academic qualifications and research potential.
- A student who completed a bachelor’s degree in history and has some research experience through undergraduate research opportunities may need to complete additional coursework or exams to gain admission to a PhD program in history. This is because PhD programs in history often require extensive coursework and training in research methods and theoretical frameworks, which students may not have gained through their undergraduate studies alone.
It is important for students to research the admission requirements and expectations for PhD programs in their chosen field before deciding whether to pursue a master’s degree or apply directly to a PhD program after completing their bachelor’s degree. Students may also want to reach out to professors and advisors in their field to discuss their options and receive guidance on the application process.
Please visit my article on “How to Build a Strong Research Portfolio in 07 Easy Steps” . This article will help you in building a strong research portfolio. Visit my blog post sections on writing research papers for journals and writing research papers for conferences . These articles will help you in writing quality papers for journals and conferences.
Examples of Successful PhD students who did not have a Master’s Degree
While it is less common for students to enter a PhD program without a master’s degree, there are examples of successful PhD students who have done so. These students have demonstrated exceptional academic qualifications, research potential, and perseverance in their programs. Some examples of successful PhD students who did not have a master’s degree include:
- Dr. Jennifer Doudna: Dr. Doudna is a biochemist who won the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 2020 for her work on the CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing system. She entered a PhD program in biochemistry at Harvard University directly after completing her bachelor’s degree at Pomona College. She completed her PhD in just four years and went on to a successful career in academia and research.
- Dr. Maryam Mirzakhani: Dr. Mirzakhani was a mathematician who won the Fields Medal, often considered the highest honour in mathematics, in 2014. She completed her bachelor’s degree in mathematics in Iran and then entered a PhD program in mathematics at Harvard University without completing a master’s degree. She completed her PhD in just three years and went on to a successful career in academia and research.
- Dr. David Gelernter: Dr. Gelernter is a computer scientist and artist who completed his bachelor’s degree in mathematics and classical Hebrew literature at Yale University. He then entered a PhD program in computer science at the same institution without completing a master’s degree. He completed his PhD in three years and went on to a successful career in academia and research.
These examples demonstrate that it is possible for students to succeed in PhD programs without completing a master’s degree. However, it is important to note that these students had exceptional academic qualifications, research potential, and perseverance and that their success was not guaranteed.
Students who are considering applying to PhD programs without completing a master’s degree should carefully consider their own academic qualifications and research potential and should seek guidance and support from advisors and mentors in their field.
Top Universities Offering PhD without Master’s Degree
While it is less common for universities to offer PhD programs without a master’s degree, there are some prestigious institutions around the world that do accept students into PhD programs without a master’s degree in certain fields. Here are some examples:
- Harvard University, USA : Harvard’s Graduate School of Arts and Sciences allows exceptional students to apply directly to their PhD programs without a master’s degree in fields such as physics, chemistry, mathematics, and computer science.
- Stanford University, USA : Stanford’s School of Engineering offers a direct PhD program for exceptional students in fields such as electrical engineering, computer science, and mechanical engineering, without requiring a master’s degree.
- University of Cambridge, UK : The University of Cambridge’s PhD programs in sciences and engineering fields may admit students without a master’s degree on a case-by-case basis, considering their qualifications and research potential.
- Imperial College London, UK : Imperial College London’s PhD programs in engineering and physical sciences may admit students directly from a bachelor’s degree, based on their qualifications and potential for research.
- ETH Zurich, Switzerland: ETH Zurich, a leading institution in science and engineering, may admit students into their PhD programs without a master’s degree, considering their academic achievements and research potential.
- IIT Delhi, India : a leading institution in engineering, admit students into their PhD programs without a master’s degree, considering their academic achievements and research potential.
It’s important to note that the admission requirements and policies for PhD programs without a master’s degree can vary by institution and field of study and may be subject to change. It’s always recommended to thoroughly research and review the specific requirements of each institution and program you are interested in, and contact the admissions offices for up-to-date and accurate information.
Direct PhD Offered in Various Continents/Countries
- Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT)
- California Institute of Technology (Caltech)
- Stanford University
- Harvard University
- Princeton University
- University of Cambridge (UK)
- University College London (UK)
- ETH Zurich (Switzerland)
- Technical University of Munich (Germany)
- University of Amsterdam (Netherlands)
- Australian National University
- University of Melbourne
- University of Sydney
- University of Queensland
- Monash University
- National University of Singapore
- Tsinghua University (China)
- University of Tokyo (Japan)
- Seoul National University (South Korea)
- Indian Institutes of Technology (IITs) – Various campuses in India
These universities, among many others, offer direct PhD programs across a wide range of disciplines including engineering, natural sciences, social sciences, humanities, and more. It’s important to research each program carefully to understand its specific requirements, application process, and available funding opportunities.
Pursuing a PhD without a master’s degree is possible but it is less common and comes with its own set of challenges. In this article, we have discussed the pros and cons of doing a PhD without a master’s degree, fields in which it is more common to enter a PhD program without a master’s degree, and fields in which a master’s degree is often required for admission to a PhD program. We have also provided some advice on how to apply for a PhD program without a master’s degree and shared examples of successful PhD students who did not have a master’s degree.
For students who are considering pursuing a PhD without a master’s degree, it is important to carefully consider their academic qualifications and research potential. They should also seek guidance and support from advisors and mentors in their field, and consider completing additional coursework or exams to prepare for the rigors of a PhD program.
In conclusion, the decision to pursue a PhD without a master’s degree is a personal one and should be made after careful consideration of the individual’s goals, strengths, and weaknesses. We encourage readers to engage with the topic further by researching specific PhD programs and seeking advice from mentors and advisors in their field.
Upcoming Events
- Visit the Upcoming International Conferences at Exotic Travel Destinations with Travel Plan
- Visit for Research Internships Worldwide

Recent Posts
- Best 05 Research Journals for Publications in September 2024
- Best 5 Journals for Quick Review and High Impact in August 2024
- 05 Quick Review, High Impact, Best Research Journals for Submissions for July 2024
- Top Mistakes to Avoid When Writing a Research Paper
- Average Stipend for Research/Academic Internships
- All Blog Posts
- Research Career
- Research Conference
- Research Internship
- Research Journal
- Research Tools
- Uncategorized
- Research Conferences
- Research Journals
- Research Grants
- Internships
- Research Internships
- Email Templates
- Conferences
- Blog Partners
- Privacy Policy
Copyright © 2024 Research Voyage
Design by ThemesDNA.com

We have 35 PhD without masters PhD Projects, Programmes & Scholarships
All disciplines
All locations
Institution
All Institutions
All PhD Types
All Funding
PhD without masters PhD Projects, Programmes & Scholarships
Philosophy phd (option of joint phd with national university of singapore), self-funded phd students only.
The PhD opportunities on this programme do not have funding attached. You will need to have your own means of paying fees and living costs and / or seek separate funding from student finance, charities or trusts.
Humanities Research Programme
Humanities Research Programmes present a range of research opportunities, shaped by a university’s particular expertise, facilities and resources. You will usually identify a suitable topic for your PhD and propose your own project. Additional training and development opportunities may also be offered as part of your programme.
PhD in International Business and Strategy at Henley Business School
Funded phd programme (students worldwide).
Some or all of the PhD opportunities in this programme have funding attached. Applications for this programme are welcome from suitably qualified candidates worldwide. Funding may only be available to a limited set of nationalities and you should read the full programme details for further information.
Business Research Programme
Business Research Programmes present a range of research opportunities, shaped by a university’s particular expertise, facilities and resources. You will usually identify a suitable topic for your PhD and propose your own project. Additional training and development opportunities may also be offered as part of your programme.
PhD in Finance at Henley Business School
Phd studentship for research on psychological safety in elite performance training, arts research programme.
Arts Research Programmes present a range of research opportunities, shaped by a university’s particular expertise, facilities and resources. You will usually identify a suitable topic for your PhD and propose your own project. Additional training and development opportunities may also be offered as part of your programme.
Informatics and System Science PhD Opportunities
Accounting and financial management phd opportunities, phds at henley business school, phd in marketing & reputation at henley business school, phd in leadership, organisations and behaviour at henley business school, hybrid modelling for net-zero circular manufacturing: value chain transformation analysis, phd research project.
PhD Research Projects are advertised opportunities to examine a pre-defined topic or answer a stated research question. Some projects may also provide scope for you to propose your own ideas and approaches.
Funded PhD Project (Students Worldwide)
This project has funding attached, subject to eligibility criteria. Applications for the project are welcome from all suitably qualified candidates, but its funding may be restricted to a limited set of nationalities. You should check the project and department details for more information.
Role of Defects on Mechanical Behaviour of Single Crystal Superalloys
Funded phd project (uk students only).
This research project has funding attached. It is only available to UK citizens or those who have been resident in the UK for a period of 3 years or more. Some projects, which are funded by charities or by the universities themselves may have more stringent restrictions.
Object categorisation and word learning in infants
This project does not have funding attached. You will need to have your own means of paying fees and living costs and / or seek separate funding from student finance, charities or trusts.
Understanding the influence of final annealing on the behaviour of Zr-Nb-Sn-Fe alloys during irradiation
Evaluating the just transition to effect policy change, heat mitigation and management for females.
FindAPhD. Copyright 2005-2024 All rights reserved.
Unknown ( change )
Have you got time to answer some quick questions about PhD study?
Select your nearest city
You haven’t completed your profile yet. To get the most out of FindAPhD, finish your profile and receive these benefits:
- Monthly chance to win one of ten £10 Amazon vouchers ; winners will be notified every month.*
- The latest PhD projects delivered straight to your inbox
- Access to our £6,000 scholarship competition
- Weekly newsletter with funding opportunities, research proposal tips and much more
- Early access to our physical and virtual postgraduate study fairs
Or begin browsing FindAPhD.com
or begin browsing FindAPhD.com
*Offer only available for the duration of your active subscription, and subject to change. You MUST claim your prize within 72 hours, if not we will redraw.

Create your account
Looking to list your PhD opportunities? Log in here .
Filtering Results

- People Directory
- Safety at UD

Graduate Programs
- History Workshops
- Careers in History
- Student Organizations
- Internships and Fellowships
- Scholarships and Awards
History (MA)
History (PhD)
- Financial Aid and Awards
- Dissertations in Progress
- Make a Gift
Get More Info >

About Our Graduate Programs
The Department of History trains students to be professional historians in a range of careers. Students in our graduate program receive mentoring from a faculty that includes specialists in the history of the United States, Latin America, Europe, the Middle East, Africa, and Asia. Our curriculum emphasizes the building blocks of historical methods, including historiography, archival research, and critical thinking. Students use written archives, visual sources, oral history, and material culture to explore the past from a variety of perspectives. Our M.A. and Ph.D. graduates are employed in colleges and universities, secondary schools, and museums and other public humanities institutions.
The Department has a graduate enrollment of about 55 students at all stages of their graduate careers. A self-governing History Graduate Student Association serves as a liaison between students and faculty. Two graduate students serve on the Department’s Graduate Studies Committee, which administers the graduate program.
Look through our graduate programs

African American Public Humanities Initiative
The Department of History also participates in the University's African American Public Humanities Initiative , an interdisciplinary program integrating the disciplines of history, English, art history and Africana studies to train students for a broad range of careers in and beyond the academy.
Benefits of the AAPHI include fully-funded 5-year tuition and stipend and additional funding for summer research/internships and professional development.
Prospective graduate students interested in being considered for the African American Public Humanities Initiative scholarship should indicate their interest by checking the AAPHI interest box in their application and indicating their interest in their personal statement.
Learn MORE ABOUT AAPHI
Hagley Program in the History of Capitalism, Technology, and Culture
For more than 50 years the Hagley Program in the History of Capitalism, Technology, and Culture in the University of Delaware’s Department of History has been training M.A.- and Ph.D.-level students in the history of industrialization, capitalism, technology, consumption, business, labor and the environment. The program offers students an enriched graduate education including a range of resources and opportunities not normally available in the university setting. A large number of our students develop an expertise in the study of material culture, and many earn certificates in museum studies. Our alumni include more than 150 distinguished historians, museum professionals, archivists and others.
Interested in the program?
Please visit the Hagley Program in the History of Capitalism, Technology and Culture website for further information.
Supporting tomorrow's leaders, scholars and innovators
The University of Delaware holistically supports its graduate students, beginning with their health and wellbeing . Benefits include a subsidized health plan and physical and behavioral health services. UD fosters a culture of academic excellence , with committed faculty and staff and access to state-of-the-art research facilities and technology. UD prioritizes professional development with job training, internships and industry partnerships. Graduates further enhance their professional growth and visibility with opportunities to work on interdisciplinary research teams, present their work at conferences and publish in academic journals. Visit the links below to learn how UD is supporting society’s future leaders, scholars, and innovators.

Academic Support >
Professional development >, student life >, college of arts & sciences.
- Prospective Students
- Current Students
- News & Events
- Research & Innovation
- Alumni & Friends
- College Operations
- Undergraduate
- Continuing education
- Engage with us
- Support for researchers
- Using research to engage
- Recognition
- Oxford profiles
- Oxford and coronavirus
- Filming in Oxford
- Find An Expert

COMMENTS
The benefits of a Masters degree. While it's possible to undertake a PhD without a Masters, there are several benefits to consider: Research experience: Masters programmes often include comprehensive research training and the opportunity to complete significant research projects. Networking: Masters provides invaluable opportunities to ...
The History Department offers 5 years of financial support to PhD students. No funding is offered for the co-terminal and terminal M.A. programs. A sample Ph.D. funding package is as follows: 1st year: 3 quarters fellowship stipend and 1 summer stipend. 2nd year: 2 quarters TAships, 1 quarter fellowship stipend, and 1 summer stipend.
Yes, it is possible to get a Ph.D. without having a Master's degree first. Conventionally, if you wanted to pursue a Ph.D., you would first get your Bachelor's degree, then your Master's degree, and then apply for a PhD. However, there are a few unconventional ways of getting a Ph.D. Firstly, you can opt to bypass your Master's degree ...
And finally, doing a Master's at the same university where you want to pursue your PhD is one of the smartest moves you can make. It shows loyalty to the university and gets you the right contacts among teachers. It's almost a sure pass to a doctoral programme. 3. A Master's is the only way to a PhD in a new field.
To be considered for a PhD without a Master's, at a minimum you will be expected to have a Bachelors degree. For students looking to enrol onto a STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths) PhD, a relevant Bachelors in a 3-year undergraduate course is usually expected. However, this is not the case for students looking to apply to non ...
Study History Where It Is Made. AU's PhD in History will prepare you for a career as an educator, researcher, analyst, and writer working in academia, public and institutional history, and other fields requiring investigative and analytical skills. In this program, you will develop a deeper understanding of how historians investigate and interpret the past while you explore the past with ...
Start dates (semester dates) PhD by distance learning. 3-4 years full-time. 4-6 years part-time. Apply for PhD by distance learning. January. September. If your passion lies in research, our doctoral degrees give you the independence to focus on a specialism of your choice. You'll have the flexibility to work from anywhere in the world.
Johns Hopkins University. Baltimore, MD. #10 in History. Save. 4.5. Earning a graduate degree in history involves analysis, research and presentations. In some cases, students must also complete a ...
The PhD by Distance mode is available to all applicants for eligible HCA PhD programmes, who will apply via the Postgraduate Degree Finder. Applicants will select between on-campus and distance options, as well as between part-time and full-time options. PhD by Distance students will receive the same level of support and supervision as on ...
Statement of Purpose. Your statement of purpose should include why you want to study history in graduate school, why you want to study at Harvard, and indicate your research interests and potential advisors. The required writing sample should be of remarkable quality and ask historical questions. Reading ability in any languages necessary for ...
Admissions Process for the History PhD: Each year the department receives nearly 400 applications to the doctoral program and offers admission to about 6% of applicants. The typical incoming class size is 16 students. The admissions process is extremely competitive, but if you are serious about pursuing a PhD in history, you are encouraged to ...
Graduate Program. The goal of the doctoral program is to train students to become both skilled scholars and conscientious teachers. Throughout the program students work with advisors and other faculty members as they engage in coursework, prepare for and take the general exam, work as teaching fellows, and research and write the dissertation ...
Find your school in just 60 seconds. Yes, it is possible to earn a PhD without a master's degree. Though the traditional path entails completing a master's program before embarking on a doctorate, some schools and programs offer options to skip the master's entirely. Actually, in select cases, it's the preferred approach.
The Department of History's doctoral degree program seeks to train talented historians for careers in scholarship, teaching, and beyond the academy. The department typically accepts 22 Ph.D. students per year. Additional students are enrolled through various combined programs and through HSHM.
FindAPhD. Search Funded PhD Projects, Programmes & Scholarships in History & Archaeology, PhD without masters. Search for PhD funding, scholarships & studentships in the UK, Europe and around the world.
Saybrook University offers a PhD in Clinical Psychology program that is fully online. Students who do not hold a master's degree must complete 103 to 109 credits to graduate, while those who do have a master's in a related field must complete 100 to 106 credits. The program can typically be completed in 5 years.
The PhD usually came after the Bachelor's degree for many years in the United Kingdom. There was no real need to successfully gain a Master's degree before embarking on this mammoth task of empirical research. Whilst some undergraduate degrees still lead to a Master's qualification, and many people still complete Master degrees, it is possible to do a PhD without a Masters degree.
2024-25 Edition. History, Ph.D. The Doctoral Program in History is designed to provide students with advanced historical research skills and a solid grounding in the theory and methodology of history. This combination reflects the Department's conviction that scholars should approach significant questions about the past with rigor and ...
Key Takeaways: It is possible to pursue a PhD without a master's degree, though some schools and programs may have specific requirements. Completing a master's degree before a PhD can help clarify research interests, provide additional academic experience, and make you more competitive in the job market. Directly enrolling in a PhD program ...
The PhD program in History enables you to conduct research at the highest level and begin your career as an academic historian or prepare for a wide range of academic and professional careers. You'll work alongside CGU faculty-scholars who specialize in U.S. and European history and draw on expert faculty from the highly ranked Claremont ...
The short answer is no; it is possible to get a PhD without a master's (I did). However, there are some important caveats. Book a Free Consultation. Do You Need a Master's to Get a PhD? The History. The system of higher education in the United States evolved from the system established in the United Kingdom.
A direct PhD program, sometimes referred to as an integrated or combined PhD program, is a doctoral-level academic program that allows students to pursue a PhD degree without first obtaining a master's degree. In traditional PhD programs, students typically complete a master's degree before embarking on their doctoral studies.
PhD studentship at Guildhall School of Music & Drama, in association with Loughborough University. This opportunity is offered with a full fee waiver in the first instance, with the possibility of further funding. Read more. Funded PhD Programme (Students Worldwide) Arts Research Programme. More Details.
African American Public Humanities Initiative. The Department of History also participates in the University's African American Public Humanities Initiative, an interdisciplinary program integrating the disciplines of history, English, art history and Africana studies to train students for a broad range of careers in and beyond the academy.. Benefits of the AAPHI include fully-funded 5-year ...
European History since 1500; British History; A major field committee requires at least three members of the graduate faculty, two of whom must be from the Department of History. Degree requirements and pathway to degree for the PhD in US History. Degree requirements and pathway to degree for the PhD in British or European History
As a graduate student, you will have access to the University's wide range of world-class resources including libraries, museums, galleries, digital resources and IT services.. The Bodleian Libraries is the largest library system in the UK. It includes the main Bodleian Library and libraries across Oxford, including major research libraries and faculty, department and institute libraries.