Essay Papers Writing Online
How to craft an effective critique essay – a step-by-step guide to capturing readers’ attention, providing insightful analysis, and offering constructive feedback.

Evaluating someone else’s writing can be a challenging task, but with the right tools and approach, you can become a skillful critic in no time. Whether you’re analyzing a piece of literature, an article, or a research paper, a critique essay allows you to delve into the elements that make up a strong written work.
By honing your critical thinking skills, you’ll be able to identify the strengths and weaknesses of a piece and provide insightful feedback. Through this process, you’ll not only improve your own writing abilities but also enhance your understanding and appreciation of the written word.
In this comprehensive article, we will equip you with the essential techniques and strategies needed to write an effective critique essay. From analyzing the structure and organization of a piece to evaluating the author’s arguments and evidence, you’ll learn how to assess a work’s strengths and weaknesses with precision and clarity.

What is a Critique Essay and Why is it Important?
A critique essay is a type of academic writing that involves analyzing and evaluating a piece of work, such as a book, film, artwork, or research paper. Unlike a simple summary or review, a critique essay goes beyond providing a surface-level examination of the work and delves into an in-depth analysis of its strengths, weaknesses, and overall value.
But why is writing a critique essay important? Well, there are several reasons. Firstly, it allows you to develop critical thinking skills by carefully examining and assessing the merits of a work. This type of analysis helps you become more discerning and thoughtful in your judgments, which is a valuable skill in many aspects of life.
In addition, writing a critique essay encourages you to become an active participant in the intellectual discourse surrounding a particular topic or field. By engaging with a work and providing your own analysis, you are contributing to the ongoing conversation and expanding the collective understanding of the subject matter.
Furthermore, a critique essay can serve as a useful tool for the creator of the work being critiqued. Constructive criticism can provide valuable insights and suggestions for improvement, helping the creator gain a fresh perspective and refine their skills.
Ultimately, the importance of writing a critique essay lies in its ability to foster critical thinking, contribute to intellectual discourse, and provide constructive feedback. Whether you are a student honing your analytical skills or a professional offering insights in your field, learning how to effectively critique a work is a valuable and essential skill.
Choosing a Topic for Your Critique Essay

When it comes to writing a critique essay, the first and most important step is choosing a topic that is both interesting and suitable for critique. The topic you choose will determine the direction and focus of your essay, as well as the arguments and evidence you will present. It is crucial to select a topic that you are passionate about and have a strong opinion on, as this will make the writing process more enjoyable and engaging.
When considering potential topics for your critique essay, it can be helpful to brainstorm a list of subjects that you have recently encountered in your studies, personal life, or current events. This can include books, movies, artworks, scientific studies, political speeches, or social issues. Reflect on your experiences and think about which topics have sparked your interest or elicited an emotional response.
Once you have a list of potential topics, narrow it down to one that you feel confident in critiquing. Consider the availability of resources and research materials related to the topic, as well as the relevance and significance of the subject matter. It is important to choose a topic that is not too broad or too narrow, but one that allows for a thorough analysis and evaluation.
Furthermore, when selecting a topic for your critique essay, consider the potential audience and the purpose of your writing. Are you writing for a specific academic or professional audience, or for a general readership? Is your goal to persuade, inform, or entertain? Understanding your audience and purpose will help you choose a topic that is relevant, engaging, and appropriate for your intended readers.
In conclusion, the process of choosing a topic for your critique essay requires careful consideration and reflection. By selecting a topic that you are passionate about, narrowing down your options, and considering the audience and purpose of your writing, you can ensure that your critique essay is engaging, informative, and well-structured.
Effective Methods for Analyzing and Evaluating the Work

When it comes to critiquing a piece of work, it is important to employ effective methods for analyzing and evaluating the work. These methods allow you to objectively assess the strengths and weaknesses of the work while providing constructive feedback.
One method for analyzing the work is to carefully examine the overall structure and organization. This involves evaluating the flow of ideas and the logical progression of the work. Pay attention to how well the work introduces and supports its main argument or thesis statement. Look for any inconsistencies or gaps in the logic and assess the effectiveness of the transitions between ideas.
Additionally, it is important to assess the use of evidence and examples in the work. Look for both quantitative and qualitative evidence that supports the main argument. Evaluate the credibility and relevance of the sources cited and determine if they strengthen the overall argument. Consider the quality of the examples provided and how well they illustrate the key points of the work.
Another critical aspect to evaluate in the work is the clarity and effectiveness of the writing style. Assess the use of language, considering factors such as clarity, conciseness, and precision. Look for any instances of wordiness or ambiguity and consider how well the writer communicates their ideas. Pay attention to the use of tone and voice and evaluate if they are appropriate for the intended audience.
Furthermore, it is essential to consider the originality and creativity of the work. Analyze whether the ideas presented are innovative and unique, or if they rely heavily on existing research and ideas. Evaluate the extent to which the writer brings a fresh perspective or contributes new insights to the topic. Consider the level of critical thinking and depth of analysis demonstrated in the work.
Finally, it is crucial to provide constructive feedback when evaluating the work. Identify specific strengths and weaknesses and provide evidence to support your analysis. Offer suggestions for improvement and recommend areas where the writer can further develop their ideas or arguments. Remember to maintain a balance between positive and negative feedback to help the writer grow and improve their work.
- Analyze the overall structure and organization of the work
- Assess the use of evidence and examples
- Evaluate the clarity and effectiveness of the writing style
- Analyze the originality and creativity of the ideas presented
- Provide constructive feedback and suggestions for improvement
By utilizing these effective methods for analyzing and evaluating the work, you will be able to provide a comprehensive critique that offers valuable insights and helps the writer enhance their work.
Tips for Writing a Strong and Persuasive Critique Essay
When crafting a critique essay, it is essential to adopt a strong and persuasive writing style to effectively convey your thoughts and opinions. By employing certain techniques and considerations, you can enhance the impact of your critique and make it more persuasive. This section will provide valuable tips to help you write a compelling critique essay.
| Be clear and concise | |
| Provide evidence and examples | |
| Offer a balanced perspective | |
| Use persuasive language and rhetorical devices | |
| Structure your critique effectively | |
| Consider your target audience | |
| Support your arguments with credible sources |
First and foremost, clarity and conciseness are key. Make sure your critique is written in a clear and straightforward manner, avoiding any unnecessary jargon or complex language. This will ensure that your ideas are easily understood by your readers, allowing them to fully grasp your perspective.
Additionally, providing evidence and examples is crucial to strengthen your critique. Back up your opinions with credible sources, such as research studies, statistical data, or expert opinions. This will make your arguments more persuasive and lend credibility to your critique.
It is also important to offer a balanced perspective in your critique. While expressing your own views, be sure to acknowledge and address counterarguments or differing opinions. This will demonstrate your ability to consider multiple perspectives and make your critique more comprehensive and well-rounded.
Using persuasive language and rhetorical devices can significantly enhance the impact of your critique. Employ techniques such as persuasive appeals (ethos, logos, pathos), rhetorical questions, metaphors, and analogies to captivate your readers and engage them on an emotional and intellectual level.
Structuring your critique in a logical and organized manner is another essential aspect. Break down your critique into distinct sections, such as introduction, body paragraphs discussing various aspects of the subject, and a conclusion summarizing your main points and reinforcing your overall perspective. This will make your critique more coherent and reader-friendly.
Consider your target audience when writing your critique. Tailor your language, tone, and style to resonate with your intended readers. Adapt your arguments and examples to align with their interests, values, and beliefs. This will make your critique more relatable and persuasive to your specific audience.
Lastly, support your arguments with credible sources. Incorporating research findings, expert opinions, or firsthand experiences will strengthen the validity of your critique and provide additional weight to your arguments. This will make your critique more persuasive and enhance its overall impact.
By following these tips, you can ensure that your critique essay is not only strong but also persuasive. By employing clear and concise language, providing evidence and examples, offering a balanced perspective, using persuasive language and rhetorical devices, structuring effectively, considering your target audience, and supporting your arguments with credible sources, you can craft a compelling critique essay that effectively conveys your thoughts and opinions.
Related Post
How to master the art of writing expository essays and captivate your audience, convenient and reliable source to purchase college essays online, step-by-step guide to crafting a powerful literary analysis essay, unlock success with a comprehensive business research paper example guide, unlock your writing potential with writers college – transform your passion into profession, “unlocking the secrets of academic success – navigating the world of research papers in college”, master the art of sociological expression – elevate your writing skills in sociology.
How to Write a Critique Paper: Format, Tips, & Critique Essay Examples
A critique paper is an academic writing genre that summarizes and gives a critical evaluation of a concept or work. Or, to put it simply, it is no more than a summary and a critical analysis of a specific issue. This type of writing aims to evaluate the impact of the given work or concept in its field.
Want to learn more? Continue reading this article written by Custom-writing experts! It contains:
- best tips on how to critique an article or a literary work,
- a critique paper example with introduction, body, and conclusion.
💁 What Is a Critique Paper?
- 👣 Critical Writing Steps
👀 Critical Essay Types
📝 critique paper format, 📑 critique paper outline, 🔗 references.
A critique is a particular academic writing genre that requires you to carefully study, summarize, and critically analyze a study or a concept. In other words, it is nothing more than a critical analysis. That is all you are doing when writing a critical essay: trying to understand the work and present an evaluation. Critical essays can be either positive or negative, as the work deserves.
👣 How to Write a Critique Essay: Main Steps
Starting critique essays is the most challenging part. You are supposed to substantiate your opinion with quotes and paraphrases, avoiding retelling the entire text. A critical analysis aims to find out whether an article or another piece of writing is compelling. First, you need to formulate the author’s thesis: what was the literary work supposed to convey? Then, explore the text on how this main idea was elaborated. Finally, draft your critique according to the structure given below.
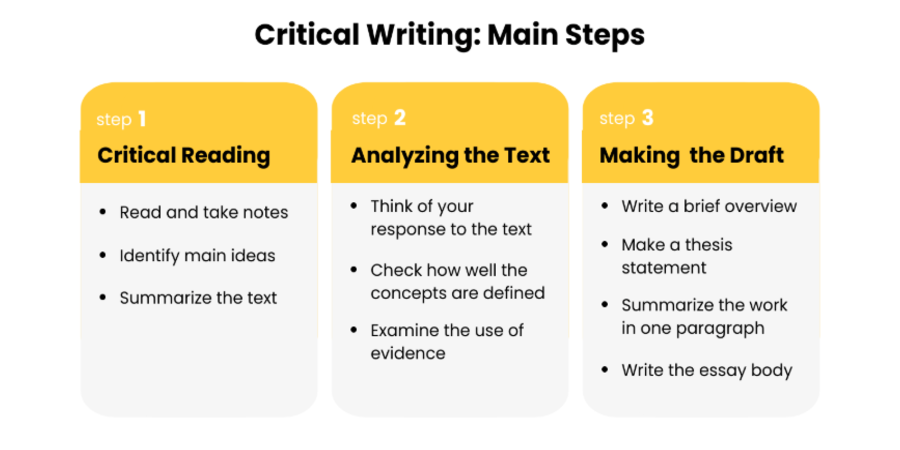
Step 1: Critical Reading
1.1. Attentively read the literary work. While reading, make notes and underline the essentials.
- Try to come into the author’s world and think why they wrote such a piece.
- Point out which literary devices are successful. Some research in literary theory may be required.
- Find out what you dislike about the text, i.e., controversies, gaps, inconsistency, or incompleteness.
1.2. Find or formulate the author’s thesis.
- What is the principal argument? In an article, it can be found in the first paragraph.
- In a literary work, formulate one of the principal themes, as the thesis is not explicit.
- If you write a critique of painting, find out what feelings, emotions, or ideas, the artist attempted to project.
1.3. Make a summary or synopsis of the analyzed text.
- One paragraph will suffice. You can use it in your critique essay, if necessary.
- The point is to explore the gist.
Step 2: Analyzing the Text
After the reading phase, ask yourself the following questions :
- What was your emotional response to the text? Which techniques, images, or ideas made you feel so?
- Find out the author’s background. Which experiences made them raise such a thesis? What other significant works have they written that demonstrate the general direction of thought of this person?
- Are the concepts used correctly in the text? Are the references reliable, and do they sufficiently substantiate the author’s opinion?
Step 3: Drafting the Essay
Finally, it is time to draft your essay. First of all, you’ll need to write a brief overview of the text you’re analyzing. Then, formulate a thesis statement – one sentence that will contain your opinion of the work under scrutiny. After that, make a one-paragraph summary of the text.
You can use this simple template for the draft version of your analysis. Another thing that can help you at this step is a summary creator to make the creative process more efficient.
Critique Paper Template
- Start with an introductory phrase about the domain of the work in question.
- Tell which work you are going to analyze, its author, and year of publication.
- Specify the principal argument of the work under study.
- In the third sentence, clearly state your thesis.
- Here you can insert the summary you wrote before.
- This is the only place where you can use it. No summary can be written in the main body!
- Use one paragraph for every separate analyzed aspect of the text (style, organization, fairness/bias, etc.).
- Each paragraph should confirm your thesis (e.g., whether the text is effective or ineffective).
- Each paragraph shall start with a topic sentence, followed by evidence, and concluded with a statement referring to the thesis.
- Provide a final judgment on the effectiveness of the piece of writing.
- Summarize your main points and restate the thesis, indicating that everything you said above confirms it.
You can evaluate the chosen work or concept in several ways. Pick the one you feel more comfortable with from the following:
- Descriptive critical essays examine texts or other works. Their primary focus is usually on certain features of a work, and it is common to compare and contrast the subject of your analysis to a classic example of the genre to which it belongs.
- Evaluative critical essays provide an estimate of the value of the work. Was it as good as you expected based on the recommendations, or do you feel your time would have been better spent on something else?
- Interpretive essays provide your readers with answers that relate to the meaning of the work in question. To do this, you must select a method of determining the meaning, read/watch/observe your analysis subject using this method, and put forth an argument.
There are also different types of critiques. The University of North Carolina-Chapel Hill, in the article “ Writing critiques ,” discusses them as well as the appropriate critique language.
Critique Paper Topics
- Critique of the article Is Google Making Us Stupid? by Nicholas Carr .
- Interpret the symbolism of Edgar Alan Poe’s The Black Cat .
- Examine the topicality of the article Impact of Racial/Ethnic Differences on Child Mental Health Care .
- Critical essay on Alice Walker’s short story Everyday Use .
- Discuss the value of the essay The Hanging by George Orwell.
- A critique on the article Stocks Versus Bonds: Explaining the Equity Risk Premium .
- Explore the themes Tennessee Williams reveals in The Glass Menagerie.
- Analyze the relevance of the article Leadership Characteristics and Digital Transformation .
- Critical evaluation of Jonathan Harvey’s play Beautiful Thing .
- Analyze and critique Derek Raymond’s story He Died with His Eyes Open .
- Discuss the techniques author uses to present the problem of choice in The Plague .
- Examine and evaluate the research article Using Evidence-Based Practice to Prevent Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia .
- Explore the scientific value of the article Our Future: A Lancet Commission on Adolescent Health and Wellbeing .
- Describe the ideas E. Hemingway put into his A Clean, Well-Lighted Place .
- Analyze the literary qualities of Always Running La Vida Loca: Gang Days in L. A .
- Critical writing on The Incarnation of Power by Wright Mills.
- Explain the strengths and shortcomings of Tim Kreider’s article The Busy Trap .
- Critical response to Woolf’s novel Mrs. Dalloway .
- Examine the main idea of Richard Godbeer’s book Escaping Salem .
- The strong and weak points of the article The Confusion of Tongues by William G. Bellshaw .
- Critical review of Gulliver’s Travels .
- Analyze the stylistic devices Anthony Lewis uses in Gideon’s Trumpet.
- Examine the techniques Elie Wiesel uses to show relationship transformation in the book Night .
- Critique of the play Fences by August Wilson.
- The role of exposition in Achebe’s novel Things Fall Apart.
- The main themes John Maxwell discusses in his book Disgrace .
- Critical evaluation of Ray Bradbury’s Fahrenheit 451 .
- The ideas and concept of the book The Vegetarian Imperative .
- Different points of view on one historical figure in the book Two Lives of Charlemagne .
Since the APA critique paper format is one of the most common, let’s discuss it in more detail. Check out the information below to learn more:
The APA Manual recommends using the following fonts:
- 11-point Calibri,
- 11-point Arial,
- 10-point Lucida Sans Unicode,
- 12-point Times New Roman,
- 11-point Georgia,
- 10-point Computer Modern.
Add 1-inch margins on all sides.
📌 Page numbers
Page numbers should appear at the top right-hand corner, starting with the title page.
📌 Line spacing
The entire document, including the title page and reference list, should be double-spaced.
📌 Title page
The title page should include the following information:
- page number 1 in the top right-hand corner of the page header,
- paper title,
- the student’s name,
- the name of the department and the college or university,
- course number and name,
- the instructor’s name,
- due date (the date format used in your country).
📌 Critique paper title
The title of your critique paper should be no more than 12 words. In addition, it should be centered and typed in bold using title case.
📌 In-text citations
For the in-text citation, provide the author’s last name and publication year in brackets. If you are using direct citation, add the page number after the year.
📌 References
The last page of your paper should include a list of all sources cited in your essay. Here’s a general format of book and journal article citations you should use:
Book: Last name, First initial. Middle initial. (Year). Book title: Subtitle . Publisher.
Journal article: Last name, First initial. Middle initial. (Year). Title of the article. Journal Title, volume (issue number), start page–end page.
The main parts of good critical response essays are:
- Introduction. The introduction is the most essential part of the critical response. It should be concise and include the author and title of the work being analyzed, its main idea, and a strong thesis statement.
- Summary. This should be brief and to the point. Only the author’s/creator’s main ideas and arguments should be included.
- Analysis/interpretation. Discuss what the author’s/creator’s primary goal was and determine whether this goal was reached successfully. Use the evidence you have gathered to argue whether or not the author/creator achieved was adequately convincing (remember there should be no personal bias in this discussion).
- Evaluation/response. At this point, your readers are ready to learn your objective response to the work. It should be professional yet entertaining to read. Do not hesitate to use strong language. You can say that the work you analyzed was weak and poorly-structured if that is the case, but keep in mind that you have to have evidence to back up your claim.
- Conclusion. The last paragraph of your work should restate the thesis statement, summarize the key points, and create a sense of closure for the readers.
Critique Paper Introduction
The introduction is setting the stage for your analysis. Here are some tips to follow when working on it:
- Provide the reader with a brief synopsis of the main points of the work you are critiquing .
- State your general opinion of the work , using it as your thesis statement. The ideal situation is that you identify and use a controversial thesis.
- Remember that you will uncover a lot of necessary information about the work you are critiquing. You mustn’t make use of all of it, providing the reader with information that is unnecessary in your critique. If you are writing about Shakespeare, you don’t have to waste your or your reader’s time going through all of his works.
Critique Paper Body
The body of the critique contains the supporting paragraphs. This is where you will provide the facts that prove your main idea and support your thesis. Follow the tips below when writing the body of your critique.
- Every paragraph must focus on a precise concept from the paper under your scrutiny , and your job is to include arguments to support or disprove that concept. Concrete evidence is required.
- A critical essay is written in the third-person and ensures the reader is presented with an objective analysis.
- Discuss whether the author was able to achieve their goals and adequately get their point across.
- It is important not to confuse facts and opinions . An opinion is a personal thought and requires confirmation, whereas a fact is supported by reliable data and requires no further proof. Do not back up one idea with another one.
- Remember that your purpose is to provide the reader with an understanding of a particular piece of literature or other work from your perspective. Be as specific as possible.
Critique Paper Conclusion
Finally, you will need to write a conclusion for your critique. The conclusion reasserts your overall general opinion of the ideas presented in the text and ensures there is no doubt in the reader’s mind about what you believe and why. Follow these tips when writing your conclusion:
- Summarize the analysis you provided in the body of the critique.
- Summarize the primary reasons why you made your analysis .
- Where appropriate, provide recommendations on how the work you critiqued can be improved.
For more details on how to write a critique, check out the great critique analysis template provided by Thompson Rivers University.
If you want more information on essay writing in general, look at the Secrets of Essay Writing .
Example of Critique Paper with Introduction, Body, and Conclusion
Check out this critical response example to “The Last Inch” by James Aldridge to show how everything works in practice:
Introduction
In his story “The Last Inch,” James Aldridge addresses the issue of the relationship between parents and children. The author captured the young boy’s coming into maturity coinciding with a challenging trial. He also demonstrated how the twelve-year-old boy obtained his father’s character traits. Aldridge’s prose is both brutal and poetic, expressing his characters’ genuine emotions and the sad truths of their situations.
Body: Summary
The story is about Ben Ensley, an unemployed professional pilot, who decides to capture underwater shots for money. He travels to Shark Bay with his son, Davy. Ben is severely injured after being attacked by a shark while photographing. His last hope of survival is to fly back to the little African hamlet from where they took off.
Body: Analysis
The story effectively uses the themes of survival and fatherhood and has an intriguing and captivating plot. In addition, Ben’s metamorphosis from a failing pilot to a determined survivor is effectively presented. His bond with his son, Davy, adds depth and emotional importance to the story. At the same time, the background information about Ben’s past and his life before the shark attack could be more effectively integrated into the main story rather than being presented as separate blocks of text.
Body: Evaluation
I find “The Last Inch” by James Aldridge a very engaging and emotional story since it highlights the idea of a father’s unconditional love and determination in the face of adversity. I was also impressed by the vivid descriptions and strong character development of the father and son.
Conclusion
“The Last Inch” by James Aldridge is an engaging and emotional narrative that will appeal to readers of all ages. It is a story of strength, dedication, and the unbreakable link between father and son. Though some backstory could be integrated more smoothly, “The Last Inch” impresses with its emotional punch. It leaves the readers touched by the raw power of fatherly love and human will.
📚 Critique Essay Examples
With all of the information and tips provided above, your way will become clearer when you have a solid example of a critique essay.
Below is a critical response to The Yellow Wallpaper by Charlotte Perkins Gilman.
When speaking of feminist literature that is prominent and manages to touch on incredibly controversial issues, The Yellow Wallpaper is the first book that comes to mind. Written from a first-person perspective, magnifying the effect of the narrative, the short story by Charlotte Perkins Gilman introduces the reader to the problem of the physical and mental health of the women of the 19th century. However, the message that is intended to concern feminist ideas is rather subtle. Written in the form of several diary entries, the novel offers a mysterious plot, and at the same time, shockingly realistic details.
What really stands out about the novel is the fact that the reader is never really sure how much of the story takes place in reality and how much of it happens in the psychotic mind of the protagonist. In addition, the novel contains a plethora of description that contributes to the strain and enhances the correlation between the atmosphere and the protagonist’s fears: “The color is repellent, almost revolting; a smoldering unclean yellow, strangely faded by the slow-turning sunlight” (Gilman).
Despite Gilman’s obvious intent to make the novel a feminist story with a dash of thriller thrown in, the result is instead a thriller with a dash of feminism, as Allen (2009) explains. However, there is no doubt that the novel is a renowned classic. Offering a perfect portrayal of the 19th-century stereotypes, it is a treasure that is certainly worth the read.
If you need another critique essay example, take a look at our sample on “ The Importance of Being Earnest ” by Oscar Wilde.
And here are some more critique paper examples for you check out:
- A Good Man Is Hard to Find: Critique Paper
- Critique on “The Yellow Wallpaper” by Charlotte Perkins Gilman
- “When the Five Rights Go Wrong” Article Critique
- Homer’s Iliad and Odyssey — Comparison & Critique
- Benefits and Disadvantages of Prone Positioning in Severe Acute Respiratory Distress: Article Critique
- Reducing Stress in Student Nurses: Article Critique
- Management of Change and Professional Safety – Article Critique
- “Views of Young People Towards Physical Activity”: Article Critique
Seeing an example of a critique is so helpful. You can find many other examples of a critique paper at the University of Minnesota and John Hopkins University. Plus, you can check out this video for a great explanation of how to write a critique.
- Critical Analysis
- Writing an Article Critique
- The Critique Essay
- Critique Essay
- Writing a Critique
- Writing A Book Critique
- Media Critique
- Tips for an Effective Creative Writing Critique
- How to Write an Article Critique
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to LinkedIn
- Share to email

What is a creative essay, if not the way to express yourself? Crafting such a paper is a task that allows you to communicate your opinion and tell a story. However, even using your imagination to a great extent doesn’t free you from following academic writing rules. Don’t even get...

A compare and contrast essay — what is it? In this type of paper, you compare two different things or ideas, highlighting what is similar between the two, and you also contrast them, highlighting what is different. The two things might be events, people, books, points of view, lifestyles, or...

What is an expository essay? This type of writing aims to inform the reader about the subject clearly, concisely, and objectively. The keyword here is “inform”. You are not trying to persuade your reader to think a certain way or let your own opinions and emotions cloud your work. Just stick to the...
![what is critique essay Short Story Analysis: How to Write It Step by Step [New]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/man-sits-end-trolltunga-before-mountains-284x153.jpg)
Have you ever tried to write a story analysis but ended up being completely confused and lost? Well, the task might be challenging if you don’t know the essential rules for literary analysis creation. But don’t get frustrated! We know how to write a short story analysis, and we are...

Have you ever tried to get somebody round to your way of thinking? Then you should know how daunting the task is. Still, if your persuasion is successful, the result is emotionally rewarding. A persuasive essay is a type of writing that uses facts and logic to argument and substantiate...
![what is critique essay Common Essay Mistakes—Writing Errors to Avoid [Updated]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/avoid-mistakes-ccw-284x153.jpg)
One of the most critical skills that students gain during their college years is assignment writing. Composing impressive essays and research papers can be quite challenging, especially for ESL students. Nonetheless, before learning the art of academic writing, you may make numerous common essay mistakes. Such involuntary errors appear in:...

You’re probably thinking: I’m no Mahatma Gandhi or Steve Jobs—what could I possibly write in my memoir? I don’t even know how to start an autobiography, let alone write the whole thing. But don’t worry: essay writing can be easy, and this autobiography example for students is here to show...
![what is critique essay Why I Want to Be a Teacher Essay: Writing Guide [2024]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/senior-male-professor-writing-blackboard-with-chalk3-284x153.jpg)
Some people know which profession to choose from childhood, while others decide much later in life. However, and whenever you come to it, you may have to elaborate on it in your personal statement or cover letter. This is widely known as “Why I Want to Be a Teacher” essay.
![what is critique essay Friendship Essay: Writing Guide & Topics on Friendship [New]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/smiley-female-friends-fist-bumping-284x153.jpg)
Assigned with an essay about friendship? Congrats! It’s one of the best tasks you could get. Digging through your memories and finding strong arguments for this paper can be an enjoyable experience. I bet you will cope with this task effortlessly as we can help you with the assignment. Just...

When you are assigned an autobiography to write, tens, and even hundreds of questions start buzzing in your head. How to write autobiography essay parts? What to include? How to make your autobiography writing flow? Don’t worry about all this and use the following three simple principles and 15 creative...

A life experience essay combines the elements of narration, description, and self-reflection. Such a paper has to focus on a single event that had a significant impact on a person’s worldview and values. Writing an essay about life experience prompts students to do the following: You may struggle with such...

Who has made a significant impact in your life and why? Essay on the topic might be challenging to write. One is usually asked to write such a text as a college admission essay. A topic for this paper can be of your choice or pre-established by the institution. Either...
May I know who’s the author? For my citation activity.

Hello, Kriszha! You can reference it as a web source/web page.
Wow…great work… kindly can you assist me in writing a critique about indiscipline in a school
That’s an interesting demonstration I watched. However, my weakness is that I’m very poor in language and analysing issues.
Hi, can you help me for my assignment about article critiquing?
I need your help if you can send me a full written dissertation..thank you
This is gud
Can you help me to my activities
Thank you so much! This really helped me!
How to Write a Critical Essay
Hill Street Studios / Getty Images
- An Introduction to Punctuation
Olivia Valdes was the Associate Editorial Director for ThoughtCo. She worked with Dotdash Meredith from 2017 to 2021.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Olivia-Valdes_WEB1-1e405fc799d9474e9212215c4f21b141.jpg)
- B.A., American Studies, Yale University
A critical essay is a form of academic writing that analyzes, interprets, and/or evaluates a text. In a critical essay, an author makes a claim about how particular ideas or themes are conveyed in a text, then supports that claim with evidence from primary and/or secondary sources.
In casual conversation, we often associate the word "critical" with a negative perspective. However, in the context of a critical essay, the word "critical" simply means discerning and analytical. Critical essays analyze and evaluate the meaning and significance of a text, rather than making a judgment about its content or quality.
What Makes an Essay "Critical"?
Imagine you've just watched the movie "Willy Wonka and the Chocolate Factory." If you were chatting with friends in the movie theater lobby, you might say something like, "Charlie was so lucky to find a Golden Ticket. That ticket changed his life." A friend might reply, "Yeah, but Willy Wonka shouldn't have let those raucous kids into his chocolate factory in the first place. They caused a big mess."
These comments make for an enjoyable conversation, but they do not belong in a critical essay. Why? Because they respond to (and pass judgment on) the raw content of the movie, rather than analyzing its themes or how the director conveyed those themes.
On the other hand, a critical essay about "Willy Wonka and the Chocolate Factory" might take the following topic as its thesis: "In 'Willy Wonka and the Chocolate Factory,' director Mel Stuart intertwines money and morality through his depiction of children: the angelic appearance of Charlie Bucket, a good-hearted boy of modest means, is sharply contrasted against the physically grotesque portrayal of the wealthy, and thus immoral, children."
This thesis includes a claim about the themes of the film, what the director seems to be saying about those themes, and what techniques the director employs in order to communicate his message. In addition, this thesis is both supportable and disputable using evidence from the film itself, which means it's a strong central argument for a critical essay .
Characteristics of a Critical Essay
Critical essays are written across many academic disciplines and can have wide-ranging textual subjects: films, novels, poetry, video games, visual art, and more. However, despite their diverse subject matter, all critical essays share the following characteristics.
- Central claim . All critical essays contain a central claim about the text. This argument is typically expressed at the beginning of the essay in a thesis statement , then supported with evidence in each body paragraph. Some critical essays bolster their argument even further by including potential counterarguments, then using evidence to dispute them.
- Evidence . The central claim of a critical essay must be supported by evidence. In many critical essays, most of the evidence comes in the form of textual support: particular details from the text (dialogue, descriptions, word choice, structure, imagery, et cetera) that bolster the argument. Critical essays may also include evidence from secondary sources, often scholarly works that support or strengthen the main argument.
- Conclusion . After making a claim and supporting it with evidence, critical essays offer a succinct conclusion. The conclusion summarizes the trajectory of the essay's argument and emphasizes the essays' most important insights.
Tips for Writing a Critical Essay
Writing a critical essay requires rigorous analysis and a meticulous argument-building process. If you're struggling with a critical essay assignment, these tips will help you get started.
- Practice active reading strategies . These strategies for staying focused and retaining information will help you identify specific details in the text that will serve as evidence for your main argument. Active reading is an essential skill, especially if you're writing a critical essay for a literature class.
- Read example essays . If you're unfamiliar with critical essays as a form, writing one is going to be extremely challenging. Before you dive into the writing process, read a variety of published critical essays, paying careful attention to their structure and writing style. (As always, remember that paraphrasing an author's ideas without proper attribution is a form of plagiarism .)
- Resist the urge to summarize . Critical essays should consist of your own analysis and interpretation of a text, not a summary of the text in general. If you find yourself writing lengthy plot or character descriptions, pause and consider whether these summaries are in the service of your main argument or whether they are simply taking up space.
- Critical Analysis in Composition
- Writing About Literature: Ten Sample Topics for Comparison & Contrast Essays
- What Is a Critique in Composition?
- Definition and Examples of Analysis in Composition
- A Critical Analysis of George Orwell's 'A Hanging'
- What Are the Different Types and Characteristics of Essays?
- literary present (verbs)
- Book Report: Definition, Guidelines, and Advice
- personal statement (essay)
- Definition Examples of Collage Essays
- Definition and Examples of Evaluation Essays
- Composition Type: Problem-Solution Essays
- What Is Plagiarism?
- The Power and Pleasure of Metaphor
- Quotes About Close Reading
- What Is a Compelling Introduction?

- Writing well
How to write a critique
- Starting well
- How to write an annotated bibliography
- How to write a case study response
- How to write an empirical article
- How to write an essay
- How to write a literature review
- How to write a reflective task
- How to write a report
- Finishing well
Before you start writing, it is important to have a thorough understanding of the work that will be critiqued.
- Study the work under discussion.
- Make notes on key parts of the work.
- Develop an understanding of the main argument or purpose being expressed in the work.
- Consider how the work relates to a broader issue or context.
Example template
There are a variety of ways to structure a critique. You should always check your unit materials or Canvas site for guidance from your lecturer. The following template, which showcases the main features of a critique, is provided as one example.
Introduction
Typically, the introduction is short (less than 10% of the word length) and you should:
- name the work being reviewed as well as the date it was created and the name of the author/creator
- describe the main argument or purpose of the work
- explain the context in which the work was created - this could include the social or political context, the place of the work in a creative or academic tradition, or the relationship between the work and the creator’s life experience
- have a concluding sentence that signposts what your evaluation of the work will be - for instance, it may indicate whether it is a positive, negative, or mixed evaluation.
Briefly summarise the main points and objectively describe how the creator portrays these by using techniques, styles, media, characters or symbols. This summary should not be the focus of the critique and is usually shorter than the critical evaluation.
Critical evaluation
This section should give a systematic and detailed assessment of the different elements of the work, evaluating how well the creator was able to achieve the purpose through these. For example: you would assess the plot structure, characterisation and setting of a novel; an assessment of a painting would look at composition, brush strokes, colour and light; a critique of a research project would look at subject selection, design of the experiment, analysis of data and conclusions.
A critical evaluation does not simply highlight negative impressions. It should deconstruct the work and identify both strengths and weaknesses. It should examine the work and evaluate its success, in light of its purpose.
Examples of key critical questions that could help your assessment include:
- Who is the creator? Is the work presented objectively or subjectively?
- What are the aims of the work? Were the aims achieved?
- What techniques, styles, media were used in the work? Are they effective in portraying the purpose?
- What assumptions underlie the work? Do they affect its validity?
- What types of evidence or persuasion are used? Has evidence been interpreted fairly?
- How is the work structured? Does it favour a particular interpretation or point of view? Is it effective?
- Does the work enhance understanding of key ideas or theories? Does the work engage (or fail to engage) with key concepts or other works in its discipline?
This evaluation is written in formal academic style and logically presented. Group and order your ideas into paragraphs. Start with the broad impressions first and then move into the details of the technical elements. For shorter critiques, you may discuss the strengths of the works, and then the weaknesses. In longer critiques, you may wish to discuss the positive and negative of each key critical question in individual paragraphs.
To support the evaluation, provide evidence from the work itself, such as a quote or example, and you should also cite evidence from related sources. Explain how this evidence supports your evaluation of the work.
This is usually a very brief paragraph, which includes:
- a statement indicating the overall evaluation of the work
- a summary of the key reasons, identified during the critical evaluation, why this evaluation was formed
- in some circumstances, recommendations for improvement on the work may be appropriate.
Reference list
Include all resources cited in your critique. Check with your lecturer/tutor for which referencing style to use.
- Mentioned the name of the work, the date of its creation and the name of the creator?
- Accurately summarised the work being critiqued?
- Mainly focused on the critical evaluation of the work?
- Systematically outlined an evaluation of each element of the work to achieve the overall purpose?
- Used evidence, from the work itself as well as other sources, to back and illustrate my assessment of elements of the work?
- Formed an overall evaluation of the work, based on critical reading?
- Used a well structured introduction, body and conclusion?
- Used correct grammar, spelling and punctuation; clear presentation; and appropriate referencing style?
Further information
- University of New South Wales: Writing a Critical Review
- University of Toronto: The Book Review or Article Critique
Global links and information
- Referencing and using sources
- Background and development
- Changes to QUT cite|write
- Need more help?
- Current students
- Current staff
- TEQSA Provider ID: PRV12079 (Australian University)
- CRICOS No. 00213J
- ABN 83 791 724 622
- Last modified: 28-May-2024
- Accessibility
- Right to Information
- Feedback and suggestions

Acknowledgement of Traditional Owners
QUT acknowledges the Traditional Owners of the lands where QUT now stands.

Writing Critiques
Writing a critique involves more than pointing out mistakes. It involves conducting a systematic analysis of a scholarly article or book and then writing a fair and reasonable description of its strengths and weaknesses. Several scholarly journals have published guides for critiquing other people’s work in their academic area. Search for a “manuscript reviewer guide” in your own discipline to guide your analysis of the content. Use this handout as an orientation to the audience and purpose of different types of critiques and to the linguistic strategies appropriate to all of them.
Types of critique
Article or book review assignment in an academic class.
Text: Article or book that has already been published Audience: Professors Purpose:
- to demonstrate your skills for close reading and analysis
- to show that you understand key concepts in your field
- to learn how to review a manuscript for your future professional work
Published book review
Text: Book that has already been published Audience: Disciplinary colleagues Purpose:
- to describe the book’s contents
- to summarize the book’s strengths and weaknesses
- to provide a reliable recommendation to read (or not read) the book
Manuscript review
Text: Manuscript that has been submitted but has not been published yet Audience: Journal editor and manuscript authors Purpose:
- to provide the editor with an evaluation of the manuscript
- to recommend to the editor that the article be published, revised, or rejected
- to provide the authors with constructive feedback and reasonable suggestions for revision
Language strategies for critiquing
For each type of critique, it’s important to state your praise, criticism, and suggestions politely, but with the appropriate level of strength. The following language structures should help you achieve this challenging task.
Offering Praise and Criticism
A strategy called “hedging” will help you express praise or criticism with varying levels of strength. It will also help you express varying levels of certainty in your own assertions. Grammatical structures used for hedging include:
Modal verbs Using modal verbs (could, can, may, might, etc.) allows you to soften an absolute statement. Compare:
This text is inappropriate for graduate students who are new to the field. This text may be inappropriate for graduate students who are new to the field.
Qualifying adjectives and adverbs Using qualifying adjectives and adverbs (possible, likely, possibly, somewhat, etc.) allows you to introduce a level of probability into your comments. Compare:
Readers will find the theoretical model difficult to understand. Some readers will find the theoretical model difficult to understand. Some readers will probably find the theoretical model somewhat difficult to understand completely.
Note: You can see from the last example that too many qualifiers makes the idea sound undesirably weak.
Tentative verbs Using tentative verbs (seems, indicates, suggests, etc.) also allows you to soften an absolute statement. Compare:
This omission shows that the authors are not aware of the current literature. This omission indicates that the authors are not aware of the current literature. This omission seems to suggest that the authors are not aware of the current literature.
Offering suggestions
Whether you are critiquing a published or unpublished text, you are expected to point out problems and suggest solutions. If you are critiquing an unpublished manuscript, the author can use your suggestions to revise. Your suggestions have the potential to become real actions. If you are critiquing a published text, the author cannot revise, so your suggestions are purely hypothetical. These two situations require slightly different grammar.
Unpublished manuscripts: “would be X if they did Y” Reviewers commonly point out weakness by pointing toward improvement. For instance, if the problem is “unclear methodology,” reviewers may write that “the methodology would be more clear if …” plus a suggestion. If the author can use the suggestions to revise, the grammar is “X would be better if the authors did Y” (would be + simple past suggestion).
The tables would be clearer if the authors highlighted the key results. The discussion would be more persuasive if the authors accounted for the discrepancies in the data.
Published manuscripts: “would have been X if they had done Y” If the authors cannot revise based on your suggestions, use the past unreal conditional form “X would have been better if the authors had done Y” (would have been + past perfect suggestion).
The tables would have been clearer if the authors had highlighted key results. The discussion would have been more persuasive if the authors had accounted for discrepancies in the data.
Note: For more information on conditional structures, see our Conditionals handout .

Make a Gift
- All eBooks & Audiobooks
- Academic eBook Collection
- Home Grown eBook Collection
- Off-Campus Access
- Literature Resource Center
- Opposing Viewpoints
- ProQuest Central
- Course Guides
- Citing Sources
- Library Research
- Websites by Topic
- Book-a-Librarian
- Research Tutorials
- Use the Catalog
- Use Databases
- Use Films on Demand
- Use Home Grown eBooks
- Use NC LIVE
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary vs. Secondary
- Scholarly vs. Popular
- Make an Appointment
- Writing Tools
- Annotated Bibliographies
- Summaries, Reviews & Critiques
- Writing Center
Service Alert

Article Summaries, Reviews & Critiques
- Writing an article SUMMARY
- Writing an article REVIEW
Writing an article CRITIQUE
- Citing Sources This link opens in a new window
- About RCC Library
Text: 336-308-8801
Email: [email protected]
Call: 336-633-0204
Schedule: Book-a-Librarian
Like us on Facebook
Links on this guide may go to external web sites not connected with Randolph Community College. Their inclusion is not an endorsement by Randolph Community College and the College is not responsible for the accuracy of their content or the security of their site.
A critique asks you to evaluate an article and the author’s argument. You will need to look critically at what the author is claiming, evaluate the research methods, and look for possible problems with, or applications of, the researcher’s claims.
Introduction
Give an overview of the author’s main points and how the author supports those points. Explain what the author found and describe the process they used to arrive at this conclusion.
Body Paragraphs
Interpret the information from the article:
- Does the author review previous studies? Is current and relevant research used?
- What type of research was used – empirical studies, anecdotal material, or personal observations?
- Was the sample too small to generalize from?
- Was the participant group lacking in diversity (race, gender, age, education, socioeconomic status, etc.)
- For instance, volunteers gathered at a health food store might have different attitudes about nutrition than the population at large.
- How useful does this work seem to you? How does the author suggest the findings could be applied and how do you believe they could be applied?
- How could the study have been improved in your opinion?
- Does the author appear to have any biases (related to gender, race, class, or politics)?
- Is the writing clear and easy to follow? Does the author’s tone add to or detract from the article?
- How useful are the visuals (such as tables, charts, maps, photographs) included, if any? How do they help to illustrate the argument? Are they confusing or hard to read?
- What further research might be conducted on this subject?
Try to synthesize the pieces of your critique to emphasize your own main points about the author’s work, relating the researcher’s work to your own knowledge or to topics being discussed in your course.
From the Center for Academic Excellence (opens in a new window), University of Saint Joseph Connecticut
Additional Resources
All links open in a new window.
Writing an Article Critique (from The University of Arizona Global Campus Writing Center)
How to Critique an Article (from Essaypro.com)
How to Write an Article Critique (from EliteEditing.com.au)
- << Previous: Writing an article REVIEW
- Next: Citing Sources >>
- Last Updated: Mar 15, 2024 9:32 AM
- URL: https://libguides.randolph.edu/summaries
Improve your writing in one of the largest and most successful writing groups online
Join our writing group!
Critique vs. Criticism: How to Write a Good Critique, with Examples

by Daniel Rodrigues-Martin
Understanding critique vs. criticism
We all assign merit to the information we experience daily. We “judge” what we hear on the news. We “evaluate” a university lecture. We “like” or “dislike” a movie, a meal, a photo, a story. We’re all critics.
Some writer-readers struggle with this point, especially if they are young to writing and editing. Sitting in a judgment of another writer’s work often feels distasteful, and doing so may conjure negative memories of when we were misunderstood or dismissed by others.
Conversely, we might be willing to share our opinions with other writers while struggling with our competence. We can’t seem to say anything constructive. If we’re critiquing on Scribophile, we may feel that we are wasting one of the author’s coveted “spotlight” critiques.
Having used Scribophile on-and-off since 2009, I’ve seen countless readers qualify their commentary on my own work (“I don’t read your genre,” “I haven’t read your previous chapters,” “I’m not good with grammar,” etc.) and I’ve seen even more cry woe on the forums about how they can’t critique because they’re not experienced enough, not educated enough, or not talented enough. Others decry the very sort of criticism writers’ groups and workshop sites like Scribophile foster, suggesting that the perfunctory nature of such criticism is ultimately more harmful than helpful.
Scribophile as a community thrives on the principle of serious commitment to serious writing, and the foundation of that commitment is reading and responding to others’ work. If you want to explore some elements helpful to improving your critiquing skills, I invite you to get yourself some hot caffeine, strap on your thinking cap, and read on.
How to write a great critique in 3 steps
Listed here are some ideas I’ve found helpful for approaching others’ work; these tips are about your mindset as a critic. These ideas are by no means exhaustive. The best teacher is experience, and I encourage all writers to reflect on the ways in which they approach others’ work as well as how they can best contribute to the growth of others on and off of Scribophile.
1. If you’re genuine, you’ll be constructive
Being constructive means coming to the critique with the ultimate goal of helping the writer improve. It means always criticizing with good intentions for the writer. It does not equate to coddling—being so nice you’ll never say a hard thing—nor does it equate to browbeating—being so hard you’ll never say a nice thing.
Being dishonest or refusing to offer valid criticism where you’re able is a disservice to the writer. Don’t shy away from honesty. Few things are more constructive than hard truths delivered by critics who genuinely want to help and who tailor their criticism with an attitude of genuine interest.
As you interact with works on Scribophile or elsewhere, remember to always approach the task of criticism with a desire to be genuinely helpful. If your criticism is built on this foundation, your commentary will be constructive regardless of your competence and experience.
2. No jerks
As for literary criticism in general: I have long felt that any reviewer who expresses rage and loathing for a novel or a play or a poem is preposterous. He or she is like a person who has put on full armor and attacked a hot fudge sundae or a banana split. —Kurt Vonnegut
Few things will more quickly deflate a writer than unnecessarily harsh criticism. Being honest and being brutal are not the same thing. Critics must learn to express hard truths without coddling and without being jerks.
Even rude people can be good writers with valuable insights into the craft. The problem is that if you express valid insights obnoxiously, the author won’t care. In order for people to listen, they must feel that the person criticizing them has their best interest in mind, and being harsh doesn’t communicate your best interest.
In my earliest days writing, I received some negative criticism from a writer who decided to berate me for penning a bad phrase rather than explaining to me why the phrase didn’t work. Because he was rude, I insulated myself to his criticism. Years later, I reviewed the work and realized his criticism was valid. The problem was not the content of his criticism, but its malicious delivery. Had he come to my work with the desire to be genuinely helpful, I would have listened to what he had to say, and I might even have gained some enlightenment during a formative time in my writing career. The critic did me doubly wrong not only by being obnoxious, but by retarding my growth as a writer.
Unnecessarily harsh criticism is a sign of literary and personal immaturity. Don’t be a jerk.
3. Don’t be too timid
Flattering friends corrupt. —St. Augustine
Every writer likes to be praised, especially by those not obligated to praise them due to marital status or having given birth to them. But depthless praise can be just as damaging as heartless criticism. The reason for this is that it offers no real commentary on the work.
Refusing to offer criticism where it’s needed is one of the greatest disservices you as a critic can do for other writers. Some critics may fret that their criticism might be too discouraging if fully disclosed. Critics must contend with the reality that writing is art, people have opinions about art, and those opinions are not always going to be eruptions of praise. There is no safer environment to honestly and succinctly point out problem areas in a piece of writing than a forum designed for that very purpose.
None of this is to say that you shouldn’t commend a piece of work if it truly is fantastic or that you should not highlight the gems within a work. Again: constructive criticism is honest criticism. If a work is so well-crafted in your eyes that nothing worse than grammatical hiccups are present, tell the writer. They deserve to know they’ve done a fine job. Sometimes people genuinely deserve a “well done.” Don’t skimp on encouragement where it can be authentically offered. Even if a piece is messy, do your best to find a few strong points to highlight. It will express your best interest—especially if you had a lot of hard things to say.
The difference between a critique vs. criticism is whether it’s constructive
Be constructive , meaning, have the best intentions for helping the writer. This may mean telling hard truths. If hard truths must be told, do so respectfully. If praise is deserved, offer it. Highlight the strong points of a piece—even if they are far outweighed by the negative points. Be genuine in your motivations, and genuine action will follow.
Considering authorial intent while critique writing
This section concerns authorial intent and has as its purpose the critic’s growth as an interpreter of that intent. This section is not so much about judging an author’s intent as it’s about being aware of that intent and factoring that awareness into your commentary.
1. Context is king
It is important to appreciate the amount of subjectivity and pre-understanding all readers and listeners bring to the process of interpreting acts of human communication. But unless a speaker or author can retain the right to correct someone’s interpretation by saying ‘but that’s not what I meant’ or ‘that’s not even consistent with what I meant,’ all human communication will quickly break down. —Craig L. Blomberg
While interpreters are always within their rights to read whatever they want however they want to, what they are not at liberty to decide is authorial intent —what the author desired the audience to receive from their work.
As a reader and a critic, you must be careful to understand an author’s work on their own terms while also interpreting those words. There is a substantial difference between, “This is how I’m hearing what you’re saying,” and, “This is what I say your words mean.” Don’t presume to tell an author what their work is supposed to mean, but do tell them how you’re interpreting what they’ve written.
A work-in-progress can suffer from a variety of ailments. Contextual questions are not cut-and-dry like questions of syntax, grammar, or, to a degree, plotting. Questions of context have to do with the interaction of author intent and reader interpretation. They’re murky waters to navigate because you as the reader have to exercise a bit of telepathy; you have to try and get inside the author’s head, ultimately “What is the author trying to convey with this sentence, this piece? Who is this piece for, and will it successfully communicate with that target audience? Is it clear that there is a target audience?”
Some authors are great at genre pieces; they know all the chords to strike, they know what the tone of the piece should be, the kinds of characters who should appear. Other authors can completely muck it up. They’ll write a romance piece that reads like a technical manual or a flowery memoir with a tangle of dead-ending tangents. It’s not always easy and natural for new critics to explain why something does or doesn’t work, but innately, we know. When those moments come up, let the author know.
2. The unintended/unspoken
Asking the question, “Is that really what you meant?” isn’t always bad. All of us have been misunderstood. Sometimes the results are humorous, but other times, we’re grateful for the opportunity to correct misunderstandings.
If in your criticism you find yourself questioning the use of a word or phrase, or even of a character, idea, or plot point, it’s advisable to bring such questions to the writer’s attention. It may just be you, but it may not just be you. Unless the writer has a philosophical axe to grind, they probably mean to communicate clearly, and it should at least be made known that they may have botched it up.
Conversely, there are instances where things left unwritten speak volumes. Perhaps a character “falls off the radar” in mid-scene, and it leaves you scratching your head? It may be appropriate to point out confusing instances of the unwritten for the author’s consideration.
Because my own novel employs many neologisms, critics jumping in mid-story often highlight those neologisms to make sure I’m using them as intended. While it can get tedious to say to myself, “Yes, that is what it means,” I am always thankful for keen eyes. This is the kind of sharp, considerate criticism each of us should aim for and be thankful for if we receive it.
3. Accounting for genre and intended audience
A genre is “A category of artistic composition, as in music or literature, marked by a distinctive style, form, or content.” When reading an author’s work, it’s crucial to take into account its genre and intended audience. If you’re even-handed in your critiquing, you’ll at some point be reading a story in a genre you might not otherwise touch, and while you might wish Twilight had been a one-off rather than a worldwide phenomenon, it’s inappropriate to harshly judge an author’s work simply because you don’t like their sort of story.
Consider the question of author intent and how that intent will resonate with an intended (or unintended!) audience. Sometimes, you must ignore whether or not a story resonates with you personally. Instead, ask yourself if it would resonate with your vampire-novel-loving daughter. Are the story, plot devices, characters, and verbiage appropriate for the intended audience? If yes, why or why not? If no, why or why not? Your personal tastes should not dictate the quality of your criticism. Train yourself to offer valuable insight even on writing you’d never pay money to read.
Remember these principles when reading work outside your sphere of interest. Being constructive doesn’t mean you have to love or even like the work. If something is written well, it’s written well—prejudices aside. If you’re truly unable to be objective, you would do the writer a better service by moving on.
4. Don’t pretend to be a non-writer
A film director watches other films differently than a moviegoer. A chef tastes a meal differently than the average person. As a writer, you necessarily see stories differently than non-writers. That’s not a bad thing.
We can be helpful to other writers by sharing our gut reactions no differently than an unversed beta reader. On the other hand, writers should be able to explain with more clarity than the average person why something does or doesn’t work in a story. A writer’s insight is of a different quality than a non-initiate’s insight. Both are needed for success, because if a writer one day moves on to pitch their work to those in the literary establishment, that work will not be judged by average readers until after it has survived the professional gauntlet.
All readers have the ability to share their gut reactions, but not all readers can slip on their “writer glasses” and offer critique on that level. Good critiques provide both types of insight, so as a fellow writer, bring your full experience to bear in helping others embarking on the same journey.
Understanding intent is part of a good critique
As best as you’re able, judge an author’s work on the basis of their intent—this includes noting instances of the unintended! In consideration of genre, judge the work not on the basis of your interest in the genre, but on the author’s skill at writing a piece that strikes the proper chords within the genre they’ve chosen. It’s not possible for you to read as a reader only, so don’t pretend to be something you’re not.
What makes a good critique?
A good writer may come out of any intellectual discipline at all. Every art and science gives the writer its own special ways of seeing, gives him experience with interesting people, and can provide him with means of making a living… It is not necessary—or perhaps even advisable—that the young writer major in literature. —John Gardner
Contrary to the belief of a lot of new writers, learning to write and critique doesn’t require sixty-four credits of college English or an MFA. Plenty of writers and editors don’t hold English or Creative Writing degrees, and while I in no way wish to discourage those who choose to improve their writing and reviewing by taking the high road of formal education, neither do I wish to discourage the 98% of you reading this who haven’t and won’t be able to front the money and time for such an education.
The ability to forge valid criticism is an applied skill learned through a combination of technical knowledge and experience. We’re fortunate to live in an age where vast quantities of technical information are available at our fingertips. Contemporary writers are able to write informed literature like never before. So, too, are critics able to fact-check writers like never before.
Just as you’re willing to fact-check history or science before you include something in your story, it doesn’t hurt to do that for those you critique. Granted, they should do that themselves, but maybe they’re writing a genre you write, or maybe they’re writing about your field of work or interest? Being educated or experienced in any field will enrich not only your writing, but your critiquing. If you’re a fry cook, your ability to write or critique a scene in a modern commercial kitchen is better than that of someone who hasn’t had that experience. Because you know what it’s like to really work in a kitchen, you can speak to the authenticity of any such scene, and you can speak to the authenticity of the kinds of people who work in commercial kitchens. Your grammar may not be the best, but you still have something valuable to contribute.
Great writers are keen observers of life, and their writing both informs and is by informed by life. Bring the authenticity of your life to your writing and your criticism. You have perspectives, knowledge, and experiences others don’t. As you read and respond to authors, employ the skills and knowledge you already possess. Put your formal and informal education and your life experience to work. This is what it means to “write what you know” and, in our case, “critique what you know.”
Immerse yourself in all sorts of stories to get better at critiquing
One of the cardinal “writing for dummies” rules is that if you want to write well, you need to read a lot. I don’t doubt the validity of this statement, but books are only one medium of storytelling among many. My contention is that by immersing yourself in movies, television, and other storytelling mediums, you can learn about dialogue, plot, characterization, and all the other aspects of “storytelling” that appear no matter what medium you choose.
If you want to understand what makes a story great, seek out great stories. Immerse yourself in them. Though you may not be able to verbalize it, your innate understanding of what makes a narrative work will grow. This will improve both your writing and your critiquing.
Steal critiquing techniques from smart people–yourself included
Consider the critiques that have been most helpful to you. Why did they work? Reread them if you must. Then find a way to adapt the good things from those critiques into your own criticism.
Consider the critiques you’ve shared that have been helpful to others. What stood out to the author? You may even consider asking an author for feedback on your critique. Ask how you could have been more helpful.
Critiquing is a skill you can improve over time just like writing itself. But like writing, it takes practice and discipline. Make it easier on yourself by nurturing what works.
A reading list to improving your critique writing skills
There are many solid books on writing that will not only improve your writing, but your critical reading skills. Rather than provide you a hundred sources, here are a few I’ve been able to get my claws on, have dug into, and can personally vouch for:
Good Prose , by Tracy Kidder & Richard Todd. The writer-editor combo of The Atlantic share their wisdom through a tightly-edited, insightful, and entertaining survey of nonfiction writing that has plenty of benefit for writers of all stripes. The book’s section on “proportion and order” in narrative has revolutionized my own thinking about how stories should be structured.
How to Write Science Fiction and Fantasy , by Orson Scott Card. A good resource if you write these genres, Card provides practical advice on publishing, agents, etc., in addition to familiarizing the reader with dos and don’ts for writing Sci-Fi/Fantasy, including some technical questions. The book’s a bit dated by now—especially the parts about the publishing world—but there are some nuggets of timeless truth within.
On Becoming a Novelist , by John Gardner. Despite the Modernistic tendency of abusing the pronoun “he,” this may be the most formative thing I’ve read about novel writing. It’s slim, readable, practical, and comprehensive.
On Writing , by Stephen King. Something of an autobiography penned by one of the most successful authors of all time, this book is snappy, humorous, entertaining, and more than a little instructive for anyone looking to write and read better. King reminds his fellow writers that “Life isn’t a support system for art; it’s the other way around.”
Story , by Robert McKee. Considered by many to be the “screenwriter’s bible,” Story belongs in the library of every serious writer whether or not they ever aspire to the silver screen. McKee is a master of properly balancing a plot to satisfy an audience, and all writers should glean from his wisdom.
The Modern Library Writer’s Workshop , by Stephen Koch. Koch flexes his student’s muscles by providing copious citations from the masters who have graced the past few centuries of literature. The author fades into the background at points while readers are treated to the musings and experiences of Dostoevsky, Flannery O’Connor, Hemingway, and others.
The Writer’s Journey: Mythic Structure for Writers , by Christopher Vogler. Vogler is one of the most proficient living writers of the entertainment industry. Working primarily from the theses of the late cultural anthropologist, Joseph Campbell, Vogler illustrates the plot devices and character tropes that underlie the world’s oldest stories. Recommended for new writers of the speculative fiction genres and those who wish to write epics.
The value of criticism and critiquing
The arts too can be taught, up to a point; but except for certain matters of technique, one does not learn the arts, one simply catches on. —John Gardner
The value of criticism is twofold: First and most obviously, it helps others. Second, and maybe not as apparent if you’re new to critiquing: It improves your own writing.
As you examine the work of others, you’ll be able to see what works and what doesn’t work. You will begin to notice patterns as you edit your own writing, and you’ll begin to sift out the problem areas. It’s difficult to judge your own work objectively. Doing it for others helps you get a clear head and recognize the ways in which you do the very things you criticize others for doing.
This article hasn’t had as a goal the outlining of a criticism “process.” The reason for this is that I could no more outline a criticism process than I could outline a fiction writing process. There is no single monolithic “right way to do it” that will unequivocally work for everyone. Herein are general guidelines and considerations that I’ve found helpful over the years and that others have appreciated. If you write critiques constructively, taking consideration of what the author is trying to do, and if you do so authentically, drawing on your experiences and knowledge, you’re on the right track for writing great critiques. The details of how exactly you accomplish that will become clearer to you as you engage in criticism. As in any discipline: Seek feedback and keep going.
Appendix I: “Line edits” and “critiques”
“Line edits” and “critiques” are not the same thing. These two types of reader responses address different issues, and in order to ensure that you receive the kind of criticism you’re seeking, you need to know what you’re displaying.
A “line edit” is a thorough, line-by-line examination of a manuscript. A good line edit requires an editor with a keen eye for detail and a working knowledge of contemporary grammar, syntax, and idiomatic English. The purpose of a line edit is to make a manuscript as readable as possible by removing technical errors. Typically, works that receive line edits receive them because they’re in need of them.
A “critique” is an in-depth review, touching on characterization, plot, theme, scene structure, poetry of language, and other related factors. Notice how I didn’t list anything about spelling or proper comma usage? It’s because that’s not critiquing; that’s editing. Typically, works that receive criticism as described here are free or mostly free of errors that distract readers from the story.
No one is perfect, and one of the best tools at our disposal on Scribophile is the inline critique option. Having never read nor submitted a flawless piece of writing for review, I can tell you that no one should be ashamed to receive a line edit. There are many sharp eyes and sharp minds browsing Scribophile, and even the best writer’s eyes glaze over after so many hours of staring at a white screen.
That said, part of what is absolutely necessary to receive genuine criticism as described above is a readable text. An unreadable text has never, in my experience, provided foundation for a fantastic piece of writing. Messy prose screams “messy story.” If you want criticism of story, your text must be as clean as possible.
If you’re willing to admit that your mastery of the technicalities of writing is not the sharpest, by all means, employ the knowledge and expertise of those on this site who do; it’s a wonderful resource. Readers can’t truly resonate with your story until you weave a piece of art that makes them forget they’re experiencing a piece of art. When you’re able to achieve this, you’ve removed the hurdles preventing your reader from authentically engaging with the story you’ve created. It’s at this stage in your writing that you can consistently receive deep criticism.
This is, of course, not to say that imperfect prose can’t be critiqued. Part of writing great critiques is learning to spot the gems in the story and encouraging the writer to press onward in spite of any shortcomings. If you’re honest and genuine, this won’t be a problem.
If all else fails, list at the top of your submitted piece the sort of critique you’re seeking by highlighting specific questions. “I’d love to know how you reacted when X happened,” for example. This will encourage readers to engage with the sorts of questions you’re asking.
Appendix II: The Benefits and Limits of Critique Groups
If you understand how to best leverage critique groups, they will be helpful and formative to your growth. As written above, critiquing others helps you grow; but there is more. The benefits of critique groups are threefold.
First, broad exposure. Want to know what people outside of your social circle will think of your work? A critique group will expose your work to people of different backgrounds. You can learn how a teen writer with big dreams or a Native American ex-botanist writing a memoir in retirement reacts to your story. This is the type of demographic insight you’d pay good money for when it comes time to sell your book. Even in small chunks, it’s valuable to know how different people experience your work.
Second, many eyes forge sharper prose. If three different people all trip over the same thing in your text, the problem is most likely not those three people, but your text. Especially if your text is hot off the press, you can catch errors early, and writers tend to be sharper with these sorts of things than the general population. Go look up the cost of a professional manuscript editor in your area, and you’ll be glad for many eyes combing over your writing.
Third, and most importantly: networking. The goal of sites like Scribophile and in-person critique groups should be to develop a network of people who will read the entirety of your work. Don’t get angry at forks for not being spoons—a reader jumping in mid-story will never give you the same level of commentary as someone who’s been reading since chapter one. If you’re ready for that level of reading, you need others to agree to read the book from start to finish. Use critique groups and sites like Scribophile to build relationships. Be attentive to others and share good critiques with them. As your relationships deepen, you’ll eventually find yourself with a list of contacts to trade with. But this requires you to be the kind of person people want reading their work. Behave professionally, and over time, you’ll find yourself surrounded by likeminded individuals who will give you the kind of meaty, informed commentary you need. The rule of thumb with critique groups and workshop websites is: You get out what you put in to them.
Appendix III: Still confused?
If you have questions I have failed to address in this article, I encourage you to contact me privately here on Scribophile or to reach out on social media. I’m happy to help.
Get feedback on your writing today!
Scribophile is a community of hundreds of thousands of writers from all over the world. Meet beta readers, get feedback on your writing, and become a better writer!
Join now for free

Related articles

What Distinguishes Literary Nonfiction From Traditional Nonfiction

How to Find a Literary Agent

How to Get an ISBN

What is a Literary Agent?

What Is a Beta Reader? (And Why You Need One!)

How to Become a Beta Reader
- Dissertation
- PowerPoint Presentation
- Book Report/Review
- Research Proposal
- Math Problems
- Proofreading
- Movie Review
- Cover Letter Writing
- Personal Statement
- Nursing Paper
- Argumentative Essay
- Research Paper
- Discussion Board Post
Critique Essay: Your Comprehensive Guide to Writing A+ Critique Essays

Table of Contents
Just like a concept essay , a critique essay is an essential assignment that examines another author’s work to analyze and interpret it. This task is common in college, and it’s also called an analytical essay .
But how do you handle this task and score excellent grades? This guide delves into all the details of composing an A+ critical paper. Read to learn more.
What Is a Critique Essay?
Let’s set the ball rolling by defining a critique essay . It is an academic assignment that summarizes a text and critically evaluates its validity. It aims to evaluate a given text’s impact in a specific discipline and shows whether the evaluated text achieved its intended goal or didn’t.
This assignment needs careful study of the texts before summarizing and critically analyzing them. Your main task is to understand the piece and present your critical assessment. Your final verdict can be negative or positive, depending on the work’s quality and analysis. We can summarize this paper in the following four terms.
- A description that gives readers a sense of the writer’s overall goal with their publications.
- An analysis that examines how the text’s structure and language convey its meaning.
- An interpretation that states each of the work’s parts’ significance.
- An assessment that judges the piece’s overall worth or value.
Types of Critique Essays
Critique essays come in three main forms, as discussed below.
- Descriptive
This essay examines a text or other works. It primarily focuses on a work’s specific features. Comparing and contrasting your analysis subject to a classic example of its genre is also possible.
- Evaluative
This analytical essay estimates a work’s value. It shows if it’s as good as you expected based on the recommendations or if you feel it wasted your time.
- Interpretive
Interpretive essays give your readers answers relating to a work’s meaning. To achieve this goal, you must choose a technique for establishing that meaning. For instance, you may read, watch, or observe your analysis subject before floating arguments.

Critique Essay Outline
Writing an excellent critique essay is difficult without an outline. An outline is the only way to save writing time and organize your ideas where they should fit. This step requires you to determine the evidence and arguments you will evaluate. These arguments support and validate your thesis statement.
Additionally, your paper’s outline shows you how your essay will look. After creating the wireframe, you may adjust it or add more details to make your writing more effective. Your skeleton takes the traditional five-paragraph essay format.
Introduction
Your work needs an introduction paragraph. This section opens with an introductory phrase about the work you are analyzing. It tells the reader what you will critique, who the author is, and provide its publication date. The intro specifies the work’s core argument. Its third sentence contains your thesis statement.
Your work requires a summary paragraph to show the reader what you discussed in the body paragraphs. This section follows your introduction and leads to a detailed discussion.
Your main body comprises three to five paragraphs or more if necessary. Each section addresses a given text dimension, like bias, tone, style, or organization. Moreover, every paragraph confirms your thesis statement regarding the piece’s effectiveness. Each body paragraph opens with a topic sentence summarizing the subsection. Next, you introduce your evidence and close the chapter by referring to the thesis.
Your conclusion gives your final verdict on a given piece’s effectiveness. This strong conclusion paragraph summarizes your main ideas and paraphrases your thesis statement to confirm that everything you discussed confirmed it.
How to Start a Critique Essay
Starting your critique essay is easy if you follow the correct process. This discussion explores how to commence this assignment.
Critical Reading
- Read the Literary Piece Carefully
Your journey starts by reading the piece you have to critique to understand it. Your careful reading should immerse you into the author’s world and imagine why they drafted their work. Also, take note and underscore essential facts. Your assignment must also highlight which literary tools succeeded in achieving the material’s goal. Lastly, determine what you dislike about the piece, such as incompleteness, gaps, or inconsistencies.
- Formulate the Author’s Thesis
Use the text you read to formulate the author’s thesis or primary arguments. You can find this argument in the paper’s introduction. If you are handling literary work, create one of the key themes because the thesis isn’t clear.
- Summarize the Analyzed Text
You need one paragraph to summarize your paper’s content and give the reader a gist of what you covered. It should come between the introduction and the three body paragraphs.
Analyze the Text
Analyze your text before composing your assignment. Your analysis should lead you to the following critical questions:
- How did your emotions respond to the text, and which methods, images, or ideas made you feel so?
- Based on the author’s background, which experiences made them formulate such a thesis?
- What other significant works has the author produced to demonstrate their general thought direction?
- Have you used the concepts correctly in the text?
- Are your references reliable, and do they adequately prove the author’s judgment?
Write Your Critical Essay
Lastly, draft your critique essay by writing a brief overview of the text you are examining. Next, formulate your thesis statement reflecting your stand on the work you are critiquing. Afterward, write a summary paragraph that captures the paper’s essence. Below are essential questions to ask and answer to ensure you did the correct thing:
- Who created the piece you are critiquing?
- Did you present your work objectively or subjectively?
- What is your work’s aim, and were they attained?
- What methods, styles, and media did the author use, and did they achieve their goal?
- What assumptions underlie the work, and how do they influence its validity?
- What forms of evidence or persuasion did you use, and is your evidence interpreted fairly?
- How is the material structured?
- Does the work favor a specific interpretation or viewpoint, and how effective is it?
- Does the work promote an understanding of vital ideas or theories?
- How does the piece resonate or fail to resonate with primary concepts or other works in its discipline?
Example of Critique Essay On Articles
An article-related critique essay is a paper that evaluates an article to determine its effectiveness in attaining a goal. An article could comprise opinions, personal experiences, and external research. This essay entertains, informs, persuades, or educates readers. An article critique differs from a summary because a summary doesn’t offer a critical analysis. A critique, in its turn, resembles a review because it evaluates the author’s ability to fulfill its stated purpose. Your article critique must back its claims regarding an issue through evidence in the text and other external sources.
A Sample Article Critique Paper
Nothing teaches better than an excellent model of what you are learning. Here’s a sample article critique paper.
The Education Sector Cannot Solve Problems It Doesn’t Acknowledge (David and Nelson, 2021). New York, a state in the United States of America, fully understands this problem and has formulated initiatives and policies to improve equity in public schools at all levels. Education policymakers have implemented an All-Inclusive Response Strategy(ARS) to achieve this noble goal. The practical goal of this strategy is to ensure that all New York children enjoy inclusive education. This approach seeks to eliminate biases, barriers, or power dynamics that discourage students’ learning potential. Acknowledging educational challenges and committing to developing solutions is the most critical step school administrators can take to support the education system. However, these principal players should formulate proper thought, research, and policy guidelines to ensure their policies and strategies include all the potential issues and leave enough room for improvement.
The procedures also proposed religious tolerance and accommodation, anti-discrimination, and all forms of harassment. This inclusive policy must have sound techniques for how other stakeholders will implement, review, and monitor it henceforth. Fortunately, New York has succeeded on this front. This article evaluates how well this equity program was executed in the state as it endeavors to promote equity and inclusivity in its public schools…
Do you still have questions regarding a critique essay ? This section answers some of the most frequently asked questions in this essay.
What are the five parts of a critique essay ?
A perfect critique paper comprises five sections, namely: the introduction, the summary paragraph, the first paragraph, the second paragraph, the third paragraph, and the conclusion.
What is an example of a critique?
A critique essay example should meet all assignment requirements. It also comprises all the essential components, as mentioned in question one.
What are the four rules of critique?
The four rules governing a good critique essay are as follows:
- An effective introduction that provides a quick background review, defines the necessary terminology, and ends with a thesis.
- A summary that gives a broad overview of what the source discusses.
- A critique that shows your personal opinion, supported by evidence.
A conclusion that summarizes your main ideas, reminds your readers of your thesis, and concludes the paper.

How Can I Make An A+ Editing Checklist For My Essay?
How to start a research paper, 100 proposal topics ideas for your assignment.
Definition of Critique
Examples of critique in literature, example #1: the guardian (by philip hope-wallace), example #2: the washington post (by the washington post), example #3: hamlet: poem unlimited (by harold bloom), example #4: the daily telegraph (by victoria lambert), function of critique, post navigation.
How to Structure and Write an Effective Critique Paper
Critique papers are an essential part of academic writing, especially in the fields of humanities and social sciences. They involve analyzing a piece of work and objectively evaluating its strengths and weaknesses. Writing a critique paper can be challenging, requiring careful reading, research, and analysis. Yet, it is possible to produce a high-quality essay with careful planning and attention to detail.
This article will teach you how to write an article critique by explaining the types of critique essays, their structure, and the steps involved in how to write a critique essay. The article also provides essay tips for producing a well-written and effective critique.
What is a Critique Paper?
A critique paper is an academic paper as a response to a body of work, such as a play, concept, scholarly article, poetry, book, or research paper. Its purpose is to objectively assess the work in question, highlighting its strengths and weaknesses. But also to provide a detailed analysis of its content, structure, and methodology.
This kind of essay can be one of the trickiest assignments, and not everyone can produce a well-scrutinized, original piece of writing. That’s why many students reach for assistance from analytical essay writing services that guarantee to handle the job with the help of professional writers and experts. These services proved to be of high quality and effective support to many schoolers who chose to try them in a variety of different disciplines.
Knowing how to write an article critique requires careful reading, analysis, and an evaluative approach. A well-written critique paper example demonstrates the writer’s ability to analyze and evaluate works. It should also be organized logically, guiding the reader through the analysis. Additionally, writers should be aware of their biases and assumptions and strive to critique objectively. On a final note, it’s essential to review the guidelines and follow the required structure. This is to ensure that the article critique meets the assignment’s expectations.
Types of Critical Essays
There are several types of essays of this kind, each with its approach and focus. To follow we have a list of the most common ones.
Descriptive
A descriptive critical essay combines elements of descriptive writing with a thorough analysis. In this type of essay, the writer describes a particular work in detail and then evaluates it based on certain criteria. They can provide a deep and insightful understanding of the work using sensory details and descriptive language.
An evaluative essay consists of a personal judgment to evaluate the value or effectiveness of a particular work or idea. In this type of essay, the writer analyzes the work and expresses their opinion on its merits or shortcomings. At the same time, they must avoid personal bias and focus on facts rather than one’s opinions or feelings. However, it’s also essential to provide a personal perspective and interpretation of the work as long as it’s supported by evidence.
Interpretive
This type of essay involves analyzing and interpreting the meaning and significance of the work being evaluated. It delves deeper into the themes, symbolism, and underlying conveyed messages. When writing an interpretive essay, it’s important to be clear and concise. Avoid confusing the reader by using jargon or unnecessarily complex language.
Structure of Critique Paper
The structure of a typical critique essay example includes an introduction, a summary, an analysis, and a conclusion. The paper format is a crucial element. Just like when you write your research papers , a critique benefits from a clear one to guide the reader. Therefore, work on defining the critique essay outline before starting the writing process. One of the most common formatting styles to adopt is the APA format (APA: American Psychological Association), which has specific rules and guidelines. And keep in mind that some specific elements should be included in each section:
Introduction: The introduction’s function is to provide background relevant information. It should also include the thesis statement, which is the writer’s main argument or position on the topic. The thesis statement should be clear and specific and presented in a way that engages the reader.
Summary: The summary provides an overview of the text. It must be objective, unbiased, and accurately summarize the piece’s main points. The summary has to be brief and to the point and should only include the most important details of the work.
Analysis: The analysis is where the writer provides their evaluation of the text being critiqued. This section is the most detailed and extensive part of the paper, containing the facts that prove your main argument and support your thesis. The analysis should focus on the thesis statement and provide a clear and logical argument.
Conclusion: In the conclusion, the paper’s main points are summarized, and the thesis statement is restated to emphasize the writer’s main position. It should provide a final evaluation of the work and include recommendations for improvement.
Essential Steps to Write a Critique Essay
Critique writing requires a thoughtful and detailed approach. You can find below the essential steps to follow:
Read and observe the work:
Before beginning the essay, you should read and observe the work, taking notes on its relevant elements. It is crucial to pay attention to details and to identify both strengths and weaknesses.
Conduct research:
In addition to analyzing the work, you need to research the author, director, or artist and the work’s historical and cultural context. This step can be time and effort-consuming. That’s why as a student who’s probably stuck with many assignments, you can consider to pay for research paper , which will solve the problem most efficiently. The research can provide valuable insights into the work and help you develop a more informed critique.
Develop a thesis statement:
Based on the analysis of the work and any research conducted, you should develop a clear and specific thesis statement that accurately presents your main argument or evaluation of the piece.
Write your critique:
Once you have your thesis statement, you can begin writing your critique essay. Begin by providing some background information on the work in an introduction. In the body of your essay, provide evidence and analysis to support your evaluation. Use specific examples and quotes from the text to support your arguments. Consider including external sources to provide additional context or compare the work to similar works. Finally, end your essay with a conclusion summarizing your main points and restating your thesis statement.
Revise and edit:
After completing the first draft of your essay, you should revise and edit it carefully. Pay attention to your argument’s structure, clarity, and coherence. Also, ensure that your essay logically progresses from one concept to the next. It’s important to note that when you format an essay , considerations may vary depending on the assignment’s specific requirements. Some may require additional sections, such as a discussion of the author’s background or a comparison to other works.
How to start a critique paper?
Starting a critique paper requires careful consideration and preparation. It is important to read and understand the subject thoroughly, including its purpose, structure, and context. Once you have a clear understanding of the subject, you should identify specific criteria to use in your evaluation, such as style, structure, effectiveness, relevance, and accuracy. Taking notes on the subject’s strengths, weaknesses, and areas for improvement will help you organize your thoughts, and creating an outline that includes the introduction, analysis, and conclusion will ensure a well-structured paper. Finally, a strong thesis statement that clearly states your evaluation of the subject and the criteria you will use to evaluate it is crucial to the success of your critique paper.
How can I write a critique paper on a research article?
To write a critique paper on a research article, it is essential to consider key areas such as the research question and hypothesis, methodology, results, and overall evaluation. Firstly, determine whether the research question is clear, relevant, and testable. Secondly, evaluate the methodology used in the study to determine whether it’s appropriate for the research question. Thirdly, analyze the results presented in the research article to determine whether they are consistent with the research question and hypothesis. Lastly, evaluate the overall quality and contribution of the research article to the field. By considering these areas, you can provide a comprehensive critique of the research article.
What is the difference between summarizing and critiquing an article?
Many students struggle to distinguish between the two. They often summarize the work, neglecting to adopt a personal approach and use analytical skills. In such cases, custom essay writing service Edusson is the best option to handle the job for you. It also helps you improve your critical thinking and practical skills.
Related posts:
- 6 Step Process for Essay Writing
- How to Write a Diagnostic Essay (Without Fail)
- The Full Guide to Writing Comparison Essays with Point-by-Point Method
- Footnotes 101: A Guide to Proper Formatting
Improve your writing with our guides

How to Write a Scholarship Essay

Definition Essay: The Complete Guide with Essay Topics and Examples

Critical Essay: The Complete Guide. Essay Topics, Examples and Outlines
Get 15% off your first order with edusson.
Connect with a professional writer within minutes by placing your first order. No matter the subject, difficulty, academic level or document type, our writers have the skills to complete it.
100% privacy. No spam ever.


Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 8: Being Critical
8.1 What Makes a Critique a Critique?
Learning Objectives
- Define what it means to critique
- Explain the differences between a critique and other essay forms
This section will introduce you to another essay form instructors often ask their students to produce: the critique.
A critique is a written work critically analyzing or evaluating another piece of writing; also known as a review or critical response.
What Is a Critique?
When you see the word critique , the first thing you may think of is to criticize . In actuality, critiques do not need to look only at the negative aspects of a source; they can also focus on the positive components or even have a mix of the positive and negative elements. They are critical response papers analyzing and evaluating an original source , such as the academic journal article you are being asked to use for this assignment.
Self-Practice Exercise 8.1
H5P: Reading Critical Response
Read the following short critique, and then come up with a list of elements you believe make this a critique as opposed to an expository paper.
Vetter and Perlstein’s work on terrorism and its future is an excellent basis for evaluating views and attitudes to terrorism before the tragic events of 9/11. Written in 1991, the book provides an objective (but more theoretical) view on what terrorism is, how it can be categorized, and to what ideology it can be linked. Perspectives on Terrorism is a multifaceted review of numerous factors that impact and influence the global development of terrorism; those studying sociology or criminal justice might find ample information regarding the ideological roots and typology of terrorism as a phenomenon and as a specific type of violent ideology that has gradually turned into a dominant force of political change.
Vetter and Perlstein (1991) begin their work with the words “it has almost become pro forma for writers on terrorism to begin by pointing out how hard it is to define the term terrorism.” However, the authors do not waste their time trying to define what terrorism is; rather, they are trying to look at terrorism through the prism of its separate elements, and objectively evaluate the concept of public acceptability of terrorism as a notion. Trying to answer the two critical questions “why surrogate the war?” and “who sponsors terrorism?” Vetter and Perlstein (1991) evaluate terrorism as a unjustifiable method of violence for the sake of unachievable goals, tying the notion of terrorism to the notion of morality.
To define terrorism in its present form it is not enough to determine the roots and the consequences of particular terrorist act; nor is it enough to evaluate the roots and the social implications of particular behavioural characteristics beyond morality. On the contrary, it is essential to tie terrorism to particular political conditions, in which these terrorist acts take place. In other words, whether the specific political act is terrorist or non-terrorist depends on the thorough examination of the social factors beyond morality and law. In this context, even without an opportunity to find the most relevant definition of terrorism, the authors thoroughly analyze the most important factors and sociological perspectives of terrorism, including the notion of threat, violence, publicity, and fear.
Typology of terrorism is the integral component of our current understanding of what terrorism is, what form it may take, and how we can prepare ourselves to facing the challenges of terrorist threats. Vetter and Perlstein (1991) state that “finding similarities and differences among objects and events is the first step toward determining their composition, functions, and causes.” Trying to evaluate the usefulness of various theoretical perspectives in terrorism, the authors offer a detailed review of psychological, sociological, and political elements that form several different typologies of terrorism. For example, Vetter and Perlstein (1991) refer to the psychiatrist Frederick Hacker, who classifies terrorists into crazies, criminals, and crusaders. Later throughout the book, Vetter and Perlstein provide a detailed analysis of both the criminal and the crazy types of terrorists, paying special attention to who crusaders are and what role they play in the development and expansion of contemporary terrorist ideology. Vetter and Perlstein recognize that it is almost impossible to encounter an ideal type of terrorist, but the basic knowledge of terrorist typology may shed the light onto the motivation and psychological mechanisms that push criminals (and particularly crusaders) to committing the acts of political violence.
Perspectives on Terrorism pays special attention to the politics of terrorism, and the role, which ideology plays in the development of terrorist attitudes in society. “Violence or terrorism can be used both by those who seek to change or destroy the existing government or social order and those who seek to maintain the status quo” (Vetter & Perlstein, 1991). In other words, the authors suggest that political ideology is integrally linked to the notion of terrorism. With ideology being the central element of political change, it necessarily impacts the quality of the political authority within the state; as a result, the image of terrorism is gradually transformed into a critical triangle with political authority, power, and violence at its ends. In their book, Vetter and Perlstein (1991) use this triangle as the basis for analyzing the political assumptions, which are usually made in terms of terrorism, as well as the extent to which political authority may make violence (and as a result, terrorism) legally permissible. The long sociological theme of terrorism that is stretched from the very beginning to the very end of the book makes it particularly useful to those who seek the roots of terrorism in the distorted political ideology and blame the state as the source and the reason of terrorist violence.
Vetter, H.J. & Perlstein, G.R. (1991). Perspectives on terrorism (Contemporary issues in crime and justice). Pacific Grove, CA, USA: Brooks/Cole Publishing Company.
Taken from: http://www.custom-essays.org/examples/Perspectives_on_Terrorism_Essay_Vetter__Perlstein.html
List three to five elements you think make this a critique.
How a Critique Is Different
A critique is different from an expository essay which is, as you have learned, a discussion revolving around a topic with multiple sources to support the discussion points. As you can see in Self – Practice Exercise 8.1 , depending on the type of critique you are writing, your reference page could include one source only. However, as you may discuss topical ideas within the original source, you may also want to include secondary sources to which you can compare and contrast the original source’s ideas, but you need to always connect your discussion points back to the original source. Figure 8.1: Critiquing v ersus Other Essay Forms shows visual representations of what a critique structure could look in comparison to another essay, such as one that is expository or persuasive in purpose.
If you look at the mind map for the critique, you can see how all of the discussion points stem from and relate back to the original article and how all of the discussion points can be interconnected. Also, the bubble labelled Secondary Sources/Support shows you can integrate secondary sources to compare and contrast when discussing either rhetorical or idea points. In the second diagram, you can see that the supporting ideas relate to the central topic, but they are extensions of the topic each with their own supporting forms of evidence. There is less emphasis placed on synthesis of ideas, although this is something you can still do when composing this type of essay.
The Purpose of Critiquing
In a post-secondary environment, your instructors will expect you to demonstrate critical thinking skills that go beyond simply taking another person’s ideas and spitting out facts. They will want you to show your ability to assess and analyze any type of information you use; they will also want to see that you have used sources to develop ideas of your own. Critiquing, or critical analysis, demonstrates you are able to connect ideas, arrive at your own conclusions, and develop new directions for discussion. You are also showing you have strong background knowledge on the topic in order to provide feedback on another person’s discussion on the issue.
Critical analysis appears in many forms in the academic world. It is present when you select appropriate sources for your support; you practise it when you choose what information from those sources to include as your evidence; you demonstrate it when you start breaking down your topic to develop discussion points. Very importantly, you also use critical analysis or thinking when you synthesize, or blend, your ideas with those of experts. This means you go beyond a statement of facts and take a stance on a topic. In this case of a critique, you not only state your view on an idea or issue but also on one core source of information on that topic: you insert your ideas into the text’s conversation.
Elements of a Critique
Often people go online for to read reviews of services or products. They sometimes make personal choices based on those reviews, such as what movie to go to or which restaurant to eat at. When you ask for a recommendation, the person you are asking will usually give you a brief summary of the experience then break his or her opinion down into smaller aspects—good and bad. For example, imagine you want to visit a new restaurant, and you ask your friend to recommend a place. Here is a sample response:
There is an amazing Japanese restaurant called Mega Sushi at the corner of Main and 12th. The food, atmosphere, and service are great. The food is always excellent, and they have a lot of original creations or spins on traditional Japanese food, but it still tastes authentic. The ingredients are always incredibly fresh, and you never have to worry about ordering the sashimi. The decor is also very authentic and classic, and the entire place is incredibly clean.
The service is generally very good—they even bring you a free sample roll while you wait for your food—but it can be a little slow during the dinner rush because it is such a popular place. Also, the prices are a little high because an average roll costs $15, but for the amazing food you get, it is totally worth it! I love this place!
When you break this example into sections, you can see the first and second sentences give the reviewer’s general opinion of the restaurant; they also summarize the main components the reviewer will cover. The review is then broken into smaller categories or points. Notice that not all the points covered are positive: while the food and atmosphere are good, the service has both positive and negative aspects but is overall good. Also, the prices are high, but the writer states that people who eat there get good value for their money. Providing a generalized description first, the reviewer introduced the topic to the audience; she then analyzed individual aspects or components of the experience with examples to help convince the audience of her perspective. Not everyone may have the same positive experience, of course. What if it was someone’s first time at this particular restaurant, and she arrived during the dinner rush feeling very hungry and had to wait a long time for a table? Not knowing how good the food is and that it is worth the wait, she may just leave, so her general impression of the restaurant would probably not be favourable. Whether the experience would be positive or negative would depend on an individual’s personal experience and situation. The same is true for any critique. No two people will have exactly the same response to a source because of who they are, the time, and their prior experiences. When critiquing, you are responding to anything that sparks a response in you when you are reading a source. When reading your article, pay close attention to any time you have to reread a sentence or paragraph. Make note of this; at the time you may not know why you have an issue with that section. Just realize that there was a point where you had to stop and make a notation of some sort on the paper. Once you have finished reading, you can go back and think about what the issue actually was. Maybe the vocabulary was difficult; maybe the author’s grammar was awkward and confusing; maybe the ideas did not make sense how they were organized; maybe you completely disagreed with the idea the author presented. Also, maybe something you read really sparked your interest, and you have the same opinion as the author, or perhaps the vocabulary was academic but not overly challenging where you would need to use a dictionary (the guiding questions for each critique form provided below will help you with this). All of these responses are valid and are things you can write about in your critique. Any critique, no matter if it is of a book, an article, or a movie, needs to contain the following elements:
- Example: In Smith’s (2009) article, he effectively argues his case for the reinstatement of capital punishment in Canada.
- This would be the same as if you were writing a summary of any source you read.
- You will decide on these points based on your reactions and personal preferences using the guiding questions for each of the forms below as suggestions.
Writing for Success - 1st Canadian H5P Edition Copyright © 2021 by Tara Horkoff is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

In order to continue enjoying our site, we ask that you confirm your identity as a human. Thank you very much for your cooperation.

Writing a Critique
- About this Guide
- What Is a Critique?
- Getting Started
- Components of a Critique Essay
Types of Critiques
There are many types of critiques. Critiques can be written on:
- Literary works
- Published works
- Drafts of works
- Policies, of any kind
- Works of art
Anywhere that criticism can exist, a critique can follow to evaluate arguments, identify gaps, and/or make recommendations.
Defining Critique
A critique evaluates a resource. It requires both critical reading and analysis in order to present the strengths and weaknesses of a particular resource for readers. The critique includes your opinion of the work. Because of the analytics involved, a critique and a summary are not the same. For quick reference, you can use the following chart in order to determine if your paper is a critique or a summary.
| Gives an overview of key concepts discussed in the work | Yes | Yes |
|---|---|---|
| Includes introduction, body, and conclusion paragraphs | Yes | Sometimes |
| Names the author and title of the work to be discussed | Yes | Yes |
| Provides your opinion of the work | Yes | No |
| Identifies gaps in the resource and/or research that the author missed | Yes | No |
| Requires close reading of a text | Yes | No |
| Requires you to analyze the text | Yes | No |
| May use supporting evidence from the text, such as quotes, to support your interpretation | Yes | No |
Looking for more information on writing a summary or an abstract? Check out our Writing a Summary guide .
- << Previous: About this Guide
- Next: Getting Started >>
- Last Updated: Jul 31, 2024 9:19 AM
- URL: https://library.tiffin.edu/critique
How to Write Critical Reviews
When you are asked to write a critical review of a book or article, you will need to identify, summarize, and evaluate the ideas and information the author has presented. In other words, you will be examining another person’s thoughts on a topic from your point of view.
Your stand must go beyond your “gut reaction” to the work and be based on your knowledge (readings, lecture, experience) of the topic as well as on factors such as criteria stated in your assignment or discussed by you and your instructor.
Make your stand clear at the beginning of your review, in your evaluations of specific parts, and in your concluding commentary.
Remember that your goal should be to make a few key points about the book or article, not to discuss everything the author writes.
Understanding the Assignment
To write a good critical review, you will have to engage in the mental processes of analyzing (taking apart) the work–deciding what its major components are and determining how these parts (i.e., paragraphs, sections, or chapters) contribute to the work as a whole.
Analyzing the work will help you focus on how and why the author makes certain points and prevent you from merely summarizing what the author says. Assuming the role of an analytical reader will also help you to determine whether or not the author fulfills the stated purpose of the book or article and enhances your understanding or knowledge of a particular topic.
Be sure to read your assignment thoroughly before you read the article or book. Your instructor may have included specific guidelines for you to follow. Keeping these guidelines in mind as you read the article or book can really help you write your paper!
Also, note where the work connects with what you’ve studied in the course. You can make the most efficient use of your reading and notetaking time if you are an active reader; that is, keep relevant questions in mind and jot down page numbers as well as your responses to ideas that appear to be significant as you read.
Please note: The length of your introduction and overview, the number of points you choose to review, and the length of your conclusion should be proportionate to the page limit stated in your assignment and should reflect the complexity of the material being reviewed as well as the expectations of your reader.
Write the introduction
Below are a few guidelines to help you write the introduction to your critical review.
Introduce your review appropriately
Begin your review with an introduction appropriate to your assignment.
If your assignment asks you to review only one book and not to use outside sources, your introduction will focus on identifying the author, the title, the main topic or issue presented in the book, and the author’s purpose in writing the book.
If your assignment asks you to review the book as it relates to issues or themes discussed in the course, or to review two or more books on the same topic, your introduction must also encompass those expectations.
Explain relationships
For example, before you can review two books on a topic, you must explain to your reader in your introduction how they are related to one another.
Within this shared context (or under this “umbrella”) you can then review comparable aspects of both books, pointing out where the authors agree and differ.
In other words, the more complicated your assignment is, the more your introduction must accomplish.
Finally, the introduction to a book review is always the place for you to establish your position as the reviewer (your thesis about the author’s thesis).
As you write, consider the following questions:
- Is the book a memoir, a treatise, a collection of facts, an extended argument, etc.? Is the article a documentary, a write-up of primary research, a position paper, etc.?
- Who is the author? What does the preface or foreword tell you about the author’s purpose, background, and credentials? What is the author’s approach to the topic (as a journalist? a historian? a researcher?)?
- What is the main topic or problem addressed? How does the work relate to a discipline, to a profession, to a particular audience, or to other works on the topic?
- What is your critical evaluation of the work (your thesis)? Why have you taken that position? What criteria are you basing your position on?
Provide an overview
In your introduction, you will also want to provide an overview. An overview supplies your reader with certain general information not appropriate for including in the introduction but necessary to understanding the body of the review.
Generally, an overview describes your book’s division into chapters, sections, or points of discussion. An overview may also include background information about the topic, about your stand, or about the criteria you will use for evaluation.
The overview and the introduction work together to provide a comprehensive beginning for (a “springboard” into) your review.
- What are the author’s basic premises? What issues are raised, or what themes emerge? What situation (i.e., racism on college campuses) provides a basis for the author’s assertions?
- How informed is my reader? What background information is relevant to the entire book and should be placed here rather than in a body paragraph?
Write the body
The body is the center of your paper, where you draw out your main arguments. Below are some guidelines to help you write it.
Organize using a logical plan
Organize the body of your review according to a logical plan. Here are two options:
- First, summarize, in a series of paragraphs, those major points from the book that you plan to discuss; incorporating each major point into a topic sentence for a paragraph is an effective organizational strategy. Second, discuss and evaluate these points in a following group of paragraphs. (There are two dangers lurking in this pattern–you may allot too many paragraphs to summary and too few to evaluation, or you may re-summarize too many points from the book in your evaluation section.)
- Alternatively, you can summarize and evaluate the major points you have chosen from the book in a point-by-point schema. That means you will discuss and evaluate point one within the same paragraph (or in several if the point is significant and warrants extended discussion) before you summarize and evaluate point two, point three, etc., moving in a logical sequence from point to point to point. Here again, it is effective to use the topic sentence of each paragraph to identify the point from the book that you plan to summarize or evaluate.
Questions to keep in mind as you write
With either organizational pattern, consider the following questions:
- What are the author’s most important points? How do these relate to one another? (Make relationships clear by using transitions: “In contrast,” an equally strong argument,” “moreover,” “a final conclusion,” etc.).
- What types of evidence or information does the author present to support his or her points? Is this evidence convincing, controversial, factual, one-sided, etc.? (Consider the use of primary historical material, case studies, narratives, recent scientific findings, statistics.)
- Where does the author do a good job of conveying factual material as well as personal perspective? Where does the author fail to do so? If solutions to a problem are offered, are they believable, misguided, or promising?
- Which parts of the work (particular arguments, descriptions, chapters, etc.) are most effective and which parts are least effective? Why?
- Where (if at all) does the author convey personal prejudice, support illogical relationships, or present evidence out of its appropriate context?
Keep your opinions distinct and cite your sources
Remember, as you discuss the author’s major points, be sure to distinguish consistently between the author’s opinions and your own.
Keep the summary portions of your discussion concise, remembering that your task as a reviewer is to re-see the author’s work, not to re-tell it.
And, importantly, if you refer to ideas from other books and articles or from lecture and course materials, always document your sources, or else you might wander into the realm of plagiarism.
Include only that material which has relevance for your review and use direct quotations sparingly. The Writing Center has other handouts to help you paraphrase text and introduce quotations.
Write the conclusion
You will want to use the conclusion to state your overall critical evaluation.
You have already discussed the major points the author makes, examined how the author supports arguments, and evaluated the quality or effectiveness of specific aspects of the book or article.
Now you must make an evaluation of the work as a whole, determining such things as whether or not the author achieves the stated or implied purpose and if the work makes a significant contribution to an existing body of knowledge.
Consider the following questions:
- Is the work appropriately subjective or objective according to the author’s purpose?
- How well does the work maintain its stated or implied focus? Does the author present extraneous material? Does the author exclude or ignore relevant information?
- How well has the author achieved the overall purpose of the book or article? What contribution does the work make to an existing body of knowledge or to a specific group of readers? Can you justify the use of this work in a particular course?
- What is the most important final comment you wish to make about the book or article? Do you have any suggestions for the direction of future research in the area? What has reading this work done for you or demonstrated to you?

Academic and Professional Writing
This is an accordion element with a series of buttons that open and close related content panels.
Analysis Papers
Reading Poetry
A Short Guide to Close Reading for Literary Analysis
Using Literary Quotations
Play Reviews
Writing a Rhetorical Précis to Analyze Nonfiction Texts
Incorporating Interview Data
Grant Proposals
Planning and Writing a Grant Proposal: The Basics
Additional Resources for Grants and Proposal Writing
Job Materials and Application Essays
Writing Personal Statements for Ph.D. Programs
- Before you begin: useful tips for writing your essay
- Guided brainstorming exercises
- Get more help with your essay
- Frequently Asked Questions
Resume Writing Tips
CV Writing Tips
Cover Letters
Business Letters
Proposals and Dissertations
Resources for Proposal Writers
Resources for Dissertators
Research Papers
Planning and Writing Research Papers
Quoting and Paraphrasing
Writing Annotated Bibliographies
Creating Poster Presentations
Writing an Abstract for Your Research Paper
Thank-You Notes
Advice for Students Writing Thank-You Notes to Donors
Reading for a Review
Critical Reviews
Writing a Review of Literature
Scientific Reports
Scientific Report Format
Sample Lab Assignment
Writing for the Web
Writing an Effective Blog Post
Writing for Social Media: A Guide for Academics
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Our 2024-25 Student Contest Calendar
Ten challenges that invite teenagers to engage, experiment, reflect and create — via writing, photography, audio, video and more.

By The Learning Network
Our annual Contest Calendar is probably the single most powerful thing we publish all year. Teachers tell us they plan their classes around our challenges, and tens of thousands of teenagers around the globe participate by creating narratives, reviews, videos, opinion pieces, podcasts, illustrations, photo essays and more.
For us, these contests are an honor and a joy to host. We love learning from young people — about what moves them and makes them mad, what intrigues and confuses and delights and defines them.
This year, we are bringing back some recent and longtime favorites, as well as introducing a few new challenges.
To begin, we have two options this fall in response to the U.S. election, though students around the globe are welcome. In September, we open with a series of special forums that invite teenagers to have thoughtful conversations about their civic and political identities, values and beliefs. Then, if they choose, they can work alone or with others to make something in response — whether in writing, video, audio or visual art. (Students can participate in one or both challenges, and we have a related invitation for educators .)
In the spring, we’re offering “My List,” a twist on our long-running review contest. This time, students can choose any collection of three to five works of art or culture to group in some way and then tell us why we should — or shouldn’t — check them out.
We’ll be posting the full rules and guidelines for each contest here when it opens. but for now you can look at the related resources we’ve provided, as well as last year’s rules, which will largely remain the same for our returning contests.
We are having trouble retrieving the article content.
Please enable JavaScript in your browser settings.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access. If you are in Reader mode please exit and log into your Times account, or subscribe for all of The Times.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access.
Already a subscriber? Log in .
Want all of The Times? Subscribe .
Main Navigation
- Contact NeurIPS
- Code of Ethics
- Code of Conduct
- Create Profile
- Journal To Conference Track
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Proceedings
- Future Meetings
- Exhibitor Information
- Privacy Policy
NeurIPS 2024 Datasets and Benchmarks Track
If you'd like to become a reviewer for the track, or recommend someone, please use this form .
The Datasets and Benchmarks track serves as a venue for high-quality publications, talks, and posters on highly valuable machine learning datasets and benchmarks, as well as a forum for discussions on how to improve dataset development. Datasets and benchmarks are crucial for the development of machine learning methods, but also require their own publishing and reviewing guidelines. For instance, datasets can often not be reviewed in a double-blind fashion, and hence full anonymization will not be required. On the other hand, they do require additional specific checks, such as a proper description of how the data was collected, whether they show intrinsic bias, and whether they will remain accessible. The Datasets and Benchmarks track is proud to support the open source movement by encouraging submissions of open-source libraries and tools that enable or accelerate ML research.
The previous editions of the Datasets and Benchmarks track were highly successful; you can view the accepted papers from 2021 , 2002 , and 2023 , and the winners of the best paper awards 2021 , 2022 and 2023
CRITERIA. W e are aiming for an equally stringent review as the main conference, yet better suited to datasets and benchmarks. Submissions to this track will be reviewed according to a set of criteria and best practices specifically designed for datasets and benchmarks , as described below. A key criterion is accessibility: datasets should be available and accessible , i.e. the data can be found and obtained without a personal request to the PI, and any required code should be open source. We encourage the authors to use Croissant format ( https://mlcommons.org/working-groups/data/croissant/ ) to document their datasets in machine readable way. Next to a scientific paper, authors should also submit supplementary materials such as detail on how the data was collected and organised, what kind of information it contains, how it should be used ethically and responsibly, as well as how it will be made available and maintained.
RELATIONSHIP TO NeurIPS. Submissions to the track will be part of the main NeurIPS conference , presented alongside the main conference papers. Accepted papers will be officially published in the NeurIPS proceedings .
SUBMISSIONS. There will be one deadline this year. It is also still possible to submit datasets and benchmarks to the main conference (under the usual review process), but dual submission to both is not allowed (unless you retracted your paper from the main conference). We also cannot transfer papers from the main track to the D&B track. Authors can choose to submit either single-blind or double-blind . If it is possible to properly review the submission double-blind, i.e., reviewers do not need access to non-anonymous repositories to review the work, then authors can also choose to submit the work anonymously. Papers will not be publicly visible during the review process. Only accepted papers will become visible afterward. The reviews themselves are not visible during the review phase but will be published after decisions have been made. The datasets themselves should be accessible to reviewers but can be publicly released at a later date (see below). New authors cannot be added after the abstract deadline and they should have an OpenReview profile by the paper deadline. NeurIPS does not tolerate any collusion whereby authors secretly cooperate with reviewers, ACs or SACs to obtain favourable reviews.
SCOPE. This track welcomes all work on data-centric machine learning research (DMLR) and open-source libraries and tools that enable or accelerate ML research, covering ML datasets and benchmarks as well as algorithms, tools, methods, and analyses for working with ML data. This includes but is not limited to:
- New datasets, or carefully and thoughtfully designed (collections of) datasets based on previously available data.
- Data generators and reinforcement learning environments.
- Data-centric AI methods and tools, e.g. to measure and improve data quality or utility, or studies in data-centric AI that bring important new insight.
- Advanced practices in data collection and curation that are of general interest even if the data itself cannot be shared.
- Frameworks for responsible dataset development, audits of existing datasets, identifying significant problems with existing datasets and their use
- Benchmarks on new or existing datasets, as well as benchmarking tools.
- In-depth analyses of machine learning challenges and competitions (by organisers and/or participants) that yield important new insight.
- Systematic analyses of existing systems on novel datasets yielding important new insight.
Read our original blog post for more about why we started this track.
Important dates
- Abstract submission deadline: May 29, 2024
- Full paper submission and co-author registration deadline: Jun 5, 2024
- Supplementary materials submission deadline: Jun 12, 2024
- Review deadline - Jul 24, 2024
- Release of reviews and start of Author discussions on OpenReview: Aug 07, 2024
- End of author/reviewer discussions on OpenReview: Aug 31, 2024
- Author notification: Sep 26, 2024
- Camera-ready deadline: Oct 30, 2024 AOE
Note: The site will start accepting submissions on April 1 5 , 2024.
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
Q: My work is in scope for this track but possibly also for the main conference. Where should I submit it?
A: This is ultimately your choice. Consider the main contribution of the submission and how it should be reviewed. If the main contribution is a new dataset, benchmark, or other work that falls into the scope of the track (see above), then it is ideally reviewed accordingly. As discussed in our blog post, the reviewing procedures of the main conference are focused on algorithmic advances, analysis, and applications, while the reviewing in this track is equally stringent but designed to properly assess datasets and benchmarks. Other, more practical considerations are that this track allows single-blind reviewing (since anonymization is often impossible for hosted datasets) and intended audience, i.e., make your work more visible for people looking for datasets and benchmarks.
Q: How will paper accepted to this track be cited?
A: Accepted papers will appear as part of the official NeurIPS proceedings.
Q: Do I need to submit an abstract beforehand?
A: Yes, please check the important dates section for more information.
Q: My dataset requires open credentialized access. Can I submit to this track?
A: This will be possible on the condition that a credentialization is necessary for the public good (e.g. because of ethically sensitive medical data), and that an established credentialization procedure is in place that is 1) open to a large section of the public, 2) provides rapid response and access to the data, and 3) is guaranteed to be maintained for many years. A good example here is PhysioNet Credentialing, where users must first understand how to handle data with human subjects, yet is open to anyone who has learned and agrees with the rules. This should be seen as an exceptional measure, and NOT as a way to limit access to data for other reasons (e.g. to shield data behind a Data Transfer Agreement). Misuse would be grounds for desk rejection. During submission, you can indicate that your dataset involves open credentialized access, in which case the necessity, openness, and efficiency of the credentialization process itself will also be checked.
SUBMISSION INSTRUCTIONS
A submission consists of:
- Please carefully follow the Latex template for this track when preparing proposals. We follow the NeurIPS format, but with the appropriate headings, and without hiding the names of the authors. Download the template as a bundle here .
- Papers should be submitted via OpenReview
- Reviewing is in principle single-blind, hence the paper should not be anonymized. In cases where the work can be reviewed equally well anonymously, anonymous submission is also allowed.
- During submission, you can add a public link to the dataset or benchmark data. If the dataset can only be released later, you must include instructions for reviewers on how to access the dataset. This can only be done after the first submission by sending an official note to the reviewers in OpenReview. We highly recommend making the dataset publicly available immediately or before the start of the NeurIPS conference. In select cases, requiring solid motivation, the release date can be stretched up to a year after the submission deadline.
- Dataset documentation and intended uses. Recommended documentation frameworks include datasheets for datasets , dataset nutrition labels , data statements for NLP , data cards , and accountability frameworks .
- URL to website/platform where the dataset/benchmark can be viewed and downloaded by the reviewers.
- URL to Croissant metadata record documenting the dataset/benchmark available for viewing and downloading by the reviewers. You can create your Croissant metadata using e.g. the Python library available here: https://github.com/mlcommons/croissant
- Author statement that they bear all responsibility in case of violation of rights, etc., and confirmation of the data license.
- Hosting, licensing, and maintenance plan. The choice of hosting platform is yours, as long as you ensure access to the data (possibly through a curated interface) and will provide the necessary maintenance.
- Links to access the dataset and its metadata. This can be hidden upon submission if the dataset is not yet publicly available but must be added in the camera-ready version. In select cases, e.g when the data can only be released at a later date, this can be added afterward (up to a year after the submission deadline). Simulation environments should link to open source code repositories
- The dataset itself should ideally use an open and widely used data format. Provide a detailed explanation on how the dataset can be read. For simulation environments, use existing frameworks or explain how they can be used.
- Long-term preservation: It must be clear that the dataset will be available for a long time, either by uploading to a data repository or by explaining how the authors themselves will ensure this
- Explicit license: Authors must choose a license, ideally a CC license for datasets, or an open source license for code (e.g. RL environments). An overview of licenses can be found here: https://paperswithcode.com/datasets/license
- Add structured metadata to a dataset's meta-data page using Web standards (like schema.org and DCAT ): This allows it to be discovered and organized by anyone. A guide can be found here: https://developers.google.com/search/docs/data-types/dataset . If you use an existing data repository, this is often done automatically.
- Highly recommended: a persistent dereferenceable identifier (e.g. a DOI minted by a data repository or a prefix on identifiers.org ) for datasets, or a code repository (e.g. GitHub, GitLab,...) for code. If this is not possible or useful, please explain why.
- For benchmarks, the supplementary materials must ensure that all results are easily reproducible. Where possible, use a reproducibility framework such as the ML reproducibility checklist , or otherwise guarantee that all results can be easily reproduced, i.e. all necessary datasets, code, and evaluation procedures must be accessible and documented.
- For papers introducing best practices in creating or curating datasets and benchmarks, the above supplementary materials are not required.
- For papers resubmitted after being retracted from another venue: a brief discussion on the main concerns raised by previous reviewers and how you addressed them. You do not need to share the original reviews.
- For the dual submission and archiving, the policy follows the NeurIPS main track paper guideline .
Use of Large Language Models (LLMs): We welcome authors to use any tool that is suitable for preparing high-quality papers and research. However, we ask authors to keep in mind two important criteria. First, we expect papers to fully describe their methodology, and any tool that is important to that methodology, including the use of LLMs, should be described also. For example, authors should mention tools (including LLMs) that were used for data processing or filtering, visualization, facilitating or running experiments, and proving theorems. It may also be advisable to describe the use of LLMs in implementing the method (if this corresponds to an important, original, or non-standard component of the approach). Second, authors are responsible for the entire content of the paper, including all text and figures, so while authors are welcome to use any tool they wish for writing the paper, they must ensure that all text is correct and original.
REVIEWING AND SELECTION PROCESS
Reviewing will be single-blind, although authors can also submit anonymously if the submission allows that. A datasets and benchmarks program committee will be formed, consisting of experts on machine learning, dataset curation, and ethics. We will ensure diversity in the program committee, both in terms of background as well as technical expertise (e.g., data, ML, data ethics, social science expertise). Each paper will be reviewed by the members of the committee. In select cases where ethical concerns are flagged by reviewers, an ethics review may be performed as well.
Papers will not be publicly visible during the review process. Only accepted papers will become visible afterward. The reviews themselves are also not visible during the review phase but will be published after decisions have been made. Authors can choose to keep the datasets themselves hidden until a later release date, as long as reviewers have access.
The factors that will be considered when evaluating papers include:
- Utility and quality of the submission: Impact, originality, novelty, relevance to the NeurIPS community will all be considered.
- Reproducibility: All submissions should be accompanied by sufficient information to reproduce the results described i.e. all necessary datasets, code, and evaluation procedures must be accessible and documented. We encourage the use of a reproducibility framework such as the ML reproducibility checklist to guarantee that all results can be easily reproduced. Benchmark submissions in particular should take care to ensure sufficient details are provided to ensure reproducibility. If submissions include code, please refer to the NeurIPS code submission guidelines .
- Was code provided (e.g. in the supplementary material)? If provided, did you look at the code? Did you consider it useful in guiding your review? If not provided, did you wish code had been available?
- Ethics: Any ethical implications of the work should be addressed. Authors should rely on NeurIPS ethics guidelines as guidance for understanding ethical concerns.
- Completeness of the relevant documentation: Per NeurIPS ethics guidelines , datasets must be accompanied by documentation communicating the details of the dataset as part of their submissions via structured templates (e.g. TODO). Sufficient detail must be provided on how the data was collected and organized, what kind of information it contains, ethically and responsibly, and how it will be made available and maintained.
- Licensing and access: Per NeurIPS ethics guidelines , authors should provide licenses for any datasets released. These should consider the intended use and limitations of the dataset, and develop licenses and terms of use to prevent misuse or inappropriate use.
- Consent and privacy: Per NeurIPS ethics guidelines , datasets should minimize the exposure of any personally identifiable information, unless informed consent from those individuals is provided to do so. Any paper that chooses to create a dataset with real data of real people should ask for the explicit consent of participants, or explain why they were unable to do so.
- Ethics and responsible use: Any ethical implications of new datasets should be addressed and guidelines for responsible use should be provided where appropriate. Note that, if your submission includes publicly available datasets (e.g. as part of a larger benchmark), you should also check these datasets for ethical issues. You remain responsible for the ethical implications of including existing datasets or other data sources in your work.
- Legal compliance: For datasets, authors should ensure awareness and compliance with regional legal requirements.
ADVISORY COMMITTEE
The following committee will provide advice on the organization of the track over the coming years: Sergio Escalera, Isabelle Guyon, Neil Lawrence, Dina Machuve, Olga Russakovsky, Joaquin Vanschoren, Serena Yeung.
DATASETS AND BENCHMARKS CHAIRS
Lora Aroyo, Google Francesco Locatello, Institute of Science and Technology Austria Lingjuan Lyu, Sony AI
Contact: [email protected]
| NeurIPS uses cookies to remember that you are logged in. By using our websites, you agree to the placement of cookies. |

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A critique essay is a type of academic writing that involves analyzing and evaluating a piece of work, such as a book, film, artwork, or research paper. Unlike a simple summary or review, a critique essay goes beyond providing a surface-level examination of the work and delves into an in-depth analysis of its strengths, weaknesses, and overall ...
A critique is a response to a body of work, be it a performance, concept, argument, scholarly article, poem or book. If you write a critique, you can present your opinion of the work or provide an alternative opinion. Critiques typically include the following: Description of the work, including its purpose, the creator and the intention
The critique is your evaluation of the resource. A strong critique: Discusses the strengths of the resource. Discusses the weaknesses of the resource. Provides specific examples (direct quotes, with proper citation) as needed to support your evaluation. Discusses anything else pertinent to your evaluation, including.
A critique may include a brief summary, but the main focus should be on your evaluation and analysis of the research itself. What steps need to be taken to write an article critique? Before you start writing, you will need to take some steps to get ready for your critique: Choose an article that meets the criteria outlined by your instructor.
A critical essay is written in the third-person and ensures the reader is presented with an objective analysis. Discuss whether the author was able to achieve their goals and adequately get their point across. It is important not to confuse facts and opinions. An opinion is a personal thought and requires confirmation, whereas a fact is ...
A critical essay is a form of academic writing that analyzes, interprets, and/or evaluates a text. In a critical essay, an author makes a claim about how particular ideas or themes are conveyed in a text, then supports that claim with evidence from primary and/or secondary sources. In casual conversation, we often associate the word "critical ...
How to write a critique. Before you start writing, it is important to have a thorough understanding of the work that will be critiqued. Study the work under discussion. Make notes on key parts of the work. Develop an understanding of the main argument or purpose being expressed in the work. Consider how the work relates to a broader issue or ...
Writing Critiques. Writing a critique involves more than pointing out mistakes. It involves conducting a systematic analysis of a scholarly article or book and then writing a fair and reasonable description of its strengths and weaknesses. Several scholarly journals have published guides for critiquing other people's work in their academic area.
A critique asks you to evaluate an article and the author's argument. You will need to look critically at what the author is claiming, evaluate the research methods, and look for possible problems with, or applications of, the researcher's claims. Introduction. Give an overview of the author's main points and how the author supports those ...
None of this is to say that you shouldn't commend a piece of work if it truly is fantastic or that you should not highlight the gems within a work. Again: constructive criticism is honest criticism. If a work is so well-crafted in your eyes that nothing worse than grammatical hiccups are present, tell the writer.
Written by MasterClass. Last updated: Jun 7, 2021 • 3 min read. Critical analysis essays can be a daunting form of academic writing, but crafting a good critical analysis paper can be straightforward if you have the right approach. Explore.
Example of Critique Essay On Articles An article-related critique essay is a paper that evaluates an article to determine its effectiveness in attaining a goal. An article could comprise opinions, personal experiences, and external research.
Critique is a literary technique that means to critically evaluate a piece of literary work, or a political or philosophical theory in detail. A critique could be a critical essay, an article evaluating a literary piece, or a review. It may be just like a summary that identifies the central issue, raises questions, takes notice of theoretical ...
The structure of a typical critique essay example includes an introduction, a summary, an analysis, and a conclusion. The paper format is a crucial element. Just like when you write your research papers, a critique benefits from a clear one to guide the reader. Therefore, work on defining the critique essay outline before starting the writing ...
Writing a Critique. To critique a piece of writing is to do the following: describe: give the reader a sense of the writer's overall purpose and intent. analyze: examine how the structure and language of the text convey its meaning. interpret: state the significance or importance of each part of the text. assess: make a judgment of the work ...
A critique is different from an expository essay which is, as you have learned, a discussion revolving around a topic with multiple sources to support the discussion points. As you can see in Self-Practice Exercise 8.1, depending on the type of critique you are writing, your reference page could include one source only.
An essay critique is an analysis of a work in the context of its intent. It is more than simply a review, a set of likes and dislikes. It is designed to determine if a written work has fulfilled ...
What is a Critique? An overview of the standard critique essay. Getting Started Tips to set yourself up for success when writing a critique Components of a Critique Essay The components of a critique essay and how to write them; Examples Example critique articles; Get Help Provides links to additional resources that were not otherwise mentioned.
A critique evaluates a resource. It requires both critical reading and analysis in order to present the strengths and weaknesses of a particular resource for readers.The critique includes your opinion of the work. Because of the analytics involved, a critique and a summary are not the same. For quick reference, you can use the following chart in order to determine if your paper is a critique ...
To write a good critical review, you will have to engage in the mental processes of analyzing (taking apart) the work-deciding what its major components are and determining how these parts (i.e., paragraphs, sections, or chapters) contribute to the work as a whole. Analyzing the work will help you focus on how and why the author makes certain ...
the article, taking the main points of each paragraph. The point of the diagram is to. show the relationships between the main points in the article. Ev en better you might. consider doing an ...
The Critique Essay It's your first essay in ENG 112, and, of course, you want to do well. This handout offers some helpful hints for writing the first essay—The Critique. Remember the author! The critique essay is not about concerned with the content of the article - but whether or
A negative critique might be said to be "criticism" in the way we often understand the term "to criticize," but critiques can be positive too. ... book, a report on a research study or experiment, or an analysis published in an academic journal. These more complex essays usually present more opportunities for issues to critique. ...
A week after announcing her run for president, Kamala Harris has yet to tell voters how she will address the key issues facing the nation. The vice president's platform will likely be in the ...
Critical thinking is used while you address real problems, question it, and look for solution to solve it. As an …show more content… This means developing questions and finding answers to those questions. Critical thinking can be used at every stage of an investigation, from the beginning of the crime to preparing for court.
in critical and emerging technology areas.To accomplish the goals of the USG NSSCET, the USG must continue existing coordination efforts, and should take the following immediate actions when they ...
In the spring, we're offering "My List," a twist on our long-running review contest. This time, students can choose any collection of three to five works of art or culture to group in some ...
This paper examines the significance and impact of broad-based and industrial policies on economic diversification in developing economies, supported by a literature review, case studies, and IMF analyses. Economic diversification entails shifting from traditional sectors, like agriculture and mining, to a variety of high-quality services and sectors. This transition is crucial for adapting to ...
Papers will not be publicly visible during the review process. Only accepted papers will become visible afterward. The reviews themselves are also not visible during the review phase but will be published after decisions have been made. Authors can choose to keep the datasets themselves hidden until a later release date, as long as reviewers ...