- The PhD Journey - Stages of a Doctoral Degree

The PhD Journey
Written by Mark Bennett
A PhD typically involves between three and four years of full-time study, culminating in a thesis which makes an original contribution to your field.
The process of getting a PhD is made up of quite a few components and milestones, from the literature review and writing up your dissertation right through to the viva examination at the end.
This section is a guide on how to do a PhD, providing in-depth advice and information on some of the main challenges and opportunities you’ll meet along the way!.
Get funding updates straight to your inbox
Sign up to our weekly newsletter for the latest funding advice and guidance from our team of experts.
7 stages of the PhD journey
A PhD has a few landmark milestones along the way. The three to four year you'll spend doing a PhD can be divided into these seven stages.
- Preparing a research proposal
- Carrying out a literature review
- Conducting research and collecting results
- Completing the MPhil to PhD upgrade
- Participating in PhD teaching, conferences and publications
- Writing your thesis
- Defending your PhD results at a viva voce
We've expanded on what you can expect from each stage below.
1. Preparing a research proposal
Strictly speaking, your research proposal isn’t part of your PhD. Instead it’s normally part of the PhD application process.
The research proposal sets out the aims and objectives for your PhD: the original topic you plan to study and / or the questions you’ll set out to answer.
It also explains why your work is worthwhile and why it fits with the expertise and objectives of your university.
Finally, a PhD proposal explains how you plan to go about completing your doctorate. This involves identifying the existing scholarship your work will be in dialogue with and the methods you plan to use in your research.
All of this means that, even though the proposal precedes the PhD itself, it plays a vital role in shaping your project and signposting the work you’ll be doing over the next three or more years.
2. Carrying out a literature review
The literature review is normally the first thing you’ll tackle after beginning your PhD and having an initial meeting with your supervisor.
It’s a thorough survey of work in your field (the current scholarly ‘literature’) that relates to your project or to related topics.
Your supervisor will offer some advice and direction, after which you’ll identify, examine and evaluate existing data and scholarship.
In most cases the literature review will actually form part of your final PhD dissertation – usually setting up the context for the project, before you begin to explain and demonstrate your own thesis.
Sometimes a literature review can also be evaluated as part of your MPhil upgrade .
Research vs scholarship
Research and scholarship are both important parts of a PhD. But they aren't the same thing - and it's helpful to know the difference. Research is the original work you produce with your thesis. Scholarship is the expert understanding of your subject area that enables you to conduct valuable research.
3. Conducting research and collecting results
Once you’ve carried out your literature review, you’ll move from scholarship to research .
This doesn’t mean you’ll never read another academic article or consult someone else’s data again. Far from it. You’ll stay up to date with any new developments in your field and incorporate these into your literature review as necessary.
But, from here on in, your primary focus in your PhD process is going to be investigating your own research question. This means carrying out organised research and producing results upon which to base your conclusions.
Types of PhD research
The research process and the type of results you collect will depend upon your subject area:
- In Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics (STEM) subjects you’ll focus on designing experiments, before recording and analysing their outcomes. This often means assembling and managing complex numerical datasets – sometimes in collaboration with the rest of your laboratory or workshop.
- In Social Science subjects you’ll be more focussed on designing surveys or conducting case studies. These will produce quantitative or qualitative data, depending on the nature of your work.
- In Arts and Humanities subjects you’ll often have less raw data, but that doesn’t mean you won’t be working with ‘hard’ factual information. You’ll analyse texts, sources and other materials according to an accepted methodology and reflect upon the significance of your findings.
Whatever subject you’re in, this research work will account for the greater part of your PhD results. You’ll have regular meetings with your supervisor, but the day-to-day management of your project and its progress will be your own responsibility.
In some fields it’s common to begin writing up your findings as you collect them, developing your thesis and completing the accompanying dissertation chapter-by-chapter. In other cases you’ll wait until you have a full dataset before reviewing and recording your conclusions.
4. Completing an MPhil to PhD upgrade
At UK universities it’s common to register new PhD students for an MPhil before ‘ upgrading ’ them to ‘full’ doctoral candidates. This usually takes place after one year of full-time study (or its part-time equivalent).
Forcing you to register for a ‘lesser’ degree may seem strange, but it’s actually an important part of the training and development a PhD offers:
- As an MPhil student you’re able to comprehend your field and produce new research.
- As a PhD student you’re able to go that crucial step further and produce the significant original contribution to knowledge that defines a doctorate.
The MPhil upgrade is when you take the step from the former to the latter.
The MPhil upgrade exam
Upgrading from MPhil to PhD registration usually involves a form of oral exam – similar to the viva voce that concludes a PhD. But, unlike a full viva, the MPhil upgrade is less formal and only covers part of your thesis.
In most cases you’ll submit a small amount of the material you’ve produced so far. This could be a draft of your first chapter (or part of it) and / or your literature review. You could also be asked to reflect on your progress in general.
You’ll then sit down with your supervisor and someone else from your department (familiar with your field, but unrelated to your project). They’ll offer feedback on the quality of your work and ask questions about your findings.
The aim of the process won’t be to examine your drafts so much as to confirm that your project has the potential to justify a PhD – and that you’re on track to complete it on time.
‘Failing’ a PhD upgrade is actually quite rare. Your university may ask you to repeat the procedure if they are concerned that you haven’t made sufficient progress or established a viable plan for the rest of your project.
What is an MPhil?
The MPhil (Master of Philosophy) is also a research degree, but its scope is more limited than a PhD (Doctor of Philosophy). And no, just like a PhD, an MPhil isn’t necessarily a Philosophy qualification. Our guide covers all you need to know about the difference between a MPhil and PhD .
5. PhD teaching, conferences and publications
During the PhD process, you’ll have lots of opportunities to take part in extra-curricular activities, such as teaching, academic conferences and publications.
Although it isn’t usually compulsory to participate in these, they can be an incredibly rewarding experience and will look great on your CV.
Teaching during a PhD normally involves hosting undergraduate seminars or supervising students in the lab, as well as marking work and providing feedback.
Academic conferences are an excellent way to network with like-minded colleagues and find out the latest developments in your field. You might even be able to present your own work to your peers at one of these events.
Publishing during a PhD will help you increase your academic profile, as well as give you experience of the peer review process. It’s not normally a requisite of your PhD, but publications will certainly help if you plan on applying for postdoc positions.
6. Writing your thesis
As the culmination of three or more years of hard work, the thesis (or dissertation) is the most important part of the procedure to get your PhD, presenting you with the opportunity to make an original scholarly contribution to your discipline.
Our guide to writing your thesis covers everything you need to know about this lengthy research project, from structure and word count to writing up and submission.
We’ve also written a guide to the PhD dissertation abstract , which is an important part of any thesis.
7. Defending your PhD results at a viva voce
Unlike other degrees, a PhD isn’t normally marked as a piece of written work. Instead your dissertation will be submitted for an oral examination known as a viva voce (Latin for ‘living voice’).
This is a formal procedure, during which you ‘defend’ your thesis in front of appointed examiners, each of whom will have read your dissertation thoroughly in advance.
Examiners at a viva voce
A PhD is normally examined by two academic experts:
- One will be an internal examiner, usually appointed from elsewhere in your faculty and department. They won’t be directly associated with your project, but will have sufficient expertise to assess your findings.
- The other will be an external examiner. They will be a recognised expert in the area you are researching, with a record of relevant research and publication. Most universities in the UK allow you to invite an external examiner of your choice, provided there is no existing conflict of interest.
Your supervisor will help you prepare for the viva and will offer advice on choosing an external examiner. However, they will not normally be present during the examination.
The PhD timeline
| Meet with your and discuss your proposed project. Here you will clarify any changes that are needed and agree a schedule of meetings and a plan of work for the following months. | |
| Clarify the direction of your research, methods and the necessity of any research trips. You will also discuss your training and development needs and begin working towards a . | |
| Hand in of an advanced , thesis plan and timetable for completion. This will then be discussed in the with two internal examiners. | |
| Biannual review with your supervisor(s) to discuss your progress to date and feasibility of completing on time. | |
| You will have made considerable progress on your research by the end of the second year. You may have begun drafting your and engaging in professional activities such as , , and skills training. All of your progress will be discussed in another annual review. | |
| Most of the third year will be spent writing up and redrafting your . You may also engage in professional activities such as , and . | |
| Application for examination and nominate your examiners. | |
| and assisting work such as a skills development log. | |
| Usually the will take place within 10 weeks of the examiners receiving your thesis. | |
| Most PhD students pass with corrections and are given a period to edit the thesis. The length of time given will depend on whether you pass with major or minor corrections. | |
| Receipt of award and graduation! |
Ready to take the next step?
There's lots more information about how to get a PhD in our advice section . Or, if you're ready to start looking at different projects, why not check out one of the thousands of current PhD opportunities in our database?

Not sure how PhD study will differ from a Masters? In this guide, we take a look at how the two qualifications compare, including applications, course structure, assessment and more.

Every student will need to write an abstract for their PhD dissertation. Here's everything you need to know about what an academic abstract is and how to write one.

What can you expect from a PhD? What's life actually like as a postgraduate student? Read our guides to the doctoral research experience.

The viva voce is the final oral exam at the end of a PhD degree. Our guide explains the usual viva format, covers common questions and explains how to prepare.
FindAPhD. Copyright 2005-2024 All rights reserved.
Unknown ( change )
Have you got time to answer some quick questions about PhD study?
Select your nearest city
You haven’t completed your profile yet. To get the most out of FindAPhD, finish your profile and receive these benefits:
- Monthly chance to win one of ten £10 Amazon vouchers ; winners will be notified every month.*
- The latest PhD projects delivered straight to your inbox
- Access to our £6,000 scholarship competition
- Weekly newsletter with funding opportunities, research proposal tips and much more
- Early access to our physical and virtual postgraduate study fairs
Or begin browsing FindAPhD.com
or begin browsing FindAPhD.com
*Offer only available for the duration of your active subscription, and subject to change. You MUST claim your prize within 72 hours, if not we will redraw.

Do you want hassle-free information and advice?
Create your FindAPhD account and sign up to our newsletter:
- Find out about funding opportunities and application tips
- Receive weekly advice, student stories and the latest PhD news
- Hear about our upcoming study fairs
- Save your favourite projects, track enquiries and get personalised subject updates

Create your account
Looking to list your PhD opportunities? Log in here .

- How Long Does A PhD Take?
- Doing a PhD
Sometimes, just knowing how long a PhD takes can be enough to sway your decision on whether a research degree is for you. So with that in mind, exactly how long does a PhD take?
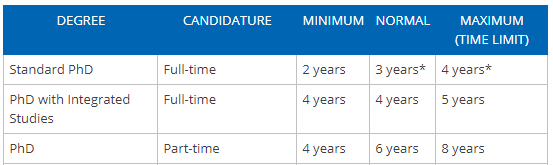
In the UK, a full-time PhD takes 3 to 4 years to finish whilst a part-time PhD takes twice as long at 6 to 7 years. Alongside these average durations, there are time limits on how long you can be enrolled on to a PhD programme. To discover these limits, the factors which most influence doctoral degree durations and how the UK durations compare to international PhDs, continue reading on.
How Long Does It Take to Get a Full-time PhD?
In the UK, a full-time PhD will typically take you 3 to 4 years. You will usually spend the first three years on the technical aspects of your doctorate. This includes undertaking independent research, designing your research methodology and collecting and analysing data. You will then spend an additional academic year on writing up your PhD thesis and sitting your viva.
How Long Does It Take to Get a Part-time PhD?
In the UK, a part-time PhD will typically take you 6 to 7 years; twice as long as doing a full-time PhD. The reason for this is that as a part-time PhD student, you would dedicate around 20 hours per week to your PhD as opposed to the typical 40 hours full-time students would put into their subject.
How Long Does a Distance Learning PhD Take?
Similarly, distance learning PhD’s take an average of 6 to 7 years to complete. This is because the vast majority of students who undertake a distance learning PhD do so because they can’t relocate closer to the university. Although these commitments will differ, they often mean the student isn’t able to dedicate 40 hours per week to their studies.
Students in STEM disciplines will often take longer to finish a distance learning doctorate degree than those in non-STEM disciplines. This because the progress of a STEM PhD student will be limited by how often they can access a laboratory for experiment work.
How Does Funding Impact a PhD’s Duration?
In reality, the actual time it will take you to complete your PhD degree will depend on your funding situation.
If you’re receiving funding , it will usually only cover you for 3.5 years if you’re studying full-time or for 7 years at half the stipend if you’re studying part-time. Although this could vary slightly, most PhD funding providers, e.g. Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC), follow this timescale as indicated on their ‘ length of PhD studentships’ page. Because of this, most students who obtain scholarships try to complete their PhD within the timeframe of their funding so they don’t incur additional fees which they need to cover themselves.
It’s also worth noting that some funded PhD positions have additional conditions attached to them as part of their eligibility requirements. For example, they may require teaching undergraduate students, hosting laboratory sessions or attend presentations and conferences. This will be especially true if you’re on a Graduate Teaching Assistantship (GTA). Although these shouldn’t add considerable time to the length of a PhD programme, they have the potential to do so if they aren’t managed properly.
As self-funded students cover their own annual tuition fees and other associated costs, how long they’ll spend to complete their PhD project will largely depend on their own personal financial situation. Because of this, most self-funded PhD students find it best to complete their PhD study in the shortest time-frame they can manage.
Are There Deadlines?
Yes – unfortunately, all good things must come to an end! Within the UK, the deadline for your PhD is defined as the last date which you must submit your final thesis by. This date is set by your university’s overall regulations and varies depending on the arrangements of your PhD, e.g. whether it’s full or part time. In the vast majority of cases, the adopted deadlines are four years for full-time PhDs and seven years for part-time PhDs from the date you were officially registered onto your programme, as shown below from the University of Leicester’s registration guidance page .

This time-frame may vary from university to university. For example, the University of Sheffield adopts an additional year for part-time PhDs as shown below.
Can I Complete It Faster?
Although it’s possible to complete a full-time PhD in under 3 years, it’s a significant feat that’s rarely heard of. When these feats occur, they’re usually where the doctoral student already has extensive knowledge and experience in their field before undertaking their PhD.
Whilst it’s possible to complete a part-time PhD in under 6 years, it largely depends on your commitments outside your studies. For example, if you have a part-time career alongside your PhD, it’s unlikely that you’ll be able to commit the additional hours required to complete your doctorate a year faster.
However, if instead of a steady part-time job you take on occasional work as a freelancer, you’ll be able to set aside many more hours towards your doctoral degree.
Will Having only A Bachelor’s Degree or Being an International Student Limit My Rate of Progression?
Not at all. While there are benefits to having a Master’s degree such as an additional year of learning and greater research experience due to your fourth-year dissertation project, this doesn’t mean not having one would limit you. A PhD is very different to both Bachelor and Master degrees due to being heavily research-based, therefore, both types of students will have just as much to learn on their way to completing their doctorate.
Similarly, whether you’re an international student will bear no influence on the duration of your PhD.
Finding a PhD has never been this easy – search for a PhD by keyword, location or academic area of interest.
How Does This Compare to the Duration of EU and US PhDs?
PhD hosted by universities within the EU, such as those in France, Norway and Spain, have the same programme structure as those within the UK. As a result, there are no noticeable differences in the time to complete a doctorate between UK and EU institutions.
However, this is not the case in the US. Compared to PhDs conducted within the UK or EU, PhDs conducted within the US take considerably longer to obtain. According to a 2017 study conducted by the National Science Foundation, a US government agency which supports research and higher education, the average time to get a PhD within the US is 5.8 years. Besides this, the average completion time can further increase depending on the disciplines. For example, they found doctorates within the humanities and arts to take an average of 7.1 years to achieve.
The primary reason for this difference is the way PhD degrees are structured within the United States. As mentioned previously, PhDs conducted within UK and EU universities are essentially broken into two sections – one covering the analytical aspects and the other covering the writing up aspects. However, within the US, doctorate programmes comprise additional sections. PhD students are first required to undertake 2 to 3 years of courses, which cover a broad range of topics related to their schools’ discipline. This is then followed by coursework and several examinations, which only once passed can the PhD candidate then start working on their research project and dissertation.
Browse PhDs Now
Join thousands of students.
Join thousands of other students and stay up to date with the latest PhD programmes, funding opportunities and advice.
- Skip to main content
- Prospective Students
- Current Students
- Apply Apply
- Follow Us

How Do You Get a PhD? A Guide to the PhD Timeline

Everyone who considers a doctoral degree knows a PhD is a big commitment.
Not only will it require all your mental energy, focus, and persistence, but it will also require a significant investment of your time. Your particular area of research, your institution’s policies and procedures, and the standard expectations within your field affect how long it takes to earn a PhD. The average PhD length is five or six years, while some students may take eight or nine years.
Regardless of how long a PhD program takes, there are some common stages of a PhD that all doctoral students share. These significant and essential milestones shape the timeline for earning your doctorate . Read on as we take you through each step and explore the typical steps to a doctorate degree.

How Long Do PhD Programs Take?
The number of credit hours that you need to complete your doctoral coursework might depend on several factors: do you already have a master’s degree? Will you earn one en route to the doctorate? Or do you even need one?
Different disciplines and research interests have their own PhD process, but even within your field of study, institutions may have diverse pathways for obtaining that terminal degree. For most, coursework will take anywhere from two to three years to complete.
During this time, students can serve as graduate research or teaching assistants or could even lead their own courses as instructors. In many degree programs, students develop their potential dissertation topics through their coursework and define their research plans in the next few years.
Steps to Getting a PhD: PhD Qualifying Exam and Comprehensive Exam
Many programs set up academic checkpoints to help keep students on track during their PhD journeys. The timing varies by program, but one of the most common – and possibly most stressful – forms of benchmarking is the PhD comprehensive exam or qualifying exam. Often administered around the end of the student’s coursework, these exams are your chance to demonstrate what you learned in your classes.
A faculty committee from your department oversees testing. Usually comprised of at least three members, your professors ask questions or assign writing prompts based on your experience in the program thus far. The format is generally a combination of written and oral exams designed to test your expertise in your discipline’s methodologies and significant content areas.
To better prepare yourself, research the number and kind of qualifying benchmarks the program will require in the university catalog before you begin your program. This will allow you and your advisor to effectively plan out the first few years of your degree and give you an idea of how you’ll be evaluated throughout your program.
Doctoral Dissertation Prospectus and Defense
You may be required to complete and defend a dissertation prospectus before officially becoming a PhD candidate. A prospectus is a document outlining your dissertation plan, which includes an explanation of your research topic, a potential outline of your dissertation, the methodologies you intend to employ, the significance of your research question, and a bibliography including sources that form the foundation of your research.
Your prospectus allows your dissertation advisor to understand the scope of your project. It should be thorough enough that they can provide useful feedback to help shape your research plan. After some revisions, an approved prospectus is the green light to move into the next stage of your PhD.
Advancement to Doctoral Candidacy
If you have heard the term ABD – “All But Dissertation” – then that means you are in the home stretch of your doctoral program!
Well, sort of…only your dissertation remains!
Doctoral Dissertation Research and Writing
While you’ve made it through the coursework and qualifying exams, the dissertation is the culminating component of the doctoral degree. At this point, your approved research plan is ready to be set into motion. Depending on your discipline, this could be the stage where you travel extensively to conduct fieldwork, explore archives, or visit labs to collaborate on projects that relate to your dissertation work. For many students, the research phase can take a couple of years, but some may be able to complete it in one.
Writing your dissertation can be one of the most challenging parts of the whole PhD process. Not only are you condensing years of research into a single cohesive document, but you are also formulating graphs, charts, and other textual references to help clarify your argument. Often, formatting can be a major challenge for many students.
In this stage, it’s most helpful to seek out resources to help you with the writing process. Many universities have dissertation writing workshops where you can learn best practices, as well as support groups where students meet regularly and help keep each other accountable. Most universities also offer competitive dissertation completion grants, supporting students with additional funding so they focus more of their time and effort on completing this undertaking.
Dissertation Defense
Everyone gets nervous about this major rite of passage. It can be difficult to take criticism over something you have poured your heart and soul into for years. Remember, though, that a good advisor will not let you defend if you’re not ready, and you literally wrote the book on your topic!
The dissertation defense is not intended to tear your work apart but rather is your opportunity to prove your expertise to your dissertation committee. Many defenses are open to observers, so you should attend a few in advance of your own, especially within your department, to get a sense of what it’s like.
First, you’ll present the main points of your thesis. Then the committee will ask questions so they can clearly understand your arguments. Finally, they’ll send you out of the room while they deliberate and decide if you pass or not. If all goes well, you’ll be addressed as “Doctor” the next time you walk into the room!
Get Started on Your PhD Journey Today
No matter what your particular timeline looks like as you work toward your doctorate, know that the faculty and other students within your program are frequently a huge source of support — which means you won't do this alone! Additionally, every school has resources to assist PhD students, from libraries to writing centers to dedicated student support services.
If you are excited about beginning your PhD journey, we invite you to request more information or reach out to one of our admissions professionals today. Best of luck as you begin this transformational experience!
learn more about
what it takes to apply to and succeed in a PhD program. Explore our resource — A Guide to Choosing, Applying for, and Thriving in a PhD Program!
hbspt.cta._relativeUrls=true;hbspt.cta.load(3974384, 'aeb4e03d-f8e9-4232-9726-8852204e83e1', {"useNewLoader":"true","region":"na1"});
Request more, information.
Complete the form to reach out to us for more information

Published On
More articles, recommended articles for you, what can you do with a phd in history.
You’re a history buff — the person everyone wants on their trivia team. You can rattle off the...
The 6 Best Types of PhD Programs for English Majors
If you’re reading this, you’re probably exploring your options for advancing your undergraduate...
Unlocking Possibilities: What Can You Do With a PhD in English?
The world of academia has long been associated with the pursuit of knowledge, scholarly research...
Browse articles by topic
Subscribe to.

- Youth Program
- Wharton Online
How the PhD Program Works
Program Overview
Completing your doctorate at Wharton requires 5 years of full-time study. The first 2 years in the program prepare you for admission to candidacy by taking courses, qualifying exams, and starting research projects. In the last few years, you are primarily conducting research full-time including writing and defending your doctoral dissertation.
Admission to candidacy.
You begin by taking courses required for your program of study. All programs requires a preliminary exam, which may be either oral or written.
Some programs may have further requirements, such as an additional exam or research paper. If you enter with a master’s degree or other transfer credit, you may satisfy the formal course requirements more quickly.
Beginning the Wharton PhD Curriculum How the first two years of the Wharton program helped students discover their interests, learn the tools of the profession, and fuel their passion for teaching.
The Doctoral Dissertation
Upon successful completion of coursework and passing a preliminary examination, you are admitted to candidacy for the dissertation phase of your studies.
Your doctoral dissertation should contain original research that meets standards for published scholarship in your field. You are expected to be an expert in the topic you choose to research.
You are admitted to candidacy for the dissertation phase of your studies upon successful completion of coursework and passing a preliminary examination, but you can start thinking about and working on research of relevance at any time.
The dissertation process culminates with a “defense,” in which you defend the proposal orally before your dissertation committee.
While working on your dissertation, you interact extensively with Wharton faculty. Together with interested faculty, you create your own research community that includes your dissertation advisor and dissertation committee.
Policies and Procedures
Get more detailed explanation of course requirements, academic standards, the Teacher Development Program, time limits, and dissertation procedures and requirements.
Sample Program Sequence
Years 1 & 2.
Coursework Examination Research Papers Research Activities Field-Specific Requirements
Directed Reading & Research Admission to Candidacy Formulation of Research Topic
Years 4 & 5
Continued Research Oral Examination Dissertation
Hear From Our Doctoral Community
Closing the tenure gap for business faculty of color.
The Wharton School
How This PhD Student Discovered a Dynamic Research Community at Wharton
Conducting ground-breaking research at wharton.
Frequently asked questions
How long does it take to get a phd.
This varies by country. In the United States, PhDs usually take between 5–7 years: 2 years of coursework followed by 3–5 years of independent research work to produce a dissertation.
In the rest of the world, students normally have a master’s degree before beginning the PhD, so they proceed directly to the research stage and complete a PhD in 3–5 years.
Frequently asked questions: Graduate school
In the US, most graduate school applications require you to include:
- Transcripts from previous educational institutions
- Standardized test scores (such as the GRE or MCAT)
- A graduate resume
- 2–3 letters of recommendation
- A statement of purpose
Some programs may ask you to write a personal statement in addition to, or instead of, a statement of purpose. You may also be asked to an interview .
Always carefully read the application instructions for the specific program you’re applying to.
Most medical school programs interview candidates, as do many (though not all) leading law and business schools.
In research programs, it depends—PhDs in business usually do, while those in economics normally do not, for example.
Some schools interview everyone, while others only interview their top candidates. Look at the websites of the schools you’re applying to for more information on whether they conduct interviews.
In addition to thinking about your answers for the most commonly asked grad school interview questions , you should reach out to former and current students to ask their advice on preparing and what sort of questions will be asked.
Look back through your resume and come up with anecdotes that you could use for common questions, particularly those that ask about obstacles that you overcame. If you’re applying for a research program, ensure that you can talk about the previous research experience you’ve had.
You should also read as much research in your field as possible. Research the faculty at the schools you’re applying to and read some of their papers. Come up with a few questions that you could ask them.
Graduate schools often ask questions about why you are interested in this particular program and what you will contribute.
Try to stay away from cliche answers like “this is a good program” or “I got good grades in undergrad” and focus instead on the unique strengths of the program or what you will bring to the table. Understand what the program is looking for and come up with anecdotes that demonstrate why you are a good fit for them.
Different types of programs may also focus on different questions:
- Research programs will often ask what topics you’d like to research and who you would like to work with, as well as specific questions about your research background.
- Medical schools are interested in your personal motivation, qualities such as integrity and empathy, and how you’d respond to common ethical dilemmas.
- Business schools will focus on your past work experience and future career prospects, and may be particularly interested in any experience you have managing or working with others.
Some students apply to graduate school straight from undergrad, but it’s also common to go back to school later in life. The ideal time to do so depends on various financial, personal, and career considerations . Graduate school is a big commitment, so you should apply at a time when you can devote your full attention to it.
Your career path may also determine when you should apply. In some career fields, you can easily progress without a graduate degree, while in others—such as medicine, business, and law—it’s virtually impossible to move up the career ladder without a specific graduate degree.
Most graduate school applications for American graduate programs are due in December or January for a September start.
Some types of programs, especially law school, are rolling applications, meaning that the earlier you apply, the earlier you’ll hear back. In this case, you should aim to apply as early as possible to maximize your chances.
Medical school follows a completely separate timeline with much earlier deadlines. If you’re applying for medical school, you should speak to advisors at your university for more information.
A good starting point to aim for is about 18 months before you would start the program, or 6–9 months before the applications are due.
In the first few months of the process, research programs and study for any standardized exams you might need.
You can then begin writing your personal statements and statements of purpose , as well as contacting people to write your letters of recommendation . Ensure that you give recommenders plenty of time to complete their letters (ideally around 2–4 months).
In the US, the graduate school application process is similar whether you’re applying for a master’s or a PhD . Both require letters of recommendation , a statement of purpose or personal statement , a resume or CV , and transcripts. Programs in the US and Canada usually also require a certain type of standardized test—often the GRE.
Outside the US, PhD programs usually also require applicants to write a research proposal , because students are expected to begin dissertation research in the first year of their PhD.
A master’s degree usually has a higher upfront cost, but it also allows you to start earning a higher salary more quickly. The exact cost depends on the country and the school: private universities usually cost more than public ones, and European degrees usually cost less than North American ones. There are limited possibilities for financial aid.
PhDs often waive tuition fees and offer a living stipend in exchange for a teaching or research assistantship. However, they take many years to complete, during which time you earn very little.
This depends on the country. In the United States, you can generally go directly to a PhD with only a bachelor’s degree, as a master’s program is included as part of the doctoral program.
Elsewhere, you generally need to graduate from a research-intensive master’s degree before continuing to the PhD.
A PhD, which is short for philosophiae doctor (doctor of philosophy in Latin), is the highest university degree that can be obtained. In a PhD, students spend 3–5 years writing a dissertation , which aims to make a significant, original contribution to current knowledge.
A PhD is intended to prepare students for a career as a researcher, whether that be in academia, the public sector, or the private sector.
A master’s is a 1- or 2-year graduate degree that can prepare you for a variety of careers.
All master’s involve graduate-level coursework. Some are research-intensive and intend to prepare students for further study in a PhD; these usually require their students to write a master’s thesis . Others focus on professional training for a specific career.
It’s best to ask in person if possible, so first reach out and request a meeting to discuss your graduate school plans.
Let the potential recommender know which programs you’re applying to, and ask if they feel they can provide a strong letter of recommendation . A lukewarm recommendation can be the kiss of death for an application, so make sure your letter writers are enthusiastic about recommending you and your work!
Always remember to remain polite. Your recommenders are doing you a favor by taking the time to write a letter in support of your graduate school goals.
This depends on the program that you are applying for. Generally, for professional programs like business and policy school, you should ask managers who can speak to your future leadership potential and ability to succeed in your chosen career path.
However, in other graduate programs, you should mostly ask your former professors or research supervisors to write your recommendation letters , unless you have worked in a job that corresponds closely with your chosen field (e.g., as a full-time research assistant).
Choose people who know your work well and can speak to your ability to succeed in the program that you are applying to.
Remember, it is far more important to choose someone who knows you well than someone well-known. You may have taken classes with more prominent professors, but if they haven’t worked closely with you, they probably can’t write you a strong letter.
The sections in your graduate school resume depend on two things: your experience, and the focus of the program you’re applying to.
Always start with your education. If you have more than one degree, list the most recent one first.
The title and order of the other sections depend on what you want to emphasize. You might include things like:
- Professional experience
- Voluntary and extracurricular activities
- Publications
- Awards and honors
- Skills and certifications
The resume should aim for a balance between two things: giving a snapshot of what you’ve done with your life so far, and showing that you’re a good candidate for graduate study.
A resume is typically shorter than a CV, giving only the most relevant professional and educational highlights.
An academic CV should give full details of your education and career, including lists of publications and presentations, certifications, memberships, grants, and research projects. Because it is more comprehensive, it’s acceptable for an academic CV to be many pages long.
Note that, outside of the US, resume and CV are often used interchangeably.
No, don’t include your high school courses and grades. The education section should only detail your college education.
If you want to discuss aspects of high school in your graduate school application, you can include this in your personal statement .
A resume for a graduate school application is typically no more than 1–2 pages long.
Note, however, that if you are asked to submit a CV (curriculum vitae), you should give comprehensive details of all your academic experience. An academic CV can be much longer than a normal resume.
Always carefully check the instructions and adhere to any length requirements for each application.
If you’re applying to multiple graduate school programs, you should tailor your personal statement to each application.
Some applications provide a prompt or question. In this case, you might have to write a new personal statement from scratch: the most important task is to respond to what you have been asked.
If there’s no prompt or guidelines, you can re-use the same idea for your personal statement – but change the details wherever relevant, making sure to emphasize why you’re applying to this specific program.
If the application also includes other essays, such as a statement of purpose , you might have to revise your personal statement to avoid repeating the same information.
The typical length of a personal statement for graduate school applications is between 500 and 1,000 words.
Different programs have different requirements, so always check if there’s a minimum or maximum length and stick to the guidelines. If there is no recommended word count, aim for no more than 1-2 pages.
A statement of purpose is usually more formal, focusing on your academic or professional goals. It shouldn’t include anything that isn’t directly relevant to the application.
A personal statement can often be more creative. It might tell a story that isn’t directly related to the application, but that shows something about your personality, values, and motivations.
However, both types of document have the same overall goal: to demonstrate your potential as a graduate student and s how why you’re a great match for the program.
Ask our team
Want to contact us directly? No problem. We are always here for you.
- Email [email protected]
- Start live chat
- Call +1 (510) 822-8066
- WhatsApp +31 20 261 6040

Our team helps students graduate by offering:
- A world-class citation generator
- Plagiarism Checker software powered by Turnitin
- Innovative Citation Checker software
- Professional proofreading services
- Over 300 helpful articles about academic writing, citing sources, plagiarism, and more
Scribbr specializes in editing study-related documents . We proofread:
- PhD dissertations
- Research proposals
- Personal statements
- Admission essays
- Motivation letters
- Reflection papers
- Journal articles
- Capstone projects
Scribbr’s Plagiarism Checker is powered by elements of Turnitin’s Similarity Checker , namely the plagiarism detection software and the Internet Archive and Premium Scholarly Publications content databases .
The add-on AI detector is powered by Scribbr’s proprietary software.
The Scribbr Citation Generator is developed using the open-source Citation Style Language (CSL) project and Frank Bennett’s citeproc-js . It’s the same technology used by dozens of other popular citation tools, including Mendeley and Zotero.
You can find all the citation styles and locales used in the Scribbr Citation Generator in our publicly accessible repository on Github .

- Youth Program
- Wharton Online
Wharton Stories
What to expect from a phd schedule.
Take a look at a current student’s schedule and get the insider perspective from doctoral students and coordinators on what to expect from a PhD schedule.
The life of a PhD candidate can be stressful as you adjust to a rigorous academic and research schedule. Penn and Wharton offer a variety of resources to help support you in the transition to PhD life.
Wharton’s sense of community offers a level of comfort when reaching out to faculty as well as fellow students to help solve problems. Doctoral students and coordinators give the insider view on what to expect from a PhD schedule.
Class and Research First
The first two years of a PhD program are mainly made up of classes and the beginning stages of research. Deborah Small , the doctoral coordinator for the Marketing program , said, “It starts with heavy duty coursework and a lot of specific requirements. At the end of your first year, there are qualifying exams on all the core marketing courses. Second year they still have a lot of coursework to do, but more of that is elective with a focus more on their interests. During those years they’re expected to get started on research.”
In addition to taking classes and getting started with research, the Marketing program requires students to write two papers. The first research paper is due at the end of the second year, the other is due at the end of the third year.
The Real Estate and Business Economics and Public Policy programs run like the Marketing program. Fernando Ferreira , coordinator for the programs, said, “During the first year they complete six core courses. In the second year, the focus shifts to field courses and to independent research. They have two professors advising them in that year.”
After completing the main courses, students shift to conducting independent research. For REAL and BEPP students this means writing three dissertation chapters during the third and fourth years.
Time for Conferences and Seminars
Because coursework is usually completed by the second half of the program, there’s time for students to attend lectures and seminars. Andrea Contigiani , a fifth year student in the Management program, said, “In my fourth year, I usually attended a seminar around lunchtime. Wharton has an incredible seminar series throughout the year, with a good seminar happening almost everyday. Occasionally, I attended other events, like MBA events or speaker series. I then go back to research for most of the afternoon.”
Prof. Small said, “Students are expected to actively participate in seminars and activities. They’re also encouraged to go to academic conferences and try to present their work at those conferences. It is similar to the expectations of being a faculty member, minus teaching.”
Classes take up the majority of the first two years of the programs. When the focus then switches to research, you’re expected to work independently. Sometimes that can be intimidating. You become your own boss, which is an adjustment from being told what to do and when to do it.
So how do you manage it? Get advice from students and coordinators.
Posted: August 4, 2017
- Work/Life Balance
Doctoral Programs
Matthew caulfield.
Hometown Ocean City, New Jersey
Concentration Management and Legal Studies & Business Ethics
Doctoral Stage Second Year
Typical Day at a Glance
8:30 am Wake up and get ready for the day
9:15 am Get to PhD Offices, respond to emails, check philosophy blogs and read news
10:30 am Journal article readings
11:30 am Meet with advisor
12:00 pm Attend departmental seminar speaker and lunch
1:30 pm Attend Wharton Social Impact Doctoral Community meeting
3:00 pm Attend business ethics seminar
5:00 pm Read for class
7:00 pm Meet with nonparametric statistics study group
8:00 pm Complete homework
12:00 am Go home
1:00 am Bedtime
What is your favorite part about Wharton?
First, the faculty are excellent. They are often leading experts in their fields, and they can offer advice that would be hard to find elsewhere.
Second, the other PhD students are just as passionate about research as you would hope. A huge part of my scholarly development has been due to the discussions I have had with other graduate students.
Third, the Wharton name can offer you serious advantages. In the course of research, I think industry practitioners as well as other academics have been more willing to talk or correspond with me because I am a graduate student at Wharton.
Related Content

Avoiding the Pitfalls of Drinking at Your Office Holiday Party

How Wharton Students Are Supporting COVID-19 Relief Efforts

AAMBAA Co-Presidents Partner with Classmates to Take a Stand Against Racism

Wharton San Francisco Entrepreneur Reflects on First Year

How GRIP Empowered This Wharton Undergraduate to Explore British Baking and Business

Why This Bioengineering PhD Student Pursued Impact Investing

How Wharton’s EMBA Program Helped this Petroleum Engineer Transition to a Business Role

How the Financial Crisis Led This MBA Student to the U.S. Treasury

Teaching the Future of Work

What Prof. Matthew Bidwell’s Research Reveals about Career Mobility

7 Takeaways from Project Sage 2.0, the Global Scan of Gender Lens Private Equity, VC, and Private Debt Funds

How a Huntsman Student Gained Perspective on Social Responsibility

Lipman Fellows Build Communities, in the World and on Campus

How This EMBA Student Is Bringing Wharton Insights Back to Amazon

Roaming Rwanda: How GRIP Gave This Wharton Undergraduate A Glimpse Into Global Health

How Long Does it Take To Get A PhD? Doctorate Degree Timeline
Starting a PhD means you’re ready for a big academic adventure, full of tough challenges and exciting discoveries.
If you’re thinking about going for it, you’re probably wondering just how much time you’ll need to commit to this big goal.
For full-time PhD students, the journey typically take 3-6 years. However, if you’re juggling other commitments and opt for a part-time PhD, the timeline can extend to 7 years to complete, sometimes more.
This article breaks down what the PhD journey looks like, what can make it longer or shorter, and some tips on how to make it through.
If you’re curious about how long it’ll take to add ‘Dr.’ before your name, you’re in the right place. Let’s dive into the world of PhD timelines!
How Long Does It Take To Get A PhD?
The answer here isn’t straightforward, as it hinges on various factors, including:
- the discipline,
- the institution, and
- whether you’re a full-time or part-time student.
For full-time PhD students, the journey typically take 3-6 years. However, if you’re juggling other commitments and opt for a part-time PhD, the timeline can extend to 7 years to complete, sometimes more.

Distance learning PhD programs offer flexibility but similarly require a substantial time commitment, often mirroring the length of part-time studies.
The heart of a doctoral program is the dissertation, a rigorous research project that demands an in-depth exploration of your chosen field. This phase alone can take several months to years, significantly influencing the overall length of your PhD journey.
Beyond the dissertation, coursework, exams, and sometimes teaching responsibilities add layers to the doctoral experience.
The requirements for a PhD vary widely across disciplines and institutions. For instance, a doctorate in the sciences might involve extensive lab work, potentially extending the time to completion.
In contrast, a doctorate in the arts could hinge more on coursework and creative output, leading to variations in the timeline.
Does A Doctorate Degree Take Longer Than Masters?
A doctorate degree typically takes longer to complete than a master’s degree.
While a master’s program can often be completed in 1-2 years of full-time study, a doctoral program usually requires 4-6 years, depending on the:
- research complexity, and
- whether the student is enrolled full-time or part-time.
The doctoral journey is more than just additional coursework; it involves conducting original research, writing a comprehensive dissertation, and often teaching or engaging in professional development activities.
The dissertation phase, which requires students to contribute new knowledge to their field, is particularly time-consuming and can extend the duration of a PhD program significantly.
The time it takes to complete a doctorate can be influenced by your
- research topic,
- funding availability, and
- the level of support from advisors and faculty.
Master’s programs are typically more structured, with a clearer set of coursework requirements and a shorter thesis or capstone project, leading to a quicker path to graduation.

Why Does It Take So Long To Finish Doctoral Program?
Starting a doctoral program is a significant commitment, often taking longer than anticipated. If you wonder why it takes so long, here are a couple of reasons you can think about:
Extensive Coursework
Initially, you might think coursework in your PhD study is just a continuation of your previous studies.
Doctoral level courses are a different beast. They demand not just understanding but the ability to critically analyze and apply complex concepts.
Each course can feel like a mini research project, requiring more than just classroom attendance. This phase lays the foundation but is time-consuming.
The Dissertation
The heart of your doctoral journey is your dissertation. This isn’t just a long essay or an extended research paper. It’s an original contribution to your field, requiring:
- exhaustive research,
- experimentation, and
Some students find their research path straightforward, while others may hit unexpected roadblocks or need to pivot their focus, extending the time required.
Part-Time Study
Many PhD candidates choose a part-time path due to work, family, or other commitments. While this flexibility is crucial for many, it stretches the duration of the program.
What a full-time student might complete in 4-6 years, part-time students might take 7 years or more to finish.
Funding and Resources
Access to funding and resources can significantly impact the timeline. Some projects require extensive fieldwork, specialised equipment, or access to rare materials. Delays in funding or accessing necessary resources can stall progress.
If funding is an issue, consider applying for work outside of the university. You can also try your luck with the university, as a research or teaching assistant , or more.

Academic Publishing
As part of the doctoral process, many students are encouraged or required to publish their findings.
However, the process of submitting to academic journals, undergoing peer review, and possibly revising and resubmitting, is lengthy.
This step is crucial for the academic community but adds time to the doctoral timeline. If may help to start writing and publishing work earlier to ensure you have enough time to finish.
Faculty Supervision and Mentorship
The relationship with your advisor or supervisory committee is pivotal. These mentors gatekeep your studies, as they:
- guide your research,
- provide feedback, and
- approve your progress.
Scheduling conflicts, feedback loops, and the iterative nature of research can add semesters or even years to your timeline.
Personal Growth and Professional Development
Beyond the academic requirements, doctoral students often engage in teaching, attend conferences, and network within their academic community. These activities contribute to your professional development but also extend your time in the program.
Factors That Influence The Time To Get A PhD
The time it takes to complete PhD is influenced by a multitude of factors, each significant in its own right. Let’s delve deeper into these elements to understand the intricacies of the PhD voyage.
The Scope of Research :
The ambition of your research can significantly dictate the duration of your PhD. Some projects will need more time and commitment, especially if they:
- Demand extensive fieldwork,
- elaborate experiments, or
- groundbreaking theoretical developments.
Imagine embarking on a quest that not only seeks answers but also questions the very foundations of your field. Such endeavours are thrilling but inherently time-consuming, often extending the PhD journey beyond the typical timeframe.
Program Structure and Requirements
The architecture of a PhD program—its coursework, qualifying exams, and other prerequisites—lays the groundwork for your academic expedition.
Programs with a heavy load of initial coursework aim to equip you with a broad foundation, yet this can elongate the path to your actual dissertation work.
Mode of Study
The decision between full-time and part-time study is pivotal. A full-time commitment allows you to immerse yourself in research, ideally hastening progress.
Yet, life’s obligations may necessitate a part-time route, extending the journey but offering flexibility.
Distance learning, with its inherent flexibility, caters to those balancing diverse commitments, yet this mode, too, can stretch the timeline, particularly if it lacks the immediacy and intensity of on-campus engagement.
Quality of Supervision
The symbiotic relationship with your advisor is the compass guiding your research voyage. An advisor who is both a mentor and a critic, offering timely and constructive feedback, can expedite your journey.
Less engaged supervision may leave you adrift, prolonging the process as you navigate the academic waters largely on your own.
Worse still, if you are unlucky enough, you may end up with supervisors that not only does not help you, but actively attempt to make your study life difficult. These nightmare scenarios do exist, and you should be aware of them.
Financial Stability
The financial underpinnings of your PhD endeavor are more critical than often acknowledged. Consistent funding allows you to dedicate yourself fully to your research, free from financial distractions.
Conversely, the absence of stable support might necessitate part-time employment, diluting focus and extending the timeline.
Resource Availability
Access to specialized resources—be it state-of-the-art laboratories, rare archival collections, or cutting-edge software—can be the wind in your PhD sails.
Limited or delayed access to these essential tools, however, can stall progress, turning what could be a swift journey into a prolonged odyssey.
If you found yourself in a position without the right resources to complete your PhD, consider to propose your university to allow you to work with other universities with what you need. If this is not possible, you can always transfer university, although this would mean more work.
Publishing Requirements
The adage “publish or perish” holds particularly true in the realm of PhD studies. The process of getting your research published, from initial submission to eventual acceptance, is fraught with delays and revisions. Each publication cycle can add months to your timeline,
Yet these publications are crucial stepping stones towards establishing your academic credibility. In fact, some universities want you to publish papers to graduate.
Personal Life and Circumstances
The journey towards a PhD is not undertaken in academic isolation. Life, with its unforeseen challenges and responsibilities, continues.
Personal circumstances can impact your ability to devote time and energy to your studies, necessitating pauses or a reduction in research intensity.
These issues can range from situation such as:
- such as health issues,
- family commitments, or
- significant life events

Tips To Earn Your Doctoral Degree Fast
Earning a doctoral degree is a significant academic endeavor, often perceived as a marathon rather than a sprint. However, with strategic planning and focused effort, you can navigate this journey more swiftly than you might expect.
Here are some tips to help you earn your doctoral degree faster, drawing from the experiences and strategies of successful PhD candidates.
Choose Your Program Wisely
The structure of the PhD program you choose can greatly influence how long it takes to complete your degree. Programs that allow you to start your dissertation research early, even while completing your coursework, can save you a considerable amount of time.
Some program are designed to integrate dissertation work with coursework, enabling a more seamless transition into the research phase.
Opt for Full-Time Study If Possible
While part-time PhD programs offer flexibility for working professionals, full-time study allows for a more immersive research experience.
Dedicating all your working hours to your doctoral research can expedite the process, reducing the time it takes to get your PhD significantly.
Secure Adequate Funding
Financial stability is key to focusing fully on your research without the distraction of part-time work. Look for:
- scholarships,
- grants, and
- funding opportunities from your institution.
You can also try to secure funding from external sources like the National Science Foundation.
Secure funding not only supports your financial needs but also often comes with academic resources that can accelerate your research progress.
Develop a Strong Relationship with Your Advisor
Your advisor is your guide through the PhD process. A supportive advisor can provide invaluable feedback, help you navigate academic challenges, and keep you on track.
Regular meetings and clear communication with your advisor can help you refine your research direction and avoid time-consuming pitfalls.
Focus Your Research
A well-defined research question can provide a clear path forward. The more focused your research, the less likely you are to get bogged down in unmanageable amounts of data or tangential studies.
It’s about depth rather than breadth; delving deeply into a specific area can lead to significant contributions to your field and a quicker path to completion.

Take Advantage of Existing Research and Resources
Don’t reinvent the wheel. Building on existing research and utilizing available resources can save you time. This includes:
- leveraging datasets,
- using established methodologies, and c
- ollaborating with other researchers.
Access to resources like specialized labs or archives, as provided by your institution, can also streamline the research process.
Stay Organized and Manage Your Time Effectively
Good time management is crucial. Set realistic goals, create a timeline for your research and writing, and stick to it.
Tools like Gantt charts can help you visualize your PhD timeline, including key milestones like coursework completion, comprehensive exams, and dissertation chapters.
Get Your PhD Without Taking Too Much Time – Possible
The journey to obtaining a PhD is a unique blend of personal commitment, academic rigor, and research innovation.
While the timeline can vary widely, most candidates find themselves immersed in their studies and research for anywhere from 4 to 6 years. Exceptions can happen, and you may finish earlier or later.
Key factors like your field of study, the nature of your research, and your personal life circumstances play significant roles in shaping your individual journey.
Remember, earning a PhD is more than just a race to the finish line; it’s a profound journey of learning, discovery, and personal growth. Embrace the journey, stay focused, and the day you earn the title of ‘Doctor’ will be a milestone to remember.

Dr Andrew Stapleton has a Masters and PhD in Chemistry from the UK and Australia. He has many years of research experience and has worked as a Postdoctoral Fellow and Associate at a number of Universities. Although having secured funding for his own research, he left academia to help others with his YouTube channel all about the inner workings of academia and how to make it work for you.
Thank you for visiting Academia Insider.
We are here to help you navigate Academia as painlessly as possible. We are supported by our readers and by visiting you are helping us earn a small amount through ads and affiliate revenue - Thank you!

2024 © Academia Insider

- Home »
- Blog »
How Long Does It Take To Get A PhD (Doctorate)?
Find your perfect postgrad program search our database of 30,000 courses.
- by Charlotte King
- In General , PHD
As with many things in life, how long it takes you to get a PhD depends mostly on you. Because doctorate degrees are flexible, the duration of study can vary. But if you work hard and are disciplined, how long will it take you to get a PhD
How long is a full-time PhD?
In most cases, PhD research involves full-time study. You should expect to dedicate around 35 hours per week to your work. However, in busy periods, such as writing up your thesis , you may need to work for considerably longer.
In the UK, it usually takes three to four years of full-time study to gain a PhD. Time is spent carrying out research and collecting data towards a thesis. Your thesis can take a year to write and will offer an original contribution to your subject.Once you have completed your thesis you will usually have to undertake a PhD viva to present, explain and defend your research.
Most students begin a PhD after completing a relevant masters course. A masters degree will usually take around one year to complete if you are studying full time, or two to five years if you are studying part time. So from undergraduate to doctorate, you should expect it to take at least four years full time.
In Europe, the time it takes to gain a PhD can vary depending on the country and the subject of study. For example, in Germany, a PhD in a scientific subject might take two to three years full time, and a doctorate in the arts or humanities may take four to six years full time. In Norway, all PhDs usually take three years on a full-time basis. Most countries are similar to the UK, where you complete your PhD once you have done a relevant masters course.
In Norway , all PhDs usually take three years on a full-time basis – here is a great explanation from the University of Oslo . It can take up to six years to complete a PhD on a part-time basis, but this way of studying is unusual.
The USA has a different university set up to the UK and Europe as most doctorate degrees are gained by going to Graduate School straight after you have completed your undergraduate degree. This means that the time it takes to gain your masters-level qualification is built into the time it takes to get your PhD. It is common for it to take four to five years to gain a Doctorate from the time you start Graduate School, but it can take up to eight years of full-time study. It depends on the institution and the type of PhD you choose.
Some institutions, like Franklin University, allow students to transfer credits and count professional work experience towards their doctorate degrees, so you could complete a PhD in as little as three years.
How long is a part-time PhD?
Studying for a PhD part time is a good way to accommodate other work or life commitments alongside your research. Typically, it takes twice as long as a full-time PhD and you will study for around 20 hours a week.
Not many PhD students undertake their doctorate on a part-time basis, but those who do will have between five and seven years to complete their PhD.
Part-time PhDs are unusual in Europe. In Germany, you could expect a PhD to take four to eight years. France is similar to Germany, and it takes around three to four years for a full-time doctorate in the sciences, and four to five years for a doctorate degree in the arts and humanities. At the University of Oslo, it can take up to six years to complete a PhD on a part-time basis.
Part-time and online PhDs are more common in the USA and these take anywhere from five to 10 years to complete.
How long is a distance learning PhD?
There are some doctorate degrees which are studied by distance learning. These online PhDs allow students to study at a location and time that suits their schedule. These tend to be part time only and usually take up to seven years to complete.
Entry requirements for a PhD
In the UK the vast majority of PhD candidates will begin a PhD after completing a relevant masters course . A masters degree will usually take around one year to complete if you are studying full time, or two to five years if you are studying part time. Once you've gained this qualification you can move onto the doctorate after you have excelled at your PhD interview.
Different countries in Europe have different traditions and regulations surrounding doctorate degrees. Most countries are similar to the UK, where you complete your PhD once you have done a relevant masters course.
Why does it take so long to complete a PhD?
Due to the complexity of the study and the amount of original research required, PhDs typically take longer to complete than other undergraduate degrees. It can take a long time to create a thesis, since you must make an original and noteworthy contribution to your field.
What is the deadline for finishing a PhD?
The deadline for submitting your PhD will be set by your university. In the UK, the deadline is defined by the last date on which you can submit your thesis. For most PhDs, the deadline is four years for full-time students and seven years for part-time students. It may be possible to extend the deadline up to four years, but this is at the discretion of the university.
Does funding impact the length of a PhD?
Generally, PhD funding providers will cover you for a set amount of time during the course of your PhD. Most students will aim to finish their PhD within the timeframe set by their funding provider to avoid incurring additional fees.
Self-funded students cover their own tuition fees and other related costs, therefore many self-funded students aim to complete their PhDs in the shortest time possible.

Read more about postgraduate tuition fees on our fees and funding information page .
Find your ideal PhD
Search for your ideal PhD or browse our collection of helpful PhD articles on Postgrad.
Editor’s note: this blog post was originally published in April 2018, it now contains some updated information.
amber is one of many potential private accommodation options for international postgraduate students. Other private student accommodation options are available and Postgrad.com advises you to research all your options thoroughly before making such a commitment. Postgrad Solutions accepts no responsibility for your choice of student accommodation and does not endorse or support amber.
Related articles
Dos & Don'ts Of A PhD Interview
How To Get A PhD
How To Find A PhD
How Much Does It Really Cost To Study A PhD In The UK?
Are You Ready For A PhD?
Postgrad Solutions Study Bursaries
Elisha June 25, 2019, 9:49 p.m.
I’m Wanting to be a child therapist so what degree would I need for this and how long would I be at uni for Thankyou
Charlotte King June 28, 2019, 1:59 p.m.
Hi Elisha, A bachelors degree in counselling, social work, or child psychology is often a good start for a child counselling career, and most child counsellors are usually required to earn graduate degrees as well. So that would be a minimum of 4 years study.
Amoo Monsuru Olukayode Nov. 24, 2021, 2:44 a.m.
I want to study abroad in any UK country
Charlotte King Dec. 6, 2021, 9:37 p.m.
We have a comprehensive section on postgraduate study in the UK to help you make your decision > https://www.postgrad.com/study-in-uk/ I hope it helps.
Juli Hanes March 9, 2023, 4:42 p.m.
You always provide great examples and real-world applications, thank you for your valuable contributions.
Charlotte King March 13, 2023, 5:08 p.m.
Thanks Juli!
Leave a comment
All contributors must be over 16 year olds
By submitting your comment you agree to our privacy policy .
- Accommodation
- Coronavirus (Covid-19)
- Distance Learning / Online Study
- Infographic
- International Students
- Jobs and Careers
- Mature Students
- MBA Programs
- Personal Statement
- Student Life
- Student Welfare
- Study Abroad
- Study Advice
- Study In Australia
- Study In Europe
- Study In Ireland
- Study in UK
- Study In USA
- Theses and Dissertations
- Top 10 Lists
- Universities

Exclusive bursaries Open day alerts Funding advice Application tips Latest PG news
Complete Our Destination Survey

Take 2 minutes to complete our Destination Survey for the chance to win a Postgrad Study Bursary worth £2,000.
All we need to know is:
- Your university
- Your PG course
What is a PhD? Advice for PhD students
How long does it take to get a doctorate degree how do you get into grad school are you qualified to do a phd answers to these questions and more.
What is a PhD?
A PhD, which stands for “doctor of philosophy”, is the most advanced academic degree. It’s earned through extensive research on a specific topic, demonstrating expertise and contributing new knowledge to the field.
What does “PhD” mean?
The term “PhD” is often used as a synonym for any doctoral-level qualification. Doctorate degrees can often be split into two categories: MPhil and PhD.

Download your Study Abroad Guide for FREE!
An MPhil is similar to a PhD as it includes a research element (which is usually shorter and less in-depth than a PhD thesis, and often more akin to a dissertation undertaken at undergraduate or master’s level).
MPhil students focus more on interpreting existing knowledge and theory and critically evaluating other people’s work rather than producing their own research. The precise nature and definition of an MPhil can vary among institutions and countries.
A PhD, meanwhile, follows a more widely known and traditional route and requires students, often referred to as “candidates”, to produce their own work and research on a new area or topic to a high academic standard.
PhD requirements vary significantly among countries and institutions. The PhD, once completed, grants the successful candidate the title of “doctor of philosophy”, also called PhD or DPhil.
What is a professional doctorate?
A professional doctorate is a kind of degree that helps people become experts in their fields. Instead of focusing mainly on theory and research like a regular PhD, a professional doctorate is all about practical skills and knowledge.
This kind of doctorate is great for students who want to get better at their jobs in areas like teaching, healthcare, business, law or psychology. The courses and projects in these programmes are designed to tackle real problems you might face at work.
For example, you might have heard of the doctor of education (EdD), doctor of business administration (DBA), doctor of psychology (PsyD) or doctor of nursing practice (DNP). These programmes combine learning, hands-on projects and sometimes a thesis paper or essay to show you’re skilled at solving on-the-job challenges.
How long does it take to study a PhD?
The time required to complete a PhD can vary significantly based on several factors. Generally, a full-time PhD programme takes around three to six years to finish. However, it’s important to take into account individual circumstances and the nature of the research involved.
1. Full-time vs. part-time: If you’re studying full-time, dedicating most of your time to your studies, it usually takes about three to four years to complete a PhD. However, studying part-time while managing other commitments might extend the duration. Part-time PhDs can take around six to eight years, and sometimes even longer.
2. Nature of research: The complexity of your research proposal can influence the time required. Certain research questions may involve intricate experiments, extensive data collection or in-depth analysis, potentially leading to a longer completion timeline.
3. Field of study: The subject area you’re researching can also affect the necessary time. Some fields, such as sciences or engineering, might involve more hands-on work, while theoretical subjects might require more time for literature review and analysis.
4. Supervision and support: The guidance and availability of your academic supervisor can affect the pace of your research progress. Regular meetings and effective communication can help keep your studies on track.
5. Thesis writing: While the research phase is crucial, the stage of writing your thesis is equally significant. Organising and presenting your research findings in a clear and cohesive manner can take several months.
6. External commitments: Personal commitments, such as work, family or health-related factors, can influence your study time. Some students need to balance these alongside their PhD studies, potentially extending the duration.
7. External Funding: The availability of funding can also affect your study duration. Some funding might be linked to specific project timelines or research objectives.
So, although a PhD usually takes between three and six years of full-time study, with potential variations based on research complexity, enrolment as part-time or full-time, field of study and personal circumstances. It’s vital to have a realistic understanding of these factors when planning your PhD journey.
How long is a PhD in the UK?
In the UK, the length of a PhD programme typically ranges from three to four years of full-time study. As explained above, there are many factors to consider.
How long is a PhD in the US?
Similarly to the UK, in the United States, the duration of a PhD programme can vary widely depending on the field of study, research topic and individual circumstances. On average, a full-time PhD programme in the US typically takes between five and six years to complete.
Why does it take longer to study a PhD in the US?
PhD programmes generally take longer to complete in the US than in the UK due to various factors in the education systems and programme structures of each country:
1. Programme structure: UK PhD programmes often emphasise early, focused research from the first year, leading to shorter completion times. In contrast, US programmes commonly include more initial coursework in your first and second year and broader foundational training, which can extend the overall duration.
2. Course work requirements: Many US PhD programmes require a lot of course work, which can lengthen the time needed to finish. UK programmes tend to have fewer or no course work demands, allowing students to concentrate primarily on research skills.
3. Research funding: In the UK, PhD funding is often awarded with specific timeframes in mind, motivating completion of the research degree in the agreed duration. In the US, funding approaches can vary, requiring students to secure funding from multiple sources, potentially affecting their progress and completion time.
4. Teaching responsibilities: Some US PhD students take on teaching roles as part of their funding, dividing their time and potentially prolonging their studies.
5. Research approach: Differences in research methodologies and project scopes can affect the time needed for data collection, experimentation and analysis.
6. Academic culture: The US education system values a well-rounded education, including coursework and comprehensive exams. This can extend the time before full-time research begins. UK PhD programmes often prioritise independent research early on.
7. Part-time and work commitments: US PhD candidates might have more flexibility for part-time work or other commitments, which can affect research progress.
8. Dissertation requirements: US PhD programmes generally include a longer and more comprehensive dissertation, involving more chapters and a broader exploration of the research topic.
These variations in programme structures, funding models and academic cultures contribute to the differing completion times between the two countries.
What qualifications do you need for a PhD?
To be eligible for a PhD programme, certain educational qualifications are generally expected by universities. These qualifications serve as indicators of your readiness to engage in advanced research and contribute to the academic community.
First, an undergraduate or bachelor’s degree in a relevant field is typically the most common requirement. This degree provides you with a foundational understanding of the subject and introduces you to basic research methodologies. It serves as a starting point for your academic journey.
Do you need a master’s degree to get into a PhD programme?
In addition to an undergraduate degree, many PhD programmes also require candidates to hold postgraduate or master’s degrees, often in fields related to the intended PhD research. A master’s degree offers a deeper exploration of the subject matter and enhances your research skills. Possessing a master’s degree signifies a higher level of expertise and specialisation.
The combination of both undergraduate and postgraduate degrees demonstrates a solid academic background. This background is crucial before you engage in doctoral study because pursuing a PhD involves more than just knowledge; it requires advanced research abilities, critical thinking and the capacity to provide an original contribution and new insights into the chosen field of study.
While these qualifications are usually requested, there are exceptions. Some institutions offer direct-entry programmes that encompass bachelor’s, master’s and PhD degrees in a streamlined structure. This approach is often seen in scientific and engineering disciplines rather than humanities.
In exceptional cases, outstanding performance during undergraduate studies, coupled with a well-defined research proposal, might lead to direct entry into a PhD programme without requiring a master’s degree.
Admission requirements can vary between universities and programmes. Some institutions might have more flexible prerequisites, while others could have more stringent criteria. Make sure that you thoroughly research all admission requirements of the PhD programmes you’re interested in to ensure you provide the right information.
Are PhD entry requirements similar in other countries?
PhD entry requirements in Canada and Australia can be somewhat similar to those in the UK and the US, but there are also some differences. Just like in the UK and the US, having a bachelor’s degree followed by a master’s degree is a common way to qualify for a PhD in Canada and Australia. However, the exact rules can vary, such as how much research experience you need or the grades you should have.
In Canada and Australia, as in the UK and the US, international students usually need to show their English language skills through tests like IELTS or TOEFL. And, like in other places, you might need to give a research proposal to explain what you want to study for your PhD.
But remember, even though there are some similarities, each country has its own rules.
PhD diary: Preparing for a PhD Nine things to know before doing a PhD Women in STEM: undertaking PhD research in cancer Studying for a part-time PhD: the challenges and the benefits Is it possible to do a three-year PhD as an international student? Looking for PhD tips? Why not check Twitter PhD diary: Where do I begin? How to do a PhD on a budget
How much does it cost to study a PhD?
The cost of pursuing a PhD can vary significantly between international and home (domestic) students, and it depends on the country, university and programme you choose.
United Kingdom (UK)
Home students in the UK often pay lower tuition fees compared with international students. Home students might also have access to government funding or subsidised tuition rates.
International students typically pay higher tuition fees, which can vary widely depending on the university and programme. Fees can range from around £10,000 to £25,000 or more per year.
United States (US)
PhD programme costs in the US can be quite high, especially for international students. Public universities often have lower tuition rates for in-state residents compared with out-of-state residents and international students.
Private universities in the US generally have higher tuition fees, and international students might be charged higher rates than domestic students.
Canadian universities often charge higher tuition fees for international students compared with domestic students.
Some universities offer funding packages that include tuition waivers and stipends for both domestic and international doctoral students.
In Australia, domestic students (Australian citizens and permanent residents) usually pay lower tuition fees than international students.
International students in Australia might have higher tuition fees, and costs can vary based on the university and programme.
Apart from tuition fees, other aspects play a role in the overall financial consideration:
PhD studentship: Many universities offer PhD studentships that provide financial support to research students, covering both tuition fees and a stipend for living expenses.
Stipend and housing: Stipends are designed to cover living expenses. Stipend amounts can vary depending on the university and location. If you’re studying in London in the UK, stipends might be higher to account for the higher living costs in the city. Some universities also offer subsidised or affordable housing options for doctoral students.
Tuition and stipend packages: Some PhD programmes provide funding packages that include both tuition waivers and stipends. These packages are to help relieve the financial burden on students during their doctoral studies.
Research the financial support options provided by the universities you’re interested in to make an informed decision about the cost of your PhD journey.
What funding options are available for PhD candidates?
PhD candidates have various funding options available to support their studies and research journeys. Some of these options include:
PhD scholarships: Scholarships are a common form of financial aid for PhD candidates. They are awarded based on academic merit, research potential or other specific criteria. Scholarships can cover tuition fees and provide a stipend for living expenses.
Bursaries: Bursaries are another form of financial assistance offered to students, including PhD candidates, based on financial need. They can help cover tuition fees or provide additional financial support.
In the UK, specific funding options are available:
Regional consortium: Some regions have research consortiums that offer funding opportunities for doctoral candidates. These collaborations can provide financial support for research projects aligned with specific regional needs.
UK research institute: Research councils in the UK often offer stipends to PhD candidates. These stipends cover living expenses and support research work.
University-based studentship: Many UK universities offer studentships. You can read more about these above.
In the USA, there are also funding options available:
Research assistantships (RAs): Many universities offer research assistantships where PhD candidates work on research projects under the guidance of faculty members. In exchange, they receive stipends and often have their tuition waived.
Teaching assistantships (TA): Teaching assistantships involve assisting professors in teaching undergraduate courses. In return, PhD candidates receive stipends and sometimes tuition remission.
Fellowships: Fellowships are competitive awards that provide financial support for PhD candidates. They can come from universities, government agencies, private foundations and other institutions. Fellowships can cover tuition, provide stipends and offer research or travel funds.
Graduate assistantships: Graduate assistantships include a range of roles, from research and teaching to administrative support. These positions often come with stipends and sometimes include tuition benefits.
External grants and fellowships: PhD candidates can apply for grants and fellowships from external organisations and foundations that support research careers in specific fields. Examples include the National Science Foundation (NSF) and the Fulbright Programme.
Employer sponsorship: In some cases, employers might sponsor employees to pursue PhDs, especially if the research aligns with the company’s interests.
You can read about the current available scholarships for international students of all education levels on our website .
What does a PhD Involve?
How does a PhD work?
A PhD includes thorough academic research and significant contributions to your chosen field of study. The timeline for completing a PhD can significantly vary based on the country, college or university you attend and the specific subject you study.
The duration of a PhD programme can vary based on factors such as the institution’s requirements and the academic discipline you’re pursuing. For instance, the timeline for a PhD in a science-related field might differ from that of a humanities discipline.
UK PhD timeline example
Looking at a typical PhD degree in a London higher education institution, we can consider this example timeline.
In the initial year of your PhD, you’ll collaborate closely with your designated academic supervisor. This collaboration involves refining and solidifying your research proposal, which lays the foundation for your entire doctoral journey.
This is also the time to establish a comprehensive plan, complete with well-defined milestones and deadlines. A crucial aspect of this year is conducting an extensive literature review, immersing yourself in existing academic works to understand the landscape of your chosen research area. It’s important to make sure that your research idea is original and distinct from prior studies.
As you begin the second year, you’ll actively collect data and gather information related to your research topic. Simultaneously, you’ll initiate the process of crafting your thesis. This involves combining your research findings and analysis into sections of your thesis document.
This is also the phase where you might have opportunities to share your research insights at academic meetings, conferences or workshops. Depending on the programme, you might even engage in teaching activities. Some PhD candidates also begin contributing to academic journals or books, showcasing their findings to a broader audience.
The third year of a PhD programme often marks the final stage of your research efforts. This is when you dedicate substantial time to writing and finalising your complete thesis. Once your thesis is completed to the highest standard, you’ll submit it for thorough evaluation.
A significant milestone in the third year is the viva voce, an oral examination where you’ll defend your thesis before a panel of experts in your field. The viva voce is an opportunity to showcase your deep understanding of your research and defend your findings.
Why should you do a PhD?
For many people, acquiring a doctorate degree is the pinnacle of academic achievement, the culmination of years of commitment to higher education.
However, the act of pursuing a PhD can be a complex, frustrating, expensive and time-consuming exercise. But with the right preparation, some sound advice and a thorough understanding of the task at hand, your years as a doctoral student can be some of the most rewarding of your life.
People choose to work towards a doctorate for many reasons. If you are looking to pursue an academic position, such as university lecturer or researcher, then a PhD is usually required.
Many people obtain a PhD as part of a partnership with an employer, particularly in scientific fields such as engineering, where their research can prove useful for companies.
In some cases, however, PhDs are simply down to an individual’s love of a subject and their desire to learn more about their field.
What are some benefits of studying a PhD?
Pursuing a PhD can have many benefits that extend beyond academic achievement, encompassing personal growth, professional advancement and meaningful contributions to knowledge.
One of the most notable benefits of a PhD is the potential for tenure in academia. Attaining tenure provides a level of job security that allows you to delve into long-term research projects and make enduring contributions to your field. It signifies a stage where you can explore innovative ideas and pursue in-depth research, fostering your academic legacy.
While not obligatory, the opportunity to collaborate on research projects with your supervisor is another valuable aspect of a PhD pursuit. These collaborations might even come with financial compensation, offering real-world experience, skill development and practical applications of your research. Engaging in such collaborations can enrich your research portfolio and refine your research methodologies.
A pivotal aspect of a PhD journey is the chance to publish your original research findings. By disseminating your work in academic journals or presenting it at conferences, you contribute to the expansion of knowledge within your field. These publications establish your expertise and reputation among peers and researchers worldwide, leaving a lasting impact.
The pursuit of a PhD can provide a unique platform to build a diverse network of colleagues, mentors and collaborators. Engaging with fellow researchers, attending conferences and participating in academic events offer opportunities to make valuable connections. This network can lead to collaborations, expose you to a spectrum of perspectives and pave the way for future research endeavours.
What is a PhD thesis? And what is a PhD viva?
A PhD thesis will be produced with help from an academic supervisor, usually one with expertise in your particular field of study. This thesis is the backbone of a PhD, and is the candidate’s opportunity to communicate their original research to others in their field (and a wider audience). PhD students also have to explain their research project and defend their thesis in front of a panel of academics. This part of the process is often the most challenging, since writing a thesis is a major part of many undergraduate or master’s degrees, but having to defend it from criticism in real time is arguably more daunting. This questioning is known as a “viva”, and examiners will pay particular attention to a PhD’s weaknesses either in terms of methodology or findings. Candidates will be expected to have a strong understanding of their subject areas and be able to justify specific elements of their research quickly and succinctly.
In rare cases, students going for a PhD may instead be awarded an MPhil if the academic standard of their work is not considered fully up to par but still strong enough to be deserving of a qualification.
Can you do a PhD part time?
Many PhD and MPhil candidates choose to pursue their qualification part time, in order to allow time to work and earn while studying. This is especially true of older students, who might be returning to academia after working for a few years.
When applying, you should always speak to the admissions team at your university to ensure this is possible and then continue to work with your supervisor to balance all your commitments.
Can I do a PhD through distance learning?
This is something else that you will need to check with your university. Some institutions offer this option, depending on the nature of your research.
You will need to be clear how many times you will need to travel to your university to meet with your supervisor throughout your PhD.
Your PhD supervisor
Choosing the right PhD supervisor is essential if you want to get the most out of your PhD. Do your research into the faculty at the institution and ensure that you meet with your proposed supervisor (either virtually or in person) before fully committing.
You need to know that not only do they have the right expertise and understanding of your research but also that your personalities won’t clash throughout your PhD.
Remember, to complete your PhD, you will need a strong support network in place, and your supervisor is a key part of that network.
Coping with PhD stress
If you do decide to embark on a doctorate, you may well encounter stress and anxiety. The work involved is often carried out alone, the hours can be long and many students can suffer from the pressure they feel is on their shoulders.
Ensuring that you check in regularly with your emotions and your workload is crucial to avoid burnout. If you have other commitments, such as a job or a family, then learning to balance these can feel overwhelming at times.
Give yourself regular breaks, speak to your supervisor and ensure that you know what university resources and support systems are available to you in case you need to access them.
Post-doctorate: what happens after you finish your PhD?
Many PhD graduates pursue a career in academia, while others will work in industry. Some might take time out, if they can afford to, to recover from the efforts of PhD study.
Whatever you choose to do, undertaking a PhD is a huge task that can open up a range of doors professionally. Just remember to take some time out to celebrate your achievement.
How does a PhD affect salary and earning potential?
How much does a professor with a PhD make a year?
Professors with PhDs can earn different amounts depending on where they work and their experience. In the UK, a professor might make around £50,000 to £100,000 or more each year. In the US, it's between about $60,000 and $200,000 or even higher. The exact salary depends on things like the place they work, if they have tenure, and what they teach.
How much does a PhD add to salary?
Having a PhD can make your salary higher than if you had a lower degree. But exactly how much more you earn can change. On average, people with PhDs earn more than those with bachelor’s or master’s degrees. The increase in salary is influenced by many things, such as the job you do, where you work and what field you’re in.
In fields such as research, healthcare, technology and finance, your knowledge and skills from your PhD can potentially help you secure a higher salary position.
In the end, having a PhD can boost your earning potential and open doors to well-paying jobs, including professorships and special roles in different areas. But the exact effect on your salary is influenced by many things, so ensure you weigh the cost against the benefit.
How to choose a PhD programme?
Choosing a PhD programme involves defining your research interest, researching supervisors and programme reputation, evaluating funding options, reviewing programme structure, considering available resources, assessing networking opportunities, factoring in location and career outcomes, visiting the campus if possible and trusting your instincts.
How can I find available PhD programmes?
You can find available PhD programmes by visiting university websites, using online directories such as “FindAPhD”, checking professional associations, networking with professors and students, following universities on social media, attending career fairs and conferences, contacting universities directly and exploring research institutes’ websites.
How to apply for a PhD programme?
To apply for a PhD programme:
Research and select universities aligned with your interests.
Contact potential supervisors, sharing your proposal, CV and references.
Prepare application materials: research proposal, CV, recommendation letters and a writing sample.
Ensure you meet academic and language-proficiency requirements.
Complete an online application through the university’s portal.
Pay any required application fees.
Write a statement of purpose explaining your motivations.
Provide official transcripts of your academic records.
Submit standardised test scores if needed.
Some programmes may require an interview.
The admissions committee reviews applications and decides.
Apply for scholarships or assistantships.
Upon acceptance, review and respond to the offer letter.
Plan travel, accommodation and logistics accordingly.
Remember to research and follow each university’s specific application guidelines and deadlines.
How to apply for a PhD as an international student?
Many stages of the PhD application process are the same for international students as domestic students. However, there are sometimes some additional steps:
International students should apply for a student visa.
Take language proficiency tests such as TOEFL or IELTS if required.
Provide certificates if needed to validate your previous degrees.
Show evidence of sufficient funds for tuition and living expenses.
Check if you need health insurance for your chosen destination.
Translate and authenticate academic transcripts if necessary.
Attend orientation sessions for cultural adaptation.
Apply for university housing or explore off-campus options.
Familiarise yourself with international student support services.
Ben Osborne, the postgraduate student recruitment manager at the University of Sussex explains in detail how to apply for a PhD in the UK .
Giulia Evolvi, a lecturer in media and communication at Erasmus University, Rotterdam explains how to apply for a PhD in the US .
Finally, Samiul Hossain explores the question Is it possible to do a three-year PhD as an international student?
Q. What is a PhD? A. A PhD is the highest level of academic degree awarded by universities, involving in-depth research and a substantial thesis.
Q. What does “PhD” mean? A. “PhD” stands for doctor of philosophy, recognising expertise in a field.
Q. What is a professional doctorate? A. A professional doctorate emphasises practical application in fields such as education or healthcare.
Q. How long does it take to study a PhD? A. It takes between three and six years to study a full-time PhD programme.
Q. How long is a PhD in the UK? A. It takes around three to four years to study a full-time UK PhD.
Q. How long is a PhD in the US? A. It takes approximately five to six years to complete a full-time US PhD.
Q. Why does it take longer to study a PhD in the US? A. US programmes often include more course work and broader training.
Q. What qualifications do you need for a PhD? A. You usually need an undergraduate degree as a minimum requirement, although a master’s might be preferred.
Q. Do you need a master’s degree to get into a PhD programme? A. Master’s degrees are preferred but not always required.
Q. Are PhD entry requirements similar in other countries? A. Entry requirements are similar in many countries, but there may be additional requirements. Make sure to check the university website for specific details.
Q. How much does it cost to study a PhD? A. The cost of PhD programmes vary by country and university.
Q. What funding options are available for PhD candidates? A. Scholarships, assistantships, fellowships, grants, stipends are all funding options for PhD candidates.
Q. What does a PhD involve? A. PhDs involve research, seminars, thesis, literature review, data analysis and a PhD viva.
Q. Why should you do a PhD? A. There are many reasons to study a PhD including personal growth, research skills, contributions to academia and professional development.
Q. What are some benefits of studying a PhD? A. Benefits of graduating with a PhD include achieving tenure, collaborations with colleagues, publication of your work, and networking opportunities.
Q. What is a PhD thesis? A. A PhD thesis is a comprehensive document that showcases the original research conducted by a PhD candidate.
Q. What is a PhD viva? A. A PhD viva, also known as a viva voce or oral examination, is the final evaluation of a PhD candidate’s research and thesis where the panel asks questions, engages in discussions and assesses the depth of the candidate’s understanding and expertise.
Q. Can you do a PhD part-time? A. Yes, part-time options are available for PhDs.
Q. Can I do a PhD through distance learning? A. Some universities offer online PhDs; you can find out more on their websites.
Q. How to choose a PhD programme? A. You can find PhD programmes through research, by contacting faculty, checking resources and considering location.
Q. How can I find available PhD programme? A. You can find available PhD programmes on university sites, through directories and by networking.
Q. How to apply for a PhD programme A. To apply for a PhD programme, research suitable universities and programmes, get in touch with potential supervisors, gather required documents like transcripts and reference letters, complete the online application, pay any necessary fees and submit a statement of purpose and research proposal. If needed, meet language-proficiency criteria and attend interviews. After acceptance, explore funding choices, confirm your spot and get ready for the programme’s start.
Q. How to apply for a PhD as an international student A. To apply for a PhD as an international student, follow similar steps to domestic students, but you need to include securing a student visa and passing language requirements.
Q. What is a PhD dropout rate? A. The dropout rate from PhDs varies but is approximately 30-40 per cent.
Q. How does a PhD affect salary and earning potential? A. A PhD can boost earning potential, especially in research, technology, healthcare and academia. Impact varies by job, industry and location. Experience, skills and demand also influence salary.
Q. How to address a person with a PhD? A. When addressing someone with a PhD, it’s respectful to use “Dr”, followed by their last name, whether they have a PhD in an academic field or a professional doctorate. For instance, “Dr. Smith”.
Q. Is there a difference between a PhD and a doctorate? A. The terms “PhD” and “doctorate” are often used interchangeably, though a PhD is a specific type of doctorate focused on original research. A doctorate can refer more broadly to any doctoral-level degree, including professional doctorates with practical applications.
Q. What is the difference between a PhD and an MD? A. A PhD is a doctor of philosophy, awarded for academic research, while an MD is a doctor of medicine, focusing on medical practice. They lead to different career paths and involve distinct areas of study.
Q. What is the difference between a PhD and a professional doctorate? A. A PhD is an academic research-focused degree, while a professional doctorate emphasises applying research to practical fields such as education or business. PhDs often involve original research, while professional doctorates focus on real-world application.
Q. What is the difference between UK and US PhDs? A. The difference between UK and US PhDs lies mainly in structure and duration. UK PhDs often have shorter durations and a stronger emphasis on independent research from an early stage. US PhDs typically include more initial coursework and broader foundational training before full-time research begins.
Q. What is the difference between a PhD student and a candidate? A. A PhD student is actively studying and researching in a doctoral programme, while a PhD candidate has completed programme requirements except for the dissertation and is close to completion.
Q. What’s the difference between a PhD and an EdD? A. A PhD and an EdD (doctor of education) differ in focus. A PhD emphasises research and academic contributions, while an EdD focuses on applying research to practical educational issues.
Q. What’s the difference between a PhD and a DBA? A. A PhD and a DBA (doctor of business administration) differ in purpose. A PhD emphasises theoretical research and academia, while a DBA is practice-oriented, aimed at solving real business problems.
Q. What’s the difference between a PhD and a PsyD? A. A PhD and a PsyD (doctor of psychology) differ in emphasis. A PhD focuses on research and academia, while a PsyD emphasises clinical practice and applying psychological knowledge.
Q. What’s the difference between a PhD and an LLD? A. A PhD and an LLD (doctor of laws or Legum doctor) are distinct. A PhD is awarded in various disciplines, while an LLD is usually an honorary degree for significant contributions to law.
Q. What’s the difference between a PhD and an MD-PhD? A. A PhD and an MD-PhD differ. An MD-PhD is a dual degree combining medical training (MD) with research training (PhD).
Q. What is the Cambridge PhD? A. A Cambridge PhD involves original research guided by a supervisor, resulting in a thesis. It’s offered at the University of Cambridge .
Q. What is the Oxford DPhil? A. An Oxford DPhil is equivalent to a PhD and involves independent research leading to a thesis. The term “DPhil” is unique to the University of Oxford .
Q. What is the PhD programme acceptance rate? A. PhD acceptance rates vary by university, field and competition. Prestigious universities and competitive fields often have lower acceptance rates.
Q. What is a PhD supervisor? A. A PhD supervisor guides and supports a student’s research journey, providing expertise and feedback.
Q. What is a PhD panel? A. A PhD panel evaluates a candidate’s research, thesis and oral defence. It consists of experts in the field.
Q. What is a PhD stipend? A. A PhD stipend is a regular payment supporting living expenses during research, often tied to teaching or research assistant roles.
Q. What is a PhD progression assessment? A. A PhD progression assessment evaluates a student’s progress, often confirming their continuation in the programme.
Q. What is a PhD defence? A. A PhD defence, or viva, is the final oral examination where a candidate presents and defends their research findings and thesis before experts.
You may also like

.css-185owts{overflow:hidden;max-height:54px;text-indent:0px;} Pursuing a PhD in neuroscience
Luis Humberto Eudave Ramos

Why study a PhD in English literature?
John Francis Davies

8 habits to help you get through your PhD
Shabana Khan
Register free and enjoy extra benefits
How long will it take to get a PhD in Sociology at Harvard?
It all depends on the student. Some students complete the program in five years, some in as many as seven or eight years.
Sample Timeline
Below is a sample timeline for a student striving to complete their degree in five to six years.
- Coursework (see Course Progression )
- General written exam in August, prior to beginning year 2
- Apply for pre-doctoral fellowships
Second Year
- Begin working on Qualifying Paper
- Finish all coursework (including Qualifying Paper Seminar and Teaching Practicum)
- Teaching Fellowships and Research Assistantships
- Complete Qualifying Paper
- Begin (and possibly defend) dissertation proposal (prospectus)
- Apply for dissertation fellowships
Fourth Year
- Defend dissertation prospectus no later than April 30th
- Advancement to candidacy
- Begin writing dissertation
- Apply for dissertation fellowships and external aid for Year 6
- Write dissertation--possibly defend dissertation, submit manuscript, and graduate
- See “Fifth Year” above
Students participating in a joint degree program (other than the Sociology & Social Policy, Organizational Behavior, or AAAS joint degree programs) can expect to take an additional one or two years to complete the program, depending upon the requirements of the other degree program.
If you have any questions that cannot be answered on our website, contact the Sociology Graduate Program Coordinator .
Graduate Office
660 William James Hall
Office Hours (Fall 2023) Monday, 10:00 a.m.-6:00 p.m. (remote) Tuesday, 10:00 a.m.-6:00 p.m. (on campus) Wednesday, 10:00 a.m.-6:00 p.m. (on campus) Thursday, 10:00 a.m.-6:00 p.m. (remote) Friday, 10:00 a.m.-6:00 p.m. (remote)
Email [email protected]
Phone 617.495.3813
Director David Pedulla
Program Coordinator Jessica Matteson
Educational resources and simple solutions for your research journey

The PhD Journey: Stages of a Doctoral Journey
Embarking on a PhD journey is more than a path to academic achievement; it’s an adventure filled with excitement, discovery, and, sometimes, inevitable challenges. This journey, lasting typically 3-5 years, is not just intellectually taxing but also an emotionally enriching experience that shapes one’s professional and personal growth.
Unlike undergraduate or master’s programs, a PhD degree is less structured and more self-directed. This freedom, while exhilarating, can also be daunting. PhD candidates often face pressure to publish and contribute new knowledge to their field, a task that tests both mental and emotional resilience.
Yet, the excitement of delving deep into a subject you are passionate about, the thrill of discovering new knowledge, and the opportunity to work with leading experts are what make this journey rewarding and fulfilling. In this article, we will take a step-by-step look at how to make it to the finish line of your PhD journey.
- Research and planning: Your doctoral journey begins with identifying a topic that ignites your passion. Develop a research design and proposal, and choose a supervisor aligned with your research interests. Creating a strategic plan will help you focus more closely on your responsibilities and will enable you to map out the direction of your research work.
- Conducting a literature review: A vital step in the PhD journey; here, you identify knowledge gaps and decide on your research methodology . A carefully conducted, detailed literature review provides a firm theoretical base and enables researchers to contextualize their work and make it relevant. The process can be as exhilarating as it is rigorous, laying a solid foundation for your research.
- Collating and analyzing data: Post-literature review, you’ll collect and analyze data. Whether through surveys, interviews, or experiments, this stage is where your research starts taking shape, offering the first glimpse of potential findings and their impact. Whichever method is employed, it is important to ensure that data collection is done without any prejudice and confirmation bias.
- Managing PhD Responsibilities : Beyond research, PhD students engage in activities like teaching, attending conferences, and publishing. These responsibilities, while optional, are opportunities to grow your academic profile and can be as rewarding as they are challenging.
- Writing a thesis: Arguably the most daunting yet satisfying part of your PhD journey . Writing a thesis demands clear communication and meticulous referencing. It’s common to face self-doubt and writer’s block, but overcoming these challenges is part of the doctoral journey’s learning curve.
- Editing and proofreading: After spending long hours on your research, this stage requires a detailed review of your work. Editing and proofreading are crucial for ensuring clarity and coherence in your thesis. Look for possible errors in grammar, language, and syntax, weed out potential plagiarism, and ensure that there are no logical loops or biases. Getting your manuscript reviewed by a colleague or supervisor may throw up errors you may have inadvertently missed or may even help you look at some aspects of your research with a new perspective.
- Defending your findings: The final hurdle of your PhD journey is defending your research to a committee. While this can be a nerve-wracking process, this stage tests your knowledge and conviction in your work and is an opportunity to showcase the significance of your research
The pursuit of a doctoral degree goes beyond academic titles. It’s a journey of intellectual curiosity, pushing boundaries, and making meaningful social contributions. Perseverance and dedication are key. For those embarking on this journey, remember to embrace not just the challenges, but also the excitement and opportunities for growth that come with pursuing your dreams in the world of research.
R Discovery is a literature search and research reading platform that accelerates your research discovery journey by keeping you updated on the latest, most relevant scholarly content. With 250M+ research articles sourced from trusted aggregators like CrossRef, Unpaywall, PubMed, PubMed Central, Open Alex and top publishing houses like Springer Nature, JAMA, IOP, Taylor & Francis, NEJM, BMJ, Karger, SAGE, Emerald Publishing and more, R Discovery puts a world of research at your fingertips.
Try R Discovery Prime FREE for 1 week or upgrade at just US$72 a year to access premium features that let you listen to research on the go, read in your language, collaborate with peers, auto sync with reference managers, and much more. Choose a simpler, smarter way to find and read research – Download the app and start your free 7-day trial today !
Related Posts

What are Experimental Groups in Research

What is a Review Article? How to Write it?
- Crimson Careers
- For Employers
- Harvard College
- Harvard Kenneth C. Griffin Graduate School of Arts & Sciences
- Harvard Extension School
- Premed / Pre-Health
- Families & Supporters
- Faculty & Staff
- Prospective Students
- First Generation / Low Income
- International Students
- Students of Color
- Students with Disabilities
- Undocumented Students
- Varsity Athletes
- Explore Interests & Make Career Decisions
- Create a Resume/CV or Cover Letter
- Expand Your Network
- Engage with Employers
- Search for a Job
- Find an Internship
- January Experiences (College)
- Find & Apply for Summer Opportunities Funding
- Prepare for an Interview
- Negotiate an Offer
- Apply to Graduate or Professional School
- Access Resources
- AI for Professional Development and Exploration
- Arts & Entertainment
- Business & Entrepreneurship
- Climate, Sustainability, Environment, Energy
- Government, Int’l Relations, Education, Law, Nonprofits
- Life Sciences & Health
- Technology & Engineering
- Still Exploring
- Talk to an Advisor
How Long Does It Take to Get a Ph.D. Degree?
- Share This: Share How Long Does It Take to Get a Ph.D. Degree? on Facebook Share How Long Does It Take to Get a Ph.D. Degree? on LinkedIn Share How Long Does It Take to Get a Ph.D. Degree? on X

Earning a Ph.D. from a U.S. grad school typically requires nearly six years, federal statistics show.

(CAIAIMAGE/TOM MERTON/GETTY IMAGES)
A Ph.D. is most appropriate for someone who is a “lifelong learner.”
Students who have excelled within a specific academic discipline and who have a strong interest in that field may choose to pursue a Ph.D. degree. However, Ph.D. degree-holders urge prospective students to think carefully about whether they truly want or need a doctoral degree, since Ph.D. programs last for multiple years.
According to the Survey of Earned Doctorates, a census of recent research doctorate recipients who earned their degree from U.S. institutions, the median amount of time it took individuals who received their doctorates in 2017 to complete their program was 5.8 years. However, there are many types of programs that typically take longer than six years to complete, such as humanities and arts doctorates, where the median time for individuals to earn their degree was 7.1 years, according to the survey.
Some Ph.D. candidates begin doctoral programs after they have already obtained master’s degrees, which means the time spent in grad school is a combination of the time spent pursuing a master’s and the years invested in a doctorate. In order to receive a Ph.D. degree, a student must produce and successfully defend an original academic dissertation, which must be approved by a dissertation committtee. Writing and defending a dissertation is so difficult that many Ph.D. students drop out of their Ph.D. programs having done most of the work necessary for degree without completing the dissertation component. These Ph.D. program dropouts often use the phrase “ all but dissertation ” or the abbreviation “ABD” on their resumes.
According to a comprehensive study of Ph.D. completion rates published by The Council of Graduate Schools in 2008, only 56.6% of people who begin Ph.D. programs earn Ph.D. degrees.
Ian Curtis, a founding partner with H&C Education, an educational and admissions consulting firm, who is pursuing a Ph.D. degree in French at Yale University , says there are several steps involved in the process of obtaining a Ph.D. Students typically need to fulfill course requirements and pass comprehensive exams, Curtis warns. “Once these obligations have been completed, how long it takes you to write your dissertation depends on who you are, how you work, what field you’re in and what other responsibilities you have in life,” he wrote in an email. Though some Ph.D. students can write a dissertation in a single year, that is rare, and the dissertation writing process may last for several years, Curtis says.
[ READ: What Is a Doctorate or a Doctoral Degree? ]
Curtis adds that the level of support a Ph.D. student receives from an academic advisor or faculty mentor can be a key factor in determining the length of time it takes to complete a Ph.D. program. “Before you decide to enroll at a specific program, you’ll want to meet your future advisor,” Curtis advises. “Also, reach out to his or her current and former students to get a sense of what he or she is like to work with.”
Curtis also notes that if there is a gap between the amount of time it takes to complete a Ph.D. and the amount of time a student’s funding lasts, this can slow down the Ph.D. completion process. “Keep in mind that if you run out of funding at some point during your doctorate, you will need to find paid work, and this will leave you even less time to focus on writing your dissertation,” he says. “If one of the programs you’re looking at has a record of significantly longer – or shorter – times to competition, this is good information to take into consideration.”
Pierre Huguet, the CEO and co-founder of H&C Education, says prospective Ph.D. students should be aware that a Ph.D. is designed to prepare a person for a career as a scholar. “Most of the jobs available to Ph.D. students upon graduation are academic in nature and directly related to their fields of study: professor, researcher, etc.,” Huguet wrote in an email. “The truth is that more specialization can mean fewer job opportunities. Before starting a Ph.D., students should be sure that they want to pursue a career in academia, or in research. If not, they should make time during the Ph.D. to show recruiters that they’ve traveled beyond their labs and libraries to gain some professional hands-on experience.”
Jack Appleman, a business writing instructor, published author and Ph.D. candidate focusing on organizational communication with the University at Albany—SUNY , says Ph.D. programs require a level of commitment and focus that goes beyond what is necessary for a typical corporate job. A program with flexible course requirements that allow a student to customize his or her curriculum based on academic interests and personal obligations is ideal, he says.
[ READ: Ph.D. Programs Get a Lot More Practical. ]
Joan Kee, a professor at the University of Michigan with the university’s history of art department, says that the length of time required for a Ph.D. varies widely depending on what subject the Ph.D. focuses on. “Ph.D. program length is very discipline and even field-specific; for example, you can and are expected to finish a Ph.D, in economics in under five years, but that would be impossible in art history (or most of the humanities),” she wrote in an email.
Jean Marie Carey, who earned her Ph.D. degree in art history and German from the University of Otago in New Zealand, encourages prospective Ph.D. students to check whether their potential Ph.D. program has published a timeline of how long it takes a Ph.D. student to complete their program. She says it is also prudent to speak with Ph.D. graduates of the school and ask about their experience.
Bennett urges prospective Ph.D. students to visit the campuses of their target graduate programs since a Ph.D. program takes so much time that it is important to find a school that feels comfortable. She adds that aspiring Ph.D. students who prefer a collaborative learning environment should be wary of graduate programs that have a cut-throat and competitive atmosphere, since such students may not thrive in that type of setting.
[ READ: 4 Fields Where Doctorates Lead to Jobs. ]
Alumni of Ph.D. programs note that the process of obtaining a Ph.D. is arduous, regardless of the type of Ph.D. program. “A Ph.D. is a long commitment of your time, energy and financial resources, so it’ll be easier on you if you are passionate about research,” says Grace Lee, who has a Ph.D. in neuroscience and is the founder and CEO of Mastery Insights, an education and career coaching company, and the host of the Career Revisionist podcast.
“A Ph.D. isn’t about rehashing years of knowledge that is already out there, but rather it is about your ability to generate new knowledge. Your intellectual masterpiece (which is your dissertation) takes a lot of time, intellectual creativity and innovation to put together, so you have to be truly passionate about that,” Lee says.
Erin Skelly, a graduate admissions counselor at the IvyWise admissions consulting firm, says when a Ph.D. students struggles to complete his or her Ph.D. degree, it may have more to do with the student’s academic interests or personal circumstances than his or her program.
“The time to complete a Ph.D. can depend on a number of variables, but the specific discipline or school would only account for a year or two’s difference,” she wrote in an email. “When a student takes significantly longer to complete a Ph.D. (degree), it’s usually related to the student’s coursework and research – they need to take additional coursework to complete their comprehensive exams; they change the focus of their program or dissertation, requiring extra coursework or research; or their research doesn’t yield the results they hoped for, and they need to generate a new theory and conduct more research.”
Skelly warns that the average completion time of a Ph.D. program may be misleading in some cases, if the average is skewed based on one or two outliers. She suggests that instead of focusing on the duration of a particular Ph.D. program, prospective students should investigate the program’s attritition and graduation rates.
“It is worthwhile to look at the program requirements and the school’s proposed timeline for completion, and meet current students to get their input on how realistic these expectations for completion are,” Skelly says. “That can give you an honest idea of how long it will really take to complete the program.”
Searching for a grad school? Access our complete rankings of Best Graduate Schools.
2024-2025 Catalog
Doctoral degrees.
The University of Idaho awards the degree of Doctor of Philosophy in recognition of high achievement in scholarly and research activity. The degree of Doctor of Education is granted for high scholarly attainment and in recognition of the completion of academic preparation for professional practice. See the "Ph.D. and Ed.D. Procedures" tab for more details. The Doctor of Athletic Training is offered through the College of Education and the Department of Movement Sciences (see the "DAT Procedures" tab for more details).
The major professor and program offering a particular doctoral program indicate the general philosophy of the degree program, the objectives of courses and seminars, the research specialties available, and requirements unique to the department. Admission to the doctoral program is granted only to those who have a recognized potential for completing the degree.
Requirements for Doctoral Degrees
Credit requirements.
For the Ph.D. and Ed.D., a minimum of 78 credits beyond the bachelor's degree is required.; At least 52 credits must be at the 500 level or above and at least 33 of the 78 credits must be in courses other than 600 (Doctoral Research and Dissertation). A maximum of 45 research credits in 600 (Doctoral Research and Dissertation) including 6 credits of 599 (Non-thesis Research) or 500 (Master's Research and Thesis) may be in the 45 research credits used toward the degree. For the D.A.T., a minimum of 66 credits is required and follows a prescribed set of courses set by the program.
Courses numbered below 300 may not be used to fulfill the requirements for a doctoral degree; courses numbered 300-399 may be used only in supporting areas and are not to be used to make up deficiencies. Individual programs may require additional course work. Applicants having a doctoral degree may obtain a second doctoral degree subject to the approval of the Graduate Council. The Graduate Council will establish the requirements for the second degree.
Credit Limitations for Transfer, Correspondence Study, and Non-degree
For the Ph.D. and Ed.D. degrees, a student must complete at least 39 of the 78 required credits at the University of Idaho (U of I) while matriculated in the College of Graduate Studies. Credits can be transferred to U of I with the consent of the student's major professor, the committee (if required by the program), the program's administrator, and the dean of the College of Graduate Studies. Credits can be transferred only if the institution from which the credits are being transferred has a graduate program in the course's discipline. All credits used toward graduate degrees must be from regionally accredited American institutions or from non-US institutions recognized by the appropriate authorities in their respective countries. Transfer credits are subject to all other College of Graduate Studies rules and regulations. Correspondence study courses may be applied to the degree only with the prior written approval of the College of Graduate Studies. Courses used toward an undergraduate degree, professional development courses, and courses on a professional development transcript are not available to be used toward a doctoral degree.
Time Limits
Of the credits submitted to satisfy the requirements for a Ph.D. or Ed.D. degree, a maximum of 30 may be more than eight years old when the degree is conferred, provided the student's committee and program administrator determine that the student has kept current in the subjects concerned. Graduation must occur no later than five years after the date on which the candidate passed their preliminary or general examination. These time limitations can be extended only on recommendation of the committee and approval by the Graduate Council.
Awarding Doctoral Degrees to Members of the Faculty
Regulations are outlined in Section 4920 of the Faculty-Staff Handbook.
Particular Requirements for the Ed.D. Degree
A period of professional practice is required for the Doctor of Education degree; the period involved is determined by the student's supervisory committee. While the Ed.D. is a College of Education degree, you should consult with the departments in the College of Education to learn of specific emphasis requirements.
Procedures for Doctor of Philosophy and Doctor of Education Degrees
Appointment of major professor and committee.
Refer to " Appointment of Major Professor and Committee for All Degree Seeking Graduate Students " in the preceding General Graduate Regulations section. In addition, a doctoral supervisory committee consists of at least four people: the major professor as chair and at least one additional UI faculty member from the program, the balance of the committee may be made up of faculty members from a minor or supporting area, and faculty members from a discipline outside the major. If the committee has a co-chair, the minimum number of committee members is five.
Qualifying Examination
The qualifying examination is a program option and serves to assess the background of the student in both the major and supporting fields and to provide partially the basis for preparation of the student's study program. A particular program may or may not require a master's degree as a prerequisite for the qualifying evaluation. As soon as the program's qualifications are met, a supervisory committee is appointed.
Preparation of Study Plan
Refer to " Preparation and Submission of Study Plan " in the preceding General Graduate Regulations section.
Preliminary Examination for Ph.D. Degree
The preliminary examination should be scheduled only after the student has completed the majority of the courses on their study plan. The student is required to be registered during the semester the preliminary examination is taken. The student's committee certifies to the College of Graduate Studies the results of the preliminary examination and if passed, the student is advanced to candidacy. Graduation must occur no later than five years after the date on which the candidate passed their examination. If the preliminary examination is failed, it may be repeated only once; the repeat examination must be taken within a period of not less than three months or more than one year following the first attempt. If a student fails the preliminary examination a second time, or the program does not allow the student to repeat the examination after the first failure or the student does not retake the examination within one year, the student is automatically moved to unclassified enrollment status and is no longer in the degree program.
General Examination for Ed.D . Degree
When the student approaches the end of their course work, has completed the professional experience requirement, and has outlined the dissertation subject in detail, the supervisory committee approves the holding of the general examination. The student is required to be registered during the semester the general examination is taken. The examination is both written and oral and is intended to assess progress toward degree objectives. The student's committee certifies to the College of Graduate Studies the results of the general examination and if passed, the student is advanced to candidacy. Graduation must occur no later than five years after the date on which the candidate passed their examination. If the general examination is failed, it may be repeated only once; the repeat examination must be taken within a period of not less than three months or more than one year following the first attempt. If a student fails the general examination a second time, or the program does not allow the student to repeat the examination after the first failure or the student does not retake the examination within one year, the student is automatically moved to unclassified status and is no longer in the degree program.
See the General Graduate Regulations section regarding application for advanced degree, registration requirements, final defense and dissertation requirements.
Procedures for Doctor of Athletic Training
The culminating clinical project.
Students enrolled in the Doctor of Athletic Training (D.A.T.) will engage in research projects during the curricular phase of the program. These project(s) will lead to at least two publication ready manuscripts, and all students must meet professional authorship requirements (regardless of order). See the Department of Movement Sciences and Doctor of Athletic Training webpages for more information.
The Team (Committee)
All D.A.T. project team committees will have at least four committee members: two members of the athletic training faculty (all with graduate faculty status), the student's attending clinician (who is the student's on-site mentor during the student's residency), and an expert in the student's chosen area of clinical research. The athletic training faculty members will always chair the CCP, provide research guidance, and serve as the experts in the development of advanced practice in Athletic Training. A situation may arise in which one or both of the members of the committee that are outside of the AT program faculty may have a degree less than that of which the student is seeking; however, the intent of the third and fourth D.A.T. committee membership is to provide outside validation of the student's progress toward advanced practice and clinical utility of action research studies.
Culminating Clinical Project Hours
These dissertation hours may be used in instances when the CCP has not been successfully completed and the curricular phase of program has been completed.
Print Options
Send Page to Printer
Print this page.
Download Page (PDF)
The PDF will include all information unique to this page.

- Study Abroad Get upto 50% discount on Visa Fees
- Top Universities & Colleges
- Abroad Exams
- Top Courses
- Read College Reviews
- Admission Alerts 2024
- Education Loan
- Institute (Counselling, Coaching and More)
- Ask a Question
- College Predictor
- Test Series
- Practice Questions
- Course Finder
- Scholarship
- All Courses
- B.Sc (Nursing)
PhD: Full Form, Admission 2024, Courses, Degree, Entrance Exams, Syllabus, Career Scope

Waqar Niyazi
Content Curator
Ph.D. - Latest Notifications
- 05 August, 2024 : IIT JAM 2025 Subject-wise Syllabus PDFs Available, Download Now.
- 03 August, 2024 : IIT JAM 2025 Application Form Out (Soon), Check Details Here.
The full form of PhD is Doctor of Philosophy derived from the Latin term Philosophiae Doctor. PhD is the highest degree or doctorate awarded for research in a particular subject. The duration of PhD course is 3 years but can vary from college to college. PhD Eligibility requires students to have pursued a master’s degree or an MPhil with a minimum aggregate score of 55%.
PhD Admission is based on Ph.D entrance exams such as CSIR UGC NET, UGC NET, IIT JAM, NPAT are the top PhD entrance exams. If a candidate wishes to pursue PhD in Engineering and Technology then they must possess a valid GATE score. CSIR UGC NET is the national-level PhD entrance exam conducted twice a year. The registration process for the CSIR UGC NET exam will begin soon and the exam is scheduled for the month of December.
Furthermore, there are various PhD Scholarships available in India which help students to pursue a Ph.D. After completing their PhD degrees, students can choose from a plethora of PhD Jobs and can earn an average salary of INR 6 – 9 lakhs per annum.
Table of Contents
Doctor of Philosophy: Course Details
1.1 Why study Ph.D?
- What is Ph.D?
2.1 PhD Full form
2.2 PhD vs Doctorate
PhD Admission Process
3.1 Eligibility
3.2 UGC NET
3.3 Important Dates
- PhD Programs Types
- Ph.D Courses
5.1 Science
5.2 Arts
5.3 Medical
- PhD Colleges in India
6.1 Government Colleges
6.2 Private Colleges
- Ph.D in India
7.1 PhD in IIT
7.2 JNU PhD
7.3 DU PhD
7.4 Mumbai University PhD
| Ph.D Full Form | Doctor of Philosophy |
| PhD Duration | 4-6 Years |
| PhD Admission | Entrance Exams/Direct Admission |
| PhD Specializations | PhD Physics, PhD Computer Science, Phd Psychology, PhD History |
| Online PhD Program | IGNOU, IISc Bangalore, Dr. BR Ambedkar Open University Hyderabad |
| Top PhD Colleges | IITs, IISc, Jadavpur University, Delhi University, JNU |
Why study Ph.D?
- Ph.D. help the students to start or continue their research in a field they are passionate about.
- It helps in improving employment prospects. It can unlock many career opportunities. If someone wants to become a lecturer or University researcher then a Ph.D. degree is usually the main requirement.
- The Indian government has reduced the tax incentive for firms conducting R&D, which is consistent with the finding of the previous UNESCO Science Report (2015).
- Academic researchers contribute the bulk of all scientific and technical articles published in India.
- Higher Education Institutions and Research and Development organizations play an important role in nation building.
- There is an encouraging increase in scientific publications by Indian researchers on cutting-edge technologies.
What is PhD?
PhD or Doctor of Philosophy deals with advanced research regarding a specific subject. PhD courses are available in 3 formats which are Full Time, Part Time PhD and Online PhD. Ph.D Duration is three years which can increase to five to six years depending on the subject.
PhD Full Form
PhD full form is Doctor of Philosophy. PhD abbreviation is from a Latin term which is Philosophiae Doctor. The term philosophy has little relation to the philosophy subject. In Ph.D the term philosophy comes from the Greek word which means ‘lover of wisdom’.
PhD Full Form – Doctor of Philosophy
PhD Duration
- PhD duration is 3 years which can be extended. On an average a student completes his/her PhD in 5-7 years.
- There are many factors that determine the duration of the PhD such as knowledge of the research area, research experience, knowledge of the supervisor, relevance of the research, communication skills, availability of resources and the amount of course work.
- The minimum PhD duration is 3 years. In NIIT the average PhD duration is 3-5 years and in IITs the average PhD duration is 5-7 years.
PhD vs Doctorate
| Particulars | PhD | Doctorate |
|---|---|---|
| Objective | The main goal is to make advancements in the field while constructing new knowledge and theories. | The main goal is to advance the field by applying an existing body of knowledge, research and theory. |
| Result | Students focus on securing a high academic position and conducting theoretical research. | The focus is to practice in the field and advance to leadership positions or teaching in higher education institutions |
| Degree Requirements | Masters Degree | Master’s Degree |
| Student Focus | Students seek theoretical Research Experience | Students seek to solve practical problems in a particular field. |
PhD Degree Requirements
PhD Degree requirements is the process or the prerequisites of getting the Ph.D Degree. This is different in different countries. PhD in India follows rules described by the UGC.
PhD Degree requirements include completion of coursework, presentation of research proposal or synopsis, submission of progress reports, give pre-submission presentation and then defend the thesis in an oral debating atmosphere.
Also See: PhD Jobs
Who should study for a Ph.D?
- Students who want to make a career out of academics or research should definitely pursue a Doctor of Philosophy.
- This is a unique opportunity to broaden the horizon of the subject that an individual loves. It brings immense pride and respect to the individual who wants to do Doctor of Philosophy.
- To understand if you are capable of doing Doctor of Philosophy, the individual must have a serious conversation with lecturers and former Doctor of Philosophy students who guide better.
- Students should research different Doctor of Philosophy programs to get a general sense about what PhD Degrees are like. After understanding the whole structure then only students must decide to do a Doctor of Philosophy.
Ph.D. admission is based on enrollment to several universities. Universities accept the results of either national level or university level entrance exams. Top Ph.D. entrance exams are CSIR UGC NET, UGC NET, IIT JAM, and NPAT. If a candidate wishes to pursue PhD in Engineering and Technology then they must possess a valid GATE score. As per the recent directives of the UGC, students who complete a four-year UG degree would be able to directly apply for pursuing a PhD degree in their desired choice of course.
PhD Eligibility
- Master's degree holders are eligible for admission to doctoral programs. For some subjects, Masters in Philosophy is needed for pursuing PhD.
- The students should have at least 50-55% of marks post graduation.
- In some universities admission is offered on the basis of interviews. It may be supplemented with a written exam.
- More preference is given to candidates who have work experience in the field of research.
The National Educational Testing Bureau of UGC conducts the National Eligibility Test to determine the eligibility of Indian nationals for Assistant Professor and Junior Research Fellowship and Research Professor in Indian Universities and Colleges.
CSIR-UGC NET Exam
CSIR UGC NET is a test being conducted to determine the eligibility of Indian nationals for Junior Research Fellowship and for Lectureship /Assistant Professor in Indian universities and colleges subject to fulfilling the eligibility criteria laid down by UGC.
Important Dates
| Entrance Exam | Registration Date | Exam Date |
|---|---|---|
| UGC NET | To be Announced | June 10 – June 21, 2024 |
| CSIR NET | To be Announced | To be Announced |
| March – May, 2024 | June, 2024 | |
| August 31 – October 13, 2023 | February 3, 4, 10, 11, 2024 | |
| November 30, 2023 | December 12, 2023 | |
| To be Announced | To be Announced | |
| To be Announced | To be Announced | |
| To be Announced | To be Announced |
PhD Programs
There are 3 basic types of PhD Programmes in India. They include full time PhD, Part time PhD and Online PhD.
Full-Time PhD
- Full-Time PhD is a normal Doctor of Philosophy program. The duration of these programs ranges between 4 – 6 years.
- The cost of a full time Doctor of Philosophy program is the highest compared to other modes of PhD degrees.
- Government/ Semi-Government Fellowship Recipients, Institute Research Scholars with Teaching Assistance and Self-financed Candidates generally prefer to pursue full-time PhD program.
Part Time PhD
- PhD Programs can sometimes be done on a part-time basis. Candidates, who are working in reputed research organizations, academic Institutes and industries, situated preferably in the close vicinity to the campus are majorly granted Part-Time PhD .
- Part-time PhD takes 7-8 years to complete since Part-time doctoral students must complete the same number of academic credits and other requirements as full-time students.
- Students doing part-time PhD will have to attend a limited number of classes.
- Doctor of Philosophy students doing part-time PhD must have at least 1 year of work experience and must have NOC from the employer.
- Part-time PhD is mainly focused on research for the development of the company rather than individual research work.
A Doctor of Philosophy is an academic degree that requires about four years of extensive study and research to earn. The completion of an Online PhD results in significantly improved career prospects. For students or professionals interested in leadership, academia, consulting, research and entrepreneurship, a PhD degree can offer a required qualification.
Learn More: Online PhD Programmes
| College Name | Course Name | Duration | Fees |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manipal GlobalNXT University | Ph.D. in Education | 36 Months | USD 4000/Year |
| UNICAF - Cours en français | Ph.D. Business Administration | - | - |
| University of Stirling, UK | Ph.D. in Applied Social Research | 36-96 Months | - |
| Manipal Academy of Higher Education Dubai | Ph.D. in Education | 3 Years | USD 6150 |
| Ph.D Strategic Leadership | 30 Months | USD 595 | |
| Asia Pacific University of Technology & Innovation (APU) | Ph.D in Management | 3-4 Years | USD 11,250 |
| Institute of Lutheran Theology, USA | Ph.D. | 4-6 Years | USD 700 |
| Ph.D. | 4-5 Years | INR 16,800 | |
| Integrated Ph.D. | 7 Years | INR 16,000 | |
| Ph.D. | 3 Years | INR 16,000 |
Fully Funded PhD Programs
Students who wish to be funded during their Doctor of Philosophy must clear the NET exam. Passing the NET Exam guarantees stipend from the Government of India irrespective of the University. The student gets INR 31,000 from the Central Government after passing NET. Check: PhD Scholarships
Some of the top PhD scholarships in India that help students complete their Doctor of Philosophy courses are mentioned below:
| Scholarship Name | Institution |
|---|---|
| Prime Minister’s Research Fellowship (PMRF) | MHRD, Government of India |
| CSIR-UGC JRF Fellowship | Government of India |
| DBT-JRF Fellowship | Government of India |
| FITM – AYUSH Research Fellowships Scheme | Forum on Indian Traditional Medicine (FITM) and Ministry of Ayush |
| SAARC Agricultural PhD Scholarships | SAAR Agricultural Centre |
| Swami Vivekananda Single Child Scholarship for Research in Social Science | UGC |
| ESSO-NCESS Junior Research Fellowship | ESSO- National Centre for Earth Science Studies |
| Vision India Foundation (VIF) Fellowship | Vision India Foundation (VIF) |
| Burning Questions Fellowship Awards | Tiny Beam Fund |
| Google PhD Scholarships | |
| Jawaharlal Nehru Memorial Fund Scholarships | Jawaharlal Nehru Memorial Fund |
| ICHR Junior Research Fellowships (JRF) | Indian Council of Historical Research (ICHR) |
PhD Courses
Students have the option of doing Doctor of Philosophy according to their choice. Doctor of Philosophy is available in various streams and subjects. The various subjects available for Doctor of Philosophy according to different streams are mentioned below. See: List of PhD Courses
PhD Courses: Science Stream
There are several PhD courses in the Science stream such as PhD in Chemistry, PhD in Clinical Research, PhD in Science, PhD in Bioscience, PhD in Bioinformatics, PhD Biotechnology, PhD in Mathematical and Computational Sciences, PhD in Environmental Science and Engineering, etc.
PhD Courses: Arts stream
It is a research-based course that allows students to research in their field. This course involves the study of the complete Arts stream and all its specializations like History, English Literature, Political Science, etc
PhD Courses: Medical stream
Ph. D. courses in Medical stream covers all the major areas of medicine including Neurology, epidemiology, genetics as well as various clinical and non-clinical streams. The PhD courses under medical streams are MD Biochemistry, MD Forensic Medicine, MD anesthesiology, MD Pulmonary Medicine, PhD Physiology, MD Skin and VD, etc.
PhD Courses: Engineering Stream
Candiates can apply for PhD courses related to engineering after B.tech. After completion of PhD course in engineering stream, a candidate can start working as a project manager, electrical engineer, application engineer, research engineer, etc in companies such as Dell, Wipro, ABB, DRDO
PhD Courses: Management Stream
Areas of specialization for the PhD in management often include Accounting, Decision sciences (decision theory and decision analysis), Economics, Entrepreneurship, Ethics and legal studies, Finance and Health care management.
PhD Courses: Pharmacy Stream
PhD courses of Pharmacy stream includes Pharm.D, PhD in Pharmacy, PhD in Pharmaceutical Sciences, PhD in Pharmacology, PhD in Pharmaceutics, PhD in Pharmaceutical Chemistry, PhD in Medicinal Chemistry, etc. There are diverse roles available after completion of PhD Pharmacy, including those in clinical research, clinical trials, regulatory affairs, drug safety, business development and medical affairs
PhD Courses: Commerce Stream
Course related to PhD commerce streams are PhD in Commerce, PhD in Statistics, PhD in Commerce and Management, PhD in Accountancy, PhD in Business Economics, PhD in Banking and Finance and M.Phil in Commerce. Job opportunities include working as E-Commerce Executive, Accounts Executive, Consultant, etc in government finance sectors such as Reserve Bank of India, State Bank of India
| - |
PhD Courses: Agriculture stream
Ph D courses agriculture stream includes curses such as PhD in Agriculture, PhD in Agronomy, PhD in Genetics and Plant Breeding, PhD in Horticulture, and PhD in Agricultural Economics. PhD in Plant Pathology. In the PhD Agriculture duration, the candidates get to learn how to produce food, fiber and fuel.
PhD Courses: Law
PhD courses related to Law are PhD in Law, Doctor of Law (LL.D.), PhD in Legal Studies M.Phil in Law. The PhD in Law course brings ample opportunities for students to choose from. Interesting job profiles that attract PhD in Law graduates are Attorney, Deputy Program Manager, Administrative Coordinator, Legal Manager, Legal Counsel, Legal Consultant, and Legal Affairs Manager.
Top PhD Colleges in India
| QS India University Rankings | College Name | Fees (INR) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 58,200 | |
| 2 | 35,200 | |
| 3 | 42,900 | |
| 4 | 19,670 | |
| 5 | 50,000 | |
| 6 | 64,050 | |
| 7 | - | |
| 8 | 8,980 | |
| 9 | 28,500 | |
| 10 | 18,150 |
Top PhD Government Colleges
| College Name | Fees (INR) |
|---|---|
| 1391 | |
| 30,385 | |
| 64,100 | |
| 10,000 | |
| 10,000 | |
| 15,000 | |
| 10,000 | |
| 14,000 | |
| 12,000 | |
| 3,116 |
Top PhD Private Colleges
| College Name | Fees (INR) |
|---|---|
| 53,000 | |
| 1,50,850 | |
| 25,000 | |
| 1,20,000 | |
| 1,07,000 | |
| 59,000 | |
| 30,000 | |
| 65,000 | |
| 30,000 | |
| 75,000 |
Top PhD Colleges in Mumbai
| College Name | Fees (INR) |
|---|---|
| Bombay College of Pharmacy | 1,50,850 |
| 81,500 | |
| 23,377 | |
| 2,50,000 | |
| 40,000 | |
| 14,920 | |
| 30,000 | |
| 30,000 | |
| 65,000 | |
| 75,000 |
Top PhD Colleges in Chennai
| College Name | Fees (INR) |
|---|---|
| 25,000 | |
| 14,900 | |
| 25,000 | |
| 14,900 | |
| 30,000 |
Top PhD Colleges in Bangalore
| College Name | Fees (INR) |
|---|---|
| 1,07,000 | |
| 56,000 | |
| 36,000 | |
| 25,000 | |
| 35,000 |
Top PhD Colleges in Delhi
| College Name | Fees (INR) |
|---|---|
| 1,91,000 | |
| 1,18,000 | |
| 52,400 | |
| 4,00,000 | |
| 20,500 | |
| 1,71,000 | |
| 1,10,000 | |
| 1,28,000 | |
| 3,00,000 | |
| 80,000 |
Top PhD Colleges in Kolkata
| College Name | Fees (INR) |
|---|---|
| 25,000 | |
| 24,000 | |
| 65,000 | |
| 2,14,000 | |
| 2,24,000 | |
| 1,68,000 | |
| 4,50,000 | |
| 5,30,000 | |
| 70,000 | |
| 53,000 |
PhD in India
Top Universities in India provide the best doctor of philosophy courses in India. IITs offer good scope for research in the field of science and engineering.
IIT Bombay PhD
The minimum eligibility required for applying is 60% aggregate marks in Master's degree and the selection of the candidate is done on the basis of GATE/ CEED/ UGC-NET exams scores. A valid GATE score of at least 660 is required. The total fee of PhD is INR 1.83 lakh.
To be eligible for these programs, at IIT Bombay, candidates need to get a master's degree and crack either of these exams - UGC-NET, or GATE, or CEED. Check out the specializations, and the fees for PhD courses at the IIT Bombay, in the tabulation form below.
| Specializations | Average Fees |
|---|---|
| Financial Studies | INR 58,200 |
| Economics | |
| Intellectual Property Rights Law | |
| Computer Science and Engineering | |
| Design | |
| Biotechnology |
IIT Madras PhD
The eligibility criteria for admission to IITM PhD is the candidate must have a Master's degree by Research in Engineering/Technology with a good academic record or a 5 Year Dual Degree in Engineering or 5 Year BS+MS Dual degree from Centrally Funded Technical Institute with a good academic record. For candidates with UG from a CFTI, GATE score is not mandatory.
See: IIT Madras PhD
| Specializations | Average Fees |
|---|---|
| Computer Science | INR 19,670 |
| Biotechnology | |
| Science and Humanities |
IIT Indore PhD
Applicants must apply online through their official website Applicants are selected for admission to PhD programs through an evaluation process that includes an interview by a selection committee and the mere application does not imply admission into the Ph.D. program. The minimum education qualification required is master’s degree in the relevant Department of Engineering/ Technology and a GATE qualification.
| Specializations | Annual Average Fees |
|---|---|
| Psychology | INR 78,800 |
| Economics | |
| Physics |
IIT Bhubaneswar PhD
The eligibility criteria for admission to the IIT Bhubaneswar Ph.D. program is a Minimum of 55% marks or 6.0 CGPA (on a 10-point scale) in the Master's degree in an appropriate discipline. A provisional certificate is acceptable or a minimum of 60% marks or 6.5 CGPA (in a 10-point scale) is required in all other examinations with a valid GATE score. The candidate must be UGC-NET(JRF and LS) qualified.
See: IIT Bhubaneswar PhD
| Specializations | Annual Average Fees |
|---|---|
| Psychology | INR 43,568 |
| English | |
| Electrical Engineering |
IISC Bangalore PhD
The basic qualification required for IISC Bangalore PhD Science program is M Sc or equivalent degree in Physical Sciences/ Mathematical Sciences/ Chemical Sciences or BE / B Tech or equivalent degree in any discipline or Graduates of 4-year Bachelor of Science programs. Graduates of any course with a minimum duration of 4 years with a minimum CGPA of 8.0 are eligible to apply to the regular Ph. D. program without requiring any other National Entrance Tests.
See: PhD in IISc Bangalore
| Specializations | Average Fees |
|---|---|
| Ecological Sciences | INR 31,000 to INR 35,000 |
| Biochemistry | |
| Molecular Reproduction; Development and Genetics |
IIT Hyderabad PhD
The eligibility criteria for Ph.D. admission in the engineering departments is a Masters's degree. Candidates can apply for a direct PhD after B. Tech./B.E. with a valid GATE score. IITH admits students to the PhD program twice a year. Institute provides a monthly stipend of INR 31,000 for the first two years and INR 35,000 for the next three years.
| Specializations | Annual Average Fees |
|---|---|
| Biotechnology | INR 25,095 |
| Civil Engineering | |
| Computer Science and Engineering |
Candidates can apply either online or offline for the VTU Ph.D. program. The minimum eligibility criteria required is 6.5 CGPA. Selection will be based on work experience and previous performance. Admission to the program is merit- based. The annual fee for the program is INR 7,970 for Karnataka state candidates and INR 19,470 for other state candidates. See: PhD in VTU
| Specialization | Annual Average Fees |
|---|---|
| Civil Engineering | INR 74,100 |
| Biotechnology | |
| Architecture |
Bangalore University PhD
Admission is based on the score obtained on University Conducted-Entrance Test and performance in the interview. In order to qualify for the test, candidates need to score at least 50% out of 100.Candidates who have qualified CSIR NET/ UGC NET/ SLET/ KSET/ GATE/ JRF or hold an accredited M. Phil. Degree are exempt from the Ph. D Entrance Test.
| Specializations | Total Course Fees |
|---|---|
| Commerce | INR 44,000 |
| English | |
| Sericulture | |
| Geology |
Amity University PhD
Applications for admission to a Ph. D. program at Amity University are accepted twice a year, for January and July sessions. The admission form is to be filled and submitted online only. The required minimum qualification for admission to a Ph.D Program is a Master’s or M.Phil Degree from any accredited Indian or Foreign University in the relevant field with 55% marks. Eligible candidates will be required to appear in the Selection Process consisting of PET (Ph.D. Entrance Test) and an Interview round as per UGC’s PhD Guidelines.
| Specializations | Specializations | Specializations |
|---|---|---|
| Hospital Administration | Finance | Renewable Energy |
| Hospitality | Anthropology | Architecture and Planning |
| Psychology | Forensic Science | International Relation |
| Law | Chemistry | Cellular and Molecular Oncology |
| Commerce | English | Virology |
| Mass Communication | Pharmaceutical Sciences | Radiation Biology |
| Ecological Sciences | Computer Science and Engineering | Immunology |
| Bioinformatics | Materials and Devices | Rural Management |
| Natural Resources | Special Education | Fashion Management |
| Polymer Science and Technology | Biosensors | Defence and Strategic Studies |
| Remote Sensing | Physical Education | Horticulture |
| Travel and Tourism Management | Physiotherapy | Physiology |
| Economics | Mechanical and Automation Engineering | Microbial Technology |
Then applicants need to download the application form from Jawaharlal Nehru University's official website to apply for the course. Degree holders are eligible for admission, provided they have scored a minimum of 55 percent marks or equivalent grades. Admission is based on a national-level entrance examination followed by an interview. JNU Ph.D. research students receive a monthly stipend of Rs. 28,000 from the Govt.
| Specialization | Specialization |
|---|---|
| English | Environmental Science |
| Economics | History (Medieval and Modern) |
| Geography | Molecular Medicine |
| Philosophy | International Politics |
| Life Science | Persian |
| Law and Governance | Kannada |
| International Trade and Development | Canadian Studies |
| Hindi | Tamil |
| Physical Science | Science Policy |
| Arts | Political Science |
| Ancient History | Latin American Studies |
| Computer Systems | Cinema Studies |
| Sanskrit | Women Studies |
| Diplomacy and Disarmament | Comparative Politics |
| Korean | Media Studies |
| Japanese | Chemical Sciences |
| Spanish | Mathematical Studies |
| Social System | French |
| West Asian Studies | North East India Studies |
| German | South Asian Studies |
| Russian | Social Sciences |
| Management of Informal Sector | Chinese Studies |
| Social Exclusion and Inclusive Policy | African Studies |
| Biotechnology | International Legal Studies |
| Urdu | Political Geography |
| Linguistics | Computational Biology and Bioinformatics |
| Population Studies | International Organisation |
| Nano Science and Technology | Arabic |
| Discrimination and Ecxclusion Studies | - |
For admission to Delhi University Ph.D. program candidates must have completed Master's degree or M. Phil in the respective fields with a minimum aggregate of 55% marks at Delhi University or any other recognized University. The admission to the Program is through an entrance test DUET conducted by the university itself, which results in the shortlisting of the candidates for the interview.
| Streams | Streams |
|---|---|
| Commerce | German |
| Business Administration | Dermatology |
| Pharmacology | Obstetrics and Gynecology Nursing |
| History | Electronics and Communication |
| Political Science | Anaesthesiology |
| Resource Management and Design Application | Pediatrics |
| Fabric and Apparel Science | Business Economics |
| English | Urdu |
| Physical Education | Russian |
| Education | Sanskrit |
| Philosophy | Punjabi |
| Anthropology | Manufacturing Process and Automation Engineering |
| Economics | Persian |
| Physical Education | Electronics |
| Library and Information Science | African Studies |
| Psychology | Radiology |
| Home Science | French/ Italian/ German/ Hispanic studies |
| Surgery | Human Development and Childhood Studies |
| Botany | Buddhist Studies |
| Social Work | Pulmonary Medicine |
| Geology | Biophysics |
| Microbiology | Pathology |
| Chemistry | Instrumentation and Control |
| Hindi | Music |
| Operational Research | Plant Molecular Biology |
| Medicine | Adult Continuing Education and Extension |
| Sociology | Environment Studies |
| Linguistics | Arabic |
| Genetics | Biochemistry |
| Community Medicine | Computer Science |
| Pulmonary Medicine | Financial Studies |
| Statistics | Physiology |
| Biomedical Sciences | Medicinal Microbiology |
| Applied Science and Humanities | - |
Mumbai University PhD
Candidates can also pursue their PhD degree from Mumbai University . It is a renowned government university, offering the PhD program lasting for 3 years. Candidates need to have a masters or M.Phil degree with a minimum 55% aggregate marks from a recognised educational institute. Also, the candidates should have the valid scores of either GATE, UGC, SET, JRF ICAR, and CSIR.
| Specializations | Annual Average Fees |
|---|---|
| Life Science | INR 21,720 |
| Commerce | |
| English | |
| Education | |
| African Studies | |
| Marathi | |
| Sociology | |
| Library and Information Science |
IIT Kharagpur PhD
IIT Kharagpur is one of the best IITs in India, and also belongs among the best colleges all over the nation. It achieved the 5th rank both in 2020, and 2019, by the NIRF. IIT Kharagpur offers a total of 17 PhD courses. The minimum eligibility to pursue a doctorate degree at IIT Kharagpur , needs a minimum CGPA mark of 6.5 or aggregate marks of 60%, at postgraduate level.
| Specializations | Average Annual Fees |
|---|---|
| Science | INR 50,000 |
| Humanities and Social Science | |
| Mechanical Engineering | |
| Engineering and Technology | |
| Management Studies | |
| Working Professionals |
Top Universities around the world that offer the best Phd courses are ranked according to QS World University Rankings. The rankings of both 2021 and 2020 are provided so as to make comparative analysis of the Universities.
| Universities | 2021 | 2022 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | |
| 2 | 2 | |
| 3 | 3 | |
| 4 | 5 | |
| 5 | 4 | |
| ETH Zurich - Swiss Federal Institute of Technology | 6 | 6 |
| 7 | 7 | |
| 8 | 9 | |
| 9 | 10 | |
| 10 | 8 |
Harvard PhD
Harvard University is one of the best educational institutes all over the world. Millions of candidates set their focus to get admission to this university, to pursue their respective courses. It offers numerous programs, along with Doctorate courses, having 8 different specializations. PhD courses in this institute, bear an average course fee around INR 38 lakhs.
Also, the university offers the research programs on both full-time and part-time basis. Every candidate must crack the GRE or GMAT exam for admission to this college. The subjects on which aspirants can research in this college are -
- Computer Science
- Electrical Engineering
- Neuroscience
- Business Administration
- Molecular and Cellular Biology
- Data Science
- Computational Science and Engineering.
MIT PhD
MIT or Massachusetts Institute of Technology also comes among the top universities in the world. It is a private university, with an employment rate of 82%. It gained 3rd position among the National Universities as per the US news, in 2020. MIT is a very much renowned institute for pursuing PhD courses. It offers a total of 29 different research programs. The average course fee for doctorate programs at MIT is around 21 lakhs. All the students have to submit their GRE entrance exam scores to be eligible.
The PhD specializations offered in MIT are -
| Physics | Mathematics |
| Computational Science and Engineering | Doctor of Medicine |
| Brain and Cognitive Sciences | Nuclear Science and Engineering |
Oxford PhD
Oxford University , also belongs among the best universities in the world as per the QS World ranking and many agencies It is also regarded as the best university all over the world by many experts. It is a public research university having an acceptance rate of 15%. Oxford University has an international students percentage of 45%, and it is worth-pursuing PhD here. It offers a total of 17 research program, that are listed below -
| Computer Science | Law |
| Molecular and Cellular Medicine | Modern Statistics and Statistical Machine Learning |
| Medical Sciences | Finance |
| Surgical Sciences | Management |
Stanford PhD
Stanford University in the USA, California is one of the most distinguished research institutes all over the world. It is among the top 5 colleges of the world, and has a terrific rating when it comes to pursuing research programs at this university. It is significantly renowned for offering research programs. Candidates can access approx. 60 PhD courses, at the Stanford University. The specializations offered here, are -
| Materials Science and Engineering | Applied Physics |
| Immunology | Organizational Behavior |
| Operations Information and Technology | Cancer Biology |
| Aeronautics and Astronautics | Management Science and Engineering |
| Chemical and Systems Biology | Economic Analysis and Policy |
Cambridge PhD
Brilliants of students all over the world, come to Cambridge University , to pursue their PhD degree here. It is a private university, with a good acceptance rate of 16%. The number of international students at this institute per year is 9,000.
Candidates have to either crack GMAT or GRE entrance exam, to be eligible for the research programs at Cambridge University. It is arguably the best university to pursue PhD courses. Candidates can access a total of 66 doctorate programs here. Check out the specializations offered here, below.
| Engineering | Computer Science |
| Law | Surgery |
| Biotechnology | Business |
| Physics | Pharmacology |
| Chemistry | Genetics |
| Biological Science - EBI | Architecture |
| Biostatistics | Plant Sciences |
After pursuing a PhD, students can choose from a number of PhD Jobs . Some of the most popular job opportunities after completing a PhD Degree are mentioned below.
| Job Profile | Job Description | Average Salary |
|---|---|---|
| University Professor | A professor helps the students and guides them with their studies, researches etc. Their main role is to teach academic and vocational subjects | INR 6-10 LPA |
| Market Research Analyst | A Market Research Analyst will have the competence of gathering and analysing large amounts of data and comprehending the findings in a comprehensive way. | INR 9-12 LPA |
| Start-Up Mentors | They provide their perspective on the direction that a startup may take and they also advise on new ideas | INR 6 LPA |
| Authors | Authors holding a PhD degree write about the subject that interests readers and which they have done their specializations and researches | INR 9 LPA |
Ques. What is a PhD?
Ans. A PhD, or Doctor of Philosophy, is the highest academic degree awarded by universities. It involves original research and the contribution of new knowledge to a specific field.
Ques. How long does it take to complete a PhD?
Ans. The duration of a PhD varies, but it typically takes around 3 to 5 years. The time can be influenced by factors such as research complexity, program structure, and individual progress.
Ques. What can I get a PhD degree in?
Ans. There are multiple fields on which you can specialize in a PhD program. Some of the popular doctorate level courses are -
- Clinical Psychology
- Electronics and Communications Engineering
- Educational Leadership and Administration, etc,
Ques. Is a PhD after a Masters?
Ques. Is there an age limit for enrolling in a PhD program?
Ans. Generally, there is no age limit for enrolling in a PhD program. Admissions are based on academic qualifications, research potential, and alignment with the program's objectives.
Ques. What is the salary of a PhD?
Ques. What is the easiest PhD to get?
Ques. Can I skip my Masters and do a PhD?
Ques. Can I complete my PhD in 2 years?
Ques. Which PhD has the highest salary?
Ques. Is it free to get a PhD?
Ques. What qualities characterize a great PhD student?
Ques. Is it OK to start a PhD at age 40?
Ques. What are the right reasons for anyone to pursue a PhD?
Ans. Pursuing a PhD comes with long-term career goals and helps the aspirant make a significant contribution towards his selected field.
Most Popular Tags
154 Reviews found
Hamara vishwavidyalay
Loan/ scholarship provisions.
During Phd, you have to pay 6700 rupees fees for the course work and after the course work you have to pay 3700 rupees per sem. For the hostel, you have to pay 2400 yearly for phd candidates. and the university has given non net fellowship which is 8000 per month for every phd scholar.
Campus Life
lots of seminar conferences and workshops are organized by the university. also celebrated lots of festivals and national festivals. every year university conducts an essay writing quiz competition and many more competitions. also every year university conducts sports week.
Placement Experience
Student become eligible for campus from 2 second Year means from 4 semester. Wipro and many multi national companies. They have given 3 lakh to 4 lakhs package. 20% of students from course are getting placements offer. I'm trying to get a job in company.
The campus life was really exciting and much more new to learn during annual fest , sports and extracurricular activities on the campus. students of course used to get part in it. It really gives a great platform to show there talent.
Devika Mishra's Review On Indian Institute Of Tropical Meteorology - [IITM], Pune
There are well opportunities available for the students studying here. From clerk staff to research associate officials there are options available to all levels. One can apply online.There are options for the students to apply for the fellowship for which the students can get 5500 as stipend. For scientists in grades such as B, C, D, the approx. salary is Rs 5 lakh to Rs 6.5Lakh. Training Module helps in career improvement with promotion scheme. This leads to medical facilities, Pension benefits, transport services, canteen services etc.
I only have positive reviews to write about the college. They not only provide their students with ample opportunity to grow and learn in an understanding environment but also provide them with facilities that are necessary for the studies. I have learnt a lot and grown as a better person after spending time in this college. The faculty is not just good but understanding as well. The college doesn?t boast about itself but it upholds its reputation very well.
Keshav Bibhuti's Review On Indian Institute Of Tropical Meteorology - [IITM], Pune
To get the entrance in Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology College, candidates should achieve first class marks in M.Sc / M.Tech / MS degree or the same in Meteorology, Atmospheric Sciences, Chemistry, Ocean Sciences, Physics, Applied Mathematics, Statistics, Geophysics, or any other region of Earth Sciences or any related subject with Physics and Mathematics at the graduate stage. Those appearing for final exam can also apply but the final selection will be based on detailed interview at Pune in June or July every year. As you can submit the online forms along with CV.The original documents like mark sheet of qualifying examination and certificate of matriculation exam will be returned to the candidates right away after verification and the attested photocopy of the document will be kept by the institution of higher education for record. The candidate which is selected must pay the required charges at the time of admission.
Extracurricular activities of IITM have huge way to join in an activity you enjoy and convene new people, and they can also be an important part of your institute. In institute, students show your interests and talents. It let you take part in an activity you enjoy, whether that's playing football, painting, Sports, Gym, Computer Labs and vast collection of Books, Journals & Magazines etc. IITM provides the world class infrastructure, with hosting center for climate change research. It make students not only enjoy but also makes you happier but can also give you a much needed break from stress. It organizes obligatory general medical checkup camps for all the members of institutes.
My Ph.D review
Our college have a limited placements opportunities but in the course like Ph.D., there are millions of opportunities available for the students to apply in the government and private sector for jobs and internships and gain experience towards the same.
Course Curriculum Overview
The course educational program is significantly drawn towards the parts of research in the territory of medication. The structure of the course is progressively useful in contrast and can bring millions of opportunities to the table for students.
Rushikesh's Review On National Institute Of Virology - [NIV], Pune
The college does not host or conduct any events or extracurricular activities for the students. They do conduct a few which are educational for the students and related to their field of study. Other than that not many are conducted.
The faculty of the college are very well qualified and are trained very well. They have a lot of experience in their fields of study and pass on that knowledge to us. They help in clearing doubts and are very professional.
Sarazul's Review On National Institute Of Virology - [NIV], Pune
Our college loves to enhance the skills of ten students and hence why a lot of events such as seminars and talks hosted by different guests are conducted in our college. The students take part in order to gain more knowledge.
Fee Structure And Facilities
Comparing our institute to other institutes our Institute fee is pretty nominal and feasible. The students are given a Stipend for researching and finding more about the viruses so the students can use that to pay the fee.
PhD in Post Harvest Machinery from CIPHET
The institute was created with the sole purpose of creating practical solutions to the problems of agricultural engineering, and focusing on research and academic training for the next generation of agricultural scientists. And I can proudly say, that it lives up to its expectations.
I wanted to specialize in post harvest machinery, and the Central Institute of Post Harvest Engineering and Technology specializes in the field. I saw an invitation for application for PhD, and applied. This was followed by an interview, after which I was admitted.
PhD in Agro-processing Center from CIPHET
The institute does not have a placement cell, and with the rigorous training, seminars and workshops the employability of the researchers is never in question. There are a few options to choose from, and you can even apply to CIPHET when there are vacancies for ongoing or proposed projects.
My time here is proving to be enriching and inspiring. There are so many things to learn, and I can hardly think of a better place for that. My network circle is wonderful, and we are just a bunch of dedicated, passionate people trying to give our contribution to our respective fields.
Very good Institute
The university has a well established placement cell who ensures that the students are placed in right industries. The placement cell organizes many seminars, guest lectures, conferences, corporate meet, personality development, communication skills and counselling sessions to make the students ready for campus interview. After completing the course, students can take up various competitive examination of UPSC, Banking and other sectors.
College Events
The seniors of our institute organizes many events and festivals like Foundation day, Freshers day, sports and cultural events, Flag hosting on Republic and Independence day, Teachers day, Swachh Bharat Abhiyan, International Yoga Day etc. These festivals are organized in a very big way in which both teachers and students take part.
Good Institute for Research studies.
Overall experience as a student of this institute , i can say that the placement and job opportunities was good in our institute. Many government and private companies come to our college for campus recruitment. The training and placement cell of the institute takes care of training and placement activities for the students by inviting many companies.
Central Institute of Post Harvest Engineering and Technology was one of the best and reputed institute. The institute provides very good facilities and education to the students. The faculty and non faculty members are very good and helpful. The institute provides a very good quality education to the students. It was a proper place for studying.
Good college for Research studies.
The students committee of our college organizes many indoor and outdoor activities in our college. The college has a large playground in which many outdoor games and cultural activities are organized. As, i have very much interest in outdoor activities, so i participate in all outdoor activities organized by the college. It was a very fun and good moment for all the students.
The college organizes many events and festivals like National conference, Yoga Day, celebration of kannada Rajyotsava, World Disabled Day, Krishnamela, Holi, Celebration of Constitution Day, Diwali, observance of Vigilance Awareness week etc are organized. All teachers and students participate in all the events and festivals organized by the college.
Superb college for PhD
The admission to the college is based on the merit list. Once your name lies in the the list you are called for an interview. The interview process is important and holds a lot of weightage for the admission. Sometimes if there are a lot of candidates then a written exam is conducted.
The fee is feasible enough for students hailing from middle class. The course duration is of 2 years. I never felt any difficulty in paying the fee. The examination fee is asked differently prior to the exams which are held every semester.
Fantastic experience of my life
The teachers are educated enough. They are quite strict in terms of assignment and projects which is a good trait for a teacher. The non- faculty staff is professional. During my second year I had a problem with my attendance issue, they helped and sorted the issue immediately.
The course is extensive enough. It is based on a lot of paper work and research stuff. Instead of theoretical approach a lot of practical approach is also done. The course is for 2 year duration. Exams conducted are mostly based on the thesis and journal work.
NBAIR Review
The institute offer various job opportunities to the students. Many renowned companies visit our institute to offer placements. Many of my friends got placed in good companies and are paid quite well. Our institute also provide us with career guidance which build s our personality.
The fee structure is quite reasonable and practical. They charged Rs 62,000 per year which is prudent. The facilities are various therefore, the money we have paid is low. We are even offered guaranteed jobs after the end of the course, so the amount they are charging is justified.
Richa Rathore's Review On The Centre For DNA Fingerprinting And Diagnostics - [CDFD], Hyderabad
After the completion of our research work and PhD, there is an ample of opportunities for the candidates . There are carrier opportunities in the field of diagnostics , administrative officer post and various other golden opportunities knocks the door of the qualified candidates. Candidates can also grab the job opportunity at the same research center itself or the other depending upon their choice and interests.
The fees of the research center is quite feasible. The fees is very much economical and easily affordable. Comparing the opportunities and facilities provided to us and understanding of every thing in a modern way with modern tools and technologies , the fees seems to be the best value for money . The return on investment is great at this research center.
My college Review
The fee structure is more or less feasible the structure of the fee is described well once the student visit the college campus physically. based on which the students can apply further.But as much as i perceived many students earmark this college due to its fee structure.
Students consenting for PH.D curriculum need to apply online with all the details and an Updated Resume with work experience and the organization's name. Once this process is completed the students will receive an automated mail from college.
Raahil's Review On The Centre For DNA Fingerprinting And Diagnostics - [CDFD], Hyderabad
You should have a postgraduate degree with you. The application form is available online you can fill it with required details and then there is a walk-in interview for all the candidates and on the basis of performance in the interview admission will be taken.
After completing the doctorate degree you will have a number of options available for you. You can either apply for the post of professor for any college or university or you can opt some other options according to your preferences.
Ph.D in Science
The Centre for DNA Fingerprinting and Diagnostics is a very famous college which focuses on developing interest to research and make progress in the field of DNA Fingerprinting as well as many other related areas. In order to get admission, the candidate should have completed there post graduation in the concerned discipline. The candidate will be selected on the basis of merit and interview.
The fee structure of Ph.D in Science is very nominal and not at all expensive. The cost is around 20thousand which is a very feasible and affordable amount. Also the institution funds all the research work of the students. Hence the fee structure is very good.
Utkarsh's Review On The Centre For DNA Fingerprinting And Diagnostics - [CDFD], Hyderabad
The admission for the course would be through the interview which would be held for about three days consecutively. The base of the selection would be the candidate should possess a post-graduate in science, agriculture, or the technology related to science in a recognized university.
The events mostly celebrated in the college are the technical events and they would give high importance to the national and the international level conferences as well as the paper presentations at the college. Therefore the whole technical events would be given its importance.
Ph.D. : 43 answered questions
Ques. are master's degrees from ignou acceptable for admission into ph.d courses in top universities.
● Top Answer By Anumita Mukharjee on 28 Apr 22
Ques. Is a Phd from IGNOU worth it/valuable?
● Top Answer By Srabani Guha on 24 Jul 23
Ques. How is the Direct PhD program of IIT Madras?
● Top Answer By Arati Sinha on 29 Mar 23
Ques. What is the value of a Ph.D. degree from IIT Bombay?
● Top Answer By Karuna Nair on 13 Mar 23
Ques. Why do some students in IIT Bombay leave high-paying jobs and join grad schools for PhD?
● Top Answer By Advait Joshi on 23 Mar 23
Ques. What is the placement scenario after PhD in IIT Bombay?
● Top Answer By Advait Joshi on 17 Mar 23
Ques. Is a PhD from IGNOU valid?
● Top Answer By Pankaj Kumar on 18 Oct 22
Ques. What is the placement record of MSc applied statistics students of IIT Bombay?
● Top Answer By Poornima Sahoo on 18 Mar 23
Ques. How difficult is it to get a PhD from IISc Bangalore?
● Top Answer By Bidita Ghose on 14 Jul 23
Ques. How good is doing a PhD in BITS Pilani compared to IITs?
● Top Answer By Advait Joshi on 27 Jun 23
Ph.D. (Chemistry)
Ph.d. (physics), ph.d. (mathematics), ph.d. (biotechnology), ph.d. (zoology), ph.d. (psychology), ph.d. (business management), ph.d. (management studies), master of science [ms], ph.d. (computer science), ph.d. colleges in india.

IIMV - Indian Institute of Management
![phd course period Post Graduate Institute of Medical Education & Research - [PGIMER]](https://images.collegedunia.com/public/college_data/images/appImage/10842_MEDICAL_NEW.jpg?h=150&w=320&mode=stretch)
Post Graduate Institute of Medical Education & Research - [PGIMER]

IIM Sambalpur

IIM Sirmaur
![phd course period University Business School, Panjab University - [UBS]](https://images.collegedunia.com/public/college_data/images/appImage/19071_UBSC.jpg?h=150&w=320&mode=stretch)
University Business School, Panjab University - [UBS]
![phd course period PSG Institute of Management - [PSGIM]](https://images.collegedunia.com/public/college_data/images/appImage/1506339710cover.jpg?h=150&w=320&mode=stretch)
PSG Institute of Management - [PSGIM]

Krea University
Subscribe to our news letter.

Mechanical Engineering
- Graduate study in Mechanical Engineering
- Ph.D. programs
Ph.D. in Mechanical Engineering
The Doctor of Philosophy in Mechanical Engineering prepares students for careers in research and academia. Our collaborative faculty are investigating a diverse range of research areas like additive manufacturing, air quality, cellular biomechanics, computational design, DNA origami, energy conversion and storage, nanoscale manufacturing, soft robotics, transdermal drug delivery, transport phenomena, machine learning, and artificial intelligence.
Interested? Visit our research pages for more information, including faculty areas of expertise and research videos.
- Other Ph.D. programs
I’d like more information.
View the degree requirements in the handbook.
Doctor of Philosophy in Mechanical Engineering
Students typically complete the Ph.D. degree requirements in three to five years. Early in the program, students focus on course-work that enhances their knowledge as they prepare to conduct research.
Within one year, students must pass the departmental qualifying exam, an oral exam that tests research skills and knowledge of a core mechanical engineering subject area.
Student research forms the core of the Ph.D. program. Research involves active student-directed inquiry into an engineering problem, culminating in a written thesis and oral defense.
Ph.D. Financial Support
The majority of full-time Ph.D. students accepted through the standard application process receive fellowships that cover full tuition, the technology fee, and a stipend for living expenses for up to five years, as long as sufficient progress is made toward degree completion. These awards are sufficient to cover all expenses for the year (including summers). Students are required to pay for health insurance, the transportation fee, the activity fee, books, and course supplies. Off-campus housing is available within walking distance of campus. At least one year of residency is required for the Ph.D. We offer two ways to enter the Ph.D. program.

Advanced entry Ph.D.
The advanced entry Ph.D. is for students with an M.S. in an engineering discipline or equivalent field.
Direct Ph.D.
The direct Ph.D. is for students entering the program with a B.S. in an engineering discipline or equivalent field.
For a comprehensive overview of the programs, including degree requirements, please consult the most recent handbook
Ph.D. candidate Remesh Shrestha, co-advised by Professors Sheng Shen and Maarten de Boer, explains his research to create polymer nanowires that have high thermal conductivity:
Other Ph.D. programs and partnerships
Apply here (by these deadlines).
For spring 2023
For fall 2022
The application for fall entry opens in October.
More information
Ph.D. employment stats
Ph.D. enrollment and completion stats [pdf]
Department of History
Ph.d. program overview.
The Ph.D. program in History trains students in the skills of conducting original historical research and crafting original historical arguments. In the course of their work as historians, Brown scholars draw on a wide range of methods and engage with a variety of audiences. While training emphasizes the core skills of academic research, writing, and teaching at the college and university level, the program’s goals do not end there. Many Brown Ph.D. students explore teaching and writing for different settings and prepare for a breadth of careers that value the skills that obtaining a Ph.D. in History entails.
Students are expected to complete Brown’s Ph.D. program in five to six years. As a mid-sized program, the department values and cultivates attentive and hands-on faculty who work closely with students throughout their progress towards a degree. Critically, students in an entering cohort proceed through the program together, so that discussions across fields, geographies, and chronologies are built into the Ph.D. program.
Students accepted into the History Ph.D. program who remain in good standing are guaranteed funding for six years. Ph.D. students not supported by external fellowships work typically as teaching assistants in the second, third, and fifth (and, if relevant, a portion of the sixth) years of their program. There are also opportunities to apply for conference, research, and study grants either through the History Department or the Graduate School.
The information presented here is a summary of the Ph.D. program. For a more detailed description, see the Department of History Graduate Handbook. Prospective students should also read carefully the information supplied on the website of Brown’s Graduate School.
The Program is divided into two stages:
Stage 1: Coursework and preparation for the Preliminary Exams (Years 1-3)
During the first and second years, students take seminars that introduce the major historiographical questions and methodologies of various subfields and develop their research skills. They identify the three fields for their Preliminary Exams and begin preparation for the exams, which are usually taken in December of the third year. Students are expected to teach as teaching assistants in their second and third years.
History offers five types of Ph.D. courses, typically to be completed within the first three years of a student’s program:
1) Required seminars (4): "History Now" features cutting-edge historical research and writing, including that being written by History faculty members; "The Roots of History" traces the development of the historical profession, focusing on the major methodological and theoretical landmarks in that development; an advanced workshop, "Writing History," guides students through the writing of a publishable paper; a Dissertation Prospectus Seminar culminates in the student’s defense of the dissertation plan and proposal.
2) Field Seminars offer a broad overview of the historiography of particular fields (e.g., Early Modern Europe, Modern East Asia).
3) Thematic Seminars provide opportunities to explore a particular theme or methodological frame from a transnational and transtemporal perspective.
4) Special Topics Seminars focus on the historiography of a particular nation or region, historical "event," or historiographical debate. They allow for focused, close training, including in specialized skills and readings in languages other than English.
5) Independent Study courses, by arrangement with the instructor, offer students, individually or in small groups, opportunities to explore special interests in depth.
In addition, students will receive course credit for attending "The Practice of History," a series of professionalization workshops that provide guidance in grant-writing, applying for jobs, developing inclusive teaching practices, constructing effective syllabuses, etc.
Students typically take four courses per semester. Up to two graduate courses (exclusive of language courses) may be taken outside the department.
A typical schedule looks like this:
|
|
|
| |
|
|
Fellowship funding |
Fellowship funding | language/skills + year long research project 3 month stipend |
|
|
Teaching Assistantship (TA) - funding |
Teaching Assistantship (TA) - funding | Pre-dissertation research, grant writing, and exam prep 3 month stipend |
|
| placeholder course (prelim exam in December) Teaching Assistantship (TA) - funding |
Teaching Assistantship (TA) - funding | Dissertation research 3 month stipend |
|
|
Dissertation research Fellowship funding |
Dissertation research Fellowship funding | Dissertation research/writing 3 month stipend |
|
|
TA or Teaching Fellowship |
TA or Teaching Fellowship | Dissertation Completion Fellowship (DCP) Stipend |
|
|
DCP fellowship or DCP TA (one semester each) |
DCP fellowship or DCP TA (one semester each) | Funding ends upon graduation in May |
* Can be filled in a number of ways, including a language course, a 1000-level class, an independent study, a 2000-level class, or with a placeholder independent study with the DGS (HIST2910)
Preliminary Examinations
By the end of the first semester, students should have identified three fields (one major and two minor); these are usually subfields of the primary and secondary fields listed under Fields of Study ). These will be the areas examined in the Preliminary Examinations—three written and one oral exam—usually completed by the end of the fifth semester.
Language Requirement
Language requirements are set by the fields of study. They must be completed before the preliminary examinations are taken at the end of the fifth semester.
Stage 2: Prospectus and advancement to candidacy (Years 3-5/6)
After the successful completion of all coursework, the language requirement, and the preliminary examinations, the student, usually during the course of the sixth semester, develops a dissertation prospectus. Once the prospectus is approved by the student’s dissertation committee, the student devotes full effort (outside of work as a Teaching Assistant) to researching and writing the dissertation.
In the sixth semester, students take the Dissertation Prospectus Seminar, which provides a collaborative structure for the process of identifying viable dissertation projects, selecting a Dissertation Committee, articulating the project in the form of a dissertation prospectus, and, when appropriate, developing grant proposals based on the prospectus. The prospectus, in roughly 15 to 20 pages, states the dissertation topic, sets it in the context of the relevant secondary historical literature, explains the significance of the study, outlines the methodology to be followed, describes the types of primary sources to be used, and provides a tentative chapter outline, a bibliography, and a research plan. During the Dissertation Prospectus Defense, usually held in May or June, the Dissertation Committee reviews the prospectus and provides suggestions and advice to the student. Once the prospectus is approved, the student proceeds to conduct research on the dissertation.
Dissertation
Dissertations can vary significantly between students and among subfields. Students should consult regularly with their advisors during the dissertation research and writing process, to report progress and to ensure agreement on expectations for the dissertation. The most basic standard for a dissertation is that it makes an original contribution to the body of relevant scholarship in its field. The doctoral dissertation should be completed within four years after the student passes the preliminary examinations.
The Dissertation Defense is conducted by the graduate advisor and other members of the Dissertation Committee. Its purpose is to provide a forum for a general discussion of the dissertation—its strengths and weaknesses as a contribution to knowledge and its future prospects. If the dissertation is approved by the Dissertation Committee, the student has completed the final requirement of the Ph.D. program and can prepare to graduate.
Candidates for the Ph.D. must normally demonstrate satisfactory performance as a Teaching Assistant in undergraduate courses at Brown, or in teaching at another institution approved by the department. A Teaching Assistant usually works as a grader and section discussion leader under the guidance of the faculty member teaching the course. Ph.D. students not supported by external fellowships typically work as Teaching Assistants in the second, third, and fifth years of their program, and one semester in their sixth year. Explanation of the rights and responsibilities of teaching assistants may be found in the Department of History Graduate Handbook.
The written exam for each individual field may consist of (1) a timed, written, closed or open book exam, (2) a long essay or series of shorter essays, or (3) a draft syllabus and one or several course lectures. (Other potential outcomes must be approved ahead of time by the DGS.) The written exam may be completed (1) when the student finishes reading for a field, leaving only the oral portion for December, or (2) immediately before the oral exam in December. The oral exam, which normally takes place in December of the third year, is two hours long and consists of all three exam committee members querying the student regarding the written exams, the field at large, and/or any materials from the exam list. For more details on the preliminary exams, see the History Graduate Student Handbook.
Summary of Exam Process
- May 19 : Fields Declaration Form submitted to the student’s primary advisor (who will normally be the chair of the exam committee), the DGS, and the graduate program administrator
- Summer: Students should initiate conversations with examiners regarding lists and procedures.
- January : Preparation for the preliminarily exam should begin in earnest, continuing through the summer and fall. Students should enroll for an Independent Study in semester 4 with their primary advisor or other examiner (see above).
- March 31 : Submission of Fields Planning Form , along with drafts of the three field lists and a progress report on language and all other requirements
- September : Graduate program administrator circulates information about the oral portion of the exam.
- November : Graduate program administrator circulates schedules for the oral exams, along with all submitted written exam responses.
- Early to mid-December : Oral exams are conducted.
Sample Exam Preparation Schedule Note : This is intended only to provide a rough framework for exam preparation; individual exam processes may vary, depending on examiner and student availability and preference.
- January : Initiate reading for Field 1 (usually major field, as part of IS)
- April : Complete written exam for Field 1
- May : Initiate reading for Field 2
- July : Complete written exam for Field 2
- August : Initiate reading for Field 3
- October : Complete written exam for Field 3
- November : Review Fields 1, 2, and 3 in preparation for oral exam
December : Complete oral exams
The capstone project of the Ph.D. program is the Doctoral Dissertation. The Department’s required core course sequence concludes with the Dissertation Prospectus Seminar, which students take in the sixth semester, usually after passing their Preliminary Exams.
The Dissertation Prospectus Seminar (spring semester of the third year) provides a shared structure for the process of identifying viable dissertation projects, selecting a dissertation committee, articulating the project in the form of a dissertation prospectus, and, where appropriate, developing grant proposals based on the prospectus. The dissertation committee, the selection of which is a requirement of the course, consists of a chair and at least two additional Brown faculty members.
The dissertation committee will be responsible for evaluating the student's dissertation prospectus, to be presented no later than the end of the sixth semester. This usually takes the form of a dissertation prospectus defense, which is an important moment to bring together the dissertation committee to provide input and advice on the prospectus as well as the next steps of research and writing.
After passing the preliminary exams and obtaining approval of their dissertation prospectus by the dissertation committee, Ph.D. candidates are encouraged to proceed with speed and efficiency into the research process. During the research and writing of the thesis, it is the student's responsibility to regularly provide the graduate advisor with evidence of satisfactory progress towards completion. The doctoral dissertation should be completed within four years after the student passes the preliminary exams.
The department expects each student to have a dissertation defense The defense will normally be conducted by the graduate advisor and dissertation committee members, whether in person or via video conference. If the candidate wishes, other graduate students may attend and participate in the discussion.
A Dissertation Defense form must be filled out by the student and submitted to the Department staff. This form should be filed at the same time as the submission of the penultimate version of the dissertation, on March 15 for a May graduation, or no later than one month prior to the dissertation defense date if an October or February graduation.
If the dissertation is approved by the dissertation committee, the student has completed the final requirement of the Ph.D. and is permitted to proceed with preparations for graduation. Students are permitted by the Graduate School to graduate (having fulfilled all requirements) at three points during the year: October, February, and May. Students who wish to take part in Commencement ceremonies may elect to walk in May following their graduation (or at the time of their graduation, if in May). Brown University Commencement usually takes place the Sunday before Memorial Day. There is a separate Graduate School Ceremony as well as a Department Ceremony that graduate students are especially encouraged to attend.

Amy G. Remensnyder
- PhD Timeline
--> Also see the separate pages with on-boarding information for new PhD students <-- Information and Resources for New Graduate Students Wiki site for incoming PhD students (behind Harvard Key)
First Year (G1)
- Notify your financial aid officers of any external funding. Contact: Erin Bishop in SEAS Finance and Emily Fingerle in GSAS Financial Aid.
- Make note of the course registration deadline. (previously known as "Study Card Day"). See the GSAS Policies Academic Calendar.
- Register for courses before the deadline (previously known as "Study Card Day")
- Mid-January: Deadline for submitting materials to be reviewed at the January CHD meetings .
- Late-January: Course registration deadline (previously known as "Study Card Day").
- G1s: Your Prospective Program Plan due to the Office of Academic Programs on this day.
- Transfer of up to 3 classes of coursework may be allowed. Include the Application for Credit for Work Done Elsewhere with your Prospective Program Plan.
- April 1: Research Advisor Selection Form /Research Assistant appointment form due to Office of Academic Programs.
- Note: The April CHD meeting is the last CHD meeting in all academic year. CHD does not meet over the summer. Remember to plan ahead.
Second year (G2)
Throughout year.
- G2’s are required to serve as a Teaching Fellow in either the Fall or Spring semester.
- Make sure you complete the TF form once you line up a TF position!
- G2’s are required to take their qualifying exam in either the Fall or Spring terms.
- Email quals_defenses@seas to book a room. If you book your own room (e.g., external to SEAS) you must still email quals_defenses@seas well in advance in order for your required documentation to be ready, else your exam cannot take place.
- Upon completion of the exam, students are required to submit the Designation of Research Committee form to OAP.
- If you plan to request a delay of the qualifying exam, complete a Request to Delay Qual Exam form. Note that delays until September (i.e. start of G3 year) are typically approved as a matter of course
- Mid-September: Course Registration Deadline (previously known as "Study Card Day"). See the GSAS Policies Academic Calendar.
- Mid-October : Final Program Plan due to OAP; see the CHD page for dates.
- Late-January : Course Registration Deadline (previously known as "Study Card Day"). See the GSAS Policies Academic Calendar.
- May 1 : Advising Agreement form due to OAP.
- May: Commencement and diploma options for Masters en Route / Continuing Master’s students - You can apply to receive your S.M. degree en route to your PhD after you have completed eight of your core courses (this requirement may depend on area). You will receive your S.M. diploma, and participate in the Commencement if you choose to. However since you will be considered a non-terminal degree recipient, you will not be able to join the ceremony in Sander's Theater.
Third year (G3+) and beyond
- Meet with your Research Committee at least annually, as indicated by your area's expectations.
- Send any changes to your Final Program Plan to the CHD for review. See the CHD page for submission dates. Note that the Committee on Higher Degrees expects students not to petition for a revised Program Plan less than a year prior to the final defense in case additional coursework is required, so it's important to keep your plan up to date with your courses as actually taken.
- Inform OAP of any changes to your research committee .
- PhD candidates can review their eligibility to receive an SM en route .
- Early-September: Course Registration Deadline (previously known as "Study Card Day"). See the GSAS Policies Academic Calendar.
- Late-January: Course Registration Deadline (previously known as "Study Card Day"). See the GSAS Policies Academic Calendar
- May 1 : RA reappointment form due to OAP.
Completing your degree
Degree application.
- Check out FAS degree-completion information here (Registrar) and deadlines here (GSAS calendar)
- Complete the degree application via my.harvard by the Registrar's deadline.
- If you schedule your own room (e.g., external to SEAS) you must still email quals_defenses@seas well in advance in order for your required documentation to be ready, else your defense cannot take place. You must also get agreement from your full committee to hold your defense in a non-SEAS room.
Dissertation Submission and Commencement
- The best way to share your dissertation with others is by linking to the DASH copy. DASH uses persistent URLs and provides you with download statistics, and the DASH copy of your PDF will not include the signed Dissertation Acceptance Certificate (DAC). If you choose to post or share your PDF in some other way, you should remove the DAC page so that readers do not have access to the scanned signatures.
- Get ready for commencement by updating your email and other contact information via my.harvard.edu .
In Computer Science
- First-Year Exploration
- Concentration Information
- Secondary Field
- Senior Thesis
- AB/SM Information
- Student Organizations
- How to Apply
- PhD Course Requirements
- Qualifying Exam
- Committee Meetings (Review Days)
- Committee on Higher Degrees
- Research Interest Comparison
- Collaborations
- Cross-Harvard Engagement
- Lecture Series
- Clubs & Organizations
- Centers & Initiatives
- Alumni Stories

- Find a Person
- For EMS Faculty & Staff
- Community Resources
Department of Geography

Doctor of Philosophy (Ph.D.)
The Ph.D. is a different kind of degree from the master’s degree. A doctoral candidate in geography must be capable of making original contributions to knowledge and scholarship. For the students to make such contributions, they must concentrate on a narrow and clearly defined field of study. We require, however, that doctoral candidates know more of geography than their particular specialties; thus, any aspirant for a doctorate must obtain master’s training or its equivalent before being admitted to doctoral candidacy. In short, admission to doctoral candidacy is official recognition that a student’s general foundation in the breadth of geography is satisfactory. Students then devote their attention to developing depth in chosen specialties.
The general requirements for a doctoral degree in geography are more rigorous than those for a master’s degree. At the same time, the greater flexibility of the doctoral program allows advanced students to pursue programs of study tailored to their special interests and needs.
Progress through the degree is marked by:
- Successful performance in a verbal qualifying exam;
- Four-day written comprehensive exam, with a verbal portion after the written answers have been assessed by the committee;
- Formal dissertation proposal; and
- Verbal defense of a completed dissertation.
The four-year Ph.D. program is reserved for students who have a master’s degree from another graduate program. That can be another geography program at another university, a non-geography program at another university, or a non-geography program at Penn State.
Students entering the four-year Ph.D. program must take the doctoral qualifying exam in their first year. A committee from three of the four fields of geography and formally appointed by the Graduate Program Officer will administer the qualifying exam. The qualifying exam can take place any time during the year, but students in the four-year Ph.D. program typically take it during spring semester.
Students in the four-year Ph.D. program complete a comprehensive exam and defend their dissertation proposal in the second year. Depending on the needs of their research, and in agreement with their doctoral committee, students can fulfill these two requirements in either order. Once students have successfully passed their comprehensive exam and defended their proposal, they typically take two years to research, write, and defend their dissertations.

Our online Graduate Student Handbook explains the program requirements for all degrees.
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Phd-supervisors experiences during and after the covid-19 pandemic: a case study.

- 1 Department of Education, University of Bergen, Bergen, Norway
- 2 Department of Educational Studies in Teacher Education, Faculty of Education, Inland Norway University of Applied Sciences, Hamar, Norway
- 3 Department of Psychosocial Science, University of Bergen, Bergen, Norway
- 4 Faculty of Arts and Physical Education, Volda University College, Volda, Norway
Introduction: The COVID-19 pandemic has significantly impacted the education sector, and this case study examined nearly three hundred PhD supervisors in Norway. The study was driven by the urgent need to better understand the professional, social, and existential conditions faced by doctoral supervisors during extended societal shutdowns. This explorative case study builds on a former study among PhD candidates and investigates the experiences of doctoral supervisors when remote work, digital teaching, and digital supervision suddenly replaced physical presence in the workplace, largely between March 12, 2020, and autumn 2022, due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Methods: A mixed-methods research approach, incorporating formative dialog research and case study design, was employed to bridge the conceptual and contextual understanding of this phenomenon. The primary data sources were a survey ( N = 298, 53.7% women, 46.3% men, response rate 80.54%) and semi-structured interviews (with nine PhD supervisors). Supplementary data collection was based on formative dialog research. It included field dialog (four PhD supervision seminars), open survey responses ( n = 1,438), one focus group ( n = 5), an additional survey ( n = 85), and document analysis of PhD policy documents and doctoral supervision seminar evaluations ( n = 7). The survey data, interview data, focus group data, and supplementary data focus also retrospectively on the first year of the pandemic and were collected from August 2022 until October 2023.
Results: The findings from the explorative case study revealed that the PhD supervisors faced numerous challenges during the pandemic, both professionally and personally. For PhD supervisors who extensively worked from home over a long period, the situation created new conditions that affected their job performance. These altered conditions hindered their research capacity, their ability to follow up with their PhD candidates, and their capacity to fulfill other job responsibilities. Although the PhD supervisors received some support during the pandemic, it seems that the incremental measures provided were insufficient.
Discussion: The case study results indicate that it is more important than ever to understand the gap between the formulation, transformation, and realization arenas when distinguishing between incremental, semi-structural changes and fundamental changes in PhD regulations and guidelines brought on by societal crises. This highlights the need for better crisis preparedness at the doctoral level in the years to come.
1 Introduction
Effective doctoral supervision is crucial for guiding PhD candidates through the complexities of their research, ensuring academic rigor and the successful completion of their dissertations ( Bastalich, 2017 ; Wichmann-Hansen, 2021 ; Kálmán et al., 2022 ). The role of PhD supervisors during the pandemic and their impact on educational quality at various levels has been an under-researched area both nationally and internationally ( Börgeson et al., 2021 ; Krumsvik et al., 2022 ). Supervisors who have varying experiences and work under diverse conditions are key players in the transformation arena where central policies are applied at the institutional level. Their interaction with PhD-candidates, whether in-person or remotely, shapes partly the quality of PhD-programs and candidates’ learning experiences. The COVID-19 pandemic has influenced the education sector in numerous ways, and this case study examined nearly three hundred PhD-supervisors in Norway with a Mixed Method Research design and different methods and data. The impetus for the study was the urgent need for a better knowledge base to understand the professional, social, and existential conditions for doctoral supervisors when society is shut down for an extended period. This explorative case study builds on our former study among PhD-candidates ( Krumsvik et al., 2022 ) and investigates the experiences of doctoral supervisors when remote work, digital teaching, and digital supervision suddenly replaced physical presence in the workplace (to varying extents).
First, the introduction contextualizes the study; second, the methodology is described; third, the main part presents the results from the survey part of the study; fourth, the data from the interviews and Supplementary data are presented; fifth, the discussion and conclusion are presented.
International policy documents underline the importance of PhD-supervision [ European University Association (EUA), 2010 , 2015 ] and, in Norway, it is crucial to view PhD supervision considering the specific frame factors for the PhD’s and some general trends of changed frame factors in doctoral education over the last 10 years ( Krumsvik, 2016a , 2017 ). It is therefore important to examine such frame factors in light of PhD-supervisors’ experiences during the pandemic, but the current state of knowledge is still limited around this topic. However, “The United Kingdom Research Supervision Survey Report 2021″ found that among the 3,500 PhD supervisors in the United Kingdom, 65% felt that supervisory responsibilities have increased during the pandemic, 32% agreed that “concerns over supervision have kept me awake at night over the last 12 months” and 31% agreed that “supervising doctoral candidates makes me feel anxious over the last 12 months” ( UK Council for Graduate Education, 2021 ). With these abovementioned issues in mind, this doctoral supervision study builds on our previous research on doctoral-level education ( Krumsvik and Jones, 2016 ; Krumsvik and Røkenes, 2016 ; Krumsvik et al., 2016a , b , 2019 , 2021 ; Krumsvik et al., 2022 ) and aims to examine the experiences of PhD supervisors in Norway during the pandemic to answer the research questions below:
1. To what extent has the COVID-19 pandemic impeded the PhD supervisors’ frame factors on the micro-level, and how do they perceive this situation?
2. To what extent has the COVID-19 pandemic influenced PhD supervisors’ frame factors on the meso-level, and how do they perceive this situation?
3. How do the PhD-supervisors experience the more general aspects of their supervision role during and after the pandemic?
1.1 The Norwegian context
To contextualize the research questions to the Norwegian context, one must remember that doctoral candidates in Norway are not students per se but are employees (on a 3–4 years contract) and more regarded as colleagues than students, and in this sense, the roles are more equal than in traditional supervisory relationships at a lower level (supervisor-student). Both by having PhD fellows being considered highly competent adult employees with state employment contracts, where they receive regular salaries, and have regular offices, they are initially part of the work community found within academia with its routines, duties, and rights. Another contextual aspect is that Norwegian PhD-candidates defend their theses relatively late in their careers. The average age for a candidate’s defense is between 37 and 38 years and higher for many candidates within the humanities and social sciences. In comparison, the median age across OECD countries is 29 ( Sarrico, 2022 , p. 1304). Table 1 provides a generalized comparison of doctoral education across Nordic countries, the UK, and the US ( Andres et al., 2015 ; Burner et al., 2020 ). While such broad overviews might exaggerate differences, they provide a framework for understanding doctoral education on a spectrum. This spectrum ranges from countries with significant government influence, where PhD candidates are employed (e.g., Nordic countries), to countries with moderate government influence, where PhD candidates are not employed (e.g., the UK), and finally to countries with minimal government influence, where PhD candidates are also not employed (e.g., the US). Despite these variations, the global trend indicates that doctoral education is becoming increasingly dependent on external funding ( Bengtsen, 2023 , p. 45).
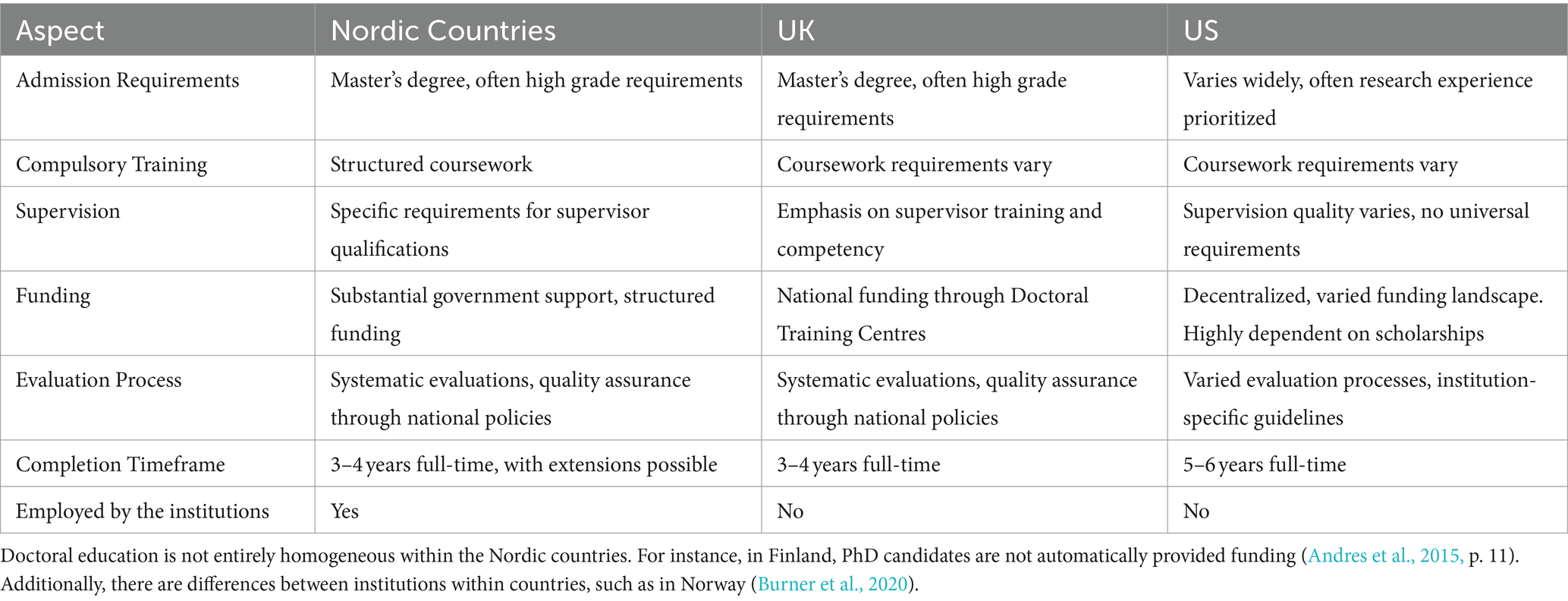
Table 1 . Overview of the Nordic PhD model in comparison to UK and US models.
In addition, women defend their theses on average 2 years later than men. Taking into account that the average age for first-time mothers in Norway is now 30.1 years, there is a lot that needs to happen within a few years, and this may sometimes affect the feasibility of their PhD-projects. This can, e.g., be related to the gender differences in Norway about parental leave days during the pandemic which is much higher for women than for men at the universities ( Krumsvik et al., 2022 ) 1 . Another contextual factor that distinguishes doctoral supervision from other supervision (at lower levels) is that over 90% of the doctoral theses in Norway are article-based theses ( Krumsvik, 2016b ; Mason and Merga, 2018 ; Solli and Nygaard, 2022 ), which implies 3–4 published articles and an extended summary or synopsis (a “kappe” in Norwegian, ranging between 50 and 90 pages). This means that the PhD-candidates receive “supervision” and feedback from approximately 8–10 referees in scientific journals on their articles, in addition to feedback from their PhD supervisors. Because of this, many PhD-supervisors are co-authoring their doctoral candidates’ publications. A final contextual aspect is the recent studies indicating a decrease in doctoral disputations nationwide in Norway over the past two years ( Steine and Sarpebakken, 2023 ) – probably as a consequence of the pandemic. In a survey, Ramberg and Wendt (2023 , p. 22) found that about 60 percent of PhD candidates and 50 percent of postdoctoral candidates ( N = 300) were delayed during the autumn of 2022. The study showed that illness or leave, often due to caregiving responsibilities during the pandemic, was the most common reason for delays among PhD candidates and postdoctoral candidates, particularly impacting women more than men. Following illness, reduced access to supervisors, empirical data, research facilities, and external partners were significant factors contributing to delays in their research activities. Nearly a third of delayed candidates reported reduced access to supervisors, and about a fifth faced issues with external partner access, highlighting the critical role of these resources in completing research projects. When it comes to the PhD-supervisors, more specifically, the supervision differs from other types of supervision in that a formal PhD agreement is signed with a binding supervisor contract that lasts for 3–4 years (the PhD period) and is signed by both the supervisor and the candidate. The supervisor also has an overarching responsibility to avoid delays and ensure that the PhD program can be completed within the standard time frame. Supervisors are primarily responsible for guiding doctoral candidates on the specific, content-related aspects of their projects. This includes helping candidates identify the knowledge frontier in their field, position their study within the research field, develop clear and consistent research questions, choose appropriate scientific and methodological approaches, and provide expert guidance in discussing results and addressing ethical issues related to the thesis. This obviously places relatively high competence requirements on the supervisors, both in terms of their academic and research skills, and in relation to the doctoral supervision itself, as poor or inadequate supervision at this level can expose the candidate to a certain “drop-out risk” in the project.
Maintaining education quality during the COVID-19 pandemic has been challenging due to the widespread shift to digital teaching, supervision, and remote work. Many university teachers were unaccustomed to the online, digital learning environment, working with PhD candidates remotely for extended periods. Some taught in hybrid settings, with some PhD candidates quarantined at home while others attended in-person classes. Additionally, others navigated ordinary learning contexts with COVID-19 precautions like masks and social distancing. This situation altered frame factors, adding complexity to the discussion of education quality.
Considering this, the case study seeks to understand if, and potentially how, external factors in pedagogical contexts over which institutions, academics, and teachers have no direct control play out. Lindensjö and Lundgren (2014) find that such external factors might have a significant impact on the outcomes of educational training, teaching, and supervision. Therefore, it is crucial to contextualize the pandemic experiences among PhD supervisors with respect to these factors, as they imply national and institutional frames for their PhD supervision. Though there exist several quantitative, survey-based studies on the impact of COVID-19 on PhD supervision (e.g., Pyhältö et al., 2023 ; Löfström et al., 2024 ), there is still a lack of in-depth qualitative understanding of the impact of COVID-19 on the supervisory relationship. The studies of Löfström et al. (2024) and Pyhältö et al. (2023) indicated that supervisors faced significant challenges in identifying when PhD candidates needed assistance and providing adequate support for their well-being during the shift to remote supervision. Supporting the progress and wellbeing of full-time candidates, who were more adversely affected by the pandemic than their part-time peers, became increasingly difficult. The increase in email communications could overwhelm supervisors, exceeding manageable levels and complicating their ability to offer timely and effective feedback. The lack of spontaneous, informal conversation, previously facilitated by in-person meetings, further hindered their ability to monitor and support the candidates effectively. These challenges were particularly pronounced for supervisors in scientific fields requiring lab work and practical training, which were severely disrupted by the pandemic, and supporting the progress and wellbeing of full-time candidates, who were more adversely affected by the pandemic than their part-time peers, became increasingly difficult. Furthermore, supervisors reported that their PhD candidates’ lack of a scholarly community and inadequate supervision were significant challenges. This reflects the supervisors’ view that the availability of a supportive research environment and adequate supervision are critical for candidates’ success ( Pyhältö et al., 2023 ). The study by Pyhältö et al. (2023) also found that supervisors generally estimated the impact on candidates’ progress and well-being to be more negative than the candidates themselves did, which may imply that supervisors have a broader perspective on the long-term consequences of disruptions like the COVID-19 pandemic. Research prior to the pandemic ( Pyhältö et al., 2012 ) has shown that apart from the importance of having clear and long-term financing, proper research facilities, and sufficient time to pursue a PhD, supervisors also stress the significance of PhD candidates’ motivation, self-regulation, efficacy, and engagement as essential personal regulators for success in the PhD process.
1.2 Theoretical framework
This case study is exploratory and intrinsic ( Stake, 1995 , 2006 ), utilizing an abductive approach to theory with frame factor theory as our theoretical framework ( Lundgren, 1999 ; Lindensjö and Lundgren, 2014 ). Frame factor theory suggests that society’s influence on education manifests through a target system, an administrative system, and a legal system. This theory, used in educational sciences and pedagogy, acts as a lens for planning and analysis, positing that external factors, beyond the control of institutions and educators, significantly affect educational outcomes. We will further explain the contextual application of frame factor theory in this case study below.
Previous research highlights a gap in (doctoral) education between the formalization and realization arenas in frame factor theory ( Lindensjö and Lundgren, 2014 ; Krumsvik et al., 2019 ). Linde (2012) introduces a transformation arena between these two, explaining the difficulty of implementing measures in complex organizations like universities. There is rarely a straightforward relationship between central decisions (formulation arena or macro-level) and their implementation (realization arena or micro-level). Policy documents require interpretation and application by faculty leaders, PhD program leaders, supervisors, and PhD candidates (transformation arena or meso-level) ( Linde, 2012 ).
Given this context, a main focus of this case study was to evaluate how Norwegian PhD supervisors managed changed frame factors and education quality during the pandemic. The Norwegian Agency for Quality Assurance in Education (NOKUT) defines education quality as “the quality of teaching classes, other learning facilities, and students’ learning outcomes in terms of knowledge, skills, and general competence” ( Skodvin, 2013 , p. 2). It is important to differentiate between educational quality, study quality, and teaching quality.
Education quality is a broad concept encompassing everything from the subject/study program level to the government’s education policy. In contrast, study quality is narrower, referring specifically to the educational institution ( Skodvin, 2013 , p. 3). Teaching quality goes further to the micro-level, focusing on course quality, teacher effectiveness, and PhD supervision. This study examined how PhD supervisors experienced COVID-19 restrictions at the micro- and meso-levels, considering two of the three levels. Figure 1 illustrates the analytical lenses in this mixed methods research (MMR) and formative dialog research case study:
Figure 1 . The analytical focus in the case study ( Krumsvik et al., 2019 ) is based on the frame factor theory ( Linde, 2012 ; Lindensjö and Lundgren, 2014 ).
2 Methodology
To understand and corroborate conditions faced by doctoral supervisors related to COVID-19 extended societal shutdowns, both in breadth and in depth, we employed a mixed-methods research design, combining quantitative data to show the strength of associations and qualitative data to explore their nature ( Johnson et al., 2007 ; Creswell and Plano Clark, 2017 ). We utilized a three-stage design, QUAL-QUANT-QUAL (qualitative-driven sequential design, Schoonenboom and Johnson, 2017 ), making it a qualitative-dominant mixed-methods study ( Johnson et al., 2007 , p. 124). Using mixed methods research allowed us to explore the complex research problem more comprehensively compared to using either quantitative or qualitative data alone. Though the approach is less common in case studies ( Tight, 2016 , p. 380), the mixed methods are increasingly used (e.g., Ertesvåg et al., 2021 ; Hall and Mansfield, 2023 ; Peters and Fàbregues, 2023 ). Advocates of such approaches consider mixed methods to “complement and extend one another and thus lead to better descriptions, clearer explanations and an enhanced understanding of phenomena, research aims and questions” ( Ertesvåg et al., 2021 , p. 655).
Specifically, an exploratory, sequential mixed-methods design was used to address the research questions ( Fetters et al., 2013 ; Creswell and Plano Clark, 2017 ). This design involves collecting and analyzing qualitative data first (QUAL), using those findings to guide the quantitative data collection and analysis in the second phase (QUANT), and then using the quantitative results to inform further qualitative data collection and analysis in the third phase (QUAL). This method integrates through building, where results from one phase inform the next.
We conducted a cumulative data collection and analysis process ( Creswell and Guetterman, 2021 ), basing survey questions on previously collected data from field dialogues, online observations, seminar evaluations, and document analysis. The questionnaire consisted of a general demographic questions (e.g., gender, educational background and what field(s) the supervisor supervised in), in addition to a range of multiple response items addressing four key themes: (1) important factors to complete a PhD, (2) supervisor challenges, (3) working from home experiences, and (4) perceived need for future competences as supervisors. Finally the questionnaire contained a range of statements measured on a Likert-scale from 1 to 5 where 3 was neutral (e.g., to what extent do you feel that your PhD-candidate(s) are on track with their doctoral project?). The qualitative interview guide ( Kvale and Brinkmann, 2015 ) was developed from the prior quantitative data (survey), and the focus group guide was based on earlier survey and qualitative interview data (see Figure 2 below). We integrated research questions, methods, interpretation, and reporting at various points, using narratives where qualitative and quantitative results are presented in different sections of the same article through the contiguous approach ( Fetters et al., 2013 ). This article primarily examines the coherence between qualitative and quantitative findings based on confirmation , expansion , or discordance ( Fetters et al., 2013 ). The approach used in the study is similar to Hall and Mansfield (2023) and the coherence is derived from joint displays using visual means.

Figure 2 . The research process. The yellow arrows show the main data sources, and the blue arrows show the Supplementary data in this article. In addition, we have conducted focus group interviews and an extra survey, which will be published in another article (since they mainly focus on academic writing with the large language models).
As a consequence of the mixed-methods design, this study combines two approaches in case study research. The first, proposed by Stake (1995 , 2006) and Merriam (2009) and Merriam and Tisdell (2016) , is situated in a social constructivist paradigm, and is attached to the qualitative part (connected to the second part of each research question). The second, based on Eisenhardt (1989) , Flyvbjerg (2011) , and Yin (2012) , approaches the case study from a post-positivist perspective ( Hyett et al., 2014 , p. 1) (connected to the first part of each research question). This intrinsic case study ( Stake, 1995 ) aims to focus on ecological validity:
“Ecological validity is the degree of correspondence between the research conditions and the phenomenon being studied as it occurs naturally or outside of the research setting” ( Gehrke, 2018 , p. 563). Informant selection was based on a purposeful method ( Maxwell, 2013 ), in which we recruited PhD supervisors from Norway.
Next, all interviews were analyzed using reflexive thematic analysis ( Braun and Clarke 2019 , 2021 ) where themes were constructed and presented in this paper (see section 4). In addition, we also conducted a sentiment analysis ( Dake and Gyimah, 2023 ) of the nine interviews (see Supplementary file ).
To answer the research question, we combined formative dialog research ( Baklien, 2004 ) and case study research ( Stake, 2006 ). Data collection consisted of fieldwork (see Supplementary file ), a survey N = 298, 53.7% women, 46.3% men, response rate 80.54%, nine semi-structured interviews (with PhD supervisors), and one focus group ( N = 5). Supplementary data consisted of an additional survey ( N = 85), PhD-policy document analysis ( N = 6), field dialogues (4 PhD supervision seminars), open survey data (1,438 responses), seminar observations ( N = 4), and reviews of relevant documents such as evaluations of doctoral supervisor seminars. We also used policy documents and regulations concerning PhD education in Norway as supplementary sources.
We focused on how PhD supervisors experienced changing frame factors, such as university lockdowns, remote work, digital teaching, digital supervision, doctoral progression, and others, with an emphasis on illuminating the micro-level (course and teaching level) from the PhD supervisors’ perspective. This focus is twofold: the program’s structure and quality directly affected the PhD- supervisors during the pandemic. The second is simply that they conducted several evaluations about matters related to the structure and quality compared with the others. However, PhD- candidates’ opinions are also important, and their views are also interwoven because some of them have been present during field dialogs and participated in the PhD-supervision seminars.
When focusing on how PhD-supervisors experience their supervision, PhD’s research progression, psychosocial aspects, their nearest superior, and the main focus are on illuminating the meso-level (institutional and program level).
2.1 Cumulative research process
In our case study, we brought the experiences and our study among PhD’s ( Krumsvik et al., 2022 ) from the period March 12, 2020, to November 30, 2021, into our design of this study. We executed an excessive cumulative data collection process (including a part during the pandemic) and analysis, especially from August 2022 – October 2023. The relatively long time period allowed the researchers to test their interpretations along the way and detect contrary evidence, e.g., reach saturation during the coding and analysis of the qualitative data ( Creswell and Guetterman, 2021 ).
3.1 Quantitative part (survey)
Above and below are the results of the quantitative part of the study, based on the survey data. This analysis is tentative and covers only the survey results. The interview data and Supplementary data will be presented later in the paper. Two hundred and forty respondents completed the survey ( N = 298, 80.54% response rate). The academic backgrounds of the supervisors were diverse, with the three largest groups coming from natural sciences, humanities, education and teacher training. The largest group of supervisors (41.75%) supervised PhD candidates in education and teacher training (see Table 2 ).
Table 2 . Distribution of supervisors by academic background and PhD supervision in various fields.
A narrow majority (58.08%) of the supervisors had submitted an article-based dissertation (see more in attachment 5 in the Supplementary file ), in the Supplementary file meaning that approximately four out of ten supervisors have not “hands on” experience with article-based thesis as their thesis in their own doctoral degree. A large majority (81.67%) had supervised PhD candidates before and after the pandemic, while 11.67% had only supervised during and after. 41.27% of the supervisors stated that the coronavirus pandemic (from March 12, 2020 - January 2022) had impeded their candidate(s) progress in their doctoral project. 21.12% agreed (to a large or very large extent) that the PhDs’ publication process of articles to scientific journals has been delayed because of the journal’s peer review process during the pandemic (i.e., journal processing times seemed to increase due to several factors including a lack of available peer reviewers because of heavy workloads, health issues, more teaching, etc.).
3.1.1 Challenges in supervision
Results in Table 3 indicate that the most commonly reported challenges faced by supervisors during the pandemic were balancing work and family life and working from home, each affecting more than a third of the supervisors. Psycho-social aspects, such as loneliness, also emerged as a notable challenge. The cancelation of conference participation and stays abroad were significant issues, reflecting the broader impact on professional development opportunities. Concerns about supervision quality were also prominent. Some supervisors reported no challenges, highlighting a degree of variability in experiences. Other challenges included delays in the peer review process for journals, difficulties with publishing, and issues related to research ethics, though these were less commonly reported.
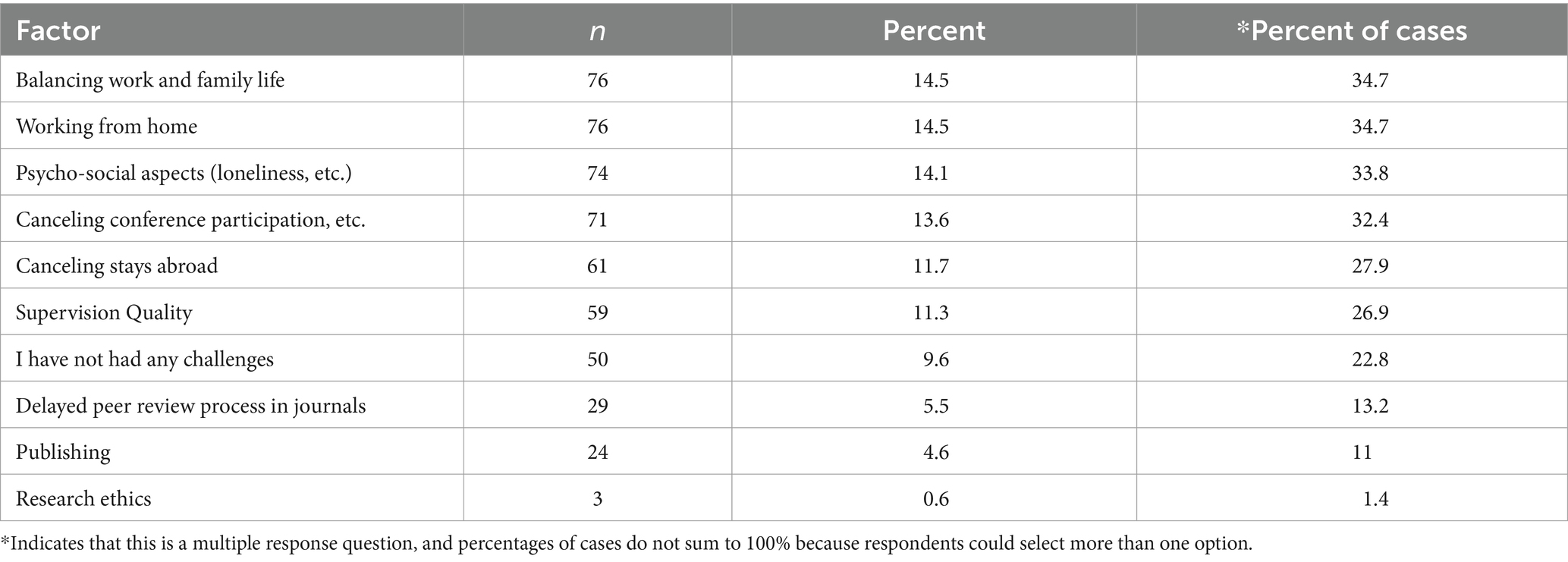
Table 3 . Challenges faced by supervisors during the pandemic in terms of supervision.
3.1.2 Challenges in working from home
Results in Table 4 indicated that supervisors faced multiple challenges while working from home during the pandemic. The most common issue was having little contact with colleagues, which affected more than six in ten supervisors. Supervisors also frequently reported having little contact with their PhD candidates. Distractions from others at home were another prevalent challenge. Many supervisors experienced an increased workload due to digital teaching from home, and lacking office equipment, such as desks and office chairs, was also commonly reported. Psycho-social aspects, such as loneliness, were significant issues as well. The lack of space and increased home responsibilities, such as childcare, were notable challenges. A smaller number of supervisors reported having no challenges at all. Other less commonly reported issues included limited access to library services and poor internet access.
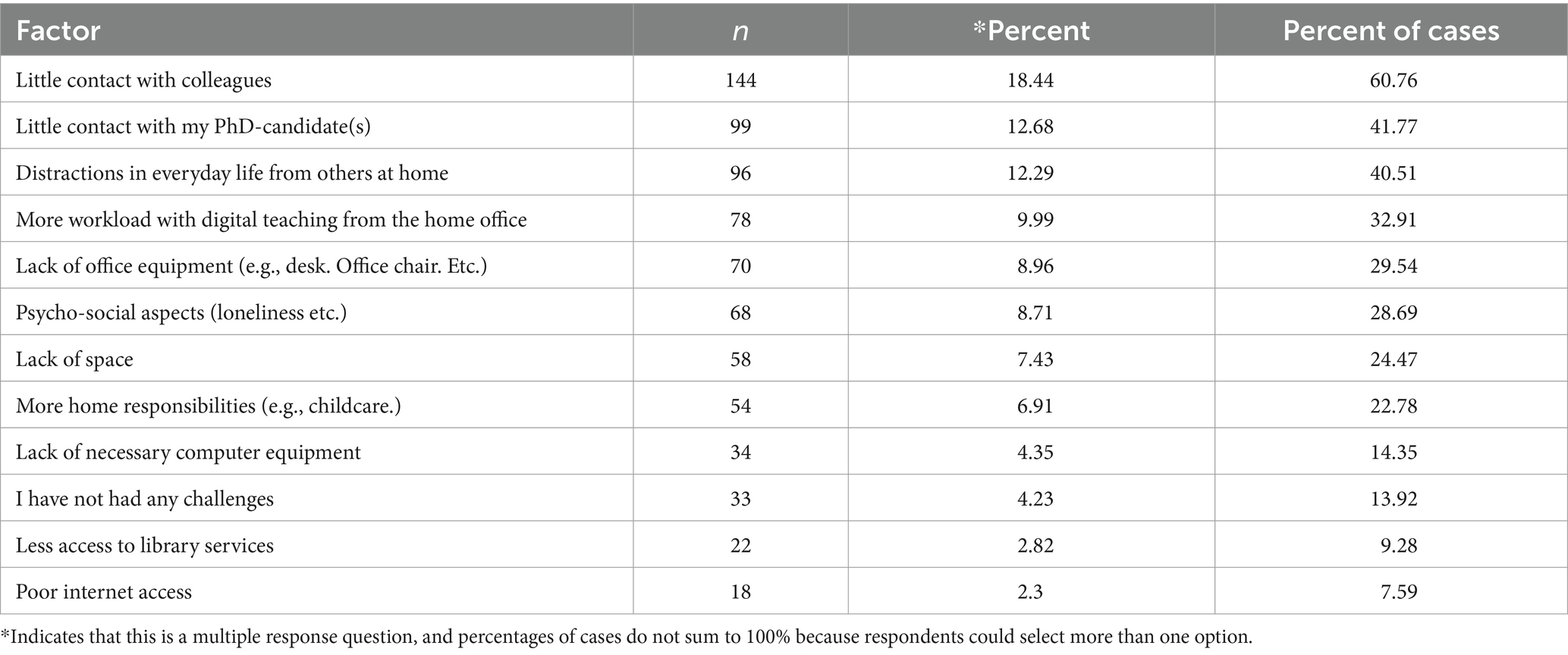
Table 4 . Challenges faced by supervisors during the pandemic working from home.
3.1.3 Factors PhD candidates need to complete their doctorate
We find that there is a high degree of consistency between what supervisors ( Table 5 ) and PhD candidates ( Table 6 ) consider to be the most important factors for completing the doctorate. In particular, it is persistence, resilience, and the ability to work independently are the most important factors, in addition to supervision and co-writing with supervisors.
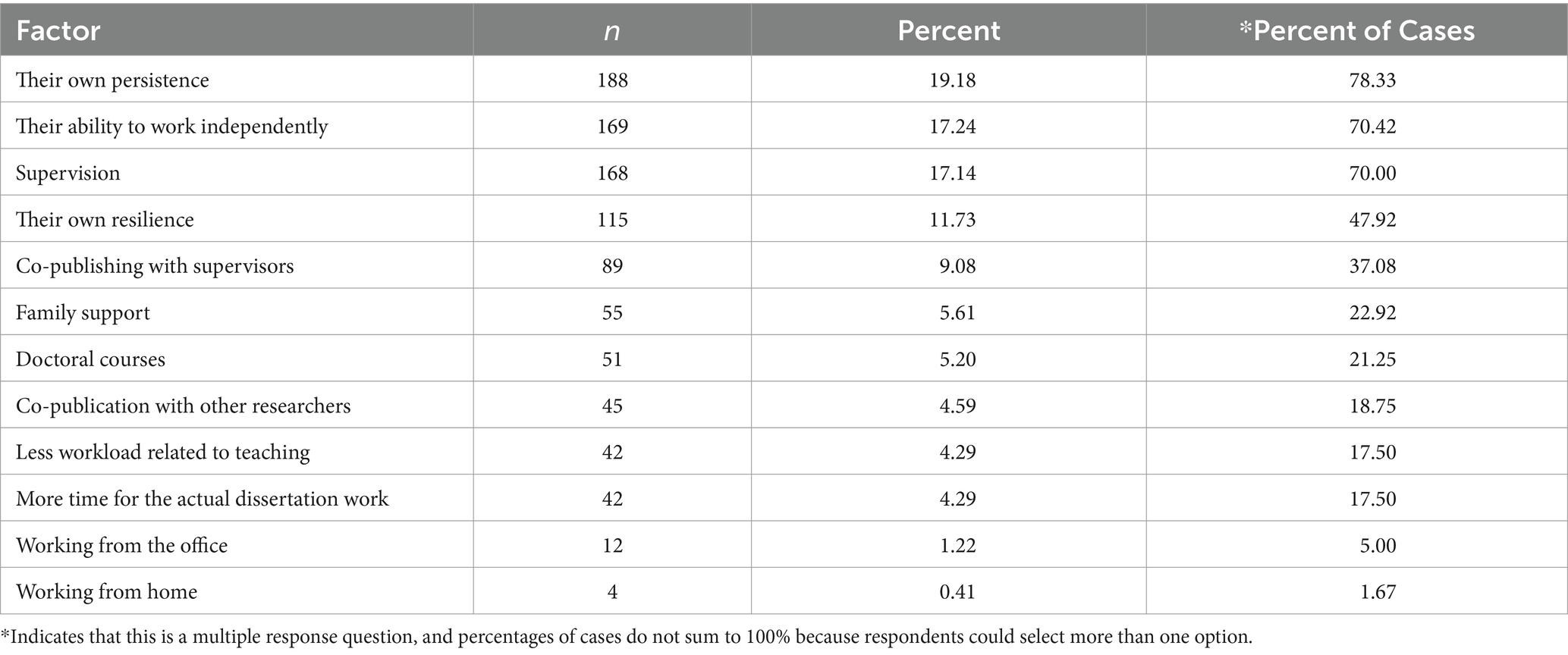
Table 5 . Most important factors in completing a PhD as reported by PhD supervisors.
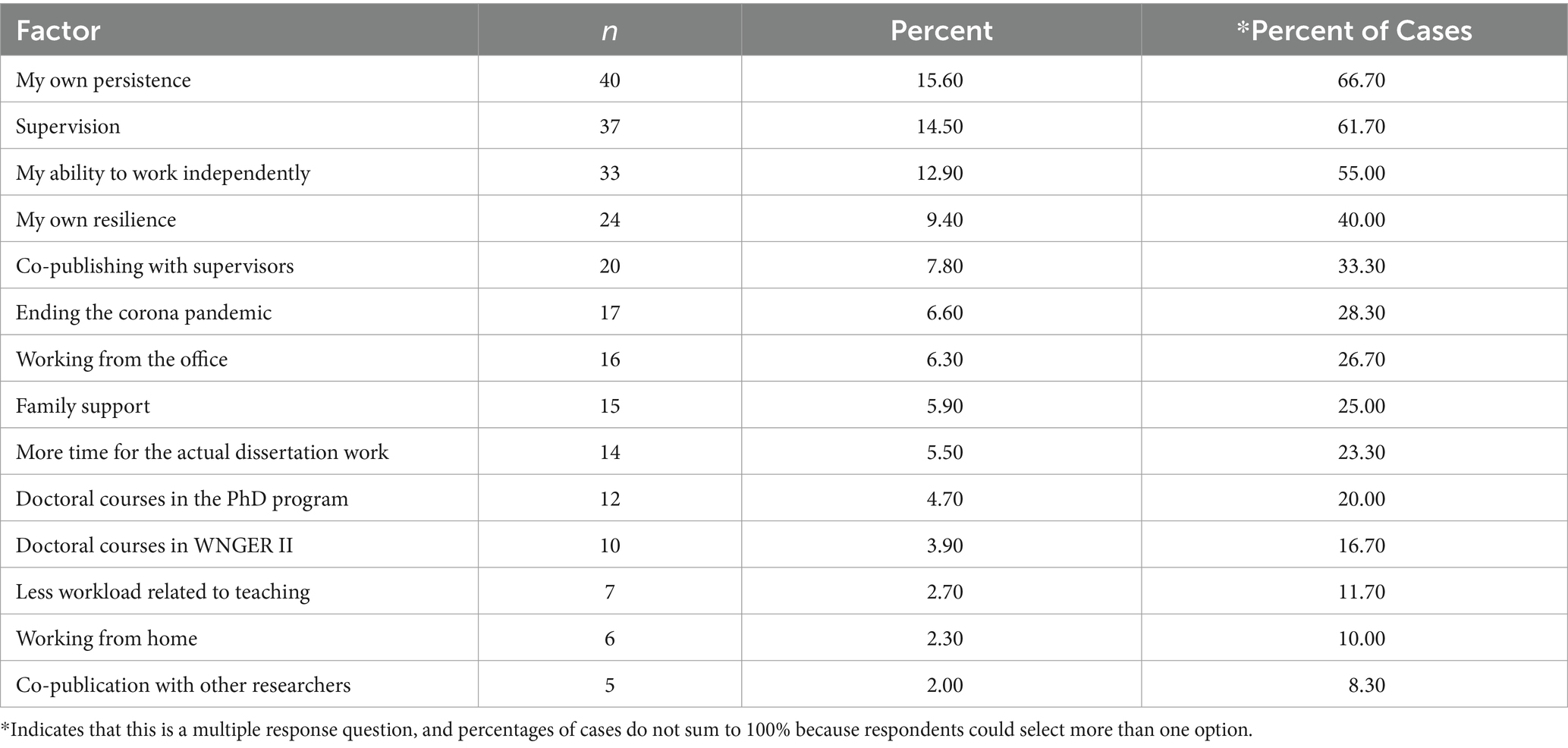
Table 6 . Most important factors in completing a PhD as reported by PhD Candidates.
Thus, there is considerable agreement between what the supervisors and the PhD candidates report, which may indicate that within the academic tradition, the doctoral journey is primarily seen as an individual endeavor (feat of strength) where the supervisor is the closest supporter.
3.1.4 Appreciation of supervision
The supervisors mostly agreed that both they and the PhD candidates value supervision. 89.91% responded they agree or strongly agree to this question for themselves, and 92.47% responded they agree or strongly agree on behalf of the PhD candidates. In comparison, 61.25% responded similarly to whether the department values supervision, while 24.17% were neutral, and 14.59% responded they disagree or strongly disagree. This may suggest that the supervisory relationship is primarily between the PhD candidate and the supervisor, with less firm ties to the institution.
When it comes to what extent the supervisors think that their institution has been accommodating regarding compensating the loss of progress due to the coronavirus pandemic for their own PhDs, 27.2% stated that this had been done to a small extent or very small extent and 29.39% stated that this had been done to a large extent or very large extent. 30.1% agreed (large extent and very large extent) that supervisory responsibilities have increased during the pandemic. 13.3% expressed (to a large or very large extent) that supervising doctoral candidates makes them feel anxious’ over the last 24 months” (pandemic), but the majority (64.3%) experienced this to a small and very small extent. 9.3% expressed (to a large and a very large extent) that concerns over doctoral supervision have kept them awake at night over the last 24 months (pandemic), but the majority (69.3%) experienced this to a small and very small extent. 56.1% of the supervisors have not discussed any challenges with the progress of their doctoral candidate(s) project due to the coronavirus pandemic with the department’s human resources manager/head.
When asked how many hours they have enshrined in their working plan per semester as the main supervisor per PhD candidate, supervisors state this varies from zero to above 80 h, but for the majority, it is between 20 and 40 h per semester (40.46%). 23.1% state they do not think that their PhD-candidate(s) are on track with their doctoral project, while 50.2% state that their PhD-candidate(s) are on track with their doctoral project. Some PhDs publish their articles in their thesis based on pre-collected data (e.g., as a part of bigger projects), while others publish their articles in their thesis based on data collections done by themselves. 58.77% of the supervisors think this affects the completion time for the last group of PhDs (large and very large extent). 53.4% of the supervisors have been co-authoring their doctoral candidates’ publications.
3.1.5 What competencies supervisors need
As seen from Table 7 , nearly half of the supervisors believed they needed more pedagogical and methodological competence related to supervision. Additionally, about one-third felt they lacked knowledge about formal aspects, such as guidelines, related to the PhD program. The supervisors reported that the guidelines for the doctoral program were somewhat clear, particularly those for article-based dissertations. This perceived clarity was positively correlated ( r = 0.23, p = 0.002) with the extent to which the institution offered “continuing professional development” (CPD), and 39.88% of the supervisors stated that their institution did not provide supervisors with CPD. Thus, while many supervisors recognized the need for enhanced pedagogical and methodological skills, as well as a better understanding of formal guidelines, the availability of CPD programs was associated with clearer doctoral program guidelines. This suggests that increasing access to professional development opportunities could improve supervisors’ competence and clarity regarding program requirements, ultimately benefiting the supervision process.
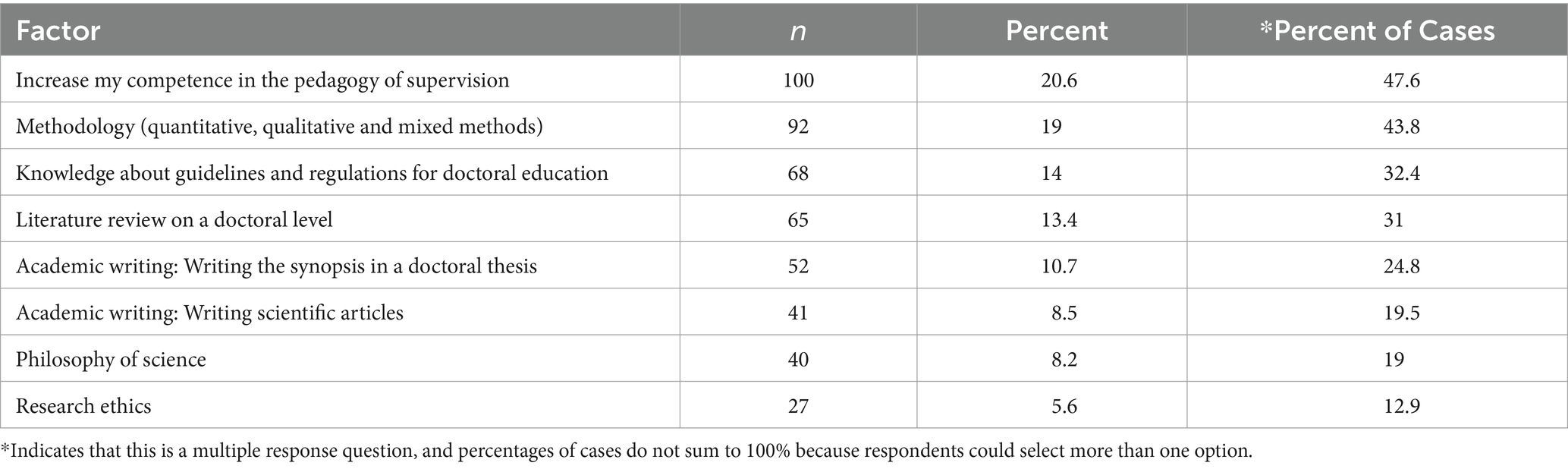
Table 7 . Competencies PhD supervisors believe they need to increase.
3.1.6 Female academics with children
About four out of ten supervisors (41.07%) agreed (to a large or very large extent) that female PhDs with children seem to have more home responsibilities than men (e.g., for childcare, household, homeschooling, own children in quarantines, etc.) during the pandemic. About three out of ten (27.77%) agreed (to a large or very large extent) that female PhDs’ (with own children) submission rates to scientific journals have been delayed as a consequence of COVID-19, considering that women seem to have more home responsibilities (e.g., for childcare, household, homeschooling, own children in quarantine, etc.) during the pandemic. About two out of ten (23.64%) agreed (to a large or very large extent) that female supervisors’ (with their own children) submission rates to scientific journals have been delayed as a consequence of COVID-19, considering that women seem to have more home responsibilities (e.g., for childcare, household, homeschooling, own children in quarantine, etc.) during the pandemic.
Cronbach’s alpha ( α = 0.87) indicated a high level of consistency among three statements concerning the increased home responsibilities faced by female researchers with children compared to their male counterparts during the pandemic. These statements highlighted that female researchers with children appeared to bear more responsibilities at home, such as childcare, household tasks, and homeschooling, and as a result, their submission rates to scientific journals had been adversely affected by COVID-19. The average response (mea n = 3.18, standard deviatio n = 0.88) indicated that the supervisors were generally neutral toward these statements. However, closer inspection revealed that female supervisors (mea n = 3.29, standard deviatio n = 0.92) agreed with these statements more than male supervisors (mea n = 3.03, standard deviatio n = 0.79), a difference that was statistically significant ( p = 0.017) but with a small effect size (Cohen’s d = 0.30). There was a positive correlation ( r = 0.23, p = 0.002) between whether the PhD candidate had considered quitting the PhD program and the three statements, which suggests that supervisors who reported that PhD candidates had considered quitting also agreed more with the statements. Conversely, a negative correlation ( r = −0.21, p = 0.002) was found between considering quitting the PhD program and the belief that the institution made sufficient efforts to compensate for the lack of progress during the pandemic, indicating that better institutional support might have reduced the likelihood of candidates considering quitting.
3.2 Qualitative part (interview data and other types of qualitative data)
We conducted a cumulative data collection process where the qualitative interview guide questions were built upon previously collected quantitative data (survey). Based on a snowballing sample ( Patton, 2015 ), we recruited nine doctoral supervisors from the humanities, social-, and educational sciences with diverse experience and approaches to supervising PhD candidates during the pandemic. Using semi-structured interviews ( Brinkmann, 2022 ), each supervisor was interviewed online using Zoom with interviews lasting from 30 to 60 min. All interviews were conducted in Norwegian and later transcribed verbatim. We followed Braun and Clarke’s, (2019 , 2021) approach to reflexive thematic analysis to analyse the interview data. The themes constructed from the analysis of the interview data focus issues, such as “The Impact of the Pandemic on Supervision,” “Home Office Experience,” Workload and Employer Support,” “PhD Candidate Preparation for Article-Based Theses,” “Competence in Supervising Article-Based Theses,” and “Guidelines and Structuring the PhD Process.”
3.2.1 Analyzing the interview with Kyle
Introduction: Kyle, aged 47, specializes in professional ethics. He completed his doctoral degree through a monographic thesis and is relatively new to supervising PhD candidates, currently guiding three, two of whom he is the main supervisor.
Impact of the Pandemic : Kyle wore two hats during the pandemic: as a PhD supervisor and as a leader of a doctoral program. He noted that the pandemic did not significantly impact his supervisees due to well-planned data collection that adapted to digital formats when necessary. His role as the program leader gave him broader insights into how other candidates fared, with some experiencing difficulties in recruiting interviewees and needing to adjust their research plans accordingly.
PhD Supervision During the Pandemic : Kyle’s supervision was largely unaffected by the pandemic as most of it was conducted digitally, catering to students located in different parts of the country. He emphasized the importance of maintaining frequent contact, especially when usual social and professional gatherings were suspended. The pivot to online platforms like Zoom and increased digital communication tools helped maintain the continuity and quality of supervision.
Home Office Experience : Working from home was generally positive for Kyle, who appreciated the reduced distractions and the ability to maintain productivity with a well-equipped home office. However, he missed informal interactions with colleagues, which were hard to replicate through digital means.
Workload and Employer Support : Kyle experienced a slight increase in workload as more effort was required to monitor and support students remotely. His interactions with his Head of Department/direct manager were supportive, helping him navigate the challenges of remote supervision.
PhD Candidate Preparation for Article-Based Theses : Kyle observed that many PhD candidates were unprepared for the intricacies of article writing, including the lengthy processes of submission and peer review. He attributed this to their educational background, which primarily focused on monographic work at the bachelor’s and master’s levels.
Competence in Supervising Article-Based Theses : Although Kyle has not written a synopsis (‘kappe’, i.e., a synthesis chapter for article-based theses) himself, he feels prepared due to his involvement in supervisor training programs that include synopsis writing. He believes in collaborative supervision where co-supervisors with more experience in specific areas can complement his guidance.
Guidelines and Structuring the PhD Process : Kyle praised the clarity of guidelines regarding the synopsis writing at his program, highlighting proactive efforts to discuss and understand these guidelines among candidates and supervisors. He supports the idea of starting the synopsis early in the PhD journey, allowing candidates to develop a clear perspective on how their articles will integrate into their larger thesis narrative.
Summary: Kyle’s approach to PhD supervision during the pandemic was proactive and adapted to the challenges of remote interactions. He emphasizes the importance of clear guidelines, structured support from the academic program, and the benefits of collaborative supervision. His perspective offers valuable insights into managing PhD supervision under crisis conditions and highlights areas for potential improvement in preparing candidates for the demands of article-based theses.
3.2.2 Analyzing the interview with Sally
Introduction: Sally, aged 46, is experienced in the field of educational sciences and professional research, having supervised 15 PhD candidates to completion. She conducted her doctoral research through an article-based thesis.
Impact of the Pandemic on PhD Candidates : Sally observed that the pandemic had a limited impact on most of her PhD candidates, except for 2–3 individuals who experienced delays, partially due to the pandemic. Disputations were delayed for some candidates who preferred physical attendance, affecting their completion timeline.
Adaptations in Supervision Methods: The pandemic made Sally diversify her supervision methods, including more frequent digital meetings with Zoom or Teams and asynchronous communications like email. She shifted from paper-based to digital comments on drafts, which enhanced the efficiency and immediacy of feedback. This change is something she intends to continue using beyond the pandemic.
Home Office Experience: Sally found working from home manageable and returned to the office as soon as feasible, particularly because she needed to balance work with family responsibilities. The transition to the home office did not significantly disrupt her supervision activities, though it introduced minor challenges like occasional distractions from family.
Increased Workload During the Pandemic: Sally reported a slight increase in her workload during the pandemic due to a need for more frequent communication to ensure the continuity and quality of supervision. This was compounded by the timing of her candidates being in critical phases of their thesis work.
Support from Employer: She felt that the focus of her institution’s support during the pandemic was more on ensuring that PhD candidates were well-supported rather than directly supporting the supervisors themselves.
Preparedness of PhD Candidates: Sally noted that while the PhD candidates were generally well-prepared academically, they often lacked specific training in writing article-based theses, a significant adjustment from writing monographic theses typical at the bachelor’s and master’s levels.
Competence in Supervising Article-Based Theses: Sally felt confident in her ability to supervise article-based theses despite recognizing the ongoing need to adapt and learn, particularly in managing the synthesis chapter or “kappen.”
Clarity of Guidelines for the Synopsis: She found the guidelines for writing the synopsis at her institution clear and involved in educational efforts to help candidates understand these guidelines better. However, she questioned whether standardization would improve understanding or unnecessarily restrict academic freedom.
Timing for Writing the Synopsis: Reflecting on her experience and current practices, Sally advocated for thinking about the synopsis early in the doctoral process but cautioned against producing extensive texts prematurely. She emphasized the importance of adapting the scope of the synopsis as the research evolves.
Use of Doctoral Committees’ Guidelines: Sally observed that adherence to guidelines varies depending on whether committee members are national or international, with international members often impressed by the candidate’s ability to publish in high-ranking journals.
Overall, Sally’s experiences and insights provide a nuanced view of PhD supervision during the pandemic, highlighting flexibility, adaptation, and the importance of maintaining high standards of communication and support. Her approach demonstrates a balance between structured guidance and allowing academic independence, aiming to foster resilience and adaptability among her PhD candidates.
3.2.3 Analyzing the interview with Gabbie
Introduction: Gabbie, aged 54, specializes in school and teacher education. She has supervised two PhD candidates to completion and is currently guiding four others. Her doctoral thesis was article-based.
Impact of the Pandemic on PhD Candidates : Gabbie observed varied impacts of the pandemic on her PhD candidates. While two of her students were minimally affected, one faced significant challenges in data collection due to difficulties in recruiting informants. This disparity seems to have been influenced by the candidates’ approaches or perhaps their personal rapport with potential informants.
Changes in Supervision Practices: The pandemic shifted Gabbie’s supervision to entirely online formats using Zoom, Teams, or phone apps. While she was accustomed to digital interaction, the lack of informal, face-to-face interactions led to a more formal and structured supervision style. The spontaneous “corridor conversations” that often enhance relational aspects of supervision were missing, which she felt detracted from the personal connection in the supervisor-supervisee relationship.
Home Office Experience: Gabbie had a positive experience working from home, finding it efficient and beneficial due to eliminating commute times and the conducive environment at home for focused work. Her family setup supported this arrangement well, allowing her to balance work and home life effectively during the pandemic.
Workload Changes During the Pandemic: Her workload in terms of PhD supervision remained roughly the same, though the nature of interactions changed. Instead of impromptu office drop-ins, there were more scheduled meetings, primarily online via Zoom or Teams, which required a different kind of preparation and possibly led to more structured discussions.
Support from Employer: Gabbie noted a lack of specific support for supervisors from her employer during the pandemic; the focus was more on ensuring that she, like other staff, was generally coping with the pandemic’s challenges. There was an emphasis on looking out for the PhD candidates’ well-being, translating into a directive for supervisors to maintain close contact and support.
Preparedness of PhD Candidates for Article-Based Theses: Similar to Kyle and Sally, Gabbie agreed with the survey findings that many candidates are not well-prepared for writing article-based theses. She attributes this to their academic background, which primarily focuses on monograph writing. She advocates for collaborative writing for the first article to help familiarize candidates with the process of scholarly writing and peer review.
Evaluation of Own Competence in Supervising Article-Based Theses: She feels confident in her supervisory skills but acknowledges that continuous learning and discussion with peers are essential for handling complex or unfamiliar issues that arise during supervision. Gabbie appreciates the collaborative nature of the supervisory teams at her institution, which helps in managing any gaps in her experience or knowledge.
Clarity of Guidelines for the Synopsis: Gabbie finds the guidelines for writing the synopsis to be somewhat unclear and open to interpretation, suggesting that more explicit guidelines could help, especially for those new to supervising or external committee members who evaluate the theses.
When to Start Writing the Synopsis : She recommends that PhD candidates consider the synopsis throughout their doctoral journey but compile it towards the end. Gabbie advises keeping a file of potential content for the synopsis from the start of the doctoral process, which can include discarded sections from articles or ideas that do not fit into the articles but are valuable for the overarching thesis narrative.
Overall, Gabbie’s experience reflects a pragmatic and flexible approach to PhD supervision. She adapts to the demands of the pandemic while trying to maintain the quality of academic mentorship. Her strategies for managing remote supervision and her positive attitude toward the enforced changes highlight a successful adaptation to the challenges posed by the pandemic.
3.2.4 Analyzing the interview with Henrik
Introduction: Henrik, aged 46, specializes in school and educational research. He has successfully guided three PhD candidates as a primary supervisor and is supervising four more. His doctoral thesis was a monograph.
Impact of the Pandemic on PhD Candidates: Henrik noted that the pandemic affected his PhD candidates differently based on the nature of their research. Those engaged in classroom interventions faced significant challenges due to pandemic-related restrictions, particularly in accessing schools and conducting fieldwork. Conversely, candidates focused on desk-based research, such as literature reviews, experienced fewer disruptions. One of his candidates, involved in empirical research, had to receive an eight-month extension due to difficulties in data collection, exacerbated by strikes in the secondary education sector.
Changes in Supervision Practices: The transition to online supervision did not significantly affect Henrik, as he was already accustomed to conducting supervision via video conferencing tools like Teams and Zoom. However, he missed the informal, face-to-face interactions that often enrich the supervisory relationship. He noted that the absence of casual corridor conversations led to a more formal and structured online interaction.
Home Office Experience: Henrik found the exclusive home office setup challenging and detrimental to his well-being. He prefers a balance between working at the office and from home. The lack of physical interaction with colleagues and the continuous remote work environment negatively impacted his mental health, requiring him to seek professional health support.
Workload Changes During the Pandemic: Henrik reported that his workload related to PhD supervision did not increase significantly during the pandemic. However, other responsibilities became more demanding, and the overall context of working from home without the usual workplace interactions made certain tasks more difficult.
Support from Employer: There was no specific support provided by his employer concerning his role as a PhD supervisor during the pandemic. Support efforts were more generalized and not tailored to the unique challenges faced by supervisors.
Concerns for PhD Candidates: Henrik was particularly concerned about the mental health of his candidates, noting that the isolation and disruption caused by the pandemic were significant stressors. He proactively discussed these issues with his candidates, acknowledging the challenges faced by those with families and those who were isolated without a support network.
Personal Health Concerns: The pandemic had a substantial impact on Henrik’s mental health, highlighting the importance of considering the well-being of supervisors along with their candidates during such crises.
Effect on Completion Times: Henrik observed that the pandemic inevitably led to delays in the completion times of his PhD candidates, with some requiring extensions. He noted a disparity in how extensions were granted, suggesting a need for more consistent criteria.
Preparation for Article-Based Theses: Henrik believes that most PhD candidates are not well-prepared to write article-based theses, as their previous academic training typically does not include writing journal articles. He spends significant time discussing the publication process with his candidates to demystify it and help them understand the expectations of journal editors and peer reviewers.
Overall Reflection: Henrik’s experience reflects the diverse impacts of the pandemic on different types of research activities and highlights the importance of flexibility and support in PhD supervision. His proactive approach to discussing mental health and the structural changes in supervision practices illustrate adaptive strategies that can be beneficial in navigating future disruptions in academic settings.
3.2.5 Analyzing the interview with Luna
Introduction: Luna, aged 55, specializes in English as an Additional Language didactics. She completed her doctoral degree with an article-based thesis and has supervised a total of 11 PhD candidates, two of whom have completed their dissertations under her primary supervision.
Impact of the Pandemic on PhD Candidates : Luna discussed the varying impacts of the pandemic on her supervisees. One candidate, who was already far along in her research when the pandemic hit, was less affected in terms of supervision but faced uncertainty and stress related to her digital dissertation defense using Zoom. For two new candidates who started during the pandemic, the experience was particularly challenging. They struggled with integrating into the academic community and adapting to remote work, significantly affecting their progress and emotional well-being.
Changes in Supervision Practices : The pandemic required Luna to adapt her supervision methods, emphasizing digital communication tools and frequent check-ins via Teams, Zoom, or phone apps. She noted that these changes allowed for maintaining close communication but shifted many supervision interactions to support coping with the emotional and logistical challenges posed by the pandemic.
Home Office Experience: Luna had a positive experience working from home, which was facilitated by having enough space and a family structure that supported a conducive work environment. She did not face significant challenges balancing work and family life, which helped maintain her productivity and well-being.
Workload Changes During the Pandemic: While her direct supervision workload remained stable, Luna’s role as a researcher education coordinator significantly increased her overall responsibilities. She was deeply involved in supporting a broader range of PhD candidates beyond her direct supervisees, which included mediating between candidates and their supervisors and helping navigate the challenges posed by the pandemic.
Support from Employer: Luna felt well-supported by her employer, particularly in terms of responsiveness to her needs and concerns as she navigated her roles during the pandemic. This support was crucial in managing the increased demands on her time and ensuring the well-being of the candidates for whom she was responsible.
Concerns for PhD Candidates: Luna expressed significant concern for the mental well-being of her candidates, noting that the pandemic exacerbated feelings of isolation and stress. She was particularly worried about those who could not integrate into the academic community or faced severe disruptions in their personal lives.
Personal Health Concerns: Despite managing her workload and maintaining her health, Luna acknowledged the intense pressures of her role during the pandemic, which were compounded by the high demands of her coordinator position.
Effect on Completion Times: Luna observed that the pandemic delayed completion times for many PhD candidates, with extensions being necessary but variably granted. She emphasized the importance of transparent and equitable handling of extension requests to ensure fairness.
Preparation for Article-Based Theses: Luna believes that PhD candidates are generally underprepared for writing article-based theses, attributing this to the educational focus on monographic rather than article-based work before the PhD level. She highlighted the importance of guidance in academic writing and understanding publication processes as essential components of PhD education.
Overall Reflection: Luna’s experience during the pandemic underscores the critical role of adaptability in supervision, the importance of mental health support for PhD candidates, and the need for clear communication and guidelines in managing extended impacts on doctoral education. Her proactive approach to addressing these challenges reflects a comprehensive and empathetic supervision style aimed at supporting candidates through unprecedented times.
3.2.6 Analyzing the interview with Lydia
Introduction: Lydia, aged 52, specializes in educational research, focusing on professional development, assessment, and teacher education. She completed her doctoral degree through a monographic thesis and has supervised three PhD candidates to completion, with six currently under her guidance.
Impact of the Pandemic on PhD Candidates: Lydia noted that the pandemic affected the progress of her PhD candidates, especially those with young children or those who started their projects around the onset of the pandemic. The challenges of remote work and caring for family members led to minor delays in their research timelines.
Changes in Supervision Practices: For candidates who had already started their projects, Lydia managed to continue effective supervision by meeting them on campus when possible. However, starting a supervisory relationship entirely online via Zoom or Teams with new candidates presented difficulties, particularly in building rapport and trust.
Home Office Experience: Lydia found working from home to be somewhat liberating and enjoyed the quiet environment, which contrasted with the often-hectic campus life. Her home setup, which included adult family members who managed their responsibilities independently, provided a conducive environment for work without significant distractions.
Workload Changes During the Pandemic: While the actual supervision tasks did not significantly increase in time, Lydia spent more effort on providing emotional support to her candidates. Discussions often veered from academic topics to personal well-being, reflecting the heightened anxieties and social isolation experienced by the candidates.
Support from Employer : Lydia expressed disappointment with her institution’s lack of direct support during the pandemic. The focus remained on expecting faculty to adapt and manage without specific interventions aimed at easing the transition to remote supervision or addressing the unique challenges posed by the pandemic.
Concerns for PhD Candidates: She was particularly concerned about the psychological well-being of her candidates, as many were navigating difficult life stages compounded by the pandemic. Lydia felt a strong responsibility to reassure them and help them maintain confidence in their ability to progress in their research.
Personal Health Concerns: Lydia did not report significant concerns about her own health, feeling relatively privileged and well-adapted to the circumstances. She maintained a positive outlook, supported by stable family dynamics and the ability to engage in outdoor activities, which helped preserve her mental well-being.
Effect on Completion Times: Acknowledging the inevitable delays caused by the pandemic, Lydia noted that extensions were likely necessary for most PhD candidates during this period. She appreciated that post-pandemic policies allowed for extensions to address disruptions, especially those related to family responsibilities.
Preparation for Article-Based Theses: Despite not having written a synopsis herself, Lydia observed that candidates often lack preparedness for writing article-based theses, a gap she attributes to the traditional focus on monographic work at earlier academic stages. She advocates for enhanced training and support for candidates transitioning to this format.
Overall Reflection: Lydia’s reflections reveal a nuanced understanding of the challenges faced by PhD candidates and supervisors during the pandemic. Her approach highlights the importance of flexibility, emotional support, and the need for institutions to provide clearer guidelines and more robust support systems to adapt to such unprecedented circumstances effectively. Her experience underscores the critical role of empathy and adaptability in academic leadership during crises.
3.2.7 Analyzing the interview with Michelle
Introduction: Michelle, 41, specializes in educational science, teacher education, and language didactics. She has previously supervised five PhD students to completion and is currently the main and co-supervisor for ten PhD candidates.
Impact of the Pandemic on PhD Candidates: Michelle reported varied impacts of the pandemic on her PhD candidates. Those who were in the final stages of their research before the pandemic began experienced minimal disruptions, benefiting from the shift to remote work which allowed them more focused time for writing. However, candidates in earlier stages of their projects or those with young children faced significant challenges due to reduced childcare hours and the need to juggle multiple responsibilities.
Changes in Supervision Practices: The pandemic greatly affected Michelle’s ability to provide regular supervision. With the demands of her own childcare responsibilities and the limitations of remote work, the frequency and quality of her interactions with her PhD candidates suffered. Supervision sessions were delayed, and Michelle had to adjust her practices, often conducting meetings via phone, online with Zoom or Teams, or in socially distanced outdoor settings.
Home Office Experience: Michelle found working from home to be extremely challenging, particularly due to the presence of young children and the constant interruptions that blurred the lines between work and home life. She experienced a persistent sense of being unable to adequately meet all her responsibilities as a supervisor and a parent.
Workload Changes During the Pandemic : Her workload related to PhD supervision became more demanding due to the difficulties in maintaining regular and effective communication. Michelle had to find creative ways to support her students, which often meant extended work hours and adapting to less conventional interaction methods.
Support from Employer: Michelle expressed significant disappointment with the lack of support from her employer during the pandemic. She felt that the institutions did not provide clear guidelines or additional support for managing the unique challenges brought on by the pandemic, leaving supervisors to manage as best they could under difficult circumstances.
Concerns for PhD Candidates: Michelle was particularly concerned about the psychological well-being of her candidates, noting that the isolation and disruptions affected different groups in varied ways. She observed that while parents were stressed and overextended, single young men often felt isolated and unproductive, which sometimes led to detrimental lifestyle changes.
Personal Health Concerns: Michelle mentioned that, like many in academia, she was accustomed to working excessively and did not have time to focus on her own health due to the demands of the pandemic situation.
Effect on Completion Times: Michelle anticipated that the pandemic would likely extend the completion times for many PhD candidates due to delays in data collection and the general disruption of academic schedules. She noted that while some extensions were granted, many were not, which added to the stress and uncertainty for the candidates.
Preparation for Article-Based Theses: Michelle believes that PhD candidates are generally not well-prepared to write article-based theses, which is often not addressed until during the PhD program itself. She emphasized the importance of structuring doctoral education to prepare better candidates for the realities of academic publishing and the peer review process.
Overall Reflection: Michelle’s experience during the pandemic highlights the complex challenges faced by PhD supervisors. Her insights underscore the need for better institutional support and clearer guidelines to navigate such unprecedented situations. Her commitment to adapting her supervisory practices despite personal and professional challenges demonstrates her dedication to her role and the success of her students.
3.2.8 Analyzing the interview with Ollie
Introduction: Ollie, aged 55, specializes in educational science and has completed his doctoral degree with a monograph. He has guided one PhD candidate to completion and is currently supervising three, with one about to defend their thesis.
Impact of the Pandemic on PhD Candidates: Ollie noted significant disruptions for his PhD candidates due to the pandemic. One candidate was fortunate to have completed major data collection just before lockdowns, which somewhat insulated their progress. However, others struggled as their research depended heavily on data collection in schools, which became nearly impossible due to access restrictions and subsequent strikes affecting the school system.
Changes in Supervision Practices: While the physical data collection was hindered, Ollie found digital supervision effective, especially for discussing and editing texts. He appreciated the direct focus on the text that digital platforms such as Teams or Zoom facilitated, contrasting with the sometimes-awkward setups of physical meetings. Nonetheless, the lack of access to schools for his candidates meant there was less content to supervise, which altered the dynamics of his guidance.
Home Office Experience: Ollie had a relatively positive experience working from home, appreciating the convenience and reduced commute time. He noted that being at home allowed for a more relaxed dress code and flexible work hours, although he acknowledged a potential for decreased social interaction and the blurring of work-life boundaries.
Workload Changes During the Pandemic: Ollie’s workload in terms of PhD supervision remained largely the same, but the nature of the supervision changed. He spent more time helping candidates pivot their projects to adapt to the new realities, which included more discussions and finding alternative approaches to research obstacles.
Support from Employer: Ollie felt that there was a lack of specific support for PhD supervisors from his employer during the pandemic. The focus seemed to be more on undergraduate and master’s students, with little attention paid to the challenges faced by PhD candidates and their supervisors.
Concerns for PhD Candidates: He was concerned about the delays and the psychological impact on his students, noting the challenges of maintaining motivation and morale under such uncertain and stressful conditions.
Personal Health Concerns: Ollie was proactive about maintaining his physical health during the pandemic, investing in ergonomic furniture to ensure comfort while working from home. He did not express concerns about his psychological health, suggesting a pragmatic approach to dealing with the pandemic’s challenges.
Effect on Completion Times: He anticipated that the pandemic would significantly delay his PhD candidates’ completion times, mainly due to disrupted data collection processes. Ollie stressed the importance of data quality and how difficulties in data collection could impact the overall quality of doctoral research and subsequent publication opportunities.
Overall Reflection: Ollie’s insights reflect a nuanced understanding of the diverse challenges posed by the pandemic to doctoral education. His adaptation to online supervision using videoconferencing platforms such as Zoom or Teams highlights the potential benefits of digital platforms for focused academic work, even as he recognizes the significant disruptions to traditional research pathways. His experience underscores the need for institutions to provide more robust support systems for doctoral candidates and supervisors, ensuring that doctoral training quality and integrity are maintained even in adverse circumstances.
3.2.9 Analyzing the interview with Tyler
Introduction: Tyler, aged 60, specializes in the philosophy of science, organization, and educational leadership. He completed his doctorate with a monograph and has guided two PhD candidates to completion, with four currently under his supervision.
Impact of the Pandemic on PhD Candidates: The pandemic significantly disrupted the plans of Tyler’s PhD candidates, particularly affecting those involved in international collaborations and empirical research. One candidate missed a crucial research stay in Italy, impacting their opportunity to engage with an international academic community. Another had to revise their empirical approach due to restricted access to schools, which was a common issue during the pandemic.
Changes in Supervision Practices: Tyler’s supervision was heavily affected by the pandemic, with all interactions moving to digital platforms, including Teams and Zoom. This shift resulted in less frequent and less personal guidance, which he felt was less effective than the planned intensive seminars abroad. Like Ollie, however, Tyler noted some benefits to digital supervision using videoconferencing platforms, such as the ability to engage with text during sessions directly.
Home Office Experience: Initially, Tyler took on additional teaching responsibilities to compensate for colleagues struggling with digital formats, which increased his workload. Over time, he found a rhythm of working from home and even appreciated the focused time that allowed him to complete a book. He alternated working from home and the office, leveraging the strengths of both environments to maintain productivity.
Workload Changes During the Pandemic: Tyler’s workload in terms of PhD supervision did not increase significantly. Digital Teams or Zoom meetings tended to be shorter and more focused, which somewhat compensated for the increased preparatory work required for effective digital instruction.
Support from Employer: Tyler expressed frustration with his institution’s management during the pandemic, particularly concerning doctoral courses and the increased bureaucratic oversight that he felt stifled academic freedom. He noted a lack of focus on the needs of PhD supervisors and candidates compared to other groups within the university.
Concerns for PhD Candidates: While not overly concerned about the mental and physical health of his candidates, Tyler was worried about the practical aspects of their research, especially those needing to conduct fieldwork, which was severely impacted by the pandemic restrictions.
Personal Health Concerns: Tyler did not express particular concerns about his health; however, he took proactive measures to ensure a comfortable working environment by investing in ergonomic office equipment.
Effect on Completion Times: Tyler anticipated that the pandemic would extend the completion times for his PhD candidates, especially due to disruptions in data collection and the broader impact on academic research activities.
Overall Reflection: Tyler’s experiences reflect the complex challenges faced by academic supervisors during the pandemic, balancing the shift to digital platforms with maintaining academic rigor and support for their candidates. His story highlights the need for institutions to provide better support and flexibility for supervisors and PhD candidates during crises, ensuring that academic standards and well-being are maintained. Tyler’s ability to adapt and find personal benefits during the pandemic, such as completing a book, also underscores the potential for finding opportunities in the face of challenges.
3.2.10 Comprehensive analysis of the Main findings across nine interviews of doctoral supervisors in Norway
3.2.10.1 overview.
This analysis integrates the findings from interviews with nine doctoral supervisors in Norway, structured by the interview guide (based on the main findings from the survey) and analyzed using Braun and Clarke’s (2021) approach to reflexive thematic analysis. The analysis focuses on how the COVID-19 pandemic affected the progression of PhD candidates and the corresponding changes in supervision practices.
Main Themes Identified:
1. Impact of the Pandemic on PhD Progression:
• Disruptions in Data Collection : Most supervisors reported significant disruptions in their candidates’ ability to collect data, especially those requiring access to external facilities like schools or international institutions. This was primarily due to lockdowns and restrictions imposed to curb the spread of the virus. As one supervisor noted: “One of my candidates had to delay their project significantly due to the inability to collect data as schools were not accessible.” (Ollie)
• Adaptations in Research Plans : Many candidates had to alter their research methodologies or adjust their empirical scopes to suit the new constraints, highlighting the flexibility required under crisis conditions. However, one of the supervisors mentioned that: “It affected them very differently. I had three candidates before the pandemic, and two of them were barely affected. However, the third struggled significantly with data collection due to difficulties in recruiting informants.” (Gabbie)
2. Changes in Supervision Practices:
• Shift to Digital Supervision : All supervisors transitioned to online platforms for conducting supervision, such as Zoom, Teams, or phone apps (e.g., Facebook Messenger, WhatsApp). While some found digital tools effective for sharing and reviewing written work, others felt the lack of physical presence reduced the quality of interaction and guidance they could provide. As one supervisor noted: “Digital supervision worked very well because it allowed sharing and discussing texts more effectively than in-person meetings. This actually enhanced the focus on the text during sessions” (Ollie).
• Increased Need for Emotional Support : Supervisors noted an increased need to support the psychological well-being of their candidates, as many struggled with isolation and stress due to the pandemic. As one supervisor noted: “I was particularly attentive to the mental health of my candidates, especially those without local family support. Regular check-ins were crucial during this period” (Gabbie).
3. Work Environment and Work-Life Balance:
• Home Office Challenges : Responses about working from home were mixed; some supervisors appreciated the flexibility and reduced commute times, while others struggled with distractions and the blending of personal and professional spaces. As one supervisor mentioned: “I actually enjoyed working from home as it provided a peaceful environment, but I missed the informal interactions with colleagues.” (Lydia)
• Institutional Support : There was a notable lack of targeted support for supervisors from their institutions. This often left supervisors and their candidates feeling overlooked in broader university responses to the pandemic. As one supervisor noted: “There was no specific support for me as a PhD supervisor during the pandemic. The general support was the same as for all staff members” (Lydia).
4. Professional Development and Academic Output:
• Delays in Academic Milestones : The pandemic delayed key academic milestones, including thesis submissions and defenses, primarily due to halted data collection and extended research timelines.
• Publication Challenges : The disruption also impacted candidates’ abilities to publish their research, a crucial component of their academic careers, due to delays and changes in their research projects.
Integration of Findings with Saldaña’s Coding Framework and Interview Guide:
• Using Saldaña’s coding method allowed for identifying recurring challenges and adaptations among the supervisors’ experiences. The thematic analysis revealed a consistent need for increased flexibility in research planning and supervision methods.
• The interview guide helped maintain a focus on how the pandemic specifically impacted various aspects of PhD supervision and candidate progression. It ensured that all relevant areas, such as changes in work routines, supervision adjustments, and overall impacts on PhD timelines, were systematically explored.
Comprehensive Assessment : The interviews collectively underscore the resilience and adaptability required by PhD candidates and their supervisors during the pandemic. They highlight several areas for improvement:
• Enhanced Institutional Support : Institutions clearly need to provide more structured support tailored to the needs of PhD candidates and supervisors during crises.
• Flexibility in Research and Supervision Plans : Adapting research plans and supervision methods to accommodate unexpected disruptions is crucial for maintaining the integrity and continuity of PhD education.
• Focus on Mental Health : The increased emotional and psychological support needed by candidates suggests that institutions should integrate mental health resources more fully into their doctoral training programs.
• Preparedness and Training : The experience has shown the importance of preparing PhD candidates for unexpected changes in their research environment, including training in digital tools and remote research methodologies.
In conclusion, the pandemic has not only disrupted traditional PhD education paths but also provided insights into how flexibility, digital preparedness, and institutional support can be enhanced to better prepare for future crises. These insights are vital for shaping resilient and adaptive academic environments that can withstand global challenges while supporting doctoral candidates’ academic and personal well-being.
From the analysis of the nine interviews, a few aspects stood out as particularly notable, offering deeper insights (expansion) into the unique challenges and responses within the context of PhD supervision during the pandemic:
1. Resilience and Innovation in Supervision:
• Some supervisors noted that despite the significant challenges, the shift to digital platforms allowed them to explore new forms of engagement with texts and supervision methods. For example, one supervisor highlighted the effectiveness of digital tools for collaborative work on documents, suggesting that these might even surpass traditional face-to-face interactions in certain aspects. This adaptation was a positive takeaway that some found surprising and worth integrating into their post-pandemic practices.
2. Diverse Impacts on Different Research Types:
• The differential impact of the pandemic on empirical versus theoretical research was striking. Supervisors of candidates who needed to conduct fieldwork, especially in schools or abroad, faced severe disruptions. As one supervisor noted: “We had to adjust research plans significantly, shifting to alternative data sources and methods where possible.” (Kyle). In contrast, those whose work was more theoretical or could be conducted remotely experienced fewer setbacks. This variance highlighted certain types of research vulnerability to external disruptions, which was a notable point of concern.
3. Underestimation of Emotional Challenges:
• Another well known, but still important aspect was the depth of emotional and psychological impacts on PhD candidates as noted by their supervisors. The extent to which these challenges affected the candidates’ productivity and well-being was significant and perhaps underappreciated by the institutions themselves. This underscores a critical area for future academic support systems to address more robustly.
4. Lack of Institutional Support:
• The widespread sentiment of insufficient institutional support was particularly striking. Several supervisors felt that there was a lack of targeted strategies to support PhD supervision during the pandemic. This lack of support was not just in terms of transitioning to online modes but also in addressing the specific needs of PhD candidates and their projects during such a disruptive period.
5. The Positive Impact of Forced Adaptation:
• Interestingly, some supervisors pointed out that the forced adaptation to new circumstances led to unexpected benefits, such as enhanced focus and productivity in certain cases, and even opportunities for personal and professional growth, such as writing a book or developing new teaching methods. These outcomes, while not universal, were surprising positives that emerged from a generally challenging time.
The sentiment analysis of the 9 interviews (see attachment 4 in the Supplementary file ) showed some individual variations, but that resilience and adaptability among doctoral supervisors during the pandemic were quite common. Supervisors recognized the challenges but overall maintained a positive and proactive stance, focusing on solutions and effective management of their supervisory roles. The objective nature of their responses indicates a practical approach to dealing with the pandemic’s impact, emphasizing the importance of communication, adaptation to remote supervision, and institutional support.
These insights not only highlight the varied experiences of PhD supervisors during the pandemic but also suggest areas for improvement in how institutions support doctoral education in times of crisis. The resilience and innovative approaches developed during this period could inform future policies and practices to better support PhD candidates and supervisors alike.
3.2.11 Integrated analysis: the main findings from the interviews and the open survey responses
To integrate and analyze the findings from the interviews (see attachment 1) and the 1,483 open survey responses (see attachment 2) from the survey among 293 doctoral supervisors, we can draw on several key themes and concerns that emerge consistently across these data sources. This approach will help us understand the broader implications of the insights gathered from different perspectives within the same study.
1. Adaptation to Digital Tools and Platforms:
• Interviews : The interviews highlighted how supervisors adapted to using digital tools for communication and supervision. This was generally seen as effective but lacking in certain qualitative aspects, particularly in building deeper relationships and managing more nuanced discussions.
• Open Survey Responses : The survey also reflected a reliance on digital tools, with many supervisors recognizing their utility in maintaining continuity. However, there was also an acknowledgment of the challenges in fully replicating face-to-face interactions.
2. Ethical and Practical Concerns with Digital Supervision:
• Interviews : Concerns were raised about the relational and ethical implications of the lack of physical presence and interaction, and the extensive use of digital tools in academic settings during the pandemic.
• Open Survey Responses : Similar concerns were noted, with supervisors emphasizing the importance of ensuring academic integrity and the genuine intellectual development of PhD candidates.
3. Impact of the Pandemic on Supervisory Practices:
• Interviews : The pandemic’s impact was a significant theme, affecting the logistical aspects of supervision and the mental well-being of both supervisors and their candidates.
• Open Survey Responses : Responses indicated varied impacts of the pandemic, with some supervisors noting increased stress and difficulty in maintaining research productivity and supervisory quality.
4. Institutional Support and Professional Development:
• Interviews : There was a noted lack of sufficient institutional support for adapting to new modes of supervision and research during the pandemic.
• Open Survey Responses : This theme was echoed in the survey responses, with mixed reports about the availability and effectiveness of continuing professional development (CPD) related to research supervision. Some respondents felt unsupported, particularly in navigating the challenges posed by remote supervision and digital tools.
5. Preparedness of PhD Candidates:
• Interviews : Discussions highlighted concerns about the varying levels of preparedness among PhD candidates, especially in writing the synopsis and adapting to new research methodologies that include digital tools and remote data collection.
• Open Survey Responses : Supervisors expressed a range of experiences regarding candidate preparedness. While some noted their candidates were well-equipped, others pointed out significant gaps, especially in writing the synopsis and article-based theses and handling the referee process, the timeline and complex research independently.
6. Valuation of Supervision:
• Interviews : Supervisors discussed feeling that their efforts were not adequately valued by institutions, with a need for greater recognition and support for their roles.
• Open Survey Responses : This sentiment was reinforced by survey data, where some supervisors felt that their contributions to doctoral training were undervalued by their institutions, particularly when compared to other academic duties.
7. Suggestions for Institutional Changes:
• Interviews : There were calls for institutions to adapt more proactively to the changing landscape of doctoral education, including better training for using digital tools and more robust support systems for both supervisors and candidates.
• Open Survey Responses : Supervisors suggested various improvements, such as more structured professional development opportunities, better guidelines for remote supervision, and enhanced support for mental health and well-being.
3.2.12 Summary
The integrated analysis across interviews and open survey responses suggests a complex landscape of doctoral supervision during and potentially beyond the pandemic era. Key themes highlight both challenges and potential areas for policy and practice enhancements:
• Digital Adaptation and Ethical Concerns : While digital tools have provided necessary solutions for continuity in supervision, they bring up ethical concerns that institutions need to address more thoroughly, particularly concerning academic integrity and the quality of student learning.
• Support and Development Needs : There is a clear need for institutions to offer more targeted support and development opportunities for supervisors, addressing both the technical aspects of digital supervision and the broader pedagogical skills required in a changing academic environment.
• Recognition and Valuation of Supervision : Supervisors feel that their work is not sufficiently valued, suggesting that institutions should reevaluate how they recognize and support supervisory roles within the academic career framework.
• Candidate Preparedness : There is variability in how prepared PhD candidates are for the demands of modern doctoral research, indicating the need for more robust preparatory programs and entry assessments.
• These insights call for a strategic reassessment of doctoral training programs, supervisory support mechanisms, and institutional policies to better align with the evolving needs of both supervisors and their candidates.
4 Limitations and future research
The present study provides in-depths insights into PhD supervision during the pandemic; however, the study also has several limitations apart from inherited limitations of self-reports and interview data. Firstly, the findings might be context-specific to the educational setting in Norway. The unique characteristics of the Norwegian educational system, cultural aspects, and institutional structures may not be entirely generalizable to other countries. However, the globalization of doctoral education, with increasing international collaborations, international publishing, and standardization of academic practices, might mitigate this issue to some extent, making the findings relevant beyond the Norwegian context. Secondly, the study lacks data on PhD supervisors’ experiences prior to the pandemic. This absence of baseline data means we cannot directly compare the pre-pandemic and pandemic periods. Nonetheless, the experiences reported in this study correspond well with prior research on academic supervision ( Pyhältö et al., 2012 , 2023 ; Löfström et al., 2024 ), indicating that the challenges and adaptations observed are not entirely unprecedented, even if intensified by the pandemic context.
Future research should aim to explore the long-lasting impacts of COVID-19 on doctoral education. It is necessary to investigate whether the changes observed in supervisory practices during the pandemic are fleeting or have led to a permanent shift in how supervision is approached. Specifically, studies should examine if new models of remote supervision, increased flexibility, and the use of digital tools will continue to be integrated into doctoral education post-pandemic, or if traditional methods will resume dominance. This is of special interest in cases where PhD supervisors and PhD candidates are located at different institutions. By addressing these questions, future research can contribute to a deeper understanding of the pandemic’s legacy on doctoral education.
5 Conclusion
In this article we examined the experiences of PhD supervisors in Norway during the pandemic to answer the research questions:
1. To what extent has the COVID-19 pandemic impeded the PhD supervisors’ frame factors on the micro- level, and how do they perceive this situation?
2. To what extent has the COVID-19 pandemic influenced PhD supervisors’ frame factors on the meso- level, and how do they perceive this situation?
We conducted a cumulative data collection process and analysis, where survey questions were based on previously collected field dialog data, online observation data, seminar evaluation data, and document analysis data. The qualitative interview guide questions were built upon previously collected quantitative data (survey), and the Supplementary data was based on previously collected quantitative data (survey) and qualitative interview data.
The coherence between qualitative and quantitative findings is mainly examined based on confirmation , expansion , or discordance in this article ( Fetters et al., 2013 ).
The findings from the explorative case study revealed that the PhD supervisors faced numerous challenges during the pandemic, both professionally and personally. They found digital supervision with their PhD fellows via platforms like Teams and Zoom to be convenient and efficient but occasionally lacking in quality. They also encountered difficulties in addressing the psychosocial aspects of their PhD candidates’ experiences and faced various research-related challenges with their PhD-candidates during the pandemic. For PhD supervisors who extensively worked from home over a long period, the situation created new conditions that affected their job performance. These altered conditions hindered their research capacity, their ability to follow up with their PhD candidates and their capacity to fulfill other job responsibilities. Although the PhD supervisors received support during the pandemic, it seems that the incremental measures provided were insufficient. The PhD regulations were established before the pandemic under normal conditions and for normal circumstances. However, it appears that no significant adjustments have been made to accommodate the extraordinary pandemic conditions, which have altered some aspects of their professional roles as academics and PhD supervisors. This was particularly critical for PhD supervisors with young children, especially female supervisors, who had to deal with lockdowns, social distancing, remote work, homeschooling, quarantine for themselves and their children, and COVID-19 illness, since the data showed that they seemed to have more home responsibilities than men during the pandemic. We also found that some supervisors thought that female PhDs’ (with own children) submission rates to scientific journals have been delayed as a consequence of COVID-19, considering that women seem to have more home responsibilities. In addition, the supervisors thought that female supervisors (with own children) submission rates to scientific journals have been delayed as a consequence of COVID-19, considering that female supervisors seem also to have more home responsibilities (e.g., for childcare, household etc.).
This slow-motion disaster lasted up to 20 months and can be perceived as an “external intervention” or a naturalistic experiment which was impossible to predict for universities and society. The case study results indicate that it is more important than ever to plan for the unforeseen in order to be better prepared for the next societal crisis. Therefore, it is important to be vigilant and understand the gap between the formulation, transformation, and realization arenas when it comes to the distinction between incremental, semi-structural changes and fundamental changes in PhD regulations and guidelines brought on by societal crises. Although some support from employers has been offered, the overall PhD guidelines, regulations, and supervision norms remained unchanged in the transformation arena (meso- level) during the pandemic. On a general level, this highlights the need for better crisis preparedness at the doctoral level in the years to come.
A common finding related to RQ1 and RQ2 and across the different data sources was that the COVID-19 pandemic has significantly impacted some of the PhD supervisors in different ways on both micro- and meso-levels, and some of them perceive this long-lasting pandemic challenging and difficult, while others have experienced this to a lesser degree. This reveals a confirmation across the quantitative and qualitative data in the study. Also, these findings mostly confirmed and expanded on the understanding of the impact of the pandemic on PhD candidates ( Krumsvik et al., 2022 ), with some minor discordance.
More specifically, the PhD supervisors in the study were somewhat satisfied with the educational quality regarding digital teaching but experienced various supervision, research-related and psycho-social challenges. Although some of the supervisors received support during the pandemic, it seems like the majority did not receive sufficient support and their workload increased significantly during the pandemic. This is due to the high complexity of frame factors that have changed the underlying premises for doctoral education during the pandemic, affecting both the PhD- supervision and the PhD candidates’ feasibility on several levels. The regulations for PhD scholarships and PhD regulations, implemented before the pandemic in 2018, were designed under normal educational and social conditions and may not fully address the challenges faced during the pandemic. Therefore, this study shows that to reduce this gap and strengthen the feasibility of the PhDs and the frame factors for PhD-supervision, the institutions must significantly enhance their preparedness to effectively manage demanding situations at both micro- and meso-levels, ensuring they are fully equipped to address future societal crises of a similar nature.
When it comes to RQ3 we find both confirmation, expansion, and discordance across the quantitative and qualitative data. We find confirmation across the quantitative and qualitative data when it comes to the variability in preparedness of PhD candidates for writing the article-based thesis. Article-based theses present unique challenges compared to traditional monograph-based dissertations, particularly in terms of integration and the breadth of skills required. One of the primary challenges with article-based theses is integrating articles that may cover slightly different aspects of a research topic into a coherent overall thesis. This integration is critical, it requires a high level of academic writing skills and ability to secure the coherence of the synopsis. Candidates often come into PhD programs with varying levels of experience in academic writing and publication. The survey and interviews, as well as Supplementary data , indicate that many candidates are not well-prepared for writing article-based theses, highlighting a need for more targeted training in academic writing and publishing early in the doctoral process. The need for robust supervisory support is acutely felt in guiding article-based theses, where candidates must navigate the complexities of publishing in peer-reviewed journals alongside synthesizing their research in the synopsis. This implies that PhD-candidates both are taking a doctoral degree in the Norwegian context and at the same time are publishing articles for the international research context, which can be challenging.
We find expansion when it comes to the need to have guidelines for the synopsis. Supervisors reported significant variation in the guidelines for the synopsis across institutions, both in the qualitative and quantitative part, which can lead to confusion and inconsistency in expectations for candidates and supervisors. Some respondents found these guidelines sufficient, while others find them unclear or obscure, complicating their task of effectively guiding PhD candidates. Clear, comprehensible guidelines are essential for ensuring that the synopsis effectively synthesizes the research in a manner that meets academic standards ( Wollenschläger et al., 2016 ).
And we find some discordance regarding variability in candidate preparedness where both strands of the data indicated a significant variability in how prepared PhD candidates are when they enroll in doctoral programs. Candidates’ preparedness often depends on their previous educational experiences, which can vary widely regarding exposure to research methods, academic writing, and critical thinking skills. The variability in preparedness suggests a need for more robust preparatory programs to equip all incoming doctoral candidates with the necessary skills and knowledge to succeed in their research endeavors. Implementing comprehensive entry assessments could help identify specific areas where candidates might need additional support, allowing programs to tailor preparatory courses or early doctoral training to address these gaps.
These findings collectively point to a need for doctoral programs to clarify guidelines, particularly for the synopsis in article-based theses, to enhance support for supervisory roles, and to develop preparatory programs that address the broad variability in candidate preparedness. This is also based on research on the need for rubrics ( Wollenschläger et al., 2016 ), which shows that transparency around requirements and guidelines is important for students learning. By tackling these issues, institutions can better prepare PhD candidates for the demands of modern doctoral research, ultimately leading to more consistent and successful outcomes in doctoral education. And despite that only 20 (8.3%) of the supervisors agreed or strongly agreed that they were supervising a PhD candidate who had considered quitting the PhD program during the pandemic, it is important to be vigilant around the (complex) reasons that causes this, since this is in many ways a drastic decision, first of all for the candidate themselves, but also for the supervisors, as well as for the society in general who has invested almost 5 million Norwegian kroner in each PhD-scholarship. Dropping out can partly be related to the observed findings that many PhD candidates were unprepared for the intricacies of article writing, including the lengthy processes of submission and peer review, attached to their educational background, which primarily focused on monographic work at the bachelor’s and master’s levels. This also implies that while PhD’s are perceived, assessed and evaluated as student/candidates when they are completing assignments in a doctoral program, there might be a quite new situation for them when they submit their articles to scientific journals with blind review, where they are evaluated as other researchers (and not only as students/candidates). Such findings (and similar findings) seem to go “under the radar” in doctoral programs in Norway and by taking into account such “tacit knowledge” we might be better prepared to bridge the formulation arena and realization arena within doctoral education in the years to come. This development also demands a vigilance within doctoral education of the importance of theory development within doctoral education since international research shows that doctoral supervision is under-theorized and lacks a solid knowledge base ( Halse and Malfroy, 2010 ; Halse, 2011 ) where also eclectic use of theories ( Dalland et al., 2023 ) can improve this area.
Author note
GPT-4o ( OpenAI, 2024 ) was employed in this article to translate interview findings to English after a general thematic analysis conducted in Norwegian and as one of several validity communities for the open survey responses. The GPT-4’s output was manually examined, edited, and reviewed by the authors. The sentiment analysis of the 9 interviews was done by the first author and by using the GPT-4o. Then it was carried out a validation of this sentiment analysis by SurveyMonkey ( SurveyMonkey, 2024 ), Claude ( Anthropic, 2024 ) and Gemini Advanced ( Google, 2024 ).
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/ Supplementary material , further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
RK: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. FR: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Validation, Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft. ØSk: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. LJ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Methodology, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. SS: Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. ØSa: Data curation, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. KH: Methodology, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank all doctoral supervisors for their responses to the surveys and for participating in interviews and focus groups on this study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/feduc.2024.1436521/full#supplementary-material
1. ^ Some of the Norwegian statistic from universities shows the following: about parental leave (day’s work) (women 69%, men 31%), sick children (day’s work) (women 69%, men 31%), self-certified sick leave (day’s work) (women 65%, men 35%) and doctor-certified sick leave (day’s work) (women 72%, men 28%) during one of the year in the pandemic ( Krumsvik et al., 2022 ).
Andres, L., Bengtsen, S. S. E., Gallego Castaño, L., Crossouard, B., Keefer, J. M., and Pyhältö, K. (2015). Drivers and interpretations of doctoral education today: National Comparisons. Frontline Learn. Res. 3, 5–22. doi: 10.14786/flr.v3i3.177
Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
Anthropic. (2024). Claude 3. Large Language Model (version 14. March 2024) . San Francisco. Available at: https://claude.ai/new
Google Scholar
Baklien, B. (2004). Følgeforskning. Sosiologi i Dag 34, 49–66.
Bastalich, W. (2017). Content and context in knowledge production: a critical review of doctoral supervision literature. Stud. High. Educ. 42, 1145–1157. doi: 10.1080/03075079.2015.1079702
Bengtsen, S. S. E. (2023). “Doctoral education in-the-world: (dis)connections between research and society” in From splendid isolation to global engagement . eds. B. Wolf, T. Schmohl, L. Buhin-Krenek, and M. Stricker (WBV Media), 43–55.
Börgeson, E., Sotak, M., Kraft, J., Bagunu, G., Biörserud, C., and Lange, S. (2021). Challenges in PhD education due to COVID-19- disrupted supervision or business as usual: a cross-sectional survey of Swedish biomedical sciences graduate students. BMC Med. Educ. 21:294. doi: 10.1186/s12909-021-02727-3
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
Braun, V., and Clarke, V. (2006). Using thematic analysis in psychology. Qual. Res. Psychol. 3, 77–101. doi: 10.1191/1478088706qp063oa
Braun, V., Clarke, V., Hayfield, N., and Terry, G. (2019). “Thematic analysis” in Handbook of research methods in health social sciences . ed. P. Liamputtong (Singapore: Springer), 843–860.
Braun, V., and Clarke, V. (2021). Thematic analysis: a practical guide. Los Angeles, CA: Sage.
Braun, V., and Clarke, V. (2019). Reflecting on reflexive thematic analysis. Qualitative Research in Sport, Exercise and Health , 11, 589–597. doi: 10.1080/2159676X.2019.1628806
Brinkmann, S. (2022). Qualitative Interviewing: Conversational Knowledge Through Research Interviews (2 ed.) . Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Burner, T., Bjerkholt, E., Gaathaug, A. V., Kleiven, S., and Ljoså, T. M. (2020). Doctorateness across higher education Institutionsin Norway. Uniped 43, 3–18. doi: 10.18261/issn.1893-8981-2020-01-02
Creswell, J. W., and Guetterman, T. C. (2021). Educational research: Planning, conducting, and evaluating quantitative and qualitative research . 6th Edn. Hoboken, NJ: Pearson.
Creswell, J. W., and Plano Clark, V. L. (2017). Designing and conducting mixed methods research . 3rd Edn. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Dake, D. K., and Gyimah, E. (2023). Using sentiment analysis to evaluate qualitative students’ responses. Educ. Inf. Technol. 28, 4629–4647. doi: 10.1007/s10639-022-11349-1
Dalland, C. P., Blikstad-Balas, M., and Svenkerud, S. (2023). Eklektisk bruk av teori i doktorgradsavhandlinger innen utdanningsforskning. Acta Didactica Norden 17, 1–24. doi: 10.5617/adno.9837
Eisenhardt, K. M. (1989). Building Theories from Case Study Research. The Academy of Management Review , 14, 532–550. doi: 10.2307/258557
Ertesvåg, S. K., Sammons, P., and Blossing, U. (2021). Integrating data in a complex mixed-methods classroom interaction study. Br. Educ. Res. J. 47, 654–673. doi: 10.1002/berj.3678
European University Association (EUA) (2010). “Salzburg II” in Recommendations. European universities’ achievements since 2005 in implementing the Salzburg principles (Brussels: European University Association (EUA)).
European University Association (EUA) (2015). Annual Report 2015 . Brussels: European University Association (EUA).
Fetters, M. D., Curry, L. A., and Creswell, J. W. (2013). Achieving integration in mixed methods designs—principles and practices. Health Serv. Res. 48, 2134–2156. doi: 10.1111/1475-6773.12117
Flyvbjerg, B. (2011). “Case study” in The SAGE handbook of qualitative research . eds. N. K. Denzin and Y. S. Lincoln. 4th ed (Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage), 301–316.
Hall, J., and Mansfield, L. (2023). The benefits and complexities of integrating mixed method findings using the pillar integration process: a workplace health intervention case study. J. Mixed Methods Res. doi: 10.1177/15586898231196287
Gehrke, P. (2018). “Ecological validity” in The SAGE Encyclopedia of Educational Research, Measurement, and Evaluation . Ed. B. Frey. (Thousand Oaks: Sage), 563–565.
Google. (2024). Gemini Advanced. Large Language Model (version 20 May 2024) . Menlo Park, California. Available at: https://gemini.google.com/advanced?hl=no
Halse, C. (2011). ‘Becoming a supervisor’: the impact of doctoral supervision on supervisors’ learning. Stud. High. Educ. 36, 557–570. doi: 10.1080/03075079.2011.594593
Halse, C., and Malfroy, J. (2010). Retheorizing doctoral supervision as professional work. Stud. High. Educ. 35, 79–92. doi: 10.1080/03075070902906798
Hyett, N., Kenny, A., and Dickson-Swift, V. (2014). Methodology or method? A critical review of qualitative case study reports. Int. J. Qual. Stud. Health Well Being 9:23606. doi: 10.3402/qhw.v9.23606
Johnson, R. B., Onwuegbuzie, A. J., and Turner, L. A. (2007). Toward a definition of mixed methods research. J. Mixed Methods Res. 1, 112–133. doi: 10.1177/1558689806298224
Kálmán, O., Horváth, L., Kardos, D., Kozma, B., Feyisa, M. B., and Rónay, Z. (2022). Review of benefits and challenges of co-supervision in doctoral education. Eur. J. Educ. 57, 452–468. doi: 10.1111/ejed.12518
Krumsvik, R. J. (2016a). Noen betraktninger om forskningsveiledning PhD- nivå (some considerations about supervision at the doctoral level). In R. J. Krumsvik. En doktorgradsutdanning i endring – Med fokus på den artikkelbaserte PhD- avhandlingen (a doctoral education in alteration – With focus on the article-based PhD thesis) (pp. 125–148). Bergen: Fagbokforlaget.
Krumsvik, R. J. (2016b). The synopsis of article-based theses. In R. J. Krumsvik. En doktorgradsutdanning i endring – Med fokus på den artikkelbaserte PhD- avhandlingen (a doctoral education in alteration – With focus on the article-based PhD thesis) (pp. 93–123). Fagbokforlaget.
Krumsvik, R. J. (2017). Trenerene i den akademiske maraton (The trainers in the academic marathon). Utdanningsforskning (Educational Research) , Oslo: The Educational Association. 1–3.
Krumsvik, R. J., and Jones, L. Ø. (2016). Hvorfor dropper “kronjuvelen” ut? (why do the “crown jewels” drop out?). Tidsskrift for Norsk Psykologforening 12, 1022–1024.
Krumsvik, R. J., Jones, L. Ø., Leer-Salvesen, K., Høydal, K. L., and Røkenes, F. M. (2019). Face-to-face and remote teaching in a doctoraleducation course: using flipped classroom, formative assessment and remoteteaching to increase the teaching quality of a literature reviewcourse. Uniped 42, 194–214. doi: 10.18261/issn.1893-8981-2019-02-07
Krumsvik, R. J., Mæland, B., and Solstad, S. H. (2021). “Doctoral education in Norway and inter-institutional collaboration within doctoral education” in The future of doctoral research . eds. A. Lee and R. Bongaardt. 1st ed. (New York, NY: Routledge), 110–119.
Krumsvik, R. J., Øfstegaard, M., and Jones, L. Ø. (2016a). Retningslinjer og vurderingskriterier for artikkelbasert PhD. Uniped 39, 78–93. doi: 10.18261/issn.1893-8981-2016-01-07
Krumsvik, R. J., Øfstegaard, M., and Jones, L. Ø. (2016b). Retningslinjer og vurderingskriterier for artikkelbasert PhD-avhandling (guidelines and assessment criteria for article-based doctoral thesis). In R. J. Krumsvik. En doktorgradsutdanning i endring – Med fokus på den artikkelbaserte PhD-avhandlingen (a doctoral education in alteration – With focus on the article-based PhD thesis) (pp. 78–93). Bergen: Fagbokforlaget, 39.
Krumsvik, R. J., and Røkenes, F. M. (2016). Literature review in the PhD thesis. In R. J. Krumsvik. En doktorgradsutdanning i endring – Med fokus på den artikkelbaserte PhD-avhandlingen (a doctoral education in alteration – With focus on the article-based PhD thesis) (pp. 51–91). Bergen: Fagbokforlaget.
Krumsvik, R. J., Skaar, Ø. O., Røkenes, F. M., Solstad, S. H., and Høydal, K. L. (2022). Experiences of WNGER II PhD. fellows during the COVID-19 pandemic – a case study. Front. Educ. 7:860828. doi: 10.3389/feduc.2022.860828
Kvale, S., and Brinkmann, S. (2015). InterViews: Learning the craft of qualitative research interviewing . 3rd Edn. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications.
Linde, G. (2012). Det ska ni veta! En introduktion till läroplansteori (3rd Edn.). Lund: Studentlitteratur.
Lindensjö, B., and Lundgren, U. P. (2014). Utbildningsreformer och politisk styrning . Stockholm: HLS Förlag.
Löfström, E., Tikkanen, L., Anttila, H., and Pyhältö, K. (2024). Supervisors’ experiences of doctoral supervision in times of change. Stud. Grad. Postdoctoral Educ. 15, 34–48. doi: 10.1108/SGPE-01-2023-0004
Lundgren, U. P. (1999). Ramfaktorteori och praktisk utbildningsplanering. Pedagogisk Forskning 4, 31–41.
Mason, S., and Merga, M. (2018). Integrating publications in the social science doctoral thesis by publication. High. Educ. Res. Dev. 37, 1454–1471. doi: 10.1080/07294360.2018.1498461
Maxwell, J. A. (2013). Qualitative research design: An interactive approach . 3rd Edn Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications.
Merriam, S. B. (2009). Qualitative research: A guide to design and implementation . Hoboken, NJ: Jossey-Bass.
Merriam, S. B., and Tisdell, E. J. (2016). Qualitative research: A guide to design and implementation . 4th Edn. Hoboken, NJ: Jossey-Bass.
OpenAI. (2024). ChatGPT (May 20204 version) [Large language model]. San Fransisco, LA Available at: https://chat.openai.com/chat
Patton, M. Q. (2015). Qualitative research & evaluation methods: Integrating theory and practic . Sage.
Peters, M., and Fàbregues, S. (2023). Missed opportunities in mixed methods EdTech research? Visual joint display development as an analytical strategy for achieving integration in mixed methods studies. Educ. Technol. Res. Dev. , 1–21. doi: 10.1007/s11423-023-10234-z
Pyhältö, K., Tikkanen, L., and Anttila, H. (2023). Is there a fit between PhD candidates’ and their supervisors’ perceptions on the impact of COVID-19 on doctoral education? Stud. Grad. Postdoct. Educ. 14, 134–150. doi: 10.1108/SGPE-05-2022-0035
Pyhältö, K., Vekkaila, J., and Keskinen, J. (2012). Exploring the fit between doctoral students’ and supervisors’ perceptions of resources and challenges Vis-à-Vis the doctoral journey. Int. J. Dr. Stud. 7, 395–414. doi: 10.28945/1745
Ramberg, I., and Wendt, K. K. (2023). Forskerhverdag under koronapandemien: Resultater fra en panelundersøkelse av norske forskere 2022 (Oslo: NIFU Working Note 9). Available at: https://hdl.handle.net/11250/3069589
Sarrico, C. S. (2022). The expansion of doctoral education and the changing nature and purpose of the doctorate. High. Educ. 84, 1299–1315. doi: 10.1007/s10734-022-00946-1
Schoonenboom, J., and Johnson, R. B. (2017). How to construct a mixed methods research design. KZfSS Kölner Zeitschrift Für Soziologie Und Sozialpsychologie 69, 107–131. doi: 10.1007/s11577-017-0454-1
Skodvin, O. J. (2013). “NOKUT og kvalitet i IKT-støttet høyere utdanning” in Ulike forståelser av kvalitet i norsk, fleksibel høyere utdanning . eds. T. Fossland, K. R. Ramberg, and E. Gjerdrum (Tromsø: Norgesuniversitetet).
Solli, K., and Nygaard, L. P. (2022). ‘Same But Different? Identifying Writing Challenges Specific to the PhD by Publication’, in Landscapes and Narratives of PhD by Publication . Eds. K. Solli and L. P. Nygaard Cham: Springer. 13–30.
Stake, R. E. (1995). The art of case study research . Thousand Oaks: Sage Publications.
Stake, R. E. (2006). Multiple case study analysis . New York, NY: The Guilford Press.
Steine, S., and Sarpebakken, B. (2023). Færre doktorgrader innenfor matematikk og naturvitenskap i 2022 . Oslo: Statistics Norway.
SurveyMonkey. (2024). SurveyMonkey . San Mateo. Available at: https://surveymonkey.com
Tight, M. (2016). “Case study research” in The BERA/Sage handbook of educational research . eds. D. Wyse, N. Selwyn, E. Smith, and L. Suter (Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications), 376–394.
UK Council for Graduate Education (2021). The UK research supervision survey report 2021 . London: UK Council for Graduate Education.
Wichmann-Hansen, G. (2021). DUT Guide on Supervision. Dansk Universitetspædagogisk Tidsskrift . 16, 1–13. doi: 10.7146/dut.v16i31.127292
Wollenschläger, M., Hattie, J., Machts, N., Möller, J., and Harms, U. (2016). What makes rubrics effective in teacher-feedback? Transparency of learning goals is not enough. Contemp. Educ. Psychol. 44–45, 1–11. doi: 10.1016/j.cedpsych.2015.11.003
Yin, R. K. (2012). Applications of case study research . 3rd Edn: Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
Keywords: PhD-supervisors, experiences, COVID-19, supervision, PhD-fellows, frame factors
Citation: Krumsvik RJ, Røkenes FM, Skaar &O, Jones L, Solstad SH, Salhus & and Høydal KL (2024) PhD-supervisors experiences during and after the COVID-19 pandemic: a case study. Front. Educ . 9:1436521. doi: 10.3389/feduc.2024.1436521
Received: 22 May 2024; Accepted: 15 July 2024; Published: 09 August 2024.
Reviewed by:
Copyright © 2024 Krumsvik, Røkenes, Skaar, Jones, Solstad, Salhus and Høydal. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY) . The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Rune J. Krumsvik, [email protected]
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Kee says funding for a humanities Ph.D. program typically only lasts five years, even though it is uncommon for someone to obtain a Ph.D. degree in a humanities field within that time frame ...
A PhD program typically takes four to seven years, but a variety of factors can impact that timeline. A PhD, or doctorate degree, is the highest degree you can earn in certain disciplines, such as psychology, engineering, education, and mathematics. As a result, it often takes longer to earn than it does for a bachelor's or master's degree.
7 stages of the PhD journey. A PhD has a few landmark milestones along the way. The three to four year you'll spend doing a PhD can be divided into these seven stages. Preparing a research proposal. Carrying out a literature review. Conducting research and collecting results. Completing the MPhil to PhD upgrade.
In the UK, a full-time PhD will typically take you 3 to 4 years. You will usually spend the first three years on the technical aspects of your doctorate. This includes undertaking independent research, designing your research methodology and collecting and analysing data. You will then spend an additional academic year on writing up your PhD ...
The average PhD length is five or six years, while some students may take eight or nine years. Regardless of how long a PhD program takes, there are some common stages of a PhD that all doctoral students share. These significant and essential milestones shape the timeline for earning your doctorate.
How the PhD Program Works. Completing your doctorate at Wharton requires 5 years of full-time study. The first 2 years in the program prepare you for admission to candidacy by taking courses, qualifying exams, and starting research projects. In the last few years, you are primarily conducting research full-time including writing and defending ...
A Ph.D. is a research degree that involves the production of original knowledge and scholarship. Doctoral degrees have traditionally been regarded as training programs for academics. As such, a Ph.D. program differs from undergraduate or Master's studies. Most Ph.D. programs involve some initial coursework (specific requirements for ...
1. PhD course length. The total length of a PhD in the USA is between 4-8 years for full-time students and 8-10 years for part-time students, depending on your field of study. PhDs can be completed in 4-5 years for students with a masters degree in an appropriate subject. Students typically dedicate 1-4 years on coursework, followed by 2-4 ...
Late-January: Course registration deadline (previously known as "Study Card Day"). Mid-February: Deadline for submitting materials to be reviewed at the March CHD meetings. G1s: Your Prospective Program Plan due to the Office of Academic Programs on this day. Transfer of up to 3 classes of coursework may be allowed.
In the United States, PhDs usually take between 5-7 years: 2 years of coursework followed by 3-5 years of independent research work to produce a dissertation. In the rest of the world, students normally have a master's degree before beginning the PhD, so they proceed directly to the research stage and complete a PhD in 3-5 years.
The first two years of a PhD program are mainly made up of classes and the beginning stages of research. Deborah Small, the doctoral coordinator for the Marketing program, said, "It starts with heavy duty coursework and a lot of specific requirements. At the end of your first year, there are qualifying exams on all the core marketing courses.
The answer here isn't straightforward, as it hinges on various factors, including: the discipline, the institution, and. whether you're a full-time or part-time student. For full-time PhD students, the journey typically take 3-6 years. However, if you're juggling other commitments and opt for a part-time PhD, the timeline can extend to 7 ...
Part-time PhDs are unusual in Europe. In Germany, you could expect a PhD to take four to eight years. France is similar to Germany, and it takes around three to four years for a full-time doctorate in the sciences, and four to five years for a doctorate degree in the arts and humanities. At the University of Oslo, it can take up to six years to ...
The precise nature and definition of an MPhil can vary among institutions and countries. A PhD, meanwhile, follows a more widely known and traditional route and requires students, often referred to as "candidates", to produce their own work and research on a new area or topic to a high academic standard.
How long will it take to get a PhD in Sociology at Harvard? It all depends on the student. Some students complete the program in five years, some in as many as seven or eight years. Sample Timeline. Below is a sample timeline for a student striving to complete their degree in five to six years. First Year. Coursework (see Course Progression)
Defending your findings: The final hurdle of your PhD journey is defending your research to a committee. While this can be a nerve-wracking process, this stage tests your knowledge and conviction in your work and is an opportunity to showcase the significance of your research. The pursuit of a doctoral degree goes beyond academic titles.
However, there are many types of programs that typically take longer than six years to complete, such as humanities and arts doctorates, where the median time for individuals to earn their degree was 7.1 years, according to the survey. Some Ph.D. candidates begin doctoral programs after they have already obtained master's degrees, which means ...
Correspondence study courses may be applied to the degree only with the prior written approval of the College of Graduate Studies. Courses used toward an undergraduate degree, professional development courses, and courses on a professional development transcript are not available to be used toward a doctoral degree. ... the period involved is ...
Applications for the 2022/23 academic year are open from March 1-11. We spoke to HSE University doctoral students about their work and about how scholarships have helped them pursue their research goals. Education international students doctoral programmes India scholarships the USA. February 25, 2022.
The full form of PhD is Doctor of Philosophy derived from the Latin term Philosophiae Doctor. PhD is the highest degree or doctorate awarded for research in a particular subject. The duration of PhD course is 3 years but can vary from college to college. PhD Eligibility requires students to have pursued a master's degree or an MPhil with a ...
These awards are sufficient to cover all expenses for the year (including summers). Students are required to pay for health insurance, the transportation fee, the activity fee, books, and course supplies. Off-campus housing is available within walking distance of campus. At least one year of residency is required for the Ph.D.
If the dissertation is approved by the dissertation committee, the student has completed the final requirement of the Ph.D. and is permitted to proceed with preparations for graduation. Students are permitted by the Graduate School to graduate (having fulfilled all requirements) at three points during the year: October, February, and May.
Sechenov University provides Master's, Ph.D., and Residency level degree programs. Below is the list of the Master and PhD programs delievered in English: Master programmes. Public Health. Linguistics. PhD programmes. Chemical Science. Biological Science. Fundamental medicine. Clinical Medicine (GM profile) Clinical Medicine (Pediatrics profile)
Mid-January: Deadline for submitting materials to be reviewed at the January CHD meetings. Late-January: Course registration deadline (previously known as "Study Card Day"). G1s: Your Prospective Program Plan due to the Office of Academic Programs on this day. Transfer of up to 3 classes of coursework may be allowed.
The Ph.D. is a different kind of degree from the master's degree. A doctoral candidate in geography must be capable of making original contributions to knowledge and scholarship. For the students to make such contributions, they must concentrate on a narrow and clearly defined field of study. We require, however, that doctoral candidates know more of geography than their particular ...
Adfress: Street, Moscow, Russia Phone:+7 (000) 000-00-00 Email: [email protected]
The Post-Change-of-Program Period. Following the Change-of-Program Period, the Post-Change-of-Program Period begins for students in select schools.Check the Academic Calendar to confirm if your school applies. During this period, students may receive faculty or departmental approval to add and/or drop courses in Vergil up until the add/drop deadline. ...
1 Introduction. Effective doctoral supervision is crucial for guiding PhD candidates through the complexities of their research, ensuring academic rigor and the successful completion of their dissertations (Bastalich, 2017; Wichmann-Hansen, 2021; Kálmán et al., 2022).The role of PhD supervisors during the pandemic and their impact on educational quality at various levels has been an under ...
The Minnesota National Guard is disputing Governor Tim Walz's military biography, saying that the Democratic vice presidential candidate did not hold the rank of command sergeant major at the time ...