Essay on Human Resource Management (HRM): Top 6 Essays
In this essay we will discuss about ‘Human Resource Management’. Find paragraphs, long and short essays on ‘Human Resource Management’ especially written for school and college students.
- Essay on Human Resource Management
Essay Contents:
- Essay on the Functions of Human Resource Management

Essay # 1. Introduction to Human Resource Management :
Men, materials, machines and money are considered as the main factors of production. Out of all these factors, men are considered as an important factor. It is very difficult to handle the other factors of production without the efficient use of human resources.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Several terms have been used by various management thinkers to represent human resources. These include ‘personnel’, ‘people at work’, ‘manpower’, ‘staff’ and ’employees. Whatever may be the term used, human resource of any organization consists of all individuals engaged in any of the organizational activities at all levels.
The importance of human factor can be judged from the point that some people consider management and personnel/human resource management as one and the same thing. Lawrence A. Appley observed that “Management and personnel administration are one and the same. They should never be separated. Management is personnel administration”. Of all the tasks of management, managing the human component is the central and most important task, because all else depends on how well it is done.
With the increase in number of employees in an organization, greater emphasis is being placed on personnel management and also on the adoption of standardized procedures and compensation plans. The personnel department helps management in using and developing appropriate manpower to achieve organizational goals.
Human resource management is responsible for how people are treated in organizations. It is responsible for bringing people into the organization, helping them perform their work, compensating them for their labors, and solving problems that arise.
Essay # 2. Definition of Human Resource Management :
Human Resource Management (HRM) has come to be recognized as an inherent part of management, which is concerned with the human resources of an organization.
Some of the definitions of human resource management as given by various persons are:
Human Resource Management is the function within an organization that focuses on recruitment, management, and providing direction for the people who work in the organization.
Human Resource Management is the understanding and application of the policy and procedures that directly affect the people working within the project team and working group. These policies include recruitment, retention, reward, personal development, training and career development.
Human Resource Management is the effective use of human resources in order to enhance organizational performance.
Human Resource Management is the organizational function that deals with issues related to people such as compensation, hiring, performance management, organization development, safety, wellness, benefits, employee motivation, communication, administration, and training.
Essay # 3. Scope of Human Resource Management :
The scope of HRM is very wide.
It covers the following aspects:
(i) Personnel Aspect :
This is concerned with manpower planning, recruitment, selection, placement, transfer, promotion, training and development, layoff and retrenchment, remuneration, incentives, productivity etc.
(ii) Welfare Aspect :
It deals with working conditions and amenities such as canteens, creches, rest and lunch rooms, housing, transport, medical assistance, education, health and safety, recreation facilities, etc.
(iii) Industrial Relations Aspect :
This covers union-management relations, joint consultation, collective bargaining, grievance and disciplinary procedures, settlement of disputes, etc.
Essay # 4. Objectives of Human Resource Management :
Objectives are predetermined goals to which individual or group activity in an organization is directed. Objectives of human resource management are influenced by organizational objectives and individual goals.
Some of the objectives of HRM are:
a. To ensure effective utilization of human resources.
b. To ensure respect for human beings.
c. To identify and satisfy the needs of individuals.
d. To achieve and maintain high morale among employees.
e. To provide the organization with well-trained and well-motivated employees.
f. To increase to the fullest the employee’s job satisfaction and self-actualization.
g. To develop and maintain a quality of work life.
h. To provide better conditions of employment.
i. To develop overall personality of each employee in its multidimensional aspect.
j. To enhance employee’s capabilities to perform the present job.
k. To provide fair wages to employees.
l. To inculcate the sense of team spirit, team work and inter-team collaboration.
Essay # 5. Nature of Human Resource Management :
Human Resource Management is a process of bringing people and organizations together so that the goals of each are met.
The various features of HRM include:
a. It is pervasive in nature as it is present in all enterprises.
b. Its focus is on results rather than on rules.
c. It tries to help employees develop their potential fully.
d. It encourages employees to give their best to the organization.
e. It is all about people at work, both as individuals and groups.
f. It tries to put people on assigned jobs in order to produce good results.
g. It helps an organization meet its goals in the future by providing for competent and well- motivated employees.
h. It tries to build and maintain cordial relations between people working at various levels in the organization.
i. It is a multidisciplinary activity, utilizing knowledge and inputs drawn from psychology, economics, etc.
Essay # 6. Functions of Human Resource Management:
Every manager in an organization has to perform the personal functions in one form or the other in order to get the things done through others.
The functions of human resource management can be classified as:
(i) Managerial Functions.
(ii) Operative Functions.
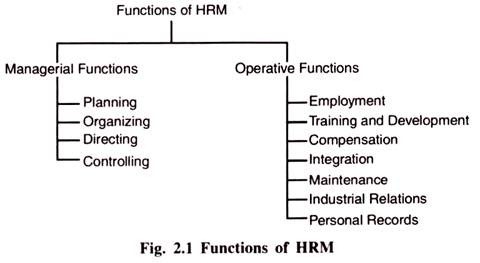
(i) Managerial Functions :
The managerial functions are mainly concerned with planning, organizing, directing and controlling the various activities of personnel management.
These functions are explained below:
(a) Planning:
Planning is deciding in advance what to do; how to do; where to do; and who is to do it. For personnel manager, planning means the determination in advance of personnel programme. Planning is concerned about present manpower positions, what number and kind of people are required for the organization.
(b) Organization:
After the establishment of organizational goals and objectives, human resource manager must design and develop organization structure to carry out the various operations. Organization involves identification and grouping the activities to be performed and dividing them among the individuals and creating authority and responsibility relationships among them.
(c) Directing:
Directing as a managerial function involves building sound industrial and human relations among people working in the organization. The direction function of the personnel manager is meant to motivate and guide the people to achieve organization goals. The employees can be motivated through salary administration, career planning, provision of health and safety requirements etc.
(d) Controlling:
Controlling function is concerned with regulation of activities in accordance with the personnel plans. It includes checking, verifying and comparing actual with the plans, identifying deviations if any and correcting them. Auditing, training programmers, analysing, labor turnover records, conducting separate interviews are some of the means for controlling the personnel management function.
(ii) Operative Functions :
Operative functions are those functions which are usually delegated to the human resource department as these require specialized skills and knowledge in their performance. All these operative functions are interacted by managerial functions. Further these functions are to be performed in conjunction with management functions.
Some of the operative functions of human resource management are:
(a) Employment :
It is the first operative function of HRM. Employment is concerned with securing and employing the people possessing required kind and level of human resources necessary to achieve the organizational objectives. It covers the functions such as job analysis, human resources planning, recruitment, selection, placement and induction.
(i) Job Analysis:
It is the process of study and collection of information relating to the operations and responsibilities of a specific job.
It includes:
i. Collection of data, information, facts and ideas relating to various aspects of jobs including men, machines and materials.
ii. Preparation of job description, job specification, job requirements and employee specification which help in identifying the nature, levels and quantum of human resources.
(ii) Human Resources Planning:
Human resource planning involves forecasting the human resource requirements of an organization and the future supply of human resources. It is a process for determination and assuring that the organization will have an adequate number of qualified persons, available at proper times, performing jobs which would meet the needs of the organization.
(iii) Recruitment:
It is the process of seeking and attracting prospective candidates against a vacancy in an organization.
After having determined the number of persons required for different jobs and requirements of different jobs, the recruitment process will begin.
The term recruitment may be defined as the process of searching the candidates for employment and stimulating them to apply for jobs in the organization. In other words, the term ‘recruitment’ stands for discovering the sources from where potential employees will be selected.
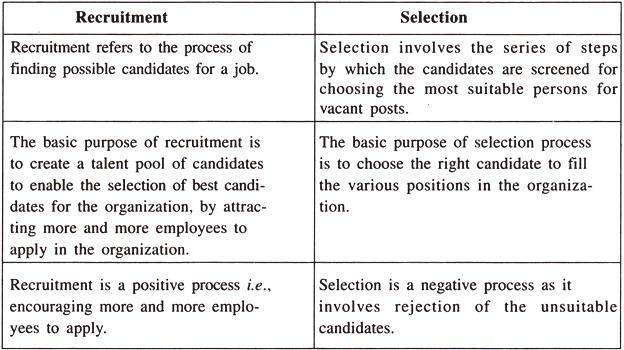
(iv) Selection:
Selection is the process of identifying and establishing the credentials of a candidate for a job to ensure success.
Recruitment vs. Selection :
Both recruitment and selection are the two phases of the employment process. Recruitment comes first and is followed by Selection.
(v) Induction and Orientation:
Induction and orientation are the techniques by which a new employee is rehabilitated in the changed surroundings and introduced to the practices, policies, purposes and people etc., of the organization.
(b) Training and Development :
This process aims to train and develop employees to improve and update their knowledge and skills, so as to help them perform their jobs better. The process also includes developing the attitudes, beliefs and values of the employees to match the organizational needs. This comprises of performance appraisal, training, management/executive development, career planning and development.
(i) Performance Appraisal:
It is the process of evaluating the performance of an employee on the job and developing a plan for improvement.
(ii) Training:
Training is the systematic development of the knowledge, skills and attitudes required to perform a job.
After the employee is selected, the most important part of human resource program is to impart training to the employee. Training plays a significant role in human resource development. Human resources are the life-blood of any organization. Only through trained and efficient employees, the organization can achieve its objectives.
Training is defined as “the art of increasing the knowledge and skill of an employee for doing a particular job”.
Since training involves time, effort and money by an organization, so an organization should carefully design its training program. The objectives and need for training should be clearly identified and the method or type of training should be chosen according to the needs and objectives established.
Need of Training:
Training is necessary both for existing and new employees. It increases the skill of the employees.
The need of training arises because of the following factors:
(a) Rapid Changes in Technology:
As the technology is changing at as fast pace, so employees must learn new techniques to make use of advanced technology.
(b) Frequent Accidents:
Due to increase in number of industrial accidents, an effective training program should be made for the safety of the employees.
(c) Quality Conscious Customers:
As the customers have become quality conscious, so there is need of training to employees for improving the quality of products.
(d) Increase in Productivity:
Effective training helps in increasing productivity and reduction in production costs of an organization.
(e) Supply of Trained Personnel:
Training ensures an efficient supply of trained employees at all levels of organization.
Benefits of Training :
Some of the benefits of training are:
a. Better performance of employees both in terms of quantity and quality of output.
b. Elimination of wastages which leads to reduction in cost of production.
c. Reduction in needs of supervision.
d. It helps in developing and improving the organizational culture.
e. Increase in morale of the employees.
f. Reduction in number of accidents.
g. Improvement in quality of work.
h. Reduction in machine breakdown and maintenance cost.
i. Increase in productivity which results in enhanced earnings for employees.
j. Increase in self-confidence.
k. More opportunity for growth/promotions.
(iii) Development:
It is the concept of developing the employees in an organization to meet future changes and challenges.
(iv) Career Planning and Development:
It refers to identifying one’s career goals and formulating plans of reaching them. It attempts to harmonize an individual’s career aspiration with organizational needs.
(c) Compensation :
Compensation function is concerned with securing adequate and equitable remuneration to persons for their contribution. Fixation of compensation or wage rates for different categories of employees is an important task of management. Function related to job evaluation, wage and salary administration, incentives, bonus and fringe benefits falls under this category.
Compensation is what employees receive in exchange for their contribution to the organization.
Generally, employees offer their service for three types of rewards:
b. Incentives.
c. Benefits.
Pay refers to the base wages and salaries employees normally receive. Incentives in the form of bonuses, commissions and profit sharing plans are incentives designed to encourage employees to produce results beyond normal expectations.
Benefits such as insurance, medical, recreational, retirement etc. represent a more indirect type of compensation.
So, the term compensation is a comprehensive one including pay, incentives, and benefits offered by employers for hiring the services of employees. In addition to these, managers have to observe legal formalities for offering physical as well as financial security to employees. All these play an important role in any HR department efforts to obtain, maintain and retain an effective workforce.
(i) Job Evaluation:
It is the systematic determination of the value of each job in relation to other jobs in the organization.
(ii) Wage and Salary Administration:
The process of formulating and operating a suitable wage and salary program is known as wage and salary administration.
(iii) Incentives:
Incentives are the rewards an employee earns in addition to regular salary based on his performance or of the collective performance.
(iv) Bonus:
Bonus is primarily a share in the surpluses and is often directly related to the organization performance.
(v) Fringe Benefits:
Fringe benefits are monetary and non-monetary benefits including disablement benefits, housing facilities, canteen facilities, conveyance facilities, educational facilities, recreational facilities, medical and welfare facilities, post-retirement benefits, etc.
(d) Integration :
The basic objective of human resource management is to secure maximum performance from the employees in order to accomplish the objectives of an organization. This is possible through better integration between the organization and its employees. The integration between the two can be achieved through three things-motivation, leadership and communication.
(e) Maintenance :
Maintenance function is basically concerned with the working conditions and welfare facilities provided to the employees. Morale and motivation of the employees is greatly influenced by these conditions. Working conditions include measures taken for health, safety and comfort of the employees. Welfare facilities include provisions of rest rooms, cafeteria, safe drinking water, education for children of employees etc.
(f) Industrial Relations :
It is the responsibility of human resource manager to maintain industrial peace in the organization. This can be done through collective bargaining, joint consultation and settlement of disputes, whenever they arise.
(g) Personnel Records :
Another function of human resource manager is to maintain the records of the employees. This is helpful in taking decisions relating to transfers and promotions, performance appraisal etc. These also help in identifying the weaknesses in the employees and the areas in which they need training.
Related Articles:
- Essay on Human Resource Management | HRM
- Essay on Merit Rating: Top 5 Essays | Human Resource Management
- Notes on Human Resource Management (HRM): Meaning and Nature
We use cookies
Privacy overview.
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |
11.1 An Introduction to Human Resource Management
- What has been the evolution of human resource management (HRM) over the years, and what is the current value it provides to an organization?
Human resource management over the years has served many purposes within an organization. From its earliest inception as a primarily compliance-type function, it has further expanded and evolved into its current state as a key driver of human capital development. In the book HR From the Outside In (Ulrich, Younger, Brockbank, Younger, 2012), the authors describe the evolution of HR work in “waves”. 1 Wave 1 focused on the administrative work of HR personnel, such as the terms and conditions of work, delivery of HR services, and regulatory compliance. This administrative side still exists in HR today, but it is often accomplished differently via technology and outsourcing solutions. The quality of HR services and HR’s credibility came from the ability to run administrative processes and solve administrative issues effectively. Wave 2 focused on the design of innovative HR practice areas such as compensation, learning, communication, and sourcing. The HR professionals in these practice areas began to interact and share with each other to build a consistent approach to human resource management. The HR credibility in Wave 2 came from the delivery of best-practice HR solutions.
Wave 3 HR, over the last 15–20 years or so, has focused on the integration of HR strategy with the overall business strategy. Human resources appropriately began to look at the business strategy to determine what HR priorities to work on and how to best use resources. HR began to be a true partner to the business, and the credibility of HR was dependent upon HR having a seat at the table when the business was having strategic discussions. In Wave 4, HR continues to be a partner to the business, but has also become a competitive practice for responding to external business conditions. HR looks outside their organizations to customers, investors, and communities to define success—in the form of customer share, investor confidence, and community reputation. HR’s credibility is thus defined in terms of its ability to support and drive these external metrics. Although each “wave” of HR’s evolution is important and must be managed effectively, it is the “outside in” perspective that allows the human resource management function to shine via the external reputation and successes of the organization.
Catching the Entrepreneurial Spirit
Human resources outsourcing—entrepreneurial ventures.
Human resources is a key function within any company, but not all companies are able to afford or justify full-time HR staff. Over the last decade, HR outsourcing has become a good business decision for many small companies whose current staff doesn’t have the bandwidth or expertise to take on the risks of employee relations issues, benefits and payroll, or HR compliance responsibilities. This has led many HR practitioners to try out their entrepreneurial skills in the areas of HR outsourcing and “fractional HR.”
Human resources outsourcing is very commonly used by smaller companies (and often large companies too) to cover such tasks as benefits and payroll management. This is an area that has been outsourced to third parties for many years. More recent is the trend to have “fractional HR” resources to help with the daily/weekly/monthly HR compliance, employee relations, and talent management issues that companies need to address. Fractional HR is a growing industry, and it has become the service offering of many entrepreneurial HR ventures. Fractional HR is essentially as it sounds—it is the offering of HR services to a company on a part-time or intermittent basis when the company may not be able to justify the cost of a full-time HR resource. An HR professional can be available onsite for a specified number of hours or days weekly or monthly, depending on the company’s needs and budget. The HR professional handles everything from HR compliance issues and training to employee issues support. Also, for companies that are keen on development of employees, the HR resource can drive the talent management processes—such as performance management, succession planning, training, and development—for companies who require more than just basic HR compliance services.
How does a business leader decide whether HR outsourcing is needed? There are generally two factors that drive a leader to consider fractional HR or HR outsourcing—time and risk. If a leader is spending too much time on HR issues and employee relations, he may decide that it is a smart tradeoff to outsource these tasks to a professional. In addition, the risk inherent in some HR issues can be very great, so the threat of having a lawsuit or feeling that the company is exposed can lead the company to seek help from a fractional HR professional.
HR entrepreneurs have taken full advantage of this important trend, which many say will likely continue as small companies grow and large companies decide to off-load HR work to third parties. Some HR companies offer fractional HR as part of their stated HR services, in addition to payroll and benefits support, compensation, and other HR programmatic support. Having a fractional HR resource in place will often illuminate the need for other HR services and program builds, which are generally supported by those same companies. Whether you are an individual HR practitioner or have a small company of HR practitioners and consultants, fractional HR and HR outsourcing can be a very viable and financially rewarding business model. It can also be very personally rewarding, as the HR professional enables smaller companies to grow and thrive, knowing that its HR compliance and processes are covered.
- What do you believe is contributing to the growth of the fractional HR and HR outsourcing trend? Do you expect this trend to continue?
- At what point should a company consider bringing on a full-time HR resource instead of using a fractional HR resource? What questions should the company ask itself?
Human resource management provides value to an organization, to a large extent, via its management of the overall employee life cycle that employees follow—from hiring and onboarding, to performance management and talent development, all the way through to transitions such as job change and promotion, to retirement and exit. Human capital is a key competitive advantage to companies, and those who utilize their human resource partners effectively to drive their human capital strategy will reap the benefits.
Human resource management includes the leadership and facilitation of the following key life cycle process areas:
- Human resources compliance
- Employee selection, hiring, and onboarding
- Performance management
- Compensation rewards and benefits
- Talent development and succession planning
Human resources is responsible for driving the strategy and policies in these areas to be in accordance with and in support of the overall business strategy. Each of these areas provides a key benefit to the organization and impacts the organization’s value proposition to its employees.
Concept Check
- How has the function of human resource management evolved over the years?
- In what way do you usually interact with human resources?
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/principles-management/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: David S. Bright, Anastasia H. Cortes
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Principles of Management
- Publication date: Mar 20, 2019
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/principles-management/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/principles-management/pages/11-1-an-introduction-to-human-resource-management
© Jan 9, 2024 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.
Strategic Human Resource Management (SHRM) Essay
- To find inspiration for your paper and overcome writer’s block
- As a source of information (ensure proper referencing)
- As a template for you assignment
Stakeholders in SHRM
How stakeholders evaluate effectiveness of shrm practice.
Modern business environment dictates that organizations need to employ effective strategies in their operations for assurance of success, survival, and growth. There are many changes taking place in the environment in which organizations operate. Therefore, organizations need to take adapt to those changes and equip themselves well with adequate ‘tools’ to help such organizations win and realize growth.
Strategic human resource management (SHRM) is a concept that has evolved to define modern organizations within perspectives of strategic planning. This research paper constitutes the goal of defining the concept, exploring it with regard to key stakeholders, and subsequently, assessing how SHRM goals can be evaluated effectively. Such information will be important especially to organizations in the process of working out their SHRM policies.
There are increasing levels of uncertainty coupled with intensification of competition that have combined to force organizations to put more emphasis on developing key core competencies (Yuksel, 2011). The development of these key competencies is seen to aim at increasing the competitive advantage of organizations in the dynamic environments.
Prahalad and Hamel (1994) observed that those organizations that possess unique and non-substitutable resources and competencies competitor organizations do not have, exhibit high chances of realizing sustainable advantage (cited in Yuksel, 2011). An organization’s competitive core competences and capabilities can be obtained from numerous sources.
Such sources include possessing effective technology, enhancing organizational learning, and encouraging strategic flexibility and innovative capacity found among the human resources (Yuksel, 2011). As a result, it can be deduced that effective creation, organization, and leverage of knowledge throughout the organizations are becoming increasingly the main sources of competitive advantage in fast changing, information-driven economy.
Boxall and Purcell (2003) contend that almost all organizations have strategies since it is the duty of organizations’ managers and employees to design and implement strategic choices for their organization to function on in achieving goals (Ojo, 2011). Known as strategic choices, organizations are forced to create and implement sustaining strategic choices that become vital in dealing with strategic problems and challenges within the organization.
In this way, a strategy may be developed and implemented by a particular company either to maintain viability of the organization or to produce sustained advantaged within the organization in dealing with the external environment (Ojo, 2011). In creating these strategies, the aspect of human resource has become important and research indicates that human resource practices play and influence the direction and shape of any particular strategy of an organization (Ojo, 2011).
Strategies represent an organization’s capacity to compete with other organizations successfully in the dynamic environment of business world. The aim of such strategy is to see an organization succeed and realize its goals while at the same time being able to survive and realize meaningful growth (Mathis and Jackson, 2010). Realizing and accepting this to be important and vital to the organization, modern-day organizations are characterized by formation of strategic plans.
In simple view, strategic plans are designed on the aim of utilizing the organization’s available resources in such a way that the organization is able to outperform its main competitors in the industry (Mathis and Jackson, 2010). Wheelen and Hunger (1995) provides a definition of strategic planning/management as “that set of managerial decisions and actions that determines the long-run performance of a corporation” (Bratton and Gold, 2001, p.39).
Given that in strategic planning there is long-term consideration, the concept can be taken to constitute all activities that have ‘vision of the future’ and at same time are updated constantly on both internal and the external environment (Bratton and Gold, 2001).
As a long as the operations and activities of an organization have to continue with an indefinite time, strategic management should constitute a continuous activity that an organization’s management team undertake. Moreover, as the process takes place, the management should encourage some forms of adjustments but all ingrained within the aspects of: management, environment, and the available resources (Bratton and Gold, 2001).
Strategic planning depends and gets enormous input from possessing the right human resource in the organization. The right human resource to be utilized in the strategic planning process may be present or the organization may need to outsource them from outside.
This entire process has resulted to what is known as strategic human resource (SHRM) in many organizations. SHRM has being described as the process that “entails providing input into organizational strategic planning and developing specific human resource initiatives to help achieve the organizational goals” (Mathis and Jackson, 2010, p.38).
Michael Armstrong, writing in a book titled ‘Strategic Human Resource Management: Guide to Action’ defines SHRM in the perspectives of organization’s strategic planning (Armstrong, 2008). According to the author, SHRM entails “an approach to the development and implementation of human resource strategies that are integrated with business strategies and enable the organization to achieve its goals” (Armstrong, 2008, p.1).
According to this definition, SHRM is a long-term process that largely succeeds on evaluating organization’s strategies and human resource strategies and how well the two categories of strategies can be merged to achieve organization goals.
SHRM as a concept cannot be divorced from the overall strategy that an organization envisions to undertake. In this way, SHRM is seen to be intertwined to the strategic objectives of an organization. Due to this, strategic human resource management has to emphasize the need for human resource plans and strategies to be formulated within the context of overall organizational strategies and objectives that are further, responsive to the changing nature of the organization’s external environment (Ojo, 2011).
This line of understanding leads to Wright and McMahan (1992) define SHRM as “the pattern of planned human resource deployments and activities intended to enable the firm to achieve its goals” (Ojo, 2011).
As such, the role of SHRM is seen to constitute all aspects that contribute to organizational performance in achieving organizational goals and objectives. The themes of SHRM have been categorized into three: process of integration all human resource key practices into a comprehensive and functional unit; an aspect of incorporating and utilizing broad organizational goals; and lastly, responding to the external environment in the most strategic and effective way (Ojo, 2011).
In this way, SHRM can be described as a comprehensive framework of human resource that constitute process of evaluating the impacts of external and internal environments and instituting the appropriate human resource measures in terms of strategy to enable sustainable adaptation of the organization.
Organization functions and carries out its activities dependent on goodwill of its stakeholders. Multiple stakeholders of an organization exist and their role in the organization defines the success, growth, and sustainability of the organization. Some of notable organizational stakeholders include the investors, organization itself, in terms of management team, employees, customers and suppliers (Schuler and Jackson, 2007).
Each of these stakeholders affects and influences an organization in one way or the other. Human resource practices have been identified to affect all these stakeholders either directly or indirectly (Schuler and Jackson, 2007). As a result, strategic planning in the organization has the ability to impact the stakeholders differently. In turn, the stakeholder may undertake initiatives of evaluating the different human resource practices in accordance to their outcome.
SHRM builds on the need to create human resource strategies that exhibit capacity to satisfy multiple stakeholders of the organization. In this way, there is always need to create SHRM practices and strategies that address the concerns of key stakeholders in the organization (Schuler and Jackson, 2007).
Investors constitute the first category of organizational stakeholders. Investors constitute all groups of people who have channeled their resources into the organization with intend of realizing positive returns on those resources. Positive returns generally come in form of profits and dividends that investors enjoy.
As a result, introduction of SHRM practices in an organization usually has the blessing of investors since it is viewed to change the current operations in the organization and improve financial performance of the organization. Organization’s employees constitute another category of stakeholders of an organization (Deckop and Deckop, 2006).
Numerous researches have been carried out on the implication of various human resource practices on employees in different organizations (Deckop and Deckop, 2006). Human resource practices that may impact employees include recruitment and selection, training and development and performance management (Deckop and Deckop, 2006).
The aim of the research on these practices has been to evaluate the impact of the practices on individual outcomes. At the same time, more research has been done on the impact of practices on employee outcome such as on job satisfaction, motivation, socialization and career success (Deckop and Deckop, 2006).
Therefore, introduction of strategies of human resource management in most cases impact employees to great length. The third type of organizational stakeholder is the consumer, usually known as product-market stakeholder (Deckop and Deckop, 2006). Activities of any organization always aim at achieving customer satisfaction with regard to organization’s products or services (Deckop and Deckop, 2006).
As a result, customer satisfaction is seen as a mediating variable between human resource practices and business performance. In introducing SHRM practices an organization aims at changing the dimension of work climate that in turn lead to customer satisfaction through customer orientation, quality emphasis, teamwork, cooperation, and involvement of customers in product designs (Deckop and Deckop, 2006).
Evaluation of SHRM practices in an organization has to consider the impact of the SHRM system on all of the organization’s multiple stakeholders (Schuler and Jackson, 2007). Creating SHRM practices aims at introducing changes in the manner activities are performed in the organization. As a result effectiveness of such practices and systems are measured on objectives such as improvement in productivity, improvement in profitability, and the ability of the organization to sustain in the future (Schuler and Jackson, 2007).
On the part of employees, effectiveness of SHRM practices normally depends on total quality of the practices on the work within the organization, the innovativeness of the practices in contributing to realization of goals in the organization, ability of the practices to contribute to job satisfaction, enhancement, and enrichment (Schuler and Jackson, 2007). At the same time, employees have been regard as key resources of an organization in ensuring the success of any SHRM system.
In this way, the effectiveness of SHRM can be evaluated on the level of commitment and engagement by employees and overall satisfaction of employees (Schuler and Jackson, 2007). On the part of customers, evaluation of SHRM system put into consideration aspects such as quality and variety of products introduced in the market, the prices at which the products are being sold and overall services that accompany the products (Schuler and Jackson, 2007).
Human resource being one of the core components of an organization has to be re-organized and re-aligned to the new developments taking place. Re-organization and re-alignment in the modern world cannot take place within traditional and usual frameworks of human resource management.
Today there is need for strategic planning solutions that can guarantee organizations success. As a result, strategic human resource management (SHRM) is a concept that defines modern organizations that aim to realize organizational goals and objectives through strategic planning of its human resource. Introduction of SHRM systems in an organization is a path that sees ability of an organization to effectively compete in the dynamic environment and sustainability while remaining focused to the goals and objectives of stakeholders.
Armstrong, M. (2008). Strategic Human Resource Management: A Guide to Action . PA: Kogan Page Publishers. Web.
Bratton, J. and Gold, J. (2001). Human resource management: theory and practice . NY: Routledge. Web.
Deckop, J. R. and Deckop, J. R. (2006). Human resource management ethics . NY: Information Age Publishing. Web.
Mathis, R. L. and Jackson, J. H. (2010). Human Resource Management . OH: Cengage Learning. Web.
Ojo, O. (2011). “Impact of strategic human resource practice on corporate performance in selected Nigerian banks.” Journal of Ege Akademik Bakis, Vol. 11, No. 3, p.339. Web.
Schuler, R. S. and Jackson, S. E. (2007). Strategic human resource management . MA: Wiley-Blackwell. Web.
Yuksel, M. (2011). “Core competencies of managers in an emerging market”. Journal of American Academy of Business, Vol. 17, No. 1, p.104. Web.
- Problems Facing in Common Wealth Bank of Australia
- Entrepreneurship Concept and Techniques
- Strategic Human Resource Management Enhances Organizational Performance in Both Good and Bad Economic Times
- An Analysis of Tarmac Group Limited
- The Features of Strategic Human Resource Management
- Strategic management at JB Hi-Fi
- The roles and functions of a supervisor
- The Relationship Between Self-Efficacy and Perceived Stress
- Contemporary Issues in Human Resource
- California Office of Emergency Services
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2018, December 27). Strategic Human Resource Management (SHRM). https://ivypanda.com/essays/strategic-human-resource-management-shrm/
"Strategic Human Resource Management (SHRM)." IvyPanda , 27 Dec. 2018, ivypanda.com/essays/strategic-human-resource-management-shrm/.
IvyPanda . (2018) 'Strategic Human Resource Management (SHRM)'. 27 December.
IvyPanda . 2018. "Strategic Human Resource Management (SHRM)." December 27, 2018. https://ivypanda.com/essays/strategic-human-resource-management-shrm/.
1. IvyPanda . "Strategic Human Resource Management (SHRM)." December 27, 2018. https://ivypanda.com/essays/strategic-human-resource-management-shrm/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Strategic Human Resource Management (SHRM)." December 27, 2018. https://ivypanda.com/essays/strategic-human-resource-management-shrm/.

ESSAY SAUCE
FOR STUDENTS : ALL THE INGREDIENTS OF A GOOD ESSAY
Essay: The importance of human resources management (HRM)
Essay details and download:.
- Subject area(s): Management essays
- Reading time: 8 minutes
- Price: Free download
- Published: 21 February 2021*
- Last Modified: 2 August 2024
- File format: Text
- Words: 2,325 (approx)
- Number of pages: 10 (approx)
- Tags: Human resource management essays
Text preview of this essay:
This page of the essay has 2,325 words. Download the full version above.
Introduction
Organizations are made of among others, human resources (HR) which is the most valuable asset in today’s dynamic world. Indeed, it is people and not organizations that constitute an organization. Achievement of organization’s objectives depends on the individually and collective efforts put in by its work force. Human resources management (HRM) may be defined as the coherent as well as strategic maximization of human resources capital in an organization towards making a return on that investment ( Gold & Bratton, 2001 ).
The practice, in its efforts, effectively attempts to maintain a ‘fit’ between the employees and the organization’s overall strategic direction. Unlike technology and processes, people have a soul, aspirations, feelings and emotions. As such, the concept of people as an asset, do not indicate perceiving them as commodities. In managing people, the manager must practice disciplines based on psychology, sociology, industrial relations as well as industrial engineering and economics. In achieving an organization’s objectives, it is possible to adjust the technology employed by increasing production speed as well as reducing the machines’ downtime. For a person, who has a soul, ability to reason and act in response, it is hard to alter the person’s working speed as well as the duration. Proper management of human resources leads to a motivated workforce, a development to loyalty and an assurance of survival and success of an organization.
This paper pays a close look at the practice management of human resources in an organization. This will encompass the importance of the practice, functions within this office and some of the motivation techniques that can be used as well as their role in achieving organizational objectives. Furthermore, the paper will focus an attention to a reputable organization in determining the applicability of incentives and compensation in HRM. Every organization has its strategic future which is broken down into objectives that are measurable and comprehensible, so that the workforce can implement ( Snell & Bohlander, 2009 ). The sensitivity and value placed on organizational strategic plan cannot be left in the hands its employees if they are incapable or not motivated. The organization has a responsibility not only to invest heavily in technology and detailed professional processes but also on its workforce and strategic management policies.
Importance of HRM
HRM as a practice significantly offers support and advice to the line management within an organization. Management of human resources must ensure an attraction, preservation, loyalty and development of highly profiled caliber of people/workforce in order to provide a competitive advantage necessary for the survival and success of the organization. The image of an organization, which develops the goodwill, is largely dependent on how well its human resources are managed (McCoy, 1999). The management of the human resources assumes the following roles. First, HRM manages the demand for human resources. Economies in which organizations are based are dynamic. There are economical shifts of growth and decline that require counteractive measures within an organizations workforce. The said measures demands both quantitative and qualitative procedures within the workforce. The practices of retrenchments, hiring, early retirements and the contract renews for the experienced are all structural adjustments that responds to economical changes affecting organizations.
Second, HRM is responsible in managing social pressure in provision of the desirable environment for the workforce. The hygiene and safety of the working environment must be always maintained as it is a motivation factor in employees’ performance. The provision of appropriate protective gear while working, pollution free environment and other working conditions is a paramount concern for the HRM office Berger, 2008). Third, HRM is important in managing political pressure usually generated by calls to hire from local labor market irrespective of the resultant factors of cost and knowledge/skills. Though it is ethical to hire from the contextual economy, political pressure should not compromise the quality and quantity of organization’s production and a resulting failure in achieving the organization objectives.
HRM also manages the technology by hiring the right workforce or alternatively developing/training the existing workforce in response to technological change. Changes in technology can contribute to obsolescence of the working force which would spill over to the organization not achieving its objectives (Jackson, 2007). HRM office must always find the most appropriate method of counteracting a technological shift by either hiring people with the needed expertise or by training the existing one. In developing an organization culture the later would be more appropriate. If the earlier alternative is adopted, the competition pressure in compensation must be properly dealt with. HRM is also important in designing and management of strategic HR planning. Strategic HR planning is the informed projection of the organizations needs for the appropriate employees, both in quantity and quality, and balancing off this with the organizations ability to sustainably meet the demands of those employees for a substantial period of time in the future. As such, the budgetary constraints associated with right hiring are checked. HRM needs to make these projections in agreement with the line/functional management’s assumptions.
It is also the responsibility of HRM to initiate, alter and manage job design. Job design is the arrangement/rearrangement of work that is aimed at checking or overcoming employee’s job dissatisfaction and alienation resulting from repetitive tasks. In curbing this state, the HRM office should conduct job enrichment, job rotation, job enlargement and job simplification exercises. All these procedures are aimed at raising productivity levels which is the ultimate goal of the HRM’s office. In cases of mergers and acquisitions, it is the sole responsibility of the HRM’s office to rationalize, orient and harmonize the human resources in the involved organizations. The fundamental issues behind mergers and acquisitions are, more often than not, undesirable and unwelcome by employees ( Bilsberry, 2005 ). The task of making an otherwise unpleasant issue acceptable lies squarely at the HRM’s office. Moreover, since work environments are different across organizations, the HRM must orient the various workforces involved to the new objectives and/ or organizational culture.
Finally, the HRM is responsible in managing implementation of change. Change may be in terms of process, organizational structure, systems and culture among others. Changes are the inevitable twists that affect the normal and known paths through which an organization operates. Some of the aforementioned twists arise internally from the organization’s need to achieve new status. Others are externally experienced due to the shifts in the business environment. The issues aforementioned under the discussion are achieved through the functions of the HRM office.
Functions of HRM
Generally, HRM management can be subdivided into three interlinked phases. The practice functions include recruiting qualified human resources, managing the employees in the working environment as well as preparing and enforcing exit of the employees from the organization. The process of recruiting employees arises from the organization’s need to properly position itself in the economy. Ideally, recruitment should follow an order closest to; vacancy advertisement, selection of potential candidates, interviewing and contracting the successful candidate(s). Once in the organization, new employees are inducted and trained. It is during work performance that issues such as motivation, compensation development, disciplinary actions, performance appraisals, career planning / development, counseling, talent management , safety management and staff communication are conducted (Gold & Bratton, 2001).
The employees continuously offer their service to the organization under the existing HRM measures until they exit. Exit may result from retrenchment, obsolescence, retiring, resignation or termination of employment. The HRM at this phase has a responsibility to counsel and prepare the exiting employee for the challenges and opportunities awaiting the employee in the future. The office should ethically hand over all the legal documents and benefits to the exiting employee for positive development of the organization’s goodwill/reputation in the corporate world. If need be, the HRM should have a succession plan for implementation at this phase. Motivation as a HRM activity can completely change the perception of employees while in the work environment. Different people in the workforce are motivated differently across and longitudinally with time. Compensation and incentive is a major motivation element that is easily applicable in many organizations since, almost every employee joins an organization with a sole/major purpose of earning.
Compensation and incentives HRM
An incentive can be defined as any factor, that can be financial or non financial that accounts for preference or stimulates/enables a specific course of action. It can as well be said to be the bonus paid on successful achievement of performance objectives. Compensation is the art of offering/giving money or something else, which can easily convert to money, for purposes of paying for work done. In general, compensation and incentive can be referred to a compensation package. A compensation package is the value placed on an employee as presented to that employee. Compensation can be categorized into three categories. First, there is non monetary compensation. This is the benefit received by an employee which cannot be tangibly valued. Such can include social and career rewards. Job security, recognition, opportunity for growth, flexible working hours, subsidized housing, magazine subscription, laundry services, elder care, are some of the non-monetary compensations (Berger, 2008). Second, compensation can be direct which is the employee’s base wage/salary expressed as salary or hourly wage as profit sharing bonuses paid based on performance. Finally, compensation can be indirect. The later includes facilities like health insurance, paid leave, moving expenses and child care being provided by the employer.
There is a corporate general consensus insisting on relating pay with performance for effectiveness. This may not necessarily be applicable in sectors such as agriculture where many performance results are dependent on factors beyond organization and employee control. Whichever the compensation used, it should also be fair with the market and not discriminating against some employees (Campbell, 2006). A job evaluation should be conducted in placing a value on employee. In such an evaluation, compensable factors such as experience, education level and job responsibility should be considered. Moreover, employees should be involved when considering their indirect compensation needs such as paid vacation, retirement planning, childcare among others. The HRM officer should regularly review the compensation package from time to time to maintain its fairness, equitability and competitiveness.
Importance of compensation and incentives in HRM practice
Use of compensation and incentives is an importance practice in HRM as it has the following advantages. First, to many employees, the basic purpose for joining an organization is to secure a pay. The value placed in such a pay and not necessarily the amount/size motivates the employees more, and as result higher productivity levels are reported. Second, compensation facilitates hiring, retention, promotion and evaluation of the workforce. Without mentioning aspects of compensation, the HRM office might find it impossible to convince people to join the organization to work or even the existing employees to assume higher responsibilities (Armstrong, 2006). Third, compensation displays legality of a contract/employment. For a contract to be valid there has to be a consideration, which is partly what a pay or remuneration package serves. Compensation, especially bonuses, which practice sharing of profits with the employees, creates a sense of belonging to the employees. This is extremely important in securing employees’ loyalty during hard times in managerial practices.
In addition, compensation assists in valuing an organization as well as determining its future. Once the HRM office is capable of properly remunerating workforce, the employees are almost assured of their organization’s survival. Usually, when an organization is going under receivership, employees are the first victim as there is reduced employee compensation, which may in acute scenarios deny them their basic livelihood. Finally, compensation and incentives are the easiest motivational practices available for use by the HRM. This is because compensation is directly linked to employee’s welfare more than the improvement of working conditions (McCoy, 1999).
HRM at Coca Cola Company
Coca Cola Company is one of the leading beverage production companies. The firm that traces back its existence in 1886 ascribes to the philosophy that, it is people and not technology creates an effective organization. Employees are regarded as assets and as such their health and benefits are highly considered. Benefits compensations and benefits given at Coca cola company include a basic pay, medical facility, bonuses, picking and dropping of employees to and fro work station, gratuity fund as well as social security. The company has never performed downsizing exercise during its existence which displays a good relationship between the company and the employees (Berger, 2008). The company also practices an open door policy. Open door policy provides an opportunity for feedback from employees and vice versa. Compensation package review is objectively done from the annual performance evaluations. At the beginning of every year, HRM office communicates the objectives of the company and reviews their achievement at the end of the same period. The training policy for employees is well established to ensure that employees do not become obsolete. For example, new employees get a three month paid training while existing employees get a full free on new technology before they can use it. Training of employees is a non tangible compensation that assures employees of their job security.
As drawn from the evaluation above, effective management on human resources requires both scientific and a human relations approaches. The emphasis is both goal oriented as well as human welfare oriented. Any successful organization must invest sufficiently on HRM aspect failure to which the wrong organization culture will be developed. In order to effectively invest on the human resources modern firms ought to institute humane employee relations policies, reviews on package offered, appraise performance regularly, build motivation-oriented culture and possibly institute open channels to assist in participative management practices where employees are deliberately engaged during decision procedures. Conclusively, HR practices are crucial for organizational general performances levels and any move to drive the firms towards higher goals ought to be premised on attainable HR strategic goals. As evidenced, strategic policies crafts a decisive goals’ path for firm’s benefit whilst building effective workforce team.
...(download the rest of the essay above)
Discover more:
- Human resource management essays
Recommended for you
- Human resource management: vauxhall motors ltd
- How to Develop & Deliver HR Strategy to Support a Strategic Plan
- The advantages of implementing IT for Human Resource Functions
About this essay:
If you use part of this page in your own work, you need to provide a citation, as follows:
Essay Sauce, The importance of human resources management (HRM) . Available from:<https://www.essaysauce.com/management-essays/the-importance-of-human-resources-management-hrm/> [Accessed 03-08-24].
These Management essays have been submitted to us by students in order to help you with your studies.
* This essay may have been previously published on Essay.uk.com at an earlier date.
Essay Categories:
- Accounting essays
- Architecture essays
- Business essays
- Computer science essays
- Criminology essays
- Economics essays
- Education essays
- Engineering essays
- English language essays
- Environmental studies essays
- Essay examples
- Finance essays
- Geography essays
- Health essays
- History essays
- Hospitality and tourism essays
- Human rights essays
- Information technology essays
- International relations
- Leadership essays
- Linguistics essays
- Literature essays
- Management essays
- Marketing essays
- Mathematics essays
- Media essays
- Medicine essays
- Military essays
- Miscellaneous essays
- Music Essays
- Nursing essays
- Philosophy essays
- Photography and arts essays
- Politics essays
- Project management essays
- Psychology essays
- Religious studies and theology essays
- Sample essays
- Science essays
- Social work essays
- Sociology essays
- Sports essays
- Types of essay
- Zoology essays

Essay on Human Resources
Students are often asked to write an essay on Human Resources in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Human Resources
Understanding human resources.
Human Resources (HR) is a department in organizations that manages people. They handle hiring, training, and employee benefits. HR plays a crucial role in building a positive workplace culture.
Roles of HR
The HR team recruits new employees and trains them. They also develop policies for a comfortable work environment. HR ensures employees are treated fairly and respectfully.
Importance of HR
HR is important because they help to maintain harmony in a company. They resolve conflicts and promote employee well-being. Therefore, HR is vital for a successful organization.
250 Words Essay on Human Resources
Introduction.
Human Resources (HR) is a multifaceted discipline that lies at the heart of any organization. It encompasses the management of people within an organization, focusing on policies, systems, and practices that influence employee behavior, attitudes, and performance.

The Evolution of HR
Key functions of hr.
HR is responsible for a wide range of functions. These include recruitment and selection, training and development, performance management, employee relations, and compensation and benefits. Each function plays a crucial role in managing the organization’s human capital.
HR and Organizational Performance
Effective HR management can significantly impact an organization’s performance. By ensuring that the right people are in the right jobs, providing opportunities for growth and development, and fostering a positive work environment, HR contributes to increased productivity and profitability.
In conclusion, HR is an indispensable part of any organization. Its role has evolved from a purely administrative function to a strategic one, influencing every aspect of an organization’s operations. As businesses continue to evolve in a rapidly changing world, the role of HR is likely to become even more critical.
500 Words Essay on Human Resources
The evolution and importance of human resources.
The concept of Human Resources (HR) has significantly evolved over the years. Initially, businesses viewed employees merely as tools for production, but today, they are recognized as the most valuable asset of an organization. The HR department plays a pivotal role in managing these assets, ensuring that both their welfare and the company’s strategic goals are harmoniously aligned.
The Role of Human Resources
The primary role of the HR department is to manage people, which includes tasks like hiring, training, evaluating, and retaining employees. They are also responsible for ensuring a safe and healthy work environment, addressing employee grievances, and fostering a positive work culture. Moreover, HR professionals work towards aligning the workforce with the company’s strategic goals, thereby driving organizational success.
HR and Organizational Strategy
The changing landscape of human resources.
The HR landscape is continuously evolving, driven by factors such as technological advancements, changing demographics, and globalization. For instance, the advent of HR technology has revolutionized HR practices. Tools like HRIS (Human Resource Information Systems) and ATS (Applicant Tracking Systems) have automated routine tasks, thereby allowing HR professionals to focus more on strategic activities. Moreover, the rise of remote work and diversity in the workforce has necessitated the development of new HR policies and practices.
Challenges Faced by HR Professionals
Despite the significant strides made in the HR field, HR professionals face numerous challenges. These include managing a diverse workforce, dealing with the changing nature of work, ensuring employee engagement and well-being, and navigating the legal and ethical issues related to HRM. Additionally, in an era of rapid technological change, HR professionals must continually update their skills and knowledge.
Future of Human Resources
In conclusion, the HR department plays a crucial role in managing the most valuable asset of an organization – its people. By aligning the workforce with the company’s strategic goals, fostering a positive work culture, and adapting to the changing business environment, HR professionals can drive organizational success.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Home — Essay Samples — Business — Human Resources — The Intricacies of on Human Resource Management
The Intricacies of on Human Resource Management
- Categories: Employee Engagement Human Resources
About this sample

Words: 529 |
Updated: 29 March, 2024
Words: 529 | Page: 1 | 3 min read

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Verified writer
- Expert in: Business

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
4 pages / 1615 words
6 pages / 2749 words
7 pages / 2980 words
1 pages / 369 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online

Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Human Resources
Human Resource (HR) is a critical aspect of organizational management, playing a pivotal role in shaping the culture, performance, and success of businesses. This essay aims to explore the definition, functions, and importance [...]
Human resources are a crucial component of the tourism industry. Without well-trained and motivated employees, businesses in the travel and hospitality sectors would fail to attract and retain customers, resulting in lost [...]
Employee self-ealuation is a process where employees assess their own performance and prode feedback to their supersors. The purpose of self-ealuation is to promote self-reflection, self-awareness, and professional growth. It is [...]
Compensation is a critical component of an organization's overall strategy for attracting, retaining, and motivating employees. Two primary forms of compensation are intrinsic and extrinsic. Intrinsic compensation refers to the [...]
Development of human resources is very essential for any organisation that would like to be a dynamic and growth-oriented. Unlike other resources, human resources have unlimited potential capabilities. The potential can be used [...]
The major problem at Pak Sweets is running a factory with different ethnicities that have continually resulted to conflicts. The ethnic conflicts at the Pak Sweets factory have escalated into riots, which have led to damage of [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
Employee Perception of HR Practices and Its Impact on Job Satisfaction
- Conference paper
- First Online: 01 August 2024
- Cite this conference paper

- D. Bindhu ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-3714-3331 11 ,
- V. A. Namreen Asif ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-8533-4488 12 ,
- Sanath Bhaskar Baikadi ORCID: orcid.org/0009-0009-1390-5996 11 ,
- Chethanraj ORCID: orcid.org/0009-0007-0069-4208 12 ,
- Nanditha Sunil ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-1542-9881 11 ,
- Chandravathi ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-1067-5389 13 &
- Neil Gladwin Dlima ORCID: orcid.org/0009-0008-3597-1831 12
Part of the book series: Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems ((LNNS,volume 1083))
Included in the following conference series:
- International Conference on Business and Technology
In today’s business world, HR practices are crucial in shaping employee experiences and organizational success. This study focuses on understanding how employees perceive workplace regulations and how it impacts their overall job satisfaction. Job satisfaction is important because it directly influences the effort and concentration employees put into their work. Our findings indicate that factors like compensation and benefits policies, career growth and development opportunities, and health and well-being initiatives have a significant impact on job satisfaction. This study stands out in the field of HR practices literature as it aims to analyse how employee perception of HR practices impacts job satisfaction. The study focuses on employees in public sector companies. To examine the mediating effect of educational qualification on employee perception and job satisfaction, regression, and SOBEL tests were used. The findings reveal that various aspects of HR practices have a positive influence on job satisfaction. These findings emphasize the significance of HR practices in shaping employee perceptions and attitudes, ultimately impacting job satisfaction.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
Subscribe and save.
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or eBook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Shrivastava, A., Purang, P.: Employee perceptions of performance appraisals: a comparative study on Indian banks. The Int. J. Human Resou. Manage. 22 (3), 632–647 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1080/09585192.2011.543639
Article Google Scholar
Agus Sugiarto, Andrian Dolfriandra Huruta: Antecedents of green creativity: the mediating role of employee green commitment and employee job satisfaction. Cogent Business & Management 10 (2), 1–28 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1080/23311975.2023.2222491
Bhargava, A., Bester, M., Bolton, L.: Employees’ Perceptions of the Implementation of Robotics, Artificial Intelligence, and Automation (RAIA) on Job Satisfaction, Job Security, and Employability. J. technol. behav. sci. 6 (1), 106–113 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41347-020-00153-8
Bryson, A., Freeman, R.B.: Employee perceptions of working conditions and the desire for worker representation in Britain and the US. J Labor Res. 34 (1), 1–29 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12122-012-9152-y
Canet-Giner, T., Redondo-Cano, A., Saorín-Iborra, C., Escribá-Carda, N.: Impact of the perception of performance appraisal practices on individual innovative behavior. Eur. J. Manag. Bus. Econ. 29 (3), 277–296 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1108/EJMBE-01-2019-0018
Das, S.K., Azmi, F.T., James, P.S.: Factors influencing employees’ perception of human resource practice: a fuzzy interpretive structural modeling approach. Jindal J. Bus. Res. 9 (1), 41–55 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1177/2278682120908557
Edwards, A.V., Marcus, S.: Employee perceptions of well-being programs. J. Soc. Behav. Heal. Sci. 12 (1), 100–113 (2018). https://doi.org/10.5590/JSBHS.2018.12.1.07
Ehnert, I.P.: Sustainable Human Resource Management: A Conceptual and Exploratory Analysis from a Paradox Perspective. Physical Verlag, Bremen, Germany (2009). https://doi.org/10.3390/su122310216
Gupta, A., Chadha, A., Tiwari, V., et al.: Sustainable training practices: predicting job satisfaction and employee behaviour using machine learning techniques. Asian Bus Manage 22 , 1913–1936 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1057/s41291-023-00234-5
Ganapathy, D., Deepak, S.: A study on reskilling and networking on linkedin on employee recruitment success and career advancement. In: Aloysius Edward, J., Jaheer Mukthar, K.P., Asis, E.R., Sivasubramanian, K. (eds.) Current Trends in Economics, Business and Sustainability. ICEBS 2023. Contributions to Environmental Sciences & Innovative Business Technology. Springer, Singapore (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-3366-2_29
George, R., Krishnakumar, S.: Significance of employee engagement and succession planning on organizational development. In: Aloysius Edward, J., Jaheer Mukthar, K.P., Asis, E.R., Sivasubramanian, K. (eds.) Current Trends in Economics, Business and Sustainability. ICEBS 2023. Contributions to Environmental Sciences & Innovative Business Technology. Springer, Singapore (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-3366-2_35
Cleveland, J.N., Hunter, S., Darcy, C., Grady, G.: Employee work–life balance outcomes in Ireland: a multilevel investigation of supervisory support and perceived organizational support. The Int. J. Human Reso. Manage. 24 (6), 1257–1276 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1080/09585192.2012.709189
Lopez-Fernández, M., Romero-Fernández, P.M., Aust, I.: Socially responsible human resource management and employee perception: the influence of manager and line managers. Sustainability 10 (12), 1–16 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3390/su10124614
Lee, J., Kim, S., Lee, J., Moon, S.: Enhancing employee creativity for a sustainable competitive advantage through perceived human resource management practices and trust in management. Sustainability 11 (8), 2305 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/su11082305
Mahmood, A., Akhtar, M.N., Talat, U., Shuai, C., Hyatt, J.C.: Specific HR practices and employee commitment: the mediating role of job satisfaction. Empl. Relat. 41 (3), 420–435 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1108/ER-03-2018-0074
Manuti, A., et al.: “Everything Will Be Fine”: A Study on the Relationship between Employees’ Perception of Sustainable HRM Practices and Positive Organizational Behaviour during COVID19. Sustainability 12 (1), 1–17 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/su122310216
Mariappanadar, S.: Sustainable human resource management: the sustainable and unsustainable dilemmas of downsizing. Int. J. Soc. Econ. 30 (1), 906–923 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1108/03068290310483779
Oluwatayo, A.A.: Employee architect’s perception of human resource practices and their job satisfaction. Built Environment Project and Asset Management 5 (1), 89–102 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1108/BEPAM-04-2013-0008
Wilkinson, M., Hill, M., Gollan, P.: The sustainability debate. Int. J. Oper. Prod. Manag. 21 (1), 1492–1502 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1108/01443570110410865
Xavier, B.: Shaping the future research agenda for compensation and benefits management: Some thoughts based on a stakeholder inquiry. Hum. Resour. Manag. Rev. 24 (1), 31–40 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hrmr.2013.08.011
Zheng, C., Molineux, J., Mirshekary, S., Scarparo, S.: Developing individual and organisational work- life balance strategies to improve employee health and wellbeing. Employee Relations 37 (3), 354–379 (2015). http://hdl.handle.net/10536/DRO/DU:30071912
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Manel Srinivas Nayak Institute of Management, Mangalore, 575001, India
D. Bindhu, Sanath Bhaskar Baikadi & Nanditha Sunil
Srinivas University, Mangalore, 575001, India
V. A. Namreen Asif, Chethanraj & Neil Gladwin Dlima
Government First Grade College Karkala, Udupi, 574104, India
Chandravathi
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to D. Bindhu .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Middle East Technical University, Northern Cyprus Campus, Güzelyurt, Türkiye
Bahaaeddin Alareeni
College of Business and Finance, Ahlia University, Manama, Bahrain
Allam Hamdan
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper.
Bindhu, D. et al. (2024). Employee Perception of HR Practices and Its Impact on Job Satisfaction. In: Alareeni, B., Hamdan, A. (eds) Navigating the Technological Tide: The Evolution and Challenges of Business Model Innovation. ICBT 2024. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, vol 1083. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-67431-0_15
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-67431-0_15
Published : 01 August 2024
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-031-67430-3
Online ISBN : 978-3-031-67431-0
eBook Packages : Engineering Engineering (R0)
Share this paper
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
The ‘What, When, and How’ of Line Managers’ Involvement in HRM Implementation:A Systematic Literature Review
42 Pages Posted: 2 Aug 2024
Aneeqa Suhail
affiliation not provided to SSRN
Jeske van Beurden
Tilburg University
Anna Bos-Nehles
The significance of the line manager's role in implementing human resource management (HRM) practices within strategic HRM literature is widely acknowledged. However, ambiguity remains about what line managers' responsibilities in HRM implementation are, when they are involved in the implementation process, and how they participate in this regard. This systematic review, drawing from the analysis of 89 articles, shed light on these aspects. Findings delineate what line managers' involvement in executing HR-related tasks entails, highlighting their less pronounced participation in decision-making, financial authority, and knowledge transfer. When line managers are involved depends on the level of HR centrality, organizational needs, line managers’ personal attributes, and other supporting factors that facilitate HRM implementation. Finally, how they are involved depends on partnership with HR professionals, employing adaptive strategies, and the agency of line managers. Based on our comprehensive analysis, the study develops an integrative framework identifying research gaps and proposes future research inquiries to understand what, when, and how line managers are involved in HRM implementation, aiming to contribute to advancing this evolving research field.
Keywords: Line managers, Involvement, HRM Implementation, systematic review, Strategic HRM.
Suggested Citation: Suggested Citation
Aneeqa Suhail (Contact Author)
Affiliation not provided to ssrn ( email ).
No Address Available
Jeske Van Beurden
Tilburg university ( email ).
P.O. Box 90153 Tilburg, DC 5000 LE Netherlands
Do you have a job opening that you would like to promote on SSRN?
Paper statistics.
Pardon Our Interruption
As you were browsing something about your browser made us think you were a bot. There are a few reasons this might happen:
- You've disabled JavaScript in your web browser.
- You're a power user moving through this website with super-human speed.
- You've disabled cookies in your web browser.
- A third-party browser plugin, such as Ghostery or NoScript, is preventing JavaScript from running. Additional information is available in this support article .
To regain access, please make sure that cookies and JavaScript are enabled before reloading the page.
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
So, Human Resources Is Making You Miserable?
Get in line behind the H.R. managers themselves, who say that since the pandemic, the job has become an exasperating ordeal. “People hate us,” one said.

By David Segal
Show of hands: Who’s fed up with human resources?
Maybe you’re irked by the endless flow of memos and forms, many of which need to be filled out, pronto. Maybe you’re irritated by new initiatives that regularly emerge from H.R., which never seems to run out of new initiatives, not all of them necessary or especially wise, in your opinion. Or you’ve got some problem with management and you don’t trust that H.R. representatives will actually help. They sure are friendly, but they get paid by the suits. In a crunch, it’s pretty clear whose side they are on.
The H.R. department bugs a lot of employees and managers, and it seems to have more detractors than ever since the pandemic began. That’s when H.R. began to administer rules about remote work and pay transparency, programs to improve diversity, equity and inclusion and everything else that has rattled and changed the workplace in the last four years.
But if the H.R. department is bothering you, here’s a fact you might find perversely consoling: You are not as aggravated or bummed out as the people who work in H.R.
That was obvious at Unleash, an annual three-day conference and expo held this year at Caesars Forum, an immense convention hall near the Las Vegas Strip. In May, the event brought together some 4,000 H.R. professionals from across the country. It was billed as a place where “global H.R. leaders come to do business and discover inspirational stories.”
It was more like a place where the H.R. department came to complain.
“Everything feels like a fool’s errand,” said Kyle Lagunas, a former H.R. executive at General Motors who now works at Aptitude Research, an H.R. advisory company based in Boston. He had just finished a highly animated presentation about H.R. tech in front of an audience of about 50 people. Now he sat in the designated media room and ranted a bit about the maddening challenges of running H.R. during and after the tumult of the pandemic.
We are having trouble retrieving the article content.
Please enable JavaScript in your browser settings.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access. If you are in Reader mode please exit and log into your Times account, or subscribe for all of The Times.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access.
Already a subscriber? Log in .
Want all of The Times? Subscribe .

Philadelphia Phillies
Director, human resources.
- Share via Email
- Share via Facebook
- Share via X
- Share via LinkedIn
- Provide HR leadership and guidance to the HR Coordinator and Talent Acquisition Specialist.
- Manage employee relations issues and investigations in consultation with the Head of Human Resources.
- Develop and lead DE&I initiatives with a passion for fostering an open and inclusive culture within the Phillies.
- Lead and ensure all hiring, onboarding, and offboarding processes are completed consistently and in compliance with all applicable federal and local laws.
- Lead and conduct organization-wide training with a strong focus on compliance and continuous development.
- Partner with the Head of Human Resources to manage and administer the annual Performance Management and Compensation Planning process.
- Develop and administer employee engagement and recognition programs in partnership with the HR team.
- Assist in the development and updating of key policies and procedures, including the annual updating of our employee manuals.
- Provide guidance and support for the auditing of key business data and the response to all MLB report requests.
- Continuously evaluate all HR programs with an eye towards improvement and implementing new and best practices.
- Oversee the exit interview process and determine the underlying reasons for separation of employment. Provide data to support trends and participate in action planning to correct any organizational concerns.
- Remain up to date on relevant HR and sports industry trends to stay in line and competitive within the marketplace.
- Other duties as assigned.
- Bachelor’s degree in human resources, organizational development, business administration, or related field
- 8+ years of progressive experience in HR; preferably as a Generalist, HRBP, HR Manager, or Director of HR.
- HR Certification is desired (e.g., PHR, SPHR, SHRM-CP, SHRM-SCP, etc.).
- Demonstrated experience developing and supporting diversity, equity and inclusion initiatives is required.
- Must be on-site a minimum of 3 days per week and occasional availability to work games.
- Strong knowledge of HR policies, procedures and best practices.
- Strong knowledge of local, state, and federal employment law to ensure compliance. Experience working in multi-state environments is preferred.
- Proven experience in change management and implementing new processes.
- Excellent attention to detail, prioritization, and organizational skills with the ability to work independently and meet deadlines in a fast-paced environment.
- Demonstrated ability to coach and influence the decisions of leaders.
- High degree of professionalism and ability to maintain confidential information.
- Ability to work with a high level of proficiency in Microsoft Office software including Word, Excel, and Outlook.
- Experience with UKG Pro software products is preferred.
Job Questions:
What is your desired salary range?
Please describe your experience developing DE&I initiatives.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Essay # 5. Nature of Human Resource Management: Human Resource Management is a process of bringing people and organizations together so that the goals of each are met. The various features of HRM include: ADVERTISEMENTS: a. It is pervasive in nature as it is present in all enterprises. b.
Human Resource management (HRM) is a premeditated methodology to manage the human resource of the organization with the help of functions like recruitment, training and development, utilizing and retaining this asset etc. (Simons, 2011). The nature of workforce in every organization demographically and psychologically vary.
This essay aims at exploring a portfolio of subjects related to human resource management and reflecting them with the seminar activities. Developing the practitioner In order to maintain a competitive advantage and retention of high quality staff, companies must ensure that training and development of the human resources is given high priority.
Strategic human resource management (SHRM) research increasingly focuses on the performance effects of human resource (HR) systems rather than individual HR practices (Combs, Liu, Hall, & Ketchen, 2006).Researchers tend to agree that the focus should be on systems because employees are simultaneously exposed to an interrelated set of HR practices rather than single practices one at a time, and ...
Human resource management provides value to an organization, to a large extent, via its management of the overall employee life cycle that employees follow—from hiring and onboarding, to performance management and talent development, all the way through to transitions such as job change and promotion, to retirement and exit. Human capital is a key competitive advantage to companies, and ...
The Human Resource Management Journal has published several research papers exploring various aspects of HR in contexts of change and turmoil from a number of perspectives. This virtual special issue on HRM in times of turmoil brings together a collection of papers which, when viewed together can help shed light on some of the challenges and ...
Strategic human resource management (SHRM) is a concept that has evolved to define modern organizations within perspectives of strategic planning. This research paper constitutes the goal of defining the concept, exploring it with regard to key stakeholders, and subsequently, assessing how SHRM goals can be evaluated effectively.
Human resources management (HRM) may be defined as the coherent as well as strategic maximization of human resources capital in an organization towards making a return on that investment ( Gold & Bratton, 2001 ). The practice, in its efforts, effectively attempts to maintain a 'fit' between the employees and the organization's overall ...
250 Words Essay on Human Resources Introduction. Human Resources (HR) is a multifaceted discipline that lies at the heart of any organization. It encompasses the management of people within an organization, focusing on policies, systems, and practices that influence employee behavior, attitudes, and performance.
The genesis of on human resource management was marked by the need to organize, manage, and oversee the workforce within organizations effectively. This field draws upon various disciplines, including psychology, sociology, and economics, to optimize the employment lifecycle, from recruitment to retirement.
Storey (1995) defines that human resource management is an individual approach to employment management which seeks to achieve competitive advantage through the strategic deployment of a highly committed and capable workforce, using an integrated array of cultural, structural and personnel techniques. II. THE ROLE OF HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT.
In this fourth annual review issue published by The International Journal of Human Resource Management (IJHRM), we are delighted to present five articles that cover some of the important areas in people management in contemporary work settings. Our review articles cover topics that are less well-researched, compared with some popular themes, as ...
Human Resource Management has strong global recognition and readership, and is filled with conceptual and empirical articles that uniquely advance the academic literature as well as having clear practical implications. We accept cutting-edge research and thought leadership on micro-, macro-, or multi-level phenomena relating to all HRM topics and issues, and utilize the full range of ...
Basically, HRM can be defined as a range of circumstances that affect the employment and contribution of people, against the criteria of coherence and appropriateness (Brewster, 1994). However, Kirkbride (1994) suggested that the use of the term HRM gives the general sense of the policies, procedures and processes involved in the management of ...
Human Resources Management If what is learned in an important college or university course is not put to use in some pragmatic way -- or understood in the larger social context -- then that learning may be viewed as meaningless time spent. No doubt there is a percentage of students that are simply going through the process of education, working for a degree that will open doors and lead ...
In today's fast-paced and competitive business world, companies are increasingly realizing the significance of HR practices in shaping employee experiences and overall organizational success (Bhargava et al. 2021).Understanding how employees perceive HR practices and their impact on job satisfaction has become a focal point of research and organizational strategy (Bryson & Freeman, 2013).
The significance of the line manager's role in implementing human resource management (HRM) practices within strategic HRM literature is widely acknowledged. However, ambiguity remains about what line managers' responsibilities in HRM implementation are, when they are involved in the implementation process, and how they participate in this regard.
Management document from Bryant and Stratton College, Buffalo, 2 pages, Wk. 5 Human Resource Essay Did you know a "bad reputation makes hiring 10% more expensive" (People HR, 2021, para.3)? If a company cannot get employees in the door, they may want to consider raising pay, offering sign-on bonuses, and providing better bene
Being an added value to the team is the key to build an effective relation internally and externally. As part of the Senior Management Team, reporting to Country Director, in addition to be the HR Lead - Head of HR department, this means I have different interactions with stake holders from all levels in the organization.
Get in line behind the H.R. managers themselves, who say that since the pandemic, the job has become an exasperating ordeal. "People hate us," one said.
Submit OpsCenter requests through the Oregon Department of Emergency Management. To discuss emerging needs, call the Staff Duty Officer at 503-373-2366. Leadership Director. Ed Flick, 503-307-6038 [email protected]. Chief of Staff. Sherryll Hoar, 503-779-9317 [email protected].
The Phillies are looking for a Director of Human Resources to join our team based at Citizens Bank Park. The Director of Human Resources will assist the Head of HR in leading the HR function by providing support for key processes. This is a hands-on role, requiring both tactical and strategic leadership ability.